The Development of the Bacterial Community of Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) during Ontogeny
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Management
2.2. Post-Mortem Sampling
2.3. Metagenomic DNA Extraction
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Taxonomic Structure of Bacterial Communities (BC) of All Developmental Stages
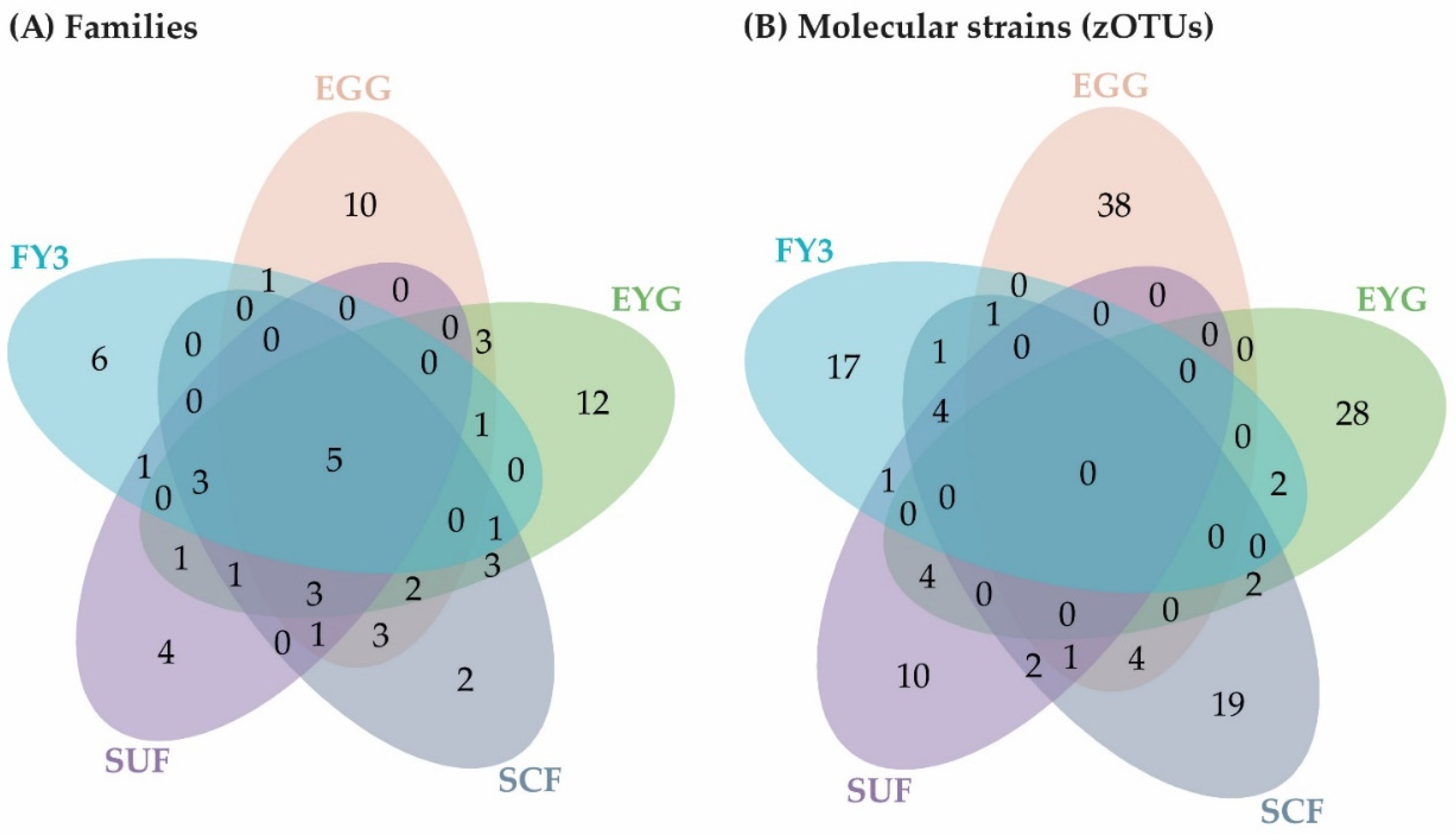
3.1.1. Description of the BC on Phylum Level
3.1.2. Description of the BC on Family Level
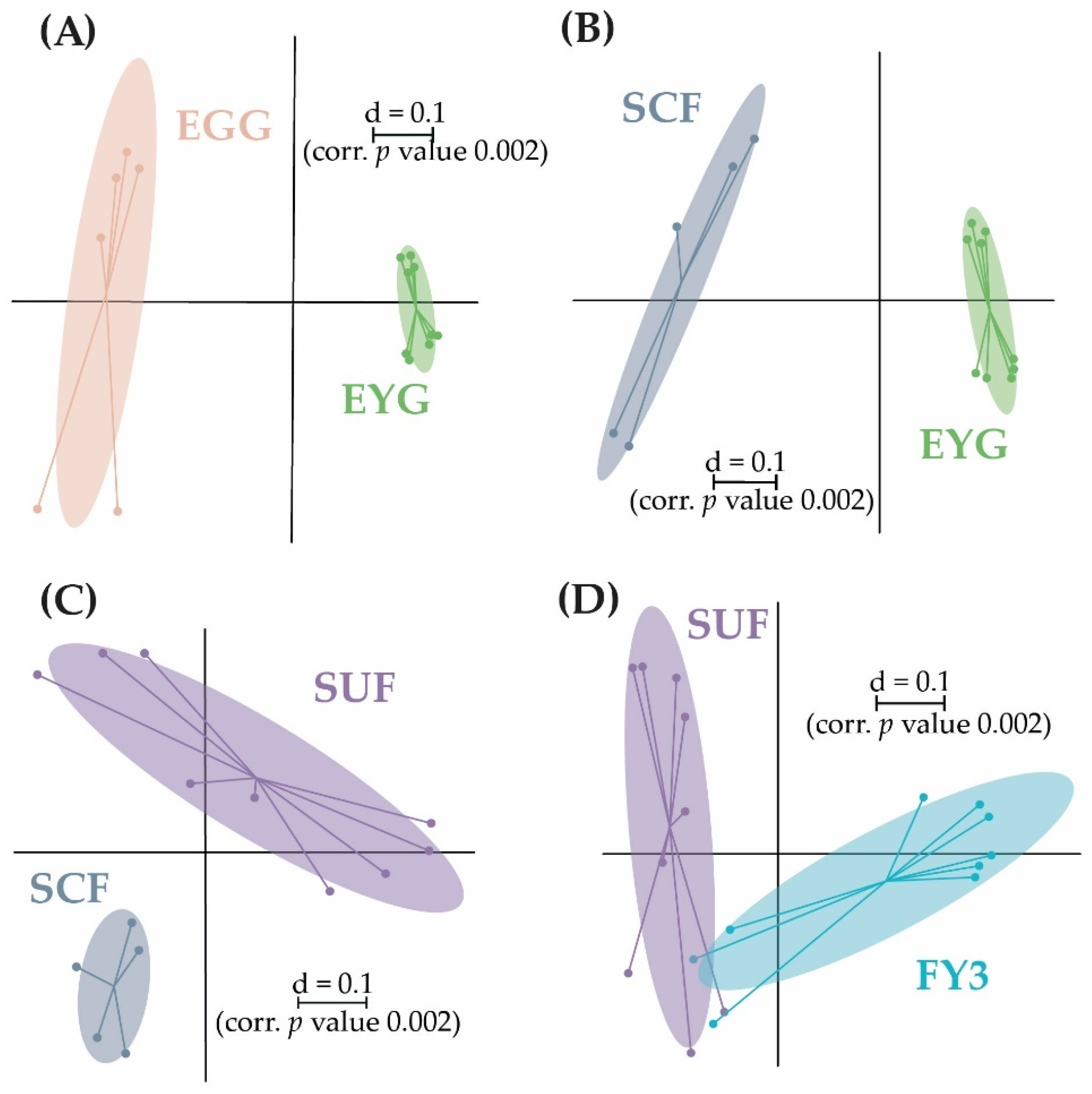
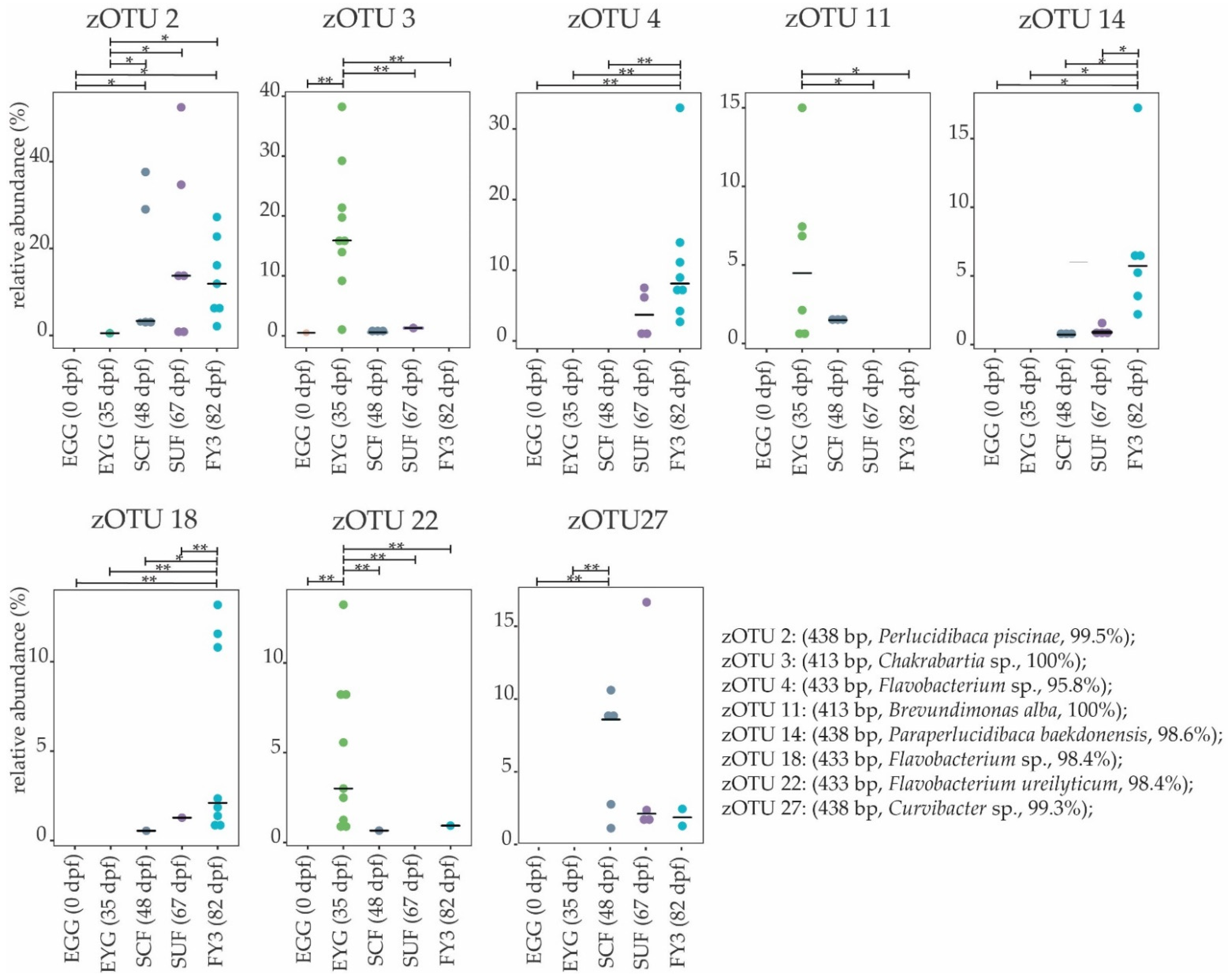
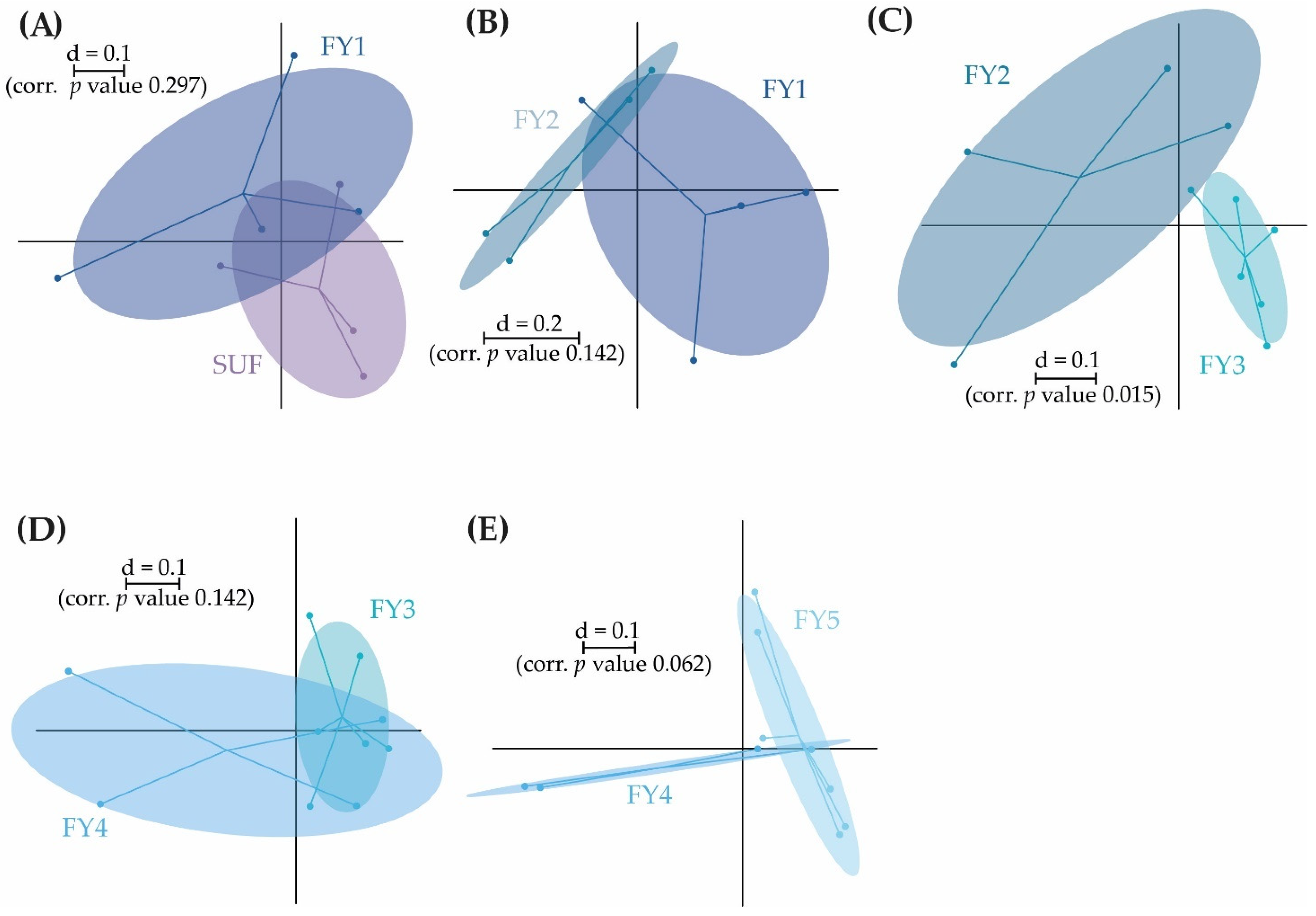
3.2. Bacterial Communities (BC) of the Early Developmental Stages from Egg to Swim-Up Fry
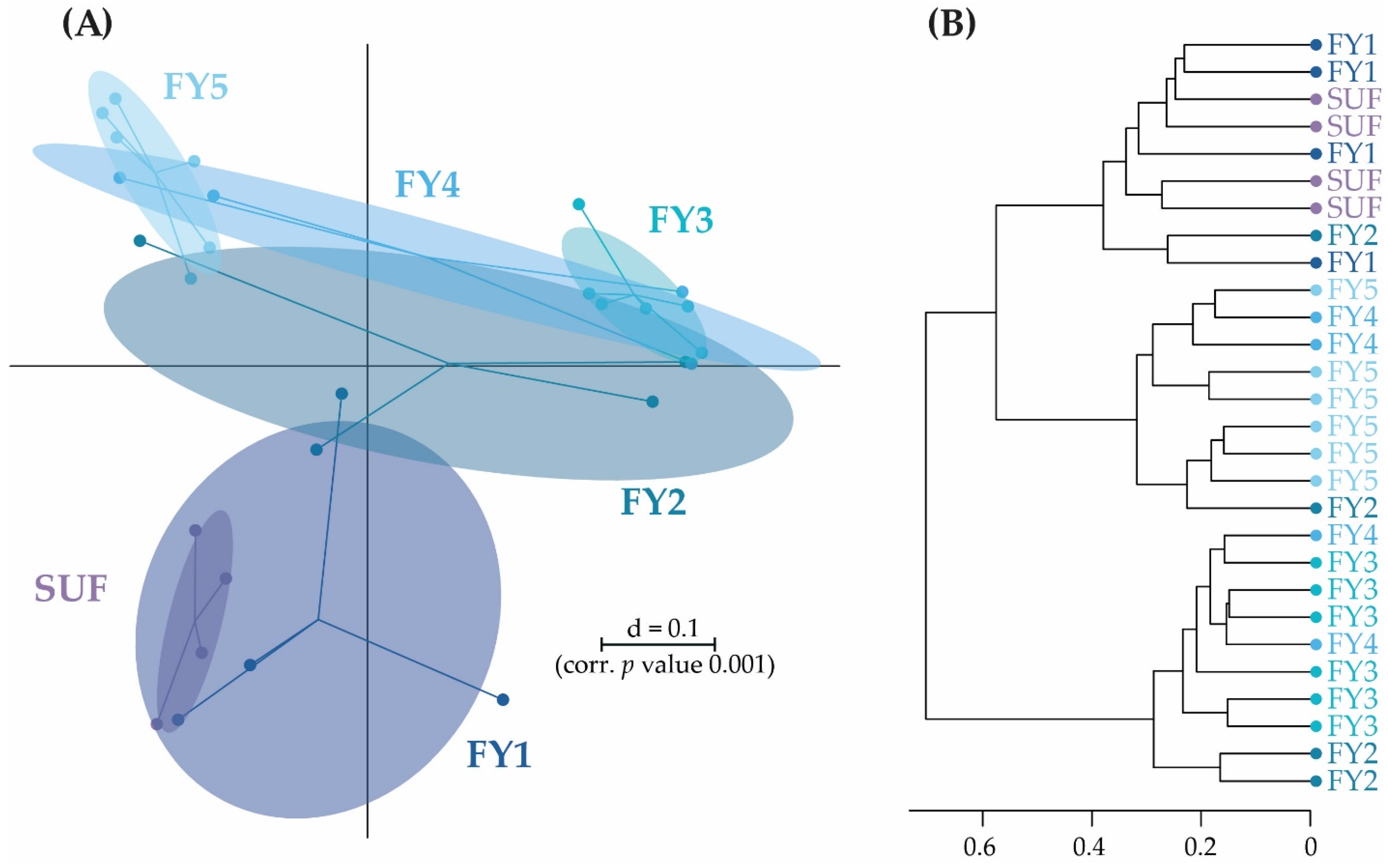
3.3. Bacterial Communities (BC) of the Late Developmental Stages from Swim-Up Fry to Fry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results; UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO. 3; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, C.; Ovando, D.; Clavelle, T.; Strauss, C.K.; Hilborn, R.; Melnychuk, M.C.; Branch, T.A.; Gaines, S.D.; Szuwalski, C.S.; Cabral, R.B. Global fishery prospects under contrasting management regimes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5125–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooke, S.J.; Twardek, W.M.; Lennox, R.J.; Zolderdo, A.J.; Bower, S.D.; Gutowsky, L.F.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Arlinghaus, R.; Beard, D. The nexus of fun and nutrition: Recreational fishing is also about food. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. Comprehensive analysis of > 30 years of data on stream fish population trends and conservation status in Bavaria, Germany. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 226, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, L.; Weis, J.S.; Cabello, F.; Pizarro, J.; Bostick, K. Chemical use in salmon aquaculture: A review of current practices and possible environmental effects. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassitta, R.; Nottensteiner, A.; Bauer, J.; Straubinger, R.K.; Hölzel, C.S. Spread of antimicrobial resistance genes via pig manure from organic and conventional farms in the presence or absence of antibiotic use. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN General Assembly. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/water-and-sanitation/ (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Hoess, R.; Geist, J. Nutrient and fine sediment loading from fish pond drainage to pearl mussel streams—Management implications for highly valuable stream ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirog, R.; Van Pelt, T.; Enshayan, K.; Cook, E. Food, Fuel, and Freeways: An Iowa Perspective on How Far Food Travels, Fuel Usage, and Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Leopold Center for Sustainable Agriculture: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; Volume 209. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, J.M. Wild brown trout Salmo trutta: An important national and international resource. Freshw. Biol. 1989, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.T. The environmental requirements of salmon and trout in fresh water. Freshw. Forum 1993, 3, 176–202. [Google Scholar]
- Eklöv, A.G.; Greenberg, L.; Brönmark, C.; Larsson, P.; Berglund, O. Influence of water quality, habitat and species richness on brown trout populations. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 54, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, B.; Jonsson, N. A review of the likely effects of climate change on anadromous Atlantic salmon Salmo salar and brown trout Salmo trutta, with particular reference to water temperature and flow. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 75, 2381–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallet, A.; Halary, S.; Duval, C.; Huet, H.; Duperron, S.; Marie, B. Disruption of fish gut microbiota composition and holobiont metabolome by cyanobacterial blooms. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysal, M.J.; Fotedar, R.; Tay, C.-Y.; Gupta, S.K. Biological filters regulate water quality, modulate health status, immune indices and gut microbiota of freshwater crayfish, marron (Cherax cainii, Austin, 2002). Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, L.G.; Rogivue, A.; Schütz, F.; Fumagalli, L.; Wedekind, C. Increased diversity of egg-associated bacteria on brown trout (Salmo trutta) at elevated temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.-C.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Lošo, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, K.R.; Schluter, J.; Coyte, K.Z.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S. The evolution of the host microbiome as an ecosystem on a leash. Nature 2017, 548, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, V.; Ransangan, J. Effect of water temperature on susceptibility of culture marine fish species to vibriosis. Int. J. Res. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Vasemägi, A.; Visse, M.; Kisand, V. Effect of environmental factors and an emerging parasitic disease on gut microbiome of wild salmonid fish. MSphere 2017, 2, e00418-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, A. Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasurer, J.W.; Cochrane, E.; Grant, A. Surface disinfection of cod Gadus morhua and haddock Melanogrammus aeglefinus eggs with bronopol. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, C.; Gessner, M.O.; Vazquez, F.; Maerki, M.; Steiner, D. Elevated resource availability sufficient to turn opportunistic into virulent fish pathogens. Ecology 2010, 91, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lokesh, J.; Kiron, V.; Sipkema, D.; Fernandes, J.M.; Moum, T. Succession of embryonic and the intestinal bacterial communities of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) reveals stage-specific microbial signatures. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, C.; Hatje, E.; Zarkasi, K.Z.; Smullen, R.; Bowman, J.P.; Katouli, M. The effect of diet and environmental temperature on the faecal microbiota of farmed Tasmanian Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.B.; Hu, C.Q.; Luo, P.; Zhang, L.P.; Chen, C. Microbiota of yellow grouper (Epinephelus awoora Temminck & Schlegel, 1842) fed two different diets. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Minniti, G.; Hagen, L.H.; Porcellato, D.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Pope, P.B.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G. The skin-mucus microbial community of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, T.M.U.; Consuegra, S.; de Leaniz, C.G. Early life stress causes persistent impacts on the microbiome of Atlantic salmon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brämick, U. Jahresbericht zur Deutschen Binnenfischerei und Binnenaquakultur 2020; Institut für Binnenfischerei e.V. Potsdam-Sacrow: Potsdam, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, S.A.; Øverland, M.; Skrede, A.; Drew, M.D. Effect of plant protein sources on growth rate in salmonids: Meta-analysis of dietary inclusion of soybean, pea and canola/rapeseed meals and protein concentrates. Aquaculture 2013, 400, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michl, S.C.; Ratten, J.-M.; Beyer, M.; Hasler, M.; LaRoche, J.; Schulz, C. The malleable gut microbiome of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Diet-dependent shifts of bacterial community structures. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michl, S.C.; Beyer, M.; Ratten, J.-M.; Hasler, M.; LaRoche, J.; Schulz, C. A diet-change modulates the previously established bacterial gut community in juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogall, E.T.; Jacob, S.; Triebskorn, R.; Schwartz, T.J.E.S.E. The impact of the anti-diabetic drug metformin on the intestinal microbiome of larval brown trout (Salmo trutta f. fario). Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierschutzgesetz. Tierschutzgesetz in der Fassung der Bekanntmachung vom 18. Mai 2006 (BGBl. I S. 1206, 1313), das zuletzt durch Artikel 105 des Gesetzes vom 10. August 2021 (BGBl. I S. 3436) geändert worden ist. 24.07.1972. Available online: https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/tierschg/BJNR012770972.html (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- German Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection. Verordnung zum Schutz von Tieren im Zusammenhang mit der Schlachtung oder Tötung und Durchführung der Verordnung (EG) Nr. 1099/2009 des Europäischen Rates (Tierschutz-Schlachtverordnung—TierSchlV); German Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection: Berlin, Germany, 2012.
- European Commission. Commission Regulation of 24 September 2009 on the Protection of Animals at Slaughter, 1099/2009/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/DE/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32009R1099 (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Godon, J.-J.; Zumstein, E.; Dabert, P.; Habouzit, F.; Moletta, R. Molecular microbial diversity of an anaerobic digestor as determined by small-subunit rDNA sequence analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 2802–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reitmeier, S.; Kiessling, S.; Neuhaus, K.; Haller, D. Comparing circadian rhythmicity in the human gut microbiome. STAR Protoc. 2020, 1, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Kläring, K.; Heinzmann, S.S.; Platz, S.; Scholz, B.; Engel, K.H.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Haller, D.; Rohn, S.; Skurk, T. Gut metabolites and bacterial community networks during a pilot intervention study with flaxseeds in healthy adult men. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1614–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Joseph, D.; Kapfhammer, M.; Giritli, S.; Horn, M.; Haller, D.; Clavel, T.J.S.r. IMNGS: A comprehensive open resource of processed 16S rRNA microbial profiles for ecology and diversity studies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UNOISE2: Improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. bioRxiv 2016, 081257. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.-M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parte, A.C.; Carbasse, J.S.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A.; Garrity, G.M. Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Fischer, S.; Kumar, N.; Clavel, T.J.P. Rhea: A transparent and modular R pipeline for microbial profiling based on 16S rRNA gene amplicons. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Partitioning diversity into independent alpha and beta components. Ecology 2007, 88, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Bittinger, K.; Charlson, E.S.; Hoffmann, C.; Lewis, J.; Wu, G.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Associating microbiome composition with environmental covariates using generalized UniFrac distances. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodan, A.; Tremaroli, V.; Brolin, H.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Levin, E. Comparing bioinformatic pipelines for microbial 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; McGinnity, P.; Dionne, M.; Letourneau, J.; Thonier, F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Derome, N. The biogeography of the atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) gut microbiome. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, G.H.; Olafsen, J.A. Bacterial Interactions in Early Life Stages of Marine Cold Water Fish. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 38, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost microbiomes: The state of the art in their characterization, manipulation and importance in aquaculture and fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bone, A.; Bekaert, M.; Papadopoulou, A.; McMillan, S.; Adams, A.; Davie, A.; Desbois, A.P. Bacterial communities of ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) eggs at a commercial marine hatchery. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpour, B.; Pinto, P.I.S.; Moutou, K.A.; Canario, A.V.M.; Power, D.M. Factors Driving Bacterial Microbiota of Eggs from Commercial Hatcheries of European Seabass and Gilthead Seabream. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, L.G.; Rogivue, A.; Fumagalli, L.; Wedekind, C. Declining diversity of egg-associated bacteria during development of naturally spawned whitefish embryos (Coregonus spp.). Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, C. Induced hatching to avoid infectious egg disease in whitefish. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brivio, M.F.; Bassi, R.; Cotelli, F. Identification and characterization of the major components of the Oncorhynchus mykiss egg chorion. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1991, 28, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Razak, S.; Griffin, M.J.; Mischke, C.C.; Bosworth, B.G.; Waldbieser, G.C.; Wise, D.J.; Marsh, T.L.; Scribner, K.T. Biotic and abiotic factors influencing channel catfish egg and gut microbiome dynamics during early life stages. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califano, G.; Castanho, S.; Soares, F.; Ribeiro, L.; Cox, C.J.; Mata, L.; Costa, R. Molecular Taxonomic Profiling of Bacterial Communities in a Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Hatchery. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roalkvam, I.; Drønen, K.; Dahle, H.; Wergeland, H.I. Microbial Communities in a Flow-Through Fish Farm for Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) During Healthy Rearing Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pheng, S.; Lee, J.J.; Eom, M.K.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.G. Paucibacter oligotrophus sp. nov., isolated from fresh water, and emended description of the genus Paucibacter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2231–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalucat, J.; Pares, R.; Schlegel, H.G. Pseudomonas taeniospiralis sp. nov., an R-Body-Containing Hydrogen Bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1982, 32, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, D.; Tan, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.Y.; Fan, Q.M.; He, X.L.; Lv, J. Rhodoferax bucti sp. nov., isolated from fresh water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3903–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, K.; Bendinger, B.; Schöning, B.; Nielsen, P.H.; Nielsen, J.L.; Baranyi, C.; Toenshoff, E.R.; Daims, H.; Wagner, M. Cohn’s Crenothrix is a filamentous methane oxidizer with an unusual methane monooxygenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2363–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, G.H.; Olafsen, J.A. Bacterial Colonization of Cod (Gadus morhua L.) and Halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) Eggs in Marine Aquaculture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, M.; Crossman, J.A.; Scribner, K.T.; Marsh, T.L. Microbial community assembly and succession on lake sturgeon egg surfaces as a function of simulated spawning stream flow rate. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Villegas, J.; García-Moreno, D.; de Oliveira, S.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. Regulation of immunity and disease resistance by commensal microbes and chromatin modifications during zebrafish development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2605–E2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapata, A.; Diez, B.; Cejalvo, T.; Gutiérrez-de Frías, C.; Cortés, A. Ontogeny of the immune system of fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.M.; Mittge, E.; Kuhlman, J.; Baden, K.N.; Cheesman, S.E.; Guillemin, K. Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation. Dev. Biol. 2006, 297, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Pamp, S.J.; Hill, J.A.; Surana, N.K.; Edelman, S.M.; Troy, E.B.; Reading, N.C.; Villablanca, E.J.; Wang, S.; Mora, J.R.; et al. Gut immune maturation depends on colonization with a host-specific microbiota. Cell 2012, 149, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingerslev, H.C.; von Gersdorff Jørgensen, L.; Lenz Strube, M.; Larsen, N.; Dalsgaard, I.; Boye, M.; Madsen, L. The development of the gut microbiota in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is affected by first feeding and diet type. Aquaculture 2014, 424–425, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, P.; Pinder, A. The respiratory development of Atlantic salmon. I. Morphometry of gills, yolk sac and body surface. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 2725–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, W.Z.; Burns, A.R.; Stagaman, K.; Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F.; Guillemin, K.; Bohannan, B.J. The composition of the zebrafish intestinal microbial community varies across development. ISME J. 2016, 10, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikouli, E.; Meziti, A.; Antonopoulou, E.; Mente, E.; Kormas, K.A. Host-Associated Bacterial Succession during the Early Embryonic Stages and First Feeding in Farmed Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparusaurata). Genes 2019, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tytler, P.; Blaxter, J.H.S. Drinking in yolk-sac stage larvae of the halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus (L.). J. Fish Biol. 1988, 32, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Choo, Y.J.; Cho, J.C. Perlucidibaca piscinae gen. nov., sp. nov., a freshwater bacterium belonging to the family Moraxellaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, S.; Kämpfer, P.; Schleifer, K.H. Limnobacter thiooxidans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel thiosulfate-oxidizing bacterium isolated from freshwater lake sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franzmann, P.D.; Skerman, V.B.D. Agitococcus lubricus gen. nov. sp. nov., a Lipolytic, Twitching Coccus from Freshwater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1981, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadstein, O.; Attramadal, K.J.K.; Bakke, I.; Forberg, T.; Olsen, Y.; Verdegem, M.; Giatsis, C.; Skjermo, J.; Aasen, I.M.; Gatesoupe, F.J.; et al. Managing the Microbial Community of Marine Fish Larvae: A Holistic Perspective for Larviculture. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsen, J. Ingestion of bacteria by cod (Gadus morhua L.) larvae. In Proceedings of the Propagation of Cod Gadus morhus L. An International Symposium, Arendal, Norway, 14–17 June 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Olafsen, J.A.; Hansen, G.H. Intact antigen uptake in intestinal epithelial cells of marine fish larvae. J. Fish Biol. 1992, 40, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, M.C.M.; Sikdar, P.K.; Frerichs, G.N.; Millar, S. The ingestion of bacteria in suspension by the common carp Cyprinus carpio L. J. Fish. Biol. 1991, 39, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, I.; Coward, E.; Andersen, T.; Vadstein, O. Selection in the host structures the microbiota associated with developing cod larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Matsuo, Y.; Matsuda, S.; Adachi, K.; Kasai, H.; Yokota, A. Rubritalea spongiae sp. nov. and Rubritalea tangerina sp. nov., two carotenoid- and squalene-producing marine bacteria of the family Verrucomicrobiaceae within the phylum ‘Verrucomicrobia’, isolated from marine animals. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklund, T.; Dalsgaard, I. Occurrence and significance of atypical Aeromonas salmonicida in non-salmonid and salmonid fish species: A review. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1998, 32, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Aeromonas salmonicida: Updates on an old acquaintance. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 120, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhille, S.; Baïda, N.; Dabboussi, F.; Hamze, M.; Izard, D.; Leclerc, H. Pseudomonas gessardii sp. nov. and Pseudomonas migulae sp. nov., two new species isolated from natural mineral waters. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49 Pt 4, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, G.S.N.; Matsumoto, G.I.; Schumann, P.; Stackebrandt, E.; Shivaji, S. Psychrophilic pseudomonads from Antarctica: Pseudomonas antarctica sp. nov., Pseudomonas meridiana sp. nov. and Pseudomonas proteolytica sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnecki, A.M.; Burgos, F.A.; Ray, C.L.; Arias, C.R. Fish intestinal microbiome: Diversity and symbiosis unravelled by metagenomics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowrey, L.; Woodhams, D.C.; Tacchi, L.; Salinas, I. Topographical mapping of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) microbiome reveals a diverse bacterial community with antifungal properties in the skin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6915–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; De Bruijn, I.; Jack, A.L.; Drynan, K.; Van Den Berg, A.H.; Thoen, E.; Sandoval-Sierra, V.; Skaar, I.; Van West, P.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Deciphering microbial landscapes of fish eggs to mitigate emerging diseases. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2002–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Navarrete, P. 16S rDNA-based analysis of dominant bacterial populations associated with early life stages of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liao, M.; Rong, X.; Liu, Q. The intestine of artificially bred larval turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) contains a stable core group of microbiota. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, L.G.; Fumagalli, L.; Wedekind, C. Effects of host genetics and environment on egg-associated microbiotas in brown trout (Salmo trutta). Microb. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4930–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giatsis, C.; Sipkema, D.; Smidt, H.; Heilig, H.; Benvenuti, G.; Verreth, J.; Verdegem, M. The impact of rearing environment on the development of gut microbiota in tilapia larvae. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abellan-Schneyder, I.; Matchado, M.S.; Reitmeier, S.; Sommer, A.; Sewald, Z.; Baumbach, J.; List, M.; Neuhaus, K. Primer, Pipelines, Parameters: Issues in 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. Msphere 2021, 6, e01202-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes Walburn, J.; Wemheuer, B.; Thomas, T.; Copeland, E.; O’Connor, W.; Booth, M.; Fielder, S.; Egan, S. Diet and diet-associated bacteria shape early microbiome development in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, A.; Jung-Schroers, V. Detection of Deefgea chitinilytica in freshwater ornamental fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, T.P.; Faisal, M. Emerging flavobacterial infections in fish: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, L.; Yu, Y.; Kong, W.; Yin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z. The change of teleost skin commensal microbiota is associated with skin mucosal transcriptomic responses during parasitic infection by Ichthyophthirius multifillis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
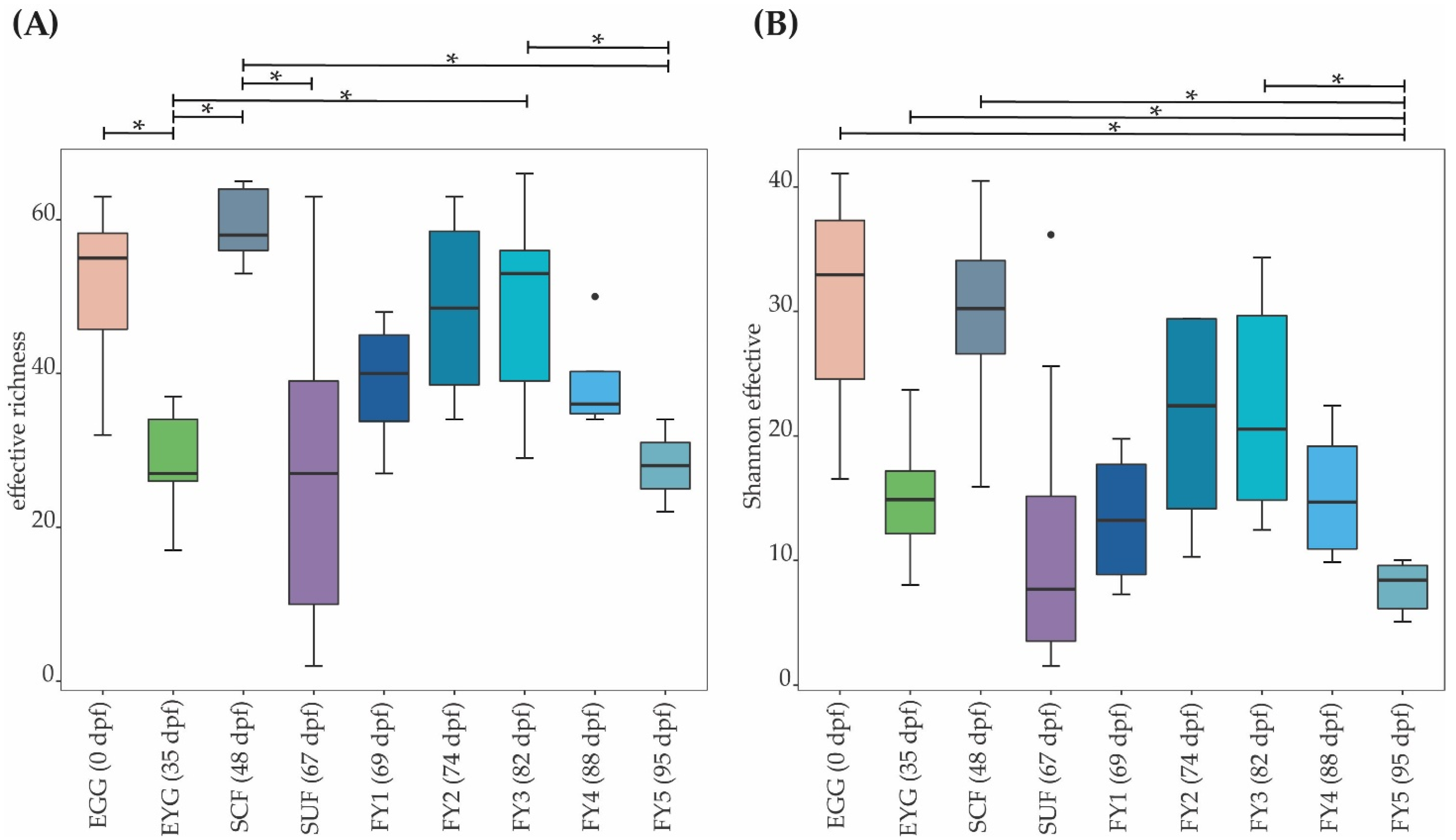
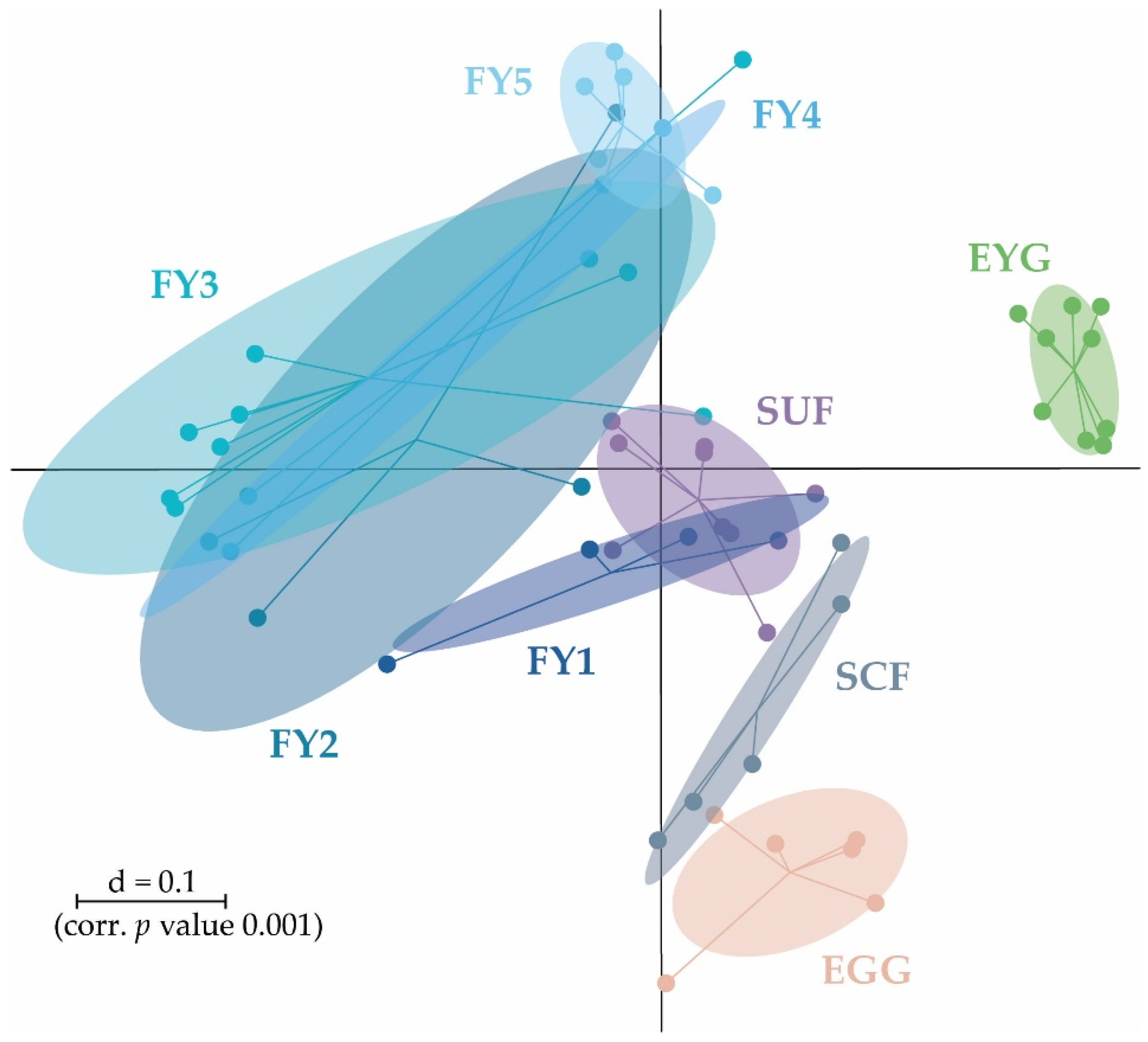
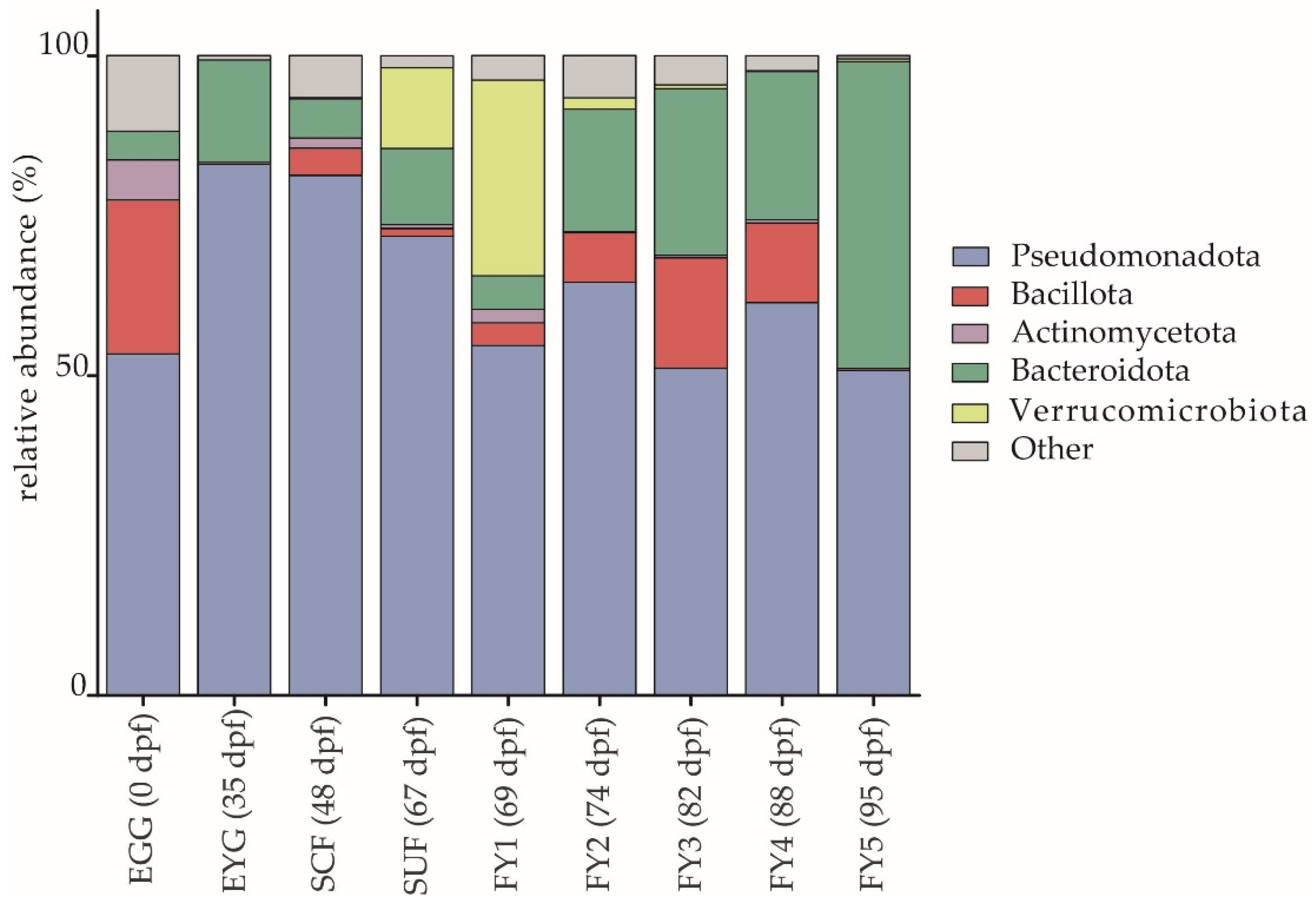

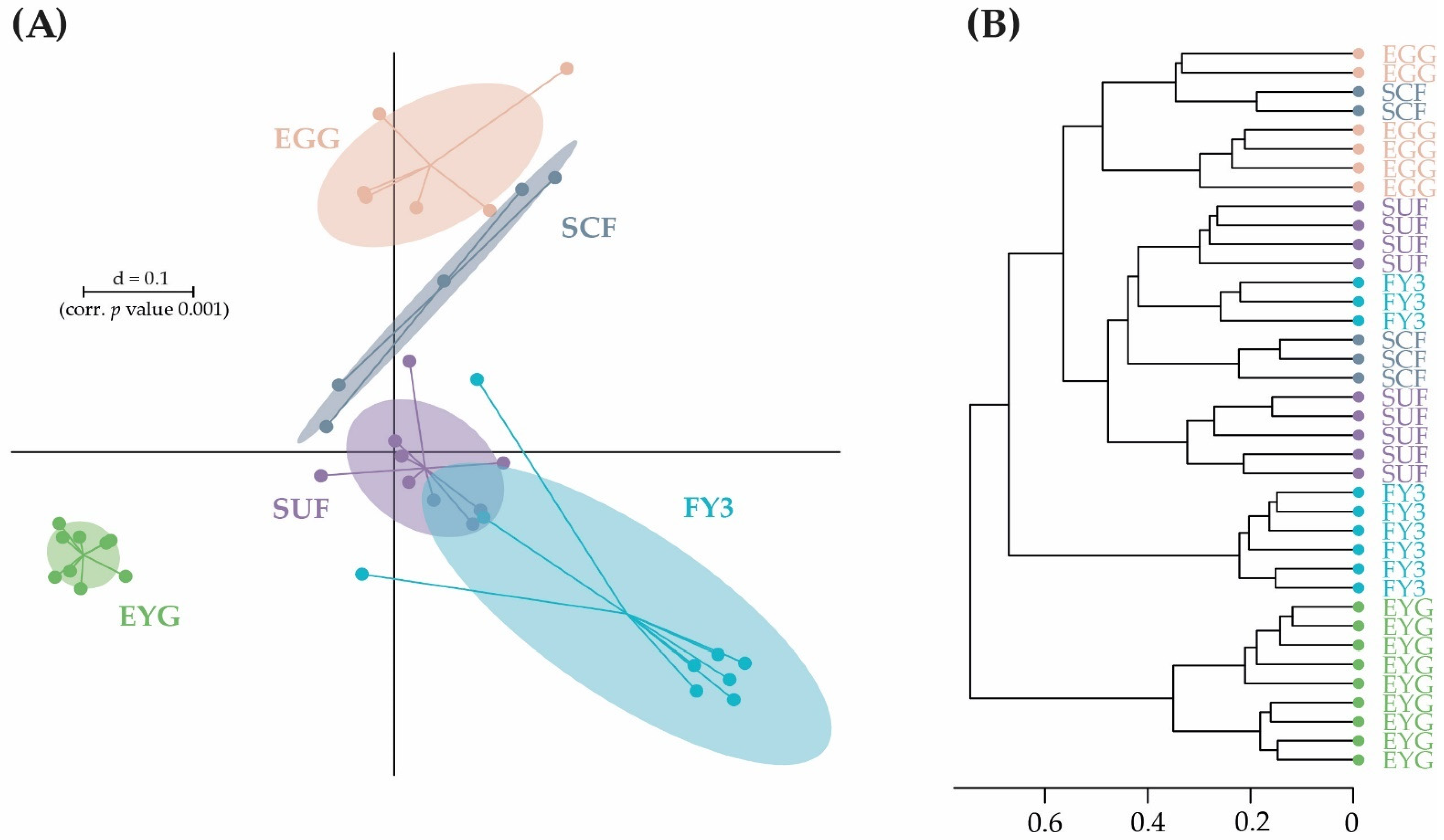


| Sample | Read Count | Effective Richness |
|---|---|---|
| EGG (0 dpf) | 20,392 | 51.2 |
| EYG (35 dpf) | 19,153 | 28.2 |
| SCF (48 dpf) | 3818 | 59.2 |
| SUF (67 dpf) | 12,610 | 28.2 |
| FY1 (69 dpf) | 6550 | 38.8 |
| FY2 (74 dpf) | 13,727 | 48.5 |
| FY3 (82 dpf) | 5720 | 48.9 |
| FY4 (88 dpf) | 8264 | 39.0 |
| FY5 (95 dpf) | 11,846 | 28.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keiz, K.; Ulrich, S.; Wenderlein, J.; Keferloher, P.; Wiesinger, A.; Neuhaus, K.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Wedekind, H.; Straubinger, R.K. The Development of the Bacterial Community of Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) during Ontogeny. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010211
Keiz K, Ulrich S, Wenderlein J, Keferloher P, Wiesinger A, Neuhaus K, Lagkouvardos I, Wedekind H, Straubinger RK. The Development of the Bacterial Community of Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) during Ontogeny. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(1):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010211
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeiz, Katharina, Sebastian Ulrich, Jasmin Wenderlein, Patrick Keferloher, Anna Wiesinger, Klaus Neuhaus, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Helmut Wedekind, and Reinhard K. Straubinger. 2023. "The Development of the Bacterial Community of Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) during Ontogeny" Microorganisms 11, no. 1: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010211
APA StyleKeiz, K., Ulrich, S., Wenderlein, J., Keferloher, P., Wiesinger, A., Neuhaus, K., Lagkouvardos, I., Wedekind, H., & Straubinger, R. K. (2023). The Development of the Bacterial Community of Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) during Ontogeny. Microorganisms, 11(1), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010211








