Natural Shikonin Potentially Alters Intestinal Flora to Alleviate Acute Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Shikonin Alleviated Inflammatory Response in a Xylene-Induced Mouse Model of Acute Ear Swelling
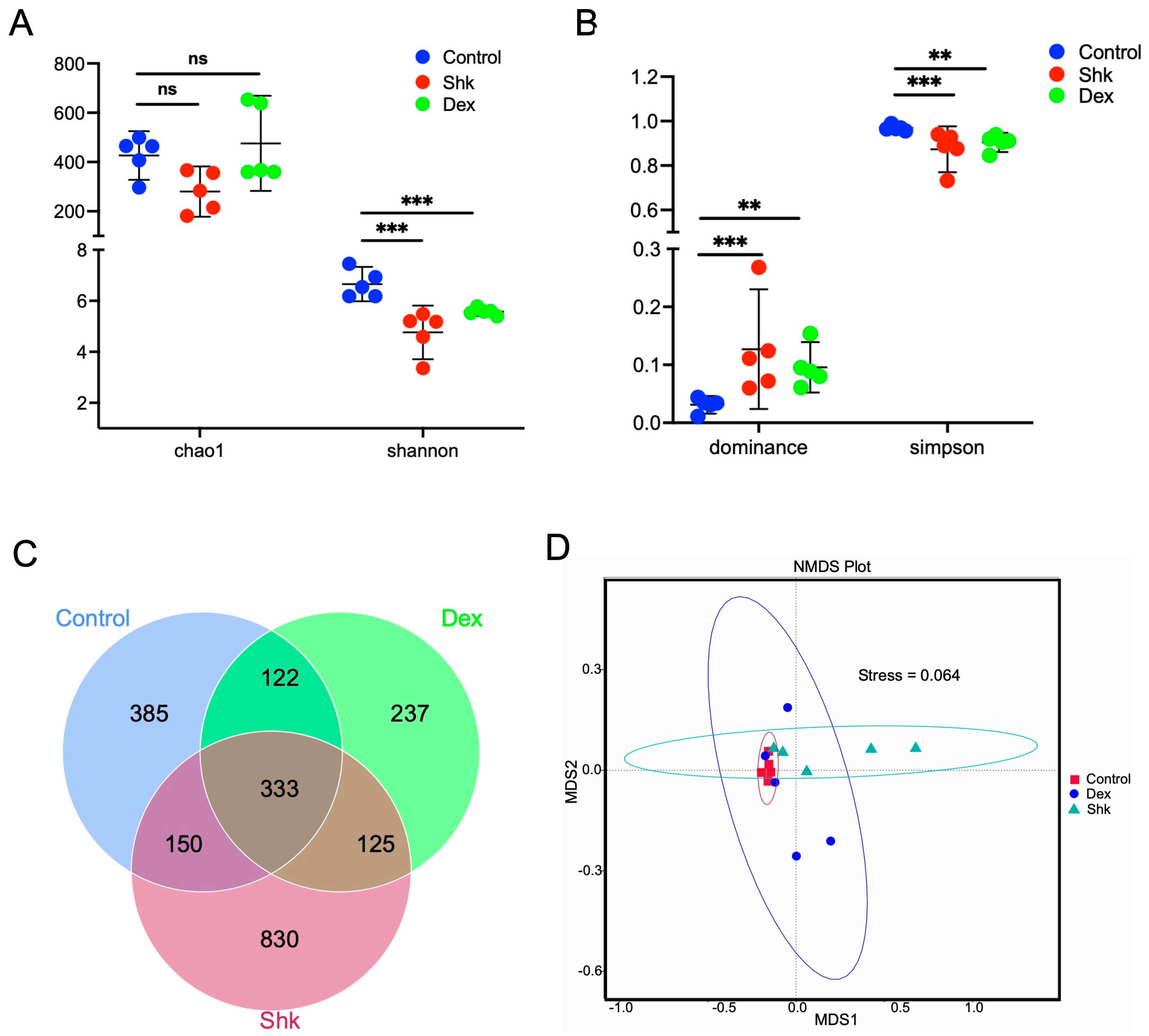
2.2. Shikonin Treatment Reduced the Diversity of Intestinal Flora in a Mouse Model of Acute Inflammation
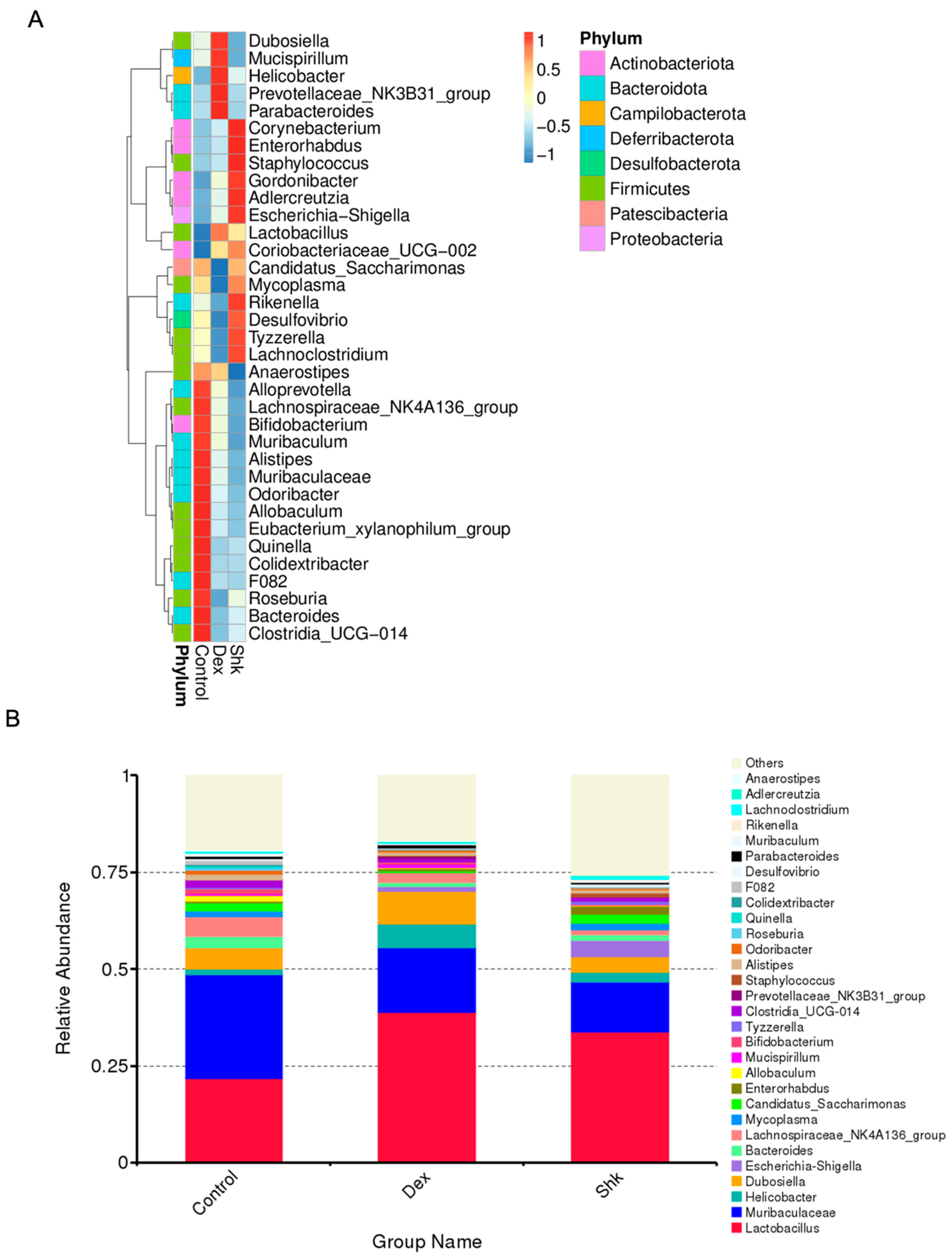
2.3. Shikonin Treatment Altered Gut Microbiota Abundance in Mice
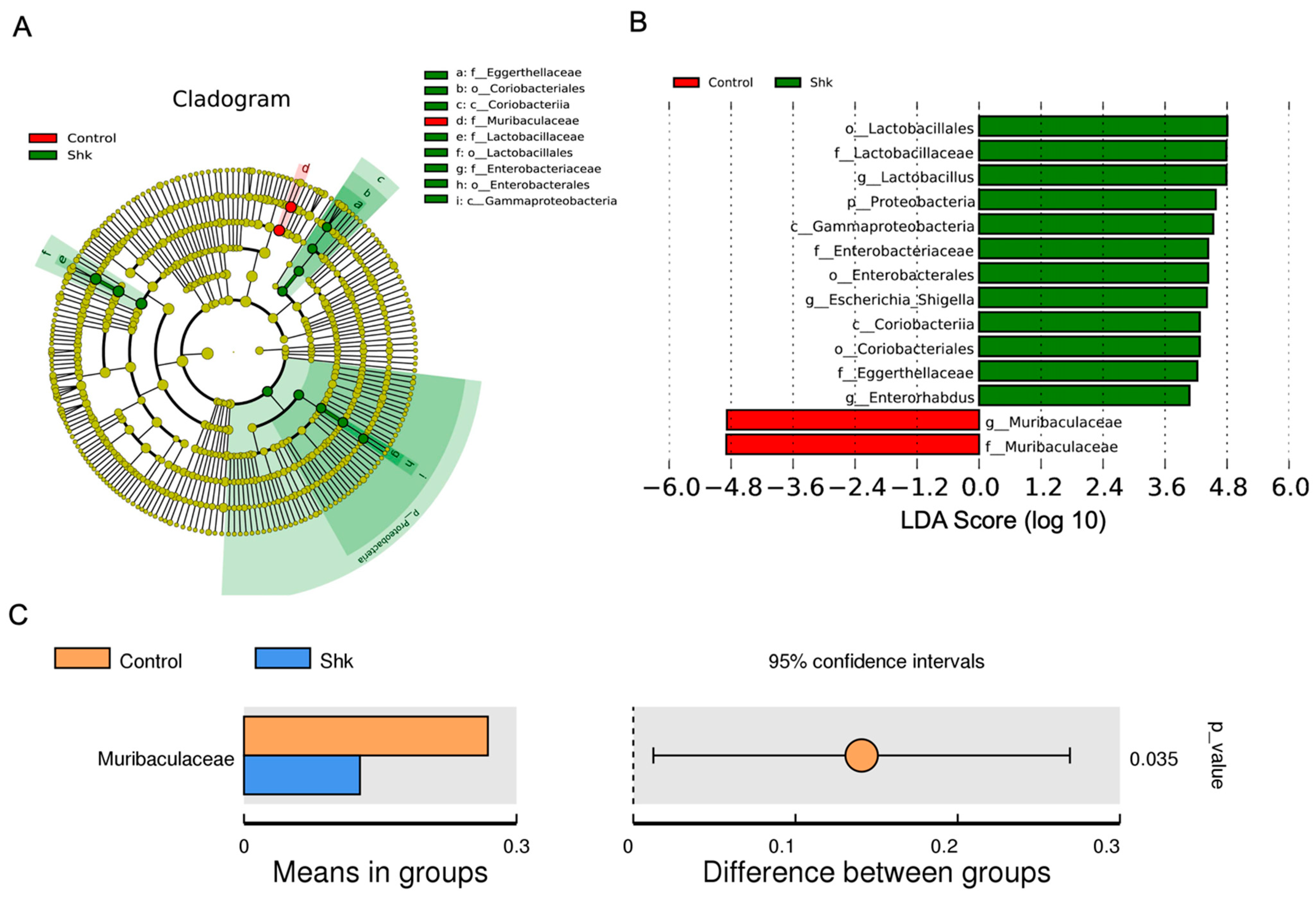
2.4. Identification of Flora Exhibiting Significantly Altered Abundance Using Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
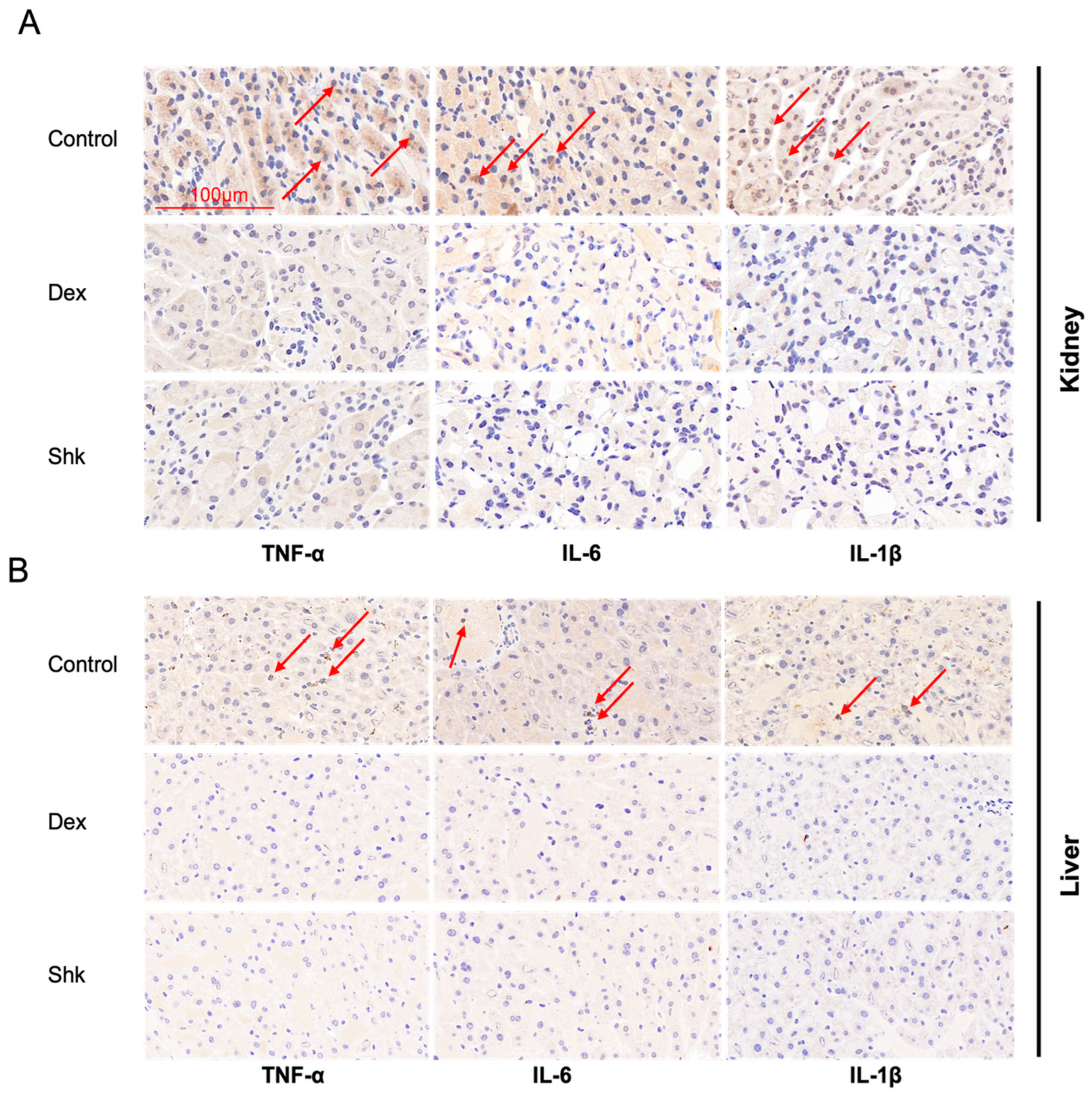
2.5. Shikonin Treatment Decreased the Expression Levels of Inflammatory Factors Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α, Interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β in the Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Animal Breeding
4.3. Mouse Feces Collection
4.4. Animal Tools and Xylene-Induced Acute Ear Edema Model of Mice
4.5. Analysis of Mouse Ear Edema
4.6. 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis for Intestinal Flora
4.7. RT-qPCR Assay
4.8. Western Blot Assay
4.9. Immunohistochemical Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garrett, W.S. The gut microbiota and colon cancer. Science 2019, 364, 1133–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.N.; Zhao, Y.Z. Gut microbiota derived metabolites in cardiovascular health and disease. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Liao, Q.F.; Lin, M.N.; Zhong, D.M.; Wei, L.; Han, B.; Miao, H.; Yao, M.C.; Xie, Z.Y. An integrated metabonomics and microbiology analysis of host-microbiota metabolic interactions in rats with Coptis chinensis-induced diarrhea. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79329–79341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Shah, Y.A.; Hussain, M.; Rabail, R.; Socol, C.T.; Hassoun, A.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rusu, A.V.; et al. Human gut microbiota in health and disease: Unveiling the relationship. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 999001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakaroun, R.M.; Olsson, L.M.; Backhed, F. The potential of tailoring the gut microbiome to prevent and treat cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 20, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Hou, T.; Zhou, M.; Cen, Q.; Yi, T.; Bai, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Gut microbiota may be involved in Alzheimer’s disease pathology by dysregulating pyrimidine metabolism in APP/PS1 mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 967747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahowald, M.A.; Rey, F.E.; Seedorf, H.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fulton, R.S.; Wollam, A.; Shah, N.; Wang, C.; Magrini, V.; Wilson, R.K.; et al. Characterizing a model human gut microbiota composed of members of its two dominant bacterial phyla. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5859–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piewngam, P.; De Mets, F.; Otto, M. Intestinal microbiota: The hidden gems in the gut? Asian Pac. J. Allergy 2020, 38, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, P.C.; Rini, B.I. Treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Current status and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Ma, L.J.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, F.M.; Zhao, C.H.; Nie, Y.Z. Insights into the role of gut microbiota in obesity: Pathogenesis, mechanisms, and therapeutic perspectives. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Ding, C.; Liang, J. Altered Gut Microbiota Associated With Hemorrhage in Chronic Radiation Proctitis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 637265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wastyk, H.C.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Perelman, D.; Dahan, D.; Merrill, B.D.; Yu, F.Q.B.; Topf, M.; Gonzalez, C.G.; Van Treuren, W.; Han, S.; et al. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell 2021, 184, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Gu, Y.; Hou, H.; Liu, T.; Ding, Y.; Cao, H. Dietary Patterns and Gut Microbiota Changes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Insights and Future Challenges. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Kim, M.; Oh, S.D.; Lee, S.M.; Sun, B.; Choi, G.S.; Kim, S.K.; Bae, H.; Kang, C.; Min, B.I. Effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidzumi rhizome on 3T3-L1 adipogenesis and an animal model of obesity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Deng, W. Antitumor effects of Chinese herbal medicine compounds and their nano-formulations on regulating the immune system microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 949332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheid, V.; Tuffrey, V.; Weijburg, T.; Bovey, M.; Ward, T. Chinese medicine treatment for menopausal symptoms in the UK health service: Is a clinical trial warranted? Maturitas 2015, 80, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Shikonin and its analogs inhibit cancer cell glycolysis by targeting tumor pyruvate kinase-M2. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4297–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, T.; Guo, S.; Jiang, K.F.; Wu, H.C.; Deng, G.Z. Shikonin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Tao, S.; Wang, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhao, P.; Rao, C.; Yang, L. ER-mediated anti-tumor effects of shikonin on breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 863, 172667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, B.J.; Zong, G.F.; Tao, R.Z.; Wei, Z.H.; Lu, Y. Crosstalk between traditional Chinese medicine-derived polysaccharides and the gut microbiota: A new perspective to understand traditional Chinese medicine. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 4125–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.P.; Zhong, Y.B.; Kang, Z.P.; Huang, J.Q.; Fang, W.Y.; Wei, S.Y.; Long, J.; Li, S.S.; Zhao, H.M.; Liu, D.Y. Curcumin regulates the homeostasis of Th17/Treg and improves the composition of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice with colitis. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1708–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Liu, B.; Tang, S.; Yasir, M.; Khan, I. The science behind TCM and Gut microbiota interaction-their combinatorial approach holds promising therapeutic applications. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 875513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wei, Y.; Gou, X.; Tian, J.; Li, M.; Tong, X. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine on gut microbiota in adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 2021, 88, 153455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Li, M.Y.; Lu, L.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; An, F.K.; Huang, K.; Fu, Z. Arenga pinnata Resistant Starch Modulate Gut Microbiota and Ameliorate Intestinal Inflammation in Aged Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Sang, T.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H. Wenzi Jiedu Recipe ameliorates colorectal cancer by remodeling the gut microbiota and tumor microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 915498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Gong, T.; Liu, M.; Ren, S.; Yang, H.; Zeng, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, L.; Ming, T.; Meng, X.; et al. Shikonin, a naphthalene ingredient: Therapeutic actions, pharmacokinetics, toxicology, clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches. Phytomedicine 2022, 94, 153805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Fang, P.; Ye, X.; Lan, X.; Xu, R.A. Evaluation of herb-drug interaction of ambrisentan with shikonin based on UPLC-MS/MS. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkosi, B.V.Z.; Padayachee, T.; Gront, D.; Nelson, D.R.; Syed, K. Contrasting Health Effects of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes Lies in Their Genomes: Analysis of P450s, Ferredoxins, and Secondary Metabolite Clusters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, Q.; Wen, Z.; Yang, M.; Fu, J.; Yin, T.; Lu, G.; Qi, J.; et al. Natural shikonin and acetyl-shikonin improve intestinal microbial and protein composition to alleviate colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Kong, H.G.; Song, G.C.; Ryu, C.M. Disruption of Firmicutes and Actinobacteria abundance in tomato rhizosphere causes the incidence of bacterial wilt disease. ISME J. 2021, 15, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, R.; Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Fang, L.; Lu, Y.; Du, G. Total flavonoids from Anchusa italica Retz. Improve cardiac function and attenuate cardiac remodeling post myocardial infarction in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.H.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Tasneem, S.; Chen, C.; Qiu, Y.X.; Li, B.; Liao, J.; et al. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects and molecular mechanisms of Kadsura heteroclita stems, an anti-arthritic Chinese Tujia ethnomedicinal herb. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilnikova, K.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Fernando, P.D.S.M.; Herath, H.M.U.L.; Cho, S.J.; Hyun, J.W. Natural Compound Shikonin Induces Apoptosis and Attenuates Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Radiation-Resistant Human Colon Cancer Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Aburaya, S.; Kaminade, K.; Aoki, W.; Saida-Munakata, Y.; Sugiyama, A.; Ueda, M.; Yazaki, K. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Lithospermum erythrorhizon Reveals Regulation of a Variety of Metabolic Enzymes Leading to Comprehensive Understanding of the Shikonin Biosynthetic Pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohberger, B.; Kaltenegger, H.; Eck, N.; Glanzer, D.; Sadoghi, P.; Leithner, A.; Bauer, R.; Kretschmer, N.; Steinecker-Frohnwieser, B. Shikonin Derivatives Inhibit Inflammation Processes and Modulate MAPK Signaling in Human Healthy and Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Si, L.T.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, H.Y.; Liu, X.S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.J. Uncovering the antitumor effects and mechanisms of Shikonin against colon cancer on comprehensive analysis. Phytomedicine 2021, 82, 153460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, J.C.; Rahama, M.; Hegazy, M.E.F.; Efferth, T. Shikonin derivatives for cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Shang, X.; Ni, Z.; Shi, G. Shikonin inhibits inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis by regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; He, J.; Song, X.; Tan, L.; Wang, M.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Peng, C. Pharmacological properties and derivatives of shikonin-A review in recent years. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 149, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Ao, H.; Peng, C.; Yan, D. Gut microbiota, a new frontier to understand traditional Chinese medicines. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assimopoulou, A.N.; Papageorgiou, V.P. Encapsulation of isohexenylnaphthazarins in cyclodextrins. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, M.; Li, X.; Luo, K. Promising Nanomedicines of Shikonin for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 1195–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Pan, T.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, X. Non-cytotoxic doses of shikonin inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha expression via activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
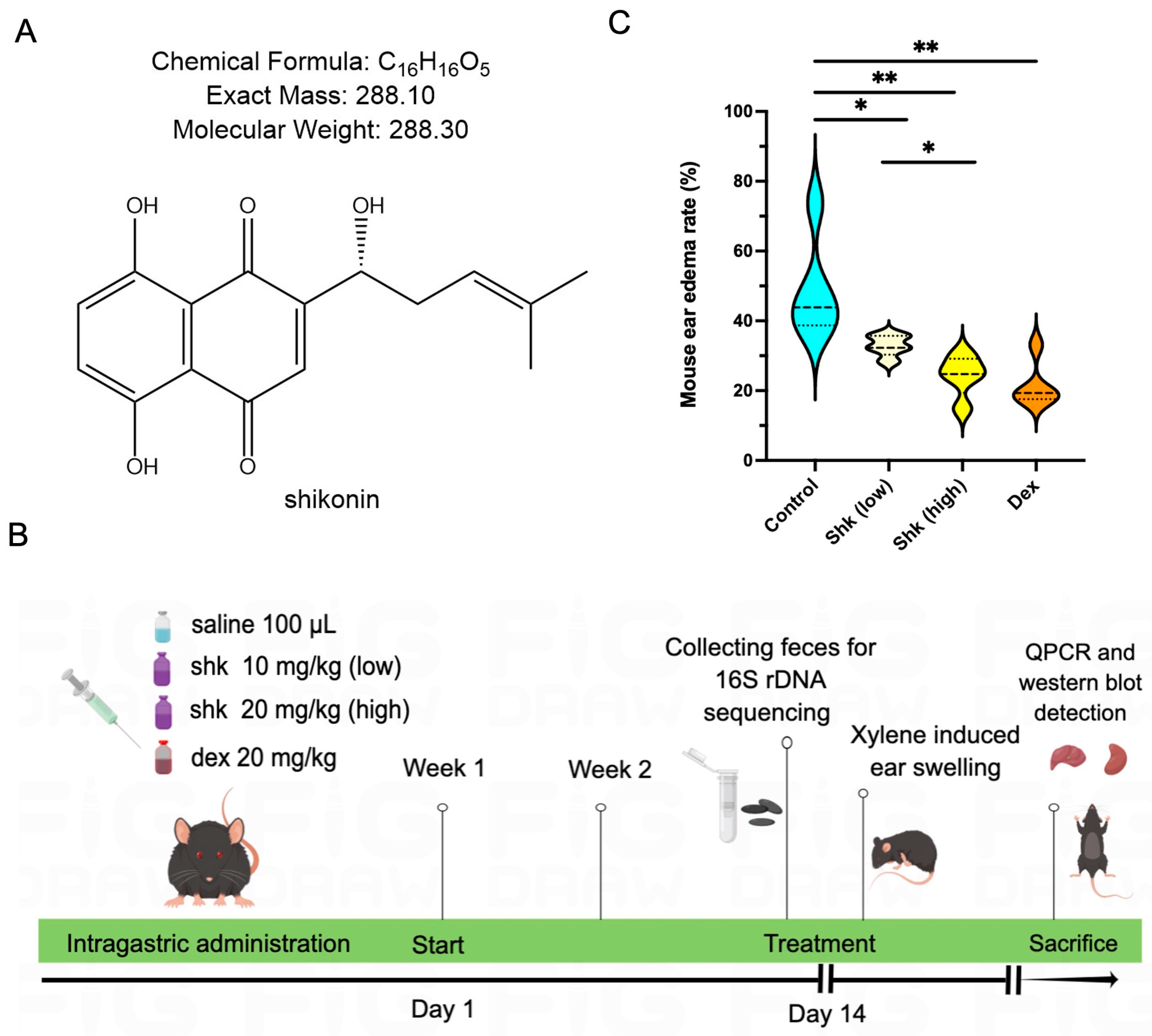

| Compounds | Anti-Inflammatory Activity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | Ear Edema Mean Weight ± SD (mg) a | Inhibition Rate (%) | p Value b | |
| Control c | 100 μL soybean oil | 13.01 ± 1.91 | -- | |
| Shikonin | 20 mg/kg | 10.12 ± 2.60 | 12.23 | * |
| Dexamethasone d | 20 mg/kg | 7.20 ± 1.24 | 12.46 | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Ju, D.; Liu, W.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, M. Natural Shikonin Potentially Alters Intestinal Flora to Alleviate Acute Inflammation. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092139
Liang Y, Ju D, Liu W, Wu D, Zhao Y, Du Y, Li X, Zhao M. Natural Shikonin Potentially Alters Intestinal Flora to Alleviate Acute Inflammation. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(9):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092139
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Ying, Dongen Ju, Wenna Liu, Dan Wu, Yujia Zhao, Yaya Du, Xi Li, and Minggao Zhao. 2023. "Natural Shikonin Potentially Alters Intestinal Flora to Alleviate Acute Inflammation" Microorganisms 11, no. 9: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092139
APA StyleLiang, Y., Ju, D., Liu, W., Wu, D., Zhao, Y., Du, Y., Li, X., & Zhao, M. (2023). Natural Shikonin Potentially Alters Intestinal Flora to Alleviate Acute Inflammation. Microorganisms, 11(9), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092139






