Distinct Effects of Chemical Toxicity and Radioactivity on Metabolic Heat of Cultured Cells Revealed by “Isotope-Editing”
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lactococcus lactis Cell Culture
2.2. Isothermal Microcalorimetry of L. lactis Cultures
2.3. Brassica Napus Cell Culture
2.4. Isothermal Microcalorimetry of B. napus Cells in the Presence of 233U
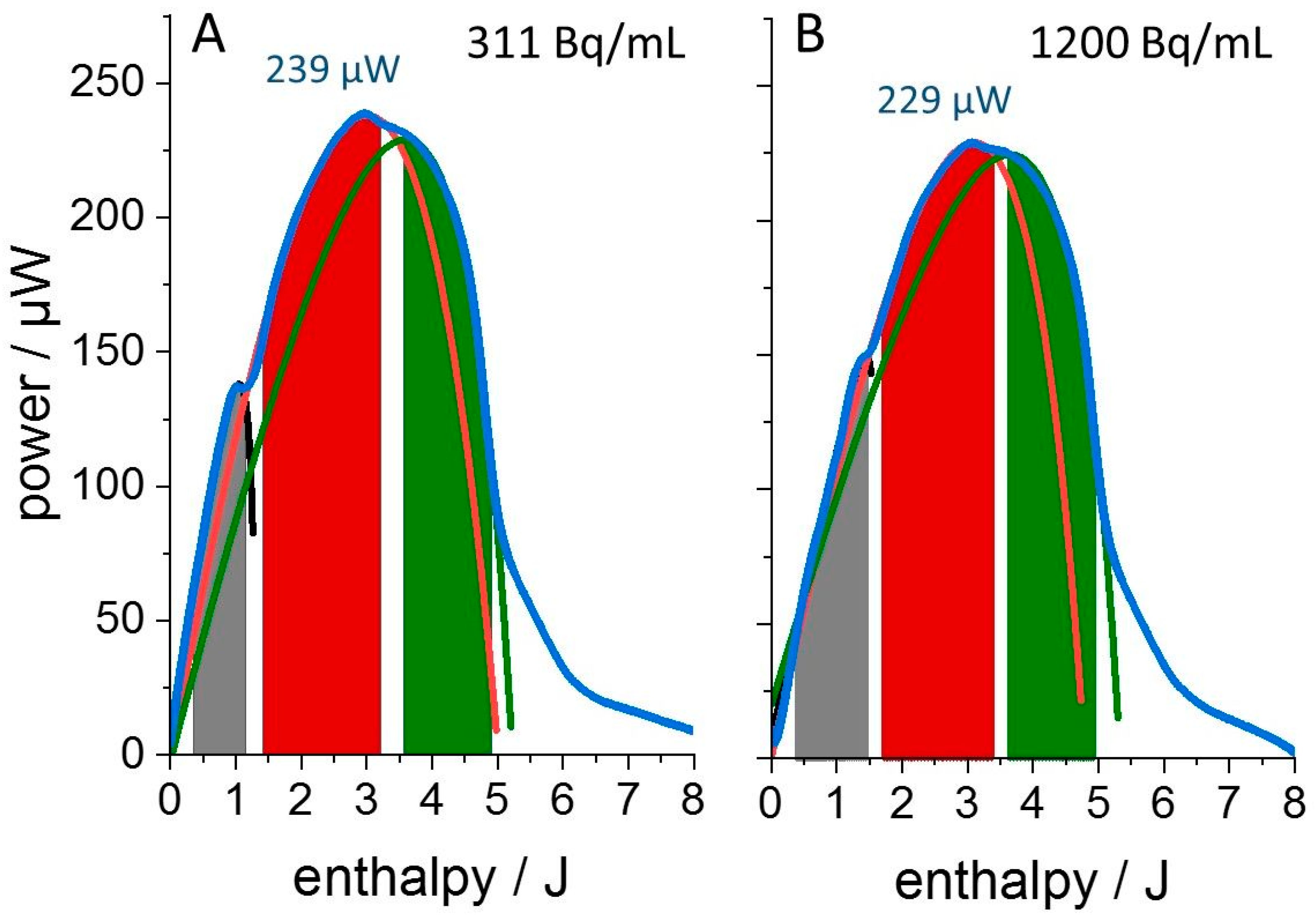
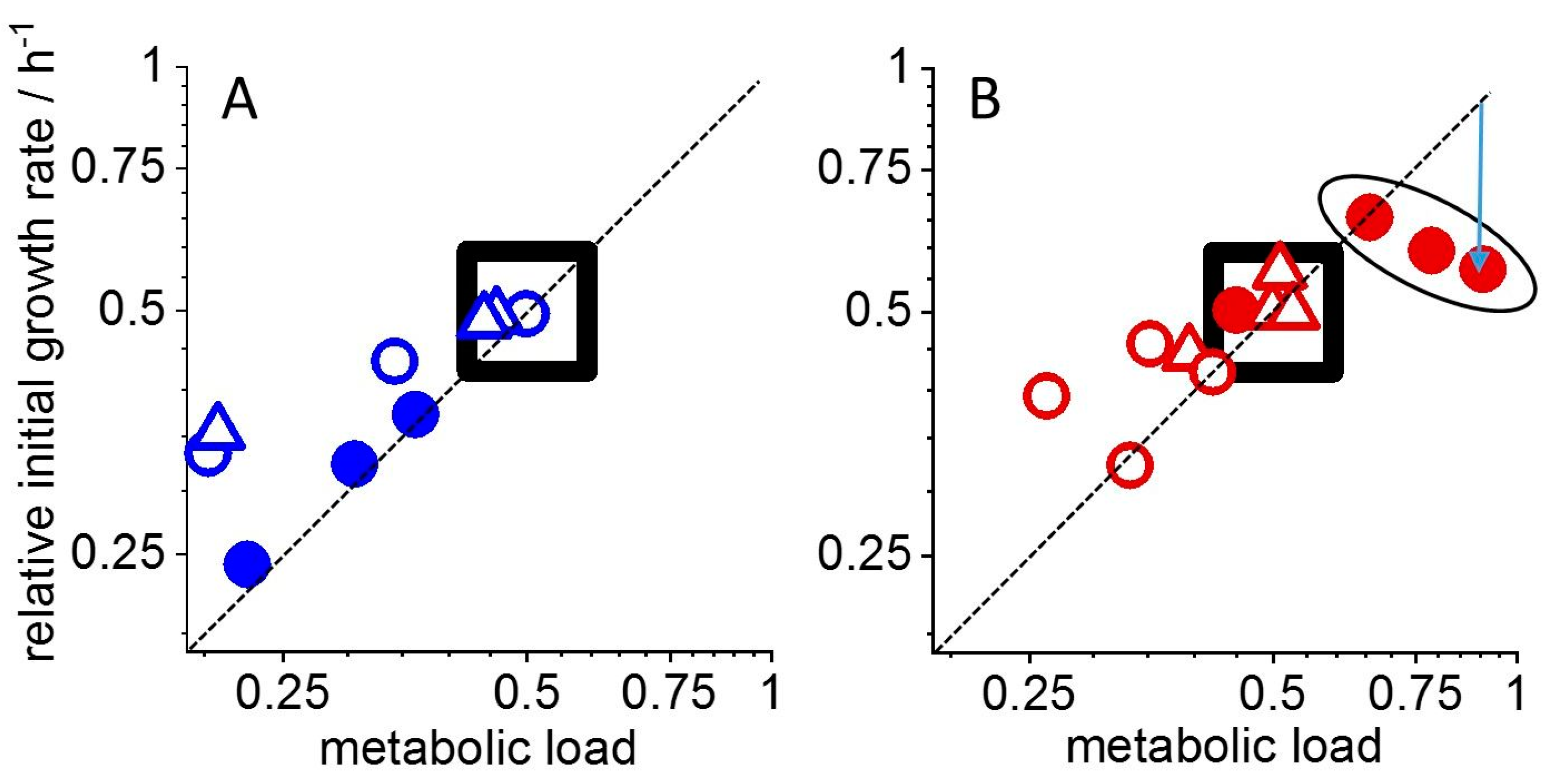
3. Results
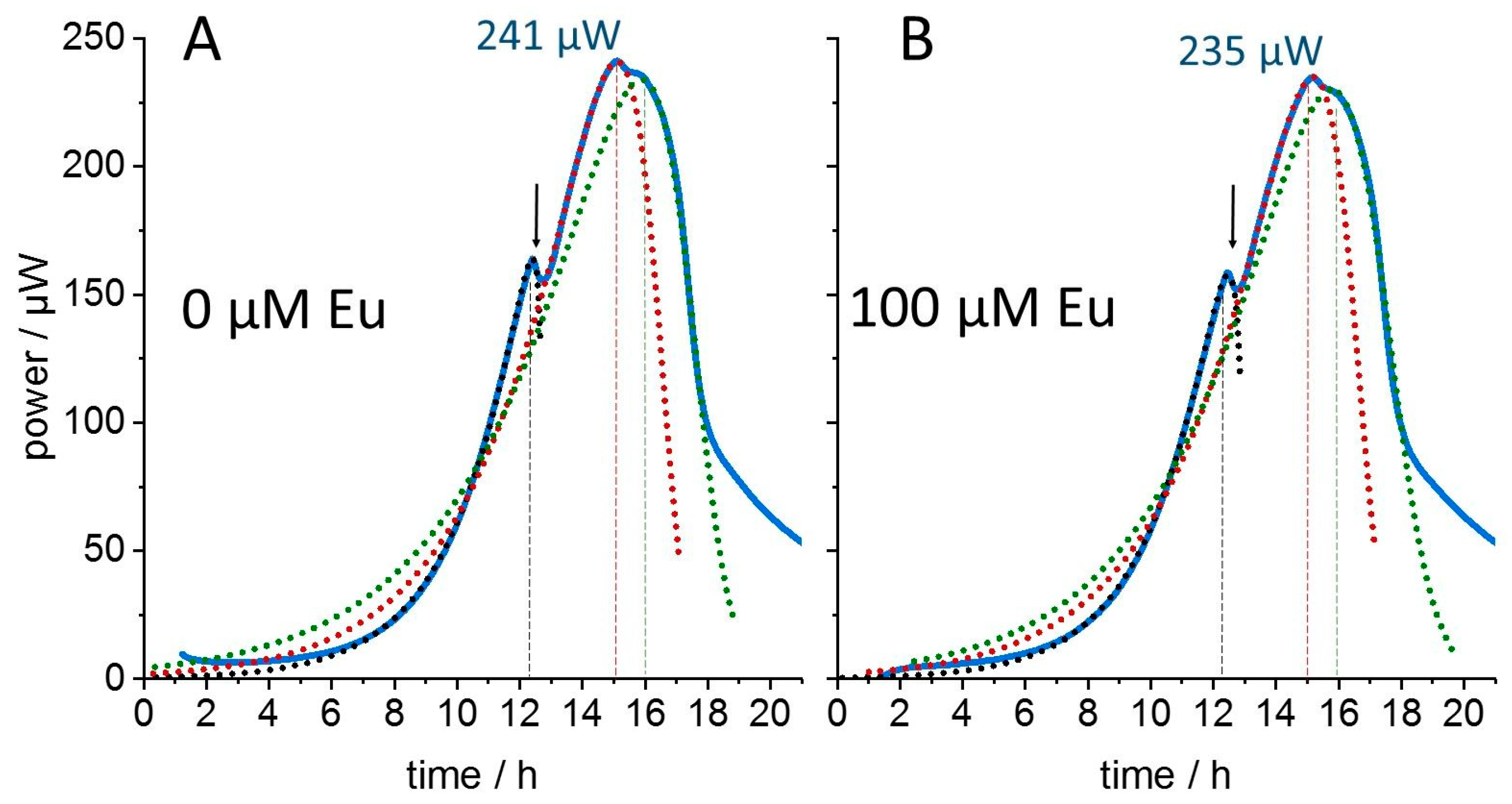
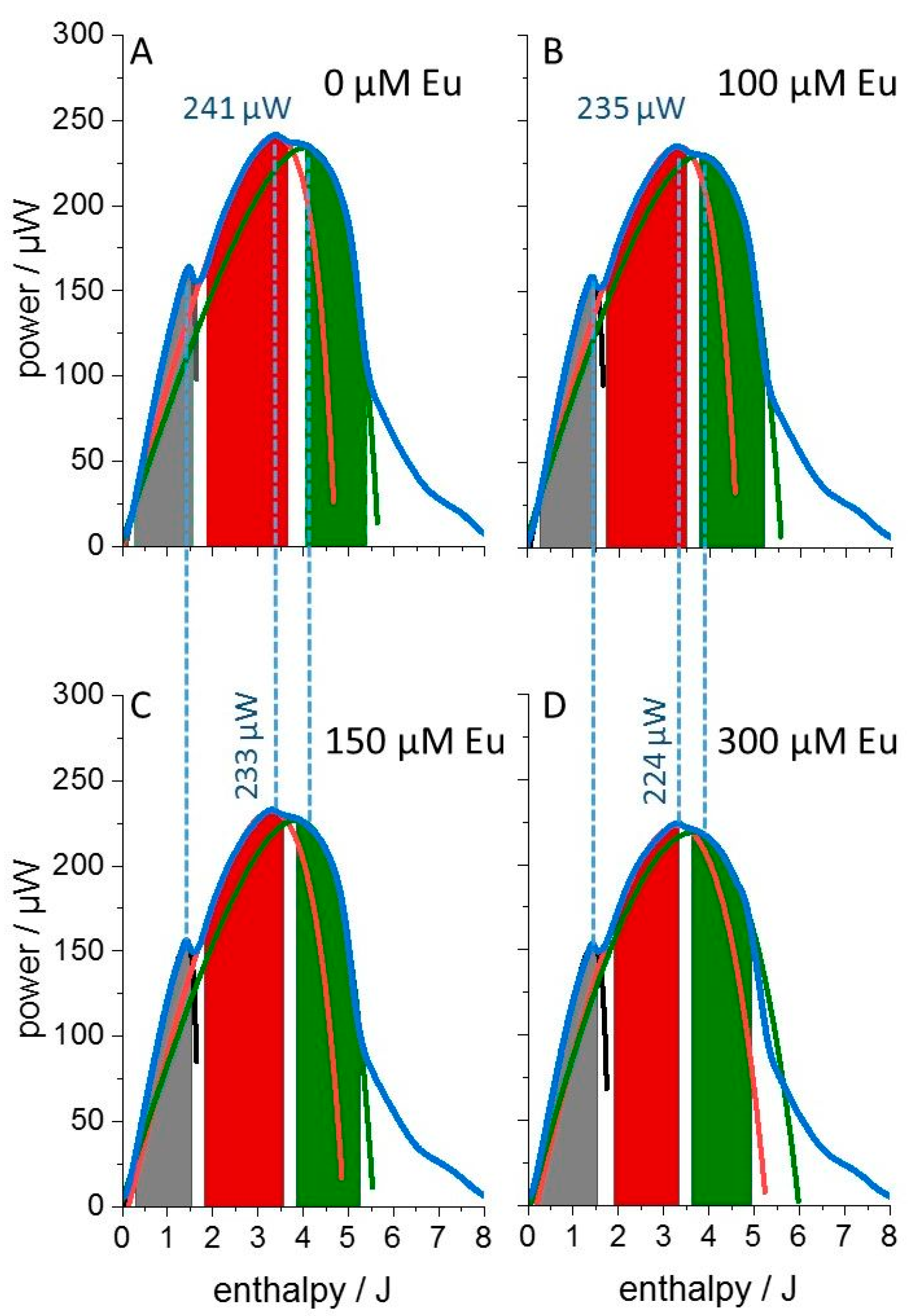
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| P(t) | Metabolic heat flow (thermal power in µW) as a function of time t (in hours) |
| H(t) | Accumulated heat (in Joule) released by cultured cell up to time t |
| H0 | maximally accumulated heat at the end of a given metabolic pathway |
| Hf | Fitting parameter in Joule (calorimetric analogon of a Monod constant) |
| Θ(H) | Metabolic load, i.e., metabolic activity relative to maximally possible activity with Θ(H) = (H0 − H)/(H0 − H + Hf) |
| r0 | Maximal intrinsic growth rate (h−1) of a culture of cells (analogous to rmax in mono-kinetics) |
| ri | Initial growth rate (ri = r0 · Θ(0)) |
References
- Eom, H.; Kang, W.; Kim, S.; Chon, K.; Lee, Y.-G.; Oh, S.-E. Improved toxicity analysis of heavy metal-contaminated water via a novel fermentative bacteria-based test kit. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, K.; Chandirika, J.U.; Vinothkanna, A.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Meng, D. Bacterial adaptive strategies to cope with metal toxicity in the contaminated environment—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao, S.G.; Ghneim-Herrera, T. Heavy Metals in Soils and the Remediation Potential of Bacteria Associated With the Plant Microbiome. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 604216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Goswami, L.; Lee, J.; Sonne, C.; Brown, R.J.C.; Kim, K.-H. Selenium in soil-microbe-plant systems: Sources, distribution, toxicity, tolerance, and detoxification. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 52, 2383–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Luo, D.; Li, Z. Uranium (U) source, speciation, uptake, toxicity and bioremediation strategies in soil-plant system: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberg, D.; Goodhead, D.T.; Frankenbergschwager, M.; Harbich, R.; Bance, D.A.; Wilkinson, R.E. Effectiveness of 1.5kev Aluminum-K and 0.3kev Carbon-K Characteristic X-Rays at Inducing DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Yeast-Cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1986, 50, 727–741. [Google Scholar]
- Prise, K.; Ahnström, G.; Belli, M.; Carlsson, J.; Frankenberg, D.; Kiefer, J.; Loöbrich, M.; Michael, B.D.; Nygren, J.; Simone, G.; et al. A review of dsb induction data for varying quality radiations. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1998, 74, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, T.J.; Delara, C.M.; Oneill, P.; Stevens, D.L. Induction and Rejoining of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in V79-4 Mammalian-Cells Following Gamma-Irradiation and Alpha-Irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1993, 64, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikjoo, H.; Munson, R.J.; Bridges, B.A. RBE-LET Relationships in Mutagenesis by Ionizing Radiation. J. Radiat. Res. 1999, 40, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yu, Q.; Qian, C.; Shao, H.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Lou, Y. Effects of different doses of electron beam irradiation on bacterial community of Portunus trituberculatus. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.H.; Oertel, J.; Solioz, M.; Fahmy, K. Mechanism of Attenuation of Uranyl Toxicity by Glutathione in Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3563–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, K.; Bargar, J.R.; Brown, J.G.E. Environmental Speciation of Actinides. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 52, 3510–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, K. Simple Growth–Metabolism Relations Are Revealed by Conserved Patterns of Heat Flow from Cultured Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choppin, G.; Liljenzin, J.O.; Rydberg, J. Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kabanova, N.; Kazarjan, A.; Stulova, I.; Vilu, R. Microcalorimetric study of growth of Lactococcus lactis IL1403 at different glucose concentrations in broth. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 496, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretenet, M.; Le Gall, G.; Wegmann, U.; Even, S.; Shearman, C.; Stentz, R.; Jeanson, S. Early adaptation to oxygen is key to the industrially important traits of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris during milk fermentation. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsmaier, E.M.; Skoog, F. Organic Growth Factor Requirements of Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1965, 18, 100–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, S.; Geipel, G.; Bok, F.; Oertel, J.; Fahmy, K. Calorimetrically Determined U(VI) Toxicity in Brassica napus Correlates with Oxidoreductase Activity and U(VI) Speciation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10843–10849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessat, J.; Sachs, S.; Moll, H.; John, W.; Steudtner, R.; Hübner, R.; Bok, F.; Stumpf, T. Bioassociation of U(VI) and Eu(III) by Plant (Brassica napus) Suspension Cell Cultures—A Spectroscopic Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6718–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzke, L.; Schaper, G.; März, J.; Kaden, P.; Huittinen, N.; Stumpf, T.; Kammerlander, K.K.; Brunner, E.; Hahn, P.; Mehnert, A.; et al. Coordination chemistry of f-block metal ions with ligands bearing bio-relevant functional groups. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 386, 267–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.; Thoenen, T.; Starke, S.; Spahiu, K.; Brendler, V. A critical review of the solution chemistry, solubility, and thermodynamics of europium: Recent advances on the Eu3+ aqua ion and the Eu(III) aqueous complexes and solid phases with the sulphate, chloride, and phosphate inorganic ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 473, 214608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanin, V.R.; de Castro, R.M.; Brown, E. 152Eu-Comments on Evaluation of Decay Data. Available online: https://hal-cea.archives-ouvertes.fr/cea-02476871 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Seltzer, S. Tables of X-Ray Mass Attenuation Coefficients and Mass Energy-Absorption Coefficients, NIST Standard Reference Database 126. Available online: https://doi.org/10.18434/t4d01f (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Smith, J.T.; Willey, N.; Hancock, J.T. Low dose ionizing radiation produces too few reactive oxygen species to directly affect antioxidant concentrations in cells. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodhead, D.T. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Energy. Health Phys. 1988, 55, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M. Radiation damage to DNA: The importance of track structure. Radiat. Meas. 1999, 31, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikjoo, H.; Uehara, S.; Emfietzoglou, D.; Brahme, A. Heavy charged particles in radiation biology and biophysics. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 075006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oertel, J.; Sachs, S.; Flemming, K.; Obeid, M.H.; Fahmy, K. Distinct Effects of Chemical Toxicity and Radioactivity on Metabolic Heat of Cultured Cells Revealed by “Isotope-Editing”. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030584
Oertel J, Sachs S, Flemming K, Obeid MH, Fahmy K. Distinct Effects of Chemical Toxicity and Radioactivity on Metabolic Heat of Cultured Cells Revealed by “Isotope-Editing”. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030584
Chicago/Turabian StyleOertel, Jana, Susanne Sachs, Katrin Flemming, Muhammad Hassan Obeid, and Karim Fahmy. 2023. "Distinct Effects of Chemical Toxicity and Radioactivity on Metabolic Heat of Cultured Cells Revealed by “Isotope-Editing”" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030584
APA StyleOertel, J., Sachs, S., Flemming, K., Obeid, M. H., & Fahmy, K. (2023). Distinct Effects of Chemical Toxicity and Radioactivity on Metabolic Heat of Cultured Cells Revealed by “Isotope-Editing”. Microorganisms, 11(3), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030584





