Associations of Infant Feeding, Sleep, and Weight Gain with the Toddler Gut Microbiome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Feeding Practices
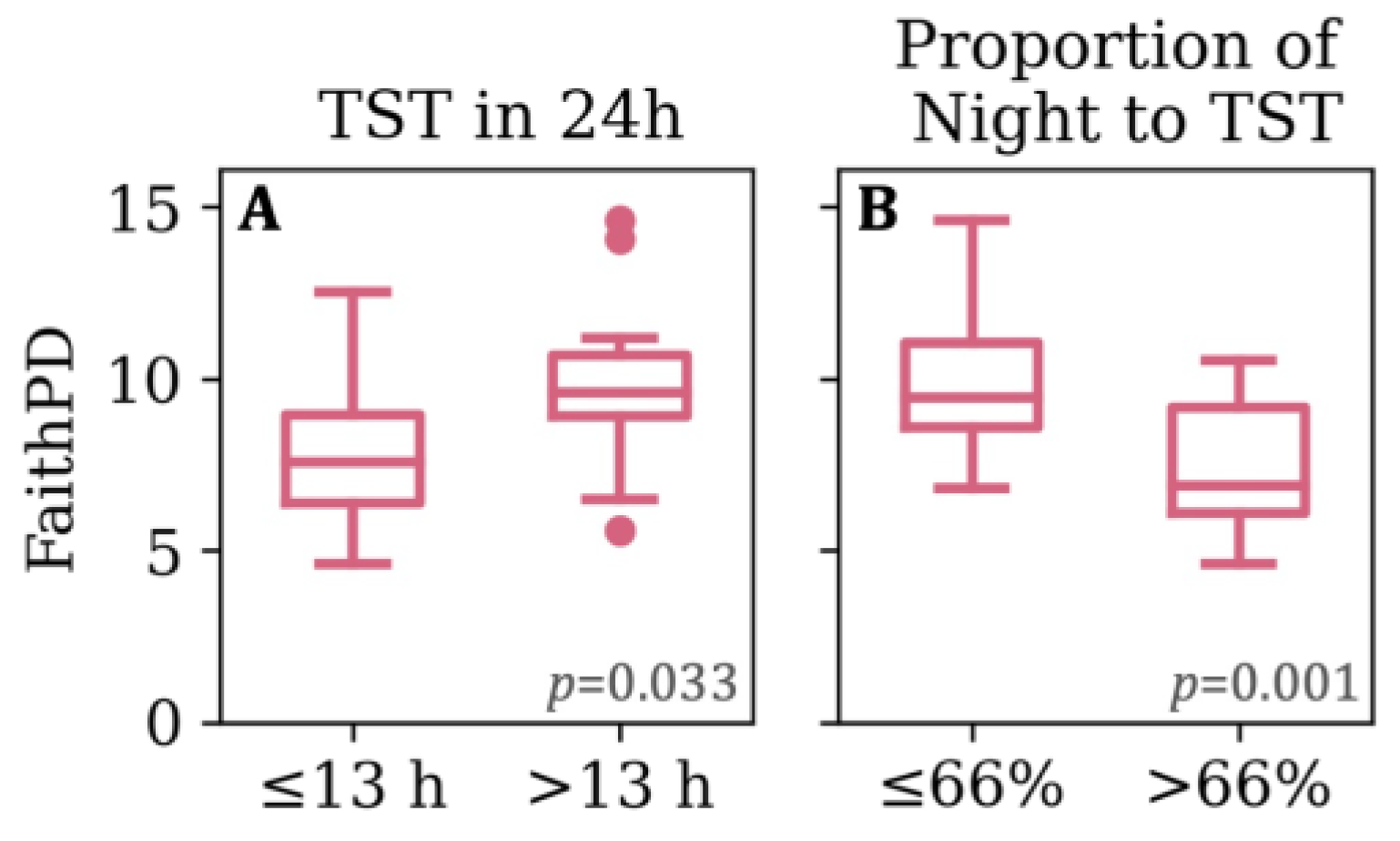
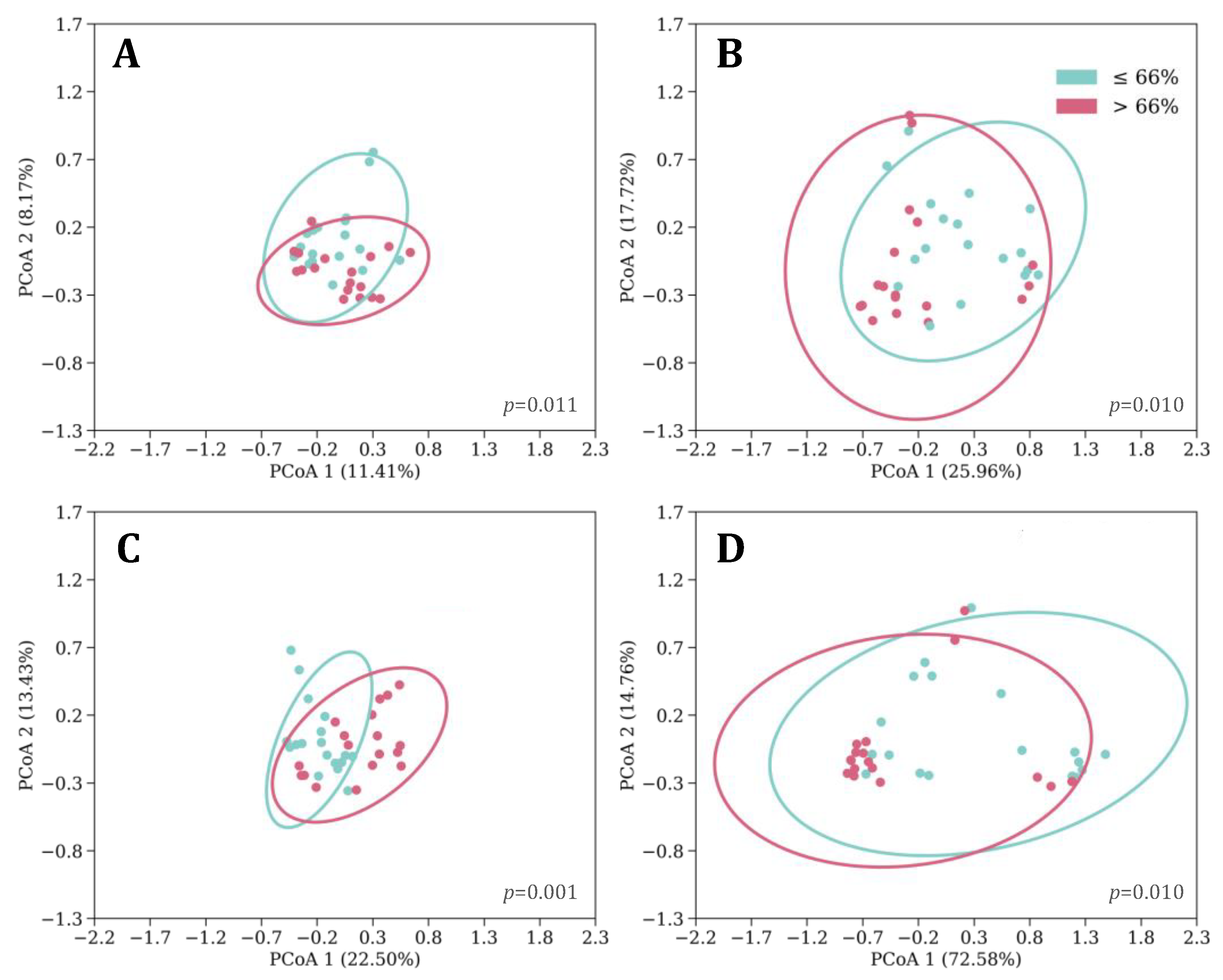
3.2. Sleeping Patterns
3.3. Rapid Weight Gain (RWG)
3.4. Feeding, Sleep, and Growth as Predictors of Phylogenetic Diversity
3.5. Microbial Taxa Differentiated by Feeding, Sleep, and Growth Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, R.; Caprio, S. The metabolic consequences of childhood obesity. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 19, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittner, L.S.; Ludington-Hoe, S.M.; Haller, H.S. Infant Obesity and Severe Obesity Growth Patterns in the First Two Years of Life. Matern. Child Health J. 2014, 18, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.S. Do breast-feeding and delayed introduction of solid foods protect against subsequent obesity? J. Pediatr. 1981, 98, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Foskey, R.J.; Allen, K.J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Koplin, J.J.; Ponsonby, A.-L.; Lowe, A.J.; Matheson, M.C.; Tang, M.L.K.; Gurrin, L.; et al. The Impact of Timing of Introduction of Solids on Infant Body Mass Index. J. Pediatr. 2016, 179, 104–110.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, E.; Schneider, N.; Broekman, B. Infant sleep and its relation with cognition and growth: A narrative review. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 9, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Kruisbrink, M.; Wallace, J.; Ji, C.; Cappuccio, F.P. Sleep duration and incidence of obesity in infants, children, and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sleep 2018, 41, zsy018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, M.E.; Whisner, C.M.; McCormick, D.; Todd, M.; Reyna, L.; Reifsnider, E. Sleep-Wake patterns in newborns are associated with infant rapid weight gain and incident adiposity in toddlerhood. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, I.M.; Savage, J.S.; Anzman-Frasca, S.; Marini, M.E.; Beiler, J.S.; Hess, L.B.; Loken, E.; Birch, L.L. Effect of a Responsive Parenting Educational Intervention on Childhood Weight Outcomes at 3 Years of Age: The INSIGHT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landhuis, C.E.; Poulton, R.; Welch, D.; Hancox, R.J. Childhood Sleep Time and Long-Term Risk for Obesity: A 32-Year Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzon, A.D.; Patton, S.R.; Koren, D. Childhood diabetes and sleep. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 1835–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, M.F. Gut Microbiota Development: Influence of Diet from Infancy to Toddlerhood. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 77, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ximenez, C.; Torres, J. Development of Microbiota in Infants and its Role in Maturation of Gut Mucosa and Immune System. Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekaboruah, E.; Suryavanshi, M.V.; Chettri, D.; Verma, A.K. Human microbiome: An academic update on human body site specific surveillance and its possible role. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2147–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuriel-Ohayon, M.; Neuman, H.; Koren, O. Microbial Changes during Pregnancy, Birth, and Infancy. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhy, F.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C.; Cotter, P.D. Composition of the early intestinal microbiota: Knowledge, knowledge gaps and the use of high-throughput sequencing to address these gaps. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Knight, R.; Blaser, M.J. Role of the microbiome in human development. Gut 2019, 68, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.C.; Castagna, V.P.; Sela, D.A.; Hillard, M.A.; Lindberg, S.; Mantis, N.J.; Seppo, A.E.; Järvinen, K.M. Gut microbiome and breast-feeding: Implications for early immune development. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Skov, T.H.; Bahl, M.I.; Roager, H.M.; Christensen, L.B.; Ejlerskov, K.T.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Licht, T.R. Establishment of Intestinal Microbiota during Early Life: A Longitudinal, Explorative Study of a Large Cohort of Danish Infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; Bailey, M.; Kamp Dush, C.; Schoppe-Sullivan, S.; Christian, L.M. Maternal Obesity Is Associated with Alterations in the Gut Microbiome in Toddlers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, H.; Zhuo, N.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, D. Comparison of gut microbiota in exclusively breast-fed and formula-fed babies: A study of 91 term infants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, C.C.; Tavalire, H.F.; Neiderhiser, J.M.; Bohannan, B.; Leve, L.D. History of breastfeeding but not mode of delivery shapes the gut microbiome in childhood. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M. Formula Supplementation of the Breastfed Infant: Assault on the Gut Microbiome. Clin. Lact. 2014, 5, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkar, S.; Kalsbeek, A.; Cheeseman, J. Potential Role for the Gut Microbiota in Modulating Host Circadian Rhythms and Metabolic Health. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.P.; Easson, C.; Lyle, S.M.; Kapoor, R.; Donnelly, C.P.; Davidson, E.J.; Parikh, E.; Lopez, J.V.; Tartar, J.L. Gut microbiome diversity is associated with sleep physiology in humans. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosicki, G.J.; Riemann, B.L.; Flatt, A.A.; Valentino, T.; Lustgarten, M.S. Self-reported sleep quality is associated with gut microbiome composition in young, healthy individuals: A pilot study. Sleep Med. 2020, 73, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, S.F.; Castro-Mejía, J.L.; Krych, L.; Leng, B.; Kot, W.; Kohler, M.; Huber, R.; Rogler, G.; Biedermann, L.; Walser, J.C.; et al. From Alpha Diversity to Zzz: Interactions among sleep, the brain, and gut microbiota in the first year of life. Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 209, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifsnider, E.; McCormick, D.P.; Cullen, K.W.; Todd, M.; Moramarco, M.W.; Gallagher, M.R.; Reyna, L. Randomized Controlled Trial to Prevent Infant Overweight in a High-Risk Population. Acad. Pediatr. 2018, 18, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, D.; Olveda, R.; Medrano, R.; Wojcicki, J.M. Excess pregnancy weight gain in latinas: Impact on infant’s adiposity and growth hormones at birth. Prev. Med. Rep. 2021, 22, 101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilley, S.P.; Harrall, K.K.; Friedman, C.; Glueck, D.H.; Cohen, C.C.; Perng, W.; Sauder, K.A.; Krebs, N.F.; Shankar, K.; Dabelea, D. Association of Maternal BMI and Rapid Infant Weight Gain With Childhood Body Size and Composition. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022059244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, F.J.; Lord, C.; Keating, D.P. Psychological Development in Infancy; Applied Developmental Psychology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 39–76. ISBN 978-0-12-041203-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeh, A.; Acebo, C.; Seifer, R.; Aytur, S.; Carskadon, M.A. Activity-based assessment of sleep-wake patterns during the 1st year of life. Infant Behav. Dev. 1995, 18, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindell, J.A.; Meltzer, L.J.; Carskadon, M.A.; Chervin, R.D. Developmental aspects of sleep hygiene: Findings from the 2004 National Sleep Foundation Sleep in America Poll. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihrshahi, S.; Battistutta, D.; Magarey, A.; Daniels, L.A. Determinants of rapid weight gain during infancy: Baseline results from the NOURISH randomised controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. 2011, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, J.Y.; Noble, L. Section on Breastfeeding Policy Statement: Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesbroek, G.; Bosch, A.A.T.M.; Wang, X.; Keijser, B.J.F.; Veenhoven, R.H.; Sanders, E.A.M.; Bogaert, D. The Impact of Breastfeeding on Nasopharyngeal Microbial Communities in Infants. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.C.; Healey, G.R.; Kelly, W.J.; Patchett, M.L.; Jordens, Z.; Tannock, G.W.; Sims, I.M.; Bell, T.J.; Hedderley, D.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Genomic insights from Monoglobus pectinilyticus: A pectin-degrading specialist bacterium in the human colon. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1437–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B.; Aggett, P.J.; Bindels, J.G.; Bung, P.; Ferré, P.; Gil, A.; Lentze, M.J.; Roberfroid, M.; Strobel, S. Growth, development and differentiation: A functional food science approach. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80, S5–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn-Holbrook, J.; Saxbe, D.; Bixby, C.; Steele, C.; Glynn, L. Human milk as “chrononutrition”: Implications for child health and development. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, M.; Le Huërou-Luron, I.; Blat, S. Effects of infant formula composition on long-term metabolic health. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2018, 9, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, S.; Chung, C.; Wang, D.; Sakwinska, O.; Colombo Mottaz, S.; Sprenger, N. Nurturing the Early Life Gut Microbiome and Immune Maturation for Long Term Health. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, R.Y.; Carlin, R.F.; Hand, I. The Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome and The Committee on Fetus and Newborn Sleep-Related Infant Deaths: Updated 2022 Recommendations for Reducing Infant Deaths in the Sleep Environment. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, E.; Adlerberth, I.; Hesselmar, B.; Saalman, R.; Strannegård, I.-L.; Åberg, N.; Wold, A.E. High Rate of Transfer of Staphylococcus aureus from Parental Skin to Infant Gut Flora. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, Z.-Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Mao, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, Z.; et al. Acute Sleep-Wake Cycle Shift Results in Community Alteration of Human Gut Microbiome. mSphere 2020, 5, e00914-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, N.; Choo-Kang, C.; Reutrakul, S.; Crowley, S.J.; Rae, D.; Bedu-Addo, K.; Plange-Rhule, J.; Forrester, T.E.; Lambert, E.V.; Bovet, P.; et al. Gut microbiota alterations in response to sleep length among African-origin adults. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lee, Y.-K.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Roles of intestinal bacteroides in human health and diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3518–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.-N.; Liu, X.-T.; Liang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-H. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar, M.; Escribano, J.; Ferré, N.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Selma-Royo, M.; Feliu, A.; Castillejo, G.; Luque, V.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Escribano, J.; et al. Gut microbiota is associated with metabolic health in children with obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, F. Infections Caused by Anaerobic Microorganisms. In Encyclopedia of Infection and Immunity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 614–627. ISBN 978-0-323-90303-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zsálig, D.; Berta, A.; Tóth, V.; Szabó, Z.; Simon, K.; Figler, M.; Pusztafalvi, H.; Polyák, É. A Review of the Relationship between Gut Microbiome and Obesity. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotz, C.; Brown, S.; Zarrinpar, A. Gut Microbiota and Their Influence on Response to Food. In Principles of Nutrigenetics and Nutrigenomics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 411–419. ISBN 978-0-12-804572-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rotevatn, T.A.; Overgaard, C.; Melendez-Torres, G.J.; Mortensen, R.N.; Ullits, L.R.; Høstgaard, A.M.B.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Bøggild, H. Infancy weight gain, parental socioeconomic position, and childhood overweight and obesity: A Danish register-based cohort study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindell, J.A.; Leichman, E.S.; Composto, J.; Lee, C.; Bhullar, B.; Walters, R.M. Development of infant and toddler sleep patterns: Real-world data from a mobile application. J. Sleep Res. 2016, 25, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | n = 126 Cohort | n = 36 Subsample | Significance (p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infant sex; female, n (%) a | 55 (43.7) | 16 (44.4) | 0.92 |
| Birth mode, n (%) a | 0.48 | ||
| 69 (54.8) | 18 (50.0) | |
| 48 (38.1) | 15 (41.7) | |
| 9 (7.1) | 3 (8.3) | |
| Infant birth weight-for-age Z score, M (SD) b | 0.42 (0.9) | 0.41 (1.0) | 0.95 |
| Rapid weight gain d at 6 months, n (%) a | 45 (35.7) | 11 (30.6) | 0.50 |
| Maternal education, n (%) a | 0.56 | ||
| 64 (50.8) | 21 (58.3) | |
| 58 (46.0) | 14 (38.9) | |
| 4 (3.2) | 1 (2.8) | |
| Maternal parity, n (%) a | 0.17 | ||
| 32 (25.4) | 5 (13.9) | |
| 35 (27.8) | 9 (25.0) | |
| 27 (21.4) | 9 (25.0) | |
| 32 (25.5) | 13 (36.1) | |
| Maternal prenatal BMI (kg/m2), M (SD) b | 35.9 (5.2) | 36.6 (6.0) | 0.36 |
| Gestational weight gain (lb), M (SD) c | 25.3 (11.2) | 25.0 (13.9) | 0.86 |
| Breastfeeding duration by 12-month follow-up (months), M (SD) c | 4.4 (4.7) | 5.1 (5.0) | 0.38 |
| Exclusive breastfeeding duration (months), M (SD) c | 2.3 (4.1) | 3.3 (4.5) | 0.48 |
| Age of introduction to solids (months), M (SD) c | 4.9 (1.1) | 4.7 (1.0) | 0.08 |
| Variable | Month | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 12 | |
| Any breastfeeding, n (%) | |||
| 25 (69.4) | 15 (41.7) | 8 (22.2) |
| 11 (30.6) | 21 (58.3) | 28 (77.8) |
| Milk exclusivity, n (%) | |||
| 16 (44.4) | 10 (27.8) | 2 (5.6) |
| 20 (55.6) | 26 (72.2) | 34 (94.4) |
| Started solids before time point, n (%) | |||
| 0 (0.0) | 31 (86.1) | 36 (100.0) |
| 36 (100.0) | 5 (13.9) | 0 (0.0) |
| Variable | Month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 12 | ||||
| M (SD) [Range] | DV (n) | M (SD) [Range] | DV (n) | M (SD) [Range] | DV (n) | |
| Bed-sharing, n (%) | 8 (22.0) | Yes (8) No (27) | ||||
| Bedtime (hh:mm) a | 21:45 (0:59) [20:00, 23:00] | <21:00 (7) ≥21:00 (28) | 21:37 (0:53) [20:00, 00:00] | <21:00 (4) ≥21:00 (32) | 21:45 (0:57) [19:00, 00:30] | <21:00 (4) ≥21:00 (32) |
| Number of wakes | 2.8 (1.4) [0, 8] | ≤3 (27) >3 (8) | 1.1 (1.0) [0, 3] | ≤1 (21) >1 (15) | 1.1 (1.0) [0, 3] | ≤1 (25) >1 (11) |
| Longest nocturnal sleep bout (h) | 4.9 (1.9) [3, 10] | ≤4 (22) >4 (13) | 7.2 (2.0) [4, 11] | ≤7 (19) >7 (17) | 8.6 (2.3) [4, 12] | ≤9 (21) >9 (15) |
| Nocturnal Sleep (h) | 9.7 (1.3) [7, 12] | ≤10 (27) >10 (8) | 8.9 (1.5) [6, 11] | ≤9 (19) >9 (17) | 9.8 (0.9) [8, 12] | ≤10 (30) >10 (6) |
| Nap frequency | 4.0 (1.3) [1, 8] | ≤4 (27) >4 (8) | 2.9 (0.9) [2, 5] | ≤3 (25) >3 (11) | 2.0 (0.9) [1, 4] | ≤2 (27) >2 (9) |
| Daytime Sleep (h) | 7.8 (1.1) [5.0, 9.0] | ≤8 (26) >8 (9) | 4.6 (2.0) [0.5, 8.0] | ≤5 (25) >5 (11) | 2.9 (1.5) [0.5, 6.0] | ≤3 (22) >3 (14) |
| 24hTST | 17.5 (1.9) [13, 21] | ≤18 (25) >18 (10) | 13.6 (2.1) [8.7, 19.0] | ≤13 (20) >13 (16) | 12.8 (1.7) [9, 16] | ≤13 (22) >13 (14) |
| Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 0.6 (0.0) [0.5, 0.7] | ≤0.56 (24) >0.56 (11) | 0.7 (0.1) [0.5, 1.0] | ≤0.66 (18) >0.66 (18) | 0.8 (0.1) [0.6, 1.0] | ≤0.77 (20) >0.77 (16) |
| Model | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rsquare Adj | 20.9 | |
| F Ratio (df) a | 5.62 (2, 33) | |
| p-value | 0.008 | |
| Parameter (SE) | p-value | |
| Intercept | 14.18 (1.99) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Night to 24hTST at 6 months | −8.07 (2.94) | 0.010 |
| ΔWeight-for-age z-scores from birth to 6 months | −0.87 (0.44) | 0.056 |
| Family | Genus | Feeding or Sleep Variable | Association | Age of Infant When Assessed | LDA Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinomycetaceae | Varibaculum | Proportion of Night to 24hTST a | 66% or less | 6 | 3.585 | 0.037 |
| Akkermansiaceae | Akkermansia | 24hTST | 13 h or less | 6 | 4.255 | 0.046 |
| Bacillaceae | Bacillus | Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.367 | 0.007 |
| Bacteroidaceae | Bacteroides | Daytime Sleep | 5 h or less | 6 | 4.802 | 0.027 |
| Proportion of Night to 24hTST | More than 66% | 6 | 4.911 | 0.002 | ||
| Bifidobacteriaceae | Bifidobacterium | Bedtime | 21:00 and after | 12 | 4.156 | 0.037 |
| 24hTST | 13 h or less | 6 | 4.175 | 0.032 | ||
| Gardnerella | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.132 | 0.005 | |
| Campylobacteraceae | Campylobacter | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.246 | 0.018 |
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.183 | 0.011 | ||
| Christensenellaceae | Christensenellaceae_R_7_group | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.232 | 0.021 |
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.190 | 0.034 | ||
| Clostridia_UCG_014 | Clostridia_UCG_014 | Bed-sharing | Bed-sharing | 1 | 3.844 | 0.027 |
| Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.989 | 0.011 | ||
| Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.567 | 0.035 | ||
| Clostridia_vadinBB60_group | Clostridia_vadinBB60_group | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.120 | 0.005 |
| Enterobacteriaceae | Escherichia_Shigella | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | More than 56% | 1 | 4.761 | 0.043 |
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 4.662 | 0.004 | ||
| Enterococcaceae | Enterococcus | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.204 | 0.016 |
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.263 | 0.027 | ||
| Erysipelotrichaceae | Holdemanella | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.416 | 0.007 |
| Solobacterium | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.660 | 0.037 | |
| Gastranaerophilales | Gastranaerophilales | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.732 | 0.000 |
| Hafniaceae | Hafnia_Obesumbacterium | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.152 | 0.005 |
| Listeriaceae | Listeria | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.159 | 0.005 |
| Methanobacteriaceae | Methanobrevibacter | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.233 | 0.005 |
| Micrococcaceae | Rothia | Any breastfeeding | No | 1 | 3.949 | 0.034 |
| Monoglobaceae | Monoglobus | Age of Starting Solids | Before 6 months | 6 | 3.421 | 0.026 |
| Muribaculaceae | Muribaculaceae | 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.004 | 0.046 |
| Oscillospiraceae | UCG_002 | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 4.050 | 0.038 |
| UCG_005 | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.135 | 0.014 | |
| Porphyromonadaceae | Porphyromonas | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.234 | 0.001 |
| 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.047 | 0.011 | ||
| Prevotellaceae | Alloprevotella | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 4.005 | 0.002 |
| Prevotella | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 4.971 | 0.027 | |
| Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 4.697 | 0.002 | ||
| Prevotellaceae_UCG_003 | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.353 | 0.005 | |
| Pseudoalteromonadaceae | Pseudoalteromonas | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.243 | 0.005 |
| RF39 | RF39 | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 56% or less | 1 | 3.473 | 0.014 |
| Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.345 | 0.022 | ||
| 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.232 | 0.037 | ||
| Sutterellaceae | Sutterella | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 56% or less | 1 | 3.792 | 0.015 |
| Tissierellales | Anaerococcus | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.345 | 0.008 |
| 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.313 | 0.002 | ||
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.474 | 0.000 | ||
| Ezakiella | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.174 | 0.008 | |
| 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.299 | 0.029 | ||
| Fenollaria | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 3.428 | 0.033 | |
| 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.287 | 0.021 | ||
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.484 | 0.002 | ||
| Finegoldia | 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.158 | 0.046 | |
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.224 | 0.007 | ||
| Gallicola | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 4.286 | 0.018 | |
| 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.738 | 0.008 | ||
| Murdochiella | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | 66% or less | 6 | 4.079 | 0.037 | |
| 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.436 | 0.020 | ||
| Peptoniphilus | 24hTST | More than 13 h | 6 | 3.365 | 0.042 | |
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.514 | 0.001 | ||
| Veillonellaceae | Dialister | Proportion of Night to 24hTST | More than 56% | 1 | 3.348 | 0.032 |
| Daytime Sleep | More than 5 h | 6 | 3.921 | 0.007 | ||
| Victivallaceae | Victivallis | Bedtime | Before 21:00 | 12 | 3.012 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olson, M.; Toffoli, S.; Vander Wyst, K.B.; Zhou, F.; Reifsnider, E.; Petrov, M.E.; Whisner, C.M. Associations of Infant Feeding, Sleep, and Weight Gain with the Toddler Gut Microbiome. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030549
Olson M, Toffoli S, Vander Wyst KB, Zhou F, Reifsnider E, Petrov ME, Whisner CM. Associations of Infant Feeding, Sleep, and Weight Gain with the Toddler Gut Microbiome. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(3):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030549
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlson, Magdalena, Samantha Toffoli, Kiley B. Vander Wyst, Fang Zhou, Elizabeth Reifsnider, Megan E. Petrov, and Corrie M. Whisner. 2024. "Associations of Infant Feeding, Sleep, and Weight Gain with the Toddler Gut Microbiome" Microorganisms 12, no. 3: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030549
APA StyleOlson, M., Toffoli, S., Vander Wyst, K. B., Zhou, F., Reifsnider, E., Petrov, M. E., & Whisner, C. M. (2024). Associations of Infant Feeding, Sleep, and Weight Gain with the Toddler Gut Microbiome. Microorganisms, 12(3), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030549






