Abstract
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacterial strain FP607T was isolated from the rhizosphere of beets in Wuhan, China. Strain FP607T exhibited significant antagonism toward several phytopathogenic bacteria, indicating that FP607T may produce antimicrobial metabolites and has a stronger biocontrol efficacy against plant pathogens. Growth-promoting tests showed that FP607T produced indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), NH3, and ferritin. The genome sequence of strain FP607T was 6,590,972 bp long with 59.0% G + C content. The optimum temperature range was 25–30 °C, and the optimum pH was 7. The cells of strain FP607T were Gram-negative, short, and rod-shaped, with polar flagella. The colonies on the King’s B (KB) agar plates were light yellow, smooth, and circular, with regular edges. A phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA sequence and a multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) showed that strain FP607T was most closely related to the type of strain Pseudomonas farris SWRI79T. Based on a polyphasic taxonomic approach, strain FP607T was identified as a novel species within the genus Pseudomonas, for which the name Pseudomonas wuhanensis sp. nov. was proposed. The type of strain used was FP607T (JCM 35688, CGMCC 27743, and ACCC 62446).
1. Introduction
The name Pseudomonas was first proposed by Migula at the end of the 19th century [1]. The genus Pseudomonas includes a diverse microbial population with members that are derived from a wide range of environments, including water, air, soil, plants, and clinical materials [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. According to the List of Prokaryotic Names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN; https://lpsn.dsmz.de (accessed on 30 December 2023)), Pseudomonas was the second-largest species, and more than 300 species had been validly published with correct names at the time of writing. The genus Pseudomonas belongs to the class gamma-proteobacteria, the order Pseudomonadales, and the family Pseudomonadaceae. Members of the genus Pseudomonas are Gram-negative, aerobic, non-spore-forming, and rod-shaped, with one or several polar flagella [4,5,11]. Pseudomonas is known for its metabolic versatility and capacity to produce abundant secondary metabolites [6,12]. They can utilize various chemical compounds as sources of carbon, nitrogen, or phosphorus, making them interesting microorganisms for processes such as bioremediation and biotransformation [2,13]. For example, Pseudomonas mediteranea S58 can produce siderophores, amylase, and protease, solubilize organic phosphorus, and show strong antagonism against a variety of plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria [14]. Some Pseudomonas spp. colonize the rhizosphere, persist throughout the growing season, and are well known for their beneficial effects on plant health. These beneficial bacteria are known as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) [14,15,16]. They enhance plant growth and health through a variety of mechanisms, including accelerating germination, stimulating growth, boosting immunity, and increasing plant yields [14,16,17,18]. Furthermore, several fluorescent Pseudomonas exhibit diverse biocontrol mechanisms, including the production of HCN, siderophores, and antibiotics [3,16,19,20].
Given that Pseudomonas are potent plant growth-promoting agents, we had a comprehensive collection and identification of Pseudomonas strains from beet rhizosphere. In the present study, we report a novel Pseudomonas species isolated from beet rhizosphere in Wuhan. Strain FP607T was subjected to phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene, multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA), average nucleotide identity (ANI), and digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) values. In vitro experiments revealed that strain FP607T has a variety of characteristics that promote plant growth, including direct antagonistic activity against plant pathogens and the production of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), NH3, and siderophores. A genome analysis showed that there were several genes or gene clusters in FP607T, which was consistent with the experimental results. This study offers a foundation for further research on how strain FP607T promotes plant growth and antagonizes pathogenic microbes. In summary, they may serve as plant growth regulators and biological control agents that shield crops from harmful organisms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Bacterial Isolation
Samples were obtained from the rhizosphere of beets in Wuhan, China. A total of 5 g of rhizosphere soil sample was suspended in 45 mL ddH2O and shaken at 220 rpm for 1 h. Gradient dilution of the supernatant was performed using ddH2O, followed by plating on King’s B (KB) agar plates (20 g/L Bacto Tryptone, 1.5 g/L MgCl2, 1.5 g/L K2HPO4, and 1.5% [vol/vol] glycerol), and then incubated at 28 °C for 24 h. Individual colonies were selected using ultraviolet (UV) illumination at 254 nm and purified for three rounds. Bacterial growth was estimated through spectrophotometric measurements at optical density OD600. The cell morphology, size, and flagellar insertion were determined using the Hitachi HT7700 transmission electron microscope (TEM) at the Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Each pure culture was preserved with glycerol at a final concentration of 20% and stored in a refrigerator at −80 °C.
2.2. Antagonistic Test
The major host of Clavibacter michiganense subsp. michiganse (Cmm) is tomatoes, which causes serious economic losses [21]. As a soil-borne pathogen, Ralstonia solanacearum (Ras) naturally infects plants via its roots, causing lethal bacterial wilt disease in several types of crops [22]. Bacterial leaf streaks are an important rice disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola spp. (Xoc) [23]. X. campestris pv. carnpestris (Xcc) can induce serious bacterial spots, causing severe damage to vegetable growth and yield [24]. X. oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) infects rice and causes bacterial leaf blight [25]. Acidovorax citrulli (Ac) causes cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch [26]. The six pathogenic bacteria were preserved in the laboratory and selected for the antagonistic test. A total of 45 mL of pre-melted nutrient agar (NA) media was incubated at 50 °C for 15 min, mixed with 5 mL of pathogenic bacterial culture, and poured onto plates. A saturated strain FP607T culture (10 µL) was dropped onto the middle of the plate. The inhibitory zones were measured after 2-d of incubation at 28 °C. All the experiments were repeated over at least three rounds, and similar results were obtained.
2.3. Identification of Plant Growth-Promoting Traits
The typical plant-promoting traits of FP607T were measured in vitro. IAA is a plant growth hormone secreted throughout the growth phase of plants, promotes cell proliferation, and increases plant volume and mass. It also promotes strain division and differentiation and controls other physiological functions [27]. The Salkowski colorimetric method was used to determine the ability of the bacteria to secrete the plant growth hormone IAA. Strain FP607T was inoculated into a triangular flask containing KB liquid medium (containing 3 mM Tryptophan), each flask containing 20 mL of medium at 28 °C and shaken at 200 rpm for 4 d. Next, 100 μL culture solution was transferred onto a transparent plastic coagulation plate, and 100 μL Salkowski colorimetric solution (50 mL 35% HClO4 + 1 mL 0.5 mol/L FeCl3) was added. IAA (100 μL) was added to the colorimetric solution with a concentration of 100 mg/L as the positive control. Microbes produce NH3 by decomposing organic nitrogen molecules. A portion of the NH3 is absorbed by microbes or plants and converted into nitrate, which promotes plant growth. The strain FP607T was transferred to peptone ammoniation medium, and the medium was mixed by shaking at 28 °C and 220 rpm for 48 h. Culture solution (200 μL) was dripped onto a white ceramic plate, and 200 μL of peptone ammoniation medium was used as a control. Three drops of Nessler’s reagent were added to the peptone ammoniation medium. Each treatment was repeated three times. The presence of yellow or brown-red precipitates indicated that the strain had NH3-producing capacity. Siderophore production was evaluated by overlaying chrome azurol S (CAS) medium on agar plates with the cultures [28]. Cellulase, protease, and amylase activities were determined using the clear-zone technique. Using standard techniques, the strains were evaluated for their capacity to break down potassium and organic and inorganic phosphorus.
2.4. Physiology and Chemotaxonomic Characterization
To identify strain FP607T, the physiological and biochemical characteristics were determined using Biolog GEN III MicroPlates™ (Biolog, Hayward, CA, USA). The utilization pattern was monitored on an OmniLog®® Incubator/Reader (Biolog, Hayward, CA, USA). API 20NE kits (bioMérieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France) were used to determine the properties of strain FP607T according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Polar lipids were detected using thin-layer chromatography (TLC). The different spots were primarily distinguished using chromogenic reagents (molybdenum phosphate, molybdenum blue, ninhydrin, D-reagent, and α-naphthol) [29]. Respiratory quinones were extracted and analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC; Shimadzu LC-20A) [30]. Cellular fatty acids were extracted and identified using gas chromatography (GC) (Agilent 7890 B) according to the protocol of the MIDI Sherlock Microbial Identification System and the RTSBA 6.1 database [31].
2.5. Molecular Identification
The amplification of a partial sequence of the 16S rRNA gene was performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with the universal primers 27F (5′-GAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-CTACGGCTACCTTGTTACGA-3′), as previously reported [32]. Strains closely related to the 16S rRNA sequence of strain FP0607T were identified using the EzBioCloud database [33]. The PCR products were sequenced by GENEWIZ Ltd. (Suzhou, China). The housekeeping genes gyrB, rpoB, rpoD, and 16s rRNA were obtained from the MLSA database (http://microbiologia.uib.es/bioinformatica/ (accessed on 31 December 2023)) using publicly available genomic sequences [34]. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method in MEGA 11 [35]. Bootstrap values were calculated for 1000 replications. Kimura’s two parameters were selected as the nucleotide substitution model to compute the evolutionary distances, and the bootstrap values were derived from 1000 bootstrap replications [36]. The ANI values between FP607T and closely related strains’ orthologous average nucleotide identity (OrthoANI) were calculated using an online EzBioCloud server (https://www.ezbiocloud.net/tools/ani (accessed on 30 November 2023)) [37]. The pairwise dDDH values were investigated by comparing genome sequences using the Genome–Genome Distance Calculator (GGDC, http://ggdc.dsmz.de/distcalc2.php (accessed on 30 November 2023)), using the alignment method Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST+) and Formula 2 for incomplete genome sequences [38].
2.6. Genome Sequencing, Annotation, and Comparative Genomic Analysis
The genomic DNA of FP607T was extracted using a commercial genomic DNA extraction kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA). Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) was performed by GENEWIZ Ltd., (Suzhou, China). Coding sequences (CDSs) were predicted using the Prodigal software and annotated against the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)’s non-redundant (NR) database. RNA sequences were predicted using the tRNAscan-SE and RNAmmer software (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/RNAmmer-1.2/ (accessed on 30 November 2023)) [39]. Functional annotation was performed using the Cluster of Orthologous Groups (COG) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases [14]. Potential secondary metabolic gene clusters were predicted using antiSMASH 7.0 [40]. CRISPR-Cas sequences were predicted using CRISPRCasFinder (https://crisprcas.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/CrisprCasFinder/Index (accessed on 30 November 2023)) [41]. MacSyFinder 2.1.2 was used to identify the secretion systems [42]. Genes in the genome can produce phenotypes that benefit plant growth. BLASTP was used to search for homologs with a threshold of 1e−5 [43]. Marker genes, including genes related to 1-ami-nocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase, indole-3-acetyl-aspartic acid hydrolase (IAA-Asp), β-galactosidase, amylase, pectinase, cellulase, and protease, were obtained from the UniProt database [44].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All the experiments were repeated in triplicate, and the means and SD are shown in this article. Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) test (p < 0.05) was used for the statistical analysis of the results.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antagonism against Phytopathogens
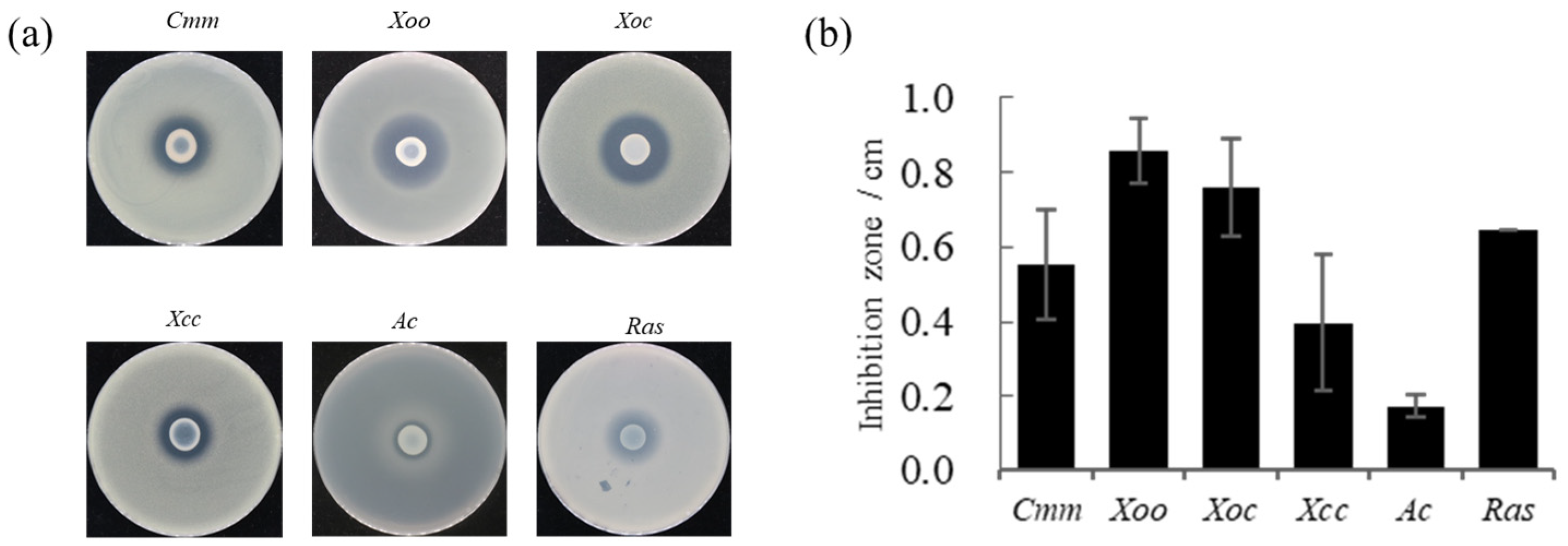
Strain FP607T had an antagonistic effect on pathogenic bacteria. The pathogenic bacteria tested included Clavibacter michiganense subsp. michiganse (Cmm), Xanthomonas oryae pv. oryzae PXO99 (Xoo), X. oryzae pv. oryzicola RS105 (Xoc) and X. campestris pv. carnpestris (Xcc), Ralstonia solanacearum (Ras), and Acidovorax avenae (Ac). A prominent bacteriostatic circle was observed on the plates, indicating that strain FP607T can inhibit the growth of Cmm, Xoo, Xoc, Xcc, Ac, and Ras (Figure 1). This further implies that FP607T can inhibit pathogenic bacteria through metabolite production rather than through direct contact.
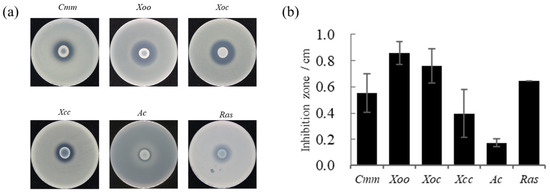
Figure 1.
In vitro antimicrobial activity of strain FP607T against various phytopathogens. (a) Six plant bacterial pathogens have been selected to test the antimicrobial activity of strain FP607T. (Cmm, Clavibacter michiganense subsp. michiganse. Xoo, Xanthomonas oryae pv. oryzae PXO99. Xoc, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola RS105. Xcc, Xanthomonas campestris pv. carnpestris. Ac, Acidovorax avenae. Ras, and Ralstonia solanacearum). (b) Antimicrobial activity has been estimated by measuring the diameter (mm) of the clear zone of growth inhibition from Figure 1a.
3.2. Plant Growth-Promoting Activities
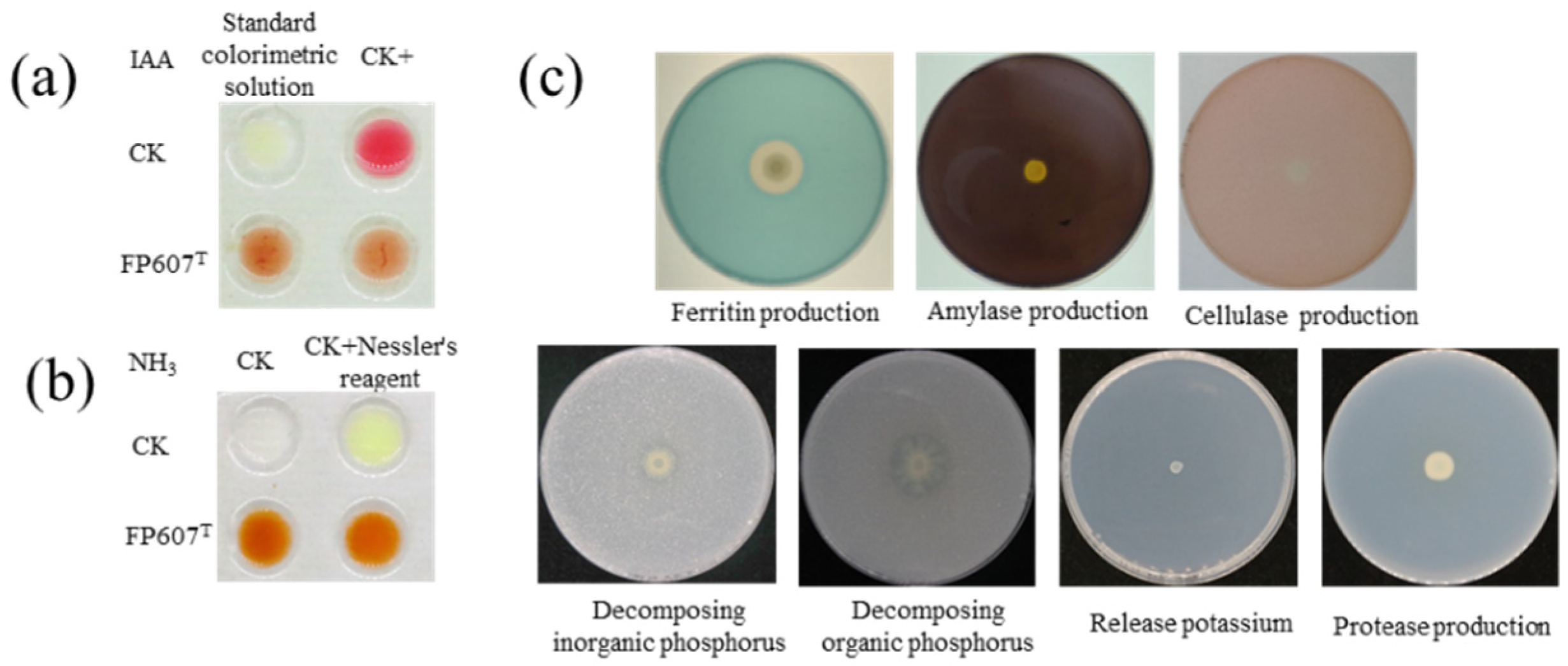
The Salkowski colorimetric results showed that strain FP607T could produce IAA because it caused the colorimetric solution to turn red upon introduction (Figure 2a). The culture broth and peptone-ammoniated medium produced a brownish-colored precipitate when three drops of Nath’s reagent were added, suggesting that the strain could produce NH3 (Figure 2b). Selective media were used to characterize several features that promoted plant development. Strain FP607T developed siderophores, as shown by the distinct hydrolytic halos that formed around the colonies. However, strain FP607T did not show a translucent aperture on subsequent identification plates, indicating that it was unable to produce cellulase, amylase, or proteases or break down potassium phosphorus, inorganic phosphorus, or organic phosphorus (Figure 2c). In conclusion, we speculated that FP607T may promote plant growth.
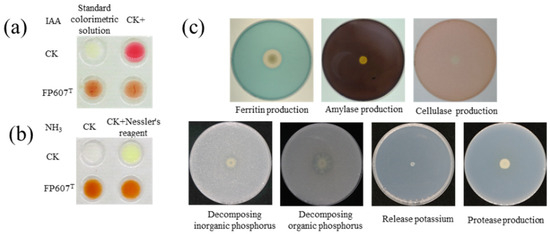
Figure 2.
In vitro test of plant growth-promoting traits of strain FP607T. (a) Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) production is shown by the visualized pink color treated with strain FP607T compared with the upper positive and negative controls. CK+ indicates that 100 μL/L of IAA was added to the colorimetric solution. (b) Ammonia production is shown from the visualized brown and yellow colors treated with FP607T (lower two replicates) compared with the water control. (c) Response of strain FP607T in various identification media. The transparent zones around the colonies are visualized through siderophore production.
3.3. 16S rRNA and MLSA Phylogenies
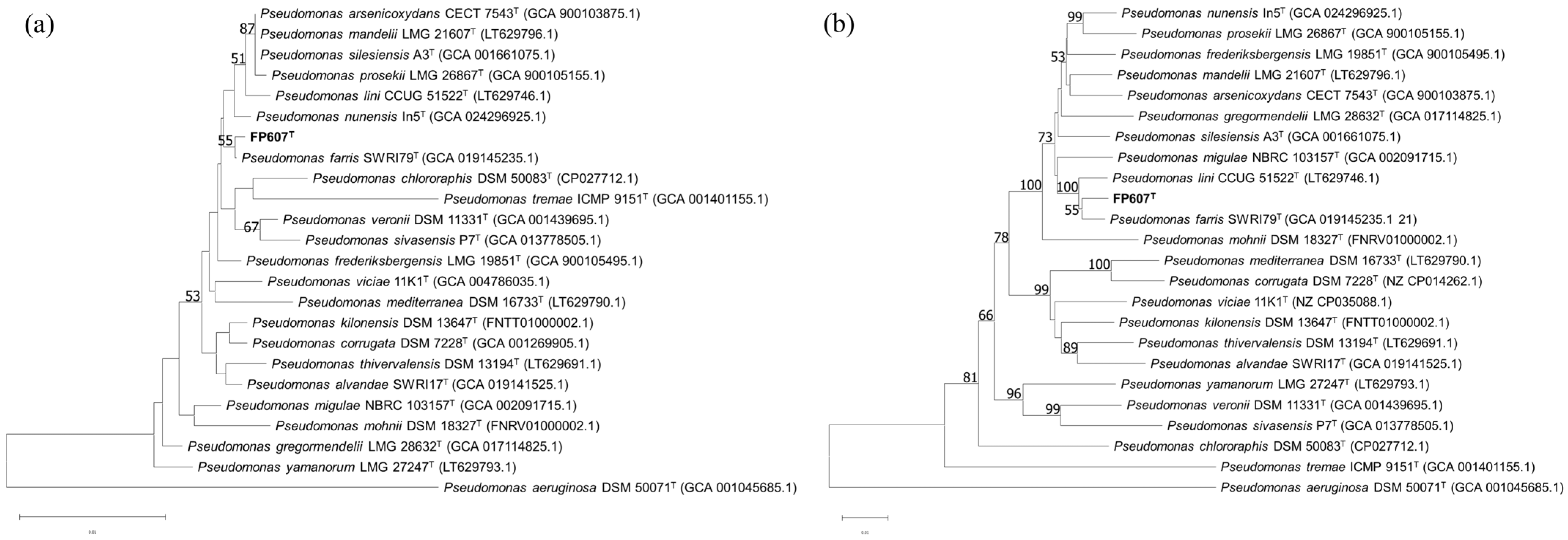
To more accurately identify the bacterium, we performed a phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene. The phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene’s sequences constructed using the NJ method indicated that FP607T formed a cluster along with Pseudomonas farris SWRI79T, with a bootstrap value of 55%. (Figure 3a) [45]. Concatenated sequences of the 16S rRNA, gyrB, rpoB, and rpoD genes were used to reconstruct a phylogenetic tree, using the same approach. The MLSA tree showed that FP607T and Pseudomonas farris SWRI79T were most closely related, with a bootstrap value of 55% (Figure 3b).
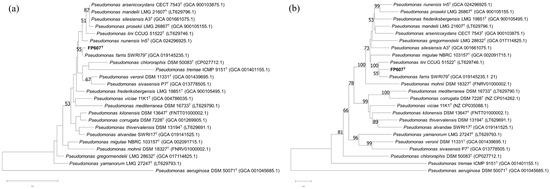
Figure 3.
(a) NJ tree based on the nearly complete 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the relationships between FP607T and other type strains. (b) NJ tree based on concatenated sequences of 16S rRNA, gyrB, rpoB, and rpoD genes showing the phylogenetic relationship between FP607T and other type strains. Bootstrap values > 50% (based on 1000 resamplings) are shown. Scale bar: 0.01 substitutions per nucleotide position.
The results of the whole-genome similarity test showed that the values between FP607T and other closely related species ranged between 86.7 and 93.6% for ANI and between 31.1 and 66.5% for dDDH, below the recommended thresholds of 95% (ANI) and 70% (dDDH) for prokaryotic species delineation, respectively (Table 1). This indicated that strain FP607T may be a new species. Strain FP607T was named P. wuhanensis FP607T and was deposited in the China General Microorganism Culture Collection (CGMCC 27743), the Japan Collection of Microorganisms (JCM 35688), and the Agriculture Culture Collection of China (ACCC 62446).

Table 1.
The dDDH and ANI values between strain FP607T and the type strains of closely related species of the genus Pseudomonas.
3.4. Physiology and Chemotaxonomic Characterization
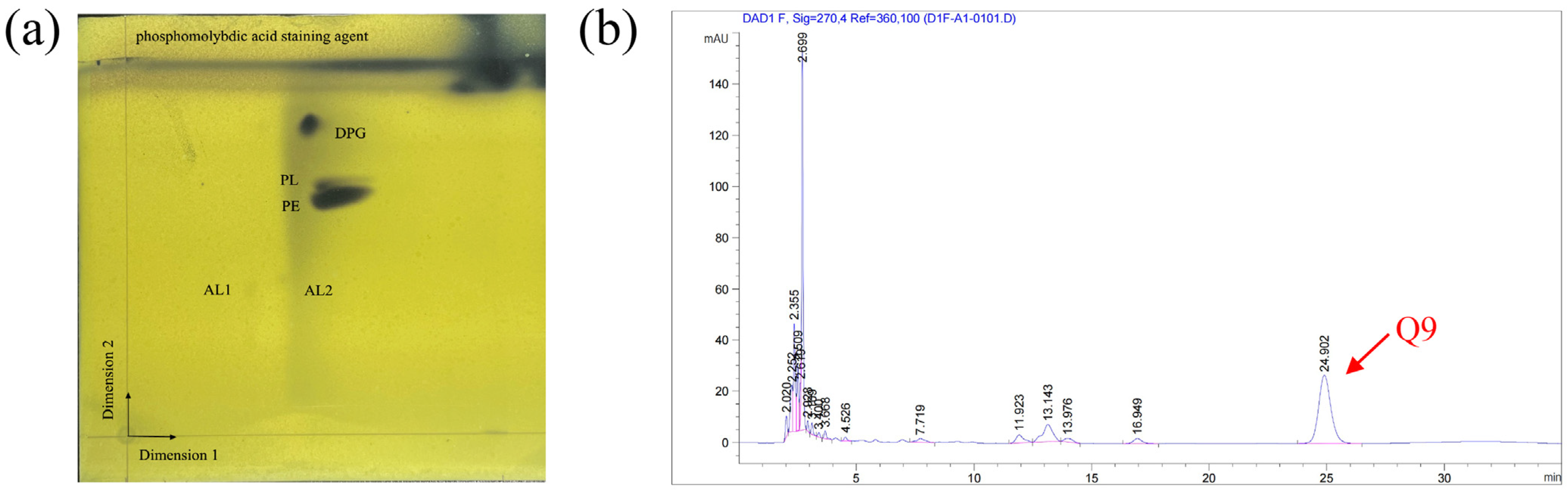
The Biolog GEN III MicroPlate™ system was used to test the carbon source utilization and chemical sensitivity of FP607T. Strain FP607T could use D-mannose, D-galactose, D-fucose, guanidine HCl, L-galactonic acid lactone, D-glucuronic acid, glucuronamide, and α-D-glucose as carbon sources for growth (Supplementary Materials Table S2), and it exhibited chemical sensitivity to sodium lactate, troleandomycin, rifamycin SV, and lincomycin. The API 20NE results showed that strain FP607T reacted with potassium nitrate, N-acetyl glucosamine, and citric acid (Supplementary Materials Table S2). The analysis of the polar lipids revealed that the cell membrane of strain FP607T contained diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), an unidentified phosphoglycolipid (PL), and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) (Figure 4a). The primary respiratory quinone of strain FP607T was ubiquinone-9 (Q-9), as shown by the peak formed in 25 min during the HPLC analysis (Figure 4b). The major fatty acids of strain FP607T contained C12:0 (13.9%), C10:0 3-OH (39.0%), C12:0 2-OH (11.4%), C12:0 3-OH (18.1%), and summed features 3 (C16:1 ω7c/C16:1 ω6c) (7.1%) and 8 (C18:1 ω7c/C18:1 ω6c) (Table 2). These findings are consistent with previous reports on the Pseudomonas species [26].
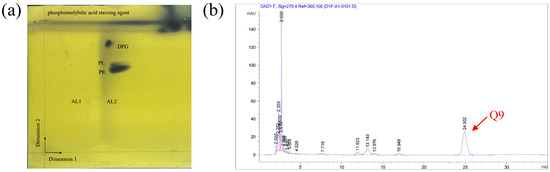
Figure 4.
(a) Two-dimensional (2D) TLC plate of polar lipids extracted from strain FP607T. Three polar lipids (DPG, PL, and PE) were detected. PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; DPG, diphosphatidylglycerol; PL, unidentified phosphoglycolipid; APL, aminophospholipid; and L, unknown polar lipids. (b) The quinone species Q-9 was detected after 25 min during the HPLC analysis.

Table 2.
Cellular fatty acid composition of strain FP607T and reference strains.
3.5. Genomic Characterization
FP607T had a genome of 6,590,972 bp with a G + C 58.99% content, and it was predicted to contain 6011 coding sequences (CDSs) with an average length of 992.90 bp. In addition, P. wuhanensis FP607T encoded 19 rRNA genes, 70 tRNAs, and 209 ncRNAs (Supplementary Materials Table S1 and Figure S1).
FP607T was equipped with several secretion systems, including type I secretion system (T1SS), type II secretion system (T2SS), type III secretion system (T3SS), and type VI secretion system (T6SS) (Supplementary Materials Figure S2), out of which T3SS and T6SS have been demonstrated to be involved in regulating plant immunity and promoting bacterial colonization and plant growth [46]. For instance, Pseudomonas fluorescens F113 employed T6SS to mediate bacterial killing and adaption to rhizosphere colonization [46]. Whether these secretion systems contribute to the antagonistic activity and benefic function of FP607T remains to be investigated. The in silico prediction revealed that almost all the closely related strains contained plant growth-promotion-associated genes encoding 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase and indoleacetamide hydrolase (iaaH). Moreover, strain FP607T showed genes encoding digestive enzymes, such as dextranase amylase and protease, but did not contain the genes for β-galactosidase, pectinase, or cellulase (Supplementary Materials Figure S2). The antiSMASH results identified 18 potential secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters, including redox-cofactor, NRPS, NRP-metallophore, HR-T2PKS, isocyanide, RiPP-like, beta-lactone, NRPS-like, and aryl polyene (Table 3). Of these, 11 were similar to known biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs), including Lankacidin, Pf-5, pyoverdine, histicorrugatin, cepacin A, pyoverdine DC3000, bacillomycin D, fengycin, pyralomicin 1a, APE Vf, and fragments. Histicorrugatin is a siderophore structurally related to corrugatin and ornicorrugatin. They can also mediate the synthesis of iron carriers. The mechanisms of action of bacterial siderophores against plant pathogenic fungi include nutrient competition, niche competition, the induction of systemic resistance in plants, and the disruption of pathogen iron homeostasis [47]. Pyoverdine (Pvd) is a major iron-chelating metabolite of Pseudomonas proteins, and its functions include antibiotic activity and metal homeostasis [47,48]. In conclusion, we speculate that strain FP607T showed a growth-promoting effect possibly because it contained secondary metabolites of siderophores. Lankacidin, cepacin A, bacillomycin D, fengycin, and its fragments are well-known antagonists. Lankacidins are a class of natural polyketide products that exhibit promising antimicrobial activity [49]. Cepacin A is an important metabolite that protects sprouted peas from moisture damage caused by Globisporangium ultimum [50]. Bacitracin D-C16 is a naturally occurring antimicrobial lipopeptide that inhibits the growth of Fusarium verticillioides in maize [51]. The fengycin family is one of the most important molecules that affect target cells at the membrane level and has a broad spectrum of antagonistic activity against plant pathogens [52]. Fragin is a metallophore, and metal chelation is the molecular basis of its antifungal activity [53]. According to this analysis, the strain FP607T possesses genes that result in the production of the aforementioned secondary metabolites, which may be crucial for the antagonistic action of the strain against harmful bacteria.

Table 3.
Putative BGCs in the FP607T genome predicted by antiSMASH.
The COG annotation results indicated that the largest COG categories were general function prediction only (COG R), amino acid transport and metabolism (COG E), and unknown function (COG S) (Supplementary Materials Figure S3). The KEGG annotation results revealed that carbohydrate metabolism (444 genes), amino acid metabolism (435 genes), and global and overview maps (375 genes) were the most abundant categories in FP607T. Several genes were involved in membrane transport (279 genes) and signal transduction (242 genes) (Supplementary Materials Figure S4).
3.6. Description of P. wuhanensis sp. nov.
The type strain P. wuhanensis FP607T was isolated from the rhizosphere of beets in Wuhan, China. The genome of P. wuhanensis FP607T was 6,590,972 bp with 59.0% GC content. The cells of strain FP607T were Gram-negative and rod-shaped (length 2.0–2.7 µm, width 0.9–1.2 µm), with polar flagella (Supplementary Materials Figure S5). The colonies on KB were light yellow, circular, and smooth with regular edges. The optimum temperature range was 25–30 °C, and the optimum pH was 7. P. wuhanensis FP607T could produce IAA, NH3, and ferritin and had plant growth-promoting functions. P. wuhanensis FP607T significantly inhibited Cmm, Xoo, Xoc, Xcc, Ac, and Ras. The API 20NE results showed that the strain P. wuhanensis FP607T could react with potassium nitrate, N-acetyl glucosamine, and citric acid. The analysis of polar lipids revealed that the cell membrane of strain P. wuhanensis FP607T contained diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), an unidentified phosphoglycolipid (PL), and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). The BIOLOG results showed that strain P. wuhanensis FP607T could utilize D-mannose, D-galactose, D-fucose, guanidine HCl, L-galactonic acid lactone, D-glucuronic acid, glucuronamide, and α-D-glucose as carbon sources for growth (Supplementary Materials Table S2) and exhibited chemical sensitivity to sodium lactate, troleandomycin, rifamycin SV, and lincomycin. The primary fatty acids of strain P. wuhanensis FP607T were C12:0, C10:0 3-OH, C12:0 2-OH, C12:0 3-OH, and summed features 3 (C16:1 ω7c/C16:1 ω6c), and 8 (C18:1 ω7c/C18:1 ω6c). The predominant isoprenoid quinone was ubiquinone-9. The phylogenetic analysis showed that FP607T was closely related to Pseudomonas farris SWRI79T. The ANI and dDDH values showed that strain FP607T was closely related to Pseudomonas farris SWRI79T, with values of 93.6% and 66.5%, respectively. Collectively, the type strain P. wuhanensis FP607T (=JCM 35,688 = CGMCC 27,743 = ACCC 62,446) was identified in this study.
4. Conclusions
Pseudomonas, as the second-largest species, are valuable microbial resources used widely in agriculture and industry [54,55,56,57,58]. This study focused on a newly discovered, patented strain of P. wuhanensis FP607T with plant-promoting properties. Strain FP607T is rich in secondary metabolites of potential growth-promoting gene clusters and can produce IAA, NH3, and siderophores, suggesting that strain FP607T is a potent PGPR with versatile beneficial characteristics. The differences in the phenotypic characteristics between the novel isolates and their phylogenetic neighbors are summarized in this paper. Morphological, chemotaxonomic, and phylogenetic analyses strongly supported the affiliation of strain FP607T as a novel species within Pseudomonas. Several characteristic features, such as physiological and biochemical characteristics, 16S rRNA gene sequences, and the MLSA, ANI, and DDH values, can be used to distinguish this strain from phylogenetically related taxa. P. wuhanensis FP607T is a plant rhizosphere probiotic that is easy to cultivate and preserve, highly efficient to use, and environmentally friendly. Collectively, the discovery of this new Pseudomonas strain is of great significance for agricultural production and supports the expansion of new resources.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms12050944/s1, Figure S1: The genome circle map of strain FP607T; Figure S2: Selected biosynthetic, secretion system-related, and catabolic genes or gene clusters were predicted using the genome sequences of strain P. wuhanensis FP607T and the related species; Figure S3: COG annotation; Figure S4: KEGG annotation; Figure S5: Micrograph of TEM of cells of strain FP607T; Table S1: General features of P. wuhanensis FP607T genome; and Table S2: Phenotypic characters that differentiate FP607T from its closest type strains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-L.W.; investigation, J.H., K.L. and J.-Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.; writing—review and editing, J.H., K.L., Y.-J.Z., J.-Z.L. and H.-L.W.; funding acquisition, H.-L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Program of Science and Technology of Beijing, China (Z191100004019025), the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFD1002001), and the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Y2019XK07, 1610132020039).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusion of this article are included in the article and Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the following: study design; collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; writing of the manuscript; or decision to publish the results.
References
- Palleroni, N.J. Introduction to the family Pseudomonadaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Starr, M.P., Stolp, H., Trüper, H.G., Balows, A., Schlegel, H.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; Volume 3, pp. 3074–3085. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski, M.A.; Furmanczyk, E.M.; Sobczak, A.; Dziembowski, A.; Lipinski, L. Pseudomonas silesiensis sp. nov. strain A3T isolated from a biological pesticide sewage treatment plant and analysis of the complete genome sequence. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, H.; Takeuchi, K.; Someya, N.; Morohoshi, T.; Satou, M. Pseudomonas solani sp. nov. isolated from the rhizosphere of eggplant in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 005942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Lu, W.; Chen, M.; Yan, Y.; Lin, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z. Pseudomonas nanhaiensis sp. nov., a lipase-producing bacterium isolated from deep-sea sediment of the South China Sea. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamtimin, T.; Anwar, N.; Abdurahman, M.; Kurban, M.; Rozahon, M.; Mamtimin, H.; Hamood, B.; Rahman, E.; Wu, M. Pseudomonas lopnurensis sp. nov., an endophytic bacterium isolated from Populus euphratica at the ancient Ugan river. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Rao, Z.; Wu, S.; Peng, F.; Xie, Z.; Long, Y. Pseudomonas benzopyrenica sp. nov., isolated from soil, exhibiting high-efficiency degradation of benzo(a)pyrene. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 006034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, E.I.; Papadioti, A.; Bibi, F.; Ashshi, A.M.; Raoult, D.; Angelakis, E. ’Pseudomonas saudimassiliensis’ sp. nov. a new bacterial species isolated from air samples in the urban environment of Makkah, Saudi Arabia. New Microbes New Infect. 2017, 16, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busquets, A.; Gomila, M.; Beiki, F.; Mulet, M.; Rahimian, H.; García-Valdés, E.; Lalucat, J. Pseudomonas caspiana sp. nov., a citrus pathogen in the Pseudomonas syringae phylogenetic group. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, W.J.; Manter, D.K. Pseudomonas kuykendallii sp. nov.: A novel γ-proteo-bacteria isolated from a hexazinone degrading bioreactor. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, H.F.; Safarik, J.; Phipps, D.; Carl, P.; Clark, D. Identification and catabolic activity of well-derived gasoline-degrading bacteria from a contaminated aquifer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 3565–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peix, A.; Ramírez-Bahena, M.-H.; Velázquez, E. The current status on the taxonomy of Pseudomonas revisited: An update. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 57, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Loper, J.E. Genomics of secondary metabolite production by Pseudomonas spp. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1408–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, M.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Pseudomonas sp. LZ-Q continuously degrades phenanthrene under hypersaline and hyperalkaline condition in a membrane bioreactor system. Biophys. Rep. 2015, 1, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Z.; Wei, H. Characterization of a versatile plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas mediterranea strain S58. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widnyana, I.K.; Javandira, C. Activities Pseudomonas spp. and Bacillus sp. to stimulate germination and seedling growth of tomato plants. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 9, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, D.; Backer, R.; Robinson, W.G.; Smith, D.L. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for cannabis production: Yield, cannabinoid profile and disease resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosier, A.; Bishnoi, U.; Lakshmanan, V.; Sherrier, D.J.; Bais, H.P. A perspective on inter-kingdom signaling in plant-beneficial microbe interactions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugtenberg, B.; Kamilova, F. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujur, R.R.A.; Das, S.K. Pseudomonas phenolilytica sp. nov., a novel phenol-degrading bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höfte, M.; Altier, N. Fluorescent pseudomonads as biocontrol agents for sustainable agricultural systems. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de León, L.; Siverio, F.; López, M.M.; Rodríguez, A. Clavibacter michiganesis subsp. michiganensis, a seedborne tomato pathogen: Healthy seeds are still the goal. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Chen, J.; Li, N.; Wang, R. Seedling Petri-dish inoculation method: A robust, easy-to-use and reliable assay for studying plant-Ralstonia solanacearum interactions. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 3709–3719. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.-N.; Wei, Z.-Q.; Zou, H.-F.; Xie, G.-G.; Wu, F.; Li, K.-J.; Jiang, W.; Tang, J.-L.; He, Y.-Q. Complete sequence and detailed analysis of the first indigenous plasmid from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, S.; Niran, J.; Li, N.; Yin, Y.; Yu, C.; Jiao, C.; Yao, M. iTRAQ proteomics reveals the regulatory response to Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria in resistant vs. susceptible pepper genotypes. Hortic. Plant J. 2022, 8, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-W.; Wu, J.; Cha, J.-S.; Zhang, L.-H. Rice bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae produces multiple DSF-family signals in regulation of virulence factor production. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assunção, E.F.; da Conceicao, C.S.; Alexandre, E.R.; da Gama, M.A.S.; de Souza Nunes, G.H.; de Souza, E.B. New sources of melon accessions with resistance to bacterial fruit blotch at different phenological stages of melon growth and to multiple strains of Acidovorax citrulli. Euphytica 2021, 217, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsangiam, S.; Thongpae, N.; Limtong, S.; Srisuk, N. Large scale production of indole-3-acetic acid and evaluation of the inhibitory effect of indole-3-acetic acid on weed growth. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Miranda, S.; Cabirol, N.; George-Téllez, R.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.; Fernández, F. O-CAS, a fast and universal method for siderophore detection. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 70, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnikin, D.E.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Athalye, M.; Schaal, A.; Parlett, J.H. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isopre-noid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 1984, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Jones, D. A note on the separation of natural mixtures of bacterial ubiquinones using reverse-phase partition thin-layer chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1981, 51, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaizu, H.; Komagata, K. Grouping of Pseudomonas species on the basis of cellular fatty acid composition and the quinone system with special reference to the existence of 3-hydroxy fatty acids. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1983, 29, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.-M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennasar, A.; Mulet, M.; Lalucat, J.; García-Valdés, E. PseudoMLSA: A database for multigenic sequence analysis of Pseudomonas species. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szcześniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Fetter, A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Metcalf, W.W.; Helfrich, E.J.N.; et al. antiSMASH 7.0: New and improved predictions for detection, regulation, chemical structures and visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Néron, B.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abby, S.S.; Rocha, E.P.C. Identification of protein secretion systems in bacterial genomes using MacSyFinder. In Bacterial Protein Secretion Systems; Journet, L., Cascales, E., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1615, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2023, 51, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, L.; Lood, C.; Höfte, M.; Vandamme, P.; Rokni-Zadeh, H.; van Noort, V.; Lavigne, R.; De Mot, R. The ever-expanding Pseudomonas genus: Description of 43 new species and partition of the Pseudomonas putida group. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, D.; Bernal, P.; Vazquez-Arias, D.; Blanco-Romero, E.; Garrido-Sanz, D.; Redondo-Nieto, M.; Rivilla, R.; Martín, M. Pseudomonas fluorescens F113 type VI secretion systems mediate bacterial killing and adaption to the rhizosphere microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, J.; Özkaya, Ö.; Kümmerli, R. Bacterial siderophores in community and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drehe, I.; Simonetti, E.; Ruiz, J.A. Contribution of the siderophores pyoverdine and enantio-pyochelin to fitness in soil of Pseudomonas protegens Pf-5. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Yao, Y.; Yeon, S.K.; Seiple, I.B. Modular approaches to lankacidin antibiotics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15116–15126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, G.; Mullins, A.J.; Petrova, Y.D.; Mahenthiralingam, E. Polyyne-producing Burkholderia suppress Globisporangium ultimum damping-off disease of Pisum sativum (pea). Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1240206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zhu, X.; Sun, J.; Meng, F.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. Bacillomycin D-C16 inhibits growth of Fusarium verticillioides and production of fumonisin B1 in maize kernels. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 181, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fira, D.; Dimkić, I.; Berić, T.; Lozo, J.; Stanković, S. Biological control of plant pathogens by Bacillus species. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 285, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenul, C.; Sieber, S.; Daeppen, C.; Mathew, A.; Lardi, M.; Pessi, G.; Hoepfner, D.; Neuburger, M.; Linden, A.; Gademann, K.; et al. Biosynthesis of fragin is controlled by a novel quorum sensing signal. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohya, M.; Watanabe, S.; Teramoto, K.; Tada, T.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Mya, S.; Zin, K.N.; Kirikae, T.; Tin, H.H. Pseudomonas yangonensis sp. nov., isolated from wound samples of patients in a hospital in Myanmar. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3597–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, D.; Défago, G. Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poblete-Morales, M.; Carvajal, D.; Almasia, R.; Michea, S.; Cantillana, C.; Levican, A.; Silva-Moreno, E. Pseudomonas atacamensis sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of desert bloom plant in the region of Atacama, Chile. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Ying, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Hao, J. Pseudomonas profundi sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1776–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silby, M.W.; Winstanley, C.; Godfrey, S.A.C.; Levy, S.B.; Jackson, R.W. Pseudomonas genomes: Diverse and adaptable. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 652–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).