Animal Models for Studying Congenital Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction to Human Pregnancy
1.1. Three Trimesters of Pregnancy
1.2. Immunological Changes during Pregnancy to Understand HEV Related Effects
1.3. Hormonal Changes during Pregnancy to Understand HEV Related Effects
2. HEV Background
2.1. HEV New Classification
2.2. Geographical Distribution of HEV
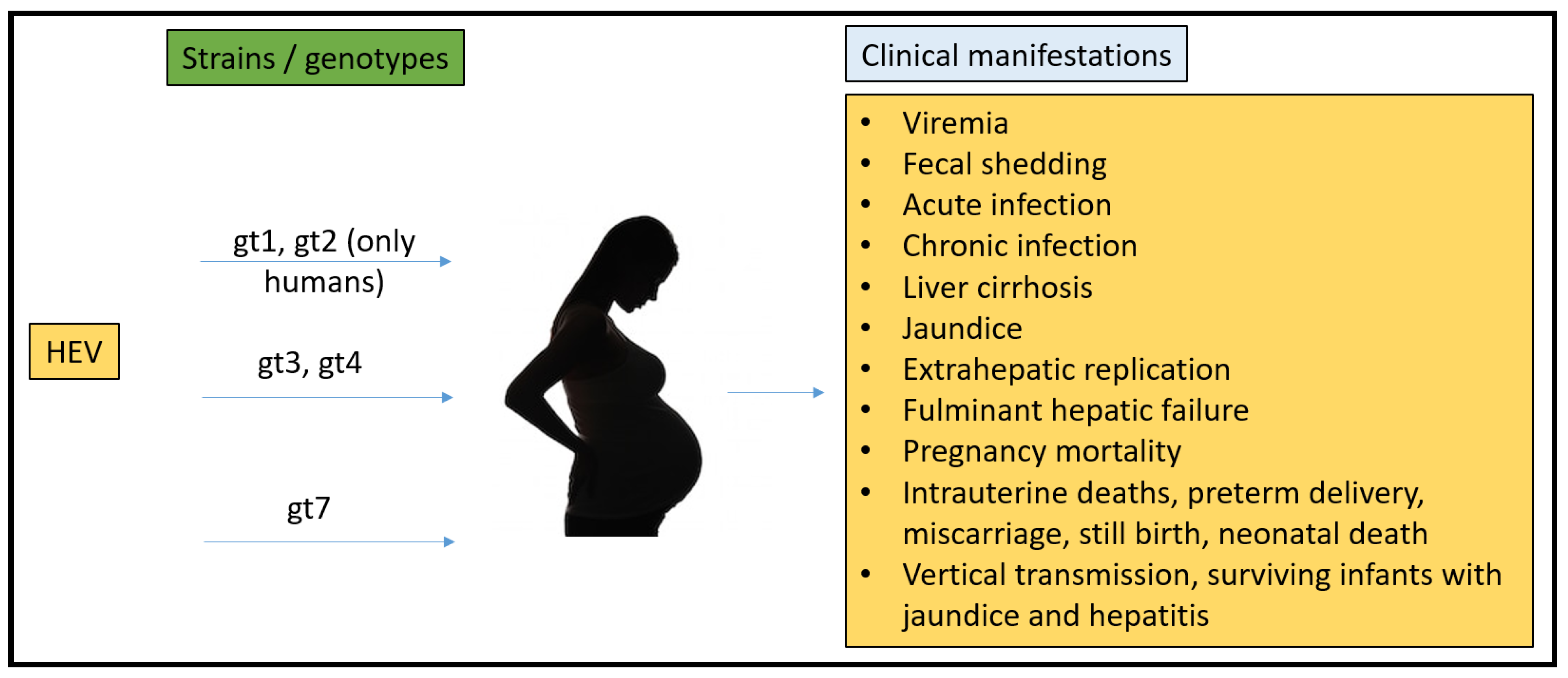
2.3. Pregnancy Mortality Reported Due to HEV
3. Characteristics of an Ideal Model Recapitulating HEV Infection in Humans
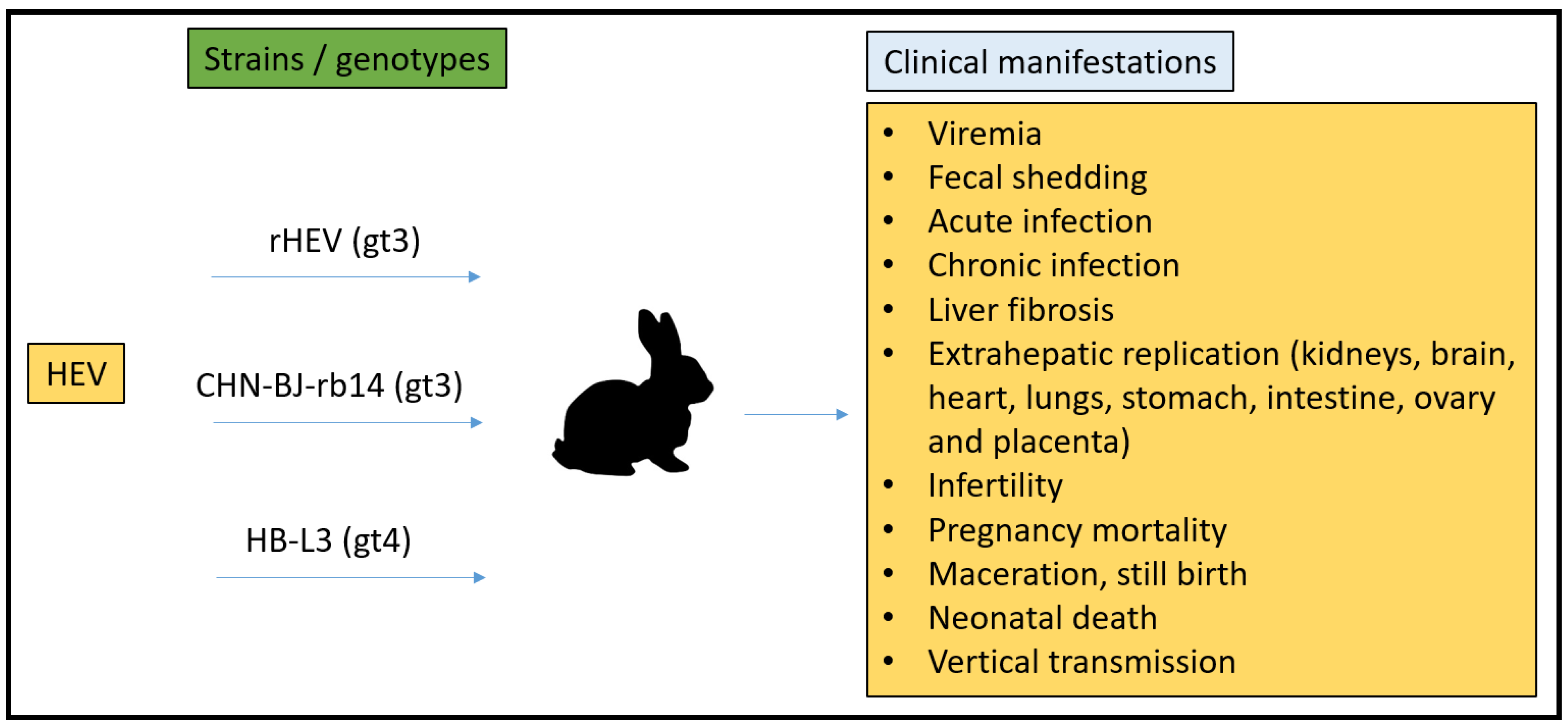
3.1. Rabbit Model
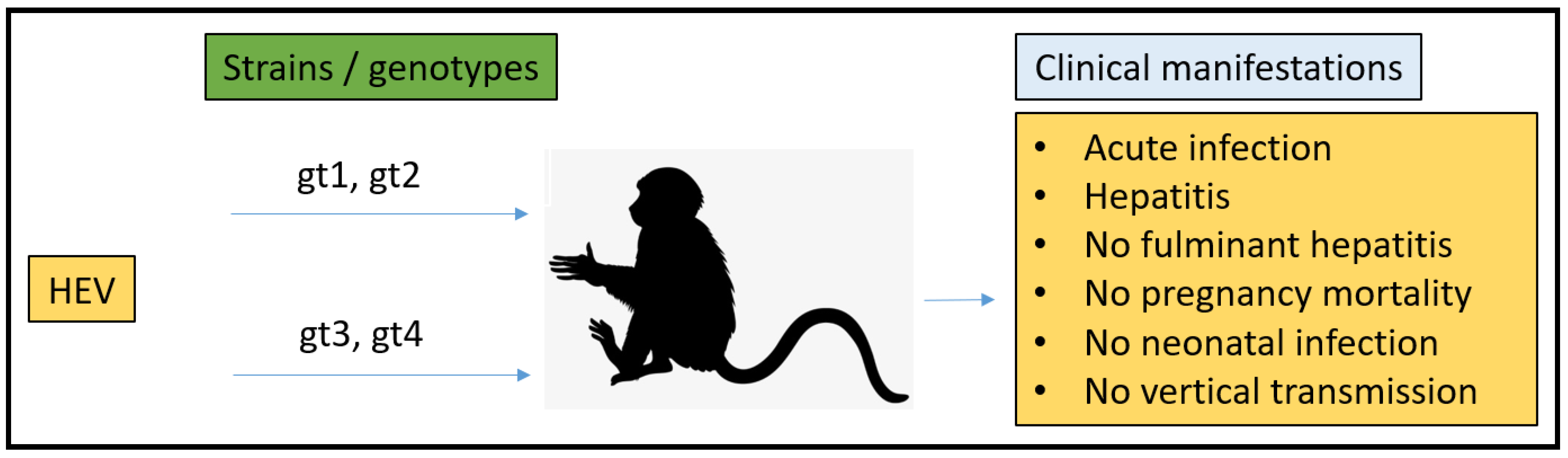
3.2. Non-Human Primates (NHPs) Model
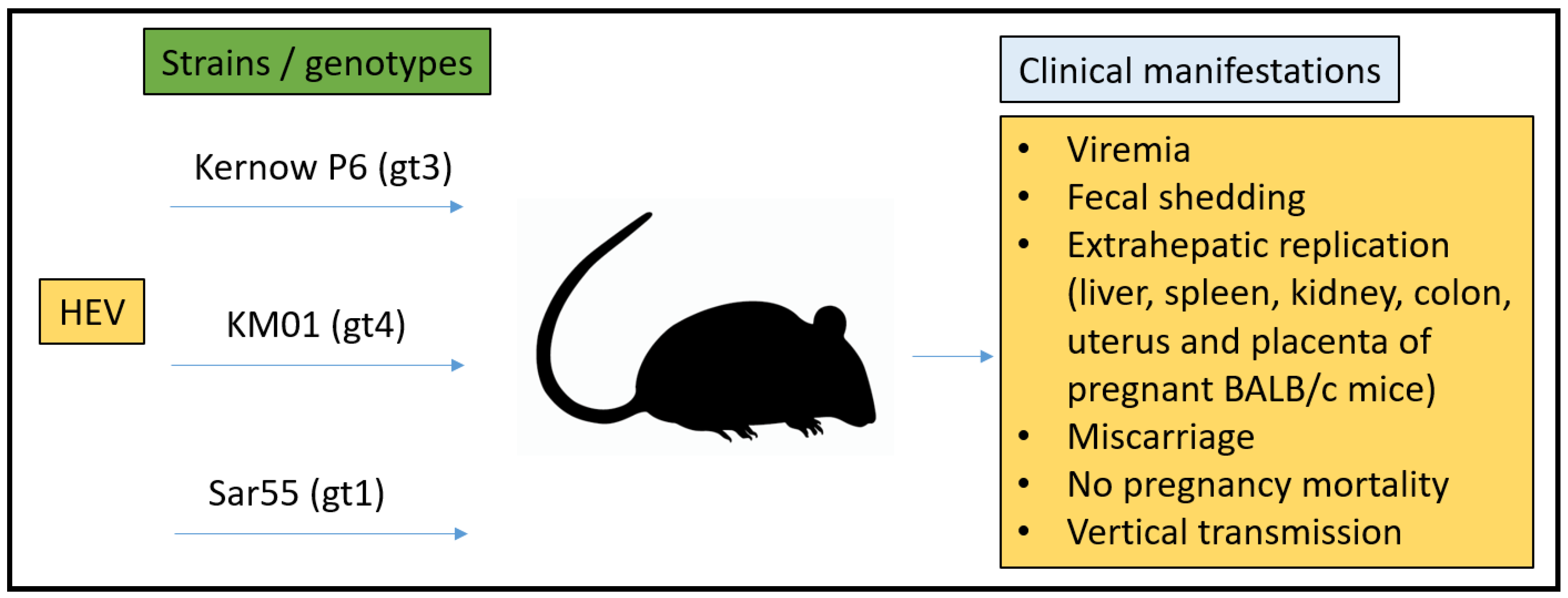
3.3. Mouse Model
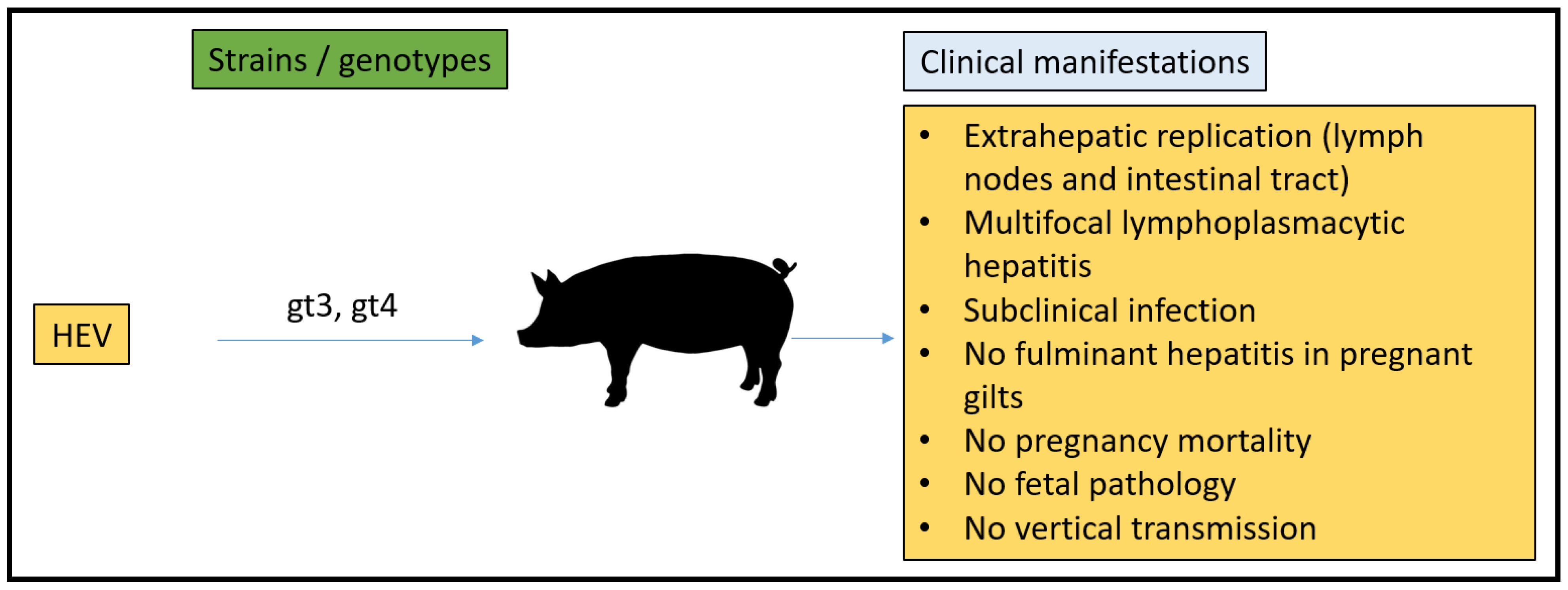
3.4. Pig Model
3.5. Chicken Model
4. In Vitro Models
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furukawa, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Sugiyama, A. A comparison of the histological structure of the placenta in experimental animals. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 27, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.E.; Lopez, K.H. Human, Reproductive Biology, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibble, J.D.; Halsey, C.R. Medical, Physiology: The, Big Picture; The McGraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Navaneethan, U.; Al Mohajer, M.; Shata, M.T. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Understanding the pathogenesis. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yadav, K.K.; Kenney, S.P. Hepatitis E Virus Immunopathogenesis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, G.; Koga, K. Macrophages and pregnancy. Reprod. Sci. 2008, 15, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, N.; Gnainsky, Y.; Granot, I.; Mor, G. Inflammation and implantation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dekel, N.; Gnainsky, Y.; Granot, I.; Racicot, K.; Mor, G. The role of inflammation for a successful implantation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014, 72, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, A. Immunology of the maternal-fetal interface. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Chiasson, V.L.; Bounds, K.R.; Mitchell, B.M. Regulation of the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-10 during Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghaeepour, N.; Ganio, E.A.; Mcilwain, D.; Tsai, A.S.; Tingle, M.; Van Gassen, S.; Gaudilliere, D.K.; Baca, Q.; McNeil, L.; Okada, R.; et al. An immune clock of human pregnancy. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaan2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PrabhuDas, M.; Bonney, E.; Caron, K.; Dey, S.; Erlebacher, A.; Fazleabas, A.; Fisher, S.; Golos, T.; Matzuk, M.; McCune, J.M.; et al. Immune mechanisms at the maternal-fetal interface: Perspectives and challenges. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, S.P.; Tomasi, T.B. Absence of MHC class II antigen expression in trophoblast cells results from a lack of class II transactivator (CIITA) gene expression. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1998, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells: Key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell 2000, 101, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granot, I.; Gnainsky, Y.; Dekel, N. Endometrial inflammation and effect on implantation improvement and pregnancy outcome. Reproduction 2012, 144, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shynlova, O.; Nadeem, L.; Zhang, J.; Dunk, C.; Lye, S. Myometrial activation: Novel concepts underlying labor. Placenta 2020, 92, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleine, B.; Rossmanith, W.G. Hormones and the Endocrine, System: Textbook of Endocrinology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arankalle, V.A.; Chadha, M.S.; Dama, B.M.; Tsarev, S.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Banerjee, K. Role of immune serum globulins in pregnant women during an epidemic of hepatitis E. J. Viral Hepat. 1998, 5, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Dizzell, S.E.; Leung, V.; Nazli, A.; Zahoor, M.A.; Fichorova, R.N.; Kaushic, C. Effects of Female Sex Hormones on Susceptibility to HSV-2 in Vaginal Cells Grown in Air-Liquid, Interface. Viruses 2016, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponta, H.; Kennedy, N.; Skroch, P.; Hynes, N.E.; Groner, B. Hormonal response region in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat can be dissociated from the proviral promoter and has enhancer properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montella, M.; D’Arena, G.; Crispo, A.; Capunzo, M.; Nocerino, F.; Grimaldi, M.; Barbieri, A.; D’Ursi, A.M.; Tecce, M.F.; Amore, A.; et al. Role of sex hormones in the Development and Progression of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 854530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taneja, V. Sex hormones determine immune response. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, A. Human, Chorionic Gonadotropin as a Pivotal endocrine immune regulator Initiating and preserving fetal tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rijhsinghani, A.G.; Thompson, K.; Bhatia, S.K.; Waldschmidt, T.J. Estrogen blocks early T cell development in the thymus. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1996, 36, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, G.C.; Mattei, A.; Gojnic, M.; Gerli, S. Progesterone and pregnancy. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 17, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Ding, J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L. Progesterone impairs antigen-non-specific immune protection by CD8 T memory cells via interferon-gamma gene hypermethylation. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, Y.T.; Chang, C.W.; Wei, R.J.; Wang, S.N. Progesterone and related compounds in hepatocellular carcinoma: Basic and clinical aspects. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 290575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debing, Y.; Moradpour, D.; Neyts, J.; Gouttenoire, J. Update on hepatitis E virology: Implications for clinical practice. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Hirai-Yuki, A.; McKnight, K.L.; Lemon, S.M. Naked viruses that aren’t always naked: Quasi-enveloped agents of acute hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.C.; Purcell, R.H.; Sreenivasan, M.A.; Prasad, S.R.; Pavri, K.M. Epidemic and endemic hepatitis in India: Evidence for a non-A.; non-B hepatitis virus aetiology. Lancet 1980, 2, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sridhar, S.; Teng, J.L.L.; Chiu, T.H.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Hepatitis E Virus Genotypes and Evolution: Emergence of Camel Hepatitis E Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, L.; Wang, J.C.; Li, T.C.; Yasutomi, Y.; Lara, J.; Khudyakov, Y.; Schofield, D.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H.; Takeda, N.; et al. Spatial configuration of hepatitis E virus antigenic domain. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montpellier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Meunier, J.C.; Saliou, J.M.; Ankavay, M.; Bull, A.; Pillez, A.; Abravanel, F.; Helle, F.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus Lifecycle and Identification of 3 Forms of the ORF2 Capsid Protein. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 211–223.e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ying, D.; Lhomme, S.; Tang, Z.; Walker, C.M.; Xia, N.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Z. Origin, antigenicity, and function of a secreted form of ORF2 in hepatitis E virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E. Hepatitis E virus ORF3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nair, V.P.; Anang, S.; Subramani, C.; Madhvi, A.; Bakshi, K.; Srivastava, A.; Shalimar Nayak, B.; Ranjith Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Synthesis of a Novel Viral Factor Mediates Efficient Replication of Genotype-1 Hepatitis E Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanggis Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Nagashima, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Kunita, S.; Hayama, E.; Tanaka, T.; Mulyanto Okamoto, H. An analysis of two open reading frames (ORF3 and ORF4) of rat hepatitis E virus genome using its infectious cDNA clones with mutations in ORF3 or ORF4. Virus Res. 2018, 249, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, K.K.; Boley, P.A.; Fritts, Z.; Kenney, S.P. Ectopic Expression of Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus ORF4 Increases Genotype 3 HEV Viral Replication in Cell Culture. Viruses 2021, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.L. Chirohepevirus from Bats: Insights into Hepatitis E Virus Diversity and Evolution. Viruses 2022, 14, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Kamar, N.; Sandres-Saune, K.; Garrouste, C.; Dubois, M.; Mansuy, J.M.; Muscari, F.; Sallusto, F.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J. Characteristics of autochthonous hepatitis E virus infection in solid-organ transplant recipients in France. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labrique, A.; Kuniholm, M.; Nelson, K. Emerging Infections; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rein, D.B.; Stevens, G.A.; Theaker, J.; Wittenborn, J.S.; Wiersma, S.T. The global burden of hepatitis E virus genotypes 1 and 2 in 2005. Hepatology 2012, 55, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshale, E.H.; Hu, D.J.; Holmberg, S.D. The two faces of hepatitis E virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.J. From barnyard to food table: The omnipresence of hepatitis E virus and risk for zoonotic infection and food safety. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teo, C.G. Much meat, much malady: Changing perceptions of the epidemiology of hepatitis E. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuniholm, M.H.; Purcell, R.H.; McQuillan, G.M.; Engle, R.E.; Wasley, A.; Nelson, K.E. Epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in the United States: Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nelson, K.E.; Kmush, B.; Labrique, A.B. The epidemiology of hepatitis E virus infections in developed countries and among immunocompromised patients. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wahlberg, N.; Belak, S.; Meng, X.J.; Liu, L. The emergence of genotypes 3 and 4 hepatitis E virus in swine and humans: A phylogenetic perspective. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Taneja, S.; Kalia, M.; Jameel, S. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus. J. Biosci. 2008, 33, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavio, N.; Meng, X.-J.; Renou, C. Zoonotic hepatitis E: Animal reservoirs and emerging risks. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, A.; Webb, G.; Ferguson, J. Clinical presentations of Hepatitis E: A clinical review with representative case histories. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rab, M.A.; Bile, M.K.; Mubarik, M.M.; Asghar, H.; Sami, Z.; Siddiqi, S.; Dil, A.S.; Barzgar, M.A.; Chaudhry, M.A.; Burney, M.I. Water-borne hepatitis E virus epidemic in Islamabad, Pakistan: A common source outbreak traced to the malfunction of a modern water treatment plant. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, C.G. Fatal outbreaks of jaundice in pregnancy and the epidemic history of hepatitis E. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 767–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, M. Hepatitis Frontiers; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Boccia, D.; Guthmann, J.P.; Klovstad, H.; Hamid, N.; Tatay, M.; Ciglenecki, I.; Nizou, J.Y.; Nicand, E.; Guerin, P.J. High mortality associated with an outbreak of hepatitis E among displaced persons in Darfur, Sudan. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arankalle, V.A.; Chobe, L.P. Hepatitis E virus: Can it be transmitted parenterally? J. Viral Hepat. 1999, 6, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Kamali, S.; Jameel, S. Vertical transmission of hepatitis E virus. Lancet 1995, 345, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.M.; Uduman, S.; Rana, S.; Kochiyil, J.K.; Usmani, A.; Thomas, L. Sero-prevalence and mother-to-infant transmission of hepatitis E virus among pregnant women in the United Arab Emirates. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001, 100, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Kamili, S.; Khuroo, M.S. Clinical course and duration of viremia in vertically transmitted hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection in babies born to HEV-infected mothers. J. Viral Hepat. 2009, 16, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, R.H. The Hepatitis Viruses: An Overview. In Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease; Nishioka, K., Suzuki, H., Mishiro, S., Oda, T., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Arankalle, V.A.; Chadha, M.S.; Tsarev, S.A.; Emerson, S.U.; Risbud, A.R.; Banerjee, K.; Purcell, R.H. Seroepidemiology of water-borne hepatitis in India and evidence for a third enterically-transmitted hepatitis agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3428–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purdy, M.A.; Khudyakov, Y.E. Evolutionary history and population dynamics of hepatitis E virus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, M.A.; Khudyakov, Y.E. The molecular epidemiology of hepatitis E virus infection. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, S.S.; Viswanathan, R. Infectious hepatitis in pregnancy during Delhi epidemic. Indian J. Med. Res. 1957, 45, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Balayan, M.S.; Andjaparidze, A.G.; Savinskaya, S.S.; Ketiladze, E.S.; Braginsky, D.M.; Savinov, A.P.; Poleschuk, V.F. Evidence for a virus in non-A.; non-B hepatitis transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Intervirology 1983, 20, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Kumar, A.; Trivedi, S.S.; Puri, M.; Sarin, S.K. Maternal and fetal outcomes in pregnant women with acute hepatitis E virus infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beniwal, M.; Kumar, A.; Kar, P.; Jilani, N.; Sharma, J.B. Prevalence and severity of acute viral hepatitis and fulminant hepatitis during pregnancy: A prospective study from north India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 21, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsega, E.; Hansson, B.G.; Krawczynski, K.; Nordenfelt, E. Acute sporadic viral hepatitis in Ethiopia: Causes, risk factors, and effects on pregnancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 14, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goumba, C.M.; Yandoko-Nakoune, E.R.; Komas, N.P. A fatal case of acute hepatitis E among pregnant women, Central African Republic. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ICDDRB. Outbreak of hepatitis E in a low income urban community in Bangladesh. Health Sci. Bull. 2009, 7, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheeda, C.A.; Navaneethan, U.; Jayanthi, V. Liver disease in pregnancy and its influence on maternal and fetal mortality: A prospective study from Chennai, Southern India. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayis, D.A.; Jumaa, A.M.; Gasim, G.I.; Karsany, M.S.; Adam, I. An outbreak of hepatitis E and high maternal mortality at Port Sudan, Eastern Sudan. Pathog. Glob. Health 2013, 107, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, J.S. The mammalian fetal membranes. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1981, 62, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadsby, J.E.; Keyes, P.L.; Bill, C.H., 2nd. Control of corpus luteum function in the pregnant rabbit: Role of estrogen and lack of a direct luteotropic role of the placenta. Endocrinology 1983, 113, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, Z.; Harrison, T.J.; Feng, R.; Zhang, C.; Qiao, Z.; Fan, J.; Ma, H.; Li, M.; Song, A.; et al. A novel genotype of hepatitis E virus prevalent among farmed rabbits in China. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.S.; Park, B.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Song, C.S.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Prevalence and genetic features of rabbit hepatitis E virus in Korea. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossaboom, C.M.; Cordoba, L.; Dryman, B.A.; Meng, X.J. Hepatitis E virus in rabbits, Virginia, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2047–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izopet, J.; Dubois, M.; Bertagnoli, S.; Lhomme, S.; Marchandeau, S.; Boucher, S.; Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Guerin, J.L. Hepatitis E virus strains in rabbits and evidence of a closely related strain in humans, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolo, I.; De Sabato, L.; Marata, A.; Martinelli, N.; Magistrali, C.F.; Monini, M.; Ponterio, E.; Ostanello, F.; Ruggeri, F.M. Serological survey of hepatitis E virus infection in farmed and pet rabbits in Italy. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, P.; Zou, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, H. Experimental infection of pregnant rabbits with hepatitis E virus demonstrating high mortality and vertical transmission. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, H. SPF rabbits infected with rabbit hepatitis E virus isolate experimentally showing the chronicity of hepatitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Xia, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Experimental infection of rabbits with genotype 3 hepatitis E virus produced both chronicity and kidney injury. Gut 2017, 66, 561–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Liu, T.; She, R.; Wu, Q.; Tian, J.; Shi, R.; Hao, W.; Ren, X.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Replication of hepatitis E virus in the ovary and promotion of oocyte apoptosis in rabbits infected with HEV-4. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 4475–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Harrison, T.J.; Ma, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Experimental infection of rabbits with rabbit and genotypes 1 and 4 hepatitis E viruses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Dai, X.; Shi, C.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhan, S.; Meng, J. Rabbit as a novel animal model for hepatitis E virus infection and vaccine evaluation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; et al. Chronic Infection With Camelid Hepatitis E virus in a Liver Transplant Recipient Who Regularly Consumes Camel Meat and Milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355–357.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Bu, Q.N.; Wang, L.; Han, J.; Du, R.J.; Lei, Y.X.; Ouyang, Y.Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.H.; Lu, F.M.; et al. Transmission of hepatitis E virus from rabbits to cynomolgus macaques. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Shi, R.; Liu, T.; She, R.; Wu, Q.; An, J.; Hao, W.; Soomro, M.H. Brain Infection by Hepatitis E Virus Probably via Damage of the Blood-Brain, Barrier Due to Alterations of Tight Junction Proteins. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, S.; He, Q.; Liang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L. Hepatitis, E-related adverse pregnancy outcomes and their prevention by hepatitis E vaccine in a rabbit model. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, W.; Song, W.T.; Fu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, H. Different susceptibility and pathogenesis of rabbit genotype 3 hepatitis E virus (HEV-3) and human HEV-3 (JRC-HE3) in SPF rabbits. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.M. Animal models of human placentation—A review. Placenta 2007, 28, S41–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, E.D.; Pepe, G.J. Placental steroid hormone biosynthesis in primate pregnancy. Endocr. Rev. 1990, 11, 124–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, K.; Meng, X.J.; Rybczynska, J. Pathogenetic elements of hepatitis E and animal models of HEV infection. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, R.H.; Engle, R.E.; Govindarajan, S.; Herbert, R.; St Claire, M.; Elkins, W.R.; Cook, A.; Shaver, C.; Beauregard, M.; Swerczek, J.; et al. Pathobiology of hepatitis E: Lessons learned from primate models. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013, 2, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarev, S.A.; Tsareva, T.S.; Emerson, S.U.; Govindarajan, S.; Shapiro, M.; Gerin, J.L.; Purcell, R.H. Successful passive and active immunization of cynomolgus monkeys against hepatitis E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10198–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsarev, S.A.; Tsareva, T.S.; Emerson, S.U.; Yarbough, P.O.; Legters, L.J.; Moskal, T.; Purcell, R.H. Infectivity titration of a prototype strain of hepatitis E virus in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 43, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticehurst, J.; Rhodes, L.L., Jr.; Krawczynski, K.; Asher, L.V.S.; Engler, W.F.; Mensing, T.L.; Caudill, J.D.; Sjogren, M.H.; Hoke, C.H., Jr.; LeDuc, J.W.; et al. Infection of Owl Monkeys (Aotus trivirgatus) and Cynomolgus Monkeys (Macaca fascicularist) with Hepatitis E virus from Mexico. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 165, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsarev, S.A.; Tsareva, T.S.; Emerson, S.U.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Ticehurst, J.; London, W.; Purcell, R.H. ELISA for Antibody to Hepatitis E virus (HEV) Based on Complete Open-Reading Frame-2 Protein Expressed in Insect Cells: Identification of HEV Infection in Primates. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsarev, S.A.; Tsareva, T.S.; Emerson, S.U.; Rippy, M.K.; Zack, P.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.H. Experimental hepatitis E in pregnant rhesus monkeys: Failure to transmit hepatitis E virus (HEV) to offspring and evidence of naturally acquired antibodies to HE.V. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Huang, F. Vertical transmission of hepatitis E virus in pregnant rhesus macaques. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardinali, N.R.; Guimarães, J.R.; Melgaço, J.G.; Kevorkian, Y.B.; Bottino, F.O.; Vieira, Y.R.; da Silva, A.C.; Pinto, D.P.; da Fonseca, L.B.; Vilhena, L.S.; et al. Cynomolgus monkeys are successfully and persistently infected with hepatitis E virus genotype 3 (HEV-3) after long-term immunosuppressive therapy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.M.; Green, J.A.; Schulz, L.C. The evolution of the placenta. Reproduction 2016, 152, R179–R189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, A.M.; Enders, A.C. Comparative aspects of trophoblast development and placentation. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2004, 2, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.A. The endocrine function of human placenta: An overview. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2016, 32, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napso, T.; Yong, H.E.J.; Lopez-Tello, J.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. The, Role of Placental, Hormones in Mediating Maternal Adaptations to Support Pregnancy and Lactation. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, F.; Chen, Q. Humanized Mouse Models for the Study of Infection and Pathogenesis of Human Viruses. Viruses 2018, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaki, H.; Oshiumi, H.; Shingai, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. Development of mouse models for analysis of human virus infections. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 61, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayed, I.M.; Verhoye, L.; Cocquerel, L.; Abravanel, F.; Foquet, L.; Montpellier, C.; Debing, Y.; Farhoudi, A.; Wychowski, C.; Dubuisson, J. Study of hepatitis E virus infection of genotype 1 and 3 in mice with humanised liver. Gut 2017, 66, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Garde, M.D.; Pas, S.D.; Van Der Net, G.; Robert, A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Haagmans, B.L.; Boonstra, A.; Vanwolleghem, T. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) genotype 3 infection of human liver chimeric mice as a model for chronic HEV infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4394–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allweiss, L.; Gass, S.; Giersch, K.; Groth, A.; Kah, J.; Volz, T.; Rapp, G.; Schöbel, A.; Lohse, A.W.; Polywka, S. Human liver chimeric mice as a new model of chronic hepatitis E virus infection and preclinical drug evaluation. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.M.; Foquet, L.; Verhoye, L.; Abravanel, F.; Farhoudi, A.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Izopet, J.; Meuleman, P. Transmission of hepatitis E virus infection to human-liver chimeric FRG mice using patient plasma. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Long, F.; He, Q.; Huang, F.; Yu, W. Successful Establishment of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Pregnant BALB/c Mice. Viruses 2019, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salek Farrokhi, A.; Zarnani, A.H.; Moazzeni, S.M. Mesenchymal stem cells therapy protects fetuses from resorption and induces Th2 type cytokines profile in abortion prone mouse model. Transpl. Immunol. 2018, 47, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Mickael, H.K.; Xu, L.; Xia, Y.; Cong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Li, T.; Wei, D.; et al. Uterine Injury Caused by Genotype 4 Hepatitis E Virus Infection Based on a BALB/c Mice Model. Viruses 2021, 13, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L. Animal Models for Hepatitis E virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 948, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corneillie, L.; Banda, D.H.; Meuleman, P. Animal Models for Hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spencer, T.E.; Johnson, G.A.; Burghardt, R.C.; Bazer, F.W. Progesterone and placental hormone actions on the uterus: Insights from domestic animals. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 71, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Halbur, P.G.; Lehman, J.R.; Webb, D.M.; Tsareva, T.S.; Haynes, J.S.; Thacker, B.J.; Emerson, S.U. A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9860–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.J. Hepatitis E virus: Animal reservoirs and zoonotic risk. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, T.P.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Halbur, P.G.; Haqshenas, G.; Guenette, D.K.; Toth, T.E.; Meng, X.J. Evidence of extrahepatic sites of replication of the hepatitis E virus in a swine model. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3040–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halbur, P.G.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Gilbert, C.; Guenette, D.; Potters, M.B.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U.; Toth, T.E.; Meng, X.J. Comparative pathogenesis of infection of pigs with hepatitis E viruses recovered from a pig and a human. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasorndorkbua, C.; Thacker, B.J.; Halbur, P.G.; Guenette, D.K.; Buitenwerf, R.M.; Royer, R.L.; Meng, X.-J. Experimental infection of pregnant gilts with swine hepatitis E virus. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 67, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.W.; Haqshenas, G.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Halbur, P.G.; Emerson, S.U.; Meng, X.J. Capped, RNA Transcripts of Full-Length cDNA Clones of Swine Hepatitis E Virus are Replication competent when Transfected into Huh7 Cells and Infectious when Intrahepatically inoculated into Pigs. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Deus, N.; Casas, M.; Peralta, B.; Nofrarias, M.; Pina, S.; Martin, M.; Segales, J. Hepatitis E virus infection dynamics and organic distribution in naturally infected pigs in a farrow-to-finish farm. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leblanc, D.; Ward, P.; Gagne, M.J.; Poitras, E.; Muller, P.; Trottier, Y.L.; Simard, C.; Houde, A. Presence of hepatitis E virus in a naturally infected swine herd from nursery to slaughter. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwknegt, M.; Rutjes, S.A.; Reusken, C.B.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Frankena, K.; de Jong, M.C.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Poel, W.H. The course of hepatitis E virus infection in pigs after contact-infection and intravenous inoculation. BMC Vet. Res. 2009, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollock, C.G.; Orosz, S.E. Avian reproductive anatomy, physiology and endocrinology. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2002, 5, 441–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haqshenas, G.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Woolcock, P.R.; Read, D.H.; Meng, X.J. Genetic identification and characterization of a novel virus related to human hepatitis E virus from chickens with hepatitis-splenomegaly syndrome in the United, States. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, A.; Bilic, I.; Prokofieva, I.; Hess, M. Phylogenetic analysis of avian hepatitis E virus samples from European and Australian chicken flocks supports the existence of a different genus within the Hepeviridae comprising at least three different genotypes. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, C.J.; Ellis, T.M.; Plant, S.L.; Gregory, A.R.; Wilcox, G.E. Sequence data suggests big liver and spleen disease virus (BLSV) is genetically related to hepatitis E virus. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 68, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.F.; Haqshenas, G.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Guenette, D.K.; Woolcock, P.R.; Larsen, C.T.; Pierson, F.W.; Elvinger, F.; Toth, T.E.; Meng, X.J. Heterogeneity and seroprevalence of a newly identified avian hepatitis e virus from chickens in the United, States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4197–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billam, P.; Huang, F.F.; Sun, Z.F.; Pierson, F.W.; Duncan, R.B.; Elvinger, F.; Guenette, D.K.; Toth, T.E.; Meng, X.J. Systematic pathogenesis and replication of avian hepatitis E virus in specific-pathogen-free adult chickens. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3429–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yugo, D.M.; Cossaboom, C.M.; Meng, X.-J. Naturally occurring animal models of human hepatitis E virus infection. ILAR J. 2014, 55, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Yin, X.; Fan, B.; Fan, X.; Wang, J. Real-time RT-PCR for H5N1 avian influenza A virus detection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Zhou, E.N.M.; Sun, Z.; Meng, X.-J. Egg whites from eggs of chickens infected experimentally with avian hepatitis E virus contain infectious virus, but evidence of complete vertical transmission is lacking. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knegendorf, L.; Drave, S.A.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Brown, R.J.P.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Resner, K.; Friesland, M.; Khera, T.; Engelmann, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication and interferon responses in human placental cells. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gouilly, J.; Chen, Q.; Siewiera, J.; Cartron, G.; Levy, C.; Dubois, M.; Al-Daccak, R.; Izopet, J.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N.; El Costa, H. Genotype specific pathogenicity of hepatitis E virus at the human maternal-fetal interface. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Othman, E.R.; Khashbah, M.Y.; Ismael, A.; Ghaliony, M.A.; Seddik, M.I.; Sayed, I.M. Evidence of the Extrahepatic Replication of Hepatitis E virus in Human Endometrial Stromal cells. Pathogens 2020, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arez, F.; Rodrigues, A.F.; Brito, C.; Alves, P.M. Bioengineered liver cell models of hepatotropic infections. Viruses 2021, 13, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, K.K.; Kenney, S.P. Animal Models for Studying Congenital Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030618
Yadav KK, Kenney SP. Animal Models for Studying Congenital Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030618
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Kush Kumar, and Scott P. Kenney. 2023. "Animal Models for Studying Congenital Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030618
APA StyleYadav, K. K., & Kenney, S. P. (2023). Animal Models for Studying Congenital Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus. Microorganisms, 11(3), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030618






