Repurposing Selamectin as an Antimicrobial Drug against Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compound
2.2. Characterization of the Bacterial Strains
2.3. Bacterial Growth Conditions
2.4. Cell Culture Conditions
2.5. Antibacterial Susceptibility Assays
2.6. Cell Cytotoxicity Test
2.7. Hemolysis Assays
2.8. Killing Kinetic Assays
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.10. Checkerboard Tests
2.11. In Silico Molecular Docking
2.12. Gentamicin Protection Assay
2.13. Biofilm Degradation Assay
2.14. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Analysis
2.15. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
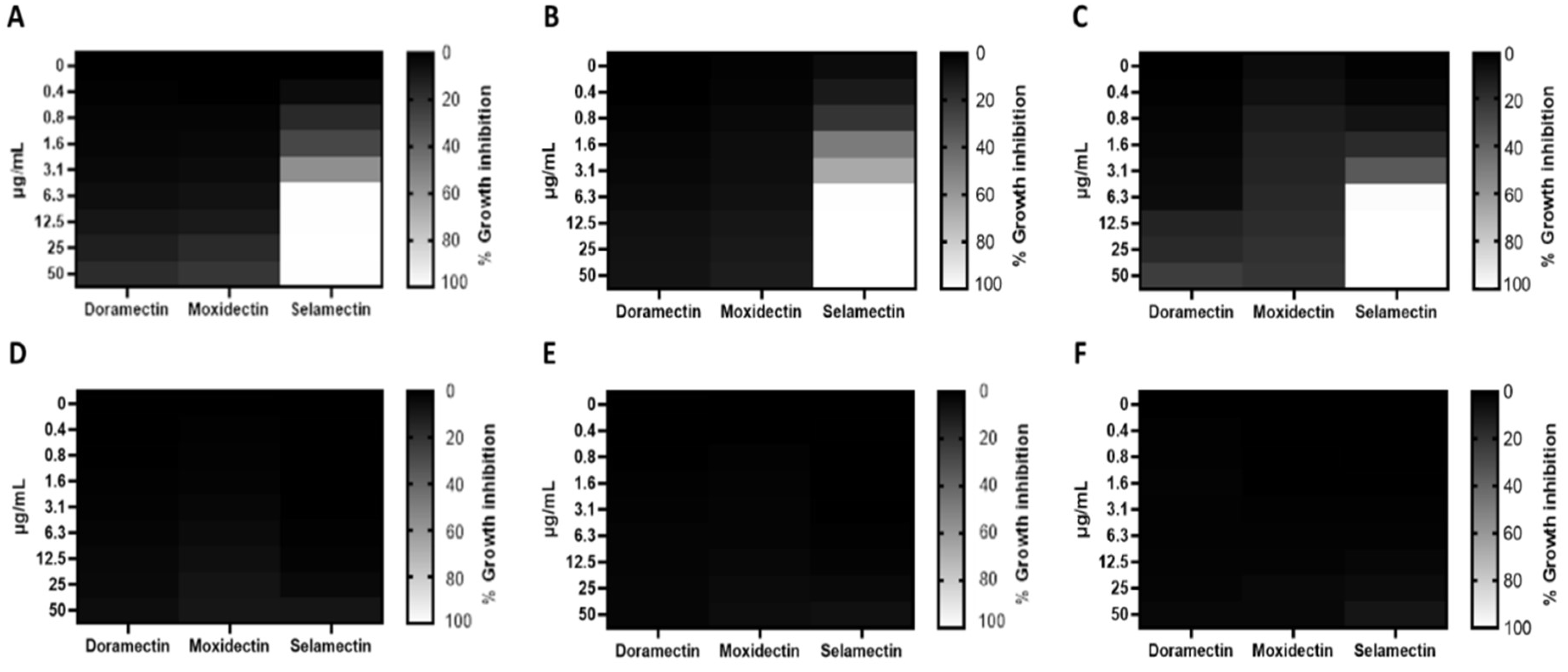
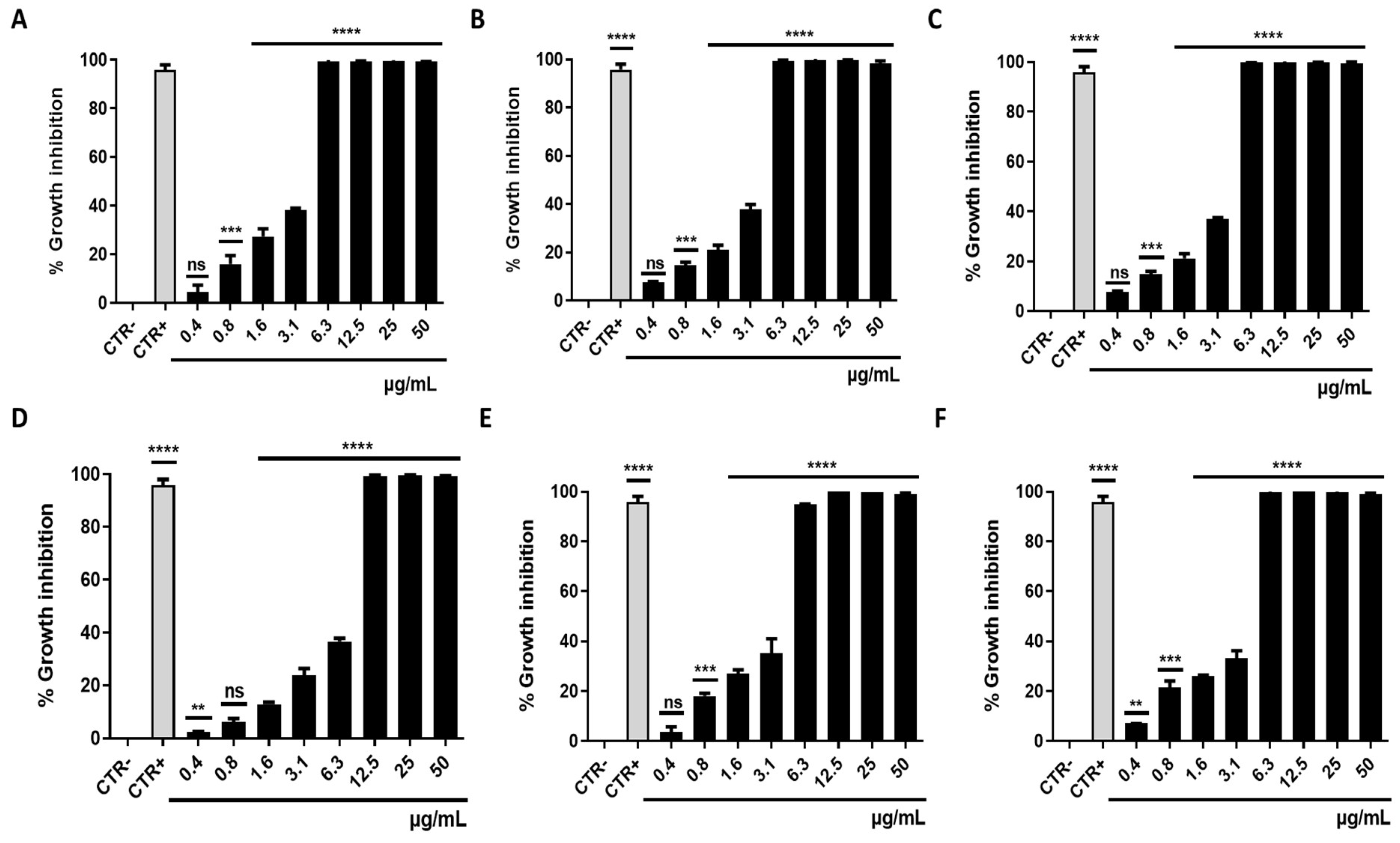
3.1. Antibacterial Activity
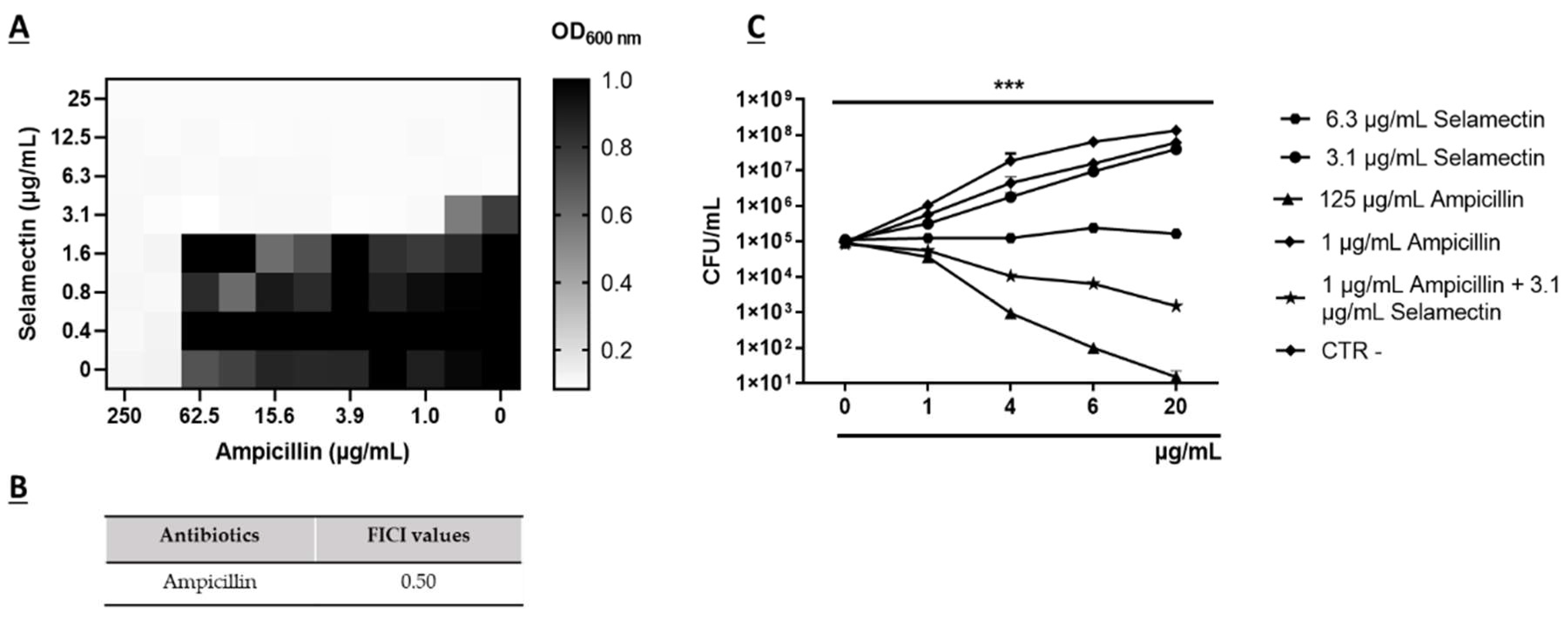
3.2. Synergistic Activity of Selamectin with Ampicillin
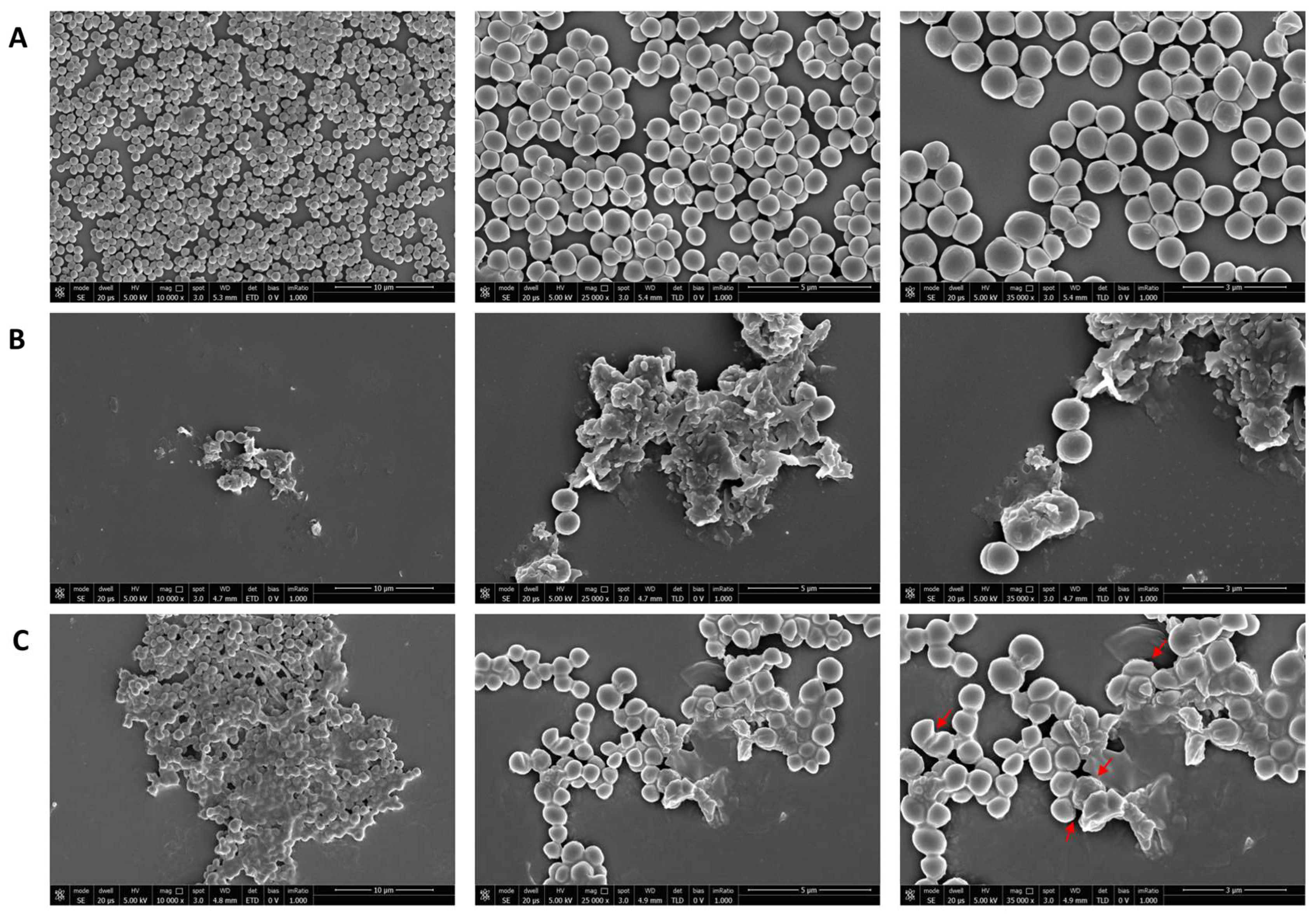
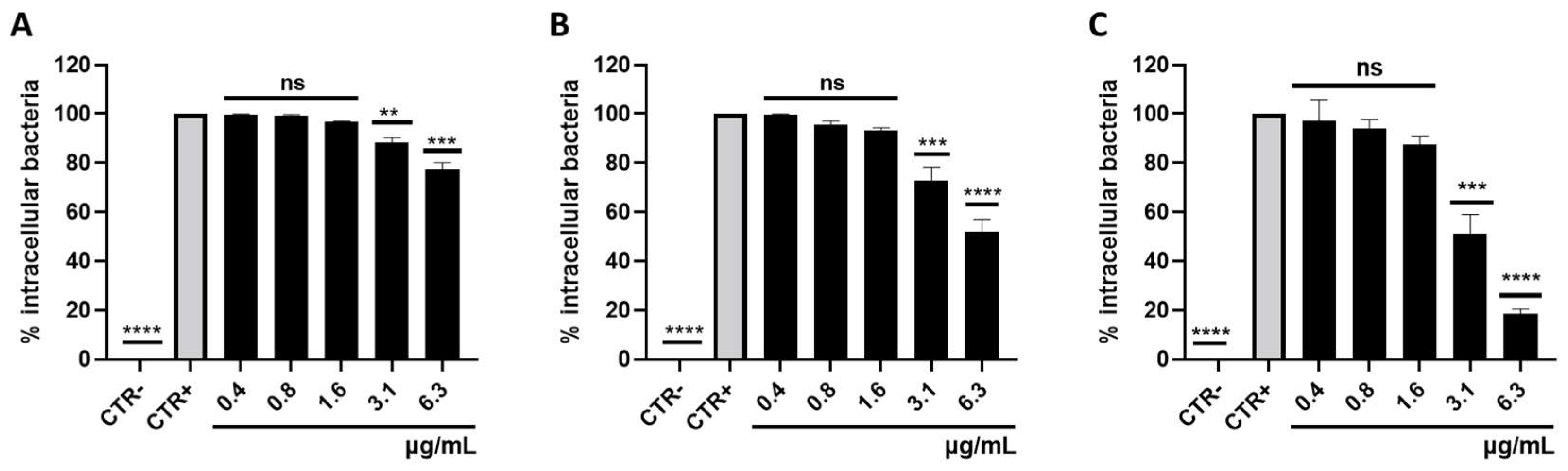
3.3. Survival of Intracellular S. aureus
3.4. Biofilm Degradation Activity
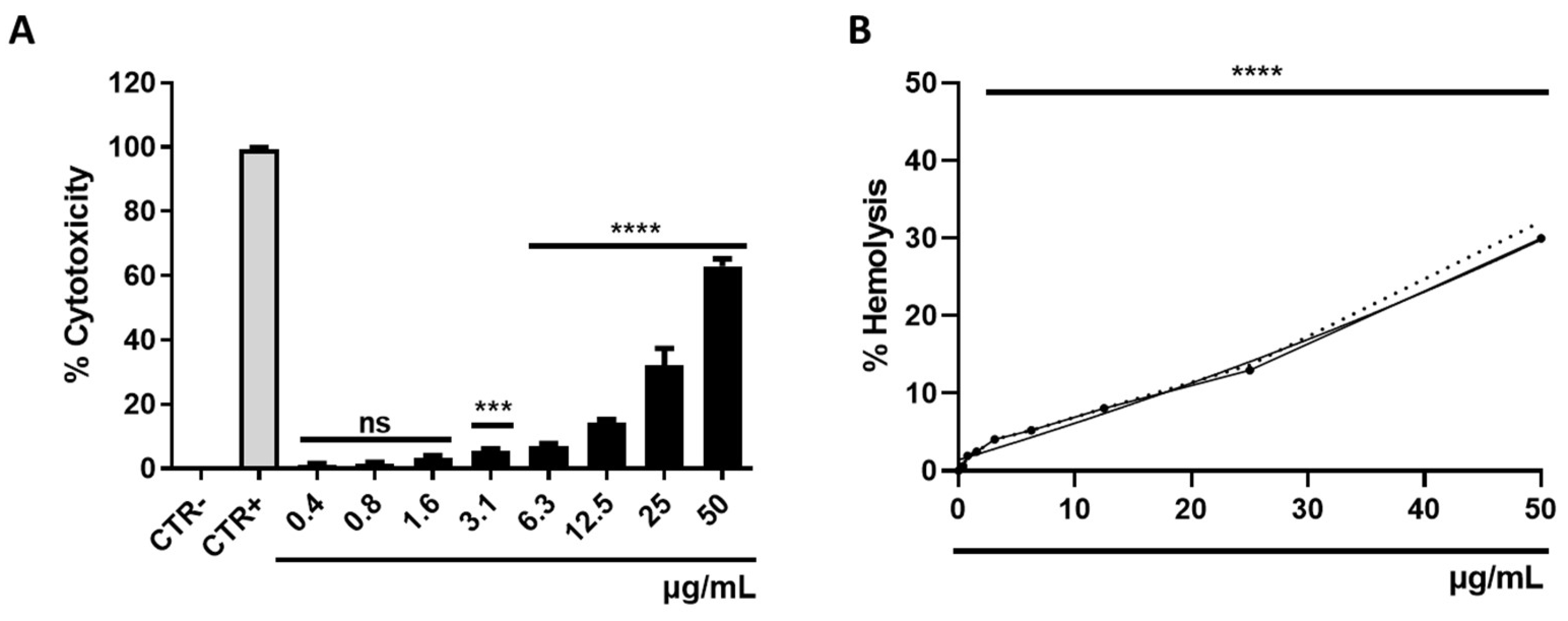
3.5. Determination of Cytotoxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koch, A.M.; Nilsen, R.M.; Eriksen, H.M.; Cox, R.J.; Harthug, S. Mortality Related to Hospital-Associated Infections in a Tertiary Hospital; Repeated Cross-Sectional Studies between 2004–2011. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2015, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Abu Bakar, M. Health Care-Associated Infections—An Overview. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voidazan, S.; Albu, S.; Toth, R.; Grigorescu, B.; Rachita, A.; Moldovan, I. Healthcare Associated Infections-A New Pathology in Medical Practice? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, G.V.; Ramadhan, T.; Ahmed, E.; Sanad, H. WHO Global Priority Pathogens List: A Bibliometric Analysis of Medline-PubMed for Knowledge Mobilization to Infection Prevention and Control Practices in Bahrain. Oman Med. J. 2019, 34, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, A.; Fernández, L.; Gutiérrez, D.; Iglesias, B.; Rodríguez, A.; García, P. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Hospitals: Latest Trends and Treatments Based on Bacteriophages. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01006-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.-B.; Yu, Z.-L.; Fu, H.-B.; Cai, Z.-H.; Chen, J. Daptomycin and Linezolid for Severe Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Psoas Abscess and Bacteremia: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 2550–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuon, F.F.; Suss, P.H.; Telles, J.P.; Dantas, L.R.; Borges, N.H.; Ribeiro, V.S.T. Antimicrobial Treatment of Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Bassler, B.L. Surviving as a Community: Antibiotic Tolerance and Persistence in Bacterial Biofilms. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serral, F.; Castello, F.A.; Sosa, E.J.; Pardo, A.M.; Palumbo, M.C.; Modenutti, C.; Palomino, M.M.; Lazarowski, A.; Auzmendi, J.; Ramos, P.I.P.; et al. From Genome to Drugs: New Approaches in Antimicrobial Discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 647060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Meenakshisundaram, S.; Manickam, M.; Sankaranarayanan, M. A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective of Drug Repositioning: Recent Advances and Challenges in Drug Discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 195, 112275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, Z.Y.; Farouk, I.A.; Lal, S.K. Drug Repositioning: New Approaches and Future Prospects for Life-Debilitating Diseases and the COVID-19 Pandemic Outbreak. Viruses 2020, 12, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.A.; Feliciano, J.R.; Pita, T.; Soeiro, C.F.; Mendes, B.L.; Alves, L.G.; Leitão, J.H. Bacterial Nosocomial Infections: Multidrug Resistance as a Trigger for the Development of Novel Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, F.A.; Forman, R.; Bataille, C.J.R.; Wynne, G.M.; Nick, M.; Russell, A.J.; Else, K.J.; Sattelle, D.B. Anthelmintic Drug Discovery: Target Identification, Screening Methods and the Role of Open Science. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1203–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, A.; Wang, J.; Xiang, W. Isolation and Identification of New Macrocyclic Lactones from a Genetically Engineered Strain Streptomyces Bingchenggensis BCJ60. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Alqahtani, A.; Ilesanmi, O.B.; Saati, A.A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Hetta, H.F.; Magdy Beshbishy, A. Avermectin Derivatives, Pharmacokinetics, Therapeutic and Toxic Dosages, Mechanism of Action, and Their Biological Effects. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-S.; Kubo, Y. Ivermectin and Its Target Molecules: Shared and Unique Modulation Mechanisms of Ion Channels and Receptors by Ivermectin. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Annunziata, F.; Martora, F.; Pepa, M.E.D.; Folliero, V.; Luongo, L.; Bocelli, S.; Guida, F.; Mascolo, P.; Campobasso, C.P.; Maione, S.; et al. Postmortem Interval Assessment by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Analysis in Murine Cadavers. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santella, B.; Folliero, V.; Pirofalo, G.M.; Serretiello, E.; Zannella, C.; Moccia, G.; Santoro, E.; Sanna, G.; Motta, O.; De Caro, F.; et al. Sepsis-A Retrospective Cohort Study of Bloodstream Infections. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squillaci, G.; Zannella, C.; Carbone, V.; Minasi, P.; Folliero, V.; Stelitano, D.; Cara, F.L.; Galdiero, M.; Franci, G.; Morana, A. Grape Canes from Typical Cultivars of Campania (Southern Italy) as a Source of High-Value Bioactive Compounds: Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. Molecules 2021, 26, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannella, C.; Chianese, A.; Palomba, L.; Marcocci, M.E.; Bellavita, R.; Merlino, F.; Grieco, P.; Folliero, V.; De Filippis, A.; Mangoni, M.; et al. Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity of the Amphibian Antimicrobial Peptide Temporin L and Its Analogs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, G.; Bayram, A.; Zer, Y.; Balci, I. Synergy Tests by E Test and Checkerboard Methods of Antimicrobial Combinations against Brucella Melitensis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance: A Rundown of a Global Crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terreni, M.; Taccani, M.; Pregnolato, M. New Antibiotics for Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains: Latest Research Developments and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, D.K.; Xu, T.; Xia, M.; Zheng, W.; Huang, R. Repurposing Drugs as COVID-19 Therapies: A Toxicity Evaluation. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panic, G.; Duthaler, U.; Speich, B.; Keiser, J. Repurposing Drugs for the Treatment and Control of Helminth Infections. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2014, 4, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.E.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H. Anthelmintics for Drug Repurposing: Opportunities and Challenges. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinesh Kumar, N.; Ter Ellen, B.M.; Bouma, E.M.; Troost, B.; van de Pol, D.P.I.; van der Ende-Metselaar, H.H.; van Gosliga, D.; Apperloo, L.; Carpaij, O.A.; van den Berge, M.; et al. Moxidectin and Ivermectin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Vero E6 Cells but Not in Human Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0154321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, X.; Li, H.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, N.; Song, Y.; Deng, X. Avermectin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect by Downregulating the Nuclear Transcription Factor Kappa-B and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation Pathway. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 23, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Si, H.F.; Shang, X.F.; Zhang, X.K.; Li, B.; Zhou, X.Z.; Zhang, J.Y. New Life for an Old Drug: In Vitro and in Vivo Effects of the Anthelmintic Drug Niclosamide against Toxoplasma Gondii RH Strain. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2019, 9, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Jha, R.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Tiwari, B.R.; Asaad, A.M. Recent Advances in Staphylococcus Aureus Infection: Focus on Vaccine Development. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.T.; Scholtz, C.H. A Review on the Effect of Macrocyclic Lactones on Dung-Dwelling Insects: Toxicity of Macrocyclic Lactones to Dung Beetles. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2015, 82, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.E.; Vilchèze, C.; Ng, C.; Jacobs, W.R.; Ramón-García, S.; Thompson, C.J. Anthelmintic Avermectins Kill Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, Including Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omansen, T.F.; Porter, J.L.; Johnson, P.D.R.; van der Werf, T.S.; Stienstra, Y.; Stinear, T.P. In-Vitro Activity of Avermectins against Mycobacterium Ulcerans. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.; Chaudhry, U.; Raza, A.; Ghosh, D.; Zhao, X. In Vitro Activity of Ivermectin against Staphylococcus Aureus Clinical Isolates. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklasińska-Majdanik, M. Mechanisms of Resistance to Macrolide Antibiotics among Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, N.; Pluschke, G.; Thompson, C.J.; Ramón-García, S. Selamectin Is the Avermectin with the Best Potential for Buruli Ulcer Treatment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Muñoz, L.; Shoen, C.; Sweet, G.; Vitoria, A.; Bull, T.J.; Cynamon, M.; Thompson, C.J.; Ramón-García, S. Repurposing Avermectins and Milbemycins against Mycobacteroides Abscessus and Other Nontuberculous Mycobacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerra-Aznárez, J.M.; Degiacomi, G.; Gašparovič, H.; Stelitano, G.; Sammartino, J.C.; Korduláková, J.; Governa, P.; Manetti, F.; Pasca, M.R.; Chiarelli, L.R.; et al. The Veterinary Anti-Parasitic Selamectin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Mycobacterium Tuberculosis DprE1 Enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, M.F.; Stephen, J.; Lekshmi, M.; Ojha, M.; Wenzel, N.; Sanford, L.M.; Hernandez, A.J.; Parvathi, A.; Kumar, S.H. Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunai, A.; Spohn, R.; Farkas, Z.; Lázár, V.; Györkei, Á.; Apjok, G.; Boross, G.; Szappanos, B.; Grézal, G.; Faragó, A.; et al. Rapid Decline of Bacterial Drug-Resistance in an Antibiotic-Free Environment through Phenotypic Reversion. Elife 2019, 8, e47088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.K.; Argudín, M.A.; Deplano, A.; Nhung, P.H.; Nguyen, H.A.; Tulkens, P.M.; Dodemont, M.; Van Bambeke, F. Antibiotic Resistance, Biofilm Formation, and Intracellular Survival as Possible Determinants of Persistent or Recurrent Infections by Staphylococcus aureus in a Vietnamese Tertiary Hospital: Focus on Bacterial Response to Moxifloxacin. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommes, J.W.; Surewaard, B.G.J. Intracellular Habitation of Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Mechanisms and Prospects for Antimicrobial Therapy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, B.; Duan, J.; Hou, B. Biofilm Inhibition Effect of an Ivermectin/Silyl Acrylate Copolymer Coating and the Colonization Dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, A.P.; Krücken, J.; Neveu, C.; Charvet, C.L.; Harmache, A.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. Pharyngeal Pumping and Tissue-Specific Transgenic P-Glycoprotein Expression Influence Macrocyclic Lactone Susceptibility in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, P.; Martens, E.; Pereira, D. Nature Nurtures the Design of New Semi-Synthetic Macrolide Antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J. In Vitro Activity and Pharmacodynamic/Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Clarithromycin and Azithromycin: Why They Matter in the Treatment of Respiratory Tract Infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Bacterial Species | Strain Number | Resistance Phenotype | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | ATCC 6538 | Multisensitive | ATCC center |
| C. striatum | ATCC BAA-1293 | Multisensitive | ATCC center |
| S. epidermidis | ATCC 12228 | Multisensitive | ATCC center |
| E. coli | ATCC 11229 | Multisensitive | ATCC center |
| K. pneumoniae | ATCC 10031 | Multisensitive | ATCC center |
| P. aeruginosa | ATCC 9027 | Multisensitive | ATCC center |
| S. aureus | CI1 | Multisensitive | Eye |
| S. aureus | CI2 | Beta-lactamase producer | Wound |
| S. aureus | CI3 | Constitutive resistance to macrolides, lincosamide, streptogramin B | Blood |
| S. aureus | CI4 | Quinolones resistance | Sputum |
| S. aureus | CI5 | Methicillin resistance | Blood |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Folliero, V.; Dell’Annunziata, F.; Santella, B.; Roscetto, E.; Zannella, C.; Capuano, N.; Perrella, A.; De Filippis, A.; Boccia, G.; Catania, M.R.; et al. Repurposing Selamectin as an Antimicrobial Drug against Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus Infections. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092242
Folliero V, Dell’Annunziata F, Santella B, Roscetto E, Zannella C, Capuano N, Perrella A, De Filippis A, Boccia G, Catania MR, et al. Repurposing Selamectin as an Antimicrobial Drug against Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus Infections. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(9):2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092242
Chicago/Turabian StyleFolliero, Veronica, Federica Dell’Annunziata, Biagio Santella, Emanuela Roscetto, Carla Zannella, Nicoletta Capuano, Alessandro Perrella, Anna De Filippis, Giovanni Boccia, Maria Rosaria Catania, and et al. 2023. "Repurposing Selamectin as an Antimicrobial Drug against Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus Infections" Microorganisms 11, no. 9: 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092242
APA StyleFolliero, V., Dell’Annunziata, F., Santella, B., Roscetto, E., Zannella, C., Capuano, N., Perrella, A., De Filippis, A., Boccia, G., Catania, M. R., Galdiero, M., & Franci, G. (2023). Repurposing Selamectin as an Antimicrobial Drug against Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus Infections. Microorganisms, 11(9), 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092242












