Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
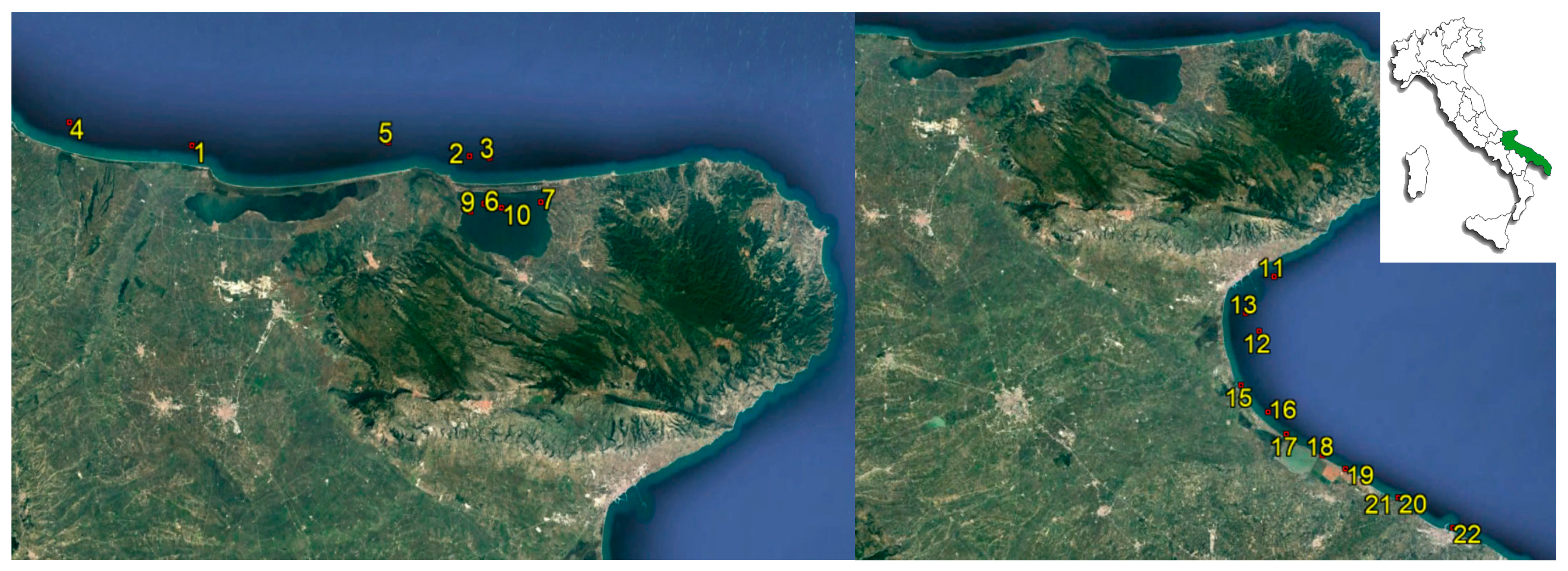
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Vibrio Detection and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Salmonella Detection and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3. Results
3.1. Salmonella Isolates and Their Antimicrobial Resistance Profile
3.2. Vibrio Isolates and Their Antimicrobial Resistance Profile
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shakerian, A.; Barton, M.D.; Akinbowale, O.L.; Khamesipour, F. Antimicrobial resistance profile and resistance genes of Vibrio species isolated from giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium Rosenbergii) raised in Iran. J. Hellenic. Vet. Med. Soc. 2018, 68, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, S.; Mridula, C.; Silvester, R.; Hatha, A.A.M. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of pathogenic Vibrios in shellfishes from Cochin market. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2014, 43, 815–824. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Oliver, J.D.; Alam, M.; Ali, A.; Waldor, M.K.; Quadri, F.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Vibrio spp. infections. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, I.N.; Chun, J.; Huq, A.; Sack, R.B.; Colwell, R.R. Genotypes associated with virulence in environmental isolates of Vibrio cholerae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2421–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Kaushik, A.; Kumar, D.; Bag, S. Foodborne pathogenic Vibrios: Antimicrobial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 30, 638331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.S.; Ryu, A.; Kwon, J.Y.; Kim, B.; Park, K. Distribution of Vibrio species isolated from bivalves and bivalve culture environments along the Gyeongnam coast in Korea: Virulence and antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates. Food Control 2019, 106, 106697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafudoulla, M.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Park, H.; Byun, K.H.; Lee, N.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.D. Genetic relationship, virulence factors, drug resistance profile and biofilm formation ability of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from mussel. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Al-Saari, N.; Mohamad, A.; Mursidi, F.A.; Mohd-Aris, A.; Amal, M.n.A.; Kasai, H.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T.; Zamri-Saad, M. Vibriosis in fish: A review on disease development and prevention. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labella, A.; Gennari, M.; Ghidini, V.; Trento, I.; Manfrin, A.; Borrego, J.J.; Lleo, M.M. High incidence of antibiotic multi-resistant bacteria in coastal areas dedicated to fish farming. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, T.T.; Berneking, L.; Rohde, H.; Chistner, M.; Schlickewei, C.; Sena Martins, M.; Schmiedel, S. Wound infection with Vibrio harveyi following a traumatic leg amputation after a motorboat propeller injury in Mallorca, Spain: A case report and review of literature. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montánchez, I.; Kaberdin, V.R. Vibrio harveyi: A brief survey of general characteristics and recent epidemiological traits associated with climate change. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 154, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2003/99/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 November 2003 on the Monitoring of Zoonoses and Zoonotic Agents, Amending Council Decision 90/424/EEC and Repealing Council Directive 92/117/EEC. 2003. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2003/99/2013-07-01 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2019 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06406. [Google Scholar]
- Maggi, P.; Carbonara, S.; Fico, C.; Santantonio, T.; Romanelli, C.; Sforza, E.; Pastore, G. Epidemiological, clinical and therapeutic evaluation of the Italian cholera epidemic in 1994. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 13, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, G.; Barbuti, S.; Leogrande, G.; Jatta, E. Osservazioni sulla diagnosi batteriologica di colera e sulle caratteristiche degli stipiti isolati nella epidemia pugliese dell’estate 1973 [Studies on the bacteriological diagnosis of cholera and on the characteristics of isolated strains in the Apulia epidemic during the summer of 1973]. Ann. Sclavo 1975, 17, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Alessiani, A.; Goffredo, E.; Mancini, M.; Occhiochiuso, G.; Faleo, S.; Didonna, A.; Fischetto, R.; Suglia, F.; De Vito, D.; Stallone, A.; et al. Evaluation of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella strains isolated from food, animal and human samples between 2017 and 2021 in southern Italy. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2020/1729 of 17 November 2020 on the monitoring and reporting of antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and commensal bacteria and repealing Implementing Decision 2013/652/EU, (2020). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dec_impl/2020/1729/oj (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 November 2003 on the control of salmonella and other specified food-borne zoonotic agents, (2003). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2003/2160/2021-04-21 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- World Health Organization. 2021 TrACSS Country Report on the Implementation of National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/antimicrobial-resistance/amr-spc-npm/tracss/tracss-2021-italy.pdf?sfvrsn=10e5e354_4&download=true (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/627 of 15 March 2019 laying down uniform practical arrangements for the performance of official controls on products of animal origin intended for human consumption in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2017/625 of the European Parliament and of the Council and amending Commission Regulation (EC) No 2074/2005 as regards official controls, (2019). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2019/627/2021-10-14 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- European Union Reference Laboratory for Monitoring of Marine Biotoxins. Community Guide to the Principles of Good Practice for the Microbiological Classification and Monitoring of Bivalve Mollusc Production and Relaying Areas with Regard to Implementing Regulation 2019/627. Issue 4. 2021. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/CRLMB/docs/docs/procedimientos/Micro_Control_Guide_DEC_2021.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs, (2005). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2005/2073/2020-03-08 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- ISO 21872–1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Determination of Vibrio spp.—Part 1: Detection of Potentially Enteropathogenic Vibrio Parahaemolyticus, Vibrio Cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Mancini, M.E.; Beverelli, M.; Donatiello, A.; Didonna, A.; Dattoli, L.; Faleo, S.; Occhiochiuso, G.; Galante, D.; Rondinone, V.; Del Sambro, L.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica from foods in Apulia and Basilicata regions (Italy) by conventional and modern methods. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria, 3rd ed.; CLSI guideline M45; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, AR, USA, 2015; Available online: https://goums.ac.ir/files/deputy_treat/md_labs_ef39a/files/CLSI-M45ed3e-2018.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Bier, N.; Schwartz, K.; Guerra, B.; Strauch, E. Survey on antimicrobial resistance patterns in Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio cholerae non-O1/non-O139 in Germany reveals carbapenemase-producing Vibrio cholerae in coastal waters. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatek, M.; Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors, and genetic profiles of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from seafood. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00537-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579–1:2017/Amd 1:2020; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp.—Amendment 1: Broader Range of Incubation Temperatures, Amendment to the Status of Annex D, and Correction of the Composition of MSRV and SC. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ISO/TR 6579–3:2014; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 3: Guidelines for Serotyping of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 12.0. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_12.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 32nd ed. In CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, AR, USA, 2022; Available online: http://em100.edaptivedocs.net/GetDoc.aspx?doc=CLSI%20M100%20ED31:2021&scope=user (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalin, N.; Srinivasan, P. Molecular characterization of antibiotic resistant Vibrio harveyi isolated from shrimp aquaculture environment in the south east coast of India. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 97, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacometti, F.; Pezzi, A.; Galletti, G.; Tamba, T.; Merialdi, G.; Piva, S.; Serraino, A.; Rubini, S. Antimicrobial resistance patterns in Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica and Escherichia coli isolated from bivalve molluscs and marine environment. Food Control 2021, 121, 107590. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-León, A.; García-Omil, C.; Rodríguez-Souto, R.R.; Lamas, A.; Garrido-Maestu, A. An evaluation of the pathogenic potential, and the antimicrobial resistance, of Salmonella strains isolated from mussels. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Hui, Y.; Su, Y.C. Effect of temperature on uptake and survival of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters (Crassostrea plicatula). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 136, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.B.; Ramamurthy, T.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Dutta, B.; Takeda, Y.; Sack, D.A. Global dissemination of Vibrio parahaemolyticus serotype O3:K6 and its serovariants. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, F.; Wegner, K.M.; Baker-Austin, C.; Vezzulli, L.; Osorio, C.R.; Amaro, C.; Ritchie, J.M.; Defoirdt, T.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Blokesch, M.; et al. The emergence of Vibrio pathogens in Europe: Ecology, evolution, and pathogenesis (Paris, 11–12th March 2015). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 830. [Google Scholar]
- Boutaib, R.; Marhraoui, M.; Oulad Abdellah, M.K.; Bouchrif, B. Comparative study on faecal contamination and occurrence of Salmonella spp. and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in two species of shellfish in Morocco. Open Environ. Sci. 2011, 5, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.K.; Farber, J.M. Trend and pattern of antimicrobial resistance in molluscan Vibrio species sourced to Canadian estuaries. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, 00799-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkonsholm, F.; Lunestad, B.T.; Aguirre Sánchez, J.R.; Martinez-Urtaza, J.; Marathe, N.P.; Svanevik, C.S. Vibrios from the Norwegian marine environment: Characterization of associated antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, D.; Bacchiocchi, I.; Masini, L.; Leoni, F.; Carraturo, A.; Giammarioli, M.; Sbaraglia, G. Antimicrobial susceptibility of potentially pathogenic halophilic vibrios isolated from seafood. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 18, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaviani, D.; Leoni, F.; Talevi, G.; Masini, L.; Santarelli, S.; Rocchegiani, E.; Susini, F.; Montagna, C.; Monno, R.; D’Annibale, L.; et al. Extensive investigation of antimicrobial resistance in Vibrio parahaemolyticus from shellfish and clinical sources, Italy. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Austin, C.; McArthur, J.V.; Lindell, A.H.; Wright, M.S.; Tuckfield, R.C.; Gooch, J.; Warner, L.; Oliver, J.; Stepanauskas, R. Multi-site analysis reveals widespread antibiotic resistance in the marine pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahouri, A.; Radouane, n.; Yacoubi, B.; Moukrim, A.; Banaoui, A. Microbiological assessment of marine and estuarine ecosystems using fecal indicator bacteria, Salmonella, Vibrio and antibiotic resistance pattern. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (ISPRA). Stato Dell’ambiente 84/2019. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/public_files/annuario-2018.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Briet, A.; Helsens, N.; Delannoy, S.; Debuiche, S.; Brisabois, A.; Midelet, G.; Granier, S.A. NDM-1-producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from imported seafood. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2578–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenni, M.; Dagot, C.; Chesneau, O.; Bibbal, D.; Labanowski, J.; Vialette, M.; Bouchard, D.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Calsat, L.; Nazaret, S.; et al. Environmental contamination in a high-income country (France) by antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and antibiotic resistance genes: Status and possible causes. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sampling Station | Area | Shellfish Species | n. Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Northern coast of Gargano | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 12 |
| 2 | Northern coast of Gargano | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 13 |
| 3 | Northern coast of Gargano | Crassostrea gigas | 13 |
| 4 | Northern coast of Gargano | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 13 |
| 5 | Northern coast of Gargano | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 15 |
| 6 | Varano lake | Ruditapes philippinarum | 6 |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis | 14 | ||
| 7 | Varano lake | Crassostrea gigas | 14 |
| 9 | Varano lake | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 13 |
| 10 | Varano lake | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 14 |
| 11 | Southern coast of Gargano | Crassostrea gigas | 6 |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis | 11 | ||
| 12 | Southern coast of Gargano | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 14 |
| 13 | Southern coast of Gargano | Modiolus barbatus | 7 |
| 15 | Southern coast of Gargano | Acanthocardia tuberculata | 8 |
| Modiolus barbatus | 1 | ||
| 16 | Southern coast of Gargano | Acanthocardia tuberculata | 8 |
| 17 | Southern coast of Gargano | Acanthocardia tuberculata | 8 |
| 18 | Coastline of BAT 1 Province | Venus gallina/Chamelea gallina | 17 |
| 19 | Coastline of BAT 1 Province | Venus gallina/Chamelea gallina | 15 |
| 20 | Coastline of BAT 1 Province | Venus gallina/Chamelea gallina | 17 |
| 21 | Coastline of BAT 1 Province | Venus gallina/Chamelea gallina | 12 |
| 22 | Coastline of BAT 1 Province | Venus gallina/Chamelea gallina | 12 |
| Sampling Station | Matrix | Vibrio Species | Resistance Pattern | MAR Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. alginolyticus | MERO, FIS, AMP, P/T4, PIP, FEP | 0.193 |
| 2 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. alginolyticus | FIS, SXT, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.161 |
| 3 | Crassostrea gigas | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, P/T4, PIP, FAZ, TAZ, FEP | 0.225 |
| 4 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| V. harveyi | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | ||
| 5 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | ||
| 6 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| V. parahaemolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | ||
| Ruditapes philippinarum | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | |
| V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | ||
| 7 | Crassostrea gigas | V. harveyi | AMP, PIP | 0.064 |
| 9 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. parahaemolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| 10 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | ||
| V. parahaemolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | ||
| 11 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. vulnificus | FIS, FAZ | 0.064 |
| 12 | Mytilus galloprovincialis | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, FAZ | 0.096 |
| V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, FAZ | 0.096 | ||
| V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, FAZ | 0.096 | ||
| 15 | Acanthocardia tuberculata | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, FAZ | 0.096 |
| 16 | Acanthocardia tuberculata | V. parahaemolyticus | FIS, AMP, FAZ | 0.096 |
| 17 | Acanthocardia tuberculata | V. alginolyticus | AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.096 |
| 18 | Venus gallina/ Chamelea gallina | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| 19 | Venus gallina/ Chamelea gallina | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| 20 | Venus gallina/ Chamelea gallina | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| 21 | Venus gallina/ Chamelea gallina | V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| 22 | Venus gallina/ Chamelea gallina | V. harveyi | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| V. parahaemolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 | ||
| V. alginolyticus | FIS, AMP, PIP, FAZ | 0.129 |
| Vibrio Species | n | Antimicrobial Agents | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOX | AZI | TET | AUG2 | STR | P/T4 | PIP | FAZ | TAZ | A/S2 | ||
| V. alginolyticus | 90 | 4.4 | 5.6 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 26.7 | 30 | 1.1 | 6.7 | ||
| V. parahaemolyticus | 17 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 11.8 | |||||
| V. harveyi | 17 | 5.9 | 17.6 | 29.4 | 11.8 | ||||||
| V. vulnificus | 1 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||
| V. cholerae | 1 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||
| Vibrio Species | n | Antimicrobial Agents | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOX | MERO | FIS | SXT | AMP | P/T4 | IMI | PIP | FAZ | TAZ | A/S2 | FEP | ||
| V. alginolyticus | 90 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 61.1 | 5.6 | 93.3 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 42.2 | 55.6 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 3.3 |
| V. parahaemolyticus | 17 | 70.6 | 76.5 | 35.3 | 94.1 | ||||||||
| V. harveyi | 17 | 17.6 | 64.7 | 23.5 | 17.6 | ||||||||
| V. vulnificus | 1 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||
| V. cholerae | 1 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mancini, M.E.; Alessiani, A.; Donatiello, A.; Didonna, A.; D’Attoli, L.; Faleo, S.; Occhiochiuso, G.; Carella, F.; Di Taranto, P.; Pace, L.; et al. Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020450
Mancini ME, Alessiani A, Donatiello A, Didonna A, D’Attoli L, Faleo S, Occhiochiuso G, Carella F, Di Taranto P, Pace L, et al. Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(2):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020450
Chicago/Turabian StyleMancini, Maria Emanuela, Alessandra Alessiani, Adelia Donatiello, Antonella Didonna, Luigi D’Attoli, Simona Faleo, Gilda Occhiochiuso, Francesco Carella, Pietro Di Taranto, Lorenzo Pace, and et al. 2023. "Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance" Microorganisms 11, no. 2: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020450
APA StyleMancini, M. E., Alessiani, A., Donatiello, A., Didonna, A., D’Attoli, L., Faleo, S., Occhiochiuso, G., Carella, F., Di Taranto, P., Pace, L., Rondinone, V., Damato, A. M., Coppola, R., Pedarra, C., & Goffredo, E. (2023). Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms, 11(2), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020450





