Underestimation of Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum in an Endemic Area of the Mediterranean Basin (Balearic Islands)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Context
2.2. Data Collection and Clinical Sampling
2.3. Ethics
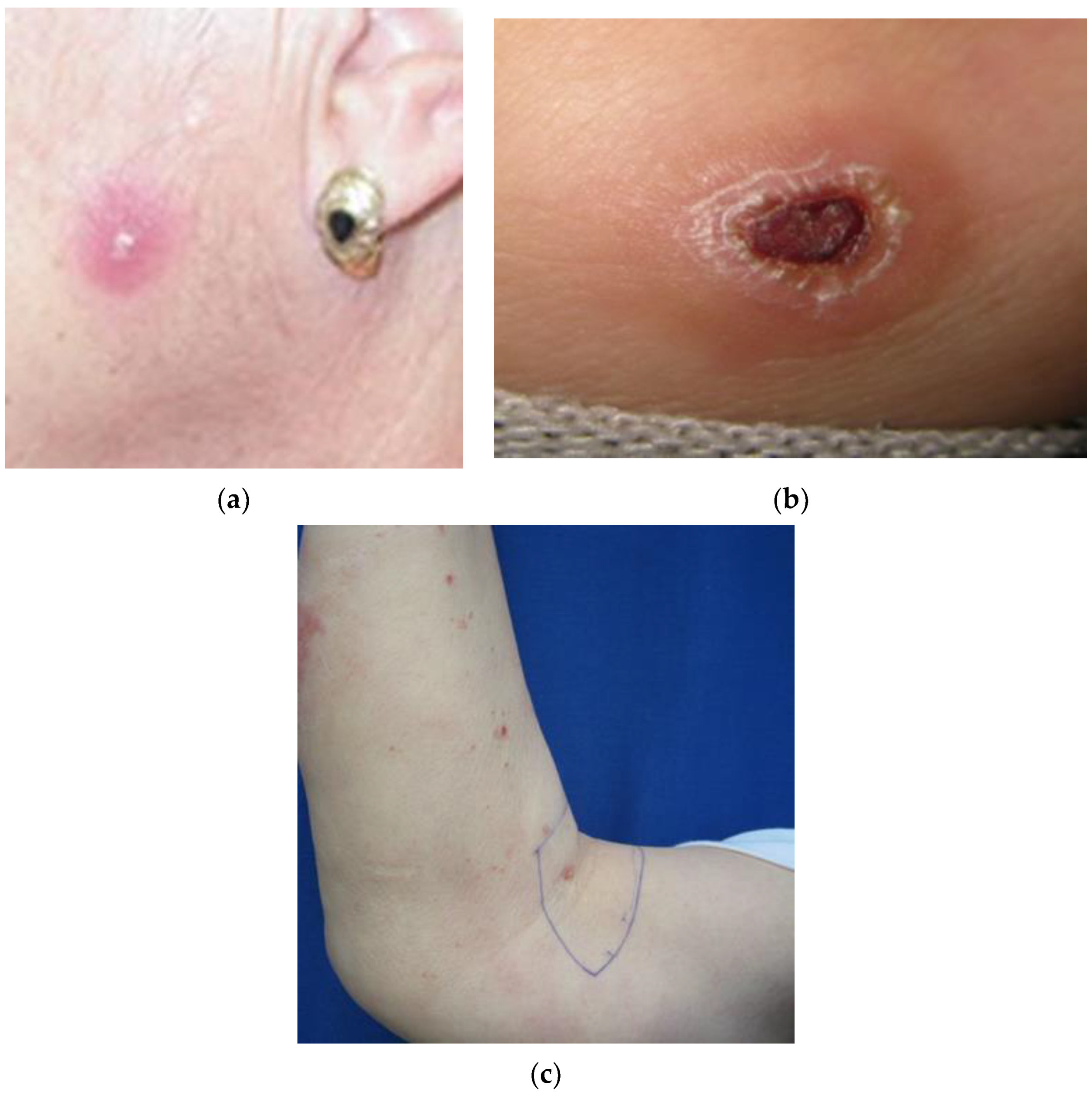
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Leishmaniasis. Fact Sheets. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Berriatua, E.; Jumakanova, Z.; Muñoz, C.; Ortuño, M.; Pérez-Cutillas, P.; Monge-Maillo, B.; Conceição, C.; Maia, C.; Pereira, A.; Rocha, R.; et al. Surveillance, Prevention and Control of Leishmaniases in the European Union and Its Neighbouring Countries; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022; ISBN 9789294985729. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Martínez, B.; Gómez Barroso, D.; Cano Portero, R. La leishmaniasis en España: Evolución de los casos notificados a la Red Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica desde 2005 a 2017 y resultados de la vigilancia de 2014 a 2017. Boletín Epidemiológico Sem. 2019, 27, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Available online: https://www.ine.es/jaxiT3/Datos.htm?t=2852 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Xarxa de Vigilància Epidemiològica de les Illes Balears. Informe 2014. 2015, 1–116. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/epidemiologia/es/informes_anuales-11681/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Xarxa de Vigilància Epidemiològica de les Illes Balears. Informe 2015. 2016, 1–114. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/epidemiologia/es/informes_anuales-11681/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Xarxa de Vigilància Epidemiològica de les Illes Balears. Informe 2016. 2017, 1–117. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/epidemiologia/es/informes_anuales-11681/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Xarxa de Vigilància Epidemiològica de les Illes Balears. Informe 2017. 2018, 1–124. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/epidemiologia/es/informes_anuales-11681/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Xarxa de Vigilància Epidemiològica de les Illes Balears. Informe 2018. 2019, 1–124. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/epidemiologia/es/informes_anuales-11681/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Riera, C.; Fisa, R.; López-Chejade, P.; Serra, T.; Girona, E.; Jiménez, M.T.; Muncunill, J.; Sedeño, M.; Mascaró, M.; Udina, M.; et al. Asymptomatic infection by Leishmania infantum in blood donors from the Balearic Islands (Spain). Transfusion 2008, 48, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akilov, O.E.; Khachemoune, A.; Hasan, T. Clinical manifestations and classification of Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2007, 46, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangüeza, O.P.; Lu, D.; Sangüeza, M.; Paniago-Pereira, C. Chapter 83. Protozoa and Worms. In Dermatology, 3rd ed.; Bolognia, J.L., Jorizzo, J.L., Schaffer, J.V., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1295–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Calonje, J.E.; Brenn, T.; Lazar, A.; Billings, S. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; Blasco Melguizo, J.; Linares Solano, J.; Burkhardt Pérez, M.P.; Naranjo Sintes, R. Leishmaniasis cutánea crónica: Respuesta a n-metil glucamina intralesional tras fracaso con paramomicina tópica. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2002, 93, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Pinto, J.; Azulay, R. Leishmaniasis. In Tropical Dermatology, 1st ed.; Tyring, S., Lupi, O., Hengge, U., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Marcoval, J.; Penín, R.M.; Sabé, N.; Valentín-Medina, F.; Bonfill-Orti, M.; Martínez-Molina, L. Cutaneous leishmaniasis associated with anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha drugs: An emerging disease. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, H.; Lindoso, J.A.L. Current diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, H.J.C.; Reedijk, S.H.; Schallig, H.D.F.H. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: Recent developments in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sector Sanitario de Llevant—IB-SALUT. Servei de Salut de les Illes Balears. Available online: https://www.ibsalut.es/es/servicio-de-salud/organizacion/ordenacion-sanitaria-territorial/sectores-sanitarios/sector-sanitario-de-llevant (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Carta de Compromissos—Hospital de Manacor. Available online: http://extranet.hmanacor.org/benvinguda/carta-de-compromissos/ (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- SITIBSA—401 006: Entorno Físico—Datos Geográficos. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/sitibsa/es/n/401_006_entorno_fisico_-_datos_geograficos-86279/ (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Pujol, A.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C.; Rocamora, V.; Boteller, D. Diagnóstico de la leishmaniosis cutánea. Valor de una técnica de reacción en cadena de la polimerasa para la detección de Leishmania infantum en muestras recogidas sobre papel de filtro versus la histología convencional y la inmunohistoquímica. Piel Form. Contin. En Dermatol. 2012, 27, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcover, M.M.; Rocamora, V.; Guillén, M.C.; Berenguer, D.; Cuadrado, M.; Riera, C.; Fisa, R. Case report: Diffuse cutaneous leishamaniasis by Leishmania infantum in a patient undergoing immunosuppressive therapy: Risk status in an endemic mediterranean area. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomás-Pérez, M.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C. The use of fluorescent fragment length analysis (PCR-FFL) in the direct diagnosis and identification of cutaneous Leishmania species. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-Ezquerra, G.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C.; Rocamora, V.; Fernández-Casado, A.; Barranco, C.; Serra, T.; Baró, T.; Pujol, R.M. Role of Leishmania spp. Infestation in nondiagnostic cutaneous granulomatous lesions: Report of a series of patients from a Western Mediterranean area. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xarxa de Vigilància Epidemiològica de les Illes Balears. Informe 2013. 2014, 1–108. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/epidemiologia/es/informes_anuales-11681/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Alonso Mestre, F. La Leishmaniosi Cutània Autòctona per Leishmania Infantum a les Illes Balears; Facultat de Farmàcia, Universitat de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Urrutia, S.; García, C.; Schoendorff, C.; Sáez, A.; Olivares, M.; García-Almagro, D. Leishmaniasis cutánea en la provincia de Toledo. Estudio de 43 pacientes. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2000, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Aguado, M.; Espinosa, P.; Romero-Maté, A.; Tardío, J.C.; Córdoba, S.; Borbujo, J. Outbreak of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Fuenlabrada, Madrid. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013, 104, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Jareño, M.; Sahuquillo-Torralba, A.; Chouman-Arcas, R.; Castro-Hernández, I.; Molina-Moreno, J.M.; Llavador-Ros, M.; Gómez-Ruiz, M.D.; López-Hontangas, J.L.; Botella-Estrada, R.; Salavert-Lleti, M.; et al. Cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis: Experience of a Mediterranean hospital. Parasit Vectors 2020, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcalde Alonso, M.; Delgado Florencio, V.; Naranjo Sintes, R. Leishmaniasis cutáneas en Granada: Características clínicas. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 1989, 80, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Daudén, E.; García, C.; Zarco, C.; López, S.; Iglesias, L. Leishmaniasis cutánea en el foco endémico de Madrid. Estudio de 31 casos. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 1990, 81, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Albero Blanes, F.; Martínez Sánchez, C.; Román Macia, P. Leishmaniasis cutánea. Alcoy: Zona endémica. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 1979, 70, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- García-Almagro, D. Leishmaniasis cutánea. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2005, 96, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conselleria Salut i Consum, Servei Salut Illes Balears. Resum. Gen. Mem. 2018, 2020, 1–63. Available online: https://www.ibsalut.es/es/servicio-de-salud/que-es-ibsalut/memorias-anuales/3750-memoria-anual-del-servicio-de-salud-de-las-islas-baleares-ano-2018 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Del Giudice, P. Multifocal cutaneous leishmaniasis. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Noto, G.; Zichichi, L.; Veraldi, S. Multifocal cutaneous leishmaniasis: A new clinical presentation of the disease. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2007, 87, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Balearic Islands | Manacor Hospital (County of Llevant) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | CL | Cases/100,000 Inhabitants | CL | Cases/100,000 Inhabitants |
| 2013 | 12 | 1.4 | 39 | 26 |
| 2014 | 17 | 2.2 | 17 | 11.3 |
| 2015 | 28 | 3.3 | 26 | 17.3 |
| 2016 | 30 | 3.3 | 24 | 16 |
| 2017 | 22 | 3.8 | 20 | 13.3 |
| Total | 109 | 126 | ||
| Age Group | Suspected Diagnosis | M | F | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18 years | Boil | 1 | 1 | |
| Mass cell tumor | 1 | 1 | ||
| Panniculitis | 1 | 1 | ||
| Granulomatous rosacea | 1 | 1 | ||
| Spitz’s nevus | 1 | 1 | ||
| Xanthogranuloma | 1 | 1 | ||
| Leishmaniasis | 9 | 14 | 23 | |
| Total | Total | 11 | 18 | 29 |
| 18–65 years | Basal cell carcinoma | 1 | 1 | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 1 | 1 | ||
| Scar | 1 | 1 | ||
| Eczema | 1 | 1 | ||
| Granulomatous disease | 1 | 1 | ||
| Erysipelas | 1 | 1 | ||
| Boil | 1 | 1 | ||
| Boil/tub | 1 | 1 | ||
| Pyogenic granuloma | 1 | 1 | ||
| Mycoses | 1 | 1 | ||
| Lymphoma | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Lichen planus | 1 | 1 | ||
| Amelanotic melanoma | 1 | 1 | ||
| Mycobacteria | 1 | 1 | ||
| Mycobacteria/fungus | 1 | 1 | ||
| Bite | 1 | 1 | ||
| Pyoderma gangrenosum | 1 | 1 | ||
| Sore | 1 | 1 | ||
| Wart/nevus | 1 | 1 | ||
| Leishmaniasis | 27 | 17 | 44 | |
| Total | Total | 32 | 32 | 64 |
| >65 years | Basal cell carcinoma | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 2 | 2 | ||
| Folliculitis | 1 | 1 | ||
| Folliculitis/scar | 1 | 1 | ||
| Actinic granuloma | 1 | 1 | ||
| Lymphoma | 1 | 1 | ||
| Lipoma | 1 | 1 | ||
| Mycobacteria | 1 | 1 | ||
| Nevus/bite | 1 | 1 | ||
| Cyst | 1 | 1 | ||
| Sarcoidosis | 1 | 1 | ||
| Tub | 1 | 1 | ||
| Leishmaniasis | 14 | 4 | 18 | |
| Total | Total | 22 | 11 | 33 |
| Total general | 65 | 61 | 126 |
| Total | Age Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18 | 18–65 | >65 | ||
| Number of cases, n (%) | 126 (100) | 29 (23.0) | 64 (50.8) | 33 (26.2) |
| Sex | ||||
| Woman, n (%) | 65 (51.6) | 11 (8.7) | 32 (25.4) | 22 (17.5) |
| Man, n (%) | 61 (48.4) | 18 (14.3) | 32 (25.4) | 11 (8.7) |
| Age | ||||
| Mean ± SD, years | 44.63 ± 25.50 | 6 ± 4 | 56 ± 4 | 75 ± 1 |
| Median, years | 49 | 5 | 55 | 57 |
| Range, years | 0–86 | 0–16 | 19–64 | 65–86 |
| Clinical Picture | Lesion Type | Sex | Total | Age | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | M | <18 | 18–65 | >65 | |||
| Single | Papule, n | 29 | 24 | 53 | 14 | 22 | 17 |
| Plaque, n | 25 | 23 | 49 | 8 | 27 | 14 | |
| Total, n (%) [CI 95%] | 55 (84.6) [73.7–91.6] | 47 (77) [64.9–85.9] | 102 (81) [73.2–86.9] | 22 (75.9) [57.6–88] | 49 (76.6) [64.8–85.4] | 31 (93.9) [79.4–99.3] | |
| Multiple * | Papule, n | 7 | 4 | 11 | 2 | 8 | 1 |
| Plaque, n | 2 | 9 | 11 | 5 | 5 | 1 | |
| Total, n (%) [CI 95%] | 9 (13.8) [7.2–24.5] | 13 (21.3) [12.8–33.3] | 22 (17.5) [11.8–25.1] | 7 (24.1) [12–42.4] | 13 (20.3) [12.1–31.9] | 2 (6.1) [0.7–20.6] | |
| Mucosa | Sore, n | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Total, n (%) [CI 95%] | 1 (1.5) [0.01–9] | 1 (1.6) [0.01–9.6] | 2 (1.6) [0.1–0.6] | 0 | 2 (3.1) [0.2–11.3] | 0 | |
| Overall total | 65 | 61 | 126 | 29 | 64 | 33 | |
| Location | Lesion Type | Sex | Total | Age | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | M | <18 | 18–65 | >65 | |||
| HN | Papule | 22 | 16 | 38 | 14 | 12 | 12 |
| Plaque | 17 | 14 | 31 | 11 | 9 | 11 | |
| Sore | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| Total HN | 40 | 31 | 71 | 25 | 23 | 23 | |
| UE | Papule | 7 | 4 | 11 | 0 | 10 | 1 |
| Plaque | 7 | 11 | 18 | 0 | 15 | 3 | |
| Total UE | 14 | 15 | 29 | 0 | 25 | 4 | |
| LE | Papule | 3 | 8 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 5 |
| Plaque | 3 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 1 | |
| Total LE | 6 | 12 | 18 | 3 | 9 | 6 | |
| T | Papule | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Plaque | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 | |
| Total T | 5 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 0 | |
| Total HN + UE + LE + T | 65 | 61 | 126 | 29 | 64 | 33 | |
| Size, mm | Sex | Total, n (%) | Age | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | M | <18 | 18–65 | >65 | ||
| 1–5 | 12 | 9 | 21 (16.6) | 8 | 11 | 2 |
| 6–10 | 40 | 29 | 69 (54.7) | 12 | 39 | 18 |
| 11–15 | 9 | 16 | 25 (19.9) | 8 | 8 | 9 |
| 16–20 | 3 | 3 | 6 (4.8) | 0 | 5 | 2 |
| >20 | 1 | 4 | 5 (4) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Total, n | 65 | 61 | 126 | 29 | 64 | 33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcover, M.M.; Rocamora, V.; Ribas, A.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C. Underestimation of Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum in an Endemic Area of the Mediterranean Basin (Balearic Islands). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010126
Alcover MM, Rocamora V, Ribas A, Fisa R, Riera C. Underestimation of Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum in an Endemic Area of the Mediterranean Basin (Balearic Islands). Microorganisms. 2023; 11(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcover, Maria Magdalena, Vicenç Rocamora, Alexis Ribas, Roser Fisa, and Cristina Riera. 2023. "Underestimation of Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum in an Endemic Area of the Mediterranean Basin (Balearic Islands)" Microorganisms 11, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010126
APA StyleAlcover, M. M., Rocamora, V., Ribas, A., Fisa, R., & Riera, C. (2023). Underestimation of Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum in an Endemic Area of the Mediterranean Basin (Balearic Islands). Microorganisms, 11(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010126






