Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Staphylococcus Bacteria as a Biocontrol Agent against Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks: Assessing Reproductive Inhibition and Mortality Rates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Bacterial Strains
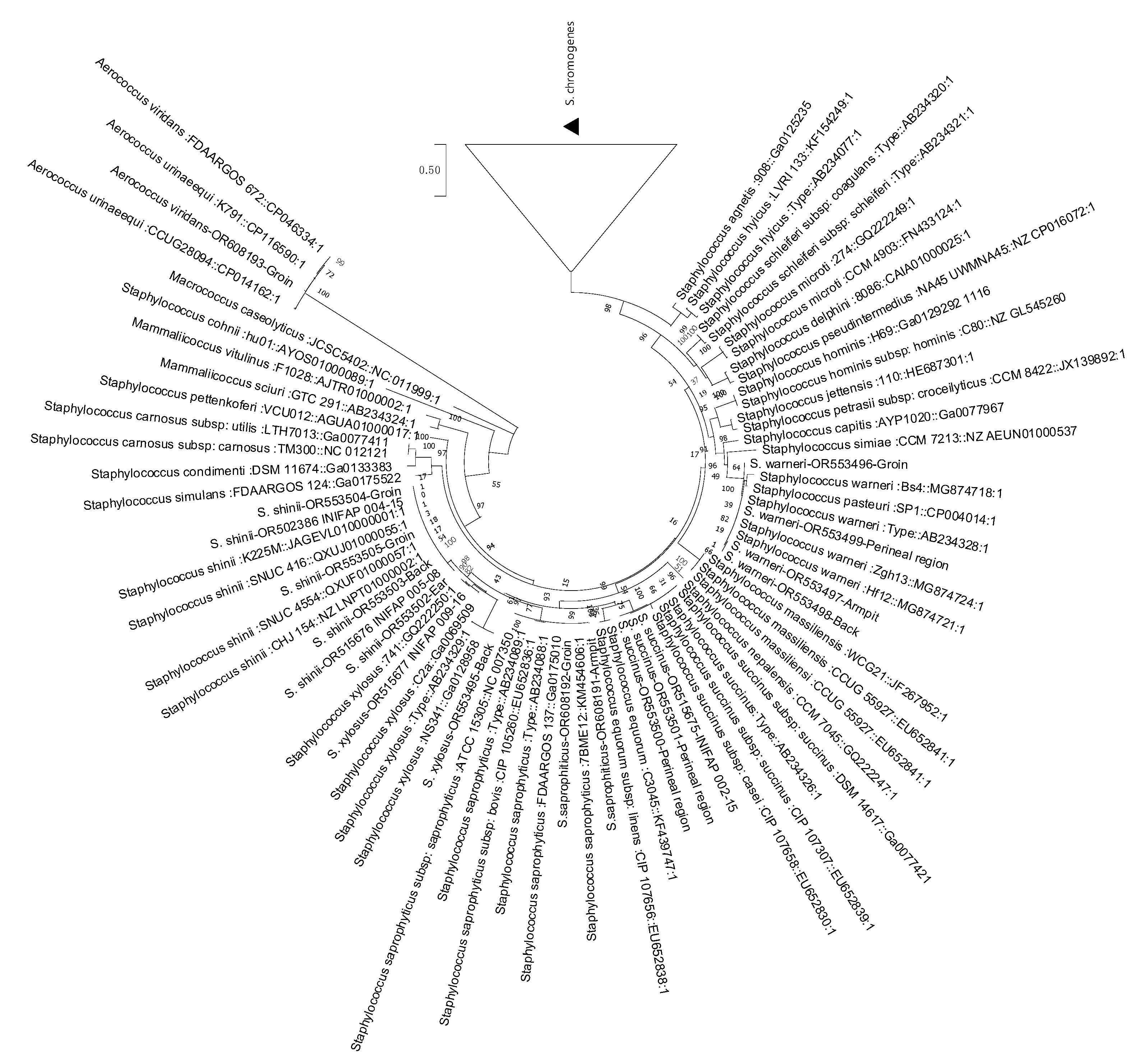
2.3. Average Nucleotide Identity Comparison
2.4. Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks for Bioassays
2.5. Modified Adult Immersion Test (AIT)
2.6. Larval Package Test (LPT)
2.7. Description of Signs of Infection
2.8. Isolation of Staphylococcus Bacteria from Bovine Skin
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Comparison of Average Nucleotide Identity
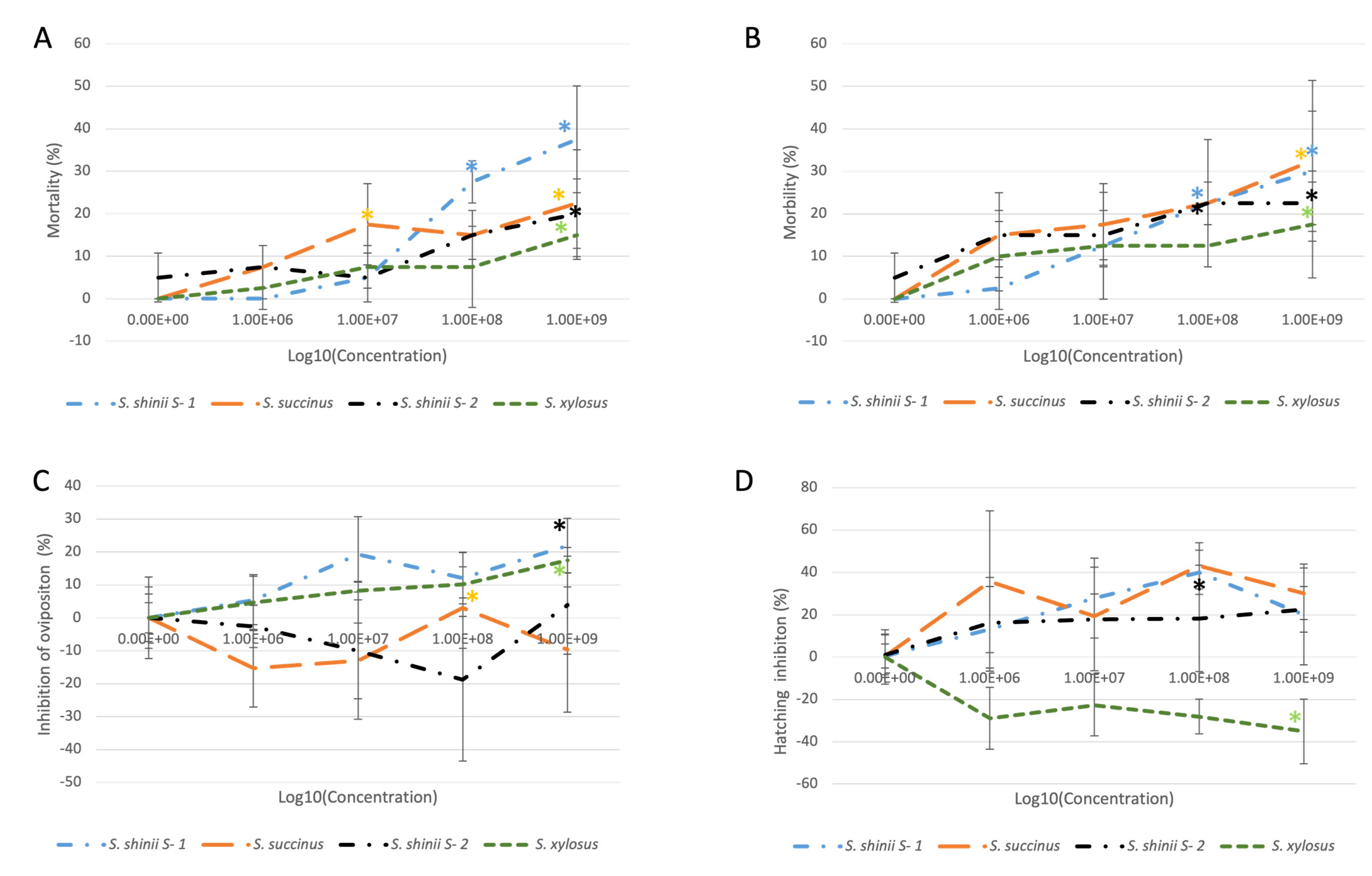
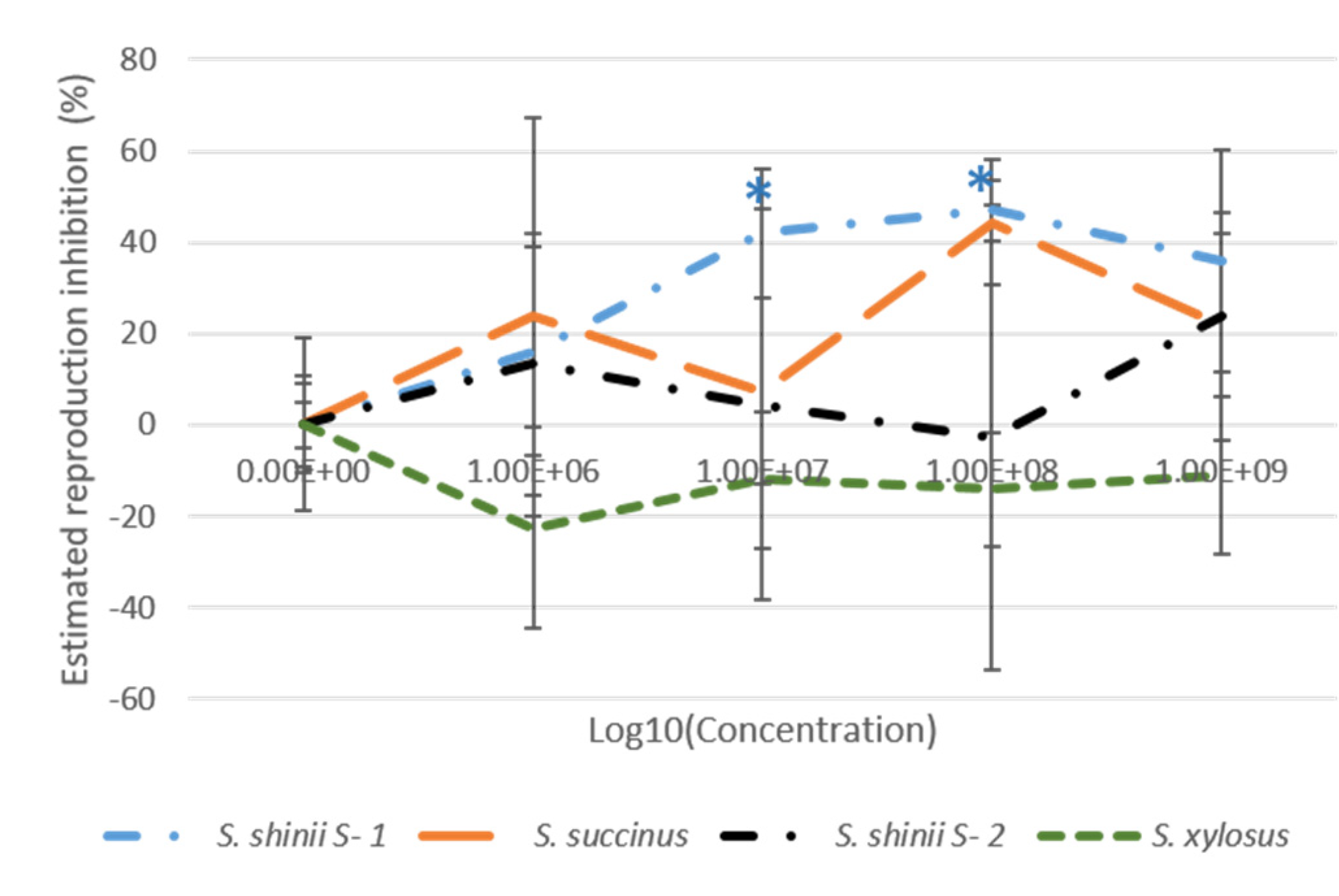
3.2. Adult Immersion Test (AIT)
3.3. Larval Package Test (LPT)
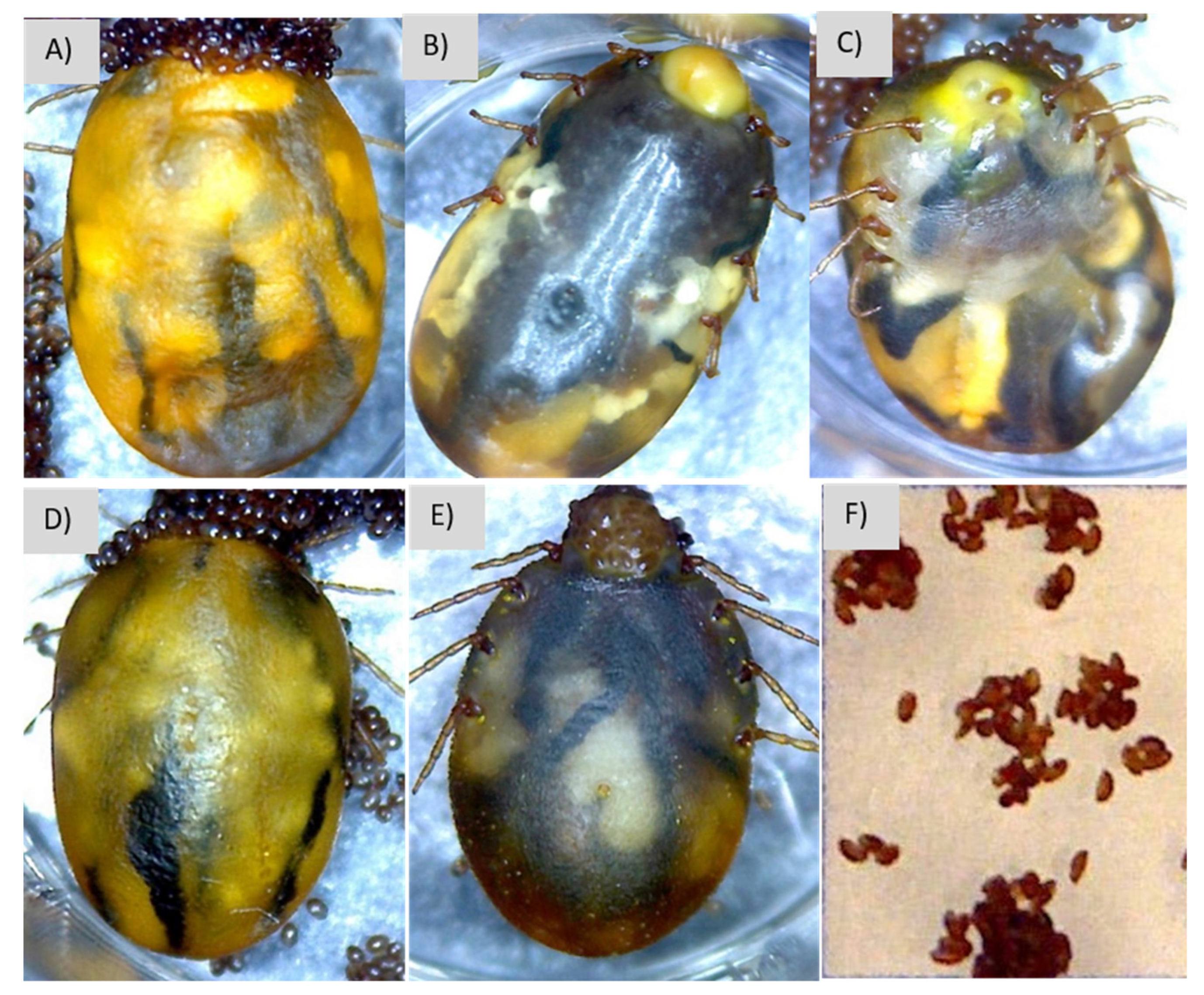
3.4. Description of Signs of Infection
3.5. Isolation of Staphylococcus Bacteria on Bovine Skin
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Vivas, R.I.; Jonsson, N.N.; Bhushan, C. Strategies for the Control of Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks in a World of Conventional Acaricide and Macrocyclic Lactone Resistance. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossio-Bayugar, R.; Miranda-Miranda, E.; Aguilar Díaz, H.; Reynaud, E. Types of Acaricide Resistance. In The Entomological Guide to Rhipicephalus; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 147–175. ISBN 978-1-5361-9619-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lew-Tabor, A.E.; Rodriguez Valle, M. A Review of Reverse Vaccinology Approaches for the Development of Vaccines against Ticks and Tick Borne Diseases. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Expert Consultation on the Sustainable Management of Parasites in Livestock Challenged by the Global Emergence of Resistance. In Proceedings of the Part 1: Current Status and Management of Acaricide Resistance in Livestock Ticks, Virtual Meeting, 9–10 November 2021; FAO Animal Production and Health Reports. FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. ISBN 978-92-5-137216-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cafarchia, C.; Pellegrino, R.; Romano, V.; Friuli, M.; Demitri, C.; Pombi, M.; Benelli, G.; Otranto, D. Delivery and Effectiveness of Entomopathogenic Fungi for Mosquito and Tick Control: Current Knowledge and Research Challenges. Acta Trop. 2022, 234, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Grzywacz, D.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Frutos, R.; Brownbridge, M.; Goettel, M.S. Insect Pathogens as Biological Control Agents: Back to the Future. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Chi, M.M.; Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I.; Galindo-Velasco, E.; Lezama-Gutiérrez, R.; Cruz-Vázquez, C. Control de Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) mediante el uso del hongo entomopatógeno Metarhizium anisopliae (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae): Revisión. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2011, 2, 177–192. [Google Scholar]
- Samish, M.; Ginsberg, H.; Glazer, I. Biological Control of Ticks. Parasitology 2004, 129, S389–S403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lormendez-Castillo, C.; Arreguín-Pérez, C.; Cossio-Bayugar, R.; Miranda-Miranda, E. Identification of Entomopathogenic Microorganisms to Rhipicephalus microplus. In A Laboratory Manual on Rhipicephalus microplus; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle, UK, 2023; pp. 233–263. ISBN 1-5275-0418-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ebani, V.V.; Mancianti, F. Entomopathogenic Fungi and Bacteria in a Veterinary Perspective. Biology 2021, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Azhahianambi, P.; de la Fuente, J. Control of Ticks of Ruminants, with Special Emphasis on Livestock Farming Systems in India: Present and Future Possibilities for Integrated Control—A Review. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 40, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, A.; Reck, J.; Santi, L.; Souza, U.A.; Dall’Agnol, B.; Klafke, G.M.; Beys-da-Silva, W.O.; Martins, J.R.; Schrank, A. Integrated Control of an Acaricide-Resistant Strain of the Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus microplus by Applying Metarhizium anisopliae Associated with Cypermethrin and Chlorpyriphos under Field Conditions. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Díaz, M.A.; Fernández-Salas, A. Entomopathogenic Fungi for Tick Control in Cattle Livestock From Mexico. Front. Fungal Biol. 2021, 2, 657694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez, A.B.; Segura, R.P.; Gómez-Vázquez, A. Control biológico de Rhicephalus (Boophilus) microplus con hongos entomopatógenos/Biological Control of Rhicephalus (Boophilus) microplus with Entomopathogenic Fungi. CIBA Rev. Iberoam. Cienc. Biol. Agropecu. 2017, 6, 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.F.; Parker, B.L.; Skinner, M. A Review of Commercial Metarhizium- and Beauveria-Based Biopesticides for the Biological Control of Ticks in the USA. Insects 2022, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ruvalcaba, M.; Peña-Chora, G.; Romo-Martínez, A.; Hernández-Velázquez, V.; de la Parra, A.B.; De La Rosa, D.P. Evaluation of Bacillus thuringiensis Pathogenicity for a Strain of the Tick, Rhipicephalus microplus, Resistant to Chemical Pesticides. J. Insect Sci. Online 2010, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lormendez, C.C.; Fernandez-Ruvalcaba, M.; Adames-Mancebo, M.; Hernandez-Velazquez, V.M.; Zuñiga-Navarrete, F.; Flores-Ramirez, G.; Lina-Garcia, L.; Peña-Chora, G. Mass Production of a S-Layer Protein of Bacillus thuringiensis and Its Toxicity to the Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus microplus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René-Martellet, M.; Minard, G.; Massot, R.; Tran Van, V.; Valiente Moro, C.; Chabanne, L.; Mavingui, P. Bacterial Microbiota Associated with Rhipicephalus sanguineus (s.l.) Ticks from France, Senegal and Arizona. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhav, M.; Baker, D.; Morgan, J.A.T.; Asgari, S.; James, P. Wolbachia: A Tool for Livestock Ectoparasite Control. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 288, 109297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Miranda, E.; Cossio-Bayugar, R.; Quezada-Delgado, M.D.R.; Sachman-Ruiz, B.; Reynaud, E. Staphylococcus saprophyticus Is a Pathogen of the Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graña-Miraglia, L.; Arreguín-Pérez, C.; López-Leal, G.; Muñoz, A.; Pérez-Oseguera, A.; Miranda-Miranda, E.; Cossío-Bayúgar, R.; Castillo-Ramírez, S. Phylogenomics Picks out the Par Excellence Markers for Species Phylogeny in the Genus Staphylococcus. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreguin-Perez, C.; Sachman-Ruiz, B.; Miranda-Miranda, E.; Aguilar Díaz, H.; Fernandez-Ruvalcaba, M.; Cossio-Bayugar, R. Caracterización de aislados bacterianos derivados de una infección natural de la garrapata del ganado Rhipicephalus microplus (ACARI: IXODIDAE) en el periodo 2010–2015. Entomol. Mex. 2016, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High Throughput ANI Analysis of 90K Prokaryotic Genomes Reveals Clear Species Boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Martinez-Ibañez, F.; Miranda-Miranda, E.; Jasso-Villazul, C.E.; Cossio-Bayugar, R. Chapter 9. Reference Tick Strains as an Important Biological Material for Acaricide-Resistance Characterization. In The Entomological Guide to Rhipicephalus; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 177–200. ISBN 978-1-5361-9635-1. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, R.O.; Ernst, S.E.; Trevino, J.L.; Gladney, W.J.; Graham, O.H. Boophilus annulatus and B. microplus: Laboratory Tests of Insecticides. J. Econ. Entomol. 1973, 66, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Acaricide Resistance: Diagnosis, Management and Prevention. Guidelines Resistance Management and Integrated Parasite Control in Ruminants; Animal Production and Health Division, Agriculture Department, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004; pp. 25–77. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Saines, E.; Hernández Ortiz, R.; Lagunes-Quintanilla, R. Chapter 4 Bioassays with Rhipicephalus microplus. In A Laboratory Manual on Rhipicephalus microplus; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2023; pp. 40–63. ISBN 1-5275-0418-2. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, B.F.; Haydock, K.P. A Method for Measuring the Acaricide-Susceptibility of the Cattle Tick Boophilus microplus (Can.). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1962, 53, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.M.; Iihara, H.; Noda, M.; Song, S.X.; Nhung, P.H.; Ohkusu, K.; Kawamura, Y.; Ezaki, T. dnaJ Gene Sequence-Based Assay for Species Identification and Phylogenetic Grouping in the Genus staphylococcus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.-S.; Li, B.; Brinks, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant, Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Fresh Produce and Description of Staphylococcus shinii sp. Nov. Isolated from Chives. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Göker, M. Validation List No. 210. Valid Publication of New Names and New Combinations Effectively Published Outside the IJSEM. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 005812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.A.; Schleifer, K.H.; Adegoke, G.O. Identification of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Farm Animals. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1985, 58, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayani, S.A.; Meraj, S.; Mohr, E.; Gries, R.; Kovacs, E.; Devireddy, A.; Gries, G. Staphylococcus Microbes in the Bovine Skin Microbiome Attract Blood-Feeding Stable Flies. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, A.; Dobson, S.J.; Yang, X.; Lacey, E.; Barker, S.C. A Survey of Bacterial Diversity in Ticks, Lice and Fleas from Australia. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 89, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, S.A.V.; Salamat, S.E.A.; Galay, R.L. Analysis of the Bacterial Community in Female Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks from Selected Provinces in Luzon, Philippines, Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 91, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraza-Guerrero, S.I.; Meza-Herrera, C.A.; García-De la Peña, C.; González-Álvarez, V.H.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Díaz-Velásquez, C.E.; Sánchez-Tortosa, F.; Ávila-Rodríguez, V.; Valenzuela-Núñez, L.M.; Herrera-Salazar, J.C. General Microbiota of the Soft Tick Ornithodoros turicata Parasitizing the Bolson Tortoise (Gopherus flavomarginatus) in the Mapimi Biosphere Reserve, Mexico. Biology 2020, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, B.P.; Rowe, S.E.; Gandt, A.B.; Nuxoll, A.S.; Donegan, N.P.; Zalis, E.A.; Clair, G.; Adkins, J.N.; Cheung, A.L.; Lewis, K. Persister Formation in Staphylococcus aureus Is Associated with ATP Depletion. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, A.H.F.M.; Vidotto, O. Distribuição anatômica e dinâmica populacional de Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus em bovinos do município de Óleo, São Paulo. Semina Ciênc. Agrár. 2018, 39, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
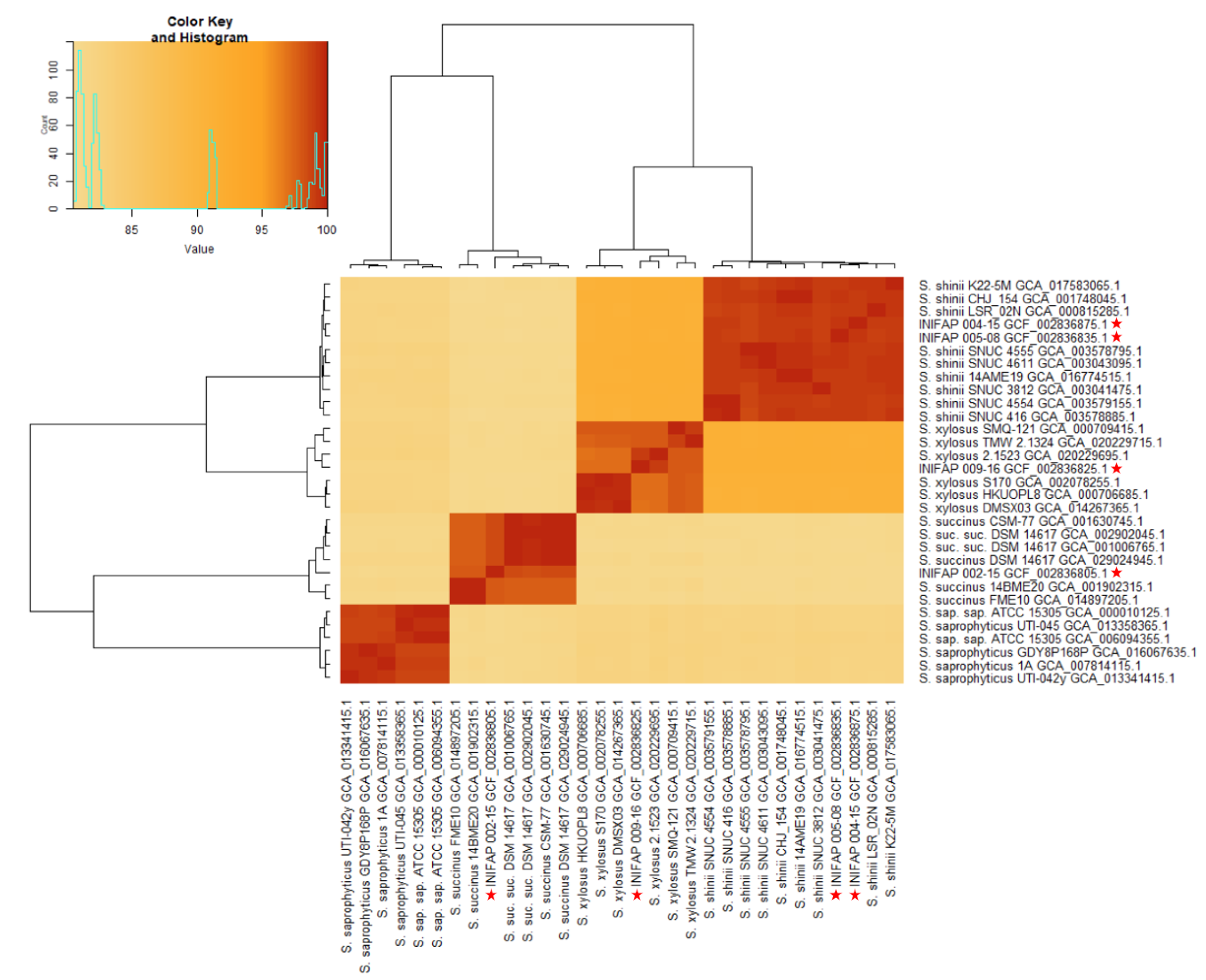
| Strain | Best Average Nucleotide Identity Genome | ANI% | Orthologous Matches | Total Fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 005-08 | Staphylococcus shinii strain CHJ_154 GCA_001748045.1 | 99.21 | 894 | 1012 |
| 004-15 | Staphylococcus shinii strain K22-5 M GCA_017583065.1 | 99.21 | 913 | 979 |
| 002-15 | Staphylococcus succinus strain DSM 14617 GCA_029024945.1 | 98.60 | 860 | 891 |
| 009-16 | Staphylococcus xylosus strain 2.1523 GCA_020229695.1 | 99.07 | 879 | 919 |
| Treatment | Mortality (SD) |
|---|---|
| Control | 19.7(±0.35) a |
| S. shinii S-1 | 67.63(±1.79) b |
| S. succinus | 66.75(±14.16) b |
| S. shinii S-2 | 64.61(±2.11) b |
| S. xylosus | 28.18(±7.05) ab |
| Treatment | Swelling | Color Change | Exudate | Limb Mobility | Dried Eggs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 (0–0) a | 0 (0–0) NS | 0 (0–0) a | 0 (0–0) a | 0 (0–0) NS |
| S. shinii S-1 | 37.5 (25–75) ab | 0 (0–25) NS | 50 (25–75) ab | 25 (25–25) ab | 0 (0–25) NS |
| S. shinii S-2 | 50 (0–100) ab | 25 (0–50) NS | 50 (25–100) ab | 25 (0–25) ab | 0 (0–0) NS |
| S. succinus | 87.5 (75–100) b | 0 (0–0) NS | 50 (0–75) ab | 62.5 (0–75) b | 0 (0–0) NS |
| S. xylosus | 62.5 (25–100) ab | 0 (0–25) NS | 87.5 (25–100) b | 25 (0–50) ab | 0 (0–0) NS |
| Armpit | Groin | Perineal Region | Back | Ears | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. chromogenes | 1 (33.3%) | 2 (29%) | 1 (25%) | 3 (50%) | 15 (94%) | 22 (61.1%) |
| S. shinii | 0 | 2 (29%) | 0 | 1 (16.6%) | 1 (6%) | 4 (11.1%) |
| S. warneri | 1 (33.3%) | 1 (14%) | 1 (25%) | 1 (16.6%) | 0 | 4 (11.1%) |
| S. saprophyticus | 1 (33.3%) | 1 (14%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (5.5%) |
| S. succinus | 0 | 0 | 2 (50%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (5.5%) |
| S. xylosus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1(16.6%) | 0 | 1 (2.7%) |
| Aerococcus spp. | 0 | 1 (14%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (2.7%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cossio-Bayugar, R.; Arreguin-Perez, C.A.; Aguilar-Diaz, H.; Miranda-Miranda, E. Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Staphylococcus Bacteria as a Biocontrol Agent against Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks: Assessing Reproductive Inhibition and Mortality Rates. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030551
Cossio-Bayugar R, Arreguin-Perez CA, Aguilar-Diaz H, Miranda-Miranda E. Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Staphylococcus Bacteria as a Biocontrol Agent against Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks: Assessing Reproductive Inhibition and Mortality Rates. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(3):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030551
Chicago/Turabian StyleCossio-Bayugar, Raquel, Cesar A. Arreguin-Perez, Hugo Aguilar-Diaz, and Estefan Miranda-Miranda. 2024. "Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Staphylococcus Bacteria as a Biocontrol Agent against Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks: Assessing Reproductive Inhibition and Mortality Rates" Microorganisms 12, no. 3: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030551
APA StyleCossio-Bayugar, R., Arreguin-Perez, C. A., Aguilar-Diaz, H., & Miranda-Miranda, E. (2024). Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Staphylococcus Bacteria as a Biocontrol Agent against Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks: Assessing Reproductive Inhibition and Mortality Rates. Microorganisms, 12(3), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030551






