Sequencing Analysis of Invasive Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Secondary to Gastrointestinal Colonization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
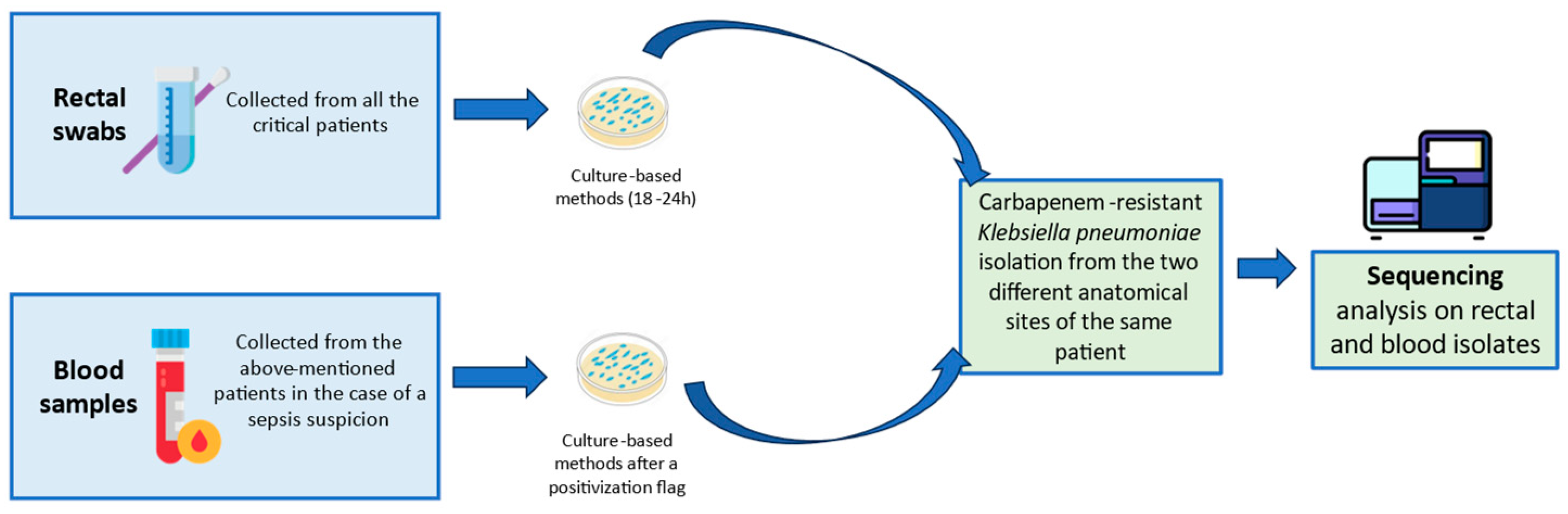
2.1. Screening Swabs Collection and Culture-Based Procedure
2.2. Molecular In-Depths of Colonizing and Disseminating Strains
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, W.; Liu, H.; Dunstan, R.A.; Li, B.; Torres, V.V.L.; Cao, J.; Chen, L.; Wilksch, J.J.; Strugnell, R.A.; Lithgow, T.; et al. Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Causing Nosocomial Bloodstream Infections in China: Molecular Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance Determinants, Informing Therapy, and Clinical Outcomes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gorrie, C.L.; Mirčeta, M.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Lam, M.M.C.; Gomi, R.; Abbott, I.J.; Thomson, N.R.; Strugnell, R.A.; Pratt, N.F.; et al. Genomic dissection of Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in hospital patients reveals insights into an opportunistic pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vandhana, V.; Saralaya, K.V.; Bhat, S.; Mulki, S.S.; Bhat, A.K. Characterization of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (Hv-Kp): Correlation of Virulence with Antimicrobial Susceptibility. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 4532707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cornaglia, G.; Courcol, R.; Herrmann, J.L.; Kahlmeter, G. European Manual of Clinical Microbiology; Prima Edizione; ESCMID: Basel, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, M.; Stefani, S.; Migliorisi, G. Bacterial Infections in Intensive Care Units: Epidemiological and Microbiological Aspects. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Del Prete, R.; Ronga, L.; Addati, G.; Magrone, R.; Abbasciano, A.; Decimo, M.; Mosca, A.; Miragliotta, G. Trends in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from the bloodstream in a teaching hospital in southern Italy. Infez. Med. 2019, 27, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Bianco, F.; Morotti, M.; Zannoli, S.; Dirani, G.; Fantini, M.; Pedna, M.F.; Farabegoli, P.; Sambri, V. Comparison of Four Commercial Screening Assays for the Detection of blaKPC, blaNDM, blaIMP, blaVIM, and blaOXA48 in Rectal Secretion Collected by Swabs. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, P.; Wu, F.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, J. Epidemiological and Molecular Characteristics of blaNDM-1 and blaKPC-2 Co-Occurrence Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Available online: https://qlik.qualitasiciliassr.it/anonimo/single/?appid=85ada16c-4b41-4bc6-9ca1-405b8243d0c2&sheet=6ad6f3ac-3369-41c5-bd72-792243f9091b&opt=ctxmenu,currsel (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Loconsole, D.; Sallustio, A.; Sacco, D.; Santantonio, M.; Casulli, D.; Gatti, D.; Accogli, M.; Parisi, A.; Zagaria, R.; Colella, V.; et al. Genomic surveillance of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae reveals a prolonged outbreak of extensively drug-resistant ST147 NDM-1 during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Apulia region (Southern Italy). J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 36, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiorno, D.; Bivona, D.A.; Cicino, C.; Trecarichi, E.M.; Russo, A.; Marascio, N.; Mezzatesta, M.L.; Musso, N.; Privitera, G.F.; Quirino, A.; et al. Omic insights into various ceftazidime-avibactam-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from two southern Italian regions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1010979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Local Run Manager Generate FASTQ Analysis Module Workflow Guide (1000000003344). Available online: https://support.illumina.com/downloads/local-run-manager-generate-fastq-module-workflow-guide-1000000003344.html (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, F. Trim Galore [Internet]. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Gorrie, C.; Jenney, A.; Follador, R.; Thomson, N.R.; Holt, K.E. Identification of Klebsiella capsule synthesis loci from whole genome data. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada, N.M.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Eiros, J.M.; Hernández, M. TORMES: An automated pipeline for whole bacterial genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4207–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.A., 3rd; Read, T.D. Bactopia: A Flexible Pipeline for Complete Analysis of Bacterial Genomes. mSystems 2020, 5, e00190-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Onori, R.; Gaiarsa, S.; Comandatore, F.; Pongolini, S.; Brisse, S.; Colombo, A.; Cassani, G.; Marone, P.; Grossi, P.; Minoja, G.; et al. Tracking Nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections and Outbreaks by Whole-Genome Analysis: Small-Scale Italian Scenario within a Single Hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joseph, L.; Merciecca, T.; Forestier, C.; Balestrino, D.; Miquel, S. From Klebsiella pneumoniae Colonization to Dissemination: An Overview of Studies Implementing Murine Models. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roe, C.C.; Vazquez, A.J.; Esposito, E.P.; Zarrilli, R.; Sahl, J.W. Diversity, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance in Isolates From the Newly Emerging Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 Lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Loconsole, D.; Accogli, M.; De Robertis, A.L.; Capozzi, L.; Bianco, A.; Morea, A.; Mallamaci, R.; Quarto, M.; Parisi, A.; Chironna, M. Emerging high-risk ST101 and ST307 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clones from bloodstream infections in Southern Italy. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mitra, S.; Dutta, S.; Basu, S. Neonatal Sepsis: The Impact of Carbapenem-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 634349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shaidullina, E.R.; Schwabe, M.; Rohde, T.; Shapovalova, V.V.; Dyachkova, M.S.; Matsvay, A.D.; Savochkina, Y.A.; Shelenkov, A.A.; Mikhaylova, Y.V.; Sydow, K.; et al. Genomic analysis of the international high-risk clonal lineage Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 395. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Calvo, M.; Migliorisi, G.; Maugeri, G.; Bongiorno, D.; Bonomo, C.; Nicitra, E.; Scalia, G.; Stefani, S. The molecular detection of carbapenem markers with a two-levels amplification screening protocol: Epidemiological and resistome insights. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1346442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zong, Z. Conjugation of a Hybrid Plasmid Encoding Hypervirulence and Carbapenem Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae of Sequence Type 592. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 852596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Henson, S.P.; Boinett, C.J.; Ellington, M.J.; Kagia, N.; Mwarumba, S.; Nyongesa, S.; Mturi, N.; Kariuki, S.; Scott, J.A.G.; Thomson, N.R.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae invasive infections over a decade at Kilifi County Hospital in Kenya. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Perry, C.; McGowan, K.; Turton, J.A.; Hope, R. Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 147: A high-risk clone increasingly associated with plasmids carrying both resistance and virulence elements. J. Med. Microbiol. 2024, 73, 001823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragupathi, N.K.D.; Bakthavatchalam, Y.D.; Mathur, P.; Pragasam, A.K.; Walia, K.; Ohri, V.; Veeraraghavan, B. Plasmid profiles among some ESKAPE pathogens in a tertiary care centre in south India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Long, J.; Zhang, J.; Xi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Duan, G. Genomic Insights into CRISPR-Harboring Plasmids in the Klebsiella Genus: Distribution, Backbone Structures, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Determinant Profiles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e0118922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lazareva, I.; Ageevets, V.; Sopova, J.; Lebedeva, M.; Starkova, P.; Likholetova, D.; Gostev, V.; Moiseenko, V.; Egorenkov, V.; Navatskaya, A.; et al. The emergence of hypervirulent blaNDM-1-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 395 in an oncology hospital. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posteraro, B.; De Maio, F.; Motro, Y.; Menchinelli, G.; De Lorenzis, D.; Marano, R.B.M.; Aljanazreh, B.; Errico, F.M.; Massaria, G.; Spanu, T.; et al. In-depth characterization of multidrug-resistant NDM-1 and KPC-3 co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream isolates from Italian hospital patients. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0330523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smorawinska, M.; Szuplewska, M.; Zaleski, P.; Wawrzyniak, P.; Maj, A.; Plucienniczak, A.; Bartosik, D. Mobilizable narrow host range plasmids as natural suicide vectors enabling horizontal gene transfer among distantly related bacterial species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 326, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Bonnin, R.A.; Nordmann, P. Genetic Features of the Widespread Plasmid Coding for the Carbapenemase OXA-48. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Mentasti, M.; Sands, K.; Portal, E.; Graham, L.; Watkins, J.; Williams, C.; Healy, B.; Spiller, O.B.; Aanensen, D.M.; et al. Genomic surveillance of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella in Wales reveals persistent spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 and adaptive evolution of pOXA-48-like plasmids. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherburne, C.K. The complete DNA sequence and analysis of R27, a large IncHI plasmid from Salmonella typhi that is temperature sensitive for transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gona, F.; Caio, C.; Iannolo, G.; Monaco, F.; Di Mento, G.; Cuscino, N.; Fontana, I.; Panarello, G.; Maugeri, G.; Mezzatesta, M.L.; et al. Detection of the IncX3 plasmid carrying bla KPC-3 in a Serratia marcescens strain isolated from a kidney–liver transplanted patient. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1454–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leavitt, A.; Chmelnitsky, I.; Carmeli, Y.; Navon-Venezia, S. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of KPC-3-Encoding Plasmid pKpQIL in the Epidemic Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 258. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4493–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.; Villa, L.; Carta, C.; Venditti, C.; Giordano, A.; Venditti, M.; Mancini, C.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 Producing KPC-3 Identified in Italy Carries Novel Plasmids and OmpK36/OmpK35 Porin Variants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2143–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, A.B.; Rosinski-Chupin, I.; Takissian, J.; Glaser, P.; Bonnin, R.A.; Naas, T. Transcriptional Landscape of a blaKPC-2 Plasmid and Response to Imipenem Exposure in Escherichia coli TOP10. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Kuang, D.; Deng, Z.; Ou, H.-Y.; Qu, J. Mobilizable plasmids drive the spread of antimicrobial resistance genes and virulence genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, X.; Dong, N.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Carbapenem Resistance-Encoding and Virulence-Encoding Conjugative Plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 29, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Hasman, H. PlasmidFinder and In Silico pMLST: Identification and Typing of Plasmid Replicons in Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS). In Horizontal Gene Transfer; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2075, pp. 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/antibiotico-resistenza/cre (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/new-genomic-surveillance-studies-reveal-circulation-multidrug-resistant (accessed on 14 June 2024).
| Number of Colonized Patients | Number of Infected Patients | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intensive care units (ICU and NICU) | 83 | 3 | 3.6% |
| Haematology Unit | 38 | 1 | 2.6% |
| Emergency Room | 20 | 2 | 10% |
| Neurological Clinic | 2 | 1 | 50% |
| Total | 143 * | 7 | 4.9% |
| General Information | Phenotypic Susceptibility Data | Molecular Data | Typing Data | Beta-Lactams Resistome Analysis | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | Code | Species | Sample Type | Meropenem MIC (mg/L) | Ceftazidime MIC (mg/L) | Ceftazidime/Avibactam MIC (mg/L) | Carba-R Result | ST | wzi | k-locus | o-locus | blaNDM | blaKPC | blaOXA | blaSHV | blaTEM | blaCTX-M | blaampH | Omp mutations | |||||
| 1 | 910091 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 32 | 32 | 2 | KPC | 101 | wzi137 | KL17 | O1/O2v1 | / | KPC-3 | / | / | / | / | / | / | SHV-212 | / | / | ampH | yes |
| 885662 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal swab | 32 | 32 | 2 | KPC | 101 | wzi137 | KL17 | O1/O2v1 | / | KPC-3 | / | / | / | / | / | / | SHV-212 | / | / | ampH | yes | |
| 2 | 887213 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 32 | 16 | 2 | KPC | 101 | wzi137 | KL17 | O1/O2v1 | / | KPC-3 | / | / | / | / | / | / | SHV-212 | / | / | ampH | yes |
| 887108 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal swab | 32 | 16 | 2 | KPC | 101 | wzi137 | KL17 | O1/O2v1 | / | KPC-3 | / | / | / | / | / | / | SHV-212 | / | / | ampH | yes | |
| 3 | 881005 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 16 | 32 | 32 | NDM | 395 | wzi2 | KL2 | O1/O2v1 | NDM-1 | / | OXA-1 | / | / | / | / | SHV-187 | / | TEM-181 | CTX-M-15 | ampH | yes |
| 878504 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal swab | 16 | 32 | 32 | NDM | 395 | wzi2 | KL2 | O1/O2v1 | NDM-1 | / | OXA-1 | / | / | / | / | SHV-187 | / | TEM-181 | CTX-M-15 | ampH | yes | |
| 4 | 911056 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 16 | 16 | 4 | KPC | 101 | wzi137 | KL17 | O1/O2v1 | / | KPC-3 | / | / | / | / | / | / | SHV-212 | / | / | ampH | yes |
| 911057 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal swab | 16 | 16 | 4 | KPC | 101 | wzi137 | KL17 | O1/O2v1 | / | KPC-3 | / | / | / | / | / | / | SHV-212 | / | / | ampH | yes | |
| 5 | 886012 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 16 | 32 | 64 | NDM/OXA-48 | 395 | wzi2 | KL2 | O1/O2v1 | NDM-1 | / | OXA-1 | / | OXA-48 | / | / | SHV-187 | / | / | CTX-M-15 | ampH | yes |
| 878757 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal swab | 16 | 32 | 64 | NDM/OXA-48 | 395 | wzi2 | KL2 | O1/O2v1 | NDM-1 | / | OXA-1 | / | OXA-48 | / | / | SHV-187 | / | / | CTX-M-15 | ampH | Yes | |
| 6 | 858616 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 16 | 32 | 2 | KPC | 307 | wzi173 | KL102 | O1/O2v2 | / | KPC-3 | OXA-1 | OXA-9 | / | SHV-28 | / | / | / | TEM-181 | CTX-M-15 | ampH | Yes |
| 878785 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal swab | 16 | 32 | 2 | KPC | 307 | wzi173 | KL102 | O1/O2v2 | / | KPC-3 | OXA-1 | OXA-9 | / | SHV-28 | / | / | / | TEM-181 | CTX-M-15 | ampH | Yes | |
| 7 | 904721 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 32 | 16 | 64 | NDM | 395 | wzi2 | KL2 | O1/O2v1 | NDM-1 | / | OXA-1 | / | / | / | / | SHV-187 | / | / | CTX-M-15 | ampH | Yes |
| 906602 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal swab | 32 | 16 | 64 | NDM | 395 | wzi2 | KL2 | O1/O2v1 | NDM-1 | / | OXA-1 | / | / | / | / | SHV-187 | / | / | CTX-M-15 | ampH | Yes | |
| Beta-lactams | Fluorochinolone | Aminoglycosides | Colistin | Fosfomycin | Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxaz | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | Sample | AMP | AMC | TZP | FEP | CAZ | CRO | CTX | CXM | AZT | CZA | C/T | MEM | IMI | MEM/VAB | CIP | LEV | AK | CN | TOB | COL | FOS | SXT |
| 1 | 910091 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 8/4 | >4/4 | >16 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >1 | >1 | >16 | >4 | >4 | ≤0.5 | ≤16 | >160 |
| 885662 | >8 | >16 | >64 | >16 | >32 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 8 | >16 | >8 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >2 | >1 | 32 | >8 | >4 | ≤0.5 | ≤16 | >160 | |
| 2 | 887213 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 2/4 | >4/4 | >16 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >1 | >1 | ≤4 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 |
| 887108 | >8 | >16 | >64 | >16 | >32 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 4 | >16 | >8 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >2 | >1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | 1 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 | |
| 3 | 881005 | >8 | >16 | >64 | >16 | >32 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | >8 | >16 | >8 | >8 | >8/8 | >2 | >1 | 32 | >8 | >8 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 |
| 878504 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | >8/4 | >4/4 | >16 | >8 | >8/8 | >1 | >1 | >16 | >4 | >4 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 | |
| 4 | 911056 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 4/4 | >4/4 | >16 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >1 | >1 | >16 | >4 | >4 | ≤0.5 | 32 | >160 |
| 911057 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 4 | >4/4 | >16 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >1 | >1 | >16 | >4 | >4 | ≤0.5 | 32 | >160 | |
| 5 | 886012 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | >8/4 | >4/4 | 16 | >8 | >8/8 | >1 | >1 | >16 | >4 | >4 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 |
| 878757 | >8 | >16 | >64 | >16 | >32 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | >8 | >16 | >8 | >8 | >8/8 | >2 | >1 | 32 | >8 | >8 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 | |
| 6 | 858616 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 2/4 | >4/4 | 16 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >1 | >1 | ≤4 | ≤1 | >4 | ≤0.5 | ≤16 | >160 |
| 878785 | >8 | >16 | >64 | >16 | >32 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | 1 | >16 | >8 | >8 | ≤2/8 | >2 | >1 | 4 | ≤1 | 8 | ≤0.5 | ≤16 | >160 | |
| 7 | 904721 | >8 | >32/2 | >64/4 | >8 | >16 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | >8/4 | >4/4 | >16 | >8 | >8/8 | >1 | >1 | >16 | >4 | >4 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 |
| 906602 | >8 | >16 | >64 | >16 | >32 | >4 | >32 | >8 | >16 | >8 | >16 | >8 | >8 | >8/8 | >2 | >1 | 32 | >8 | >4 | ≤0.5 | >64 | >160 | |
| Aerobactin | Enterobactin | Capsule Production | Salmochelin | LPS Production | Mucoid phenotype | Type 1-Fimbriae | Yersiniabactin | Phagocytosis Inhibition | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST | Sample Code | iucA | iucB | iucC | iucD | iutA | entA | entB | entC | entD | entE | entF | manB | galF | iroE | wbbM | wbbN | wbbO | wzt | rmpA2 | fimA | fimB | fimC | fimD | fimE | fimF | fimG | fimH | fimI | fimK | irp1 | irp2 | ybtE | ybtS | ybtT | ybtU | ybtX | ybtA | acrA | acrB |
| 101 | 910091 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101 | 885662 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101 | 887213 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101 | 887108 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 395 | 881005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 395 | 878504 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101 | 911056 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101 | 911057 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 395 | 886012 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 395 | 878757 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 307 | 858616 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 307 | 878785 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 395 | 904721 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 395 | 906602 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Patient 7 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate 1 | Isolate 2 | Isolate 3 | Isolate 4 | Isolate 5 | Isolate 6 | Isolate 7 | Isolate 8 | Isolate 9 | Isolate 10 | Isolate 11 | Isolate 12 | Isolate 13 | Isolate 14 | |
| 910091 | 885662 | 887213 | 887108 | 881005 | 878504 | 911056 | 911057 | 886012 | 878757 | 858616 | 878785 | 904721 | 906602 | |
| ST 101 | ST 101 | ST 101 | ST 101 | ST 395 | ST 395 | ST 101 | ST 101 | ST 395 | ST 395 | ST 307 | ST 307 | ST 395 | ST 395 | |
| PLASMIDS | IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) a | IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) a | - | - | IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) a | IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) a | - | - | IncHI1B(pNDM- MAR) a | IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) a | - | - | IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) a | IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) a |
| IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | IncFII pKP91 b | |
| IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | IncFIB(K) c | |
| IncR d | IncR d | IncR d | IncR d | - | - | IncR d | IncR d | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | ColRNAI e | |
| Col156 f | Col156 f | Col156 f | Col156 f | - | - | Col156 f | Col156 f | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| IncFIA(HI1) g | IncFIA(HI1) g | IncFIA(HI1) g | IncFIA(HI1) g | - | - | IncFIA(HI1) g | IncFIA(HI1) g | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Col440I h | Col440I h | Col440I h | Col440I h | - | - | Col440I h | Col440I h | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Col440I i | Col440I i | Col440I i | Col440I i | - | - | Col440I i | Col440I i | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IncL/M(pOXA-48) l | IncL/M(pOXA-48) l | - | - | - | - | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IncFIB(pQil) m | IncFIB(pQil) m | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maugeri, G.; Calvo, M.; Bongiorno, D.; Bivona, D.; Migliorisi, G.; Privitera, G.F.; Scalia, G.; Stefani, S. Sequencing Analysis of Invasive Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Secondary to Gastrointestinal Colonization. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010089
Maugeri G, Calvo M, Bongiorno D, Bivona D, Migliorisi G, Privitera GF, Scalia G, Stefani S. Sequencing Analysis of Invasive Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Secondary to Gastrointestinal Colonization. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010089
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaugeri, Gaetano, Maddalena Calvo, Dafne Bongiorno, Dalida Bivona, Giuseppe Migliorisi, Grete Francesca Privitera, Guido Scalia, and Stefania Stefani. 2025. "Sequencing Analysis of Invasive Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Secondary to Gastrointestinal Colonization" Microorganisms 13, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010089
APA StyleMaugeri, G., Calvo, M., Bongiorno, D., Bivona, D., Migliorisi, G., Privitera, G. F., Scalia, G., & Stefani, S. (2025). Sequencing Analysis of Invasive Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Secondary to Gastrointestinal Colonization. Microorganisms, 13(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010089







