The Renin–Angiotensin System (RAS) in COVID-19 Disease: Where We Are 3 Years after the Beginning of the Pandemic
Abstract
1. The Renin–Angiotensin System
2. The RAS and Viral Respiratory Infections
2.1. RAS and COVID-19
2.1.1. Alterations in Circulating RAS Molecules in COVID-19 Patients Compared to Healthy Subjects
2.1.2. Association between RAS Dysregulation and COVID-19 Severity or Outcome
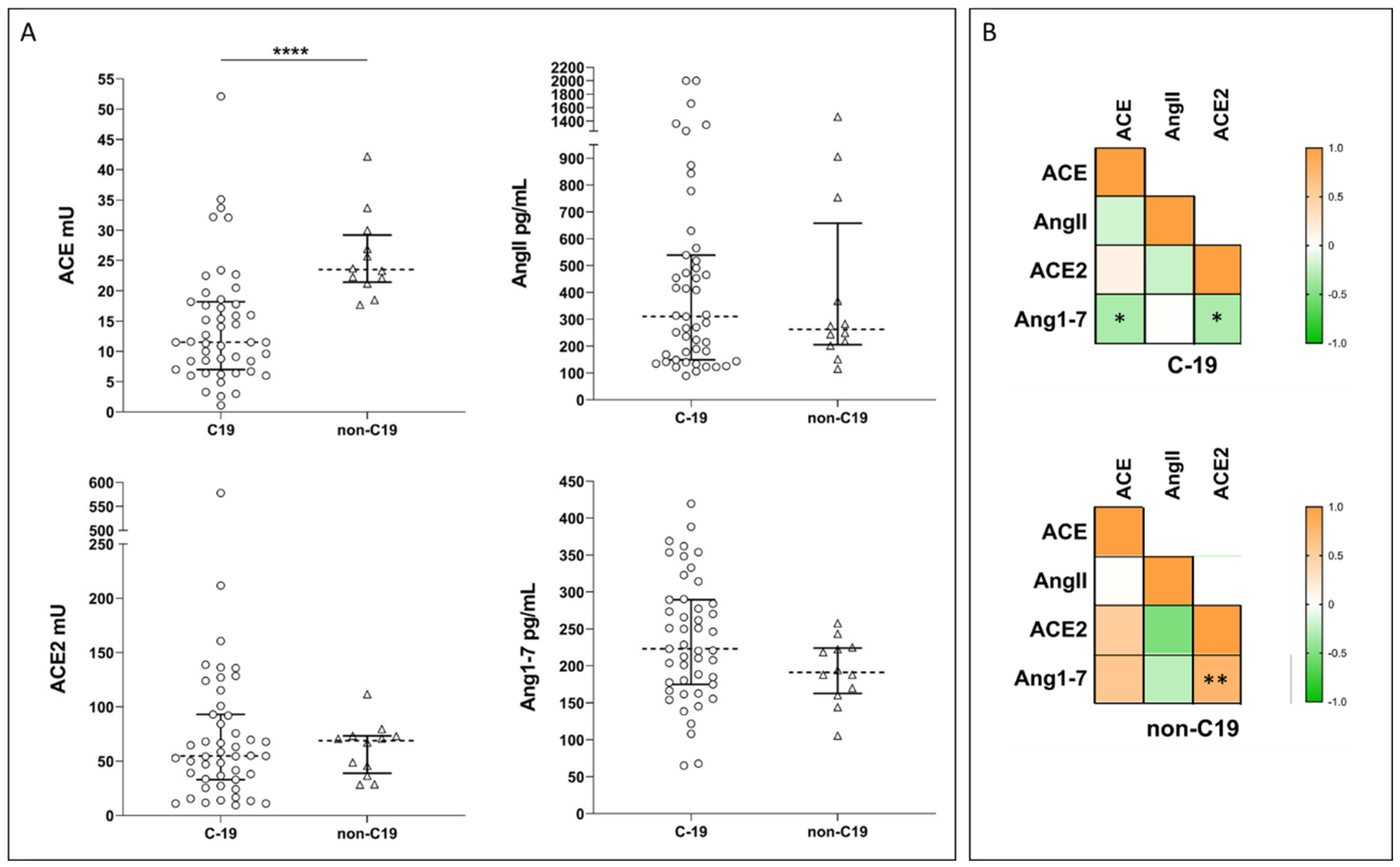
2.2. Systemic RAS during COVID-19: New Experimental Data
3. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckenstaler, R.; Sandori, J.; Gekle, M.; Benndorf, R.A. Angiotensin II receptor type 1—An update on structure, expression and pathology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, J.L.; Sigmund, C.D. Minireview: Overview of the renin-angiotensin system—An endocrine and paracrine system. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2179–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas Vargas, R.A.; Varela Millan, J.M.; Fajardo Bonilla, E. Renin-angiotensin system: Basic and clinical aspects—A general perspective. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2022, 69, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, D.L.; Casillas, O.E.; Jaramillo, H.J.; Romero-Garcia, T.; Vazquez-Jimenez, J.G. AT1 receptor downregulation: A mechanism for improving glucose homeostasis. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranduca, M.A.; Vamesu, C.G.; Tanase, D.M.; Clim, A.; Drochioi, I.C.; Pinzariu, A.C.; Filip, N.; Dima, N.; Tudorancea, I.; Serban, D.N.; et al. The RAAS Axis and SARS-CoV-2: From Oral to Systemic Manifestations. Medicina 2022, 58, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, C.M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and angiotensin-(1-7): An evolving story in cardiovascular regulation. Hypertension 2006, 47, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappel, M.C.; Ferrario, C.M. ACE and ACE2: Their role to balance the expression of angiotensin II and angiotensin-(1-7). Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, F.J.; Guy, J.L.; Lambert, D.W.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and its possible roles in hypertension, diabetes and cardiac function. Lett. Pept. Sci. 2003, 10, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanna, S.; Clifton, V.L.; Rae, K.; van Helden, D.F.; Lumbers, E.R.; Pringle, K.G. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) in Pregnancy: Preeclampsia and Small for Gestational Age. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 590787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.; Albaiceta, G.M.; Garcia-Clemente, M.; Lopez-Larrea, C.; Amado-Rodriguez, L.; Lopez-Alonso, I.; Hermida, T.; Enriquez, A.I.; Herrero, P.; Melon, S.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, ACE2) gene variants and COVID-19 outcome. Gene 2020, 762, 145102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Penninger, J.M. The renin-angiotensin system in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2006, 3, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, R.A.; Warner, F.J.; Hanchapola, I.; Yarski, M.A.; Ramchand, J.; Burrell, L.M.; Smith, A.I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 catalytic activity in human plasma is masked by an endogenous inhibitor. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguiano, L.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Soler, M.J. Circulating ACE2 in Cardiovascular and Kidney Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3231–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisman, L.S.; Keller, R.S.; Weaver, B.; Lin, Q.; Speth, R.; Bristow, M.R.; Canver, C.C. Increased angiotensin-(1-7)-forming activity in failing human heart ventricles: Evidence for upregulation of the angiotensin-converting enzyme Homologue ACE2. Circulation 2003, 108, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, N.; Federici, M.; Schutt, K.; Muller-Wieland, D.; Ajjan, R.A.; Antunes, M.J.; Christodorescu, R.M.; Crawford, C.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Eliasson, B.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4043–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrenak, J.; Simko, F. Renin-Angiotensin System: An Important Player in the Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, C.P.; Nguyen, J.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Werts, A.D.; Lu, P.; Ladd, M.R.; Fulton, W.B.; Kovler, M.L.; Wang, S.; Prindle, T., Jr.; et al. A Dynamic Variation of Pulmonary ACE2 Is Required to Modulate Neutrophilic Inflammation in Response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection in Mice. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 3000–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Rubenfeld, G.D. Fifty Years of Research in ARDS. The Epidemiology of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. A 50th Birthday Review. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanna, F.; Maglio, M.; Landini, M.P.; Fini, M. Body Localization of ACE-2: On the Trail of the Keyhole of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 594495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, C.; Yang, H.Y.; Jin, Y.F.; Duan, G.C.; Chen, S.Y. Role of Renin-Angiotensin System in Acute Lung Injury Caused by Viral Infection. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3715–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yan, Y.; Shu, Y.; Gao, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Ju, X.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from lethal avian influenza A H5N1 infections. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Guo, J.; Zou, Z.; Liu, J.; Cao, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Sheng, M.; Liu, S.; et al. Angiotensin II plasma levels are linked to disease severity and predict fatal outcomes in H7N9-infected patients. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhou, G.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, H.; Xi, Y.; Ren, J.; Duan, G. Involvement of the renin-angiotensin system in the progression of severe hand-foot-and-mouth disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197861. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Penninger, J.M. The discovery of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its role in acute lung injury in mice. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Glende, J.; Al-Falah, M.; de Vries, V.; Schwegmann-Wessels, C.; Qu, X.; Tan, L.; Tschernig, T.; Deng, H.; Naim, H.Y.; et al. Analysis of ACE2 in polarized epithelial cells: Surface expression and function as receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87 Pt 6, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Zheng, A.; Nie, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Luo, M.; Liu, H.; Tan, L.; et al. Expression cloning of functional receptor used by SARS coronavirus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 315, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.; Chen, H. Infection routes, invasion mechanisms, and drug inhibition pathways of human coronaviruses on the nervous system. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1169740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacka, I.; Bertram, S.; Herzog, P.; Pfefferle, S.; Steffen, I.; Muench, M.O.; Simmons, G.; Hofmann, H.; Kuri, T.; Weber, F.; et al. Differential downregulation of ACE2 by the spike proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and human coronavirus NL63. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, H.; Pyrc, K.; van der Hoek, L.; Geier, M.; Berkhout, B.; Pohlmann, S. Human coronavirus NL63 employs the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor for cellular entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7988–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Rao, S.; Huan, Y.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Yang, P.; Sarao, R.; Wada, T.; Leong-Poi, H.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 2005, 436, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakai-Murakami, C.; Osawa, Y.; Tokunaga, K.; Sata, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Sasazuki, T.; Ishizaka, Y. Modulation of TNF-alpha-converting enzyme by the spike protein of SARS-CoV and ACE2 induces TNF-alpha production and facilitates viral entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7809–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, E.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngcobo, G.D. Measurement of serum ACE status may potentially improve the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Afr. 2021, 14, e01039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, S.; De, S.K.; Bankura, B.; Maiti, S.; Das, M.; A Khan, G. ACE/ACE2 balance might be instrumental to explain the certain comorbidities leading to severe COVID-19 cases. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20202014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, F.; Vitiello, A. Scientific Hypothesis for Treatment of COVID-19’s Lung Lesions by Adjusting ACE/ACE2 Imbalance. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2021, 21, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Petiot, E.; Gault, N. Renin-angiotensin system blockers and COVID-19. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ardes, D.; Boccatonda, A.; Rossi, I.; Guagnano, M.T.; Santilli, F.; Cipollone, F.; Bucci, M. COVID-19 and RAS: Unravelling an Unclear Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, I.O.; Melenotte, C.; Brouqui, P.; Million, M.; Lagier, J.C.; Parola, P.; Stein, A.; La Scola, B.; Meddeb, L.; Mege, J.L.; et al. Expression of ACE2, Soluble ACE2, Angiotensin I, Angiotensin II and Angiotensin-(1-7) Is Modulated in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 625732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Fox, D.M.; Gao, C.; Stanley, S.A.; Luo, K. SARS-CoV-2 down-regulates ACE2 through lysosomal degradation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2022, 33, ar147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triana, S.; Metz-Zumaran, C.; Ramirez, C.; Kee, C.; Doldan, P.; Shahraz, M.; Schraivogel, D.; Gschwind, A.R.; Sharma, A.K.; Steinmetz, L.M.; et al. Single-cell analyses reveal SARS-CoV-2 interference with intrinsic immune response in the human gut. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2021, 17, e10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciulla, M.M. SARS-CoV-2 downregulation of ACE2 and pleiotropic effects of ACEIs/ARBs. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 985–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolberg, E.S.; Wickstrom, K.; Tonby, K.; Dyrhol-Riise, A.M.; Holten, A.R.; Amundsen, E.K. Serum ACE as a prognostic biomarker in COVID-19: A case series. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2021, 129, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutz, A.; Conen, A.; Gregoriano, C.; Haubitz, S.; Koch, D.; Domenig, O.; Bernasconi, L.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system peptide profiles in patients with COVID-19. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravi, B.; Li, Z.; Lang, C.N.; Schmid, B.; Lang, F.K.; Grad, S.; Alini, M.; Richards, R.G.; Schmal, H.; Sudkamp, N.; et al. The Tissue Renin-Angiotensin System and Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Major Human Diseases: Quo Vadis? Cells 2021, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Feng, C.; et al. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci. China. Life Sci. 2020, 63, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Del Valle, L.; Gonzalez-Pacheco, H.; Springall, R.; Marquez-Velasco, R.; Masso, F.; Brianza-Padilla, M.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Gonzalez-Flores, J.; Garcia-Avila, C.; et al. The prognostic importance of the angiotensin II/angiotensin-(1-7) ratio in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2022, 16, 17534666221122544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Nair, S.K.; Shi, Y.; Wang, P.; Montone, K.T.; Shaw, P.A.; Choi, G.H.; Ghani, D.; Weaver, J.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Decrease in Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme activity but not concentration in plasma/lungs in COVID-19 patients offers clues for diagnosis/treatment. Mol. Therapy Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 26, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Troyano, N.; Gabriel-Medina, P.; Weber, S.; Klammer, M.; Barquin-DelPino, R.; Castillo-Ribelles, L.; Esteban, A.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, M.; Ferrer-Costa, R.; Pumarola, T.; et al. Soluble Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Disease Progression in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, A.; Ziegler, L.; Havervall, S.; Rudberg, A.S.; von Meijenfeldt, F.; Lisman, T.; Mackman, N.; Sanden, P.; Thalin, C. Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is transiently elevated in COVID-19 and correlates with specific inflammatory and endothelial markers. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5908–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lier, D.; Kox, M.; Santos, K.; van der Hoeven, H.; Pillay, J.; Pickkers, P. Increased blood angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity in critically ill COVID-19 patients. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00848–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gheblawi, M.; Nikhanj, A.; Munan, M.; MacIntyre, E.; O’Neil, C.; Poglitsch, M.; Colombo, D.; Del Nonno, F.; Kassiri, Z.; et al. Dysregulation of ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 and Renin-Angiotensin Peptides in SARS-CoV-2 Mediated Mortality and End-Organ Injuries. Hypertension 2022, 79, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.M.; Benoit, S.; Lippi, G.; Benoit, J. Letter to the Editor—Circulating plasma levels of angiotensin II and aldosterone in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A preliminary report. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 63, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avanoglu Guler, A.; Tombul, N.; Aysert Yildiz, P.; Ozger, H.S.; Hizel, K.; Gulbahar, O.; Tufan, A.; Erbas, G.; Aygencel, G.; Guzel Tunccan, O.; et al. The assessment of serum ACE activity in COVID-19 and its association with clinical features and severity of the disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2021, 81, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, L.; Lecocq, M.; Bouzin, C.; Hoton, D.; Schmit, G.; Pereira, J.P.; Montiel, V.; Plante-Bordeneuve, T.; Laterre, P.F.; Pilette, C. Increased Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Loss of Alveolar Type II Cells in COVID-19-related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Fragkou, P.C.; Maratou, E.; Dimopoulou, D.; Kominakis, A.; Kokkinopoulou, I.; Kroupis, C.; Nikolaidou, A.; Antonakos, G.; Papaevangelou, V.; et al. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism, ACE activity, and COVID-19: A rather controversial hypothesis. A case-control study. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Cai, T.; Fan, L.; Lou, K.; Hua, X.; Huang, Z.; Gao, G. The potential role of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme in coronavirus disease 2019. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, S.; Cakmak, F.; Konukoglu, D.; Biberoglu, S.; Ipekci, A.; Akdeniz, Y.S.; Bolayirli, I.M.; Balkan, I.I.; Dumanli, G.Y.; Ikizceli, I. Efficacy of Serum Angiotensin II Levels in Prognosis of Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e613–e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Files, D.C.; Gibbs, K.W.; Schaich, C.L.; Collins, S.P.; Gwathmey, T.M.; Casey, J.D.; Self, W.H.; Chappell, M.C. A pilot study to assess the circulating renin-angiotensin system in COVID-19 acute respiratory failure. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L213–L218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhang, C.; Ren, W.; Yu, A.; Zhou, X. Elevation of plasma angiotensin II level is a potential pathogenesis for the critically ill COVID-19 patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.M.; Benoit, J.L.; Rose, J.; de Oliveira, M.H.S.; Lippi, G.; Benoit, S.W. Serum ACE activity and plasma ACE concentration in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2021, 81, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.M.; Benoit, J.L.; Berger, B.A.; Pulvino, C.; Lavie, C.J.; Lippi, G.; Benoit, S.W. Coronavirus disease 2019 is associated with low circulating plasma levels of angiotensin 1 and angiotensin 1,7. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, R.L.; Bombassaro, B.; Monfort-Pires, M.; Mansour, E.; Palma, A.C.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Ulaf, R.G.; Bernardes, A.F.; Nunes, T.A.; Agrela, M.V.; et al. Plasma Angiotensin II Is Increased in Critical Coronavirus Disease 2019. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 847809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 infection, A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e192–e197. [CrossRef]
- Akin, S.; Schriek, P.; van Nieuwkoop, C.; Neuman, R.I.; Meynaar, I.; van Helden, E.J.; Bouazzaoui, H.E.; Baak, R.; Veuger, M.; Mairuhu, R.; et al. A low aldosterone/renin ratio and high soluble ACE2 associate with COVID-19 severity. J. Hypertens. 2022, 40, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Hodlmoser, S.; Eskandary, F.; Poglitsch, M.; Bonderman, D.; Strassl, R.; Aberle, J.H.; Oberbauer, R.; Zoufaly, A.; Hecking, M. ACE2 Elevation in Severe COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragstrup, T.W.; Singh, H.S.; Grundberg, I.; Nielsen, A.L.; Rivellese, F.; Mehta, A.; Goldberg, M.B.; Filbin, M.R.; Qvist, P.; Bibby, B.M. Plasma ACE2 predicts outcome of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchuk, O.; Pak, A.; Palii, S.; Ivankiv, Y.; Kozak, K.; Korda, M.; Vari, S.G. Blood ACE2 Protein Level Correlates with COVID-19 Severity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrayess, M.A.; Zedan, T.H.; Alattar, A.R.; Abusriwil, H.; Al-Ruweidi, M.; Almuraikhy, S.; Parengal, J.; Alhariri, B.; Yassine, H.M.; Hssain, A.A.; et al. Soluble ACE2 and angiotensin II levels are modulated in hypertensive COVID-19 patients treated with different antihypertension drugs. Blood Press. 2022, 31, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza, M.D.C.; Ubeda, M.; Delgado, P.; Horndler, L.; Llamas, M.A.; van Santen, H.M.; Alarcon, B.; Abia, D.; Garcia-Bermejo, L.; Serrano-Villar, S.; et al. ACE2 Serum Levels as Predictor of Infectability and Outcome in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 836516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, P.; Varpaei, H.A.; Seifi, A.; Zahak Miandoab, S.; Beiranvand, S.; Mobaraki, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Abdollahi, A. Soluble ACE2 as a Risk or Prognostic Factor in COVID-19 Patients: A Cross-sectional Study. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2022, 36, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldrer, S.; Mazzi, C.; Bernardi, M.; Prato, M.; Ronzoni, N.; Rodari, P.; Angheben, A.; Piubelli, C.; Tiberti, N. Regulatory T Cells as Predictors of Clinical Course in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 789735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, F.; Annoni, F.; Dos Santos, R.A.S.; Taccone, F.S.; Rooman, M. Quantifying Renin-Angiotensin-System Alterations in COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gressens, S.B.; Leftheriotis, G.; Dussaule, J.C.; Flamant, M.; Levy, B.I.; Vidal-Petiot, E. Controversial Roles of the Renin Angiotensin System and Its Modulators During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 624052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudit, G.Y.; Pfeffer, M.A. Plasma angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Novel biomarker in heart failure with implications for COVID-19. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1818–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Nalla, L.V.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, N.; Singh, A.A.; Malim, F.M.; Ghatage, M.; Mukarram, M.; Pawar, A.; Parihar, N.; et al. Association of COVID-19 with Comorbidities: An Update. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 334–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fildes, J.E.; Walker, A.H.; Keevil, B.; Hutchinson, I.V.; Leonard, C.T.; Yonan, N. The effects of ACE inhibition on serum angiotensin II concentration following cardiac transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 78, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilsson, V.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Aspelund, T.; Jonsson, B.G.; Gudjonsson, A.; Launer, L.J.; Jennings, L.L.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Gudnason, V. Antihypertensive medication uses and serum ACE2 levels: ACEIs/ARBs treatment does not raise serum levels of ACE2. Preprint. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilsson, V.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Aspelund, T.; Jonsson, B.G.; Gudjonsson, A.; Launer, L.J.; Lamb, J.R.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Jennings, L.L.; Gudnason, V. Serum levels of ACE2 are higher in patients with obesity and diabetes. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2020, 7, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Hödlmoser, S.; Domenig, O.; Krenn, K.; Eskandary, F.; Krenn, S.; Schörgenhofer, C.; Rumpf, B.; Karolyi, M.; Traugott, M.T.; et al. The systemic renin-angiotensin system in COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gheblawi, M.; Oudit, G.Y. ; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2: A Double-Edged Sword. Circulation 2020, 142, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohaei, D.; Hollenberg, M.; Janket, S.J.; Diamandis, E.P.; Poda, G.; Prassas, I. The therapeutic relevance of the Kallikrein-Kinin axis in SARS-cov-2-induced vascular pathology. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2023, 60, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soro-Paavonen, A.; Gordin, D.; Forsblom, C.; Rosengard-Barlund, M.; Waden, J.; Thorn, L.; Sandholm, N.; Thomas, M.C.; Groop, P.H.; FinnDiane Study Group. Circulating ACE2 activity is increased in patients with type 1 diabetes and vascular complications. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.W.; Lu, L.C.; Chang, C.C.; Cho, C.C.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.S. Imbalanced plasma ACE and ACE2 level in the uremic patients with cardiovascular diseases and its change during a single hemodialysis session. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchand, J.; Burrell, L.M. Circulating ACE2: A novel biomarker of cardiovascular risk. Lancet 2020, 396, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ruiz, I. ACE2 level as a marker of CVD. Nature reviews. Cardiology 2020, 17, 759. [Google Scholar]
- Anguiano, L.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Barrios, C.; Betriu, A.; Mojal, S.; Fernández, E.; Soler, M.J. NEFRONA study. Circulating angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity in patients with chronic kidney disease without previous history of cardiovascular disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchand, J.; Patel, S.K.; Kearney, L.G.; Matalanis, G.; Farouque, O.; Srivastava, P.M.; Burrell, L.M. Plasma ACE2 Activity Predicts Mortality in Aortic Stenosis and Is Associated With Severe Myocardial Fibrosis. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosbøl, E.L.; Butt, J.H.; Østergaard, L.; Andersson, C.; Selmer, C.; Kragholm, K.; Schou, M.; Phelps, M.; Gislason, G.H.; Gerds, T.A.; et al. Association of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Use With COVID-19 Diagnosis and Mortality. JAMA 2020, 324, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, H.R.; Adhikari, S.; Pulgarin, C.; Troxel, A.B.; Iturrate, E.; Johnson, S.B.; Hausvater, A.; Newman, J.D.; Berger, J.S.; Bangalore, S.; et al. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Rea, F.; Ludergnani, M.; Apolone, G.; Corrao, G. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dambha-Miller, H.; Hinton, W.; Wilcox, C.R.; Lemanska, A.; Joy, M.; Feher, M.; Stuart, B.; de Lusignan, S.; Hippisley-Cox, J.; Griffin, S. Mortality from angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in people infected with COVID-19: A cohort study of 3.7 million people. Fam. Pract. 2023, 40, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaier, A.H. The plasma kallikrein-kinin system counterbalances the renin-angiotensin system. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvin, M.R.; Alvarez, C.; Miller, J.I.; Prates, E.T.; Walker, A.M.; Amos, B.K.; Mast, A.E.; Justice, A.; Aronow, B.; Jacobson, D. A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm. eLife 2020, 9, e59177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.W.; Shariat-Madar, Z. Human plasma kallikrein-kinin system: Physiological and biochemical parameters. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents) 2009, 7, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiadu, B.K.; Ellis, T.; Graichen, A.; Kremer, R.B.; Rusling, J.F. Quantitative detection of RAS and KKS peptides in COVID-19 patient serum by stable isotope dimethyl labeling LC-MS. Analyst 2023, 148, 5926–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolungo, L.; Beltrami, C.; Degli Esposti, C.; Lopatriello, G.; Piubelli, C.; Mori, A.; Pomari, E.; Deiana, M.; Scarso, S.; Bisoffi, Z.; et al. ACoRE: Accurate SARS-CoV-2 genome reconstruction for the characterization of intra-host and inter-host viral diversity in clinical samples and for the evaluation of re-infections. Genomics 2021, 113, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Burns, K.D. Measurement of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 Activity in Biological Fluid (ACE2). Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1527, 101–115. [Google Scholar]


| COVID-19 | Controls | ACE (Act.) | ACE (Conc.) | ACE2 (Act.) | ACE2 (Conc.) | AngII (Conc.) | Ang1-7 (Conc.) | AngII/Ang1-7 (Ratio) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitalized, n = 12 | Healthy, n = 8 | ↑ | [49] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 74 | Healthy, n = 55 | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | [50] | ||
| Hospitalized, n = 16 | Healthy, n = 17 | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | [51] | ||||
| Hospitalized, n = 519 | Healthy, n = 201 | ↓ | [52] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 114 | Healthy, n = 10 | ≈ | ↑ | [53] | |||||
| Hospitalized, n = 10 | Healthy, n = 5 | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | [54] | ||||
| Hospitalized, n = 242 | Healthy, n = 38 | ↑ | [55] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 30 | Healthy, n = 14 | ≈ | [56] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 55 | Healthy, n = 18 | ≈ | [57] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 84 | Healthy, n = 18 | ↓ | ↑ | ≈ | ↑ | [58] | |||
| Hospitalized, n = 81 | Healthy, n = 316 | ↓ | [59] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 136 | Healthy, n = 60 | ↓ | [60] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 112 | Healthy, n = 27 | ↓ | [61] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 29 | Healthy, n = 15 | ↓ | ↑ | ≈ | [42] | ||||
| Hospitalized, n = 19 | ARF non-COVID19, n = 19 | ↑ | [62] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 82 | Critically ill non-COVID19 n= 12 | ↑ | [63] | ||||||
| Hospitalized, n = 52 | Sick non-COVID19 n= 27 | ≈ | ≈ | [64] | |||||
| Hospitalized, n = 27 | Sick non-COVID19 n= 14 | ↓ | [65] |
| COVID-19 | ACE (Act.) | ACE (Conc.) | ACE2 (Act.) | ACE2 (Conc.) | AngII (Conc.) | Ang1-7 (Conc.) | AngII/Ang1-7 (Ratio) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe, n = 16 | Non-severe, n = 120 | ↓ | [60] | ||||||
| Severe, n = 59 | Non-severe, n = 128 | ↑ | [68] | ||||||
| Severe, n = 32 | Non-severe, n = 94 | ↑ | [69] | ||||||
| Severe, n = 109 | Non-severe, n = 196 | ↑ | [70] | ||||||
| Severe/critical, n = 40 | Mild, n = 42 | ↑ | [63] | ||||||
| Severe, n = 11 | Mild, n = 24 | ≈ | [57] | ||||||
| Severe, n = 263 | Mild, n = 82 | ↓ | [71] | ||||||
| Severe, n = 11 | Critical, n = 12 | ≈ | ≈ | ↑ | ≈ | [66] | |||
| COVID-19 | ACE (Act.) | ACE (Conc.) | ACE2 (Act.) | ACE2 (Conc.) | AngII (Conc.) | Ang1-7 (Conc.) | AngII/Ang1-7 (Ratio) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Died, n = 25 | Survived, n = 49 | ≈ | ≈ | ≈ | ≈ | ↑ | [50] | ||
| Died, n = 11 | Survived, n = 17 | ↑ | [74] | ||||||
| ICU/died, n = 260 | Transferred/discharged, n = 331 | ↓ | [52] | ||||||
| Mechanical ventilation/died, n = 106 | Non-ventilated survivors, n = 136 | ≈ | [55] | ||||||
| ICU, n = 8 | Discharched, n = 22 | ≈ | [56] | ||||||
| Intubated, n = 79 | Non-intubated, n = 225 | ↑ | [70] | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prato, M.; Tiberti, N.; Mazzi, C.; Gobbi, F.; Piubelli, C.; Longoni, S.S. The Renin–Angiotensin System (RAS) in COVID-19 Disease: Where We Are 3 Years after the Beginning of the Pandemic. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030583
Prato M, Tiberti N, Mazzi C, Gobbi F, Piubelli C, Longoni SS. The Renin–Angiotensin System (RAS) in COVID-19 Disease: Where We Are 3 Years after the Beginning of the Pandemic. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(3):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030583
Chicago/Turabian StylePrato, Marco, Natalia Tiberti, Cristina Mazzi, Federico Gobbi, Chiara Piubelli, and Silvia Stefania Longoni. 2024. "The Renin–Angiotensin System (RAS) in COVID-19 Disease: Where We Are 3 Years after the Beginning of the Pandemic" Microorganisms 12, no. 3: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030583
APA StylePrato, M., Tiberti, N., Mazzi, C., Gobbi, F., Piubelli, C., & Longoni, S. S. (2024). The Renin–Angiotensin System (RAS) in COVID-19 Disease: Where We Are 3 Years after the Beginning of the Pandemic. Microorganisms, 12(3), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030583





