Biodegradation of Crude Oil and Aniline by Heavy Metal-Tolerant Strain Rhodococcus sp. DH-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Isolation and Identification of the Predominant Strain
2.3. Degradation Characteristics of Aniline-Degrading Bacteria
2.4. Crude Oil Degradation Experiment
2.5. DH-2 Whole Genome Sequencing
2.6. Fluorescence Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Effect of Heavy Metal Ions on the Growth of Bacterial Strains
2.8. Soil Simulation Experiment for the Treatment of Dual Pollution of Aniline and Crude Oil in the Presence of Heavy Metals
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Aniline Degradation by Rhodococcus sp. DH-2
3.1.1. Classification and Identification of Aniline Degrading Bacteria
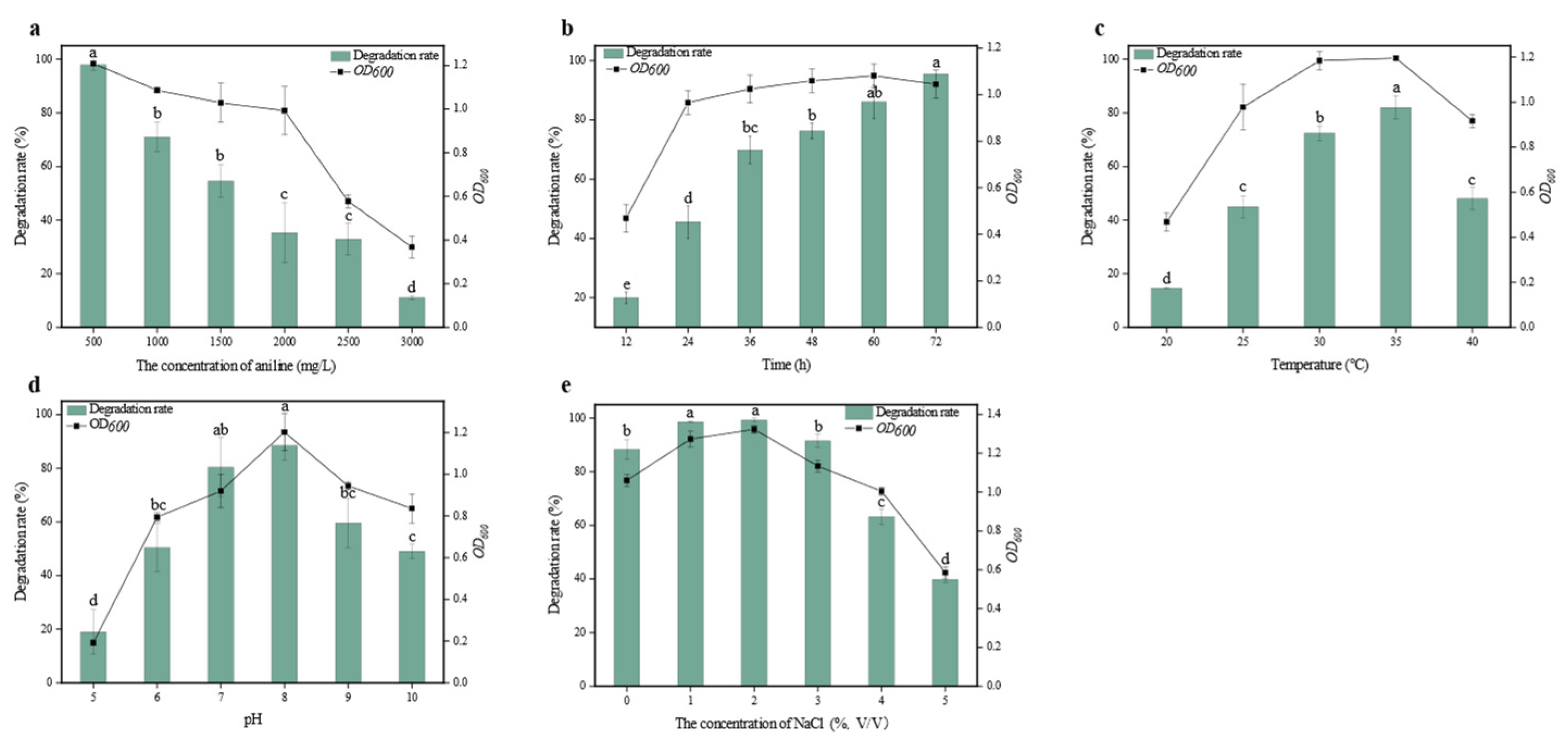
3.1.2. Influence of Environmental Conditions on the Degradation of Aniline by DH-2
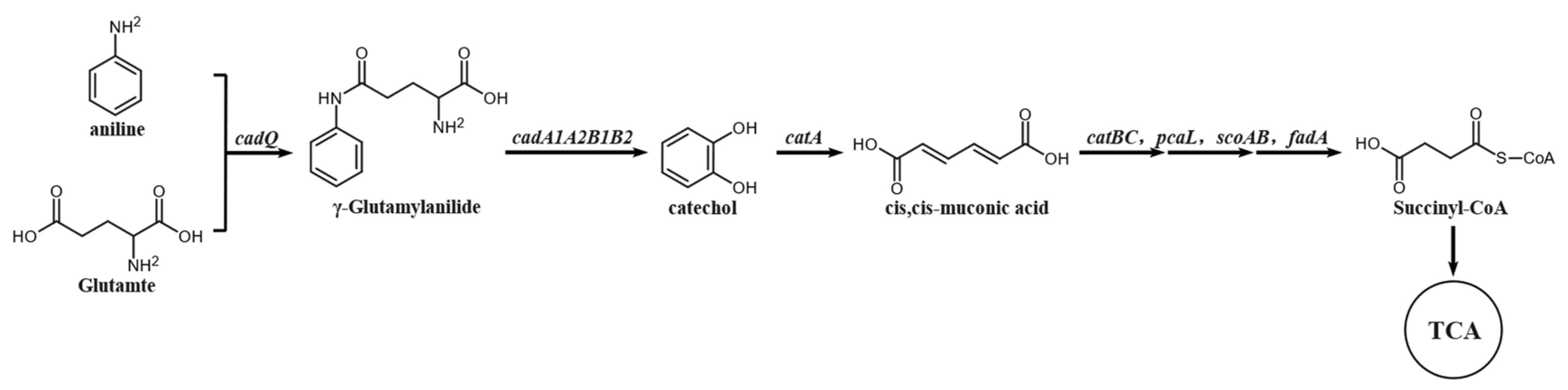
3.1.3. Analysis of the Degradation Pathway of Aniline by Strain DH-2
3.1.4. Genomic Analysis of Rhodococcus sp. DH-2
3.2. Degradation Efficacy of DH-2 in Crude Oil Contaminated Environment
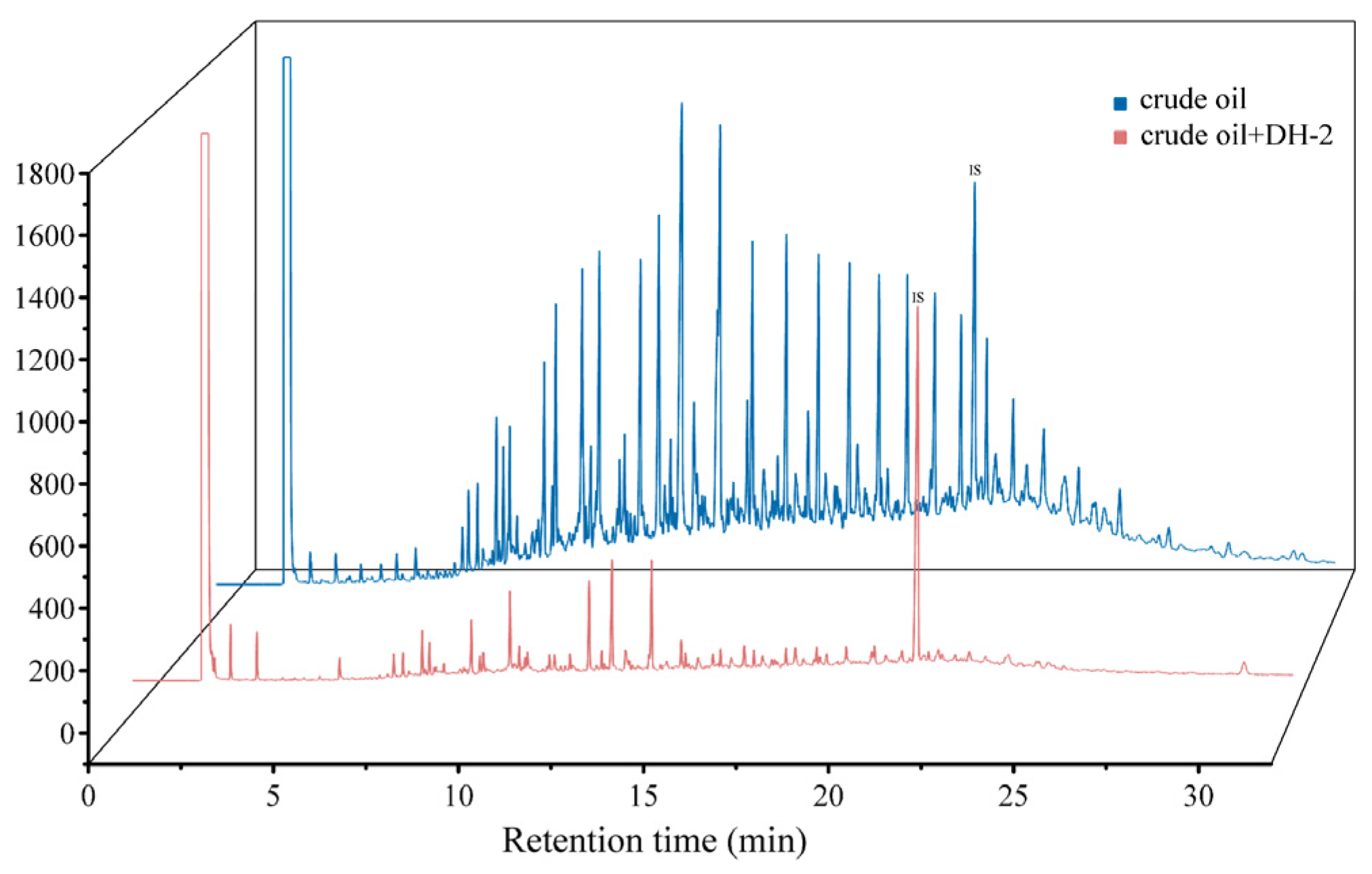
3.2.1. Degradation of Crude Oil by Strain DH-2
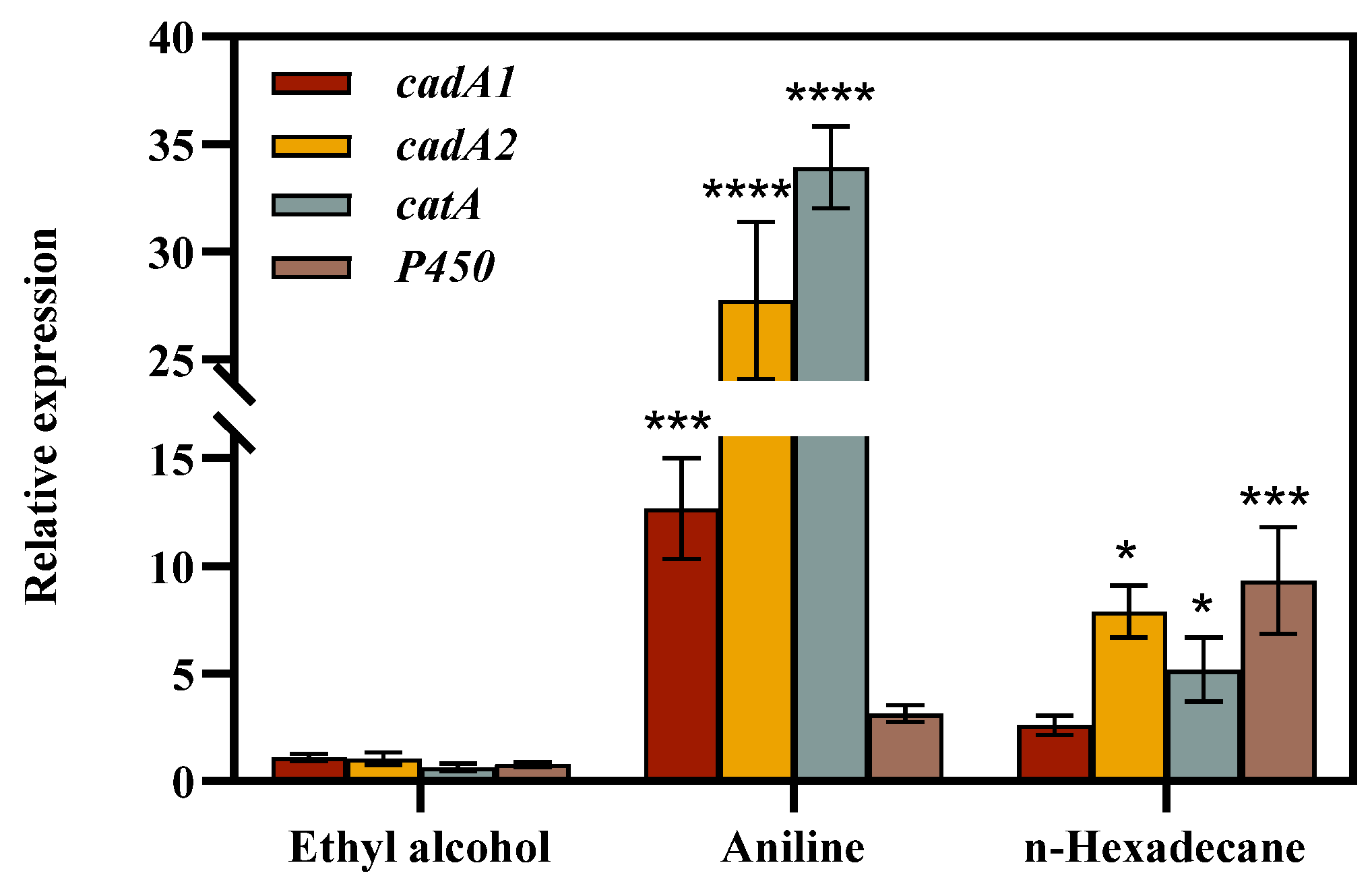
3.2.2. Fluorescence Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
3.3. Remediation of Aniline–Crude Oil–Heavy Metal Triple Contaminated Soil by DH-2
3.3.1. The Impact of Heavy Metals on the Growth of DH-2
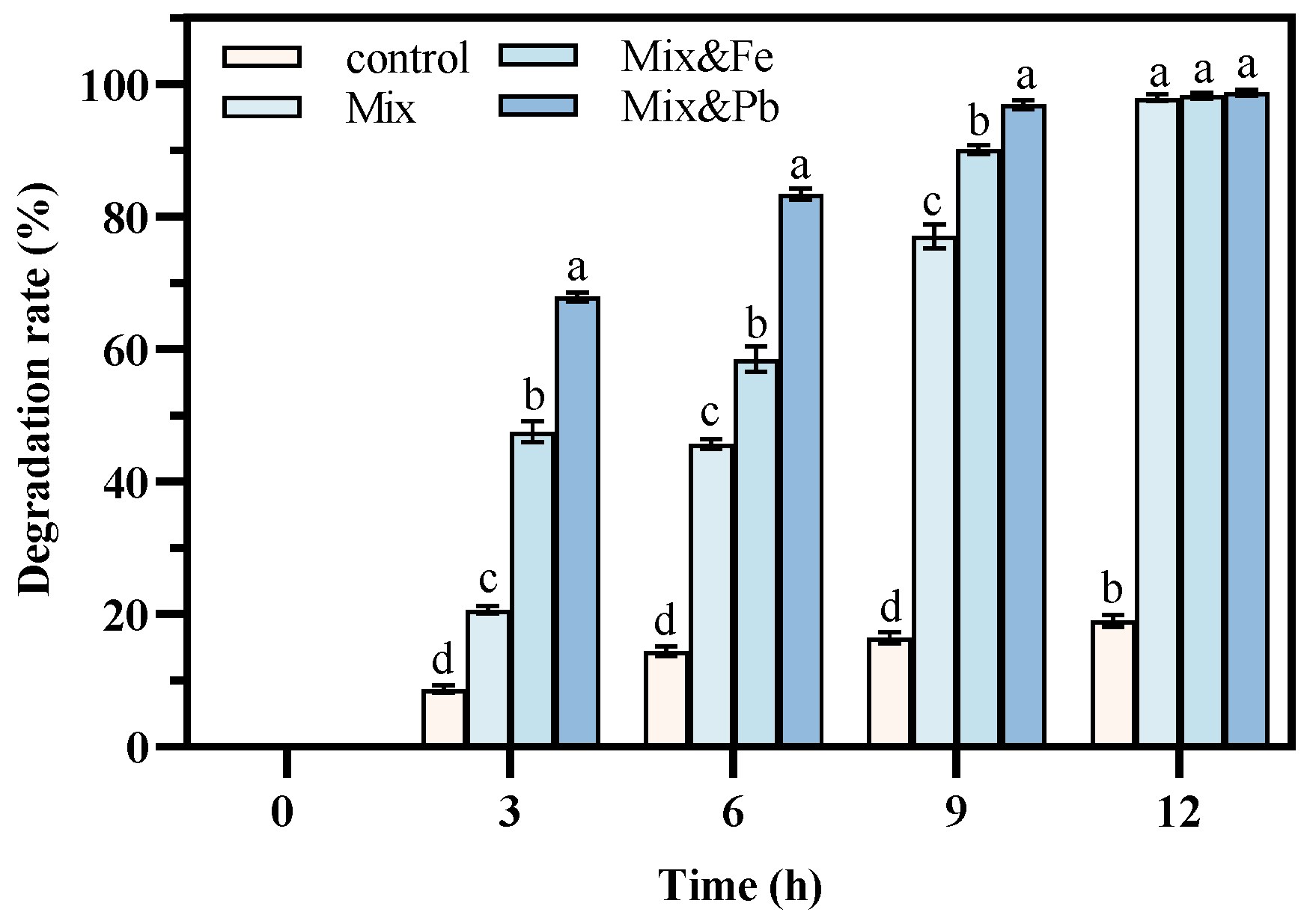
3.3.2. Soil Modelling Experiments for the Treatment of Dual Aniline and Crude Oil Contamination in the Presence of Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
4.1. A High-Effective Crude Oil and Aniline Degrading Strain Was Isolated and Identified
4.2. Degradation Genes and Enzymes of Crude Oil and Aniline Were Explored and Verified
4.3. Analysis of the Degradation of Triple Contamination of Aniline, Crude Oil and Heavy Metals in Soil
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Ye, S.; Liu, H. Degradation of Aniline and Antimony in Printing and Dyeing Wastewater by Micro-Oxygenated Hydrolytic Acidification and Their Removal Effects on Chemical Oxygen Demand and Ammonia Nitrogen. Water 2024, 16, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Sirés, I.; Scialdone, O. A critical review on latest innovations and future challenges of electrochemical technology for the abatement of organics in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 328, 122430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Hu, S.; Sun, R. Batch Adsorption and Column Leaching Studies of Aniline in Chinese Loess Under Different Hydrochemical Conditions. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, N.; Liu, G.; Bai, L.; Tang, L.; Guo, C. Genotoxicity and growth inhibition effects of aniline on wheat. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Ji, W.; Xu, N.; Gao, N.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H. Phase-selective gelators based on closed-chain glucose derivatives: Their applications in the removal of dissolved aniline/nitrobenzene, and toxic dyes from contaminated water. J. Mater. Chem. A. Mater. Energy Sustain. 2015, 3, 18953–18962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Y. Response of soil quality degradation to cultivation and soil erosion: A case study in a Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 242, 106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Duan, L.; Zheng, L.; Bahar, M.M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, W.; et al. Bacterial community profile of the crude oil-contaminated saline soil in the Yellow River Delta Natural Reserve, China. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, A.; Tanimu, G.; Ibrahim, I.; Garba, Z.N.; Yahaya, S.M.; Musa, S.G.; Merican, Z.M.A. Mitigating oil and gas pollutants for a sustainable environment—Critical review and prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 416, 137863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Shah, G.; Singhal, K.; Soni, V. Comprehensive insights into the impact of oil pollution on the environment. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 74, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, K.A.; Lewis, C.; Galloway, T.S. Current issues confounding the rapid toxicological assessment of oil spills. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, T.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Bioremediation of co-contaminated soil with heavy metals and pesticides: Influence factors, mechanisms and evaluation methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Wan, H.-F.; Song, Y.-T.; Jiang, H.; Peng, S.-L. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Agricultural Soils of the Southern Subtropics, China. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, R.; Barros, M.V. Pollution Prevention and Control Strategies, Implications, and Challenges. In Responsible Consumption and Production; Leal Filho, W., Azul, A.M., Brandli, L., Özuyar, P.G., Wall, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 552–561. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, M.; Fu, B.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, W.; Maroney, A.; Keller, A.A.; Wang, H.; Chovelon, J.M. Simultaneous removal of pharmaceuticals and heavy metals from aqueous phase via adsorptive strategy: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 236, 119924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Cui, X.; Xie, M.; Zhao, R.; Xu, L.; Ni, S.; Cui, Z. Amendments and bioaugmentation enhanced phytoremediation and micro-ecology for PAHs and heavy metals co-contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudur, L.S.; Gleeson, D.B.; Ryan, M.H.; Shahsavari, E.; Haleyur, N.; Nugegoda, D.; Ball, A.S. Implications of co-contamination with aged heavy metals and total petroleum hydrocarbons on natural attenuation and ecotoxicity in Australian soils. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Roy, K. Recent Advances on Modelling the Toxicity of Environmental Pollutants for Risk Assessment: From Single Pollutants to Mixtures. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauashdh, A.; Nagapan, S.; Jailani, J.; Gamil, Y. An integrated framework for sustainable and efficient building maintenance operations aligning with climate change, SDGs, and emerging technology. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Ning, X.; Li, Z. Research progress and hotspots on microbial remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil: A systematic review and future perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 118192–118212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ren, H.; Jin, Y.; Chai, Z.; Liu, B. The bioremediation of the typical persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by microalgae-bacteria consortia: A systematic review. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Quan, S.; Li, L.; Lei, G.; Li, S.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Yang, W. Endophytic Bacteria Improve Bio- and Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, H.; Padmesh, S.; Singh, A.; Nandy, A.; Singh, S.P.; Deshwal, R.K. Impact of veterinary pharmaceuticals on environment and their mitigation through microbial bioremediation. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1396116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Gadd, G.M. Fungal bioremediation of soil co-contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons and toxic metals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8999–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Thavamani, P.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Lee, Y.B.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Remediation approaches for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soils: Technological constraints, emerging trends and future directions. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 944–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ghani, M.U.; Sun, W.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Yan, G.; Yang, R.; Huang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Song, B. Identification of Aniline-Degrading Bacteria Using Stable Isotope Probing Technology and Prediction of Functional Genes in Aerobic Microcosms. Catalysts 2024, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Deng, W.; Lin, L.; Xu, M.; Jiang, J. Rapid screening of indigenous degrading microorganisms for enhancing in-situ bioremediation of organic pollutants-contaminated soil. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Yun, K.; Mun, S.; Chung, W.-H.; Choi, S.-Y.; Nam, Y.-D.; Lim, M.Y.; Hong, C.P.; Park, C.; Ahn, Y.J.; et al. The effect of taxonomic classification by full-length 16S rRNA sequencing with a synthetic long-read technology. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xie, J.; Shi, X.; Lian, J. Research on the Isolation, Identification and Degradation Characteristics of a Diesel Oil Degrading Strain. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 641–642, 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.-C.; Li, J.; Liang, F.-R.; Yi, M.; Xu, X.-M.; Yuan, J.-P.; Peng, J.; Wu, C.-F.; Wang, J.-H. Isolation and characterization of a novel hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Achromobacter sp. HZ01 from the crude oil-contaminated seawater at the Daya Bay, southern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvedte, E.S.; Michalski, J.; Cheng, S.; Patkus, R.S.; Tallon, L.J.; Sadzewicz, L.; Bruno, V.M.; Silva, J.C.; Rasko, D.A.; Dunning Hotopp, J.C. Evaluation of a high-throughput, cost-effective Illumina library preparation kit. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, N.; Blanco, C.; Chen, I.A.; Seelig, B. PacBio sequencing output increased through uniform and directional fivefold concatenation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Fan, Y.; Feng, J.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of cytochrome P450 gene family in Macrobrachium nipponense. Aquac. Fish. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-x.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Pang, W.-j.; Huang, J.-y.; Guo, P.; Huang, L. Biodegradation of Phenanthrene and Heavy Metal Removal by Acid-Tolerant Burkholderia fungorum FM-2. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, H. Retrospect and prospect of aerobic biodegradation of aniline: Overcome existing bottlenecks and follow future trends. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, E.; Sakai, M.; Hayashi, K.; Murakami, S.; Takenaka, S.; Aoki, K. Constitutive expression of catABC genes in the aniline-assimilating bacterium Rhodococcus species AN-22: Production, purification, characterization and gene analysis of CatA, CatB and CatC. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, F.; Jin, L.; Song, R.; Yang, F.; Ji, L.; Yu, H. In Silico simulation of Cytochrome P450-Mediated metabolism of aromatic amines: A case study of N-Hydroxylation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parades-Aguilar, J.; Calderon, K.; Agustin-Salazar, S.; Cerruti, P.; Ambrogi, V.; Gamez-Meza, N.; Medina-Juarez, L.A. Isolation and identification of metallotolerant bacteria with a potential biotechnological application. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medfu Tarekegn, M.; Zewdu Salilih, F.; Ishetu, A.I. Microbes used as a tool for bioremediation of heavy metal from the environment. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1783174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, M.; Fedi, S.; Zannoni, D. Degradation of Alkanes in Rhodococcus. In Biology of Rhodococcus; Alvarez, H.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 137–171. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; He, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, D.; Lu, W. n-Hexadecane and pyrene biodegradation and metabolization by Rhodococcus sp. T1 isolated from oil contaminated soil. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, M.; Sugiyama, K.; Sakurai, T.; Yamada, K.; Kimbara, K. Biodegradation of A-fuel oil in soil samples with bacterial mixtures of Rhodococcus and Gordonia strains under low temperature conditions. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hong Thi, P.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, J. Oil-degrading properties of a psychrotolerant bacterial strain, Rhodococcus sp. Y2-2, in liquid and soil media. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Wei, S.; Ke, T.; Wang, P.; Chen, L. Synchronous degradation of phenol and aniline by Rhodococcus sp.strain PB-1entrapped in sodium alginate-bamboo charcoal-chitosan beads. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 4405–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, X. The substrate specificity of aniline dioxygenase is mainly determined by two of its components: Glutamine synthetase-like enzyme and oxygenase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6333–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, J.B. Catechol dioxygenases. Essays Biochem. 1999, 34, 173–189. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Pantoja, D.; Donoso, R.; Agulló, L.; Córdova, M.; Seeger, M.; Pieper, D.H.; González, B. Genomic analysis of the potential for aromatic compounds biodegradation in Burkholderiales. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1091–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; Li, Z.; Pan, S.; Puyang, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ren, J.; et al. Review on remediation of organic-contaminated soil by discharge plasma: Plasma types, impact factors, plasma-assisted catalysis, and indexes for remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Q.; Wan, W. Numerical study of the longitudinally asymmetric distribution of solar energetic particles in the heliosphere. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2015, 218, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y. Comparative impact of cadmium on two phenanthrene-degrading bacteria isolated from cadmium and phenanthrene co-contaminated soil in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.W.; Toh, B.A.; Ting, Y.P.; Obbard, J.P. Biodegradation of phenanthrene by the indigenous microbial biomass in a zinc amended soil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 40, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aniline (mg/kg dry weight soil) | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Crude oil (g/kg dry weight soil) | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Fe(II) (mg/kg dry weight soil) | — | — | 20 | — |
| Pb(II) (mg/kg dry weight soil) | — | — | — | 20 |
| DH-2 (D)/abiotic (A) | A | D | D | D |
| Metal Ions | Metal Ion Concentration (mg/L) | MIC a (mg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| Zn(II) | ++++ | ++ | ++ | - | - | - | - | 15 |
| Cd(II) | ++++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | - | - | 20 |
| Fe(II) | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++++ | +++++ | ++++ | +++ | >30 |
| Pb(II) | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++ | >30 |
| Cu(II) | ++++ | - | - | - | - | - | - | — |
| Cr(III) | ++++ | ++ | ++ | + | - | - | - | 15 |
| Cr(VI) | ++++ | ++ | ++ | + | - | - | - | 15 |
| Ni(I) | ++++ | ++ | ++ | + | - | - | - | 15 |
| Mn(II) | ++++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | - | - | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Ma, J.; Huang, L.; Li, D.; Gao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Antunes, A.; Li, M. Biodegradation of Crude Oil and Aniline by Heavy Metal-Tolerant Strain Rhodococcus sp. DH-2. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112293
Luo Z, Ma J, Huang L, Li D, Gao G, Zhao Y, Antunes A, Li M. Biodegradation of Crude Oil and Aniline by Heavy Metal-Tolerant Strain Rhodococcus sp. DH-2. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(11):2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112293
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zetian, Jiajun Ma, Lei Huang, Dahui Li, Guohui Gao, Yihe Zhao, Agostinho Antunes, and Meitong Li. 2024. "Biodegradation of Crude Oil and Aniline by Heavy Metal-Tolerant Strain Rhodococcus sp. DH-2" Microorganisms 12, no. 11: 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112293
APA StyleLuo, Z., Ma, J., Huang, L., Li, D., Gao, G., Zhao, Y., Antunes, A., & Li, M. (2024). Biodegradation of Crude Oil and Aniline by Heavy Metal-Tolerant Strain Rhodococcus sp. DH-2. Microorganisms, 12(11), 2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112293







