Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Bacteriophages Identifies Two Novel Phage Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Host Strains and Their Growth
2.2. Bacteriophage Isolation and Propagation
2.3. Host Range Profiles
2.4. Phage DNA Isolation, Sequencing, and Annotation
2.5. Phylogenetic and Comparative Genomic Analyses
2.6. Electron Microscopic Imaging of the Phages
3. Results
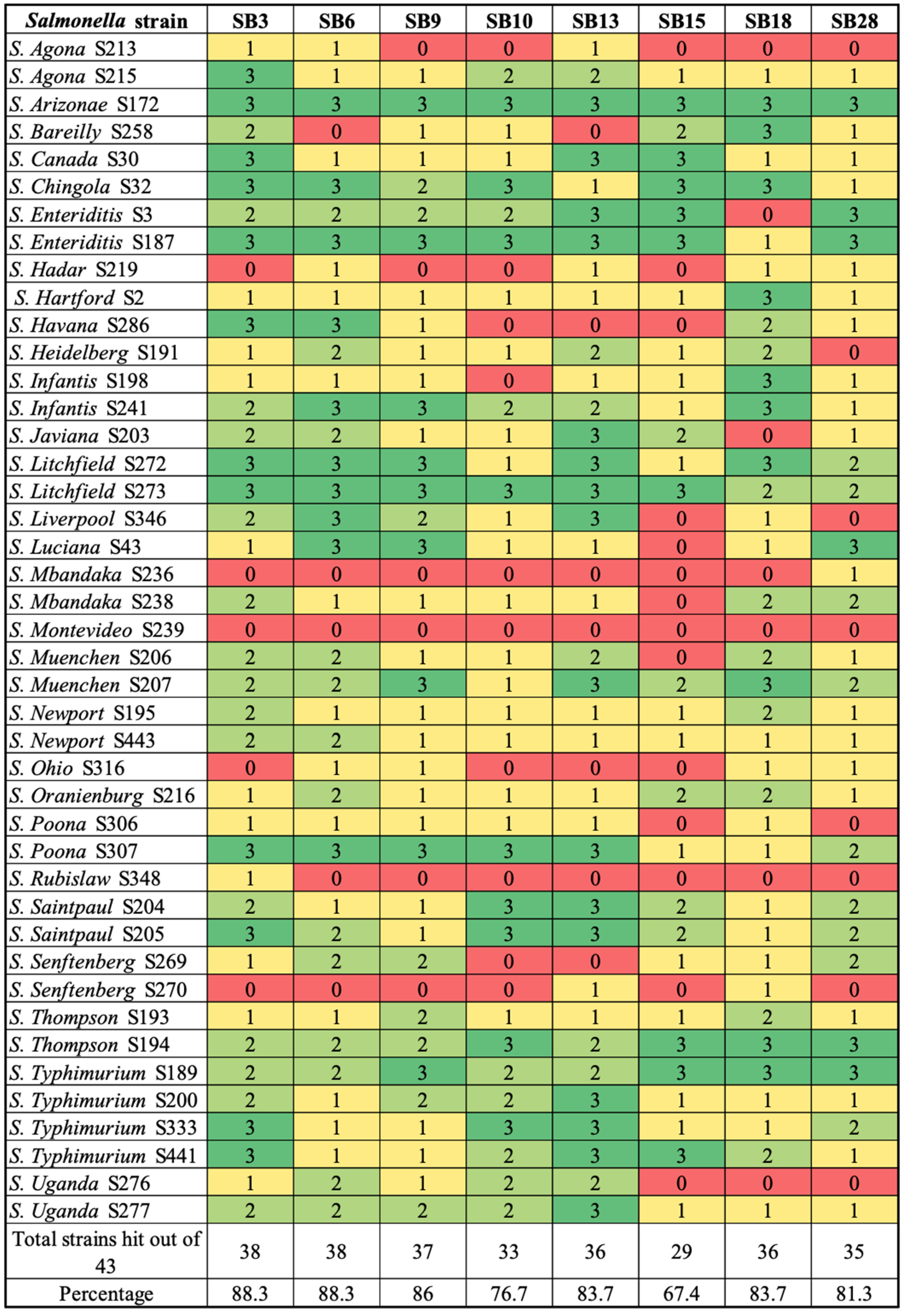
3.1. Phage Isolation and Biological Characterization by Host Range Profile
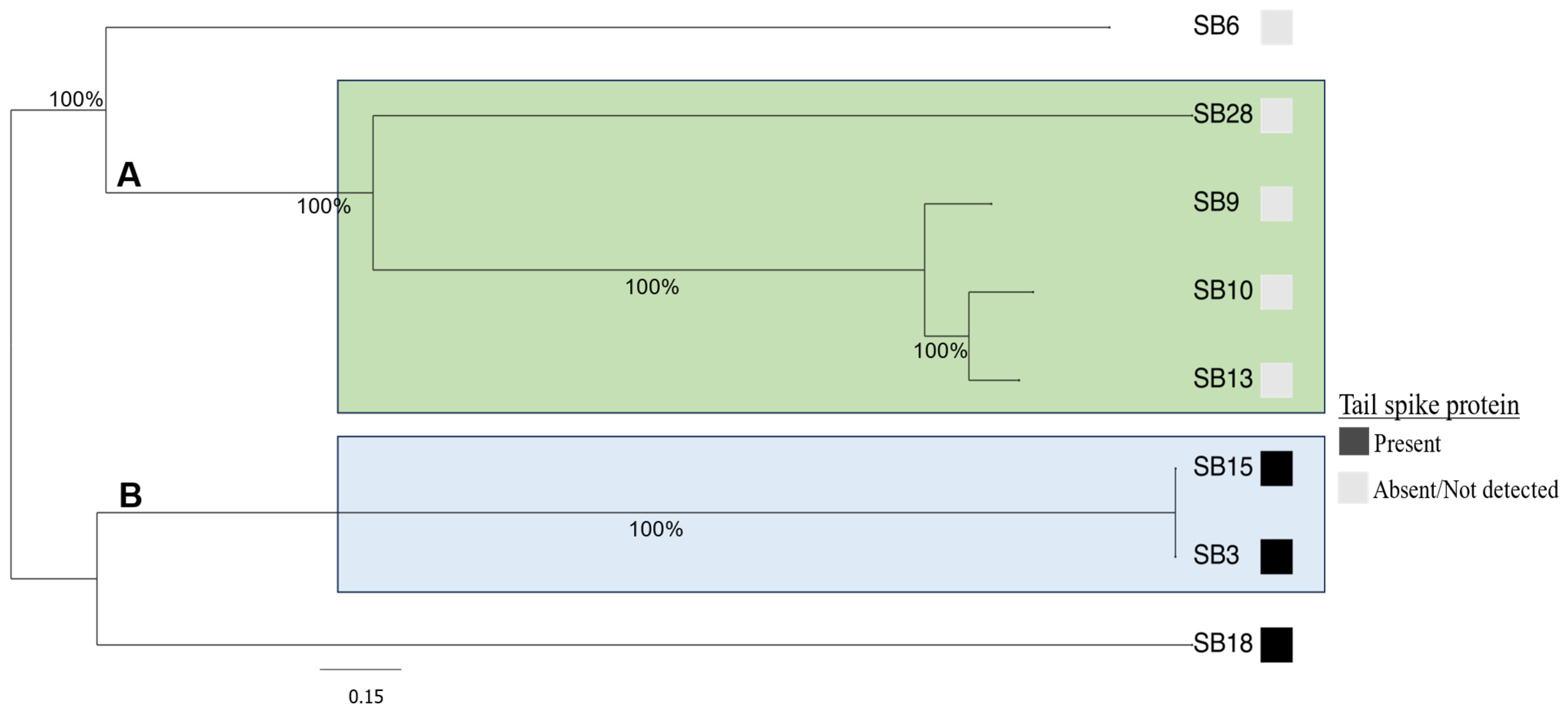
3.2. Comparative Phylogenomic Analysis of Phage Understudy
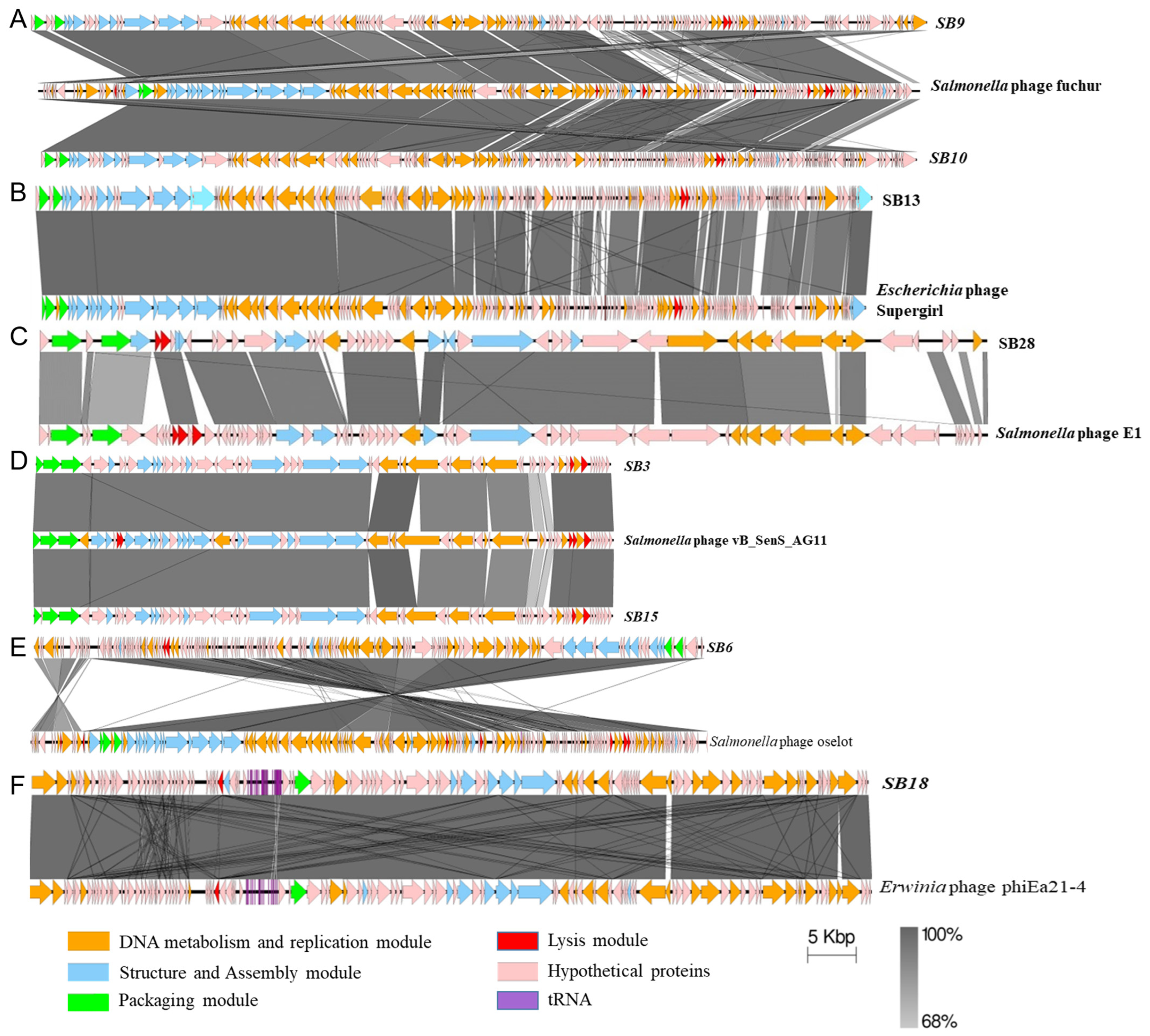
3.2.1. Comparative Gene Content Analysis of Phages under Study
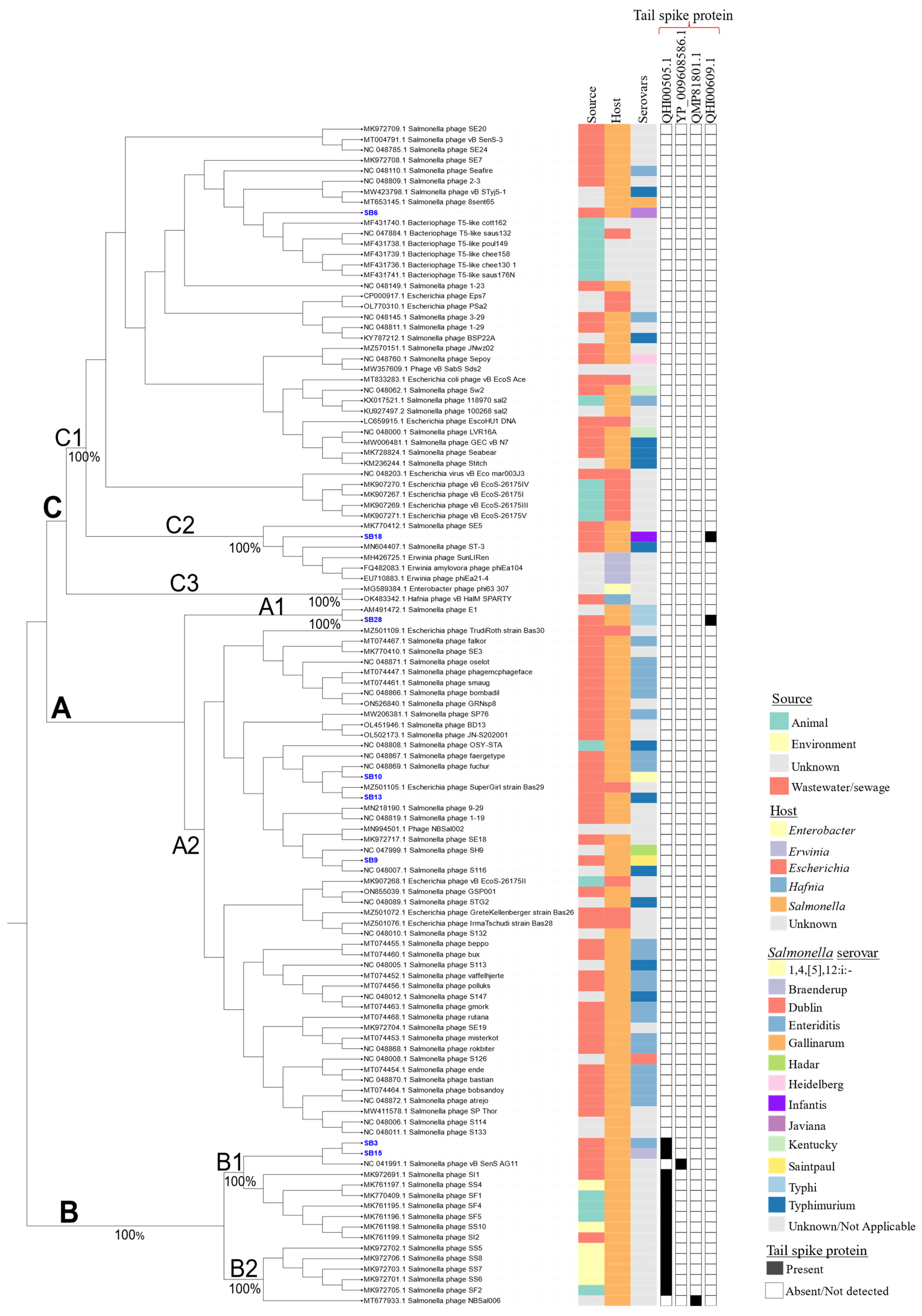
3.2.2. Assessing the Genetic Relatedness of Phages under Study with Other Salmonella Phage Genomes
3.3. Salmonella Phages under Study Are Morphologically and Taxonomically Different
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, M.K.; Murray, R.; Flockhart, L.; Pintar, K.; Fazil, A.; Nesbitt, A.; Marshall, B.; Tataryn, J.; Pollari, F. Estimates of foodborne illness–related hospitalizations and deaths in Canada for 30 specified pathogens and unspecified agents. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; International Collaboration on Enteric Disease “Burden of Illness” Studies. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars. 9th Edition. 2007. Available online: http://www.scacm.org/free/Antigenic%20Formulae%20of%20the%20Salmonella%20Serovars%202007%209th%20edition.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- PHAC. Public Health Notice by Public Health Agency of Canada: Outbreak of Salmonella Infections Linked to Peaches Imported from the United States. 2020. Available online: http://tinyurl.com/44wz9p9v (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- CFIA. Food Safety Investigation by Canadian Food Inspection Agency: Outbreak of Salmonella Infections Linked to Red Onions Imported from the United States. 2020. Available online: http://tinyurl.com/bddaefyn (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- PHAC. Public Health Notice by Public Health Agency of Canada: Outbreak of Salmonella Infections Linked to Frozen Whole Kernel Corn. 2022. Available online: http://tinyurl.com/ywywz5m7 (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- PHAC. Public Health Notice by Public Health Agency of Canada: Outbreak of Salmonella Infections Linked to Malichita and Rudy Brand Cantaloupes. 2024. Available online: http://tinyurl.com/dm94wt82 (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- Beamud, B.; García-González, N.; Gómez-Ortega, M.; González-Candelas, F.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Sanjuan, R. Genetic determinants of host tropism in Klebsiella phages. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandare, S.; Colom, J.; Baig, A.; Ritchie, J.M.; Bukhari, H.; Shah, M.A.; Sarkar, B.L.; Su, J.; Wren, B.; Barrow, P.; et al. Reviving Phage Therapy for the Treatment of Cholera. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 219, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, K.; LaBossiere, B.; Switt, A.I.M.; Delaquis, P.; Goodridge, L.; Levesque, R.C.; Danyluk, M.D.; Wang, S. Characterization of Four Novel Bacteriophages Isolated from British Columbia for Control of Non-typhoidal Salmonella in Vitro and on Sprouting Alfalfa Seeds. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, C.S.L.; Voss-Rech, D.; Alves, L.; Coldebella, A.; Brentano, L.; Trevisol, I.M. Effect of time of therapy with wild-type lytic bacteriophages on the reduction of Salmonella Enteritidis in broiler chickens. Vet.-Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.; Delaquis, P.; Goodridge, L.; Lévesque, R.; Fong, K.; Wang, S. Inactivation of Salmonella enterica on post-harvest cantaloupe and lettuce by a lytic bacteriophage cocktail. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2019, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodridge, L.; Fong, K.; Wang, S.; Delaquis, P. Bacteriophage-based weapons for the war against foodborne pathogens. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 20, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endersen, L.; Coffey, A. The use of bacteriophages for food safety. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Ward, S.; Hyman, P. More Is Better: Selecting for Broad Host Range Bacteriophages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Mor, O.; Boyle, E.C.; Grassl, G.A. Same species, different diseases: How and why typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars differ. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switt, A.I.; den Bakker, H.C.; Vongkamjan, K.; Hoelzer, K.; Warnick, L.D.; Cummings, K.J.; Wiedmann, M. Salmonella bacteriophage diversity reflects host diversity on dairy farms. Food Microbiol. 2013, 36, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaki, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Kawai, Y. Broad host range bacteriophage, EscoHU1, infecting Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica: Characterization, comparative genomics, and applications in food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 372, 109680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, K.; Lu, Y.T.; Brenner, T.; Falardeau, J.; Wang, S. Prophage Diversity Across Salmonella and Verotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Agricultural Niches of British Columbia, Canada. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 853703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, D.W.; Hudson, L.K.; Wang, J.; Denes, T.G. Characterization of a Diverse Collection of Salmonella Phages Isolated from Tennessee Wastewater. PHAGE 2023, 4, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Denes, T.G.; Hudson, L.K.; Peters, T.L.; Samir, R.; Aziz, R.K.; Noben, J.-P.; Wagemans, J.; Dueñas, F. Novel Salmonella Phage, vB_Sen_STGO-35-1, Characterization and Evaluation in Chicken Meat. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanki, A.M.; Brown, N.; Millard, A.D.; Clokie, M.R.J. Genomic Characterization of Jumbo Salmonella Phages That Effectively Target United Kingdom Pig-Associated Salmonella Serotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sritha, K.S.; Bhat, S.G. Genomics of Salmonella phage ΦStp1: Candidate bacteriophage for biocontrol. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guan, G.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, S.; Yan, T.; Tian, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wei, T.; et al. Characterization and complete genomic analysis of two Salmonella phages, SenALZ1 and SenASZ3, new members of the genus Cba120virus. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla-Navarro, S.; Catalá-Gregori, P.; Marin, C. Salmonella Bacteriophage Diversity According to Most Prevalent Salmonella Serovars in Layer and Broiler Poultry Farms from Eastern Spain. Animals 2020, 10, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.; Tremblay, D.M.; Delaquis, P.; Goodridge, L.; Levesque, R.C.; Moineau, S.; Suttle, C.A.; Wang, S. Diversity and Host Specificity Revealed by Biological Characterization and Whole Genome Sequencing of Bacteriophages Infecting Salmonella enterica. Viruses 2019, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Twest, R.; Kropinski, A.M. Bacteriophage enrichment from water and soil. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 501, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhandare, S.G. Biocontrol of V. cholerae Using Bacteriophage. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Plaque Purification. Phage Hunting Protocols. 2013. Available online: https://phagesdb.org (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- Khan Mirzaei, M.; Nilsson, A.S. Isolation of phages for phage therapy: A comparison of spot tests and efficiency of plating analyses for determination of host range and efficacy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutter, E. Phage host range and efficiency of plating. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 501, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, E.J. Preparation of a phage DNA fragment library for whole genome shotgun sequencing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 502, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Lab Manual, 4th ed.; Cold Spring Harbour Lab Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Coil, D.; Jospin, G.; Darling, A.E. A5-miseq: An updated pipeline to assemble microbial genomes from Illumina MiSeq data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattam, A.R.; Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Gerdes, S.; Kenyon, R.; Machi, D.; Mao, C.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. Assembly, Annotation, and Comparative Genomics in PATRIC, the All Bacterial Bioinformatics Resource Center. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1704, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punta, M.; Coggill, P.C.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Mistry, J.; Tate, J.; Boursnell, C.; Pang, N.; Forslund, K.; Ceric, G.; Clements, J.; et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D290–D301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Borodovsky, M.; Carver, T.J.; Cerdeno-Tarraga, A.M.; Darling, A.; Lomsadze, A.; Mahadevan, P.; Sto-thard, P.; Seto, D.; Van Domselaar, G.; et al. In silico identification of genes in bacteriophage DNA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 502, 57–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazutaka, K.; Misakwa, K.; Kei-ichi, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argimón, S.; AbuDahab, K.; Goater, R.J.E.; Fedosejev, A.; Bhai, J.; Glasner, C.; Feil, E.J.; Holden, M.T.G.; Yeats, C.A.; Grundmann, H.; et al. Microreact: Visualizing and sharing data for genomic epidemiology and phylogeography. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Harrison, E.M.; Bi, D.; Tai, C.; He, X.; Ou, H.-Y.; Rajakumar, K.; Deng, Z. TADB: A web-based resource for Type 2 toxin–antitoxin loci in bacteria and archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D606–D611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D. (Eds.) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, B.R.; Griffin, P.M.; Cole, D.; Walsh, K.A.; Chai, S.J. Outbreak-associated Salmonella enterica Serotypes and Food Commodities, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormic, Z.D.; Patel, K.; Higa, J.; Bancroft, J.; Donovan, D.; Edwards, L.; Cheng, J.; Adcock, B.; Bond, C.; Pereira, E.; et al. Bi-national outbreak of Salmonella Newport infections linked to onions: The United States experience. Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreaks of Salmonella infections associated with eating Roma tomatoes—United States and Canada, 2004. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2005, 54, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Multistate outbreaks of Salmonella serotype Poona infections associated with eating cantaloupe from Mexico--United States and Canada, 2000–2002. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2002, 51, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, K.A.; Bennett, S.D.; Mahovic, M.; Gould, L.H. Outbreaks associated with cantaloupe, watermelon, and honeydew in the United States, 1973–2011. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencay, Y.E.; Gambino, M.; Prüssing, T.F.; Brøndsted, L. The genera of bacteriophages and their receptors are the major determinants of host range. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2095–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, E.; Shaidullina, A.; Burkolter, M.; Heyer, Y.; Estermann, F.; Druelle, V.; Sauer, P.; Willi, L.; Michaelis, S.; Hilbi, H.; et al. Systematic exploration of Escherichia coli phage–host interactions with the BASEL phage collection. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, D.; Thomson, N.R.; Baker, S.; Wain, J.; Pardo, M.; Goulding, D.; Hamlin, N.; Choudhary, J.; Threfall, J.; Dougan, G. Molecular characterization of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Vi-typing bacteriophage E1. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2580–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anany, H.; Switt, A.I.; De Lappe, N.; Ackermann, H.-W.; Reynolds, D.M.; Kropinski, A.M.; Wiedmann, M.; Griffiths, M.W.; Tremblay, D.; Moineau, S.; et al. A proposed new bacteriophage subfamily: “Jerseyvirinae”. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hany, A. Biocontrol of Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens Using Immobilized Bacteriophages. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, N.S.; Hendriksen, N.B.; Hansen, L.H.; Kot, W. A New High-throughput Screening (HiTS) Method for Phages—Enabling Crude Isolation and Fast Identification of Diverse Phages with Therapeutic Potential. biPhage 2020, 1, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, S.M.; Kropinski, A.M.; Castle, A.J.; Svircev, A.M. Complete genome of the broad-host-range Erwinia amylovora phage ΦEa21-4 and its relationship to Salmonella phage felix O1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.J.; Svircev, A.M.; Smith, R.; Castle, A.J. Bacteriophages of Erwinia amylovora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2133–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runa, V.; Wenk, J.; Bengtsson, S.; Jones, B.V.; Lanham, A.B. Bacteriophages in Biological Wastewater Treatment Systems: Occurrence, Characterization, and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, N.M.; Ziadi, M.M. Wastewater as a fertility source for novel bacteriophages against multi-drug resistant bacteria. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4358–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shang, J.; Peng, C.; Sun, Y. Phage family classification under Caudoviricetes: A review of current tools using the latest ICTV classification framework. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1032186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Kropinski, A.M.; Adriaenssens, E.M. A Roadmap for Genome-Based Phage Taxonomy. Viruses 2021, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbini, F.M.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; García, M.L.; Hendrickson, R.C.; et al. Changes to virus taxonomy and the ICTV Statutes ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2023). Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colavecchio, A.; D’souza, Y.; Tompkins, E.; Jeukens, J.; Freschi, L.; Emond-Rheault, J.-G.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Boyle, B.; Bekal, S.; Tamber, S.; et al. Prophage Integrase Typing Is a Useful Indicator of Genomic Diversity in Salmonella enterica. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, H.S.; Matamouros, S.; Hager, K.R.; Brittnacher, M.J.; Rohmer, L.; Radey, M.C.; Weiss, E.J.; Kim, K.B.; Jacobs, M.A.; Sims-Day, E.H.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Characterizes Strain Diversity for Recent U.S. Salmonellosis Cases and Identifies Mutations Linked to Loss of Fitness under Nitrosative and Oxidative Stress. mBio 2016, 7, e00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankau, E.W.; Cruz Bedon, L.; Mackie, R.I. Salmonella strains isolated from Galápagos iguanas show spatial structuring of serovar and genomic diversity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pightling, A.W.; Pettengill, J.; Luo, Y.; Strain, E.; Rand, H. Genomic diversity of Salmonella enterica isolated from papaya samples collected during multiple outbreaks in 2017. Microbiology 2020, 166, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.M.J.; Mor, S.M.; Ward, M.P.; Collins, J.; Flint, J.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.A.; Abd El Ghany, M. Genomic characterisation of Salmonella enterica serovar Wangata isolates obtained from different sources reveals low genomic diversity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodagari, H.R.; Mohammed, A.B.; Wang, P.; O’Dea, M.; Abraham, S.; Robertson, I.; Habib, I. Non-typhoidal Salmonella contamination in egg shells and contents from retail in Western Australia: Serovar diversity, multilocus sequence types, and phenotypic and genomic characterizations of antimicrobial resistance. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 308, 108305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, A.; Miranda, J.M.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A. A comprehensive review of non-enterica subspecies of Salmonella enterica. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majtanova, L.; Majtan, J.; Majtan, V. Trends in phage types of Salmonella enterica serovars Enteritidis and Typhimurium isolated in Slovakia from 1995 to 2009. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 69, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.D.; Sodha, S.V.; Ayers, T.L.; Lynch, M.F.; Gould, L.H.; Tauxe, R.V. Produce-associated foodborne disease outbreaks, USA, 1998–2013. Epidemiology Infect. 2018, 146, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyedun, S.O.; Onarinde, B.A.; Swainson, M.; Dixon, R.A. Foodborne outbreaks of microbial infection from fresh produce in Europe and North America: A systematic review of data from this millennium. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanning, I.B.; Nutt, J.D.; Ricke, S.C. Salmonellosis outbreaks in the United States due to fresh produce: Sources and potential intervention measures. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesté, E.; Blanch, A.R.; Muniesa, M.; García-Aljaro, C.; Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Pascual-Benito, M.; Jofre, J. Bacteriophages in sewage: Abundance, roles, and applications. FEMS Microbes 2022, 3, xtac009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, I.; Retrofitting World’s 3rd Largest Treatment Plant with Ozonation and Improved Incinerators will Take 10 Years. CBC News. 2023. Available online: https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/montreal-wastewater-treatment-plant-1.6711208 (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- GovtCanada. Census Profile, 2021 Census of Population for Montreal. 2021. Available online: https://tinyurl.com/53fks2ad (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- Ramisetty, B.C.M.; Sudhakari, P.A. Bacterial ‘Grounded’ Prophages: Hotspots for Genetic Renovation and Innovation. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colello, R.; Ruiz, M.J.; Padín, V.M.; Rogé, A.D.; Leotta, G.; Padola, N.L.; Etcheverría, A.I. Detection and Characterization of Salmonella Serotypes in the Production Chain of Two Pig Farms in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Aiewsakun, P. Virus classification—Where do you draw the line? Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.; Brister, J.R. How to Name and Classify Your Phage: An Informal Guide. Viruses 2017, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Heu, S.; Ryu, S. Receptor diversity and host interaction of bacteriophages infecting Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohdes, C.; Resch, G.; Pirnay, J.-P.; Blasdel, B.G.; Debarbieux, L.; Gelman, D.; Górski, A.; Hazan, R.; Huys, I.; Kakabadze, E.; et al. Expert Opinion on Three Phage Therapy Related Topics: Bacterial Phage Resistance, Phage Training and Prophages in Bacterial Production Strains. Viruses 2018, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodovich, T.; Shkoporov, A.N.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Phage-mediated horizontal gene transfer and its implications for the human gut microbiome. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2022, 10, goac012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M. Bacteriophages and Food Production: Biocontrol and Bio-Preservation Options for Food Safety. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, T.G.; Feijoo-Siota, L.; Rama, J.R.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Viñas, M. Horizontal Gene Transfer Between Bacteriophages and Bacteria: Antibiotic Resistances and Toxin Production. In Horizontal Gene Transfer: Breaking Borders Between Living Kingdoms; Villa, T.G., Viñas, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 97–142. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki, S.; Yasuda, M.; Nishikawa, H.; Kuroda, M.; Ujihara, T.; Shuin, T.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Z.; Fujimoto, S.; Nasimuzzaman, M.D.; et al. Experimental protection of mice against lethal Staphylococcus aureus infection by novel bacteriophage φMR11. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, V.A. Bacteriophage lysins as effective antibacterials. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.A.; Logan, G.; Honghzuan, W.; Robert, V. The E34 Phage Tailspike Protein: An in vitro characterization, Structure Prediction, Potential Interaction with S. newington LPS and Cytotoxicity Assessment to Animal Cell Line. bioRxiv 2021. bioRxiv:2021.461090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Rabsch, W.; Broeker, N.K.; Barbirz, S. Bacteriophage tailspike protein based assay to monitor phase variable glucosylations in Salmonella O-antigens. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletic, S.; Simpson, D.J.; Szymanski, C.M.; Deyholos, M.K.; Menassa, R. A Plant-Produced Bacteriophage Tailspike Protein for the Control of Salmonella. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waseh, S.; Hanifi-Moghaddam, P.; Coleman, R.; Masotti, M.; Ryan, S.; Foss, M.; MacKenzie, R.; Henry, M.; Szymanski, C.M.; Tanha, J. Orally administered P22 phage tailspike protein reduces salmonella colonization in chickens: Prospects of a novel therapy against bacterial infections. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, I.; Ayariga, J.A.; Xu, J.; Adebanjo, A.; Robertson, B.K.; Samuel-Foo, M.; Ajayi, O.S. CBD resistant Salmonella strains are susceptible to Epsilon 34 phage tailspike protein. Front. Med. 2022, 10, 511232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phage | Salmonella Host Strain Used for Isolation * | Morphotype | New Classification | Old Classification | GenBank Accession Number | Genome Length (Kb) | No. of Coding Genes | No. of tRNA | G+C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SB3 | S. enterica ser. Enteritidis (S7) | Siphovirus | Genus: Jerseyvirus; Species: Jerseyvirus AG11 | Genus: Jerseyvirus; Species: Salmonella virus AG11 | MK578530 | 41.15 | 63 | 0 | 50.0 |
| SB6 | S. enterica ser. Javiana (S1297) | Siphovirus | Genus: Epseptimavirus | Genus: Haartmanvirus | MK809530 | 112.31 | 180 | 16 | 39.9 |
| SB9 | S. enterica ser. Saint-Paul (S1326) | Siphovirus | Genus: Epseptimavirus | Genus: Tequintavirus | MK867835 | 113.98 | 180 | 20 | 39.9 |
| SB10 | S. enterica ser. Typhimurium (S1295) | Siphovirus | Genus: Epseptimavirus; Species: Epseptimavirus fuchur | Genus: Tequintavirus; Species: Salmonella virus fuchur | MK947458 | 111.35 | 183 | 21 | 40.1 |
| SB13 | S. enterica ser. Typhimurium (S580) | Siphovirus | Genus: Epseptimavirus; Species: Epseptimavirus SB13. | Genus: Tequintavirus | MK947459 | 112.51 | 175 | 15 | 39.9 |
| SB15 | S. enterica ser. Braenderup (S3) | Siphovirus | Genus: Jerseyvirus; Species: Jerseyvirus AG11 | Genus: Jerseyvirus; Species: Salmonella virus AG11 | MK759883 | 41.44 | 73 | 0 | 50.0 |
| SB18 | S. enterica ser. Infantis (S43) | Myovirus | Genus: Ounavirinae; Species: Kolesnikvirus Ea214 | Genus: Ounavirinae; Species: Kolesnikvirus | MK759884 | 85.31 | 118 | 17 | 43.8 |
| SB28 | S. Typhi ser. T42 DEF 472 (S203) | Siphovirus | Genus: Macdonaldcampvirus; Species: Macdonaldcampvirus SB28 | Was not classified beyond Siphoviridae family | MK947460 | 45.13 | 73 | 0 | 46.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhandare, S.; Lawal, O.U.; Colavecchio, A.; Cadieux, B.; Zahirovich-Jovich, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Tompkins, E.; Amitrano, M.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Boyle, B.; et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Bacteriophages Identifies Two Novel Phage Species. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040695
Bhandare S, Lawal OU, Colavecchio A, Cadieux B, Zahirovich-Jovich Y, Zhong Z, Tompkins E, Amitrano M, Kukavica-Ibrulj I, Boyle B, et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Bacteriophages Identifies Two Novel Phage Species. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(4):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040695
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhandare, Sudhakar, Opeyemi U. Lawal, Anna Colavecchio, Brigitte Cadieux, Yella Zahirovich-Jovich, Zeyan Zhong, Elizabeth Tompkins, Margot Amitrano, Irena Kukavica-Ibrulj, Brian Boyle, and et al. 2024. "Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Bacteriophages Identifies Two Novel Phage Species" Microorganisms 12, no. 4: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040695
APA StyleBhandare, S., Lawal, O. U., Colavecchio, A., Cadieux, B., Zahirovich-Jovich, Y., Zhong, Z., Tompkins, E., Amitrano, M., Kukavica-Ibrulj, I., Boyle, B., Wang, S., Levesque, R. C., Delaquis, P., Danyluk, M., & Goodridge, L. (2024). Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Bacteriophages Identifies Two Novel Phage Species. Microorganisms, 12(4), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040695








