Phylogenomic Analyses of Three Distinct Lineages Uniting Staphylococcus cohnii and Staphylococcus urealyticus from Diverse Hosts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Media
2.2. S. cohnii Isolates
2.3. Genome Sequence and Assembly
2.4. Bioinformatics
3. Results
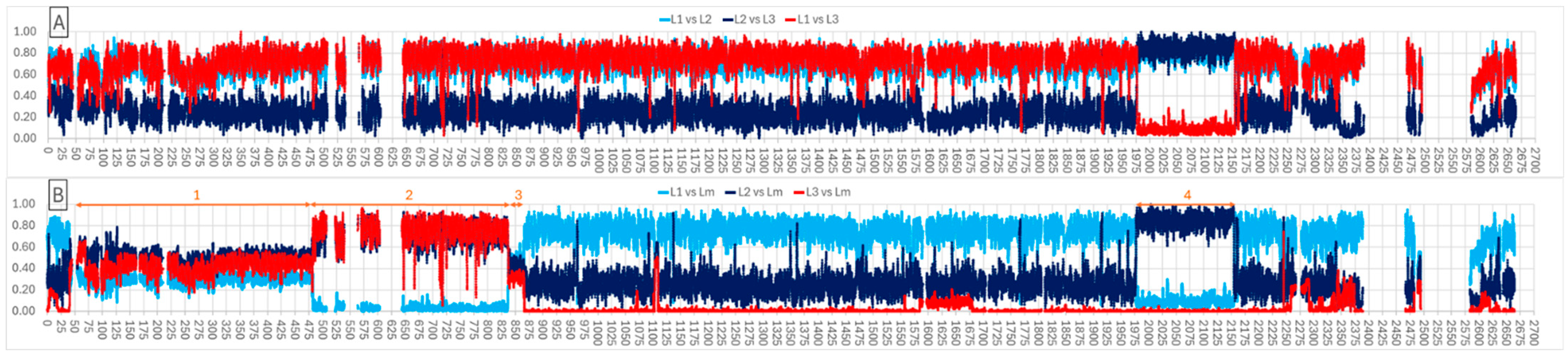
3.1. Phylogenomic Analyses Identify Three Lineages
3.2. Lineage Association with Host and Virulence
- YNSA55: China, human, survey of S. aureus, no disease state recorded
- NCTC11041: Homo sapiens skin, no disease
- FDAARGOS-538: Homo sapiens, clinical isolate
- H62: air, environmental
- Acroc: human skin, no disease state recorded
- RD01, RD04, RD09: Bacteria were isolated from multiple surfaces in washrooms on a university campus in Alberta, Canada.
- Hu-01: China Homo sapiens, skin swab, no disease
- G22B2: Homo sapiens, gall bladder
- 57: Homo sapiens, blood; opportunistic pathogen isolated from human patient
- 532: Homo sapiens, catheter; opportunistic pathogen isolated from human patient
- MUWRP0921: human UTI
- FDAARGOS_334: Homo sapiens, clinical isolate
- P3-SID1418: human skin, toe web space
- FDAARGOS_744: Homo sapiens, clinical isolate
- NBRC_109766: unknown
- RIT614: smartphone
- Nsq225: human, linezolid-resistant clinical isolate
- Nsq226: human, linezolid-resistant clinical isolate
- 3636: human oral infection
3.3. Horizontal Transfer between Lineages
3.4. Lineage Specific Polypeptides
3.5. Lineage Diagnostic qPCR
3.6. S. cohnii Plasmids
3.7. Genetic Diversity in BCO Infections
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Research Assurance
References
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. Virulence Mechanisms of Staphylococcal Animal Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, H.U.; Newman, S.S.; Roy, A.F.; Hoskins, J.D. Species of Staphylococcus isolated from animal infections. Cornell Vet. 1984, 74, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathema, B.; Mediavilla, J.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B. Evolution and taxonomy of staphylococci. In Staphylococci in Human Disease, 2nd ed.; Crossley, K., Jefferson, K., Archer, G., Folwer, V., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 31–64. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, P.B.; Barger, K.; Siewerdt, F. Limb Health in Broiler Breeding: History Using Genetics to Improve Welfare. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2019, 28, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideman, R.F.; Prisby, R.D. Bone circulatory disturbances in the development of spontaneous bacterial chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis: A translational model for the pathogenesis of femoral head necrosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 3, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideman, R.F. Bacterial chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis and lameness in broilers: A review. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wideman, R.F.; Hamal, K.R.; Stark, J.M.; Blankenship, J.; Lester, H.; Mitchell, K.N.; Lorenzoni, G.; Pevzner, I. A wire-flooring model for inducing lameness in broilers: Evaluation of probiotics as a prophylactic treatment. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilley, A.D.; Lester, H.; Pevzner, I.Y.; Anthony, N.B.; Wideman, R.F. Evaluating portable wire-flooring models for inducing bacterial chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry, E.G. The Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Cases of Staphylococcosis in Poultry. Res. Vet. Sci. 1967, 8, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibenge, F.S.; Wilcox, G.; Pass, D. Pathogenicity of four strains of Staphylococci isolated from chickens with clinical tenosynovitis. Avian Pathol. 1983, 12, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalib, A.; Riddell, C.; Osborne, A.D. Studies on the pathogenesis of Staphylococcal osteomyelitis in chickens. II. Role of the respiratory tract as a route of infection. Avian Dis. 1983, 27, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutalib, A.; Riddell, C.; Osborne, A.D. Studies on the Pathogenesis of Staphylococcal Osteomyelitis in Chickens. I. Effect of Stress on Experimentally Induced Osteomyelitis. Avian Dis. 1983, 27, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, P.T.; Smyth, J.A. Bacterial chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis (‘femoral head necrosis’) of broiler chickens: A review. Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, A.; Reeves, N.A.; Harbour, D.; Werrett, G.; Kestin, S.C. Molecular typing of strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bone and joint lesions in lame broilers by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Poult. Sci. 2001, 80, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowder, B.V.; Guinane, C.M.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Weinert, L.A.; Conway-Morris, A.; Cartwright, R.A.; Simpson, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Nübel, U.; Fitzgerald, J.R. Recent human-to-poultry host jump, adaptation, and pandemic spread of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19545–19550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekesi, N.S.; Dolka, B.; Alrubaye, A.; Rhoads, D. Analysis of Genomes of Bacterial Isolates from Lameness Outbreaks in Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.R. Livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus: Origin, evolution and public health threat. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubaye, A.A.K.; Couger, M.B.; Ojha, S.; Pummill, J.F.; Koon, J.A., II; Wideman, R.F., Jr.; Rhoads, D.D. Genome analysis of Staphylococcus agnetis, an agent of lameness in broiler chickens. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, L.L.; Thøfner, I.; Bisgaard, M.; Olsen, R.H.; Christensen, J.P.; Christensen, H. Staphylococcus agnetis, a potential pathogen in broiler breeders. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 212, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwani, A.; Adkins, P.R.F.; Ekesi, N.S.; Alrubaye, A.; Calcutt, M.J.; Middleton, J.R.; Rhoads, D.D. Whole genome comparisons of Staphylococcus agnetis isolates from cattle and chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00484-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, P.R.F.; Middleton, J.R.; Calcutt, M.J.; Stewart, G.C.; Fox, L.K. Species identification and strain typing of Staphylococcus agnetis and Staphylococcus hyicus isolates from bovine milk by use of a novel multiplex PCR assay and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1778–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, P.R.F.; Dufour, S.; Spain, J.N.; Calcutt, M.J.; Reilly, T.J.; Stewart, G.C.; Middleton, J.R. Molecular characterization of non-aureus Staphylococcus spp. from heifer intramammary infections and body sites. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5388–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, P.R.F.; Dufour, S.; Spain, J.N.; Calcutt, M.J.; Reilly, T.J.; Stewart, G.C.; Middleton, J.R. Cross-sectional study to identify staphylococcal species isolated from teat and inguinal skin of different-aged dairy heifers. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3213–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akarsu, H.; Liljander, A.; Younan, M.; Brodard, I.; Overesch, G.; Glücks, I.; Labroussaa, F.; Kuhnert, P.; Perreten, V.; Monecke, S.; et al. Genomic Characterization and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Dromedary-Associated Staphylococcaceae from the Horn of Africa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e01146-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, M.N.; Turni, C.; Gilbert, R.; Raza, A.; Allavena, R.; McGowan, M.; Constantinoiu, C.; Ong, C.T.; Tabor, A.E.; James, P. Role of Staphylococcus agnetis and Staphylococcus hyicus in the Pathogenesis of Buffalo Fly Skin Lesions in Cattle. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00873-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, D.I.; Grum, D.S.; Evans, N.P.; Russo, K.N.; Kimminau, E.A.; Trible, B.R.; Lahoti, M.M.; Novak, C.L.; Karnezos, T.P. Identification and characterization of the causative agents of Focal Ulcerative Dermatitis in commercial laying hens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1110573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrubaye, A.; Ekesi, N.S.; Hasan, A.; Koltes, D.A.; Wideman, R., Jr.; Rhoads, D. Chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis in broilers: Further defining a bacterial challenge model using standard litter flooring and protection with probiotics. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6474–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, D.D.; Pummill, J.; Ekesi, N.S.; Alrubaye, A.A.K. Horizontal transfer of probable chicken-pathogenicity chromosomal islands between Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus agnetis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, E.J.; Bacigalupe, R.; Harrison, E.M.; Weinert, L.A.; Lycett, S.; Vrieling, M.; Robb, K.; Hoskisson, P.A.; Holden, M.T.G.; Feil, E.J.; et al. Gene exchange drives the ecological success of a multi-host bacterial pathogen. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnayanti, A.; Do, A.D.T.; Alharbi, K.; Alrubaye, A. Inducing experimental bacterial chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis lameness in broiler chickens using aerosol transmission model. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloos, W.E.; Wolfshohl, J.F. Staphylococcus cohnii Subspecies: Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii subsp. nov. and Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. urealyticum subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1991, 41, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lavecchia, A.; Chiara, M.; De Virgilio, C.; Manzari, C.; Pazzani, C.; Horner, D.; Pesole, G.; Placido, A. Comparative Genomics Suggests a Taxonomic Revision of the Staphylococcus cohnii Species Complex. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldera, J.; Nedel, W.L.; Cardoso, P.R.C.; d’Azevedo, P.A. Bacteremia due to Staphylococcus cohnii ssp. urealyticus caused by infected pressure ulcer: Case report and review of the literature. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2013, 131, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Marek, A.; Stepień-Pyśniak, D.; Pyzik, E.; Adaszek, Ł.; Wilczyński, J.; Winiarczyk, S. Occurrence and characterization of Staphylococcus bacteria isolated from poultry in Western Poland. Berl. Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschr. 2016, 129, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rubaye, A.A.K.; Ekesi, N.S.; Zaki, S.; Emami, N.K.; Wideman, R.F.; Rhoads, D.D. Chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis in broilers: Further defining a bacterial challenge model using the wire flooring model. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwani, A.; Zuo, B.; Alrubaye, A.; Zhao, J.; Rhoads, D.D. A Simple, Inexpensive Alkaline Method for Bacterial DNA Extraction from Environmental Samples for PCR Surveillance and Microbiome Analyses. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwani, A. Bacterial Chondronecrosis with Osteomyelitis in Broilers: Genomics, Phylogenomics, and Methods to Detect Specific Pathogens during Outbreaks. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, AR, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, D.W.; Iandolo, J.J. Rapid isolation of DNA from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acid Res. 2022, 51, D678–D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, J.A.; Harris, S.R.; Tonkin-Hill, G.; Gladstone, R.A.; Lo, S.W.; Weiser, J.N.; Corander, J.; Bentley, S.D.; Croucher, N.J. Fast and flexible bacterial genomic epidemiology with PopPUNK. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treangen, T.J.; Ondov, B.D.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, L.; Glover, R.H.; Humphris, S.; Elphinstone, J.G.; Toth, I.K. Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: Soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzer, M. POCP-nf: An automatic Nextflow pipeline for calculating the percentage of conserved proteins in bacterial taxonomy. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.V.; Zmasek, C.M. phyloXML: XML for evolutionary biology and comparative genomics. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argimón, S.; Abudahab, K.; Goater, R.J.E.; Fedosejev, A.; Bhai, J.; Glasner, C.; Feil, E.J.; Holden, M.T.G.; Yeats, C.A.; Grundmann, H.; et al. Microreact: Visualizing and sharing data for genomic epidemiology and phylogeography. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.L.; Mullet, J.; Hindi, F.; Stoll, J.E.; Gupta, S.; Choi, M.; Keenum, I.; Vikesland, P.; Pruden, A.; Zhang, L. mobileOG-db: A Manually Curated Database of Protein Families Mediating the Life Cycle of Bacterial Mobile Genetic Elements. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0099122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, T. BLAST® Command Line Applications User Manual. 2008. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279691/ (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, S.C.; Thorpe, H.A.; Coyle, N.M.; Sheppard, S.K.; Feil, E.J. PIRATE: A fast and scalable pangenomics toolbox for clustering diverged orthologues in bacteria. GigaScience 2019, 8, giz119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynildsrud, O.; Bohlin, J.; Scheffer, L.; Eldholm, V. Rapid scoring of genes in microbial pan-genome-wide association studies with Scoary. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.J.; Nayfach, S.; Pollard, K.S. Maast: Genotyping thousands of microbial strains efficiently. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Le, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, F. SeqKit: A Cross-Platform and Ultrafast Toolkit for FASTA/Q File Manipulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalucat, J.; Mulet, M.; Gomila, M.; García-Valdés, E. Genomics in Bacterial Taxonomy: Impact on the Genus Pseudomonas. Genes 2020, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graña-Miraglia, L.; Arreguín-Pérez, C.; López-Leal, G.; Muñoz, A.; Pérez-Oseguera, A.; Miranda-Miranda, E.; Cossío-Bayúgar, R.; Castillo-Ramírez, S. Phylogenomics picks out the par excellence markers for species phylogeny in the genus Staphylococcus. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, N.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Ivanova, N.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Mavrommatis, K.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Pati, A. Microbial species delineation using whole genome sequences. Nucleic Acid Res. 2015, 43, 6761–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Quiles-Puchalt, N.; Chiang, Y.N.; Bacigalupe, R.; Fillol-Salom, A.; Chee, M.S.J.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penadés, J.R. Genome hypermobility by lateral transduction. Science 2018, 362, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, R.; Reeves, P.R. Escherichia coli in disguise: Molecular origins of Shigella. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abram, K.; Udaondo, Z.; Bleker, C.; Wanchai, V.; Wassenaar, T.M.; Robeson, M.S.; Ussery, D.W. Mash-based analyses of Escherichia coli genomes reveal 14 distinct phylogroups. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gao, F. High-quality pan-genome of Escherichia coli generated by excluding confounding and highly similar strains reveals an association between unique gene clusters and genomic islands. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Alba, J.M.; Baquero, F.; Cantón, R.; Galán, J.C. Stratified reconstruction of ancestral Escherichia coli diversification. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrubaye, A.A.K.; Ekesi, N.S.; Hasan, A.; Elkins, E.; Ojha, S.; Zaki, S.; Dridi, S.; Wideman, R.F.; Rebollo, M.A.; Rhoads, D.D. Chondronecrosis with Osteomyelitis in Broilers: Further Defining Lameness-Inducing Models with Wire or Litter Flooring, to Evaluate Protection with Organic Trace Minerals. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5422–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Isolate | Colony Color | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Exp | Bird | WGS | Lineage | CO | CS |
| 1637 | 29 | 10A | yes | 1 | p | l |
| 1649 | 29 | 10A | yes | 1 | t | t |
| 1662 | 29 | 10B | 1 | p | l | |
| 1667 | 29 | 10B | yes | 2 | w | l |
| 1670 | 29 | 10B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1638 | 29 | 11A | yes | 1 | p | l |
| 1650 | 29 | 11A | 1 | t | t | |
| 1651 | 29 | 11B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1652 | 29 | 12B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1653 | 29 | 13A | 1 | t | t | |
| 1654 | 29 | 13B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1663 | 29 | 13B | yes | 1 | p | l |
| 1655 | 29 | 14A | 1 | t | t | |
| 1656 | 29 | 14B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1657 | 29 | 2A | 1 | t | t | |
| 1658 | 29 | 2A | yes | 1 | p | l |
| 1659 | 29 | 3B | yes | 1 | p | l |
| 1664 | 29 | 3B | yes | 2 | w | l |
| 1644 | 29 | 5B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1645 | 29 | 6A | yes | 1 | t | t |
| 1636 | 29 | 6B | 1 | p | l | |
| 1646 | 29 | 6B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1661 | 29 | 9A | yes | 1 | p | l |
| 1665 | 29 | 9A | yes | 2 | w | l |
| 1669 | 29 | 9A | 1 | t | t | |
| 1639 | 29 | 9B | 1 | p | l | |
| 1648 | 29 | 9B | 1 | t | t | |
| 1666 | 29 | 9B | yes | 2 | w | l |
| 1697 | 30 | 2 | yes | 2 | t | t |
| 1725 | 30 | 3 | yes | 2 | t | t |
| 1711 | 30 | 4 | yes | 2 | w | l |
| 1701 | 30 | 6 | yes | 1 | t | t |
| 1728 | 30 | 8 | yes | 2 | p | l |
| 1714 | 30 | 10 | yes | 2 | p | l |
| 1715 | 30 | 10 | yes | 2 | p | l |
| Lineage | n | 1 | 2 | 3 | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56 | 0.99012 ± 0.00771 | 0.92023 ± 0.00566 | 0.92526 ± 0.00333 | 0.94591 ± 0.00196 |
| 2 | 40 | 0.99290 ± 0.00591 | 0.96082 ± 0.00171 | 0.94935 ± 0.00025 | |
| 3 | 23 | 0.99558 ± 0.00368 | 0.97667 ± 0.00216 | ||
| m | 5 | 0.99996 ± 0.00004 |
| Sn | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | |
| POCP | Sn | 93.9 ± 1.8 | 84.2 ± 1.4 | 85.4 ± 1.6 | 84.0 ± 0.7 |
| 1 | 90.4 ± 2.3 | 88.5 ± 1.5 | 89.2 ± 1.6 | ||
| 2 | NA | 88.2 ± 0.6 | |||
| 3 | 95.3 ± 2.0 | ||||
| ANI | Sn | 0.997 ± 0.0015 | 0.857 ± 0.0007 | 0.879 ± 0.0459 | 0.859 ± 0.0012 |
| 1 | 0.990 ± 0.0036 | 0.919 ± 0.0003 | 0.925 ± 0.0015 | ||
| 2 | NA | 0.961 ± 0.0004 | |||
| 3 | 0.997 ± 0.0017 |
| Trait | Gene Count | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bonferroni p < 0.05 | Odds Ratio | 100% Specificity and Sensitivity | ||
| >4.4 | <0.24 | |||
| Lineage 1 | 1756 | 857 | 899 | 84 |
| Lineage 2 | 1716 | 867 | 849 | 14 |
| Lineage 3 | 1311 | 707 | 604 | 13 |
| Human | 333 | 195 | 138 | 0 |
| Mammal | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Avian | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Chicken | 17 | 17 | 0 | 0 |
| Animal | 166 | 37 | 129 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
House, L.C.; Hasan, A.; Asnayanti, A.; Alrubaye, A.A.K.; Pummill, J.; Rhoads, D. Phylogenomic Analyses of Three Distinct Lineages Uniting Staphylococcus cohnii and Staphylococcus urealyticus from Diverse Hosts. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081549
House LC, Hasan A, Asnayanti A, Alrubaye AAK, Pummill J, Rhoads D. Phylogenomic Analyses of Three Distinct Lineages Uniting Staphylococcus cohnii and Staphylococcus urealyticus from Diverse Hosts. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(8):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081549
Chicago/Turabian StyleHouse, L. Caroline, Amer Hasan, Andi Asnayanti, Adnan A. K. Alrubaye, Jeff Pummill, and Douglas Rhoads. 2024. "Phylogenomic Analyses of Three Distinct Lineages Uniting Staphylococcus cohnii and Staphylococcus urealyticus from Diverse Hosts" Microorganisms 12, no. 8: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081549
APA StyleHouse, L. C., Hasan, A., Asnayanti, A., Alrubaye, A. A. K., Pummill, J., & Rhoads, D. (2024). Phylogenomic Analyses of Three Distinct Lineages Uniting Staphylococcus cohnii and Staphylococcus urealyticus from Diverse Hosts. Microorganisms, 12(8), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081549







