The Alteration of the Gut Microbiome during Ramadan Offers a Novel Perspective on Ramadan Fasting: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Recruitment and Specimen and Data Collection
2.2. Measurement of Short-Chain Fatty Acid in Fecal Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of Bioinformatics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
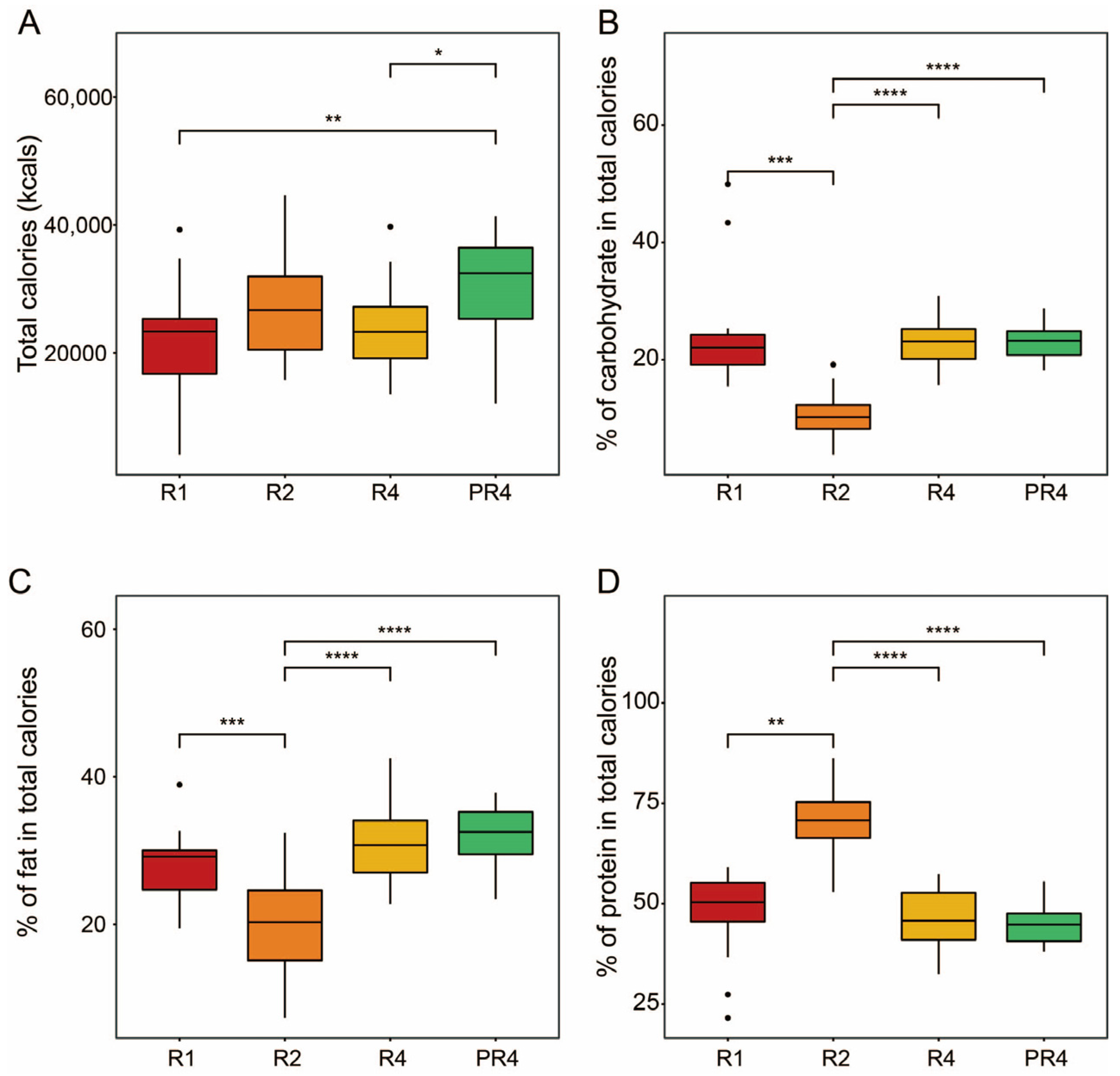
3.1. Participant and Nutritional Characteristics during Ramadan
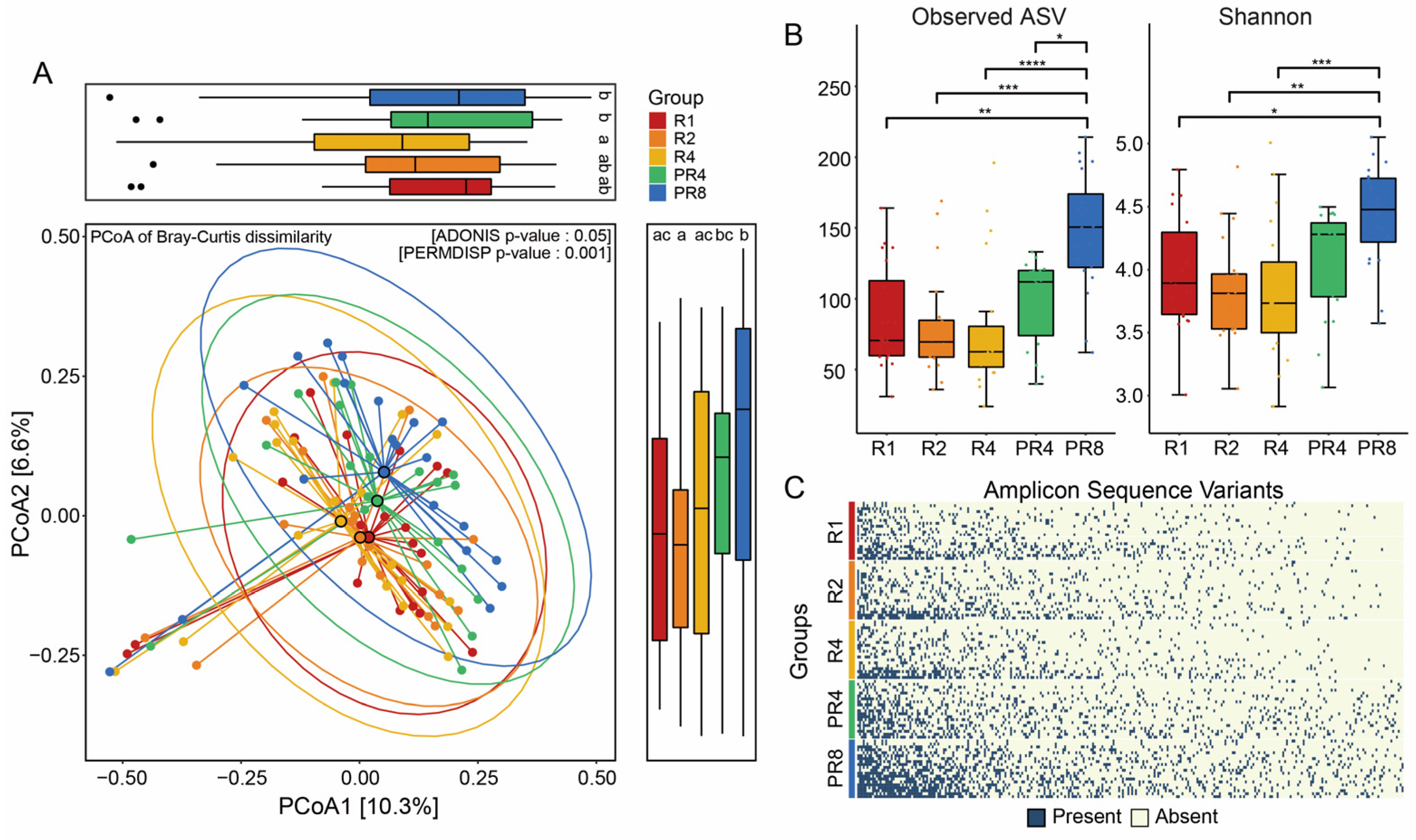
3.2. Ramadan Fasting Drives Substantial Change in Fecal Microbial Diversity
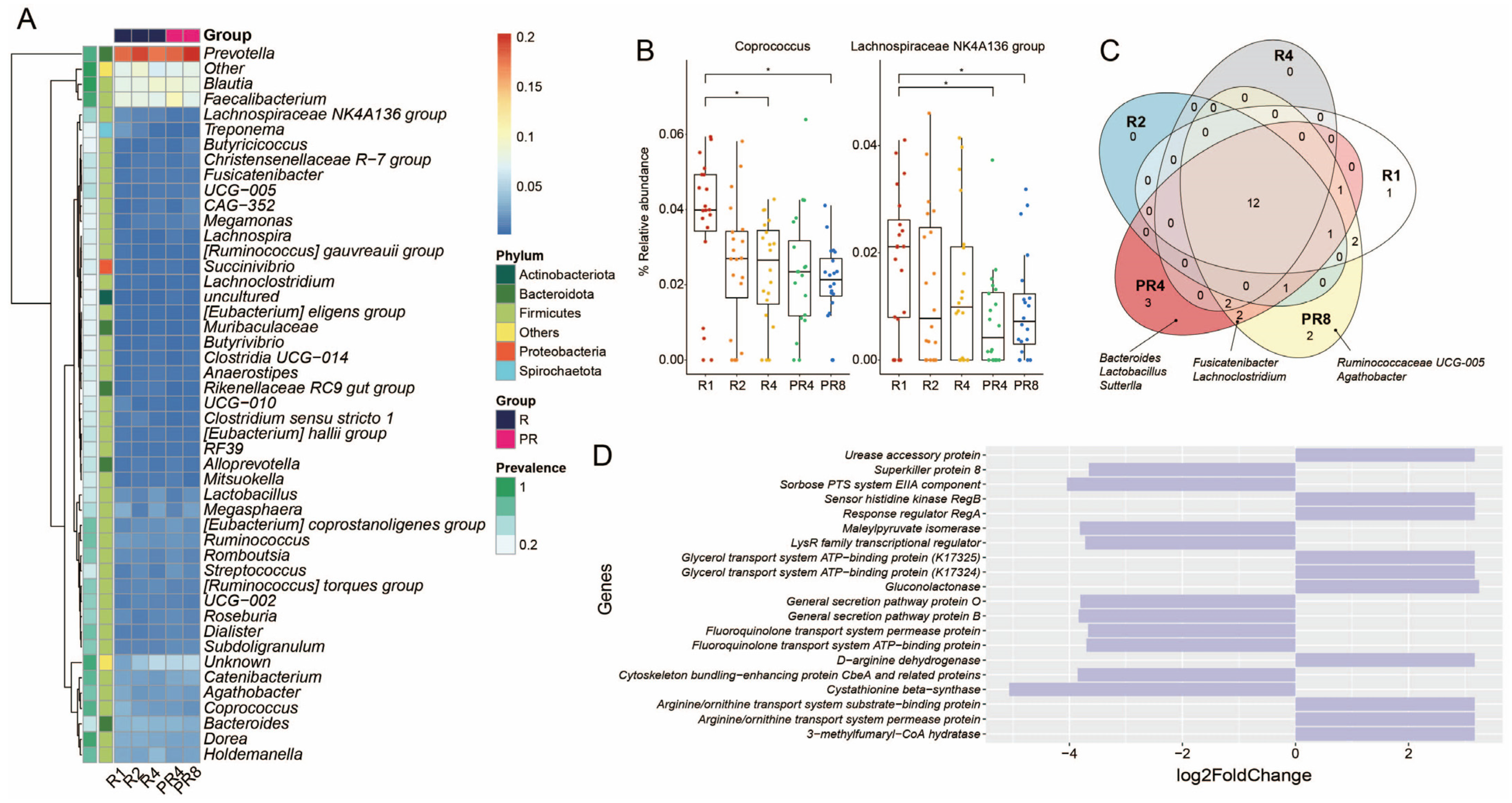
3.3. Ramadan Fasting Causes Decline of Specific Taxa and Metabolic Functions
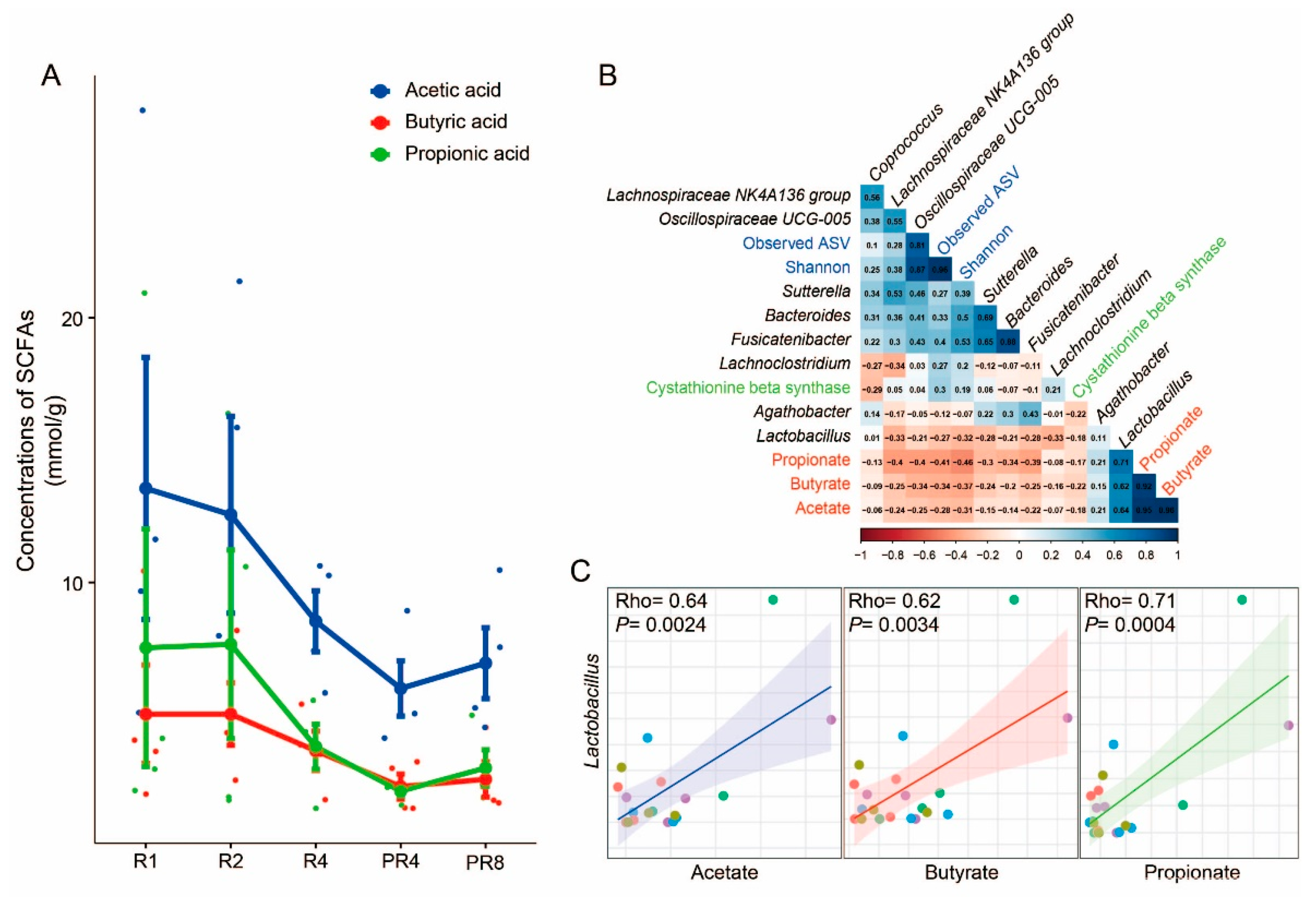
3.4. Significant Alteration in Taxa from Ramadan Are Associated with Reduction of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Microbial Diversity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakr, A.H. Fasting in Islam. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1975, 67, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, E.G. Mapping Time. The Calendar and Its History; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, J.; NE, S. Metabolic changes resulting from decreased meal frequency in adult male Muslims during the Ramadan fast. Nutr. Rep. Int. 1975, 11, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chandalia, H.; Bhargav, A.; Kataria, V. Dietary pattern during Ramadan fasting and its effect on the metabolic control of diabetes. Pract. Diabetes Int. 1987, 4, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ati, J.; Beji, C.; Danguir, J. Increased fat oxidation during Ramadan fasting in healthy women: An adaptative mechanism for body-weight maintenance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of intermittent fasting on health, aging, and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; La Bounty, P.M. Effects of intermittent fasting on body composition and clinical health markers in humans. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepanowski, J.F.; Kroeger, C.M.; Barnosky, A.; Klempel, M.C.; Bhutani, S.; Hoddy, K.K.; Gabel, K.; Freels, S.; Rigdon, J.; Rood, J. Effect of alternate-day fasting on weight loss, weight maintenance, and cardioprotection among metabolically healthy obese adults: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnason, T.G.; Bowen, M.W.; Mansell, K.D. Effects of intermittent fasting on health markers in those with type 2 diabetes: A pilot study. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmli, S.; Elmasry, R.; Ramos, M.; Fung, J. Therapeutic use of intermittent fasting for people with type 2 diabetes as an alternative to insulin. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017-221854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Roshanravan, N.; Mesri Alamdari, N.; Safaiyan, A.; Mosharkesh, E.; Hadi, A.; Barati, M.; Ostadrahimi, A. The interplay between fasting, gut microbiota, and lipid profile. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkul, C.; Yalinay, M.; Karakan, T. Structural changes in gut microbiome after Ramadan fasting: A pilot study. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkul, C.; Yalınay, M.; Karakan, T. Islamic fasting leads to an increased abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila and Bacteroides fragilis group: A preliminary study on intermittent fasting. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 30, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Verhaar, A.; Ma, Z.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Investigating Ramadan Like Fasting Effects on the Gut Microbiome in BALB/c Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 832757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; Xie, Z.; Pan, Q.; Ma, Z.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Remodeling of the gut microbiome during Ramadan-associated intermittent fasting. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouhal, H.; Bagheri, R.; Triki, R.; Saeidi, A.; Wong, A.; Hackney, A.C.; Laher, I.; Suzuki, K.; Ben Abderrahman, A. Effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on gut hormones and body composition in males with obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Healy, M. Compliance and drug therapy in fasting Moslem patients. J. Clin. Hosp. Pharm. 1986, 11, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaagaoglu, N.; Yucecan, S. Some behavioral changes observed among fasting subjects, their nutritional habits and energy expenditure in Ramadan. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 51, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Prentice, A.; Lamb, W.H.; Prentice, A.; Coward, W. The effect of water abstention on milk synthesis in lactating women. Clin. Sci. 1984, 66, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisi, V.G. Increasing awareness of health care concerns during Ramadan. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2001, 41, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wu, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, K.; Zou, F. Type 2 diabetes biomarkers of human gut microbiota selected via iterative sure independent screening method. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temraz, S.; Nassar, F.; Nasr, R.; Charafeddine, M.; Mukherji, D.; Shamseddine, A. Gut microbiome: A promising biomarker for immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ouyang, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, S.; Fu, C.; Zeng, J.; He, X. Phocea, Pseudoflavonifractor and Lactobacillus intestinalis: Three potential biomarkers of gut microbiota that affect progression and complications of obesity-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beli, E.; Yan, Y.; Moldovan, L.; Vieira, C.P.; Gao, R.; Duan, Y.; Prasad, R.; Bhatwadekar, A.; White, F.A.; Townsend, S.D. Restructuring of the gut microbiome by intermittent fasting prevents retinopathy and prolongs survival in db/db mice. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Khan, S.I.; Rana, M.I.; Ayyaz, A.; Khan, M.Y.; Imran, M. Intermittent fasting positively modulates human gut microbial diversity and ameliorates blood lipid profile. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 922727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X. Intermittent Fasting and Physical Exercise for Preventing Metabolic Disorders through Interaction with Gut Microbiota: A Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.C.; Silva, A.A.; Souza, S.L. Repercussions of intermittent fasting on the intestinal microbiota community and body composition: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angoorani, P.; Ejtahed, H.-S.; Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Siadat, S.D.; Soroush, A.R.; Larijani, B. Gut microbiota modulation as a possible mediating mechanism for fasting-induced alleviation of metabolic complications: A systematic review. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarczyk, M.M.; Miller, M.J.; Freund, G.G. The health benefits of dietary fiber: Beyond the usual suspects of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and colon cancer. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lin, K.; Sequeira, C.; Borchers, C.H. An isotope-labeled chemical derivatization method for the quantitation of short-chain fatty acids in human feces by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 854, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.J.; Tagele, S.B.; Pham, H.Q.; Jung, Y.; Ibal, J.C.; Choi, S.; Kang, G.-U.; Park, S.; Kang, Y.; Kim, S. In situ profiling of the three dominant phyla within the human gut using TaqMan PCR for pre-hospital diagnosis of gut dysbiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘ggplot2’. Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. Available online: https://search.r-project.org/CRAN/refmans/ggplot2/html/ggplot2-package.html (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Warnes, M.G.R.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Huber, W. Package ‘Gplots’. Various R Programming Tools for Plotting Data. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/gplots/index.html (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S. Introduction to the Microbiome R package. Available online: https://microbiome.github.io/tutorials/ (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Larsson, J.; Godfrey, A.J.R.; Gustafsson, P.; Eberly, D.H.; Huber, E.; Slowikowski, K.; Privé, F.; Larsson, M.J. Package ‘Eulerr’. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/eulerr/index.html (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Shetty, S.A.; Lahti, L.; de Vos, W.M.; Smidt, H. microbiomeutilities: An R Package for Utilities to Guide In-Depth Marker Gene Amplicon Data Analysis. Ecophysiological Insights into the Human Intestinal Microbiota: From Single Strains to Defined Consortia. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018. Volume 95. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, K.K.; Ma, C.X.; Fontana, L.; Peterson, L.L. Intermittent fasting in the prevention and treatment of cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, R. Scientific evidence of diets for weight loss: Different macronutrient composition, intermittent fasting, and popular diets. Nutrition 2020, 69, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.E.; Sears, D.D. Metabolic effects of intermittent fasting. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 37, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, S.; Minty, R.; O’Driscoll, T.; Willms, H.; Poirier, D.; Madden, S.; Kelly, L. Intermittent fasting and weight loss: Systematic review. Can. Fam. Physician 2020, 66, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, N.; Vollmer, M.; Holtrop, G.; Farquharson, F.M.; Wefers, D.; Bunzel, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Drew, J.E.; Williams, L.M.; Milligan, G. Specific substrate-driven changes in human faecal microbiota composition contrast with functional redundancy in short-chain fatty acid production. ISME J. 2018, 12, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Merwe, J.P.; Stegeman, J.H. Binding of Coprococcus comes to the Fc portion of IgG. A possible role in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease? Eur. J. Immunol. 1985, 15, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-R.; Chou, T.-S.; Huang, C.-Y.; Hsiao, J.-K. A Potential Probiotic-Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 Group: Evidence from the Restoration of the Dietary Pattern from a High-Fat Diet. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-48913/v1 (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Wrigley, D.M. Inhibition of Clostridium perfringens sporulation by Bacteroides fragilis and short-chain fatty acids. Anaerobe 2004, 10, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.L.; Savarino, V.; Slavin, J.L. Assessment of dietary fiber fermentation: Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri and reproducibility of short-chain fatty acid concentrations. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S114–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.T.; Perez Santiago, J.; Iablokov, S.N.; Chopra, D.; Rodionov, D.A.; Peterson, S.N. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Modulate Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition and Functional Potential. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiwaki, H.; Ito, M.; Hamaguchi, T.; Maeda, T.; Kashihara, K.; Tsuboi, Y.; Ueyama, J.; Yoshida, T.; Hanada, H.; Takeuchi, I. Short chain fatty acids-producing and mucin-degrading intestinal bacteria predict the progression of early Parkinson’s disease. npj Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogal, A.; Louca, P.; Zhang, X.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Falchi, M.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. Circulating levels of the short-chain fatty acid acetate mediate the effect of the gut microbiome on visceral fat. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Xing, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F. Microbiota populations and short-chain fatty acids production in cecum of immunosuppressed broilers consuming diets containing γ-irradiated Astragalus polysaccharides. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Vasquez, R.; Kim, S.H.; Hwang, I.-C.; Song, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Kang, D.-K. Multispecies probiotics alter fecal short-chain fatty acids and lactate levels in weaned pigs by modulating gut microbiota. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.-H.; Qian, L.-Y.; Pang, J.; Lin, J.-Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.-H.; Huang, D.-S.; Zou, H. The regulation of immune cells by Lactobacilli: A potential therapeutic target for anti-atherosclerosis therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Bao, Y.; Di, J.; Hu, C. The genus Sutterella is a potential contributor to glucose metabolism improvement after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in T2D. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buret, A.G.; Allain, T.; Motta, J.-P.; Wallace, J.L. Effects of hydrogen sulfide on the microbiome: From toxicity to therapy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2022, 36, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganster, F.; Burban, M.; De La Bourdonnaye, M.; Fizanne, L.; Douay, O.; Loufrani, L.; Mercat, A.; Calès, P.; Radermacher, P.; Henrion, D. Effects of hydrogen sulfide on hemodynamics, inflammatory response and oxidative stress during resuscitated hemorrhagic shock in rats. Critical Care 2010, 14, R165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.-F.; Yu, T.-C.; Hong, J.; Fang, J.-Y. Emerging roles of hydrogen sulfide in inflammatory and neoplastic colonic diseases. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wächtershäuser, A.; Stein, J. Rationale for the luminal provision of butyrate in intestinal diseases. Eur. J. Nutr. 2000, 39, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, J.; Kim, M. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids, T cells, and inflammation. Immune Netw. 2014, 14, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thananimit, S.; Pahumunto, N.; Teanpaisan, R. Characterization of Short Chain Fatty Acids Produced by Selected Potential Probiotic Lactobacillus Strains. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Baarlen, P.; Wells, J.M.; Kleerebezem, M. Regulation of intestinal homeostasis and immunity with probiotic lactobacilli. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, T.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.; Tang, D. Regulatory role of short-chain fatty acids in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Śliżewska, K. The effect of probiotics on the production of short-chain fatty acids by human intestinal microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Yang, J. Short-chain fatty acids: A soldier fighting against inflammation and protecting from tumorigenesis in people with diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, E.; Corr, S.C. Lactobacillus spp. for Gastrointestinal Health: Current and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, Y.; Lee, G.; Ahmad, S.; Son, H.; Kim, M.-J.; Sliti, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-E.; Shin, J.-H. The Alteration of the Gut Microbiome during Ramadan Offers a Novel Perspective on Ramadan Fasting: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082106
Jo Y, Lee G, Ahmad S, Son H, Kim M-J, Sliti A, Lee S, Kim K, Lee S-E, Shin J-H. The Alteration of the Gut Microbiome during Ramadan Offers a Novel Perspective on Ramadan Fasting: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(8):2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082106
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, YoungJae, GyuDae Lee, Sajjad Ahmad, HyunWoo Son, Min-Ji Kim, Amani Sliti, Seungjun Lee, Kyeongnam Kim, Sung-Eun Lee, and Jae-Ho Shin. 2023. "The Alteration of the Gut Microbiome during Ramadan Offers a Novel Perspective on Ramadan Fasting: A Pilot Study" Microorganisms 11, no. 8: 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082106
APA StyleJo, Y., Lee, G., Ahmad, S., Son, H., Kim, M.-J., Sliti, A., Lee, S., Kim, K., Lee, S.-E., & Shin, J.-H. (2023). The Alteration of the Gut Microbiome during Ramadan Offers a Novel Perspective on Ramadan Fasting: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms, 11(8), 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082106






