Impact of Global Warming on the Severity of Viral Diseases: A Potentially Alarming Threat to Sustainable Aquaculture Worldwide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
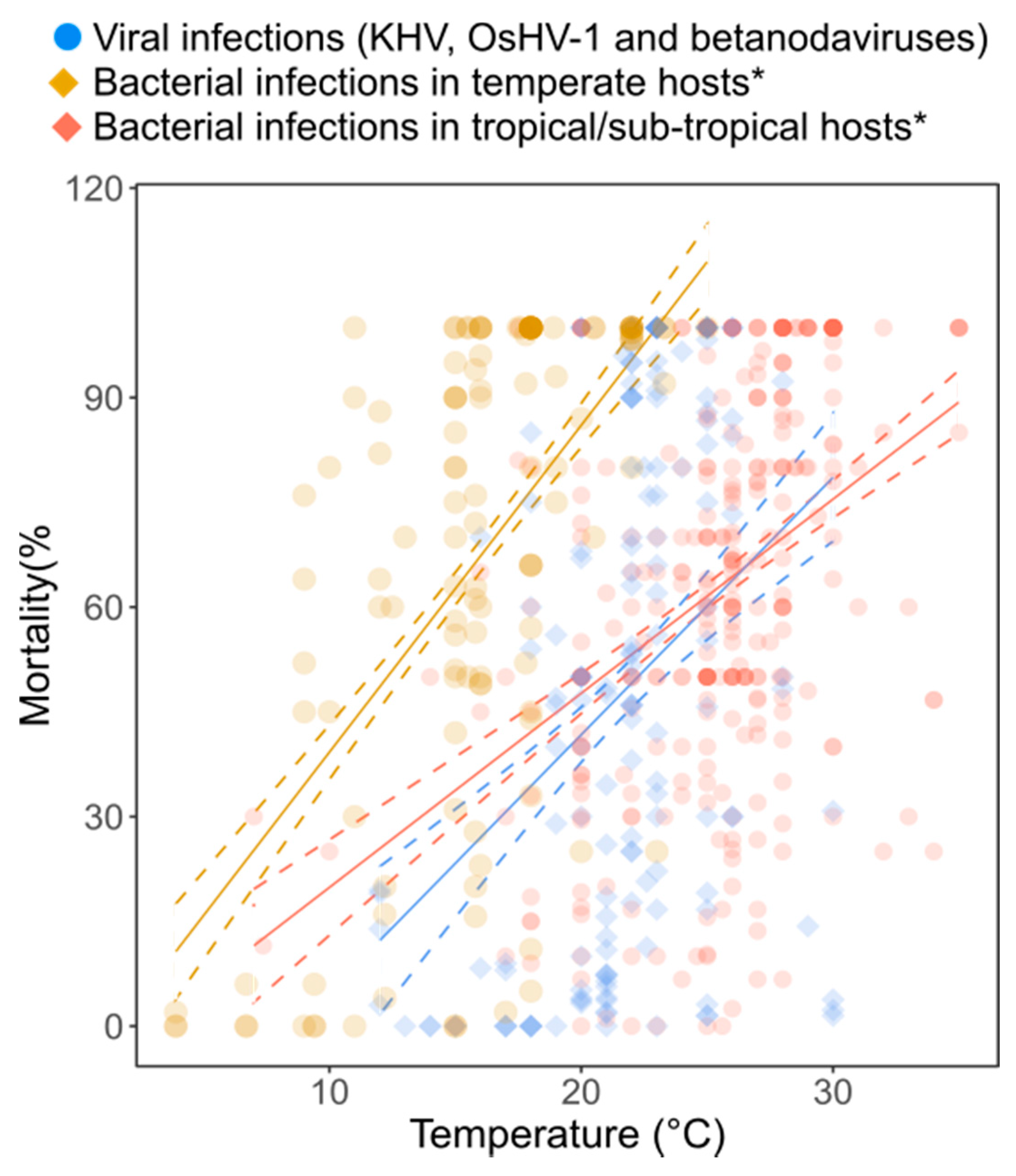
3.1. Relationship between Mortality of Virus-Infected Animals and Temperature
3.2. Model Predictions for OsHV-1, CyHV-3 and NVVs
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Global Warming on Viral Epidemics in Aquaculture Systems
4.2. Sustainable Aquaculture Practices to Prevent EID Outbreaks
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kibenge, F.D.B. Emerging viruses in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Bateman, I.J.; Hinchliffe, S.J.; Bass, D.; Hartnell, R.; Santos, E.M.; Devlin, M.J.; Feist, S.W.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; et al. Sustainable aquaculture through the One Health Lens. Nat. Food. 2020, 1, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018—Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018.
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Troell, M.; Naylor, R.L.; Metian, M.; Beveridge, M.; Tyedmers, P.H.; Folke, C.; Arrow, K.J.; Barrett, S.; Crépin, A.S.; Ehrlich, P.R.; et al. Does aquaculture add resilience to the global food system? Proc. Royal Soc. B. 2014, 111, 13257–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverter, M.; Sarter, S.; Caruso, D.; Avarre, J.-C.; Combe, M.; Pepey, E.; Pouyaud, L.; Vega-Heredía, S.; de Verdal, H.; Gozlan, R.E. Aquaculture at the crossroads of global warming and antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Comm. 2020, 11, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World bank report number 83177-glb: Agriculture and environmental services discussion paper 03. In Fish to 2030 Prospects for Fisheries and Aquaculture; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Froehlich, H.E.; Runge, C.A.; Gentry, R.R.; Gaines, S.D.; Halpern, B.S. Comparative terrestrial feed and land use of an aquaculture-dominant world. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5295–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, A.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bron, J.; Paladini, G.; Brooker, E.; Brooker, A. Economic impacts of aquatic parasites on global finfish production. Global Aquacult. Advocate. 2015, 2015, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherdon, L.V.; Magnan, A.K.; Rogers, A.D.; Sumaila, U.R.; Cheung, W.W.L. Observed and projected impacts of climate change on marine fisheries, aquaculture, coastal tourism, and human health: An update. Front. Marine Sci. 2016, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.K.; Trivedi, R.K.; Chand, B.K.; Mandal, B.; Rout, S.K. Farmers’ perceptions of climate change, impacts on freshwater aquaculture and adaptation strategies in climatic change hotspots: A case of the Indian Sundarban delta. Environ. Develop. 2017, 21, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Monier, M.N.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Faggio, C. Fish response to hypoxia stress: Growth, physiological, and immunological biomarkers. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, L.; Lee, K.; Cannito, B.; Gilmore, A.; Campbell-Lendrum, D. Globalization and infectious diseases: A review of the linkages. In Special Programme for Research & Training in Tropical Diseases (TFR); UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vezzulli, L.; Grande, C.; Reid, P.C.; Hélaouët, P.; Edwards, M.; Höfle, M.G.; Brettar, I.; Colwell, R.R.; Pruzzo, C. Climate influence on Vibrio and associated human diseases during the past half-century in the coastal North Atlantic. Proc. Royal Soc. B 2015, 113, E5062–E5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G. Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) of Penaeid Shrimps: Global Perspective. SEAFDEC. 2016. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10862/3084 (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Leung, T.L.F.; Bates, A.E. More rapid and severe disease outbreaks for aquaculture at the tropics: Implications for food security. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.; Neil, D.; Peeler, E.; Shields, J.; Small, H.; Flegel, T.; Vlak, J.; Jones, B.; Morado, F.; Moss, S.; et al. Disease will limit future food supply from the global crustacean fishery and aquaculture sectors. J. Invert. Pathol. 2012, 110, 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Pantoja, C.R.; Tang, K.F.J.; Noble, B.L.; Schofield, P.; Mohney, L.; Nunan, L.; Navarro, S. Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in the Americas. J. Invert. Pathol. 2012, 110, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinesh, R.; George, M.R.; John, K.R.; Abraham, S. TiLV—A worldwide menace to tilapiine aquaculture. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 605–607. [Google Scholar]
- Hounmanou, Y.M.G.; Mdegela, R.H.; Dougnon, T.V.; Achoh, M.E.; Mhongole, O.J.; Agadjihouèdé, H.; Gangbè, L.; Dalsgaard, A. Tilapia lake virus threatens tilapiines farming and food security: Socio-economic challenges and preventive measures in Sub-Saharan Africa. Aquacult 2018, 493, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.K.; Dugassa, G.H.; Hinzano, S.M.; Bossier, P. Causative agent, diagnosis and management of white spot disease in shrimp: A review. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 12, 822–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, C. The effects of temperature on white spot syndrome infections in Marsupenaeus japonicus. J. Invert. Pathol. 2003, 83, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workenhe, S.T.; Rise, M.L.; Kibenge, M.J.; Kibenge, F.S. The fight between the teleost fish immune response and aquatic viruses. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Corteel, M.; Dantas-Lima, J.J.; Wille, M.; Sanz, V.A.; Pensaert, M.; Sorgeloos, P.; Nauwynck, H. Effect of high water temperature (33 °C) on the clinical and virological outcome of experimental infections with white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in specific pathogen-free (SPF) Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult 2006, 261, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Corteel, M.; Dantas-Lima, J.J.; Wille, M.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Pensaert, M.B.; Sorgeloos, P.; Nauwynck, H. Impact of daily fluctuations of optimum (27 °C) and high water temperature (33 °C) on Penaeus vannamei juveniles infected with white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). Aquacult 2007, 269, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. Differences in virulence between white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) isolates and testing of some control strategies in WSSV infected shrimp. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiteit Gent, Ghent, Belgium, 2007. ISBN 9-7890-5864-126-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gunalan, B.; Soundarapandian, P.; Dinakaran, G.K. The effect of temperature and pH on WSSV infection in cultured marine shrimp Penaeus monodon (Fabricius). Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2010, 5, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, S.; Vijayan, K.K.; Alavandi, S.V.; Balasubramanian, C.P.; Santiago, T.C. Effect of temperature and salinity on the infectivity pattern of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in giant tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon (Fabricius, 1837). Indian J. Fish. 2012, 59, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Lutze, P.; Schütze, H.; Fischer, U.; Dauber, M.; Fichtner, D.; Kempter, J. Goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus) is a susceptible species for koi herpesvirus (KHV) but not for KHV disease (KHVD). Bull. Europ. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2010, 30, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Kempter, J. Detection of koi herpesvirus (KHV) after re-activation in persistently infected common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) using non-lethal sampling methods. Bull. Europ. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2011, 31, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kantzow, M.; Hick, P.; Becker, J.A.; Whittington, R.J. Effect of water temperature on mortality of Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas associated with microvariant ostreid herpesvirus 1 (OsHV-1 μVar). Aquacult. Environ. Inter. 2016, 8, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, S.; Olveira, J.G.; Bandin, I. Influence of temperature on Betanodavirus infection in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulli, S.; Gallardi, D.; Scagliarini, A.; Battilani, M.; Hedrick, R.P.; Prosperi, S. Temperature-dependency of Betanodavirus infection in SSN-1 cell line. Dis. Aqua. Organ. 2006, 68, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Aoki, H.; Nakai, T. Pathogenicity of the betanodavirus detected from diseased seven band grouper Epinephelus Semptemfasciatus. Fish Pathol. 1998, 33, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, K.; Koesharyani, I.; Mahardika, K. Effect of high water temperature on Betanodavirus infection of Fingerling Humpback grouper Cromileptes altivelis. Fish Pathol. 2007, 42, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Sheng, X.; Xing, J.; Zhan, W. Effect of temperature on immune response of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) to inactivated lymphocystis disease virus (LCDV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenen, O.L.M.; Way, K.; Bergmann, S.M.; Ariel, E. The emergence of koi herpesvirus and its significance to European aquaculture. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 2004, 24, 294. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, T.; Hirono, I.; Kurokawa, K.; Fukuda, H.; Nahary, R.; Eldar, A.; Davison, A.J.; Waltzek, T.B.; Bercovier, H.; Hedrick, R.P. Genome sequences of three koi herpesvirus isolates representing the expanding distribution of an emerging disease threatening koi and common carp worldwide. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5058–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, T. Uninformative parameters and model selection using Akaike’s information criterion. J. Wildlife Manag. 2010, 74, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, M.; Funge-Smith, S.; Subasinghe, R.P.; Phillips, M. Introductions and Movement of Two Penaeid Shrimp Species in Asia and the Pacific; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005; 78p.
- Oseko, N.; Chuah, T.T.; Maeno, Y.; Kua, B.C.; Palanisamy, V. Examination for viral inactivation of WSSV (white spot syndrome virus) isolated in Malaysia using black tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon). Japan Agricult. Res. Q. JARQ 2006, 40, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Söderhäll, K.; Söderhäll, I. Effect of water temperature on the immune response and infectivity pattern of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in freshwater crayfish. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2004, 17, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Boyko, V.; Ferralli, J.; Heinlein, M. Cell-to-cell movement of TMV RNA is temperature-dependent and corresponds to the association of movement protein with microtubules. Plant J. 2001, 22, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amari, K.; Huang, C.; Heinlein, M. Potential impact of global warming on virus propagation in infected plants and agricultural productivity. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 649768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Ke, F.; Gui, J.-F.; Zhang, Q.-Y. Environmental factors and their threshold affecting the survival of five aquatic animal viruses in different animal cells. Viruses 2022, 14, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, J.; Janssen, H.; Kuske, A.; Kurtz, J.; Scharsack, J.P. Heat and immunity: An experimental heat wave alters immune functions in three-spined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). J. Animal Ecol. 2014, 83, 744–757. [Google Scholar]
- O’Gorman, E.J.; Olafsson, O.P.; Demars, B.O.L.; Friberg, N.; Guobergsson, G.; Hannesdottir, E.H.; Jackson, M.C.; Johansson, L.S.; McLaughlin, B.; Ólafsson, J.S.; et al. Temperature effects on fish production across a natural thermal gradient. Global Change Biol. 2016, 22, 3206–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Hilaire, S.; Beevers, N.; Way, K.; Le Deuff, R.M.; Martin, P.; Joiner, C. Reactivation of koi herpesvirus infections in common carp Cyprinus carpio. Dis. Aqua. Org. 2005, 67, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, K.; Ito, T.; Sano, M. Effect of water temperature on mortality and virus shedding in carp experimentally infected with Koi Herpesvirus. Fish Pathol. 2008, 43, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Lipton, A.P. Vibrio alginolyticus associated with white spot disease of Penaeus monodon. Dis. Aquatic Organ. 2003, 57, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffan, A.; Panzarin, V.; Toson, M.; Cecchettin, K.; Pascoli, F. Water temperature affects pathogenicity of different betanodavirus genotypes in experimentally challenged Dicentrarchus labrax. Dis. Aqua. Organ. 2016, 119, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lorgeril, J.; Lucasson, A.; Petton, B.; Toulza, E.; Montagnani, C.; Clerissi, C.; Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Chaparro, C.; Galinier, R.; Escoubas, J.-M.; et al. Immune-suppression by OsHV-1 viral infection causes fatal bacteraemia in pacific oysters. Nature Comm. 2018, 9, 4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The Water-Energy-Food Nexus: A New Approach in Support of Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture. 2014. Available online: http://www.fao.org/nr/water/docs/FAO_nexus_concept.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Shifflett, S.D.; Culbreth, A.; Hazel, D.; Daniels, H.; Nichols, E.G. Coupling aquaculture with forest plantations for food, energy, and water resiliency. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, R.H.; Nhan, D.K.; Udo, H.M.J.; Kaymak, U. Factors affecting farmers’ adoption of integrated rice–fish farming systems in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Rev. Aquacult. 2012, 4, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Bunting, S.W.; Rahman, S.; Garforth, C.J. Community-based climate change adaptation strategies for integrated prawn–fish–rice farming in Bangladesh to promote social–ecological resilience. Rev. Aquacult. 2014, 6, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.V.; Sollows, J.D.; Mazid, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Hussain, M.G.; Madan, M.D. Integrating aquaculture with rice farming in Bangladesh: Feasibility and economic viability, its adoption and impact. In ICLARM Technical Report 55; ICLARM: Manila, Philippines, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Purba, S. The Economics of Rice-Fish Production Systems in North Sumatra, Indonesia: An Empirical and Model Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Gottingen, Gottingen, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Horstkotte-Wesseler, G. Socioeconomics of rice aquaculture and IPM in the Philippines: Synergies, potentials and problems. In ICLARM Technical Report 57; ICLARM: Manila, Philippines, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brudeseth, B.E.; Wiulsrød, R.; Fredriksen, B.N.; Lindmo, K.; Løkling, K.-E.; Bordevik, M.; Steine, N.; Klevan, A.; Gravningen, K. Status and future perspectives of vaccines for industrialised fin-fish farming. Fish Shell-Fish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Bontemps, N.; Lecchini, D.; Banaigs, B.; Sasal, P. Use of plant extracts in fish aquaculture as an alternative to chemotherapy: Current status and future perspectives. Aquacult 2014, 433, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Sarter, S.; Sasal, P.; Caruso, D. Moving towards more sustainable aquaculture practices: A meta-analysis on the potential of plant-enriched diets to improve fish growth, immunity and disease resistance. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutili, F.J.; Gatlin, D.M.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Baldisserotto, B. Plant essential oils as fish diet additives: Benefits on fish health and stability in feed. Rev. Aquacult. 2018, 10, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Caipang, C.M. Short-chain fatty acids as feed supplements for sustainable aquaculture: An updated view. Rev. Aquacult. 2018, 48, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, A.; Phu, T.M.; Satapornvanit, K.; Min, J.; Shahabuddin, A.M.; Henriksson, P.J.H.; Murray, F.J.; Little, D.C.; Dalsgaard, A.; Brink, P.J.V.D. Use of veterinary medicines, feed additives and probiotics in four major internationally traded aquaculture species farmed in Asia. Aquacult 2013, 412–413, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-González, A.; Almaraz-Salas, J.C.; Fierro-Coronado, J.F.; Flores-Miranda, M.C.; González-Ocampo, H.A.; Peraza-Gómez, V. The prebiotic inulin increases the phenoloxidase activity and reduces the prevalence of WSSV in whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) cultured under laboratory conditions. Aquaculture 2012, 362–363, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tan, B.; Mai, K. Dietary probiotic Bacillus OJ and isomaltooligosaccharides influence the intestine microbial populations, immune responses and resistance to white spot syndrome virus in shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquacult 2009, 291, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itami, T.; Asano, M.; Tokushige, K.; Kubono, K.; Nakagawa, A.; Takeno, N.; Nishimura, H.; Maeda, M.; Kondo, M.; Takahashi, Y. Enhancement of disease resistance of kuruma shrimp, Penaeus japonicus, after oral administration of peptidoglycan derived from Bifidobacterium thermophilum. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitamadee, S.; Srisala, J.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Double-dose β-glucan treatment in WSSV-challenged shrimp reduces viral replication but causes mortality possibly due to excessive ROS production. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 40, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.; Lusiastuti, A.M.; Taukhid; Slembrouck, J.; Komarudin, O.; Legendre, M. Traditional pharmacopeia in small scale freshwater fish farms in West Java, Indonesia: An ethnoveterinary approach. Aquaculture 2013, 416–417, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhusha, A.; Nafeez Ahmed, A.; Suryakodi, S.; Abdul Wazith, M.J.; Mithra, S.; Kanimozhi, K.; Abdul Majeed, S.; Taju, G.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. First report on the occurrence of cyprinid herpesvirus 3 in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio koi) in India. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsøe, S.; Skovgaard, K.; Sepúlveda, D.; Stratmann, A.; Vendramin, N.; Lorenzen, N. Nervous Necrosis Virus-like Particle (VLP) Vaccine Stimulates European Sea Bass Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses and Induces Long-Term Protection against Disease. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Sadowski, J.; Kiełpiński, M.; Bartłomiejczyk, M.; Fichtner, D.; Riebe, R.; Lenk, M.; Kempter, J. Susceptibility of koi × crucian carp and koi × goldfish hybrids to koi herpesvirus (KHV) and the development of KHV disease (KHVD). J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasini, L.; Berto, P.; Abbadi, M.; Buratin, A.; Toson, M.; Marsella, A.; Toffan, A.; Pascoli, F. Pathogenicity of Different Betanodavirus RGNNV/SJNNV Reassortant Strains in European Sea Bass. Pathogens 2022, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, C.A.; Reece, K.S.; Dhar, A.K.; Kirkland, P.; Morga, B.; Dégremont, L.; Faury, N.; Wippel, B.J.T.; MacIntyre, A.; Friedman, C.S. First comparison of French and Australian OsHV-1 µvars by bath exposure. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2020, 138, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Arizcun, M.; Cuesta, A. Betanodavirus genotypes produce clinical signs and mortality in the shi drum (Umbrina cirrosa), and infective particles are isolated from the damaged brain. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbeil, S.; Faury, N.; Segarra, A.; Renault, T. Development of an in situ hybridization assay for the detection of ostreid herpesvirus type 1 mRNAs in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 211, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costes, B.; Raj, V.S.; Michel, B.; Fournier, G.; Thirion, M.; Gillet, L.; Mast, J.; Lieffrig, F.; Bremont, M.; Vanderplasschen, A. The major portal of entry of koi herpesvirus in Cyprinus carpio is the skin. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kantzow, M.C.; Whittington, R.J.; Hick, P. Prior exposure to Ostreid herpesvirus 1 (OsHV-1) at 18 °C is associated with improved survival of juvenile Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) following challenge at 22 °C. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dégremont, L.; Morga, B.; Maurouard, E.; Travers, M.-A. Susceptibility variation to the main pathogens of Crassostrea gigas at the larval, spat and juvenile stages using unselected and selected oysters to OsHV-1 and/or V. aestuarianus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 183, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle, L.; Pauletto, M.; Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Petton, B.; Bargelloni, L.; Montagnani, C.; Pernet, F.; Corporeau, C.; Fleury, E. High temperature induces transcriptomic changes in Crassostrea gigas that hinder progress of ostreid herpesvirus (OsHV-1) and promote survival. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb226233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Li, X.; Weng, S.; Xie, S.; He, J. Emergence of fatal European genotype CyHV-3/KHV in mainland China. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Weng, S.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Yi, Y.; Liang, Q.; He, J. Characterization of a new cell line from caudal fin of koi, Cyprinus carpio koi, and first isolation of cyprinid herpesvirus 3 in China. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, O.; Kan, J.Z.F.; Pathirana, E.; Whittington, R.J.; Dhand, N.; Hick, P. Effect of emersion on the mortality of Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) infected with Ostreid herpesvirus-1 (OsHV-1). Aquaculture 2019, 505, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, C.S.; Reece, K.S.; Wippel, B.J.T.; Agnew, M.V.; Dégremont, L.; Dhar, A.K.; Kirkland, P.; MacIntyre, A.; Morga, B.; Robison, C.; et al. Unraveling concordant and varying responses of oyster species to Ostreid Herpesvirus 1 variants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, M.; Arizcun, M.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. Profile of Innate Immunity in Gilthead Seabream Larvae Reflects Mortality upon Betanodavirus Reassortant Infection and Replication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gémez-Mata, J.; Souto, S.; Bandín, I.; Alonso, M.D.C.; Borrego, J.J.; Labella, A.M.; García-Rosado, E. Immune Response of Senegalese Sole against Betanodavirus Mutants with Modified Virulence. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilad, O.; Yun, S.; Adkison, M.A.; Way, K.; Willits, N.H.; Bercovier, H.; Hedrick, R.P. Molecular comparison of isolates of an emerging fish pathogen, koi herpesvirus, and the effect of water temperature on mortality of experimentally infected koi. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gye, H.J.; Oh, M.J.; Nishizawa, T. Lack of nervous necrosis virus (NNV) neutralizing antibodies in convalescent sevenband grouper Hyporthodus septemfasciatus after NNV infection. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.P.; Gilad, O.; Yun, S.; Spangenberg, J.V.; Marty, G.D.; Nordhausen, R.W.; Kebus, M.J.; Bercovier, H.; Eldar, A. A Herpesvirus Associated with Mass Mortality of Juvenile and Adult Koi, a Strain of Common Carp. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2000, 12, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.P.; Waltzek, T.B.; McDowell, T.S. Susceptibility of Koi Carp, Common Carp, Goldfish, and Goldfish × Common Carp Hybrids to Cyprinid Herpesvirus-2 and Herpesvirus-3. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2006, 18, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Yin, J.; Liu, C.; Bergmann, S.M.; et al. Immersion immunization of koi (Cyprinus carpio) against cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) with carbon nanotube-loaded DNA vaccine. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Kwon, W.J.; Min, J.G.; Kim, K.I.; Jeong, H.D. Complete genome sequence and pathogenic analysis of a new betanodavirus isolated from shellfish. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Jang, Y.S.; Kim, J.O.; Oh, M.J. Altered expression of immune factors in sevenband grouper, Hyporthodus septemfasciatus following nervous necrosis virus challenge at optimal and suboptimal temperatures. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 119, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morick, D.; Faigenbaum, O.; Smirnov, M.; Fellig, Y.; Inbal, A.; Kotler, M. Mortality Caused by Bath Exposure of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Larvae to Nervous Necrosis Virus Is Limited to the Fourth Day Postfertilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3280–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Gye, H.J.; Takami, I.; Oh, M.J. Potentiality of a live vaccine with nervous necrosis virus (NNV) for sevenband grouper Epinephelus septemfasciatus at a low rearing temperature. Vaccine 2012, 30, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.; Fuhrmann, M.; Hick, P. Effect of air exposure, handling stress and imidacloprid on the susceptibility of <em>Crassostrea gigas</em> to <em>Ostreid herpesvirus 1</em> (OsHV-1). Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2019, 11, 685–699. [Google Scholar]
- Olveira, J.G.; Souto, S.; Dopazo, C.P.; Bandín, I. Isolation of betanodavirus from farmed turbot Psetta maxima showing no signs of viral encephalopathy and retinopathy. Aquaculture 2013, 406–407, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannetier, P.; Morin, B.; Clérandeau, C.; Lacroix, C.; Cabon, J.; Cachot, J.; Danion, M. Comparative biomarker responses in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) exposed to benzo[a]pyrene and challenged with betanodavirus at three different life stages. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, E.; Fuhrmann, M.; Whittington, R.; Hick, P. Influence of environment on the pathogenesis of Ostreid herpesvirus-1 (OsHV-1) infections in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) through differential microbiome responses. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, E.; Whittington, R.J.; Hick, P.M. Impact of seawater temperature on the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) microbiome and susceptibility to disease associated with Ostreid herpesvirus-1 (OsHV-1). Anim. Prod. Sci. 2022, 62, 1040–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul-Pont, I.; Evans, O.; Dhand, N.K.; Whittington, R.J. Experimental infections of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas using the Australian ostreid herpesvirus-1 (OsHV-1) µVar strain. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2015, 113, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piačková, V.; Flajšhans, M.; Pokorová, D.; Reschová, S.; Gela, D.; Čížek, A.; Veselý, T. Sensitivity of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L., strains and crossbreeds reared in the Czech Republic to infection by cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3; KHV). J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, S.; Faury, N.; Pelletier, C.; Arzul, I.; Chollet, B.; Dégremont, L.; Renault, T.; Morga, B. Monitoring Autophagy at Cellular and Molecular Level in Crassostrea gigas During an Experimental Ostreid Herpesvirus 1 (OsHV-1) Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Shi, H.; Jia, A.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X. First isolation and identification of red-grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) from adult hybrid Hulong grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × Epinephelus lanceolatus) in China. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakus, K.; Irnazarow, I.; Adamek, M.; Palmeira, L.; Kawana, Y.; Hirono, I.; Kondo, H.; Matras, M.; Steinhagen, D.; Flasz, B.; et al. Gene expression analysis of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) lines during Cyprinid herpesvirus 3 infection yields insights into differential immune responses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 37, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schikorski, D.; Faury, N.; Pepin, J.F.; Saulnier, D.; Tourbiez, D.; Renault, T. Experimental ostreid herpesvirus 1 infection of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas: Kinetics of virus DNA detection by q-PCR in seawater and in oyster samples. Virus Res. 2011, 155, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schikorski, D.; Renault, T.; Saulnier, D.; Faury, N.; Moreau, P.; Pépin, J.-F. Experimental infection of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas spat by ostreid herpesvirus 1: Demonstration of oyster spat susceptibility. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, A.; Baillon, L.; Tourbiez, D.; Benabdelmouna, A.; Faury, N.; Bourgougnon, N.; Renault, T. Ostreid herpesvirus type 1 replication and host response in adult Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, T.; Honjo, M.N.; Uchii, K.; Minamoto, T.; Doi, H.; Ito, T.; Kawabata, Z.i. Effects of daily temperature fluctuation on the survival of carp infected with Cyprinid herpesvirus 3. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.L.; Paul-Pont, I.; Evans, O.M.; Watterson, D.; Young, P.; Whittington, R.; Fougerouse, A.; Bichet, H.; Barnes, A.C.; Dang, C. Resistance of Black-lip learl oyster, Pinctada margaritifera, to infection by Ostreid herpes virus 1μvar under experimental challenge may be mediated by humoral antiviral activity. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2015, 44, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffan, A.; De Salvador, M.; Scholz, F.; Pretto, T.; Buratin, A.; Rodger, H.D.; Toson, M.; Cuenca, A.; Vendramin, N. Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus, Linnaeus) is susceptible to viral nervous necrosis: Result of an experimental infection with different genotypes of Betanodavirus. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, M.; Pires, D.; Pires, P.; Simões, M.; Pombo, A.; Santos, P.; do Carmo, B.; Passos, R.; Costa, J.Z.; Thompson, K.D.; et al. Early Immune Modulation in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Juveniles in Response to Betanodavirus Infection. Fishes 2022, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Salgado, L.; Olveira, J.G.; Dopazo, C.P.; Bandín, I. Effect of rearing density on nervous necrosis virus infection in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Mori, K.; Kuroda, A.; Nakai, T. Neutralizing antibody levels for protection against betanodavirus infection in sevenband grouper, Epinephelus septemfasciatus (Thunberg), immunized with an inactivated virus vaccine. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Subset | Model Selected | Adj. R2 | Parameter | Estimate | SE | 95% CI | p-Value | F-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Koi HV | Mortality ~ T + type of infection | 0.408 | T | 4.77 | 1.09 | 2.55 | 6.98 | <0.001 | 20.072 |
| Type of infection: injection | 16.48 | 8.23 | −0.28 | 33.23 | 0.054 | 4.002 | |||
| Ostreid HV | Mortality ~ T | 0.148 | T | 4.90 | 1.70 | 1.47 | 8.33 | 0.006 | 8.250 |
| Betanodaviruses | Mortality ~ T + type of infection + (1|Host species) + (1|Pathogen.species) | 0.719 | T | 3.78 | 0.79 | 2.18 | 5.37 | * | 20.051 |
| Life stage: larvae | 47.35 | 11.67 | 22.97 | 72.00 | * | 6.799 | |||
| Type of infection: injection | 20.579 | 5.63 | 9.29 | 31.80 | * | ||||
| All viruses | Mortality ~ T + life stage + type of infection + (1|host species) | 0.408 | T | 4.38 | 0.67 | 3.07 | 5.70 | * | 43.163 |
| Life stage: juvenile | −1.79 | 5.50 | −12.83 | 9.20 | 1.769 | ||||
| Life stage: larvae | 31.79 | 13.57 | 4.16 | 61.23 | * | ||||
| Life stage: spat | 3.31 | 13.29 | −22.99 | 29.52 | |||||
| Type of infection: injection | 11.40 | 4.80 | 1.87 | 20.89 | * | 5.631 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Combe, M.; Reverter, M.; Caruso, D.; Pepey, E.; Gozlan, R.E. Impact of Global Warming on the Severity of Viral Diseases: A Potentially Alarming Threat to Sustainable Aquaculture Worldwide. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041049
Combe M, Reverter M, Caruso D, Pepey E, Gozlan RE. Impact of Global Warming on the Severity of Viral Diseases: A Potentially Alarming Threat to Sustainable Aquaculture Worldwide. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(4):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041049
Chicago/Turabian StyleCombe, Marine, Miriam Reverter, Domenico Caruso, Elodie Pepey, and Rodolphe Elie Gozlan. 2023. "Impact of Global Warming on the Severity of Viral Diseases: A Potentially Alarming Threat to Sustainable Aquaculture Worldwide" Microorganisms 11, no. 4: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041049
APA StyleCombe, M., Reverter, M., Caruso, D., Pepey, E., & Gozlan, R. E. (2023). Impact of Global Warming on the Severity of Viral Diseases: A Potentially Alarming Threat to Sustainable Aquaculture Worldwide. Microorganisms, 11(4), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041049







