Limnofasciculus baicalensis gen. et sp. nov. (Coleofasciculaceae, Coleofasciculales): A New Genus of Cyanobacteria Isolated from Sponge Fouling in Lake Baikal, Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Collection
2.3. Microscopic Analysis
2.4. DNA Extraction and Genome Sequencing
2.5. Genome Annotation and Proteome Analysis
2.6. Average Nucleotide Identity Calculations and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution
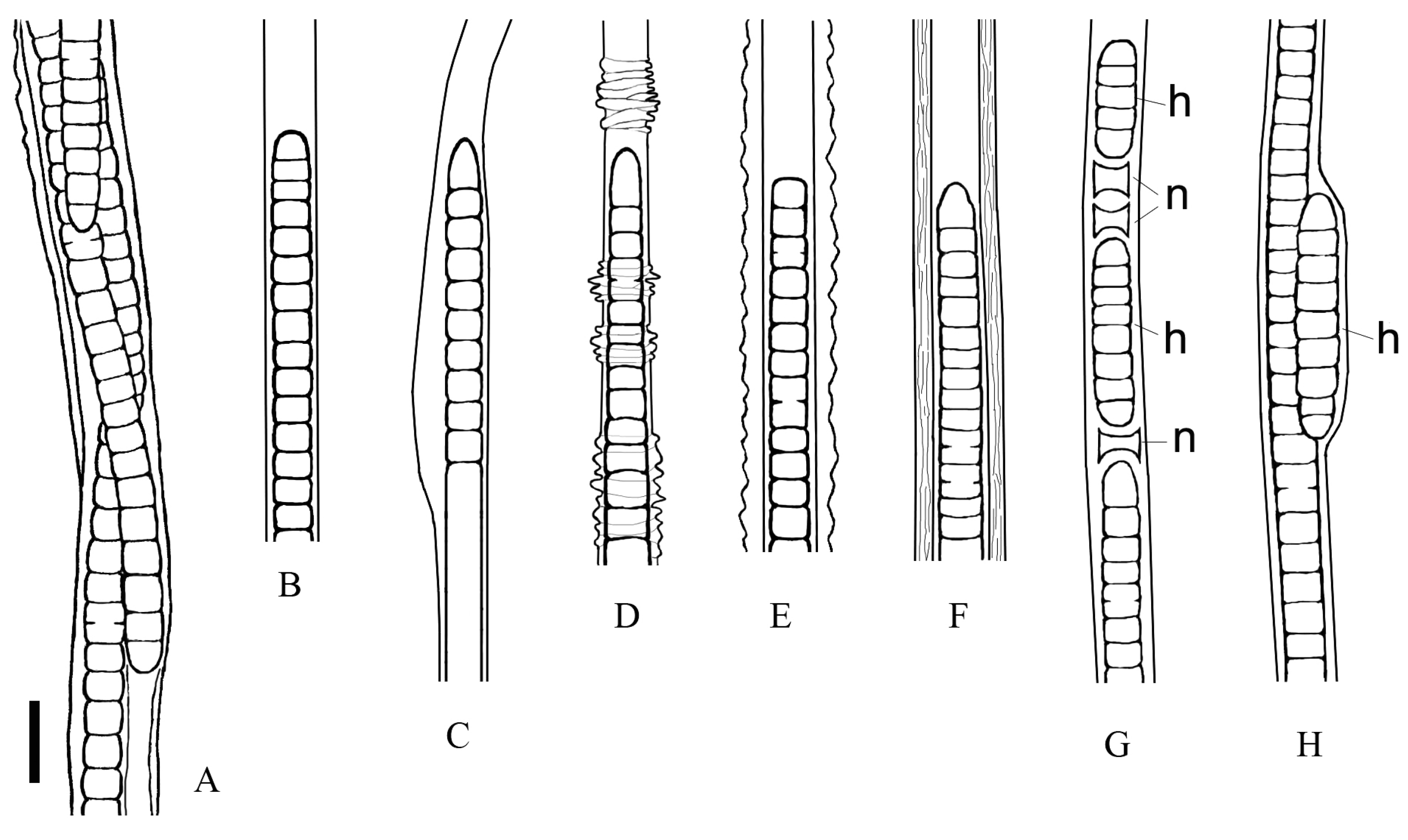
3.2. Morphological Investigation of Natural Samples and Strain
3.3. Cell Ultrastructure
3.4. Molecular and Phylogenetic 16S rRNA Gene Analyses
3.5. 16S-23S ITS Secondary Folding Structure Analysis
3.6. Average Nucleotide Identity Calculations of Concatenated Conserved Protein Sequences’ Phylogeny, Genome Statistics and Proteome Analysis
3.7. Biosynthetic Potential of Limnofasciculus Baicalensis
3.8. Taxonomic Treatment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galaziy, G.I. (Ed.) Baikal. In Atlas; Publishing House of the Federal Service for Geodesy and Cartography of Russia: Moscow, Russia, 1993; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhova, O.M.; Izmest’eva, L.R. (Eds.) Lake Baikal; Evolution and Biodiversity Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1998; p. 447. [Google Scholar]
- Izhboldina, L.A. Guide and Key to Benthonic and Periphyton Algae of Lake Baikal (Meio- and Macrophytes) with Short Notes of Their Ecology; Nauka-Center: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2007; p. 248. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshkin, O.A.; Samsonov, D.P.; Yamamuro, M.; Moore, M.V.; Belykh, O.I.; Malnik, V.V.; Sakirko, M.V.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Bondarenko, N.A.; Domysheva, V.M.; et al. Rapid ecological change in the coastal zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia): Is the site of the world’s greatest freshwater biodiversity in danger? J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Logacheva, N.F. Structural Changes in Phytoplankton of the Littoral Zone of Lake Baikal. Hydrobiol. J. 2017, 53, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravtsova, L.S.; Izhboldina, L.A.; Khanaev, I.V.; Pomazkina, G.V.; Rodionova, E.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Sakirko, M.V.; Tomberg, I.V.; Kostornova, T.Y.; Kravchenko, O.S.; et al. Nearshore benthic blooms of filamentous green algae in Lake Baikal. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, E.A.; Bondarenko, N.A.; Timoshkin, O.A. Morphotaxonomy, distribution and abundance of Spirogyra (Zygnematophyceae, Charophyta) in Lake Baikal, East Siberia. Phycologia 2018, 57, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanaev, I.V.; Kravtsova, L.S.; Maikova, O.O.; Bukshuk, N.A.; Sakirko, M.V.; Kulakova, N.V.; Butina, T.V.; Nebesnykh, I.A.; Belikov, S.I. Current state of the sponge fauna (Porifera: Lubomirskiidae) of Lake Baikal: Sponge disease and the problem of conservation of diversity. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, E.; Belykh, O.; Krasnopeev, A.; Potapov, S.; Tikhonova, I.; Khanaev, I.; Kabilov, M.; Baturina, O.; Podlesnaya, G.; Timoshkin, O. First data on cyanobacterial biodiversity in benthic biofilms during mass mortality of endemic sponges in Lake Baikal. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikova, O.; Bukshuk, N.; Kravtsova, L.; Nebesnyh, I.; Yakhnenko, A.; Butina, T.; Khanaev, I. Baikal endemic sponge disease and anthropogenic factor. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 937, 022071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikova, O.O.; Bukshuk, N.A.; Kravtsova, L.S.; Onishchuk, N.A.; Sakirko, M.V.; Nebesnykh, I.A.; Lipko, I.A.; Khanaev, I.V. Sponge Fauna of Lake Baikal in the Monitoring System: Six Years of Observations. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2023, 16, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Fedorova, G.A.; Khanaev, I.V.; Sherbakova, T.A.; Timoshkin, O.A. First detection of benthic cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal producing paralytic shellfish toxins. Toxicon 2016, 121, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, Y.; Medvezhonkova, O.; Naumova, T.; Sheveleva, N.; Lukhnev, A.; Sorokovikova, E.; Evstigneeva, T.; Timoshkin, O. Variation of sponge-inhabiting infauna with the state of health of the sponge Lubomirskia baikalensis (Pallas, 1776) in Lake Baikal. Limnology 2019, 20, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, E.A.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Bondarenko, N. Photogranules Formed by Filamentous Cyanobacteria and Algae of the Genus Spirogyra Link in the Coastal Zone of Lake Baikal. Bull. Baikal State Univ. 2020, 30, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, O. Schizophyceae. In Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien Nebst Ihren Gattungen und Wichtigeren Artn Insbesondere den Nutzpflanzen unter Mitwirkung Zahlreicher Hervorragender Fachgelehrten I. Teil 1; Abteilung, A., Engler, A., Prantl, K., Eds.; Verlag von Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1898; pp. 45–92. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Several problems of the polyphasic approach in the modern cyanobacterial system. Hydrobiologia 2017, 811, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunecký, O.; Komárek, J.; Johansen, J.; Lukešová, A.; Elster, J. Molecular and morphological criteria for revision of the genus Microcoleus (Oscillatoriales, Cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2013, 49, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, T.; Komárek, J. CyanoDB 2.0—Online Database of Cyanobacterial Genera; World-Wide Electronic Publication, University of South Bohemia & Inst. of Botany AS CR: České Budějovice, Czech Republic; Available online: http://www.cyanodb.cz (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Bd. 19/2. Cyanoprokaryota. Teil/Part 2: Oscillatoriales; Büdel, B., Krienitz, L., Gärtner, G., Schagerl, M., Eds.; Springer: Munchen, Germany, 2005; p. 759. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.D.; Stajich, J.E.; Johansen, J.R.; Huntemann, M.; Clum, A.; Foster, B.; Foster, B.; Roux, S.; Palaniappan, K.; Varghese, N.; et al. Metagenome Sequencing to Explore Phylogenomics of Terrestrial Cyanobacteria. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00221–e00258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrasiak, N.; Mühlsteinová, R.; Siegesmund, M.A.; Johansen, J.R. Phylogenetic placement of Symplocastrum (Phormidiaceae, Cyanophyceae) with a new combination S. californicum and two new species: S. flechtnerae and S. torsivum. Phycologia 2014, 53, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, P.; Poulíčková, A.; Hašler, P.; Belli, M.; Casamatta, D.A.; Papini, A. Species concepts and speciation factors in cyanobacteria, with connection to the problems of diversity and classification. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippka, R. Isolation and purification of cyanobacteria. Meth. Enzymol. 1988, 167, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Belykh, O.I.; Klimenkov, I.V.; Likhoshwai, E.V. Identification of two cyanobacterial strains isolated from the Kotel’nikovskii hot spring of the Baikal rift. Microbiology 2008, 77, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual: By T Maniatis, E F Fritsch and J Sambrook. pp 545. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York. 1982. Biochem. Educ. 1983, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; O’neill, K.R.; Haft, D.H.; DiCuccio, M.; Chetvernin, V.; Badretdin, A.; Coulouris, G.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Durkin, A.S.; et al. RefSeq: Expanding the Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline reach with protein family model curation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D1020–D1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z. antiSMASH 6.0: Improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.-C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascuel, O. BIONJ: An improved version of the NJ algorithm based on a simple model of sequence data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazutaka, K.; Misakwa, K.; Keiichi, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4453–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edler, D.; Klein, J.; Antonelli, A.; Silvestro, D. raxmlGUI 2.0: A graphical interface and toolkit for phylogenetic analyses using RAxML. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Posada, D.; Kozlov, A.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Morel, B.; Flouri, T. ModelTest-NG: A New and Scalable Tool for the Selection of DNA and Protein Evolutionary Models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 37, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Börnigen, D.; Morgan, X.C.; Huttenhower, C. PhyloPhlAn is a new method for improved phylogenetic and taxonomic placement of microbes. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, F.; Domelevo Entfellner, J.B.; Wilkinson, E.; Correia, D.; Dávila Felipe, M.; De Oliveira, T.; Gascuel, O. Renewing Felsenstein’s phylogenetic bootstrap in the era of big data. Nature 2018, 556, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Kbatovský, J.; Marea, J.; Johansen, J.R. Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacterial genera) 2014, using a polyphasic approach. Preslia 2014, 86, 295–335. [Google Scholar]
- Mareš, J.; Strunecký, O.; Bučinská, L.; Wiedermannová, J. Evolutionary Patterns of Thylakoid Architecture in Cyanobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostidis, K.; Komárek, J. Modern approach to the classification system of the Cyanophytes 3: Oscillatoriales. Algol. Stud. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1988, 50, 327–472. [Google Scholar]
- Siegesmund, M.A.; Johansen, J.R.; Karsten, U.; Friedl, T. Coleofasciculusgen. nov. (cyanobacteria): Morphological and molecular criteria for revision of the genusmicrocoleusgomont1. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Sharma, S.; Smol, J.P. Lakes in Hot Water: The Impacts of a Changing Climate on Aquatic Ecosystems. Bioscience 2022, 72, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.J. Global warming and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 619, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Kelly, L.T.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Humbert, J.-F.; Laughinghouse, H.D.; Lazorchak, J.; McAllister, T.G.; McQueen, A.; Pokrzywinski, K.; Puddick, J.; et al. Toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacterial proliferations: Challenges and solutions for enhancing knowledge and improving monitoring and mitigation. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 1824–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashiro, H.; Isomura, N.; Sakai, K. Bloom of the cyanobacterium Moorea bouillonii on the gorgonian coral Annella reticulata in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.D.V.; Caires, T.A.; Simões, M.A.d.A.; Hargreaves, P.I.; Villela, L.B.; Fistarol, G.D.O.; Cazelgrandi, A.B.J.; Pereira-Filho, G.H.; de Moura, R.L.; Pereira, R.C.; et al. Benthic Cyanobacterial Diversity and Antagonistic Interactions in Abrolhos Bank: Allelopathy, Susceptibility to Herbivory, and Toxicity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 790277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Domysheva, V.M. Trends in hydrological and hydrochemical processes in Lake Baikal under conditions of modern climate change. In Climatic Change and Global Warming of Inland Waters; Goldman, C., Kumagai, M., Robarts, R.D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 43–66. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshkin, O.A.; Moore, M.V.; Kulikova, N.N.; Tomberg, I.V.; Malnik, V.V.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Troitskaya, E.S.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Zaitseva, E.P.; et al. Groundwater contamination by sewage causes benthic algal outbreaks in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia). J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodzher, T.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Sakirko, M.V.; Tomberg, I.V. Current chemical composition of Lake Baikal water. Inland Waters 2017, 7, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravtsova, L.; Vorobyeva, S.; Naumova, E.; Izhboldina, L.; Mincheva, E.; Potemkina, T.; Pomazkina, G.; Rodionova, E.; Onishchuk, N.; Sakirko, M.; et al. Response of Aquatic Organisms Communities to Global Climate Changes and Anthropogenic Impact: Evidence from Listvennichny Bay of Lake Baikal. Biology 2021, 10, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.P.; Gerber, A.; Bedulina, D.; Timofeyev, M.A. Human impact and ecosystemic health at Lake Baikal. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, I.; Kuzmin, A.; Fedorova, G.; Sorokovikova, E.; Krasnopeev, A.; Tsvetkova, A.; Shtykova, Y.; Potapov, S.; Ivacheva, M.; Zabortzeva, T.; et al. Toxic cyanobacteria blooms of Mukhor Bay (Lake Baikal, Russia) during a period of intensive anthropogenic pressure. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2022, 25, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Camillo, C.G.; Bartolucci, I.; Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G. Sponge disease in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2013, 34, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochfeld, D.J.; Diaz, M.C.; Renegar, D.A.; Olson, J.B. Histological and ultrastructural features of Aplysina cauliformis affected by Aplysina red band syndrome. Invertebr. Biol. 2019, 138, e12247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.K.; Bejarano, S.; Nugues, M.M.; Visser, P.M.; Albert, S.; Ferse, S.C.A. Reefs under Siege—The Rise, Putative Drivers, and Consequences of Benthic Cyanobacterial Mats. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulouniriana, D.; Siboni, N.; Ben-Dov, E.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Loya, Y.; Kushmaro, A. Pseudoscillatoria coralii gen. nov., sp. nov., a cyanobacterium associated with coral black band disease (BBD). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 87, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetake, J.; Nagatsuka, N.; Onuma, Y.; Takeuchi, N.; Motoyama, H.; Aoki, T. Bacterial community changes with granule size in cryoconite and their susceptibility to exogenous nutrients on NW Greenland glaciers. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokul, J.K.; Hodson, A.J.; Saetnan, E.R.; Irvine-Fynn, T.D.L.; Westall, P.J.; Detheridge, A.P.; Takeuchi, N.; Bussell, J.; Mur, L.A.J.; Edwards, A. Taxon interactions control the distributions of cryoconite bacteria colonizing a High Arctic ice cap. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3752–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, T.; Takeuchi, N.; Mori, H.; Rathnayake, R.M.L.D.; Li, Z.; Akiyoshi, A.; Satoh, H.; Ishii, S. Redox stratification within cryoconite granules influences the nitrogen cycle on glaciers. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milferstedt, K.; Kuo-Dahab, W.C.; Butler, C.S.; Hamelin, J.; Abouhend, A.S.; Stauch-White, K.; McNair, A.; Watt, C.; Carbajal-González, B.I.; Dolan, S.; et al. The importance of filamentous cyanobacteria in the development of oxygenic photogranules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauch-White, K.; Srinivasan, V.N.; Camilla Kuo-Dahab, W.; Park, C.; Butler, C.S. The role of inorganic nitrogen in successful formation of granular biofilms for wastewater treatment that support cyanobacteria and bacteria. AMB Express 2017, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Takeuchi, N. Unmasking photogranulation in decreasing glacial albedo and net autotrophic wastewater treatment. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6391–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshkin, O.A.; Bondarenko, N.A.; Volkova, Y.A.; Tomberg, I.V.; Vishnyakov, V.S.; Malnik, V.V. Mass Development of Green Filamentous Algae of the Genera Spirogyra and Stigeoclonium (Chlorophyta) in the Littoral Zone of the Southern Part of Lake Baikal. Hydrobiol. J. 2015, 51, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, E.A. The first finding of aegagropilious, or algal balls, in the oldest freshwater Lake Baikal. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 5, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunecký, O.; Ivanova, A.P.; Mareš, J. An updated classification of cyanobacterial orders and families based on phylogenomic and polyphasic analysis. J. Phycol. 2023, 59, 12–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, J.; Carmona Magos, Y.; Beltrán Collado-Vides, L. Taxonomy and distribution of freshwater Blennothrix ganeshii Watanabe et Komárek (Oscillatoriaceae, Cyanophyceae) from central Mexico. Nova Hedwig. 2005, 80, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engene, N.; Tronholm, A.; Salvador-Reyes, L.A.; Luesch, H.; Paul, V.J. Caldora penicillata gen. nov., comb. nov. (Cyanobacteria), a pantropical marine species with biomedical relevance. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, D.; Hernández-Mariné, M.; Herdman, M.; Rippka, R. Structural and ultrastructural characterization of Symploca atlantica Gomont, strain PCC 8002 (Oscillatoriales, Cyanophyta, Cyanobacteria). Algol. Stud. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 2003, 109, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engene, N.; Rottacker, E.C.; Kaštovský, J.; Byrum, T.; Choi, H.; Ellisman, M.H.; Komárek, J.; Gerwick, W.H. Moorea producens gen. nov., sp. nov. and Moorea bouillonii comb. nov., tropical marine cyanobacteria rich in bioactive secondary metabolites. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, R.A.; Garrity, G.M.; Scott, J.J.; Amend, J.P.; Nealson, K.H.; Emerson, D. A Genus Definition for Bacteria and Archaea Based on a Standard Genome Relatedness Index. mBio 2020, 11, e02419–e02475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.L.; Gunturu, S.; Harvey, W.T.; Rosselló-Mora, R.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The Microbial Genomes Atlas (MiGA) webserver: Taxonomic and gene diversity analysis of Archaea and Bacteria at the whole genome level. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W282–W288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.F.V.; Giraldo-Silva, A.; Roush, D.; Garcia-Pichel, F. Coleofasciculaceae, a Monophyletic Home for the Microcoleus steenstrupii Complex and Other Desiccation-tolerant Filamentous Cyanobacteria. J. Phycol. 2021, 57, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandagopal, P.; Steven, A.N.; Chan, L.-W.; Rahmat, Z.; Jamaluddin, H. Bioactive Metabolites Produced by Cyanobacteria for Growth Adaptation and Their Pharmacological Properties. Biology 2021, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popin, R.V.; Alvarenga, D.O.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Fewer, D.P.; Sivonen, K. Mining of Cyanobacterial Genomes Indicates Natural Product Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Located in Conjugative Plasmids. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 684565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoupý, S.; Stanojković, A.; Pavlíková, M.; Poulíčková, A.; Dvořák, P. New cyanobacterial genus Argonema is hiding in soil crusts around the world. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenchel, T.; Finlay, B.J. The Ubiquity of Small Species: Patterns of Local and Global Diversity. Bioscience 2004, 54, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, A.R.; Carlile, A.L.; Neumann, J.M.; Kociolek, J.P.; Johansen, J.R.; Lowe, R.L.; Conklin, K.Y.; Presting, G.G. The Hawaiian freshwater algae biodiversity survey (2009–2014): Systematic and biogeographic trends with an emphasis on the macroalgae. BMC Ecol. 2014, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, A.R.; Carlile, A.L.; Vaccarino, M.A.; Johansen, J.R. Characterization of Hawaiian freshwater and terrestrial cyanobacteria reveals high diversity and numerous putative endemics. Phycol. Res. 2015, 63, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Limnofasciculus baicalensis gen. et sp. nov. (Symplocastrum sp.) | Schizothrix sp. [3] | Symplocastrum penicillatum [19] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thallus | 1–15 (60) cm, purple to red-brown, without incrustation. Fascicles with 1–10 agglutinated filaments enclosed in individual sheaths, ascending, often pseudobranched | 0.2–1 cm, blue-green, without incrustation. Filaments with 1–10 trichomes in a common sheath, aggregated to ascending fascicles, often pseudobranched | Dark green, dull blue-green, later incrusted, yellowish. Filaments with 1–5 trichomes, at the base entangled, at the ends parallel aggregated to ascending, penicillate fascicles, not (or sparsely) pseudobranched |
| Trichome width | 7–11.6 (13.4) µm | 6.6–8.3 μm | 2.4–5 (6) μm |
| Cell length | (3) 4.1–11 µm | 6–8.3 (13.5) μm | 2–9 μm |
| Filament width with one trichome | 12–15 (25) μm | 11–13 μm | No data |
| Sheath | 1–7.5 μm width. Sheaths open, colourless, firm, thin, sporadically widened or transversely folded, sometimes thick, lamellated or diffluent at the margin | 2.7–5 μm width. Firm, colourless or yellowish, not lamellated, thin | Firm, colourless, not (or sporadically) lamellated, thick in the basal part, thin in the upper part |
| Apical cell | Rounded, elongated rounded–conical, sometimes flat or stepped with nipple | Rounded, rounded–conical | Obtuse–conical, rounded–conical |
| Occurrence | Along most of the Baikal coast at depths of 3–10 m, rarely up to 20 m, on rocks, sand, encrusting and branched sponges, fishing nets, wood, steel. In autumn, after storms, in plankton, aggregated into 0.5–1.5 cm photogranules | Along most of the Baikal coast at depths of 1.5–15 m, rarely up to 40 m, on rocks, less often on sand. Often grows among Tolypothrix distorta and Cladophora spp. thalli | Freshwater, in flowing waters, waterfalls and in stony littoral of clear mountain lakes, among mosses |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sorokovikova, E.; Tikhonova, I.; Evseev, P.; Krasnopeev, A.; Khanaev, I.; Potapov, S.; Gladkikh, A.; Nebesnykh, I.; Belykh, O. Limnofasciculus baicalensis gen. et sp. nov. (Coleofasciculaceae, Coleofasciculales): A New Genus of Cyanobacteria Isolated from Sponge Fouling in Lake Baikal, Russia. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071779
Sorokovikova E, Tikhonova I, Evseev P, Krasnopeev A, Khanaev I, Potapov S, Gladkikh A, Nebesnykh I, Belykh O. Limnofasciculus baicalensis gen. et sp. nov. (Coleofasciculaceae, Coleofasciculales): A New Genus of Cyanobacteria Isolated from Sponge Fouling in Lake Baikal, Russia. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(7):1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071779
Chicago/Turabian StyleSorokovikova, Ekaterina, Irina Tikhonova, Peter Evseev, Andrey Krasnopeev, Igor Khanaev, Sergey Potapov, Anna Gladkikh, Ivan Nebesnykh, and Olga Belykh. 2023. "Limnofasciculus baicalensis gen. et sp. nov. (Coleofasciculaceae, Coleofasciculales): A New Genus of Cyanobacteria Isolated from Sponge Fouling in Lake Baikal, Russia" Microorganisms 11, no. 7: 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071779
APA StyleSorokovikova, E., Tikhonova, I., Evseev, P., Krasnopeev, A., Khanaev, I., Potapov, S., Gladkikh, A., Nebesnykh, I., & Belykh, O. (2023). Limnofasciculus baicalensis gen. et sp. nov. (Coleofasciculaceae, Coleofasciculales): A New Genus of Cyanobacteria Isolated from Sponge Fouling in Lake Baikal, Russia. Microorganisms, 11(7), 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071779









