Ruminant Salivary Microbes: Passenger or Player in the Rumen?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Management and Bolus Collection
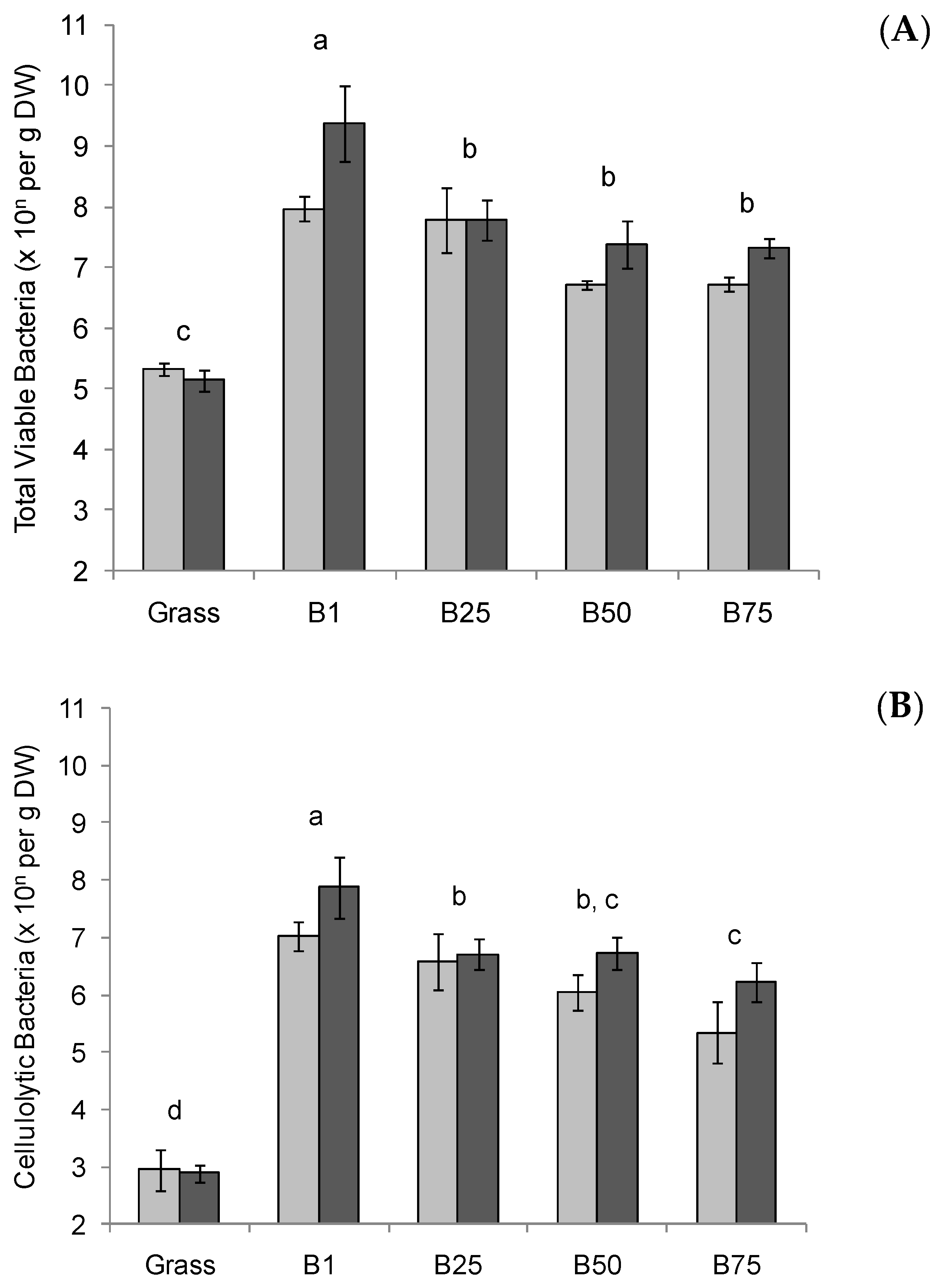
2.2. Quantification of Total Viable Anaerobic Bacteria and Cellulolytic Bacteria Associated with the Formation of Bolus Material
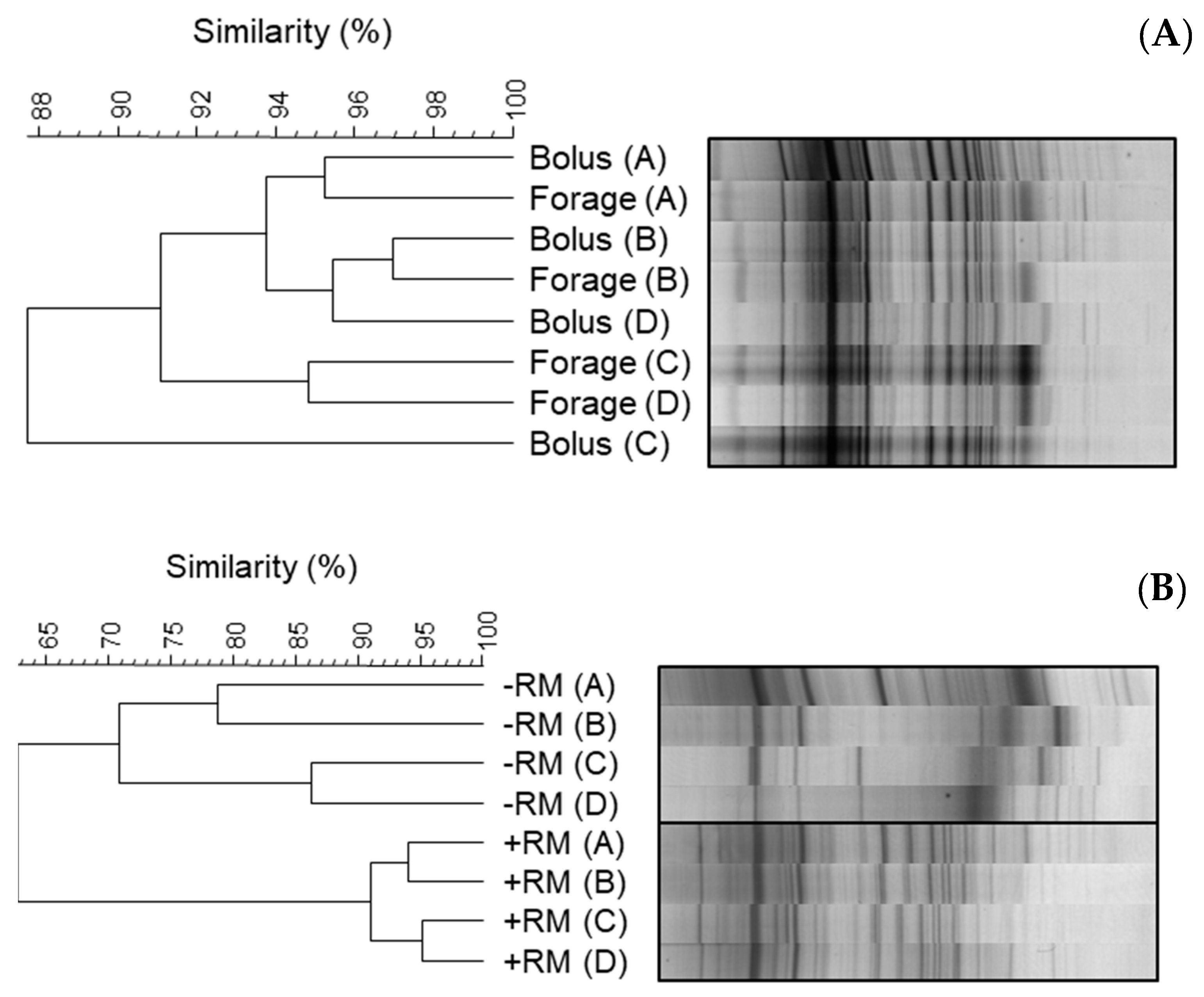
2.3. In Vitro Enrichment of Bolus-Associated Bacteria That Colonised Forage
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Bacterial 16S rDNA Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
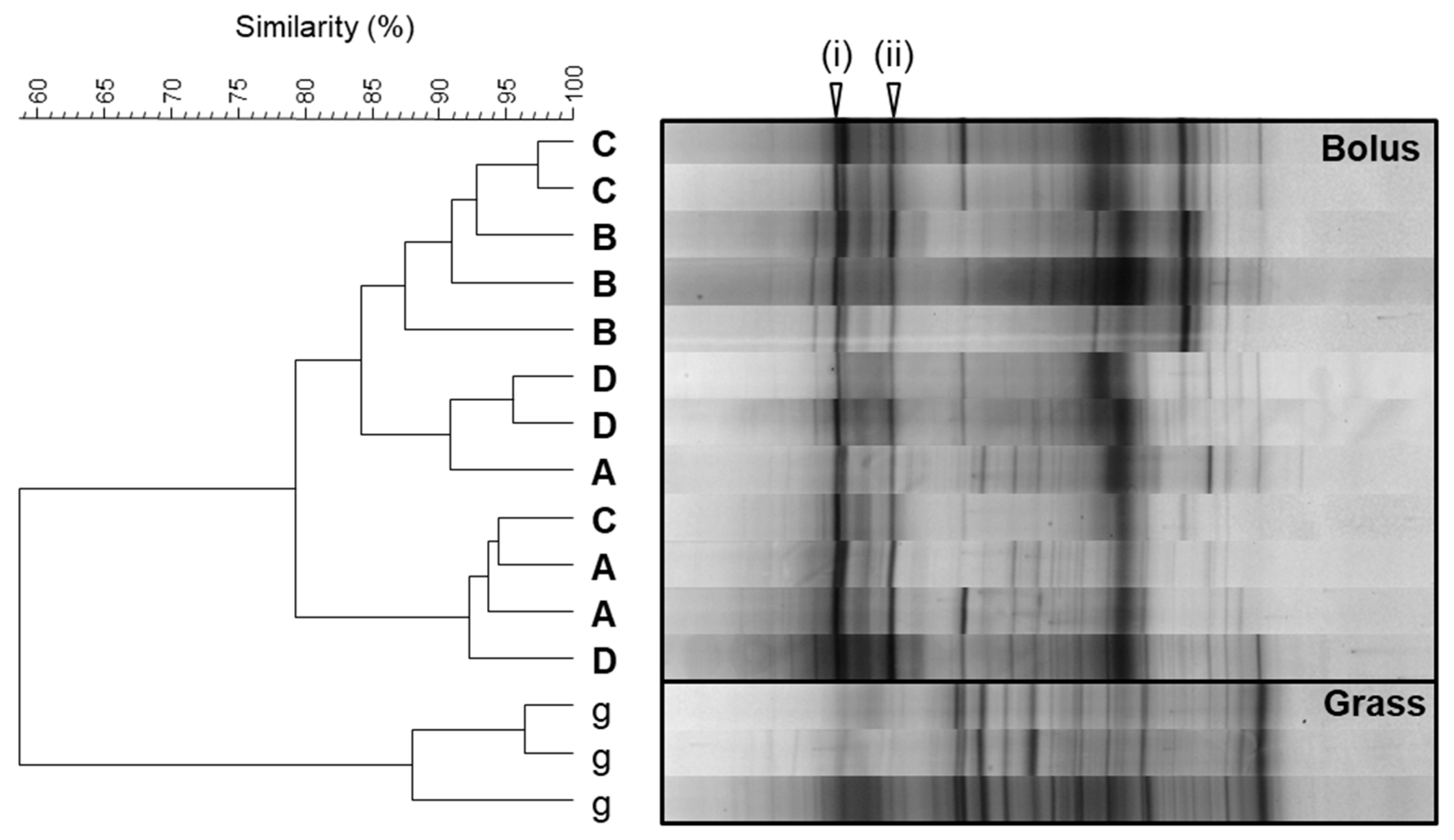
2.6. Sequencing and Analysis of DGGE Bands of Interest
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of Total Viable Anaerobic Bacteria and Cellulolytic Bacteria in Bolus Material
3.2. In Vitro Enrichment of Bolus-Associated Bacteria Able to Utilise Forage
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kay, R.N. The Influence of Saliva on Digestion in Ruminants. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1966, 6, 292–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.T.; Huffman, C.F. Some Physical and Chemical Properties of Bovine Saliva Which May Affect Rumen Digestion and Synthesis. J. Dairy Sci. 1949, 32, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhse, J.M.; Smiegielski, L.; Tuplin, M.; Guan, L.L.; Willing, B.P. Host Immune Selection of Rumen Bacteria through Salivary Secretory IgA. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Hidalgo, J.M.; Belanche, A.; Jiménez, E.; Martín-García, A.I.; Newbold, C.J.; Yáñez-Ruiz, D.R. Short Communication: Saliva and Salivary Components Affect Goat Rumen Fermentation in Short-Term Batch Incubations. Animal 2021, 15, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subharat, S.; Shu, D.; Zheng, T.; Buddle, B.M.; Janssen, P.H.; Luo, D.; Wedlock, D.N. Vaccination of Cattle with a Methanogen Protein Produces Specific Antibodies in the Saliva Which Are Stable in the Rumen. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 164, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedlock, D.N.; Janssen, P.H.; Leahy, S.C.; Shu, D.; Buddle, B.M. Progress in the Development of Vaccines against Rumen Methanogens. Animal 2013, 7 (Suppl. 2), 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapio, I.; Shingfield, K.J.; McKain, N.; Bonin, A.; Fischer, D.; Bayat, A.R.; Vilkki, J.; Taberlet, P.; Snelling, T.J.; Wallace, R.J. Oral Samples as Non-Invasive Proxies for Assessing the Composition of the Rumen Microbial Community. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelmann, S.; Kirk, M.R.; Jonker, A.; McCulloch, A.; Janssen, P.H. Buccal Swabbing as a Noninvasive Method to Determine Bacterial, Archaeal, and Eukaryotic Microbial Community Structures in the Rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7470–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J. Nutritional Ecology of the Ruminant; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorini, P.; Tamminga, S.; Gunter, S.A. Review: Behavior and Daily Grazing Patterns of Cattle. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2006, 22, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, P.; Gunter, S.A.; Beck, P.A.; Soder, K.J.; Tamminga, S. REVIEW: The Interaction of Diurnal Grazing Pattern, Ruminal Metabolism, Nutrient Supply, and Management in Cattle. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2008, 24, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Skarlupka, J.H.; Cox, M.S.; Resende, R.T.; Fischer, A.; Kalscheur, K.F.; McClure, J.C.; Cole, J.B.; Suen, G.; Bickhart, D.M. Validating the Use of Bovine Buccal Sampling as a Proxy for the Rumen Microbiota by Using a Time Course and Random Forest Classification Approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00861-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.R.; Brooks, A.E.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Merry, R.J.; Theodorou, M.K. Development of Novel Approaches to Examine Rumen Microbial Succession. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2000, 50, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.J.; Sanderson, R.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Dewhurst, R.J. Fatty Acid Profiles Associated with Microbial Colonization of Freshly Ingested Grass and Rumen Biohydrogenation. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3220–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehority, B.A.; Tirabasso, P.A.; Grifo, A.P. Most-Probable-Number Procedures for Enumerating Ruminal Bacteria, Including the Simultaneous Estimation of Total and Cellulolytic Numbers in One Medium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 2789–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, M.P.; Burkey, L.A. Cultural Methods and Some Characteristics of Some of the More Numerous Groups of Bacteria in the Bovine Rumen. J. Dairy Sci. 1953, 36, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goering, H.K.; Van Soest, P.J. Forage Fiber Analyses (Apparatus, Reagent, Procedures and Some Applications): Agriculture Handbook No. 379; U.S. Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, J.E.; Huws, S.A.; Kim, E.J.; Kingston-Smith, A.H. Characterization of the Dynamics of Initial Bacterial Colonization of Nonconserved Forage in the Bovine Rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 323–335, Erratum in FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 63, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilig, H.G.H.J.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Vaughan, E.E.; Marteau, P.; Akkermans, A.D.L.; De Vos, W.M. Molecular Diversity of Lactobacillus Spp. and Other Lactic Acid Bacteria in the Human Intestine as Determined by Specific Amplification of 16S Ribosomal DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, C.J.; Neto, E.D.; Simpson, A.J.G. Rapid Silver Staining and Recovery of PCR Products Separated on Polyacrylamide Gels. Biotechniques 1994, 17, 914–921. [Google Scholar]
- Etokebe, G.E.; Spurkland, A. Method for Avoiding PCR-Inhibiting Contaminants When Eluting DNA from Polyacrylamide Gels. Biotechniques 2000, 29, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SINA: Accurate High-Throughput Multiple Sequence Alignment of Ribosomal RNA Genes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-Species Living Tree Project (LTP)” Taxonomic Frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, E.I. Studies on Ruminant Saliva. 1. The Composition and Output of Sheep’s Saliva. Biochem. J. 1948, 43, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, T.A.; Bae, H.D.; Jones, G.A.; Cheng, K.J. Microbial Attachment and Feed Digestion in the Rumen. J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 72, 3004–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, S.; Pan, J.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tanaka, K. Kinetics of in Sacco Fiber-Attachment of Representative Ruminal Cellulolytic Bacteria Monitored by Competitive PCR. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, H.; Tomioka, N.; Nakahara, T.; Uchiyama, H. A Single Band Does Not Always Represent Single Bacterial Strains in Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis Analysis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mailem, D.M.; Kansour, M.K.; Radwan, S.S. Capabilities and Limitations of DGGE for the Analysis of Hydrocarbonoclastic Prokaryotic Communities Directly in Environmental Samples. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freitas, A.S.; Caroline Gan, F.; de David, D.B.; Roesch, L.F.W. The Microbiome Shifts throughout the Gastrointestinal Tract of Bradford Cattle in the Pampa Biome. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Takeda, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ohtani, Y.; Endo, G.; Masuda, Y.; Ito, K.; Nagura, Y.; Iwashita, K.; Mitani, T.; et al. Application of MinION Amplicon Sequencing to Buccal Swab Samples for Improving Resolution and Throughput of Rumen Microbiota Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 783058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinovich, G.J.; Burrell, P.C.; Pollitt, C.C.; Bouvet, A.; Trott, D.J. Streptococcus Henryi Sp. Nov. and Streptococcus Caballi Sp. Nov., Isolated from the Hindgut of Horses with Oligofructuose-Induced Laminitis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, C.; Meile, L.; Lacroix, C.; Stevens, M.J.A. Genomics, Evolution, and Molecular Epidemiology of the Streptococcus Bovis/Streptococcus Equinus Complex (SBSEC). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 33, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, L.; Grimont, F.; Ageron, E.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Bouvet, A. Reappraisal of the Taxonomy of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus Complex and Related Species: Description of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus subsp. nov., S. gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus subsp. nov. and S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusniok, C.; Couvé, E.; Da Cunha, V.; El Gana, R.; Zidane, N.; Bouchier, C.; Poyart, C.; Leclercq, R.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Glaser, P. Genome Sequence of Streptococcus Gallolyticus: Insights into Its Adaptation to the Bovine Rumen and Its Ability to Cause Endocarditis. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2266–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.H.; Liu, T.T.; Teng, Y.T.; Wu, H.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Wu, K.M.; Chang, C.H.; Hsu, M.T. Sequencing and Comparative Genome Analysis of Two Pathogenic Streptococcus Gallolyticus Subspecies: Genome Plasticity, Adaptation and Virulence. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
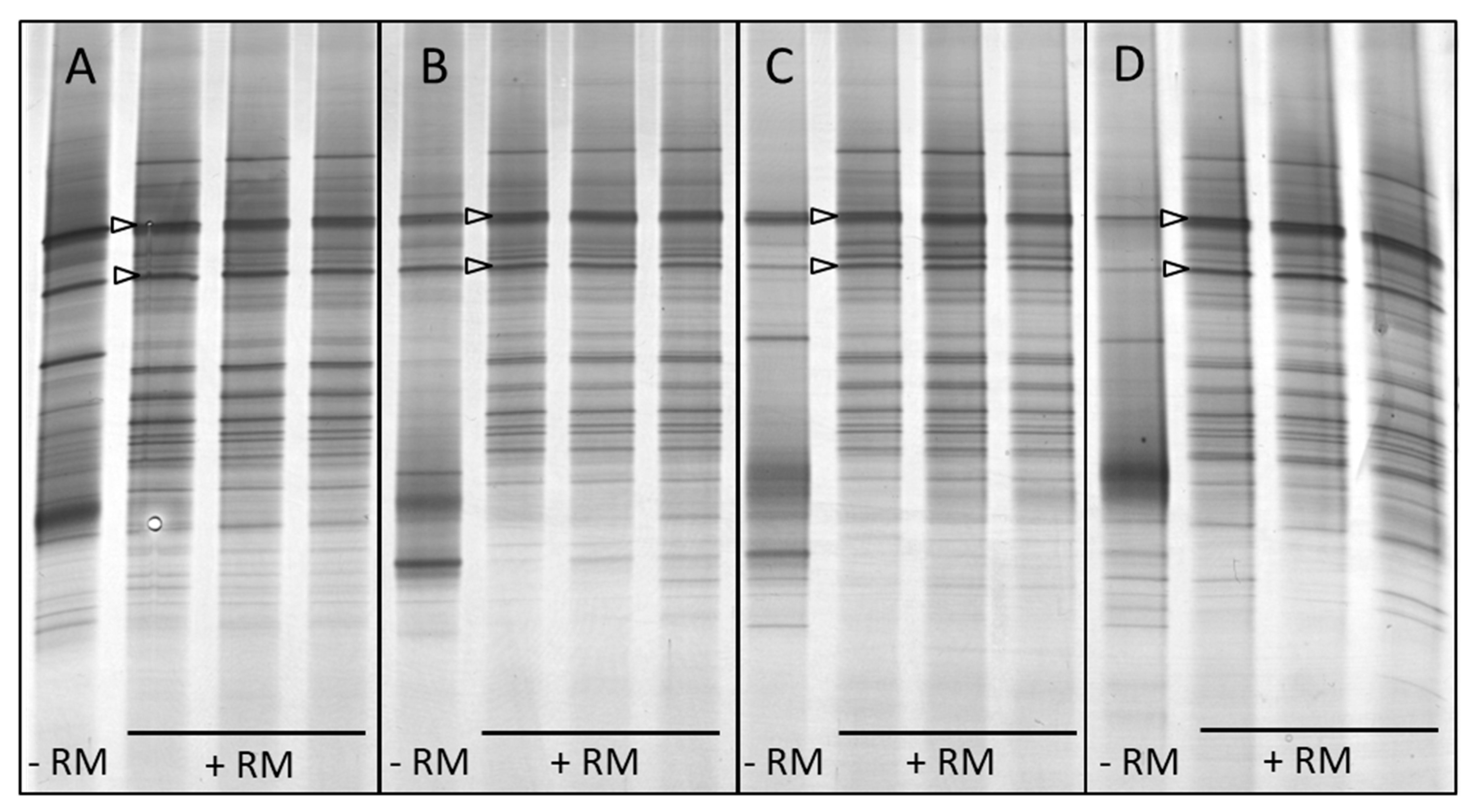

| Band Position | Cow | Clone NCBI Accession No. | Taxonomic Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| i | A | HQ009293 | Streptococcus |
| HQ009294 | Family Lachnospiraceae, genus unclassified | ||
| HQ009295 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009296 | Shuttleworthia | ||
| HQ009297 | Pantoea | ||
| B | HQ009308 | Family Microbacteriaceae, genus unclassified | |
| HQ009309 | Actinobacillus | ||
| HQ009310 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009311 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009312 | Streptococcus | ||
| C | HQ009323 | Streptococcus | |
| HQ009324 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009325 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009326 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009327 | Streptococcus | ||
| D | HQ009338 | Selenomonas | |
| HQ009339 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009340 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009341 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009342 | Streptococcus | ||
| ii | A | HQ009298 | Streptococcus |
| HQ009299 | Rhodopseudomonas | ||
| HQ009300 | Clostridium sensu stricto 1 | ||
| HQ009301 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009302 | Unclassified | ||
| B | HQ009313 | Streptococcus | |
| HQ009314 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009315 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009316 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009317 | Streptococcus | ||
| C | HQ009328 | Lactococcus | |
| HQ009329 | Citrobacter | ||
| HQ009330 | Burkholderia-Caballeronia-Paraburkholderia | ||
| HQ009331 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009332 | Mannheimia | ||
| D | HQ009343 | Streptococcus | |
| HQ009344 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009345 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009346 | Streptococcus | ||
| HQ009347 | Streptococcus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Edwards, J.E.; Kim, E.J.; Davies, D.R.; Hanafy, R.; Kingston-Smith, A.H. Ruminant Salivary Microbes: Passenger or Player in the Rumen? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102390
Edwards JE, Kim EJ, Davies DR, Hanafy R, Kingston-Smith AH. Ruminant Salivary Microbes: Passenger or Player in the Rumen? Microorganisms. 2023; 11(10):2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102390
Chicago/Turabian StyleEdwards, Joan E., Eun Joong Kim, David R. Davies, Radwa Hanafy, and Alison H. Kingston-Smith. 2023. "Ruminant Salivary Microbes: Passenger or Player in the Rumen?" Microorganisms 11, no. 10: 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102390
APA StyleEdwards, J. E., Kim, E. J., Davies, D. R., Hanafy, R., & Kingston-Smith, A. H. (2023). Ruminant Salivary Microbes: Passenger or Player in the Rumen? Microorganisms, 11(10), 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102390






