Imaging of Spondylodiscitis: A Comprehensive Updated Review—Multimodality Imaging Findings, Differential Diagnosis, and Specific Microorganisms Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Epidemiology
1.2. Complications
1.3. Clinical Features
1.4. General Biological Features
2. Imaging in the Initial Assessment of Suspected Spondylodiscitis
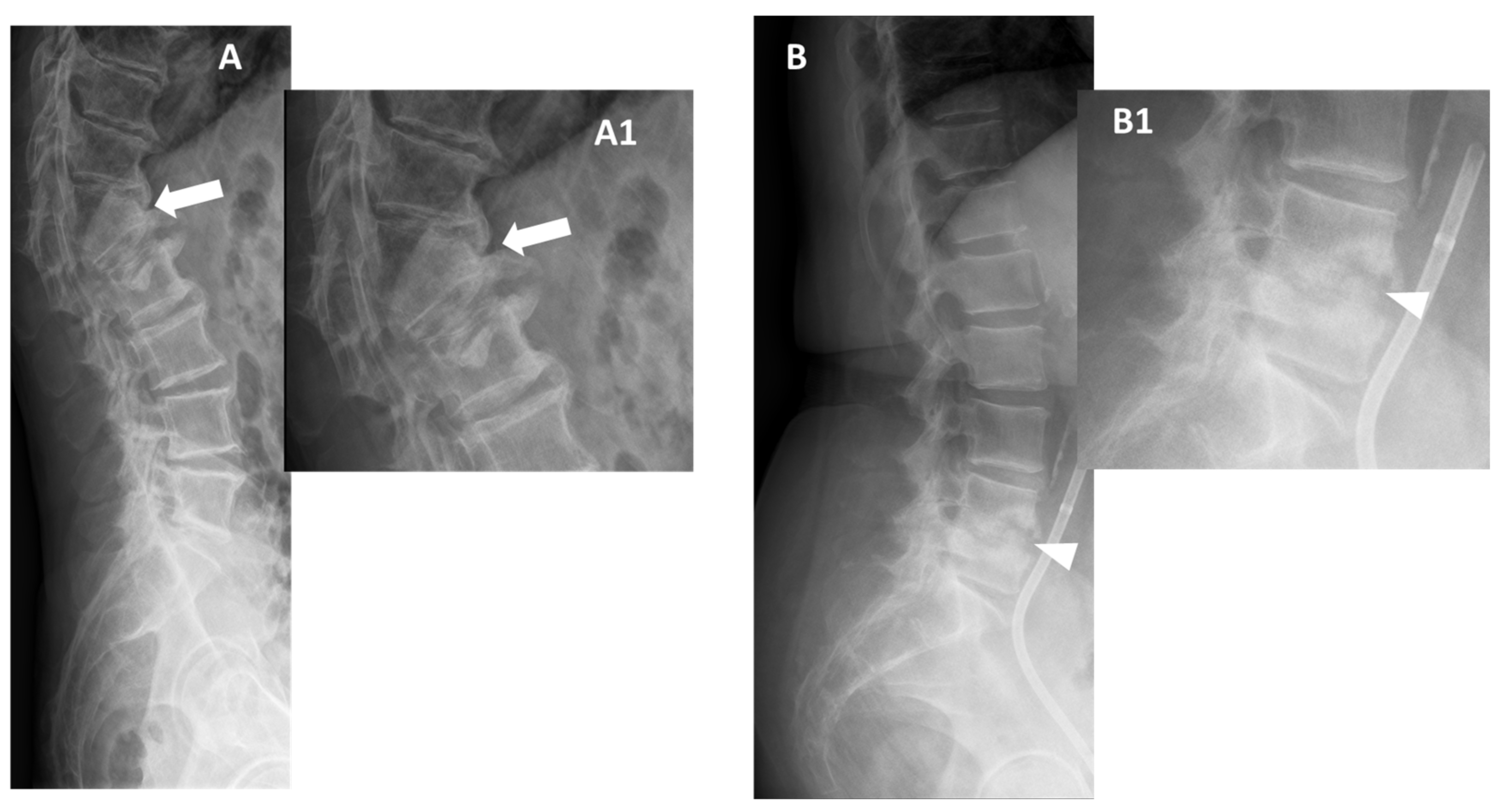
2.1. Conventional Radiographs
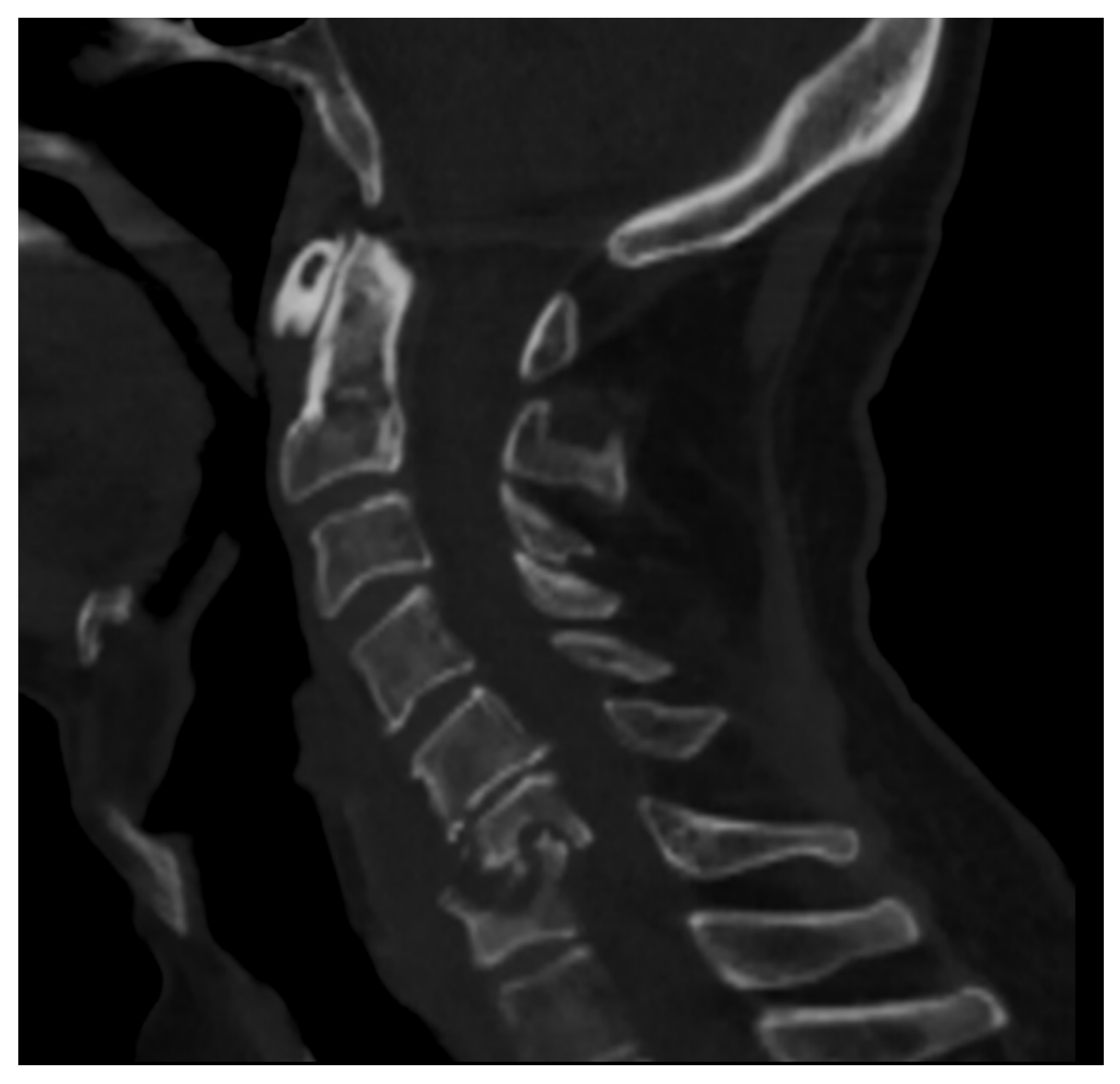
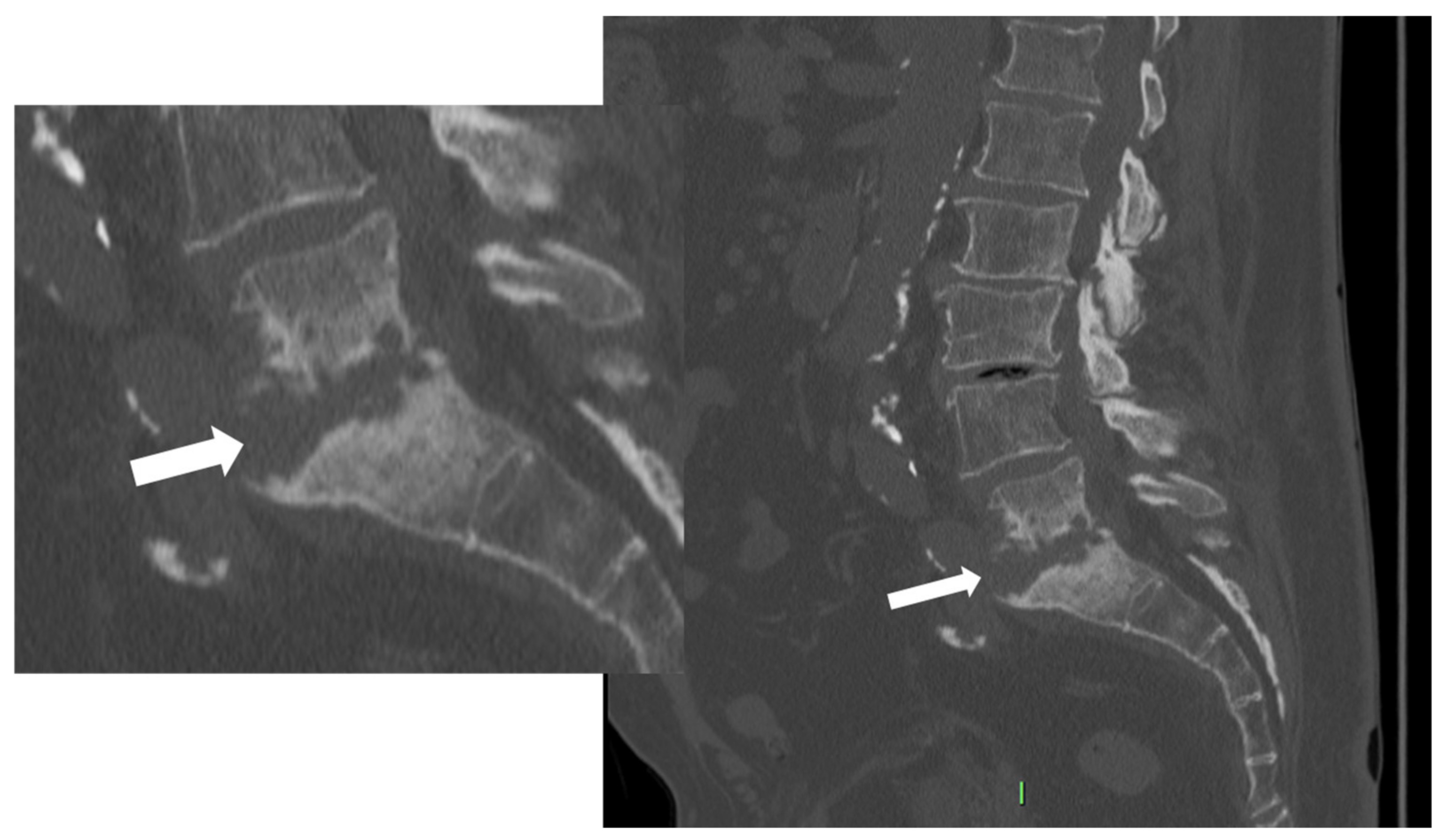
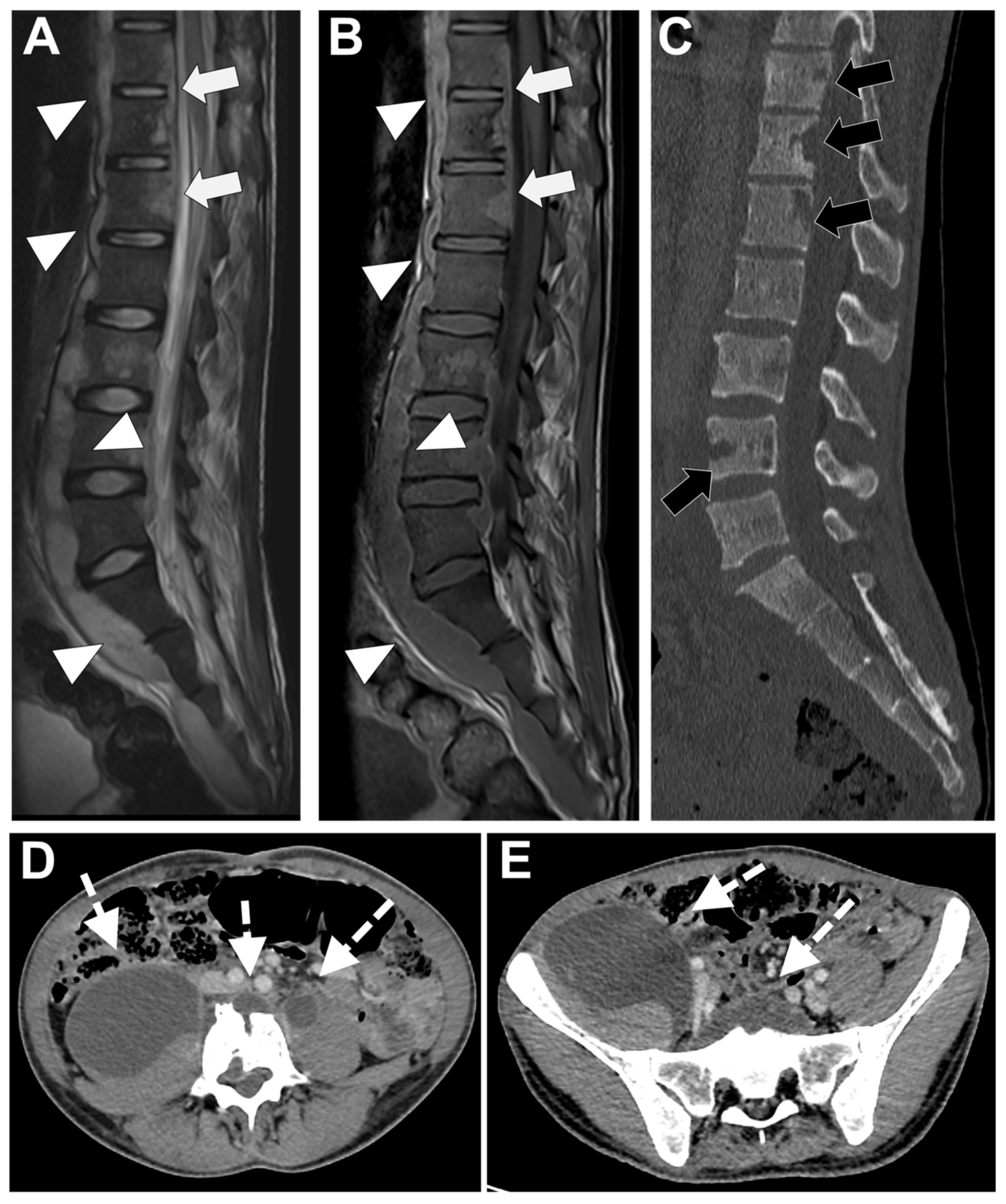
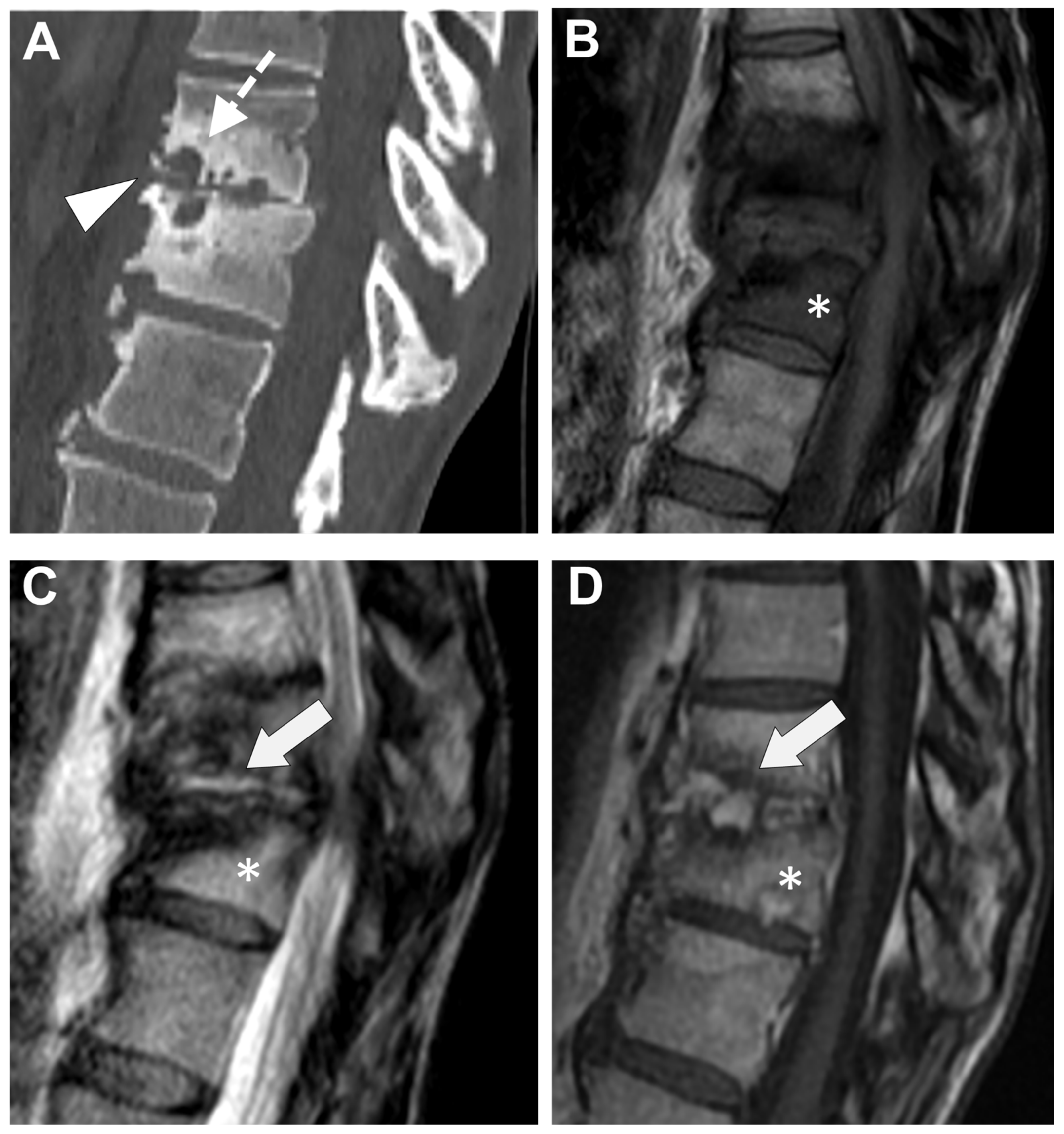
2.2. Computer Tomography (CT)
- Fragmentation or erosive changes in the vertebral endplates;
- Ill-defined reactive sclerosis or osteopenia;
- Intra-discal hypodensity;
- Soft tissue swelling that obscures the fat planes surrounding the vertebral body.
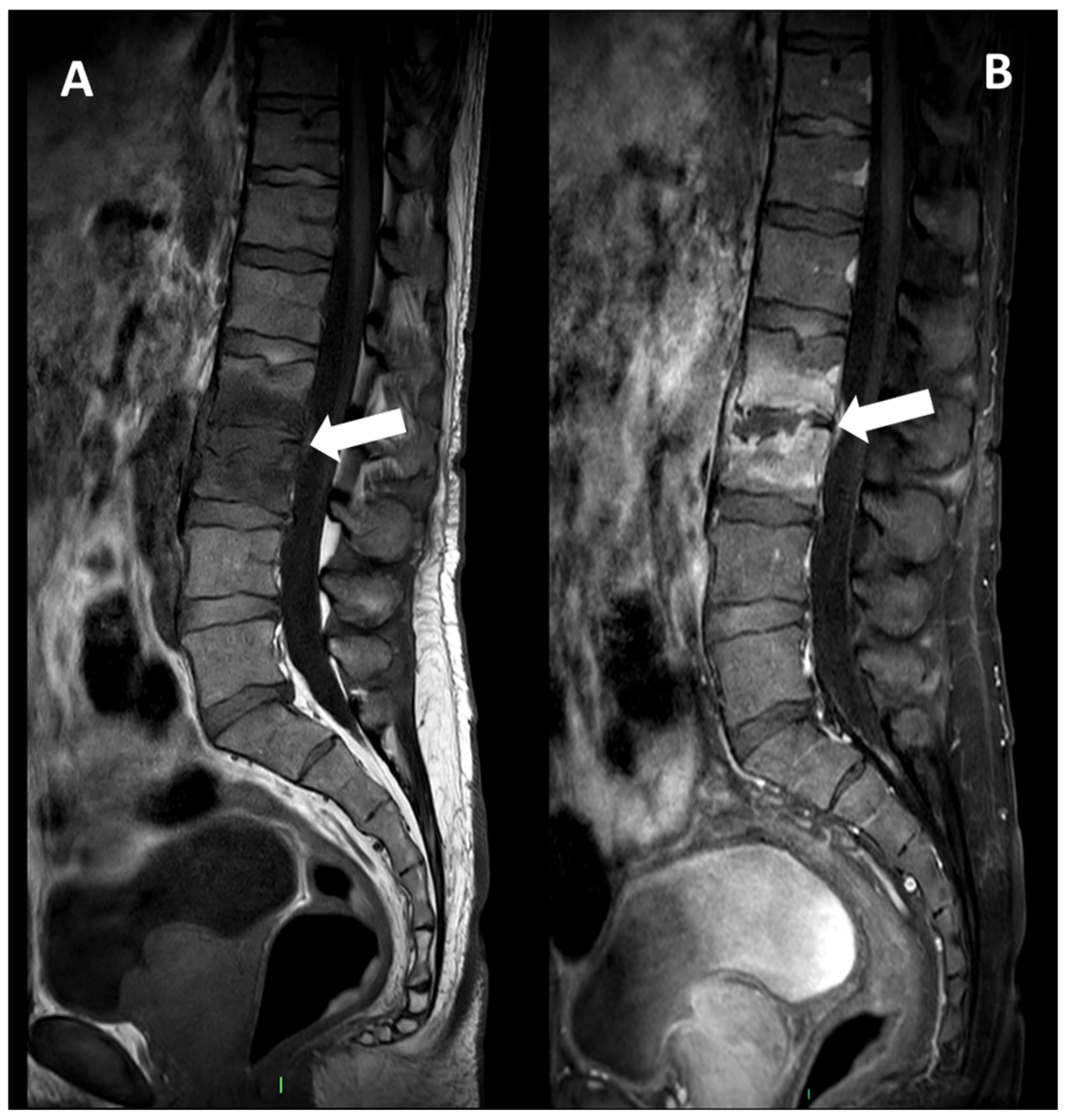
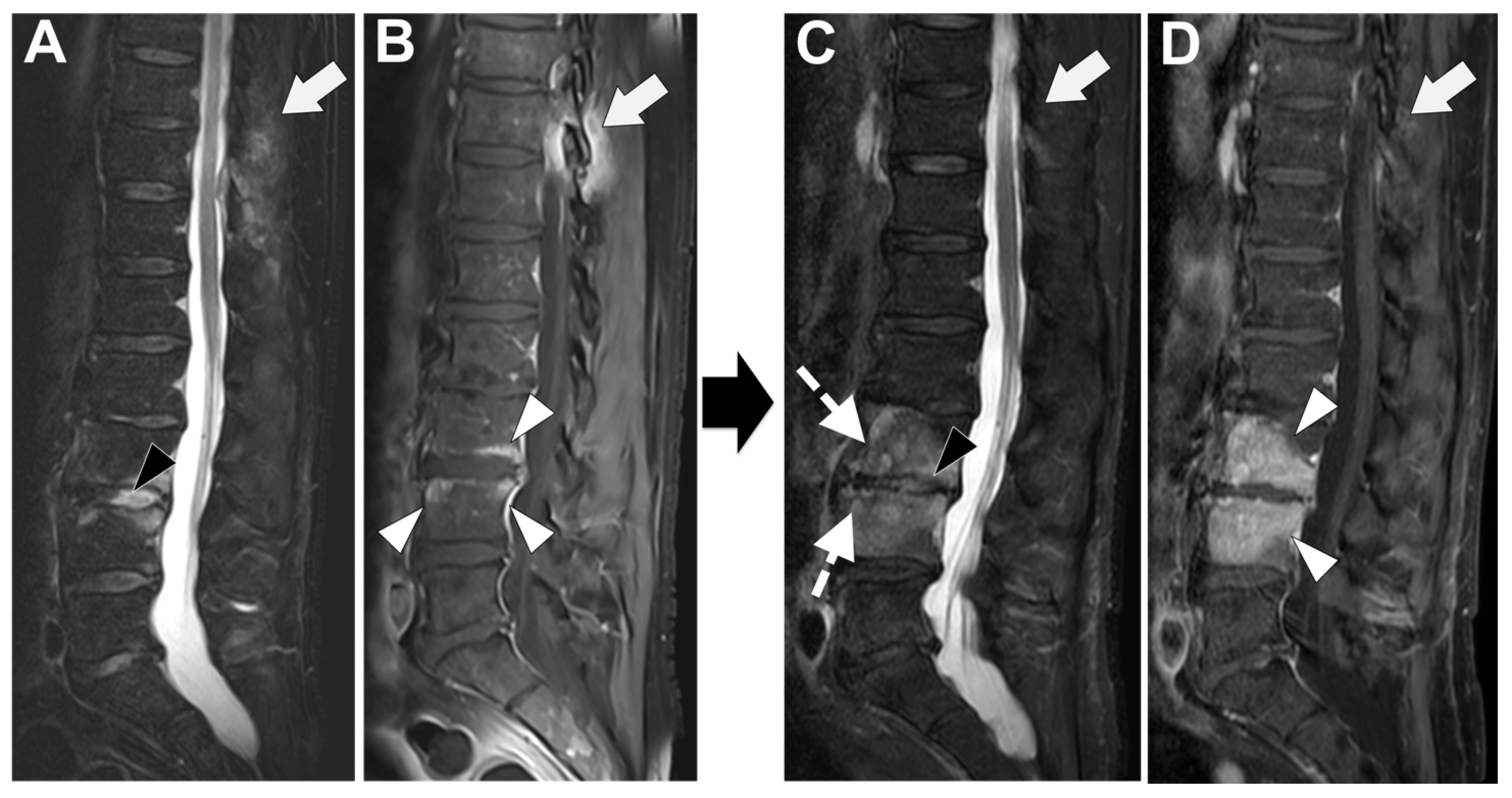
2.3. MRI
2.4. Nuclear Medicine
2.5. Imaging of Associated Conditions
3. Specific Microorganism Diagnosis
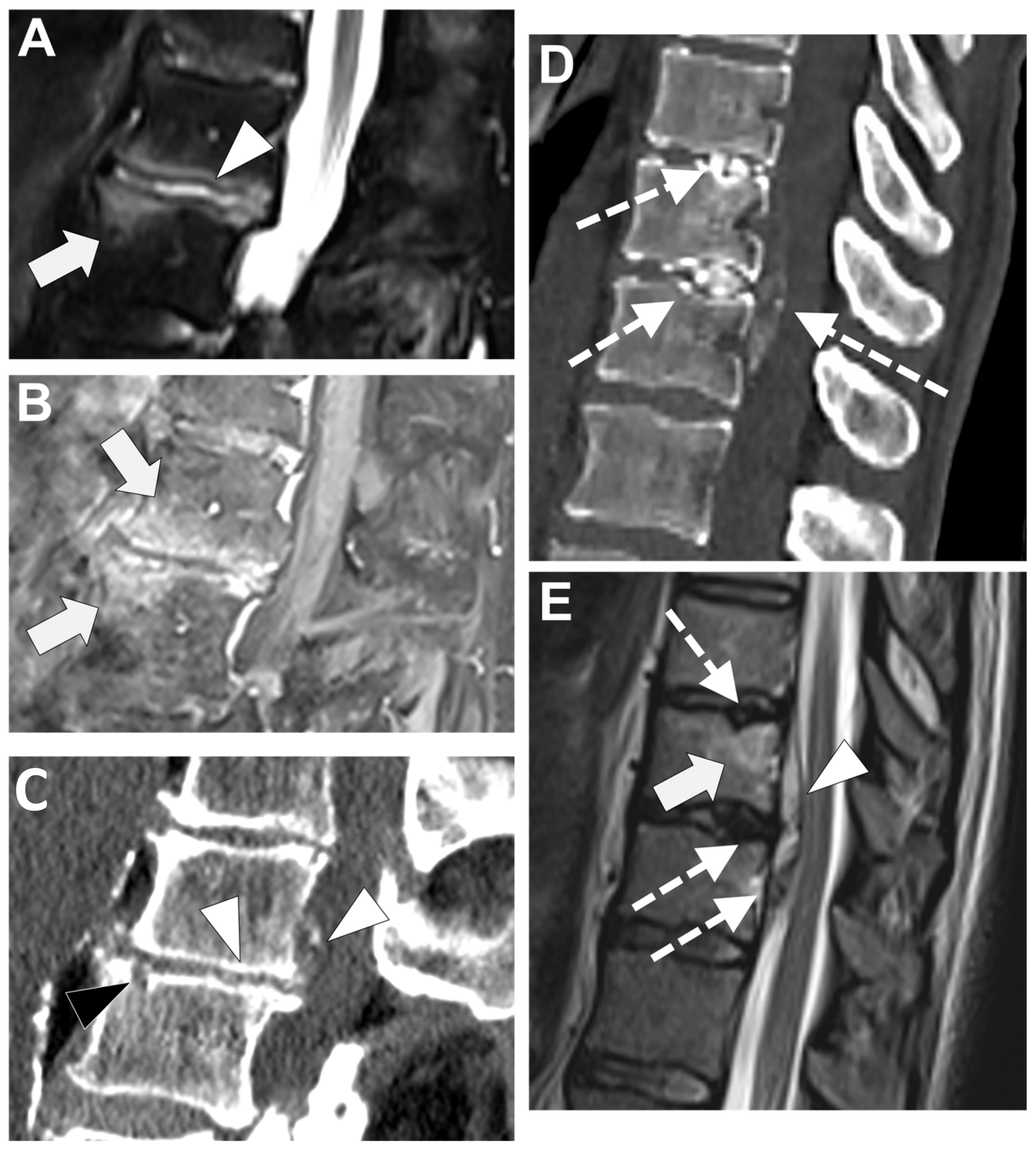
3.1. MR and Other Imaging Tools in the Differential Diagnosis between Tubercular and Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis
3.2. Other Microorganisms
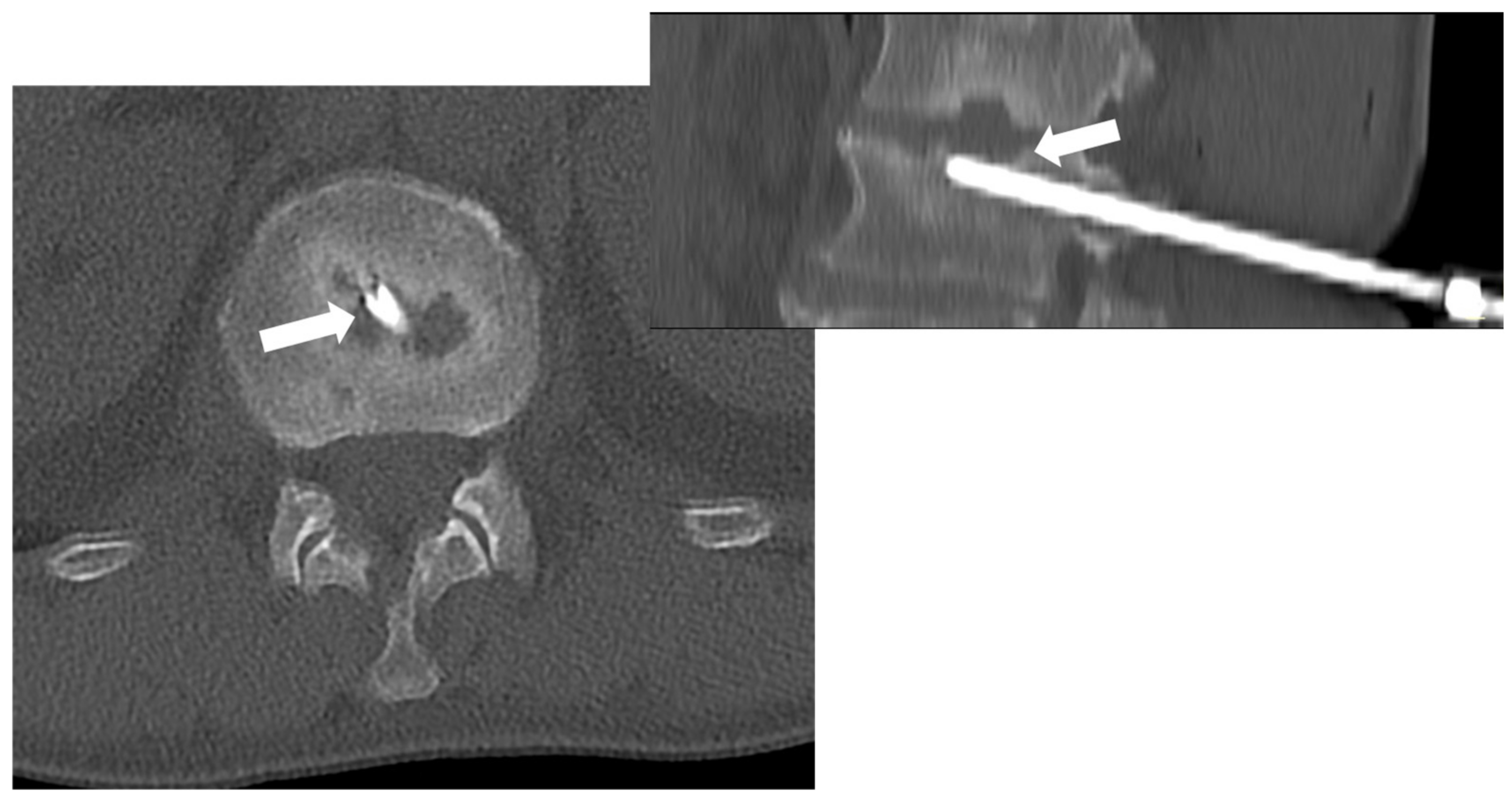
3.3. Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy
4. Differential Diagnoses
4.1. Degenerative Endplates Changes
4.2. Andersson Lesion
4.3. Spinal Involvement in SAPHO Syndrome
4.4. Micro-Crystalline Spondylodiscitis
4.5. Destructive Spondyloarthropathy in Hemodialyzed Patients
4.6. Neuropathic Spinal Arthropathy
5. Future Perspective
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grammatico, L.; Baron, S.; Rusch, E.; Lepage, B.; Surer, N.; Desenclos, J.C.; Besnier, J.M. Epidemiology of vertebral osteomyelitis (VO) in France: Analysis of hospital-discharge data 2002–2003. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelsom, J.; Solberg, C.O. Vertebral osteomyelitis at a Norwegian university hospital 1987–1997: Clinical features, laboratory findings and outcome. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 30, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joughin, E.; McDougall, C.; Parfitt, C.; Yong-Hing, K.; Kirkaldy-Willis, W.H. Causes and clinical management of vertebral osteomyelitis in Saskatchewan. Spine 1991, 16, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantoni, M.; Trecarichi, E.M.; Rossi, B.; Mazzotta, V.; Di Giacomo, G.; Nasto, L.A.; Di Meco, E.; Pola, E. Epidemiological and clinical features of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16 (Suppl. S2), 2–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Son, H.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, C.N. Incidence and treatment trends of infectious spondylodiscitis in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, S. Spinal infections. J. Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005, 87, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasto, L.A.; Colangelo, D.; Rossi, B.; Fantoni, M.; Pola, E. Post-operative spondylodiscitis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16 (Suppl. S2), 50–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.; Walter, N.; Schindler, M.; Baertl, S.; Szymski, D.; Loibl, M.; Alt, V.; Rupp, M. The Epidemiology of Spondylodiscitis in Germany: A Descriptive Report of Incidence Rates, Pathogens, In-Hospital Mortality, and Hospital Stays between 2010 and 2020. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.; Thavarajasingam, S.G.; Neuhoff, J.; Ponniah, H.S.; Ramsay, D.S.C.; Demetriades, A.K.; Davies, B.M.; Shiban, E.; Ringel, F. Epidemiological trends of pyogenic spondylodiscitis in Germany: An EANS Spine Section Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigrau, C.; Almirante, B.; Flores, X.; Falco, V.; Rodríguez, D.; Gasser, I.; Villanueva, C.; Pahissa, A. Spontaneous pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis and endocarditis: Incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 1287.e17–1287.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Mejias, M.E.; de Dios Colmenero, J.; Sanchez-Lora, F.J.; Palomino-Nicás, J.; Reguera, J.M.; de la Heras, J.G.; García-Ordonez, M.A.; Pachon, J. Postoperative spondylodiskitis: Etiology, clinical findings, prognosis, and comparison with nonoperative pyogenic spondylodiskitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, L.; Benazzo, F.; De Rosa, F.; Boriani, S.; Dallagiacoma, G.; Franceschetti, G.; Gaeta, M.; Cuzzocrea, F. A systematic review: Characteristics, complications and treatment of spondylodiscitis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23 (Suppl. S2), 117–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Yamada, K.; Yokosuka, K.; Yoshida, T.; Goto, M.; Matsubara, T.; Iwahashi, S.; Shimazaki, T.; Nagata, K.; Shiba, N.; et al. Pyogenic Spondylitis: Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment. Kurume Med. J. 2019, 65, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asperges, E.; Albi, G.; Truffelli, F.; Salvaderi, A.; Puci, F.; Sangani, A.; Zuccaro, V.; Scotti, V.; Orsolini, P.; Brunetti, E.; et al. Fungal Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review of Reported Cases. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutserimpas, C.; Chamakioti, I.; Naoum, S.; Raptis, K.; Alpantaki, K.; Kofteridis, D.P.; Samonis, G. Spondylodiscitis Caused by Aspergillus Species. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Petkova, A.S.; Zhelyazkov, C.B.; Kitov, B.D. Spontaneous Spondylodiscitis—Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment. Folia Med. 2017, 59, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pola, E.; Taccari, F.; Autore, G.; Giovannenze, F.; Pambianco, V.; Cauda, R.; Maccauro, G.; Fantoni, M. Multidisciplinary management of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Epidemiological and clinical features, prognostic factors and long-term outcomes in 207 patients. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27 (Suppl. S2), 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmuganathan, R.; Ramachandran, K.; Shetty, A.P.; Kanna, R.M. Active tuberculosis of spine: Current updates. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2023, 16, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hopkinson, N.; Stevenson, J.; Benjamin, S. A case ascertainment study of septic discitis: Clinical, microbiological and radiological features. QJM 2001, 94, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottle, L.; Riordan, T. Infectious spondylodiscitis. J. Infect. 2008, 56, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, F.L., Jr.; Galvez, L.F.; Aryan, H.E.; Ames, C.P. Recent advances: Infections of the spine. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2006, 8, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.S.; Shelly, M.J.; Timlin, M.; Powderly, W.G.; O’Byrne, J.M. Nontuberculous pyogenic spinal infection in adults: A 12-year experience from a tertiary referral center. Spine 2006, 31, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasto, L.A.; Fantoni, M.; Cipolloni, V.; Piccone, L.; Pola, E.; Schiavone Panni, A. A Detailed Analysis of Clinical Features and Outcomes of Patients with Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis Presenting without Axial Back Pain. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbari, E.F.; Kanj, S.S.; Kowalski, T.J.; Darouiche, R.O.; Widmer, A.F.; Schmitt, S.K.; Hendershot, E.F.; Holtom, P.D.; Huddleston, P.M.; Petermann, G.W.; et al. 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, e26–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylona, E.; Samarkos, M.; Kakalou, E.; Fanourgiakis, P.; Skoutelis, A. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: A systematic review of clinical characteristics. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 39, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.G.; Espersen, F.; Skinhoj, P.; Frimodt-Moller, N. Bacteremic Staphylococcus aureus spondylitis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lertudomphonwanit, T.; Somboonprasert, C.; Lilakhunakon, K.; Jaovisidha, S.; Ruangchaijatuporn, T.; Fuangfa, P.; Rattanasiri, S.; Watcharananan, S.; Chanplakorn, P. A clinical prediction model to differentiate tuberculous spondylodiscitis from pyogenic spontaneous spondylodiscitis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeone, F.J.; Husseini, J.S.; Yeh, K.J.; Lozano-Calderon, S.; Nelson, S.B.; Chang, C.Y. MRI and clinical features of acute fungal discitis/osteomyelitis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.S.; Seldomridge, J.A. Spinal infections: Diagnostic tests and imaging studies. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 444, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, J.L.; Rothman, S.; Prosper, A.; Silbergleit, R.; Lerner, A. Spine infections. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stäbler, A.; Reiser, M.F. Imaging of spinal infection. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 39, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grados, F.; Lescure, F.X.; Senneville, E.; Flipo, R.M.; Schmit, J.L.; Fardellone, P. Suggestions for managing pyogenic (non-tuberculous) discitis in adults. Joint Bone Spine 2007, 74, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbelaez, A.; Restrepo, F.; Castillo, M. Spinal infections: Clinical and imaging features. Top. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2014, 23, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyde, C.E.; Spiegl, U.J.A.; Voelker, A.; von der Hoeh, N.; Henkelmann, J. Imaging in the Diagnosis of Nonspecific pyogenic Spondylodiskitis. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2023, 84, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brant-Zawadzki, M.; Burke, V.D.; Jeffrey, R.B. CT in the evaluation of spine infection. Spine 1983, 8, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGahan, J.P.; Dublin, A.B. Evaluation of spinal infections by plain radiographs, computed tomography, intrathecal metrizamide, and CT-guided biopsy. Diagn. Imaging Clin. Med. 1985, 54, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, M.; Lazzeri, E.; Palestro, C.J. Imaging of Spondylodiscitis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 48, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagirmanjian, A.; Schils, J.; McHenry, M.; Modic, M.T. MR imaging of vertebral osteomyelitis revisited. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 167, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledermann, H.P.; Schweitzer, M.E.; Morrison, W.B.; Carrino, J.A. MR imaging findings in spinal infections: Rules or myths? Radiology 2003, 228, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Granata, F.; Ricciardi, K.; Gaeta, M.; Blandino, A. Contrast-enhanced MR imaging with fat suppression in adult-onset septic spondylodiscitis. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehn, F.E. Imaging of spine infection. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 50, 777–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Papadopoulos, D.V.; Vrioni, G.; Sioutis, S.; Sapkas, G.; Benzakour, A.; Benzakour, T.; Angelini, A.; Ruggieri, P.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; et al. Spinal Infections: An Update. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Salaffi, F.; Ceccarelli, L.; Carotti, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Polonara, G.; Facchini, G.; Golfieri, R.; Giovagnoni, A. Differentiation between infectious spondylodiscitis versus inflammatory or degenerative spinal changes: How can magnetic resonance imaging help the clinician? Radiol. Med. 2021, 126, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Righi, E.; Carnelutti, A.; Muser, D.; Di Gregorio, F.; Cadeo, B.; Melchioretto, G.; Merelli, M.; Alavi, A.; Bassetti, M. Incremental value of FDG-PET/CT to monitor treatment response in infectious spondylodiscitis. Skeletal Radiol. 2020, 49, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, D.; Solà, O.; Soriano, A.; Monegal, A.; Setoain, X.; Tomás, X.; Garcia, S.; Mensa, J.; Rubello, D.; Pons, F. A prospective study comparing whole-body FDG PET/CT to combined planar bone scan with 67Ga SPECT/CT in the Diagnosis of Spondylodiskitis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Merelli, M.; Di Gregorio, F.; Della Siega, P.; Screm, M.; Scarparo, C.; Righi, E. Higher fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) uptake in tuberculous compared to bacterial spondylodiscitis. Skeletal Radiol. 2017, 46, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, V.; Castilla-Lievre, M.A.; Guillet-Caruba, C.; Grenier, G.; Fior, R.; Desarnaud, S.; Doucet-Populaire, F.; Boué, F. (18)F-FDG PET/CT in tuberculosis: An early non-invasive marker of therapeutic response. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2012, 16, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, C.; Patel, M.; Lonner, B.S.; Tomas, M.B.; Palestro, C.J. Diagnosing spinal osteomyelitis: A comparison of bone and Ga-67 scintigraphy and magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2000, 25, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayani, I.; Syed, I.; Saifuddin, A.; Green, R.; MacSweeney, F. Vertebral osteomyelitis without disc involvement. Clin. Radiol. 2004, 59, 881–891, Erratum in Clin. Radiol. 2004, 59, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tali, E.T.; Oner, A.Y.; Koc, A.M. Pyogenic spinal infections. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2015, 25, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babic, M.; Ilaslan, H.; Shrestha, N.; Simpfendorfer, C.S. Isolated septic facet joints: An underdiagnosed distinct clinical entity. Skeletal Radiol. 2020, 49, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zeng, X.; He, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Shu, Y. The Value of MR Imaging in Comparative Analysis of Spinal Infection in Adults: Pyogenic Versus Tuberculous. World Neurosurg. 2019, 128, e806–e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, Y.; Gupta, N.; Chhabra, A.; Fukuda, T.; Soni, N.; Hayashi, D. Magnetic resonance imaging of bacterial and tuberculous spondylodiscitis with associated complications and non-infectious spinal pathology mimicking infections: A pictorial review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkelmann, J.; Bremicker, K.; Denecke, T.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; Henkelmann, R.; Heyde, C.-E.; Sabri, O.; Purz, S. Clinical suspicion of spondylodiscitis with equivocal MRI findings: Does diffusion-weighted imaging prove helpful here? Acta Radiol. 2021, 62, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naselli, N.; Facchini, G.; Lima, G.M.; Evangelisti, G.; Ponti, F.; Miceli, M.; Spinnato, P. MRI in differential diagnosis between tuberculous and pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galhotra, R.D.; Jain, T.; Sandhu, P.; Galhotra, V. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of tubercular and pyogenic spondylodiscitis. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2015, 6, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodi, E.; Grassi, R.; Iacobellis, F.; Cianfoni, A. Imaging in Spondylodiskitis. Magn. Reason. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2016, 24, 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- al-Shahed, M.S.; Sharif, H.S.; Haddad, M.C.; Aabed, M.Y.; Sammak, B.M.; Mutairi, M.A. Imaging features of musculoskeletal brucellosis. Radiographics 1994, 14, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelli Bouaziz, M.; Ladeb, M.F.; Chakroun, M.; Chaabane, S. Spinal brucellosis: A review. Skeletal Radiol. 2008, 37, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.L.; Fukui, M.B.; Meltzer, C.C.; Swarnkar, A.; Johnson, D.W.; Welch, W. Fungal spinal osteomyelitis in the immunocompromised patient: MR findings in three cases. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jung, N.Y.; Jee, W.H.; Ha, K.Y.; Park, C.K.; Byun, J.Y. Discrimination of tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic spondylitis on MRI. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 182, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y. Comparison of pyogenic spondylitis and tuberculous spondylitis. Asian Spine J. 2014, 8, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling-Shan, C.; Zheng-Qiu, Z.; Jing, L.; Rui, Z.; Li-Fang, L.; Zhi-Tao, W.; Zhong-Qiu, W. Magnetic resonance imaging features for differentiating tuberculous from pyogenic spondylitis: A meta-analysis. Skeletal Radiol. 2023, 53, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Cui, K.; Wang, Q.; Lu, T.; Zheng, J.M.; et al. Development of a Diagnostic Model for Differentiating Tuberculous Spondylitis and Pyogenic Spondylitis With MRI: A Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study. Spine 2024, 49, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Kadavigere, R.; Malla, S.; Bhat, S.N.; Saravu, K. Differentiating tubercular from pyogenic causes of spine involvement on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Infez. Med. 2023, 31, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frel, M.; Białecki, J.; Wieczorek, J.; Paluch, Ł.; Dąbrowska-Thing, A.; Walecki, J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differentatial Diagnosis of Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis and Tuberculous Spondylodiscitis. Pol. J. Radiol. 2017, 82, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinnato, P.; Colangeli, M.; Rinaldi, R.; Ponti, F. Percutaneous CT-Guided Bone Biopsies: Indications, Feasibility and Diagnostic Yield in the Different Skeletal Sites-From the Skull to the Toe. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ponti, F.; Arioli, A.; Longo, C.; Miceli, M.; Colangeli, M.; Papalexis, N.; Spinnato, P. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Bone Biopsy: Feasibility, Diagnostic Yield and Technical Notes. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chew, F.S.; Kline, M.J. Diagnostic yield of CT-guided percutaneous aspiration procedures in suspected spontaneous infectious diskitis. Radiology 2001, 218, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Pelzl, C.; Jesse, M.K.; Habibollahi, S.; Habib, U.; Gyftopoulos, S. Image-Guided Biopsy in Acute Diskitis-Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2023, 220, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Luo, T.Y.; Yang, H.F.; Yu, J.H.; Xu, X.X.; Zheng, H.J.; Li, B. Factors influencing diagnostic yield of CT-guided percutaneous core needle biopsy for bone lesions. Clin. Radiol. 2014, 69, e43–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, S. The advancement of MRI in differentiating Modic type I degenerative changes from early spinal infections. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20230551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boudabbous, S.; Paulin, E.N.; Delattre, B.M.A.; Hamard, M.; Vargas, M.I. Spinal disorders mimicking infection. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Daghighi, M.H.; Poureisa, M.; Safarpour, M.; Behzadmehr, R.; Fouladi, D.F.; Meshkini, A.; Varshochi, M.; Kiani Nazarlou, A. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating acute infectious spondylitis from degenerative Modic type 1 change; the role of b-value, apparent diffusion coefficient, claw sign and amorphous increased signal. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patel, K.B.; Poplawski, M.M.; Pawha, P.S.; Naidich, T.P.; Tanenbaum, L.N. Diffusion-weighted MRI “claw sign” improves differentiation of infectious from degenerative modic type 1 signal changes of the spine. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bron, J.L.; de Vries, M.K.; Snieders, M.N.; van der Horst-Bruinsma, I.E.; van Royen, B.J. Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions of the spine in ankylosing spondylitis revisited. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Park, Y.S.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, J.A.; Kim, T.H. The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis: Distinguishing between the inflammatory and traumatic subtypes. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2011, 93, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Cassar-Pullicino, V.N.; Casale, R.; Magarelli, N.; Semprini, A.; Colosimo, C. The SAPHO syndrome revisited with an emphasis on spinal manifestations. Skeletal Radiol. 2015, 44, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laredo, J.D.; Vuillemin-Bodaghi, V.; Boutry, N.; Cotten, A.; Parlier-Cuau, C. SAPHO syndrome: MR appearance of vertebral involvement. Radiology 2007, 242, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGauvran, A.M.; Kotsenas, A.L.; Diehn, F.E.; Wald, J.T.; Carr, C.M.; Morris, J.M. SAPHO Syndrome: Imaging Findings of Vertebral Involvement. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, A.; Botchu, R.; Grainger, M.F.; Davies, A.M.; James, S.L. Acute symptomatic calcific discitis in adults: A case report and review of literature. Skeletal Radiol. 2015, 44, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, H.; Gejyo, F.; Arakawa, M. Clinical studies of destructive spondyloarthropathy in long-term hemodialysis patients. Nephron 1992, 61, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Sundaram, M.; Cerase, A.; Magnavita, N.; Tazza, L.; Marano, P. Destructive spondyloarthropathy of the cervical spine in long-term hemodialyzed patients: A five-year clinical radiological prospective study. Skeletal Radiol. 2001, 30, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledbetter, L.N.; Salzman, K.L.; Sanders, R.K.; Shah, L.M. Spinal Neuroarthropathy: Pathophysiology, Clinical and Imaging Features, and Differential Diagnosis. Radiographics 2016, 36, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.C.; Schweitzer, M.E.; Morrison, W.B.; Przybylski, G.J.; Parker, L. Can imaging findings help differentiate spinal neuropathic arthropathy from disk space infection? Initial experience. Radiology 2000, 214, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telli, T.; Desaulniers, M.; Pyka, T.; Caobelli, F.; Forstmann, S.; Umutlu, L.; Fendler, W.P.; Rominger, A.; Herrmann, K.; Seifert, R. What Role Does PET/MRI Play in Musculoskeletal Disorders? Semin. Nucl. Med. 2023; S0001-2998(23)00091-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limkin, E.J.; Sun, R.; Dercle, L.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Robert, C.; Reuzé, S.; Schernberg, A.; Paragios, N.; Deutsch, E.; Ferté, C. Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Ni, M.; Jin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, H. Deep Learning Imaging Reconstruction Algorithm for Carotid Dual Energy CT Angiography: Opportunistic Evaluation of Cervical Intervertebral Discs—A Preliminary Study. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staartjes, V.E.; Quddusi, A.; Klukowska, A.M.; Schröder, M.L. Initial classification of low back and leg pain based on objective functional testing: A pilot study of machine learning applied to diagnostics. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grob, A.; Loibl, M.; Jamaludin, A.; Winklhofer, S.; Fairbank, J.C.T.; Fekete, T.; Porchet, F.; Mannion, A.F. External validation of the deep learning system “SpineNet” for grading radiological features of degeneration on MRIs of the lumbar spine. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S. Performance of the deep convolutional neural network based magnetic resonance image scoring algorithm for differentiating between tuberculous and pyogenic spondylitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, P.; Yimit, Y.; Abliz, D.; Mardan, M.; Xu, T.; Yusufu, A.; Cai, X.; Sheng, W.; Mamat, M. MRI-based interpretable radiomics nomogram for discrimination between Brucella spondylitis and Pyogenic spondylitis. Heliyon 2023, 10, e23584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| Conventional Radiography | Computed Tomography | Magnetic Resonance Imaging | PET-CT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low sensitivity and specificity Firs imaging tool Fast acquisition time Inexpensive Scarce evaluation of soft tissue and neural structures | High sensitivity in the detection of endplate erosions and bone disruption Fast acquisition time Possible guidance for biopsy Good evaluation of soft tissue with the use of intravenous contrast media injection Scarce evaluation of neural structures | Preferred imaging method with very high sensitivity and specificity Long acquisition time Optimal evaluation of soft tissue even without the use of intravenous contrast media injection Optimal evaluation of neural structures Relatively expensive Help in differentiating Pyogenic vs. Tubercular infections (or different microorganisms involved) | High sensitivity Relatively fast acquisition time Scarce evaluation of neural structures Good evaluation of soft tissue Relatively expensive Help in differentiating Pyogenic vs. Tubercular infections (or different microorganisms involved) |
| Imaging Features | Tuberculous Spondylitis (TbS) | Pyogenic Spondylitis (PyS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thoracic spine involvement | Present | Usually absent |
| Subligamentous spread to 3 or more vertebral bodies | Multiple body involvement | Usual involvement ≤ 2 vertebral bodies |
| Involvement of posterior elements | Present | Usually absent |
| (MRI) Paraspinal signal | Well-defined | Ill-defined |
| Paraspinal abscess | 75% of cases | 39–40% of cases |
| Epidural abscess | 56–60% of cases | 11–15% of cases |
| Intraosseous abscess | Present | Absent |
| Abscess wall | Thin and smooth | Thick and irregular |
| (MRI) Vertebral enhancement | Focal/heterogeneous | Diffuse/homogeneous |
| (MRI) Vertebral signal in T2 images | Heterogeneous | Hyperintense/homogeneous |
| (MRI) Vertebral signal in T1 images | Heterogeneous | Hypointense/homogeneous |
| Destruction of vertebral bodies | Frequent and more severe | Infrequent and mild to moderate |
| Disc destruction | Mild to moderate | Severe to complete |
| (PET) FDG SUV | Higher (mean = 12) | Lower (mean = 7) |
| CT-Guided Biopsy for Spondylodiscitis— Factors Associated with Diagnostic Yield | |
|---|---|
| Lower Diagnostic Rate | Higher Diagnostic Rate |
| Small lesion size | Large lesion size |
| Single bone sample | Multiple bone samples |
| Short sample (short needle penetration in the lesion/perpendicular needle trajectory) | Large sample (long needle penetration in the lesion/oblique needle trajectory) |
| Targeting the vertebral bone or endplates only | Targeting the disc, and/or soft-tissue involvement, and/or Fluid collection aspiration. |
| Target lesion not visible on CT | Target lesion visible on CT |
| Fungal Infection | Mycobacterium Tubercolosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crombé, A.; Fadli, D.; Clinca, R.; Reverchon, G.; Cevolani, L.; Girolami, M.; Hauger, O.; Matcuk, G.R.; Spinnato, P. Imaging of Spondylodiscitis: A Comprehensive Updated Review—Multimodality Imaging Findings, Differential Diagnosis, and Specific Microorganisms Detection. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050893
Crombé A, Fadli D, Clinca R, Reverchon G, Cevolani L, Girolami M, Hauger O, Matcuk GR, Spinnato P. Imaging of Spondylodiscitis: A Comprehensive Updated Review—Multimodality Imaging Findings, Differential Diagnosis, and Specific Microorganisms Detection. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(5):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050893
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrombé, Amandine, David Fadli, Roberta Clinca, Giorgio Reverchon, Luca Cevolani, Marco Girolami, Olivier Hauger, George R. Matcuk, and Paolo Spinnato. 2024. "Imaging of Spondylodiscitis: A Comprehensive Updated Review—Multimodality Imaging Findings, Differential Diagnosis, and Specific Microorganisms Detection" Microorganisms 12, no. 5: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050893
APA StyleCrombé, A., Fadli, D., Clinca, R., Reverchon, G., Cevolani, L., Girolami, M., Hauger, O., Matcuk, G. R., & Spinnato, P. (2024). Imaging of Spondylodiscitis: A Comprehensive Updated Review—Multimodality Imaging Findings, Differential Diagnosis, and Specific Microorganisms Detection. Microorganisms, 12(5), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050893







