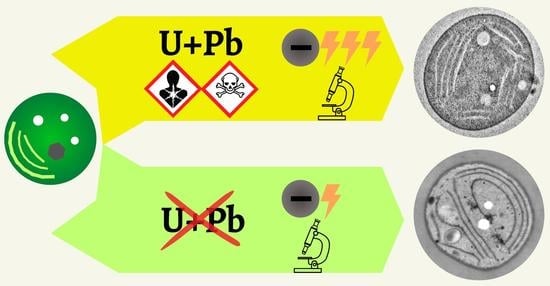
Urany-Less Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Powerful Tool for Ultrastructural Studying of Cyanobacterial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms and Their Cultivation
2.2. Sample Preparation for Electron Microscopy
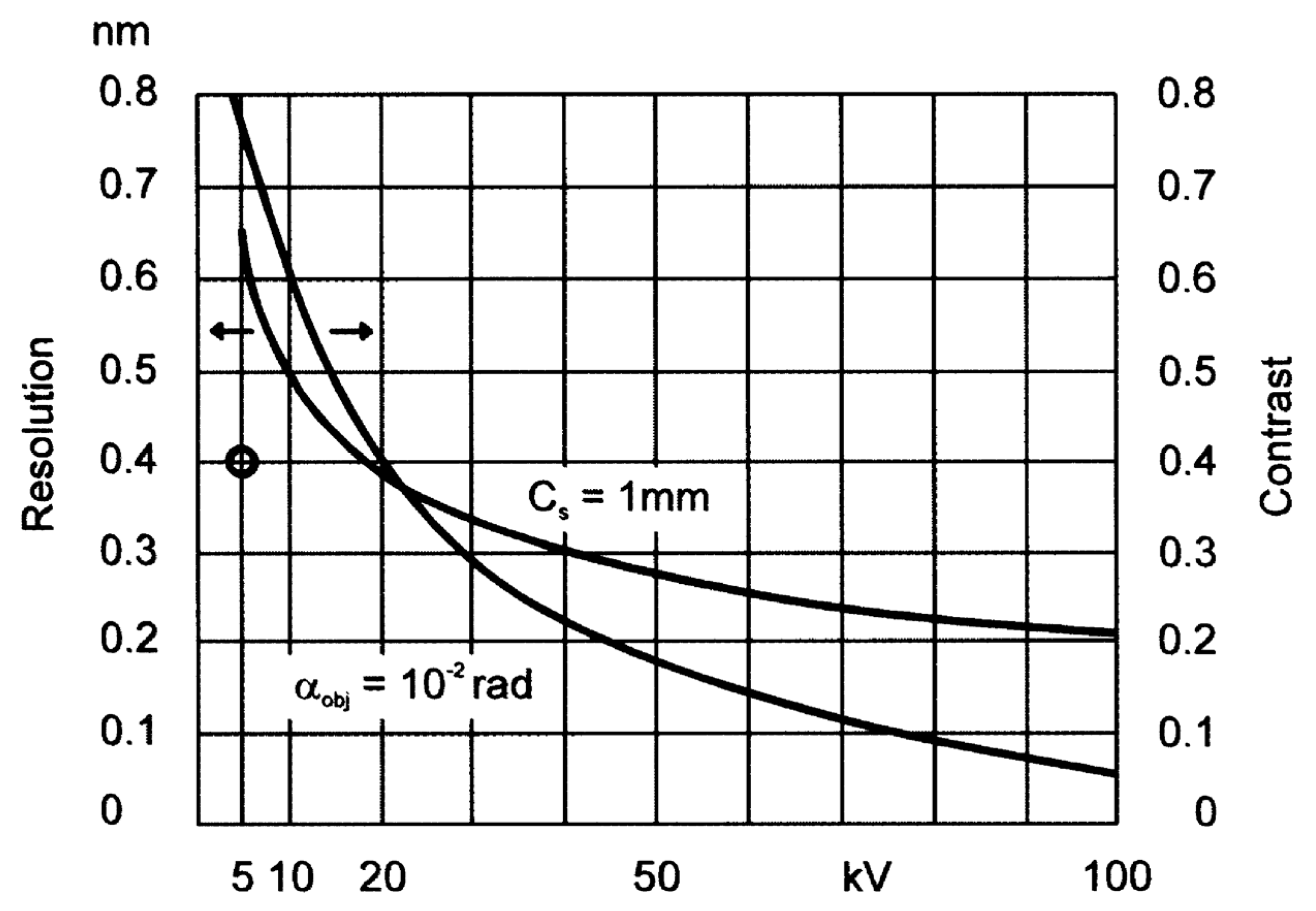
2.3. Electron Microscopy
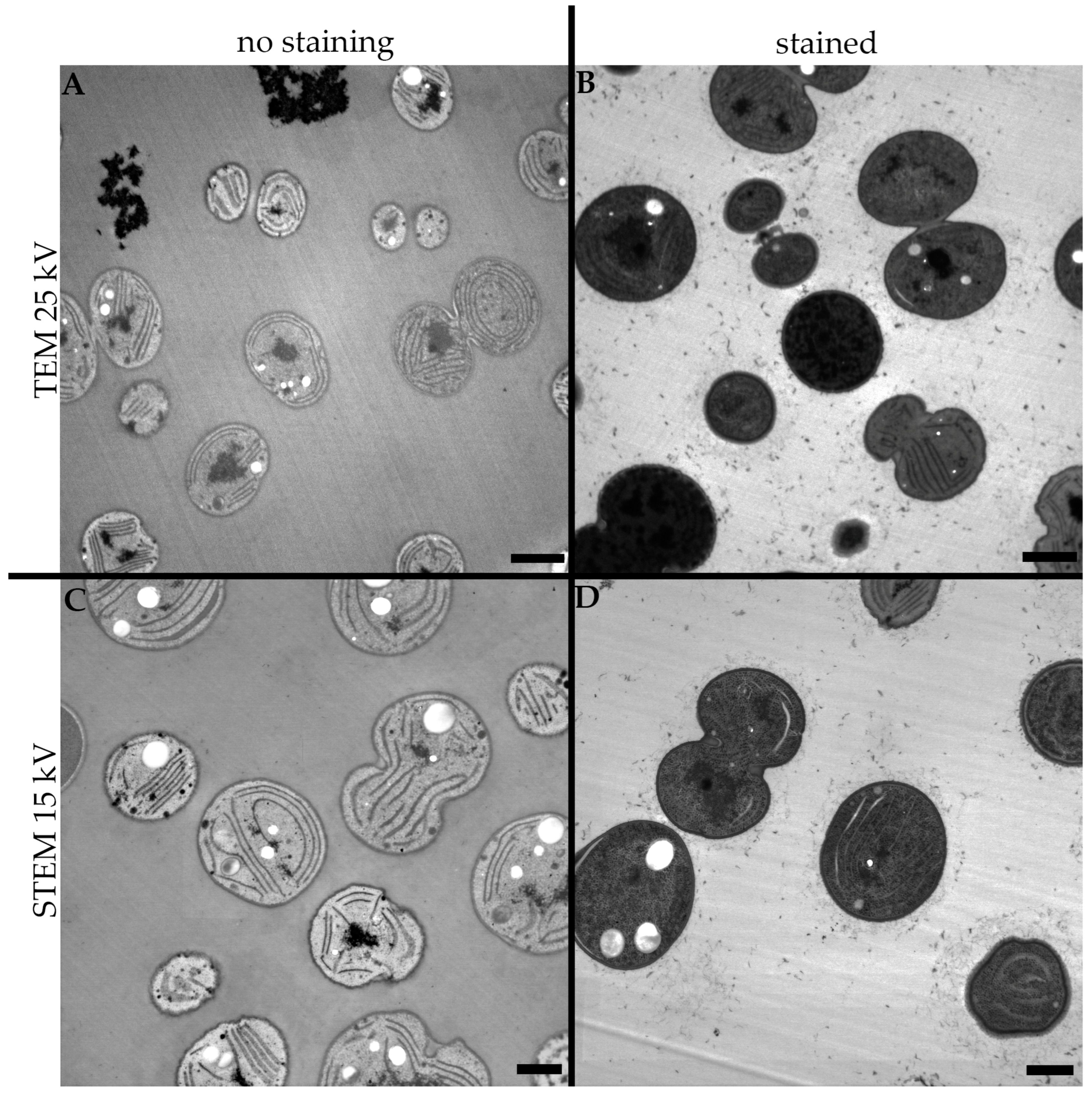
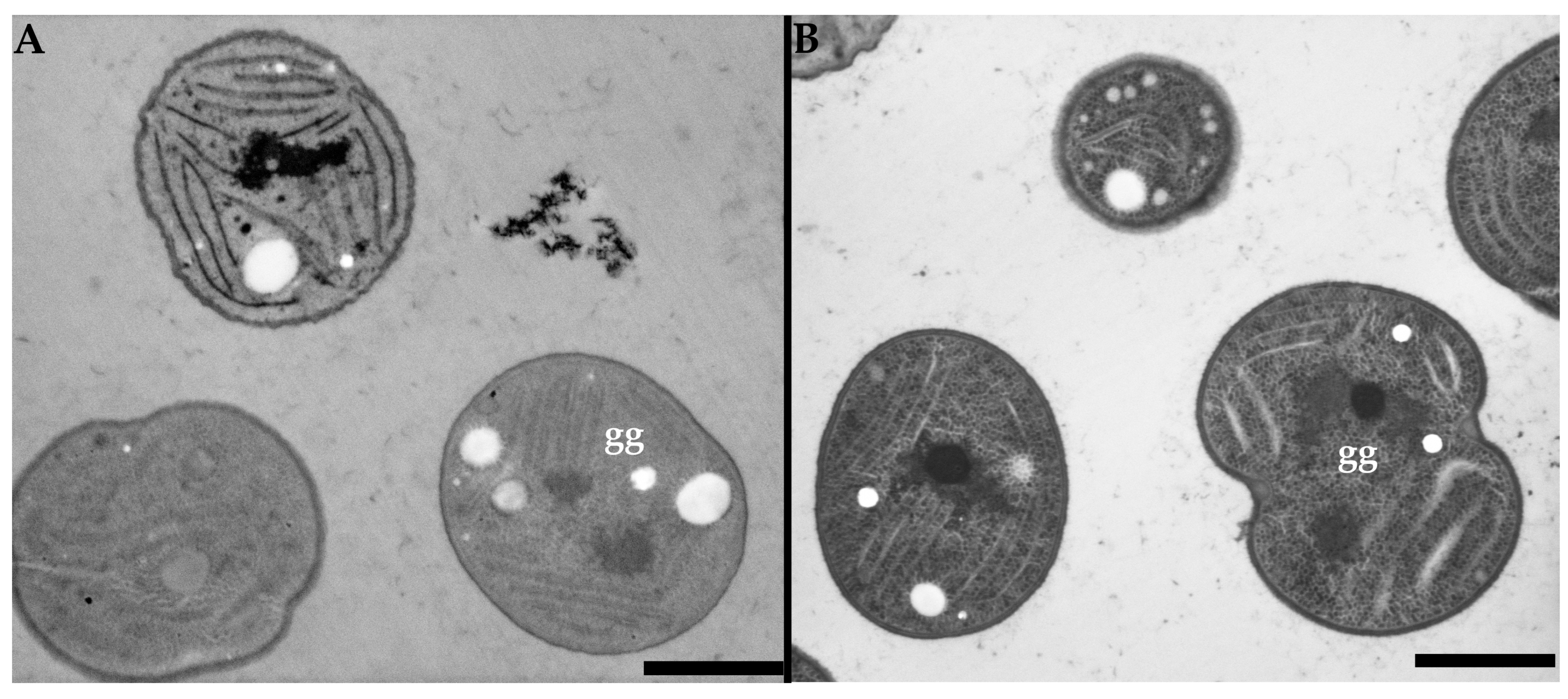
3. Results
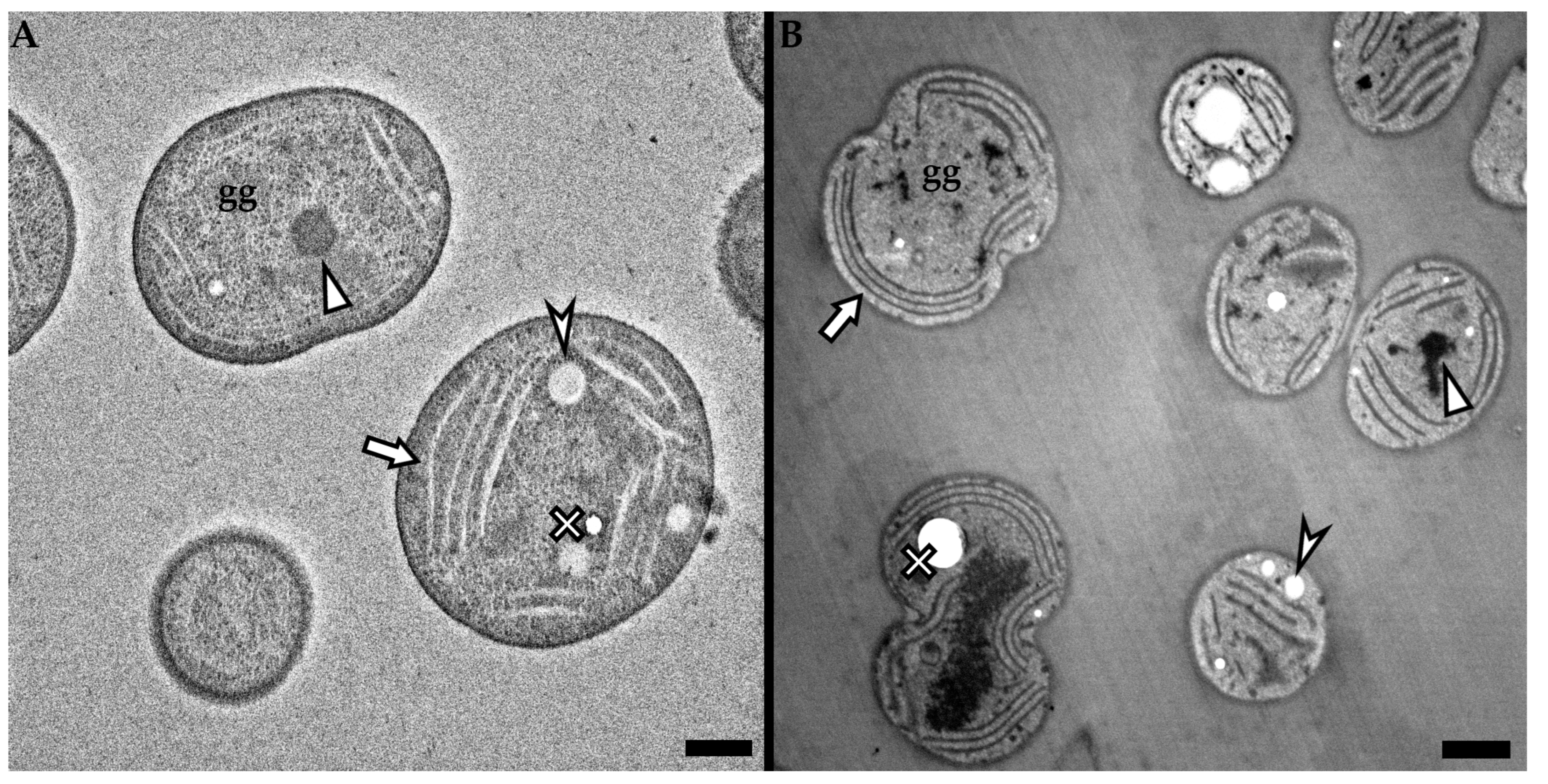
3.1. High Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy
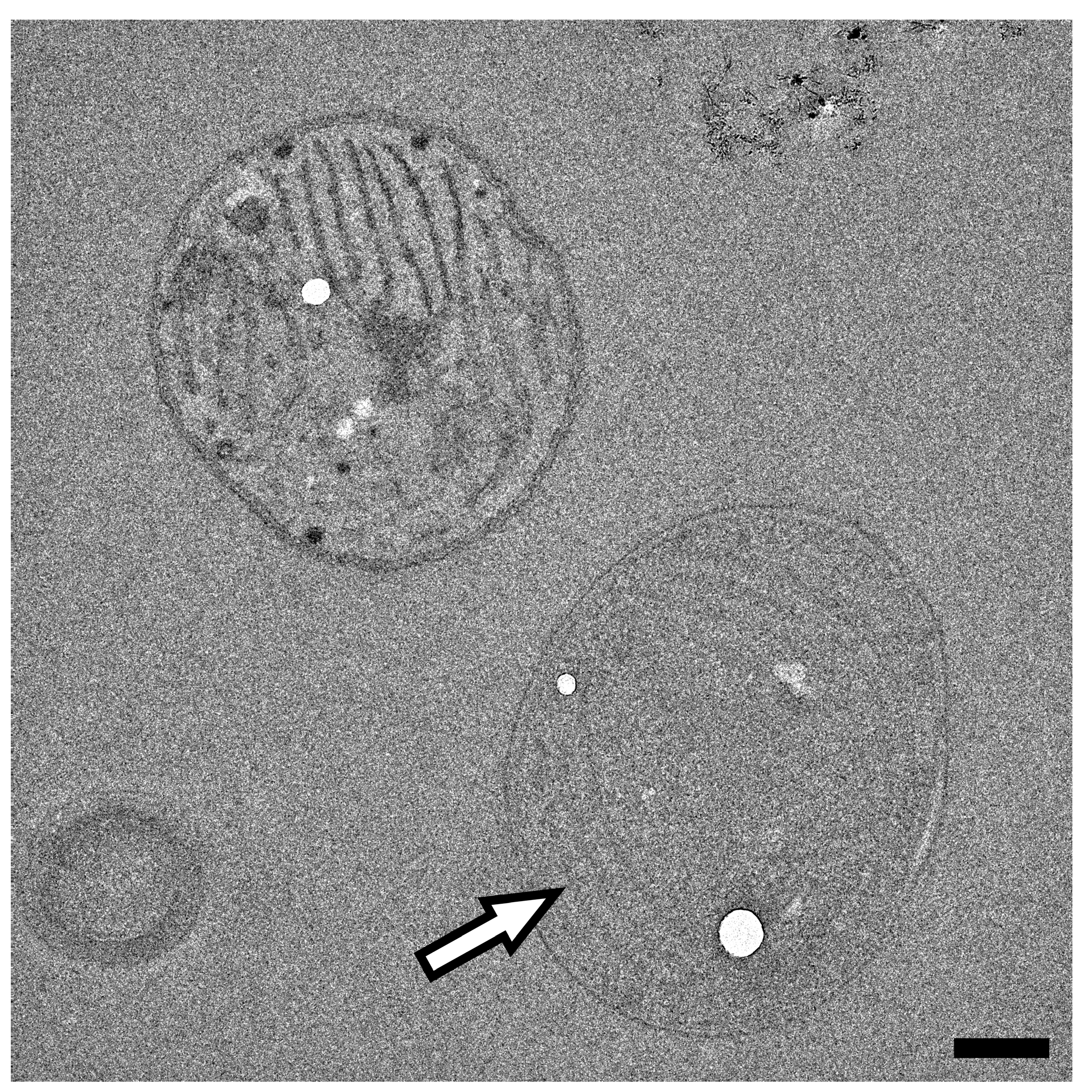
3.2. Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.3. Low Voltage Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winey, M.; Meehl, J.B.; O’Toole, E.T.; Giddings, T.H. Conventional Transmission Electron Microscopy. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.R. Transmission Electron Microscopy in Molecular Structural Biology: A Historical Survey. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 581, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakane, T.; Kotecha, A.; Sente, A.; McMullan, G.; Masiulis, S.; Brown, P.M.G.E.; Grigoras, I.T.; Malinauskaite, L.; Malinauskas, T.; Miehling, J.; et al. Single-Particle Cryo-EM at Atomic Resolution. Nature 2020, 587, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, K.M.; Fischer, N.; Paknia, E.; Chari, A.; Stark, H. Atomic-Resolution Protein Structure Determination by Cryo-EM. Nature 2020, 587, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, R.E. Mechanisms of Contrast and Image Formation of Biological Specimens in the Transmission Electron Microscope. J. Microsc. 1973, 98, 251–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, L.E.; Grünewald, K.; Boekema, E.J.; Stuart, M.C.A. A Technical Introduction to Transmission Electron Microscopy for Soft-Matter: Imaging, Possibilities, Choices, and Technical Developments. Small 2020, 16, 1906198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.; Orenstein, J.M. Processing Tissue and Cells for Transmission Electron Microscopy in Diagnostic Pathology and Research. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, J.M.; Parks, V.R. A Routine Technique for Double-Staining Ultrathin Sections Using Uranyl and Lead Salts. J. Cell Biol. 1965, 25, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R. Transmission Electron Microscopy of Yeast. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 51, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakakoshi, M.; Nishioka, H.; Katayama, E. New Versatile Staining Reagents for Biological Transmission Electron Microscopy That Substitute for Uranyl Acetate. J. Electron Microsc. (Tokyo) 2011, 60, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscardini, A.; Di Pietro, S.; Signore, G.; Parlanti, P.; Santi, M.; Gemmi, M.; Cappello, V. Uranium-Free X Solution: A New Generation Contrast Agent for Biological Samples Ultrastructure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosogi, N.; Nishioka, H.; Nakakoshi, M. Evaluation of Lanthanide Salts as Alternative Stains to Uranyl Acetate. Microscopy 2015, 64, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, J.; Giepmans, B.N.G. Neodymium as an Alternative Contrast for Uranium in Electron Microscopy. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 153, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Suzuki, K.I.; Tanaka, K. Examination of Electron Stains as a Substitute for Uranyl Acetate for the Ultrathin Sections of Bacterial Cells. J. Electron Microsc. (Tokyo) 2010, 59, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, B. Oolong Tea Extract as a Substitute for Uranyl Acetate in Staining of Ultrathin Sections Based on Examples of Animal Tissues for Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Microsc. 2017, 267, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Adachi, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Ghazizadeh, M. Oolong Tea Extract as a Substitute for Uranyl Acetate in Staining of Ultrathin Sections. J. Microsc. 2008, 229, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malac, M.; Beleggia, M.; Kawasaki, M.; Li, P.; Egerton, R.F. Convenient Contrast Enhancement by a Hole-Free Phase Plate. Ultramicroscopy 2012, 118, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majorovits, E.; Barton, B.; Schultheiß, K.; Pérez-Willard, F.; Gerthsen, D.; Schröder, R.R. Optimizing Phase Contrast in Transmission Electron Microscopy with an Electrostatic (Boersch) Phase Plate. Ultramicroscopy 2007, 107, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendayan, M.; Paransky, E. Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy in Cell Biology. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2015, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednický, F.; Coufalová, E.; Hromádková, J.; Delong, A.; Kolařík, V. Low-Voltage TEM Imaging of Polymer Blends. Polymer (Guildf) 2000, 41, 4909–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, R.F. Choice of Operating Voltage for a Transmission Electron Microscope. Ultramicroscopy 2014, 145, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummy, L.F.; Yang, J.; Martin, D.C. Low-Voltage Electron Microscopy of Polymer and Organic Molecular Thin Films. Ultramicroscopy 2004, 99, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lednický, F.; Hromádková, J.; Pientka, Z. Ultrathin Sectioning of Polymeric Materials for Low-Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy. Polymer (Guildf) 2001, 42, 4329–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendayan, M.; Londono, I.; Paransky, E. Compartmentalization of Pancreatic Secretory Zymogen Granules as Revealed by Low-Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebesářová, J.; Hozák, P.; Frank, L.; Štěpan, P.; Vancová, M. The Cutting of Ultrathin Sections with the Thickness Less than 20 Nm from Biological Specimens Embedded in Resin Blocks. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2016, 79, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, L.; Holland, G.; Laue, M. Diagnostic Electron Microscopy of Viruses With Low-Voltage Electron Microscopes. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2020, 68, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delong, A.; Hladil, K.; Kolařík, V. Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscope. Microsc. Anal. 1994, 27, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, K.; Stirnberg, M.; Eisenhut, M.; Krämer, R.; Hagemann, M. Osmotic Stress in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: Low Tolerance towards Nonionic Osmotic Stress Results from Lacking Activation of Glucosylglycerol Accumulation. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červený, J.; Sinetova, M.; Zavřel, T.; Los, D. Mechanisms of High Temperature Resistance of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: An Impact of Histidine Kinase 34. Life 2015, 5, 676–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, I.; Kanesaki, Y.; Mikami, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Murata, N. Cold-Regulated Genes under Control of the Cold Sensor Hik33 in Synechocystis. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-Y.; Klisch, M.; Häder, D.-P. Adaptation of Cyanobacteria to UV-B Stress Correlated with Oxidative Stress and Oxidative Damage. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastropetros, S.G.; Pispas, K.; Zagklis, D.; Ali, S.S.; Kornaros, M. Biopolymers Production from Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Cultivated in Wastewater: Recent Advances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 60, 107999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagels, F.; Vasconcelos, V.; Guedes, A.C. Carotenoids from Cyanobacteria: Biotechnological Potential and Optimization Strategies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möllers, K.B.; Cannella, D.; Jørgensen, H.; Frigaard, N.-U. Cyanobacterial Biomass as Carbohydrate and Nutrient Feedstock for Bioethanol Production by Yeast Fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troschl, C.; Meixner, K.; Drosg, B. Cyanobacterial PHA Production—Review of Recent Advances and a Summary of Three Years’ Working Experience Running a Pilot Plant. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudesh, K.; Taguchi, K.; Doi, Y. Effect of Increased PHA Synthase Activity on Polyhydroxyalkanoates Biosynthesis in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2002, 30, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetkorn, W.; Incharoensakdi, A.; Lindblad, P.; Jantaro, S. Enhancement of Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate Production in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 by Overexpression of Its Native Biosynthetic Genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaninova, E.; Sedlacek, P.; Mravec, F.; Mullerova, L.; Samek, O.; Koller, M.; Hesko, O.; Kucera, D.; Marova, I.; Obruca, S. Light Scattering on PHA Granules Protects Bacterial Cells against the Harmful Effects of UV Radiation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obruca, S.; Sedlacek, P.; Mravec, F.; Krzyzanek, V.; Nebesarova, J.; Samek, O.; Kucera, D.; Benesova, P.; Hrubanova, K.; Milerova, M.; et al. The Presence of PHB Granules in Cytoplasm Protects Non-Halophilic Bacterial Cells against the Harmful Impact of Hypertonic Environments. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novackova, I.; Hrabalova, V.; Slaninova, E.; Sedlacek, P.; Samek, O.; Koller, M.; Krzyzanek, V.; Hrubanova, K.; Mrazova, K.; Nebesarova, J.; et al. The Role of Polyhydroxyalkanoates in Adaptation of Cupriavidus Necator to Osmotic Pressure and High Concentration of Copper Ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Guo, J.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, S. The Role of Morphological Changes in Algae Adaptation to Nutrient Stress at the Single-Cell Level. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloto, I.; Johnston, P.; Pestana, C.J.; Lawton, L.A. Detection of Morphological Changes Caused by Chemical Stress in the Cyanobacterium Planktothrix Agardhii Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 146956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meixner, K.; Daffert, C.; Dalnodar, D.; Mrázová, K.; Hrubanová, K.; Krzyžánek, V.; Nebesářová, J.; Samek, O.; Šedrlová, Z.; Slaninova, E.; et al. Glycogen, Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Pigment Accumulation in Three Synechocystis Strains when Exposed to a Stepwise Increasing Salt Stress. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouřilová, X.; Schwarzerová, J.; Pernicová, I.; Sedlář, K.; Mrázová, K.; Krzyžánek, V.; Nebesářová, J.; Obruča, S. The First Insight into Polyhydroxyalkanoates Accumulation in Multi-Extremophilic Rubrobacter Xylanophilus and Rubrobacter Spartanus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Meene, A.M.L.; Hohmann-Marriott, M.F.; Vermaas, W.F.J.; Roberson, R.W. The Three-Dimensional Structure of the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 184, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.A.; Leapman, R.D. Development and Application of STEM for the Biological Sciences. Ultramicroscopy 2012, 123, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliex, C.; Mory, C. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy of Biological Structures. Biol. Cell 1994, 80, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzola, J.J.; Russel, L.D. Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists, 2nd ed.; Jones and Bartlett: Burlington, MA, USA, 1999; ISBN 0-7637-0192-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, S.G.; Shimoni, E.; Elbaum, M.; Houben, L. STEM Tomography in Biology. In Cellular Imaging; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 33–60. ISBN 9783319689975. [Google Scholar]
- Egerton, R.F. Radiation Damage to Organic and Inorganic Specimens in the TEM. Micron 2019, 119, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettler, S.; Dries, M.; Hermann, P.; Obermair, M.; Gerthsen, D.; Malac, M. Carbon Contamination in Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy and Its Impact on Phase-Plate Applications. Micron 2017, 96, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mrazova, K.; Bacovsky, J.; Sedrlova, Z.; Slaninova, E.; Obruca, S.; Fritz, I.; Krzyzanek, V. Urany-Less Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Powerful Tool for Ultrastructural Studying of Cyanobacterial Cells. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040888
Mrazova K, Bacovsky J, Sedrlova Z, Slaninova E, Obruca S, Fritz I, Krzyzanek V. Urany-Less Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Powerful Tool for Ultrastructural Studying of Cyanobacterial Cells. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(4):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040888
Chicago/Turabian StyleMrazova, Katerina, Jaromir Bacovsky, Zuzana Sedrlova, Eva Slaninova, Stanislav Obruca, Ines Fritz, and Vladislav Krzyzanek. 2023. "Urany-Less Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Powerful Tool for Ultrastructural Studying of Cyanobacterial Cells" Microorganisms 11, no. 4: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040888
APA StyleMrazova, K., Bacovsky, J., Sedrlova, Z., Slaninova, E., Obruca, S., Fritz, I., & Krzyzanek, V. (2023). Urany-Less Low Voltage Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Powerful Tool for Ultrastructural Studying of Cyanobacterial Cells. Microorganisms, 11(4), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040888