Facial Skin Microbiome Composition and Functional Shift with Aging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Recruitment and Sample Preparation
2.2. Skin Characterization of the Panelists
2.2.1. Questionnaire Acquisition Methodology
2.2.2. Skin Hydration Measurement
2.2.3. Skin pH Measurement
2.3. Bacterial and Fungal Sampling and DNA Extraction
- Inside the crow’s feet wrinkles (wrinkle), three samples were taken per wrinkle zone and collected for 30 s each using Puritan HydraFlock swabs mini-tipped. Following collection, all 3 samples were pooled prior to DNA extraction.
- Around the crow’s feet/under eye area, two samples were taken and collected for 60 s each using Puritan HydraFlock swabs with elongated tips.Following collection, both samples were pooled prior to DNA extraction.
- Finally, on the cheek adjacent to earlobe area (control), two samples were taken and collected for 60 s each using Puritan HydraFlock swabs with elongated tips. Following collection, both samples were pooled prior to DNA extraction.
2.4. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.5. Analysis of the Skin Microbiome
2.5.1. Taxa and Statistical Analysis
2.5.2. Metadata Analysis
2.5.3. Taxonomy Analysis—The Biological Model
2.5.4. Functional Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Skin Characterization of the Panelists
3.2. Library Preparation Results
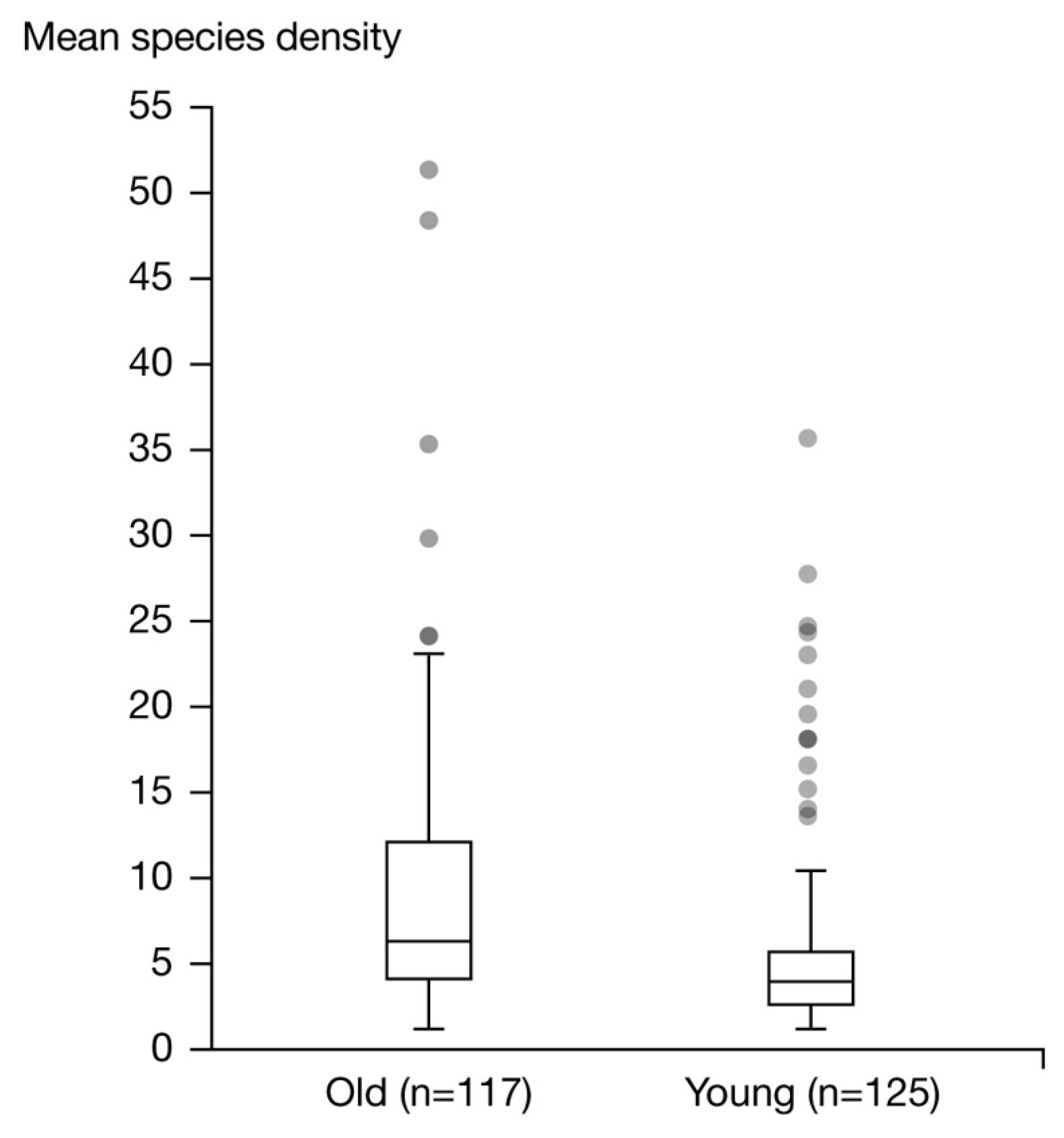
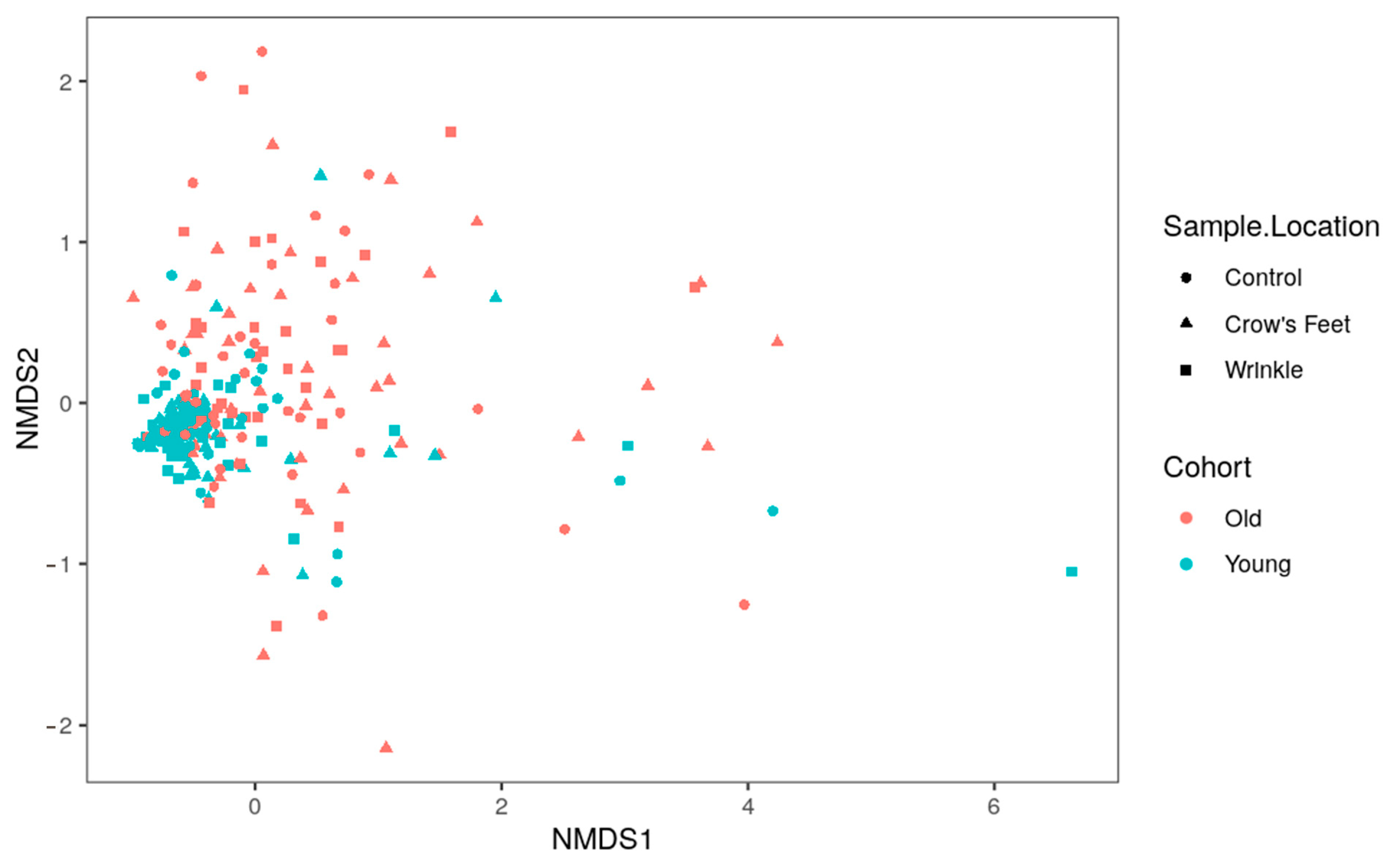
3.3. Comparison of the Microbiome of Young and Old Skin
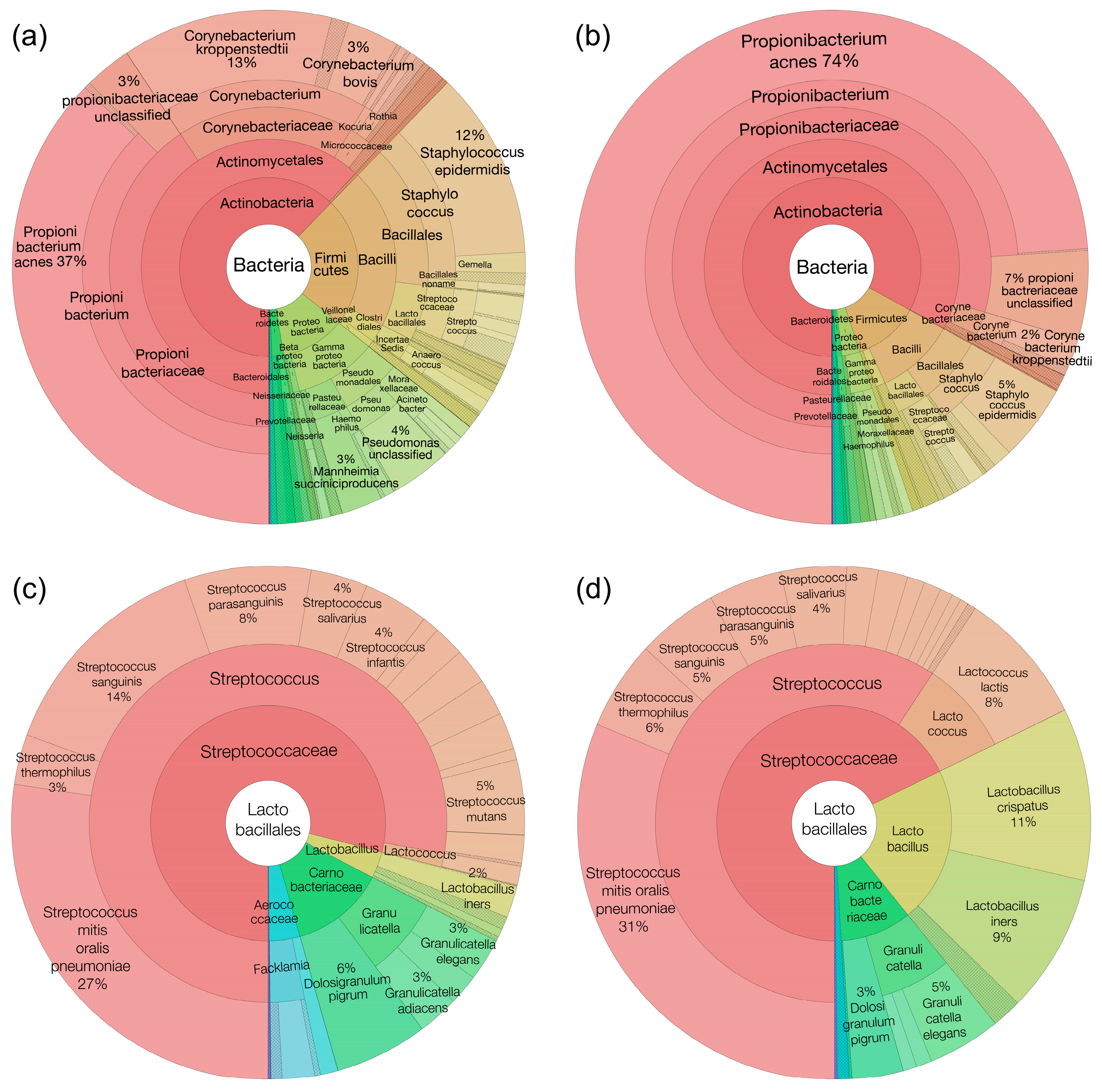
3.3.1. Taxonomy Results—Group Skin Microbiome Composition and Structure
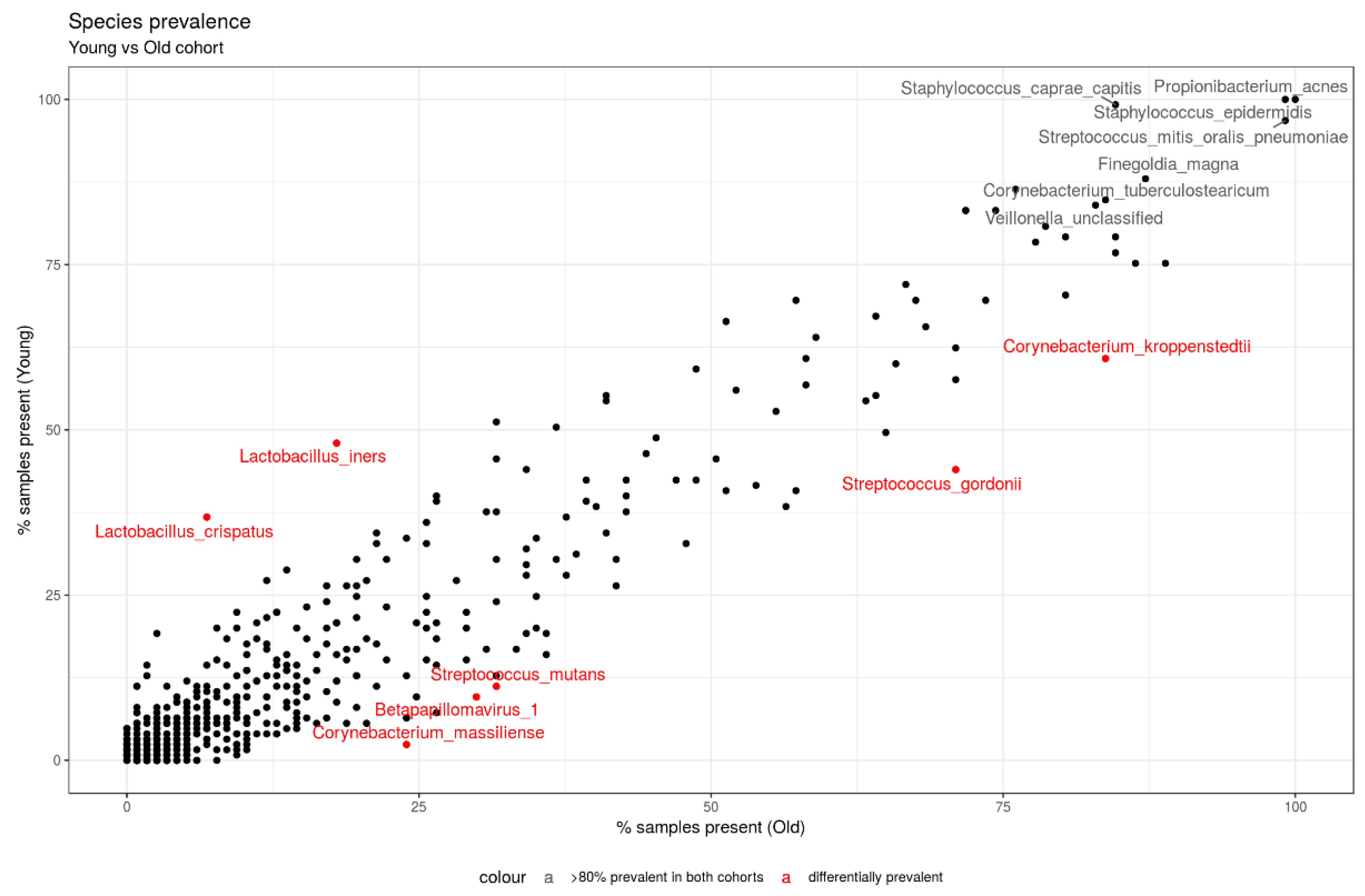
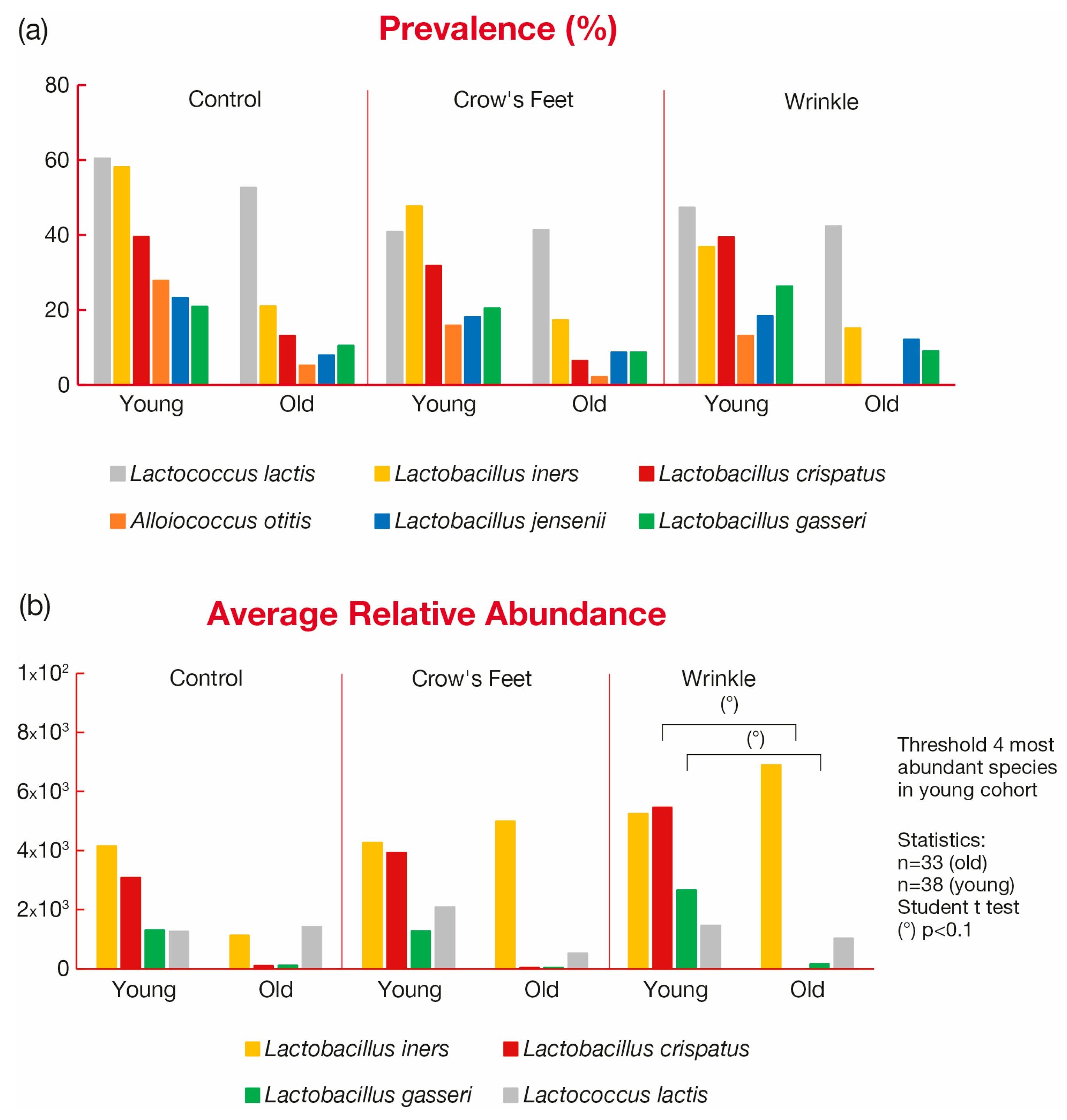
3.3.2. Taxonomy Results—Prevalence Analysis
3.3.3. Metadata Analysis Results with the Biological Model
3.3.4. Taxonomy Results—The Biological Model
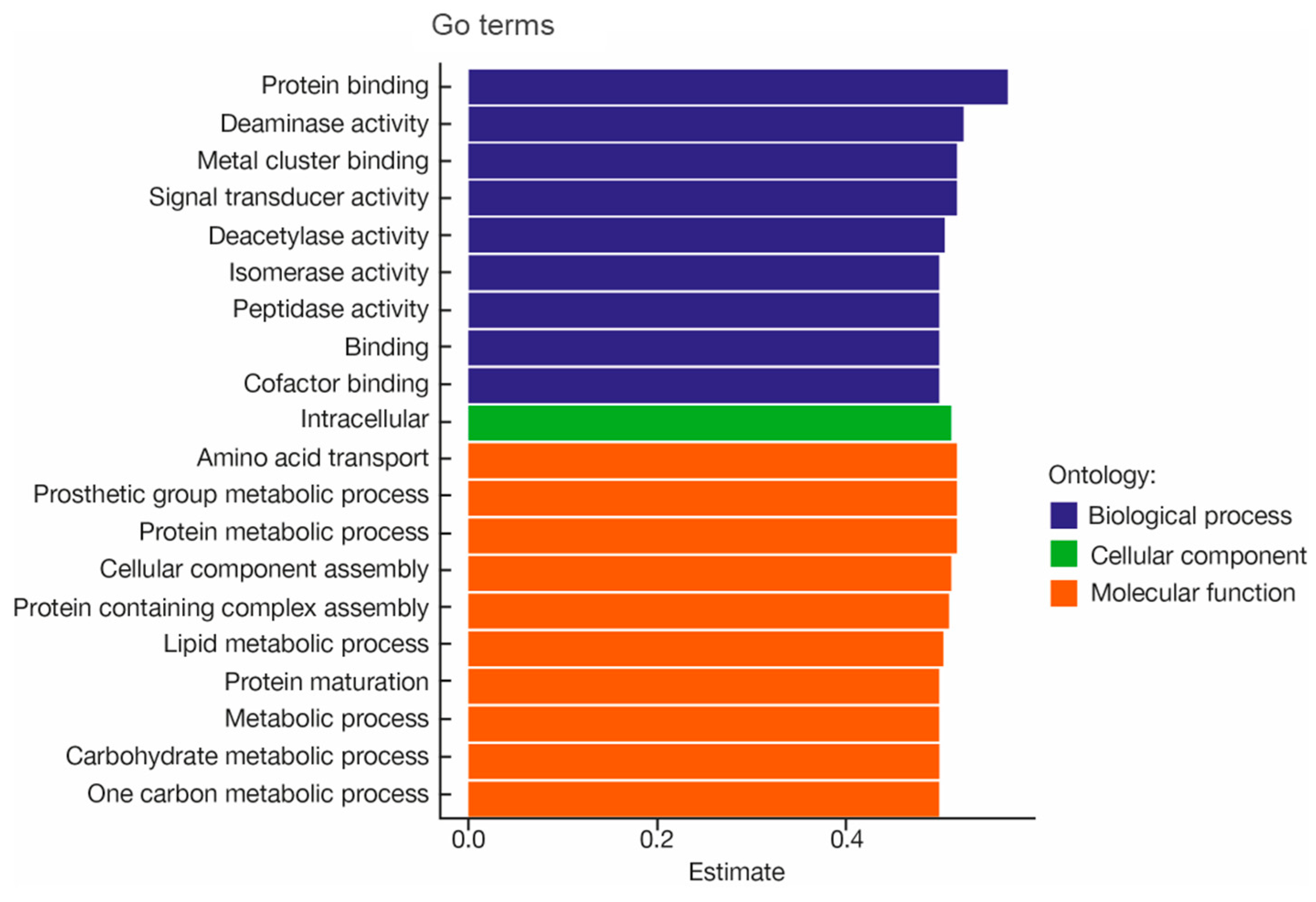
3.3.5. Functional Genomic Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flowers, L.; Grice, E.A. The Skin Microbiota: Balancing Risk and Reward. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxberger, M.; Cenizo, V.; Cassir, N.; La Scola, B. Challenges in Exploring and Manipulating the Human Skin Microbiome. Microbiome 2021, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournière, M.; Latire, T.; Souak, D.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Bedoux, G. Staphylococcus Epidermidis and Cutibacterium Acnes: Two Major Sentinels of Skin Microbiota and the Influence of Cosmetics. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, H.; Kurosumi, M.; Kanto, H. New Solution of Beauty Problem by Staphylococcus Hominis: Relevance between Skin Microbiome and Skin Condition in Healthy Subject. Skin Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The Human Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulongne, V.; Sauvage, V.; Hebert, C.; Dereure, O.; Cheval, J.; Gouilh, M.A.; Pariente, K.; Segondy, M.; Burguière, A.; Manuguerra, J.-C.; et al. Human Skin Microbiota: High Diversity of DNA Viruses Identified on the Human Skin by High Throughput Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probst, A.J.; Auerbach, A.K.; Moissl-Eichinger, C. Archaea on Human Skin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, N.; Kavanagh, K.; Tseng, S.C.G. Under the Lash: Demodex Mites in Human Diseases. Biochemist 2009, 31, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grice, E.A.; Segre, J.A. The Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.K.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Fierer, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R. Bacterial Community Variation in Human Body Habitats across Space and Time. Science 2009, 326, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findley, K.; Oh, J.; Yang, J.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.; Meyer, J.A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Nomicos, E.; Park, M.; NIH Intramural Sequencing Center Comparative Sequencing Program; et al. Topographic Diversity of Fungal and Bacterial Communities in Human Skin. Nature 2013, 498, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, J. Oxidative Stress in the Skin: Impact and Related Protection. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.; Clavaud, C.; Guinot, F.; Bourokba, N.; Nouveau, S.; Mezzache, S.; Palazzi, P.; Appenzeller, B.M.R.; Tenenhaus, A.; Leung, M.H.Y.; et al. Multi-Omics Analysis to Decipher the Molecular Link between Chronic Exposure to Pollution and Human Skin Dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.H.Y.; Tong, X.; Bastien, P.; Guinot, F.; Tenenhaus, A.; Appenzeller, B.M.R.; Betts, R.J.; Mezzache, S.; Li, J.; Bourokba, N.; et al. Changes of the Human Skin Microbiota upon Chronic Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Pollutants. Microbiome 2020, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.; Ciardiello, T.; Franzoni, M.; Pasini, F.; Giuliani, G.; Rinaldi, F. Effect of Commonly Used Cosmetic Preservatives on Skin Resident Microflora Dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moitinho-Silva, L.; Boraczynski, N.; Emmert, H.; Baurecht, H.; Szymczak, S.; Schulz, H.; Haller, D.; Linseisen, J.; Gieger, C.; Peters, A.; et al. Host Traits, Lifestyle and Environment Are Associated with Human Skin Bacteria. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dréno, B.; Araviiskaia, E.; Berardesca, E.; Gontijo, G.; Sanchez Viera, M.; Xiang, L.F.; Martin, R.; Bieber, T. Microbiome in Healthy Skin, Update for Dermatologists. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Dai, W.; Liang, Y.; Shen, C.; Li, Y.; Jiao, L.; Bian, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Distinct Skin Microbiota Imbalance and Responses to Clinical Treatment in Children With Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagnelie, M.-A.; Montassier, E.; Khammari, A.; Mounier, C.; Corvec, S.; Dréno, B. Inflammatory Skin Is Associated with Changes in the Skin Microbiota Composition on the Back of Severe Acne Patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanvit, P.; Konkel, J.E.; Jiao, X.; Kasagi, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, R.; Chia, C.; Ajami, N.J.; Smith, D.P.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Antibiotics in Neonatal Life Increase Murine Susceptibility to Experimental Psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzioueche, H.; Simonyté Sjödin, K.; West, C.E.; Khemis, A.; Rocchi, S.; Passeron, T.; Tulic, M.K. Analysis of Matched Skin and Gut Microbiome of Patients with Vitiligo Reveals Deep Skin Dysbiosis: Link with Mitochondrial and Immune Changes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keum, H.L.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, T.; Kim, S.; An, S.; Sul, W.J. Structures of the Skin Microbiome and Mycobiome Depending on Skin Sensitivity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, P.C. Skin Microbiome as Years Go By. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibagaki, N.; Suda, W.; Clavaud, C.; Bastien, P.; Takayasu, L.; Iioka, E.; Kurokawa, R.; Yamashita, N.; Hattori, Y.; Shindo, C.; et al. Aging-Related Changes in the Diversity of Women’s Skin Microbiomes Associated with Oral Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Oh, H.N.; Park, T.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.G.; An, S.; Sul, W.J. Aged Related Human Skin Microbiome and Mycobiome in Korean Women. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.; Bascom, C.C.; Hu, P.; Binder, R.L.; Fadayel, G.; Huggins, T.G.; Jarrold, B.B.; Osborne, R.; Rocchetta, H.L.; Swift, D.; et al. Aging-Associated Changes in the Adult Human Skin Microbiome and the Host Factors That Affect Skin Microbiome Composition. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1934–1946.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, P.J.; Zhou, W.; Santiago, A.; Driscoll, S.; Fleming, E.; Voigt, A.Y.; Chun, O.K.; Grady, J.J.; Kuchel, G.A.; Robison, J.T.; et al. Associations of the Skin, Oral and Gut Microbiome with Aging, Frailty and Infection Risk Reservoirs in Older Adults. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, T.; Bouslimani, A.; Huang, S.; Hansen, S.T.; Clavaud, C.; Azouaoui, A.; Ott, A.; Gueniche, A.; Bouez, C.; Zheng, Q.; et al. A Multi-Study Analysis Enables Identification of Potential Microbial Features Associated with Skin Aging Signs. Front. Aging 2024, 4, 1304705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugé, R.; Rouaud-Tinguely, P.; Breugnot, J.; Servaes, K.; Grimaldi, C.; Roth, M.-P.; Coppin, H.; Closs, B. Shift in Skin Microbiota of Western European Women across Aging. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Son, S.-M.; Park, H.; Kim, B.K.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, H.; Huh, C.S. Taxonomic Profiling of Skin Microbiome and Correlation with Clinical Skin Parameters in Healthy Koreans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Li, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Wei, Q.; Jiang, L.; Duan, C.; Jia, H.; Tan, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Integration of Skin Phenome and Microbiome Reveals the key Role of Bacteria in Human Skin Aging. Res. Sq. (preprint) 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fleming, E.; Legendre, G.; Roux, L.; Latreille, J.; Gendronneau, G.; Forestier, S.; Oh, J. Skin Microbiome Attributes Associate with Biophysical Skin Aging; Genomics. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriu, P.A.; Iker, B.; Malik, K.; Leung, H.; Mohn, W.W.; Hillebrand, G.G. New Insights into the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors That Shape the Human Skin Microbiome. mBio 2019, 10, e00839-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miranda, R.B.; Weimer, P.; Rossi, R.C. Effects of Hydrolyzed Collagen Supplementation on Skin Aging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Park, C.; Yoon, Y.; Lim, D.-H.; Yeo, H.; Kang, S.; Lee, Y.-G.; Beak, N.-I.; et al. Spermidine-Induced Recovery of Human Dermal Structure and Barrier Function by Skin Microbiome. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flament, F.; Bazin, R.; Qiu, H. Skin Aging Atlas; Éditions Med’com: Paris, France, 2017; ISBN 9782354032463. [Google Scholar]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, D.T.; Franzosa, E.A.; Tickle, T.L.; Scholz, M.; Weingart, G.; Pasolli, E.; Tett, A.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. MetaPhlAn2 for Enhanced Metagenomic Taxonomic Profiling. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubucker, S.; Segata, N.; Goll, J.; Schubert, A.M.; Izard, J.; Cantarel, B.L.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Zucker, J.; Thiagarajan, M.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Metabolic Reconstruction for Metagenomic Data and Its Application to the Human Microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, C. Well-Aging: Early Detection of Skin Aging Signs. Dermatol. Clin. 2016, 34, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Haiminen, N.; Carrieri, A.-P.; Hu, R.; Jiang, L.; Parida, L.; Russell, B.; Allaband, C.; Zarrinpar, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; et al. Human Skin, Oral, and Gut Microbiomes Predict Chronological Age. mSystems 2020, 5, e00630-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bai, X.; Peng, T.; Yi, X.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; He, T.; Wang, X.; et al. New Insights Into the Skin Microbial Communities and Skin Aging. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 565549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtimäki, J.; Karkman, A.; Laatikainen, T.; Paalanen, L.; von Hertzen, L.; Haahtela, T.; Hanski, I.; Ruokolainen, L. Patterns in the Skin Microbiota Differ in Children and Teenagers between Rural and Urban Environments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, A.M.; Gallo, R.L. Host-Microbiome Interactions and Recent Progress into Understanding the Biology of Acne Vulgaris. Microbiome 2018, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liavonchanka, A.; Hornung, E.; Feussner, I.; Rudolph, M.G. Structure and Mechanism of the Propionibacterium Acnes Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Isomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2576–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauch, A.; Schneider, J.; Szczepanowski, R.; Tilker, A.; Viehoever, P.; Gartemann, K.-H.; Arnold, W.; Blom, J.; Brinkrolf, K.; Brune, I.; et al. Ultrafast Pyrosequencing of Corynebacterium Kroppenstedtii DSM44385 Revealed Insights into the Physiology of a Lipophilic Corynebacterium That Lacks Mycolic Acids. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauch, A.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Soriano, F. A Microbiological and Clinical Review on Corynebacterium Kroppenstedtii. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, B.M.; Thompson, K.G.; Antonescu, C.; Florea, L.; Mongodin, E.F.; Bui, J.; Fischer, A.H.; Pasieka, H.B.; Garza, L.A.; Kang, S.; et al. Characterization and Analysis of the Skin Microbiota in Rosacea: A Case-Control Study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filaire, E.; Vialleix, C.; Cadoret, J.-P.; Guénard, S.; Muller, C.; Dreux-Zigha, A.; Berthon, J.-Y. Characterization of Reactive and Sensitive Skin Microbiota: Effect of Halymenia Durvillei (HD) Extract Treatment. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.M.; Ma, J.; Prince, A.L.; Antony, K.M.; Seferovic, M.D.; Aagaard, K.M. Maturation of the Infant Microbiome Community Structure and Function across Multiple Body Sites and in Relation to Mode of Delivery. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhou, M.; Song, L.; He, C. Skin Bacterial Structure of Young Females in China: The Relationship between Skin Bacterial Structure and Facial Skin Types. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.G.; Moreira, D.A.; Gullón, P.; Gullón, B.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Tavaria, F.K. Topical Application of Probiotics in Skin: Adhesion, Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm in Vitro Assays. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanghe, L.; Spacova, I.; Van Malderen, J.; Oerlemans, E.; Claes, I.; Lebeer, S. The Role of Lactobacilli in Inhibiting Skin Pathogens. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Ko, Y.; Sim, J.-H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.J. Effect of Bacteriocin Produced by Lactococcus Sp. HY 449 on Skin-Inflammatory Bacteria. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vougiouklaki, D.; Tsironi, T.; Tsantes, A.G.; Tsakali, E.; Van Impe, J.F.M.; Houhoula, D. Probiotic Properties and Antioxidant Activity In Vitro of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from Inflammation to Proliferation: A Critical Step during Wound Healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Chen, A.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, S.; Chen, D.; Yu, R. Lactobacillus for the Treatment and Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical and Experimental Evidence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1137275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, S.; Parkar, S.; Miller, E.A.; Kovarik, J.E.; Seed Health Inc. Topical Application of Lactobacillus crispatus to Ameliorate Barrier Damage and Inflammation. U.S. Patent 11826388B2, 22 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Truglio, M.; Sivori, F.; Cavallo, I.; Abril, E.; Licursi, V.; Fabrizio, G.; Cardinali, G.; Pignatti, M.; Toma, L.; Valensise, F.; et al. Modulating the Skin Mycobiome-Bacteriome and Treating Seborrheic Dermatitis with a Probiotic-Enriched Oily Suspension. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duar, R.M.; Lin, X.B.; Zheng, J.; Martino, M.E.; Grenier, T.; Pérez-Muñoz, M.E.; Leulier, F.; Gänzle, M.; Walter, J. Lifestyles in Transition: Evolution and Natural History of the Genus Lactobacillus. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, S27–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahim, O.; Wu, Q.; Price, T.K.; Pistone, G.; Diebel, K.; Bugni, T.S.; Wolfe, A.J. Phenyl-Lactic Acid Is an Active Ingredient in Bactericidal Supernatants of Lactobacillus crispatus. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e0036021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, V.; Loimaranta, V.; Pekkala, A.; Edelman, S.; Antikainen, J.; Kylväjä, R.; Laaksonen, M.; Laakkonen, L.; Finne, J.; Korhonen, T.K. Glutamine Synthetase and Glucose-6-Phosphate Isomerase Are Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins of Lactobacillus crispatus Released by Epithelial Cathelicidin LL-37. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, T.; Virkola, R.; Westerlund, B.; Bjorkman, Y.; Sillanpaa, J.; Vartio, T.; Kalkkinen, N.; Korhonen, T.K. A Collagen-Binding S-Layer Protein in Lactobacillus crispatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.; Valacchi, G. Surface Lipids as Multifunctional Mediators of Skin Responses to Environmental Stimuli. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 321494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, R.L.; Nakatsuji, T. Microbial Symbiosis with the Innate Immune Defense System of the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Descriptive Statistics | Age | Skin pH | Corneometer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old group | Average | 62.82 | 5.05 | 46.10 |
| Median | 62.00 | 5.06 | 43.00 | |
| Standard deviation | 4.69 | 0.59 | 11.37 | |
| Subjects | 49 | N/A | N/A | |
| Young group 1 | Average | 26.3 | 4.93 | 50.5 |
| Median | 26.0 | 4.89 | 50.3 | |
| Standard deviation | 5.0 | 0.47 | 11.9 | |
| Subjects | 47 | N/A | N/A |
| Metadata | Adjusted R2 | AIC 1 | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hormone supplements Y.N. | 0.045 | 734.046 | 6.950 | 0.002 |
| Shower frequency | 0.066 | 729.960 | 6.061 | 0.002 |
| Average sleep (open-ended) | 0.076 | 728.183 | 3.726 | 0.002 |
| Sleep pattern changes Y.N. | 0.086 | 726.856 | 3.265 | 0.002 |
| Processed foods frequency | 0.093 | 725.983 | 2.804 | 0.004 |
| pH | 0.099 | 725.353 | 2.554 | 0.006 |
| BMI | 0.105 | 724.822 | 2.447 | 0.006 |
| Tobacco use frequency | 0.110 | 724.320 | 2.408 | 0.008 |
| Antiaging products frequency | 0.116 | 723.673 | 2.537 | 0.004 |
| Cleansing conditioner frequency | 0.122 | 723.182 | 2.375 | 0.006 |
| Body wash non-medicated frequency | 0.128 | 722.510 | 2.538 | 0.002 |
| Personal birth | 0.133 | 722.103 | 2.275 | 0.008 |
| GO Terms in the Young Group | Variable | p-Value | Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO.0016209..antioxidant.activity | Young group | 0.001 | 0.352 |
| GO.0009372..quorum.sensing | Young group | 0.001 | 0.376 |
| GO.0001871..pattern.binding | Young group | 0.005 | 0.251 |
| GO.0031640..killing.of.cells.of.other.organism | Young group | 0.04 | 0.212 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garlet, A.; Andre-Frei, V.; Del Bene, N.; Cameron, H.J.; Samuga, A.; Rawat, V.; Ternes, P.; Leoty-Okombi, S. Facial Skin Microbiome Composition and Functional Shift with Aging. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12051021
Garlet A, Andre-Frei V, Del Bene N, Cameron HJ, Samuga A, Rawat V, Ternes P, Leoty-Okombi S. Facial Skin Microbiome Composition and Functional Shift with Aging. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(5):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12051021
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarlet, Allison, Valerie Andre-Frei, Nicolas Del Bene, Hunter James Cameron, Anita Samuga, Vimal Rawat, Philipp Ternes, and Sabrina Leoty-Okombi. 2024. "Facial Skin Microbiome Composition and Functional Shift with Aging" Microorganisms 12, no. 5: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12051021
APA StyleGarlet, A., Andre-Frei, V., Del Bene, N., Cameron, H. J., Samuga, A., Rawat, V., Ternes, P., & Leoty-Okombi, S. (2024). Facial Skin Microbiome Composition and Functional Shift with Aging. Microorganisms, 12(5), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12051021







