Abstract
Cryptosporidium spp. are zoonotic protozoan parasites with a global prevalence, with both gastrointestinal and pulmonary involvement. Though symptoms can often be relatively mild, they can become severe and even fatal in children under five, the elderly, and in immunocompromised individuals, making cryptosporidiosis a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in fragile populations. Furthermore, there is an urgent clinical need for alternative therapies against cryptosporidiosis, as currently available FDA-approved treatments are ineffective in the immunocompromised. Recent evidence in animal models suggests that the gut microbiota (GM) can influence both host and parasite biology to influence the course of Cryptosporidium infection. Here, we present GM profiles in five cases of cryptosporidiosis, associated with varying underlying pathologies. We found that moderate–severe cryptosporidiosis was characterized by a reduction in alpha-diversity and an enrichment of Enterococcus spp., while decreases in Bifidobacterium, Gemmiger, and Blautia were detectable in the milder manifestations of the disease. Our results suggest that severe cryptosporidiosis is associated with a stronger change on the GM than is age or underlying pathology. Together with previously published studies in animal models, we believe that these results suggest that the GM could be a potential therapeutic target for human patients as well, particularly in the immunocompromised for whom anti-Cryptosporidium treatment remains largely ineffective.
1. Introduction
Cryptosporidium, Tyzzer, 1907 (Eucoccidiorida: Cryptosporidiidae), is a genus comprising over 40 species of protozoan parasites, of which over 20 can also infect humans [1,2]. Infection begins with the ingestion of oocysts, most commonly from contaminated water, food, or from direct animal–human or human–human contact. Once they reach the small intestine, sporozoites are released and attach themselves to the host enterocytes, forming an intracellular but extra-cytoplasmic vacuole in which the sporozoite differentiates into a trophozoite [3]. Mitotic division of the trophozoite produces merozoites, which can behave like sporozoites by escaping the vacuole, attaching to neighboring enterocytes, and beginning the process over again. Alternatively, merozoites can also undergo sexually dimorphic differentiation and reproduce sexually, producing diploid zygotes which differentiate into oocysts. These oocysts can then either continue to re-infect the host, or be released into the environment to infect other individuals [3,4,5].
Once infected, humans most commonly present with watery diarrhea, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, and coughing [3,4,5,6]. Though many are able to cope with infection within a two-week period, even without medication, very young children, the elderly and the immunocompromised are at an increased risk of severe morbidity and mortality. One study found that, in 2016, cryptosporidiosis was globally responsible for over 48,000 deaths and a loss of 12.05 million disability-adjusted life-years in children under five, making it the fifth leading diarrheal etiology in the world [6]. Another study conducted in Africa and Asia reported even more dire numbers, finding approximately 202,000 Cryptosporidium-attributable deaths in children under two, a net increase of 59,000 deaths compared to Cryptosporidium-negative children with similar symptoms [7].
Immunocompromised individuals are at the highest risk of morbidity and mortality due to chronic cryptosporidiosis, largely due to the ineffectiveness of anti-Cryptosporidium treatment in patients with low CD4+ cell counts [3,8]. To this day, cryptosporidiosis remains a highly dangerous infection for the immunocompromised, including primary immunodeficiencies, people with cancer, and those with auto-immune disorders or transplant recipients who require pharmacological immunosuppressive therapy [3,9,10].
The commensal gut microbiota (GM) has long been recognized as a highly dynamic microbial community which, when targeted, can precipitate drastic change to human health. Modulations of the GM, either by dietary intervention, probiotic supplementation, or fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), have yielded promising results in the context of gastrointestinal diseases [11,12,13,14,15], cancer [16,17,18], metabolic disorders [19,20,21,22], and infectious diseases [23,24,25]. While GM modulations in the context of parasitic infections have been less studied, preliminary evidence suggests that there is significant interplay between the GM, the immune system, and human parasites, making GM manipulation a promising alternative to currently available antiparasitic therapies [26,27,28,29,30,31,32].
In the context of cryptosporidiosis, preclinical studies and case reports indicate that GM modulation could represent a promising therapeutic alternative to currently available anti-Cryptosporidium drugs. In immunosuppressed mice, probiotic treatment helped mice clear parasitic infection, indicating that, unlike the currently available therapies on the market, GM modulation does not require a functioning immune system to combat cryptosporidiosis. Instead, GM modulation is hypothesized to act by indole metabolism on the parasite mitosome [33,34,35,36]. In humans, probiotic treatment was found to be helpful in combatting symptoms of Cryptosporidium infection in immunocompetent children [37,38]. However, to our knowledge, no studies in immunocompromised human patients have been conducted to investigate the potential of GM modulations in combatting chronic cryptosporidiosis. Moreover, the interplay between the GM and Cryptosporidium is still not fully described or understood.
Previously, we published the first case report of the effects of chronic cryptosporidiosis on the GM of an immunocompromised child [39]. However, due to this being a single case, we were not able to determine whether the differences we observed were due to the child’s primary immunodeficiency, his liver failure, or chronic Cryptosporidium infection. Here, we profiled the GM of five patients infected with Cryptosporidium, four of whom were immunodeficient, and one of whom was immunocompetent, in order to see whether common GM signatures associated with cryptosporidiosis emerged. Cryptosporidium-induced GM modulations could indicate the most promising bacterial targets for alternative or adjuvant cryptosporidiosis therapies, particularly for immunocompromised patients with few clinical options in combatting the disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
The patients presented in this case series were admitted to Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital in Rome, Italy, for issues pertaining to their own clinical history. Patients who were positive for Cryptosporidium infection and who provided samples for GM characterization were included in this case series. All included patients or their legal guardians provided informed consent for anonymized publication of their clinical data. Furthermore, given that all patients included in this study were of different ages, and given that age has an effect on GM composition [40], GM profiles of each patient were compared to a group of 5 age-matched healthy subjects (controls; CTRLs). CTRLs were enrolled during an epidemiological survey carried out at the Microbiome Unit of Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital (BBMRI Human Microbiome Biobank, OPBG) to generate a reference biobank of samples from healthy subjects. Healthy CTRLs were defined as volunteers with no known pathologies or food allergies, within the healthy BMI range, who have not had any infectious disease, antibiotics, or probiotics in the month prior to sample collection, and who agreed to donate their stool samples for biobanking and anonymized use in clinical studies. The use of healthy subjects in this study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital, IRCCS (protocol No. 1113_OPBG_2016) and was conducted in accordance with the Principles of Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Cryptosporidium Detection in Fecal Smears by Optical Microscopy
Fecal smears were prepared for Cryptosporidium detection as previously described [41] with slight modifications. Fecal samples were collected, filtered with a 10% formalin disposable system (Parapak, 10% formalin fixative, Meridian Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA) and then prepared for microscopic observation with a modified Ziehl–Neelsen staining protocol (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). A thin fecal smear was deposited onto slides, air dried, then fixed in methanol for 5 min. The slides were incubated with Carbol fuchsin stain (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) for 30 min, rinsed with tap water and incubated with acid alcohol (1%) for 30 s. Then, slides were rinsed with tap water, incubated with methylene blue(Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Gerany) for 1 min, rinsed again with tap water and left to air dry. Each slide was examined (using oil immersion) under 100× magnification using a light microscope [42]. At least 10 fields for each of at least 5 slides were examined to perform morphometry and to count Cryptosporidium spp. oocysts in order to produce an average number of oocysts for each slide. Overall, approximately ten slides were imaged to produce a quantitative estimation of parasite oocysts for each time-point of the quantitative titration confirmed by a second operator.
2.3. Cryptosporidium Detection by PCR
DNA was extracted from stool samples with the automated QIASymphony system as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The presence of Cryptosporidium spp. DNA was confirmed with the AllPlexTM Gastrointestinal Parasite Assay as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Seegene, Seoul, Republic of Korea).
2.4. Clinical Evaluation of Cryptosporidiosis Severity
Once Cryptosporidium infection was confirmed by microscopy and molecular biology methods, patients were categorized as either mild, moderate, or severe cases based on a clinical evaluation of patient symptoms based on World Health Organization guidelines [43]. Patients with severe clinical manifestations were defined as those with chronic diarrhea, i.e., patients passing three or more loose stools per day for over 30 days. Patients with mild presentation were those with diarrhea for less than 14 days, and moderately affected patients were defined as those passing three or more loose stools per day for over 14 days but for less than one month.
2.5. Stool Sample Collection
Stool samples were collected with sterile stool collection kits and stored at 4 °C until transfer to the Microbiome Unit of the Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital. Samples were then aliquoted and stored at −80 °C until DNA extraction.
2.6. 16S rRNA Targeted Metataxonomics
16S rRNA-based sequencing was performed as previously described [44]. Briefly, DNA was extracted from stool samples with a QIAmp Fast DNA Stool mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and the V3-V4 hypervariable region was amplified with a 2× KAPA Hifi HotStart ready Mix (KAPA Biosystems Inc., Wilmington, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Illumina Nextera adaptor primers were used to index the samples, after which they were sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq Platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
Paired-end fastq files were pre-processed as patient–age-matched CTRL batches using the Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology 2 (QIIME2) v2024.5 bioinformatics pipeline [45]. The q2—DADA2 plugin was used to perform quality checks (QC) of reads and to produce the Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs) [46]. Each ASV was classified taxonomically by means of the q2—Greengenes plugin using the nucleotide database Greengenes2 v2022.10 [47]. Finally, phylogenetic analysis was performed with the q2—phylogeny align-to-tree-mafft-fasttree plugin obtaining rooted trees [45].
2.8. Statistical Analyses
Count tables, taxonomy tables, and phylogenetic trees of each sample were imported in R v4.4.1 for statistical analyses. In ecological analyses, all count tables were normalized with the rarefaction method based on the minimum sample depth. For alpha-diversity analysis, Shannon–Weiner, Simpson, and Chao-1 indices were calculated and Mann–Whitney U-tests were used to compare bacterial diversity between the two independent groups. Count tables were merged obtaining a unique count table in order to compare distance dissimilarity, calculated with the Bray–Curtis algorithm, between all groups. Hierarchical cluster analysis was performed with the Pvclust R package (version 2.2) based on the bootstrap approach (replications: 1000). To evaluate differential bacterial abundances, each count table was normalized with the Cumulative Sum Scaling (CSS) method [48] and transformed into relative abundances.
3. Results
3.1. Case Description
Case 1: The first patient, hereafter referred to as Crypto 1, was a 9-year-old child diagnosed with HIGM due to a mutation in the gene encoding for CD40L. Crypto 1 was also suffering from chronic diarrhea for three years due to a severe and chronic Cryptosporidium parvum infection that persisted even after multiple rounds of antiparasitic treatment, which precipitated sclerosing cholangitis and hepatic cirrhosis. Due to his severe liver damage and his primary immunodeficiency, Crypto 1 was admitted to undergo a liver transplant followed by a bone marrow transplant. Seven days after the liver transplant, while the patient was undergoing antibiotics and yet another round of antiparasitic treatment, we collected four stool samples over a one-week period, and selected five samples from age-matched controls (CTRLs) for comparison (Table 1).

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients.
Case 2: Crypto 2 was 26 years old, also affected by HIGM due to a genetic defect in CD40L, who had been admitted to our hospital following complaints of diarrhea and abdominal pain beginning 30 days prior, and had been undergoing antibiotic treatment as a result (Table 1). After a mild case of cryptosporidiosis was diagnosed by microscopic and molecular means, we collected three consecutive stool samples from this patient and compared them with five age-matched CTRLs.
Case 3: Crypto 3 was a 14-year-old child affected by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and was undergoing aggressive immunosuppressive therapy as a result. During this treatment, Crypto 3 acquired a gastrointestinal XDR Acinetobacter infection, for which he was undergoing antibiotic treatment and was being screened for a possible experimental FMT, in order to combat this infection and avoid sepsis, a common complication and cause of mortality in patients with SLE. During screening, Crypto 3 was also diagnosed with moderate–severe Cryptosporidium infection, upon which time the stool samples collected for screening underwent 16S rRNA metataxonomic sequencing and compared with five age-matched CTRLs.
Case 4: Crypto 4 was a 12-year-old child affected by sterile alpha motif domain containing 9 like (SAM9DL) primary immunodeficiency (SAMD9L–Ataxia–Pancytopenia Syndrome, SAPS). He was admitted to our hospital with gastrointestinal symptoms, including vomiting and diarrhea, for 10 days prior to admission. Screening for infections revealed he was positive for severe Cryptosporidium infection, and thus was not given antibiotics at the time of stool sample collection for 16S targeted metataxonomic sequencing.
Case 5: Crypto 5 was an immunocompetent, 6-year-old child with no underlying conditions, admitted because of abdominal pain, after which he was diagnosed with a mild case of cryptosporidiosis. Before treatment commenced, three stool samples were collected for 16S targeted metataxonomic sequencing and compared to five healthy age-matched CTRLs.
3.2. Patients with Moderate or Severe Cryptosporidiosis Present with Reduced Alpha-Diversity and Increased Enterococcus spp. Compared with CTRLs
We profiled the GM of our five patients by performing next-generation sequencing of the V3-V4 hypervariable region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene on two to four stool samples collected from each patient. We then compared the metataxonomic profiles of each patient to a group of five age-matched CTRLs.
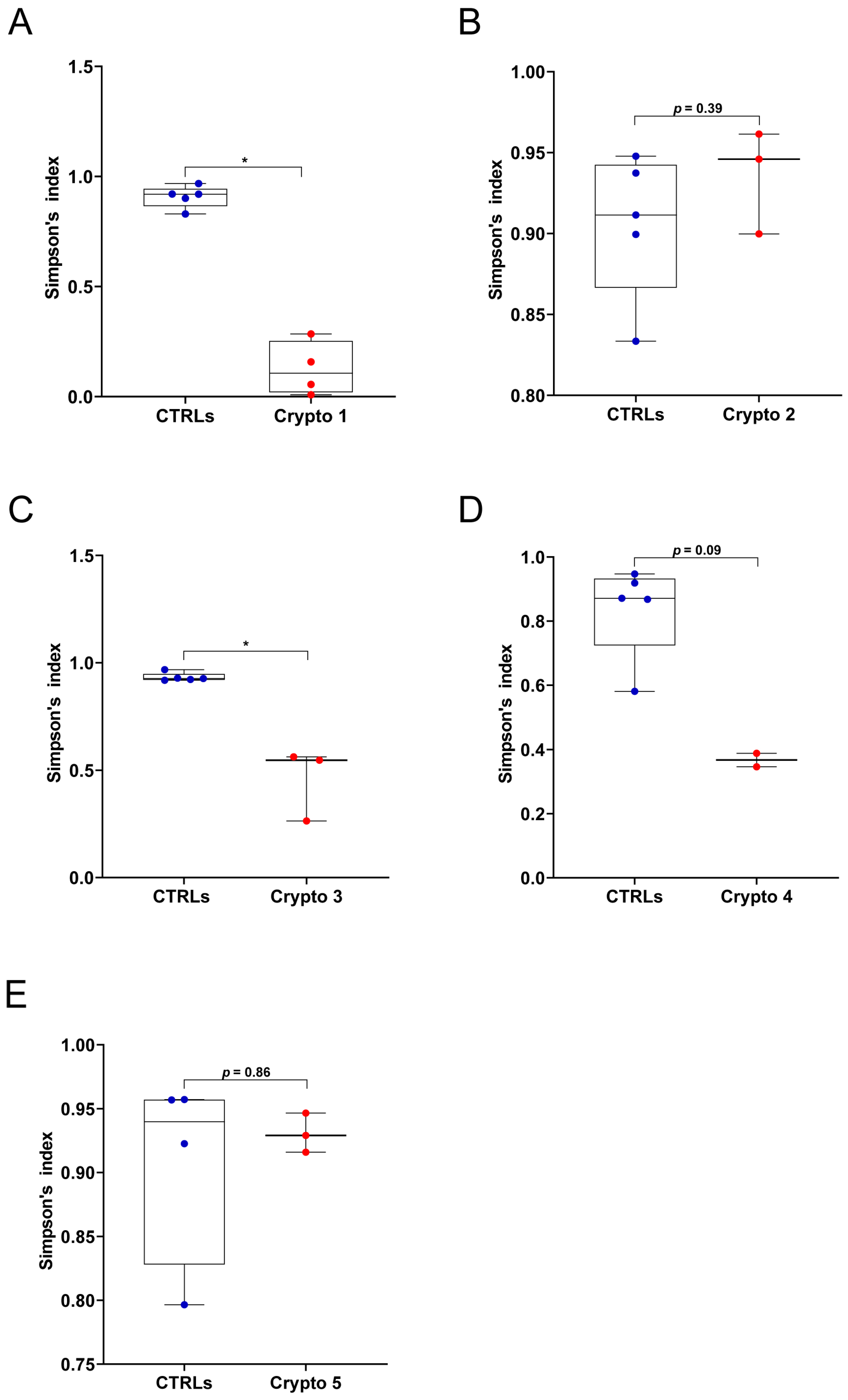
First, we measured GM alpha-diversity by calculating Simpson’s index for each patient and CTRL sample (Figure 1). We found that our three moderately–severely affected patients, namely Crypto 1 (Figure 1A), Crypto 3 (Figure 1C), and Crypto 4 (Figure 1D), all had reduced species richness in their GM when compared to their own age-matched CTRLs. On the other hand, our two mildly affected patients Crypto 2 (Figure 1B) and Crypto 5 (Figure 1E) did not have reduced alpha-diversity compared to CTRLs, suggesting that cryptosporidiosis is associated with reduced GM species richness only in the more severe manifestations of the disease.
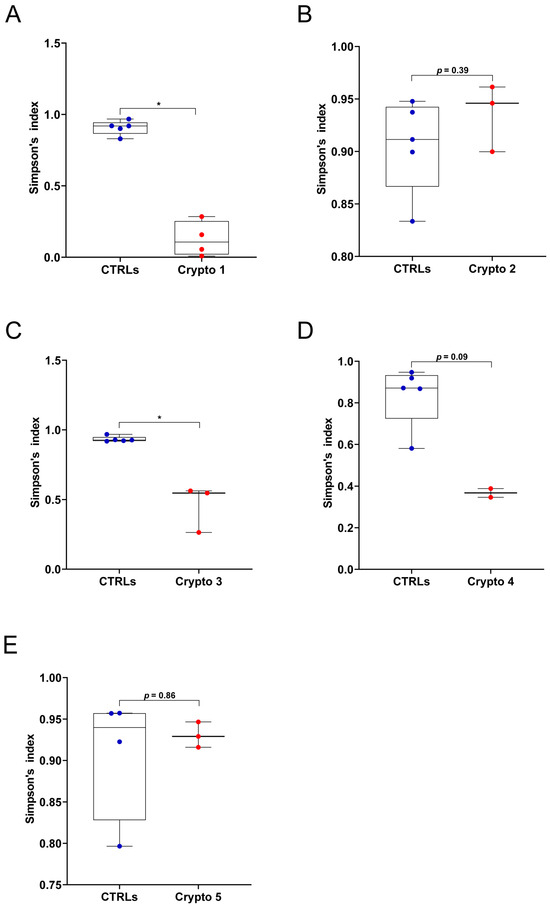
Figure 1.
GM alpha-diversity in patients with mild and moderate–severe Cryptosporidium infections. (A–E) Alpha-diversity, as measured by Simpson’s index, in Crypto 1 (A), Crypto 2 (B), Crypto 3 (C), Crypto 4 (D) and Crypto 5 (E), compared to age-matched CTRLs. Statistical analysis: Mann–Whitney U-test, * p < 0.05. Patients with moderate to severe cryptosporidiosis (A,C,D) were characterized by a reduction in alpha-diversity measurements, while mildly affected patients (B,E) had comparable alpha-diversity measurements compared to age-matched CTRLs. In red: individual Cryptosporidium-positive replicates. In blue: individual CTRL replicates.
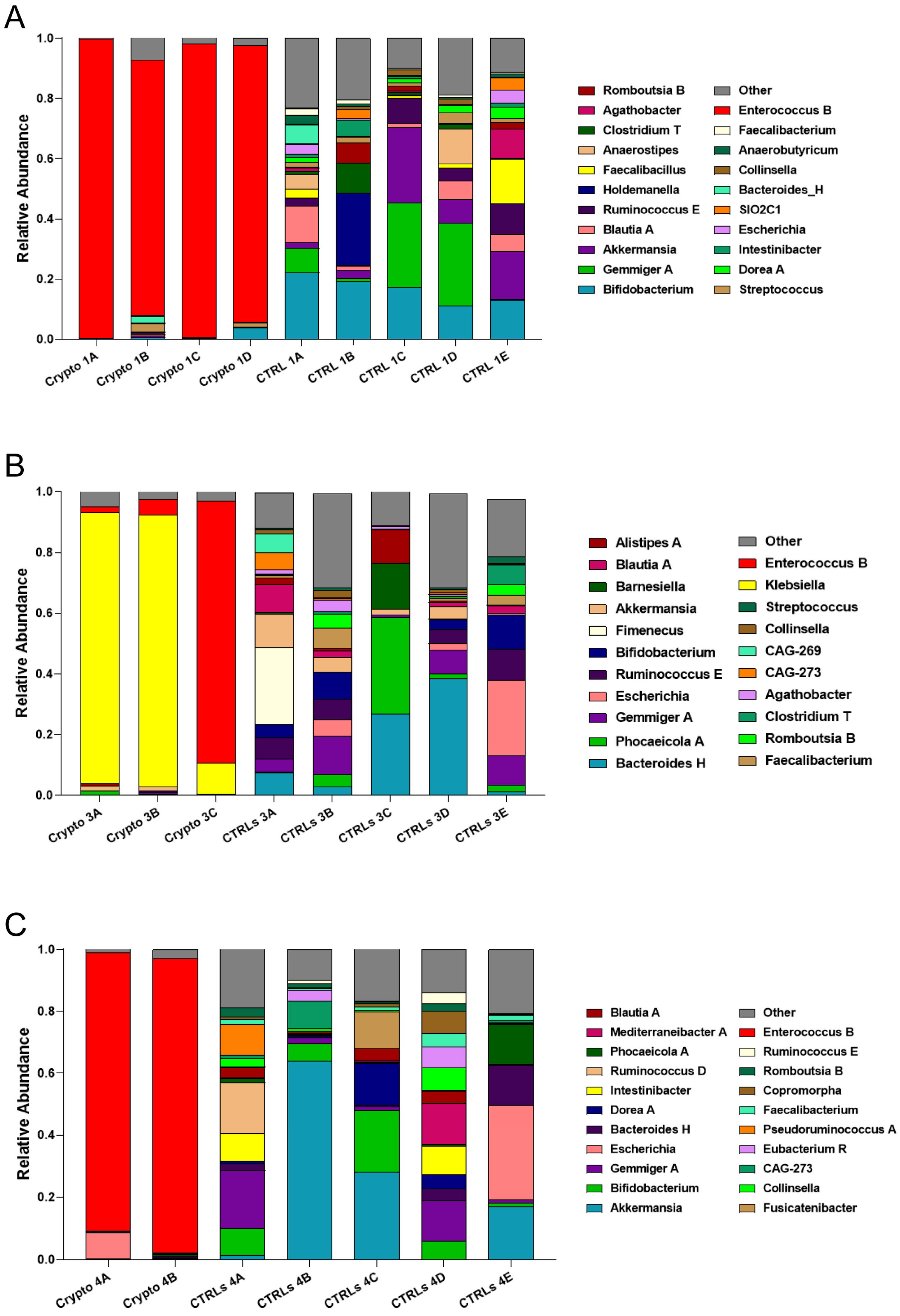
We next compared patient GM metataxonomic profiles to CTRL subjects, starting with those patients who presented with moderate–severe cryptosporidiosis. We found that, in all samples profiled from moderately–severely affected patients, one single bacterial genus predominated in the GM, with relative abundances of close to or over 90% (Figure 2). We found that Crypto 1 samples were predominantly composed of Enterococcus spp., composing between 84 and 98% of the total GM of this patient (Figure 2A), followed by Bacteroides H and Streptococcus. In two Crypto 3 samples, we found an overwhelming predominance of Klebsiella (Figure 2B) which, after sample collection, would also be diagnosed systemically in this patient. However, similar to Crypto 1, we also found a large relative abundance of Enterococcus spp. in one out of the three replicates, which was almost completely absent in CTRLs (Figure 2B). Interestingly, Crypto 4 were also found to be predominantly composed of Enterococcus spp., consistent with the results observed in Crypto 1 and Crypto 3 (Figure 2C), and despite having yet another kind of underlying immunodeficiency, and despite not having been treated with antibiotics, as the other two moderate–severely affected patients were (Table 1). The GM of age-matched CTRLs, on the other hand, were far more diverse, and were primarily composed of Bifidobacterium spp., Gemmiger spp., Akkermansia spp., and Blautia spp. (Figure 2A). These results largely explain the reduced alpha-diversity measurements illustrated in Figure 1. Taken together, these results seem to suggest that an overabundance of Enterococcus spp. is a common GM signature in patients with moderate to severe Cryptosporidium infection, regardless of underlying pathology, or antibiotic treatment.
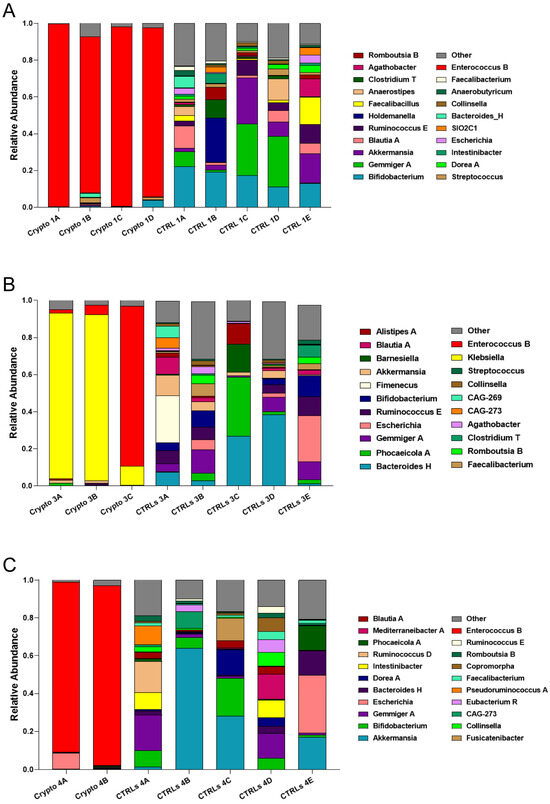
Figure 2.
GM composition of patients with moderate–severe cryptosporidiosis. (A–C) Stacked bar charts representing the relative abundance of bacterial genera in each Crypto 1 (A), Crypto 3 (B), and Crypto 4 (C) replicate and each individual age-matched CTRL. Genera detected under 1% relative abundance were grouped together and represented collectively as “other”. Moderately–severely affected patients were characterized by an overabundance of a single bacterial genus in all profiled samples.
3.3. Mild Cases of Cryptosporidiosis Were Associated with a More Diverse GM
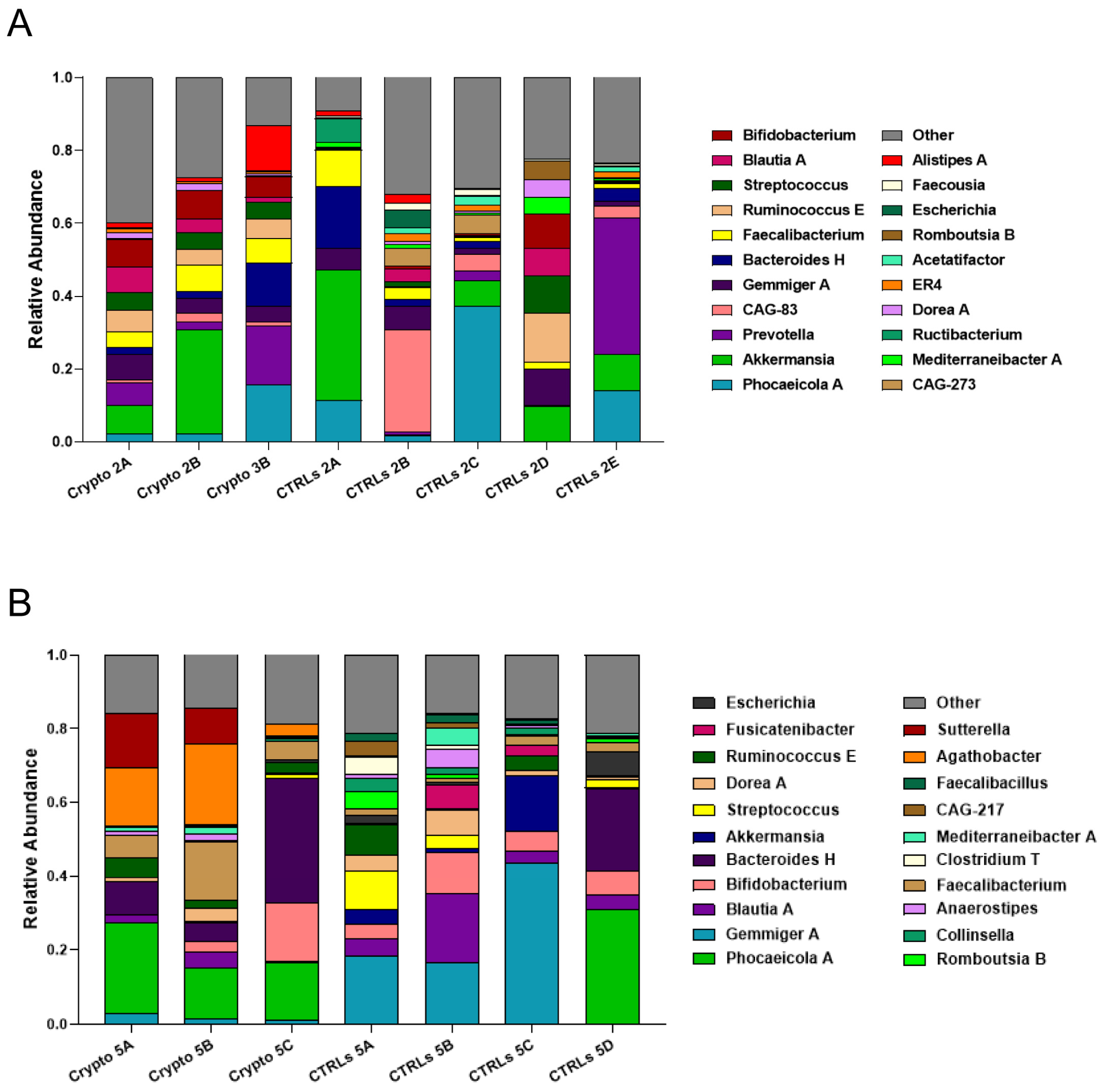
We next profiled the GM of our two mildly affected patients, each compared to their own group of age-matched CTRLs (Figure 3). We found that, unlike severely affected patients, those with a mild case of cryptosporidiosis had a far more diverse GM, consistent with the alpha-diversity measurements presented in Figure 1. We found a similar bacterial community structure between Crypto 2 and CTRLs, being mostly composed of Phocaeicola spp., Akkermansia spp., Prevotella spp., Gemmiger spp., and Bacteroides spp. (Figure 3A). Similarly, the taxonomic composition of the GM of Crypto 5 was far more diverse and far more similar to CTRLs than that observed in their severely affected counterparts (Figure 3B). The GM of Crypto 5 was composed primarily of Phocaeicola spp. and Bacteroides spp., as well as Faecalibacterium spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. (Figure 3B. The most notable differences between these two groups, however, was a decrease in Gemmiger spp. and an increase in Agathobacter spp. and Sutterella spp. in Crypto 5 compared with CTRLs (Figure 3B). Taken together, these results suggest that the more severe forms of cryptosporidiosis are associated with larger GM changes than are their mildly affected counterparts.
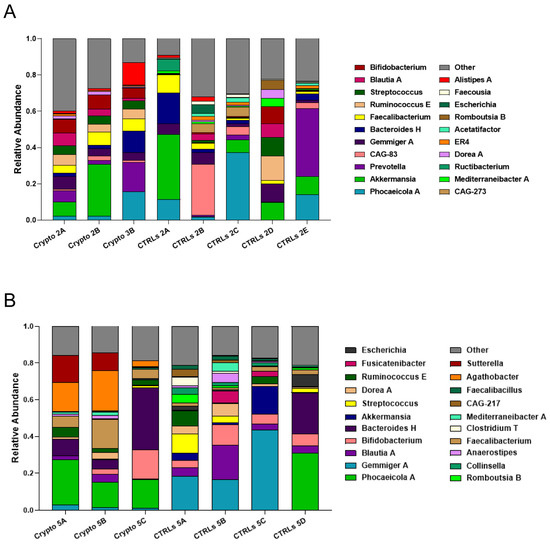
Figure 3.
GM composition of patients with mild cryptosporidiosis. The GM of mildly affected patients are diverse and somewhat similar to that of their respective healthy CTRLs. (A,B) Stacked bar charts representing the relative abundance of bacterial genera in each Crypto 2 (A) and Crypto 5 (B) replicate and each individual age-matched CTRL. Genera detected under 1% relative abundance were grouped together and represented collectively as “other”.
3.4. Patients with Severe Cryptosporidiosis Cluster Separately from Those with Mild Infection
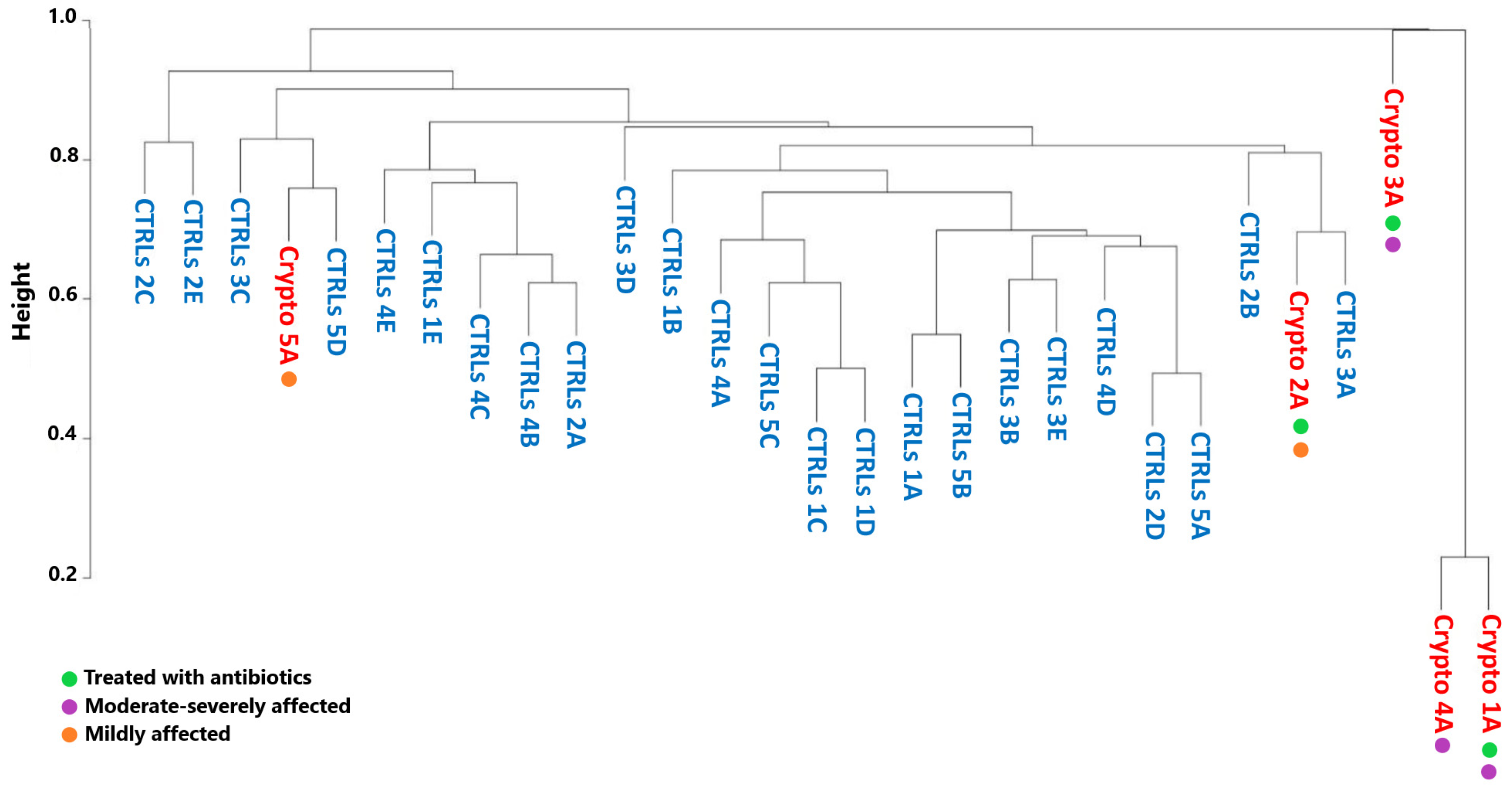
We next decided to see whether the GM profiles of patients infected with Cryptosporidium would cluster by severity, by antibiotic treatment, or with their own age-matched CTRLs. However, in order to obtain accurate GM maps on a patient-by-patient basis, our analyses thus far have involved collecting multiple samples per patient, in order to ensure that the GM signatures we observe were consistent. This also results in less variability between samples collected from the same patient, compared to the variability one would observe between samples collected from different subjects. Therefore, in order to ensure that these differences in variability are not producing statistical artefacts, we performed a Bray–Curtis analysis only considering the first sample collected from each patient (Figure 4).
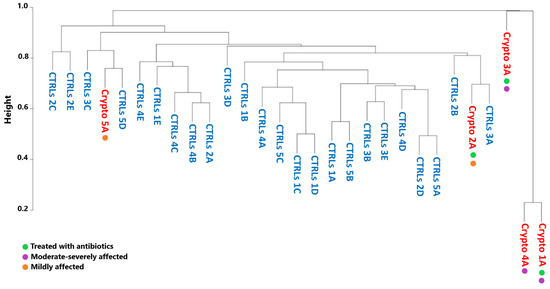
Figure 4.
Beta-diversity analyses of Crypto-positive and CTRL samples. Dendrogram representing similarity between healthy CTRLs (blue) and a single sample from each Cryptosporidium-positive patient (red) as calculated by Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. Green: patients treated with antibiotics. Purple: patients with moderate–severe cryptosporidiosis. Orange: patients with mild cryptosporidiosis.
Bray–Curtis dissimilarity produced a very separate and distinct cluster composed of the moderately–severely affected patients Crypto 1, 3 and 4 (Figure 4). On the other hand, mildly affected patients, namely Crypto 2 and Crypto 5, clustered more closely with CTRLs than with those with severe cryptosporidiosis (Figure 4). These results were particularly interesting in light of the fact that one severely affected patient (Crypto 4) was not undergoing antibiotic treatment at the time of sample collection, while one mildly-affected patient (Crypto 2) was. Despite this, Crypto 4 samples still clustered tightly with the antibiotic-treated and severely affected Crypto 1. Taken together, these results are in line with our previous observations, and indicate that patients with severe cryptosporidiosis more closely resemble each other than they do healthy subjects, despite the differences in their ages, underlying pathologies, and history of antimicrobial treatment. Furthermore, these results show that patients with mild cryptosporidiosis are more similar to CTRLs than patients with a heavier parasitic burden, suggesting that Cryptosporidium infection might affect GM ecology in a dose-dependent manner.
3.5. Common Gut Microbial Signatures of Cryptosporidium Infection
As observed above, we found that all three patients with moderate–severe cryptosporidiosis had a GM that was heavily dominated by Enterococcus spp. (Figure 2). Given the fact that these three patients all had very different underlying pathologies and ongoing treatment plans, these results seem to suggest that an overabundance of Enterococcus spp. is a common signature of severe cryptosporidiosis infection (Figure 2). However, our two patients with mild cryptosporidiosis did not have even a trend of increased Enterococcus abundance in their GM (Figure 3), which may suggest that this finding presents itself in those affected by moderate to severe infection.
Along with a drastic increase in Enterococcus, our severely affected patients also had drastically reduced relative abundances of Akkermansia, Bifidobacterium, Gemmiger, and Blautia (Figure 2). However, it is important to note that, when the GM of an individual is predominantly colonized by any single bacterial genus, mathematically, this will lead to all other abundant genera being reduced. Therefore, it is difficult to discern which of these reductions may be biologically relevant, and which are simply a statistical artefact given the high relative abundance of Enterococcus. Indeed, while Akkermansia is reduced in Crypto 1, 3, and 4, it is actually increased in Crypto 2, and was highly variable among the three replicates of Crypto 5 (Figure 3). Given these results, we cannot discern whether the reduction in Akkermansia observed in Crypto 1, 3, and 4 is a statistical artefact, or whether it is a biologically relevant event tied to Enterococcus expansion. Having said this, we did observe a substantial decrease in Bifidobacterium, Gemmiger, and Blautia in Crypto 5 as well as in Crypto 1, 3, and 4, despite the fact that the GM of Crypto 5 was not dominated by a single bacterial genus (Figure 2 and Figure 3). These results might suggest that, while an overabundance of Enterococcus may be a signature of moderate to severe cryptosporidiosis, reductions in Bifidobacterium, Gemmiger, and Blautia may be early indicators of Cryptosporidium infection.
Finally, we found that Agathobacter was substantially enriched in Crypto 5, though no trend towards this effect was observed in any other patient (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Further studies are needed to confirm whether this bacterial genus may be a marker for mild Cryptosporidium infection in immunocompetent patients, or whether it was a peculiarity of this specific subject.
4. Discussion
Last year, we presented a case report of a child with chronic cryptosporidiosis and CD40L immunodeficiency, whose GM was characterized by an increase in Enterococcus, Prevotella, and Campylobacter [39]. Although this was the first report of GM modulations in response to severe Cryptosporidium infection, it was extremely preliminary, insofar as it was impossible to determine which GM signatures may have been due to the child’s parasitic infection, his primary immunodeficiency, or his liver complications. Here, we present five patients with different underlying pathologies and ages, to see whether there are commonalities between the GMs of this otherwise diverse group of patients.
The most striking commonality found between the three patients with the more severe forms of cryptosporidiosis was a predominance of Enterococcus spp. It is important to note that the Enterococcus genus is comprised of many multi-drug-resistant species, and as such can increase substantially in the GM of patients given multiple rounds of antibiotics [49]. Though antibiotics will not act on Cryptosporidium directly, they are often used to treat the gastrointestinal symptoms commonly associated with cryptosporidiosis. Having said this, only two of the three moderately–severely affected patients had been treated with antibiotics prior to stool sample collection, as well as one of our mildly affected patients (Table 1). Indeed, as shown in Figure 4, patients who had been treated with antibiotics did not cluster together. Crypto 2, a patient treated with antibiotics and with a mild case of cryptosporidiosis, was placed by our analyses in the center of a cluster of healthy CTRLs. Furthermore Crypto 4, a moderately–affected patient with no antibiotic use prior to sample collection, clustered closely with his two severely-affected and antibiotics-treated counterparts (Figure 4). Therefore, while the increase of Enterococcus spp. in response to antibiotics has been described, antibiotic use in our patient set did not overlay with those with a predominance of Enterococcus. While these therapies may have contributed to the increase in Enterococcus observed in some patients, it does not fully explain the patterns that we observe. Furthermore, these results seem to suggest that cryptosporidiosis exerts a stronger influence on the GM than does antibiotics treatment, though further studies on larger patient cohorts are needed to confirm this.
In our patient dataset, all patients with moderate–severe cryptosporidiosis were characterized by an overabundance of Enterococcus spp. in the GM, while the two patients with mild clinical cases were not. However, despite the fact that they had very different underlying pathologies, these three patients also shared two other important clinical characteristics. The first of these is a severe immunodeficiency which, though caused by different clinical circumstances, does raise the possibility that immunodeficiency itself is enough to cause an overabundance of Enterococcus spp. in the gut. On the one hand, it is very difficult to separate the two, because immunodeficiency is one of the main factors which precipitates severe and chronic cryptosporidiosis and other infections, causing them to often be treated with, among other things, multiple rounds of antibiotics. On the other hand, there have been publications on the gut microbial composition of people with AIDS [50,51], and common variable immunodeficiency [52,53,54,55], none of which report a common signature of Enterococcus overabundance. While most of these studies have been conducted in adults, and therefore insight into the effects of immunodeficiency on pediatric GM composition are still somewhat lacking, the current literature does not suggest that immunodeficiency commonly produces a GM signature rich in Enterococcus spp.
The second common clinical characteristic shared by these three patients is multiple episodes of diarrhea, as this is one of the clinical criteria for distinguishing between mild and severe cases of cryptosporidiosis [43]. Once again, the scientific literature does not suggest a predominance of Enterococcus spp. as a common, universal signature of multiple diarrheal episodes. For example, one study of patients with diarrheal-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS-D) found a decrease of Firmicutes, the phylum in which Enterococcus spp. are classified, and an expanded population of Proteobacteria in IBS-D patients compared to healthy CTRLs [56]. Other studies on post-cholecystectomy diarrhea (PCD) found a slight but significant increase in Enterococcus spp. despite an overall decrease in the relative abundance of Firmicutes, accompanied by a large increase in Bacteroidota [57,58]. In pediatric cohorts with infectious diarrhea, studies described an overabundance of Proteobacteria, as well as a predominance of Streptococcus spp. in the GM [59,60,61,62]. However, given the wide range of ages and geographical regions sampled in the aforementioned papers, future studies on larger cohorts of Cryptosporidium-positive patients may also include diarrheal samples of different etiology, in order to control for changes in GM composition due to frequent, watery bowel movements.
Though some bacterial genera, such as Bifidobacterium, are largely associated with positive health outcomes, Enterococcus is a more diverse genus in the GM. On the one hand, it is one of the first genera to populate the human GM, and is responsible for the production of various vitamins and metabolites necessary for human health [63]. On the other hand, this genus comprises species that can become highly virulent and infective, and have been associated with increased inflammation, systemic infection, and meningitis [63,64,65,66]. However, in animal studies, probiotic administration of Enterococcus faecalis CECT 7121 has been found to interfere with parasitosis, including in immunosuppressed mouse models of cryptosporidiosis [33,67]. Similarly, Enterococcus faecium CCM8558 and Enterococcus durans ED26E/7 were found to have antiparasitic activity against Trichinella spiralis infection in mice, further underscoring the beneficial potential of some Enterococcus strains in combatting parasitic infection [68]. Unfortunately, the methodology used in this study was not able to identify which species of Enterococcus were present in these patients, which could be elucidated with future studies.
Another interesting commonality identified between these patients was a marked reduction in the genera Bifidobacterium, Gemmiger and Blautia (Figure 2 and Figure 3). While this is to be expected in patients Crypto 1, 3 and 4, given that their GMs were over 80% populated by either Enterococcus or Klebsiella, this reduction was also observed in Crypto 5, who did not have a strongly altered GM compared to age-matched CTRLs (Figure 3B). In Crypto 2, there was more variability between samples, making it impossible to conclude whether or not there was a trend in reduction of these three genera in this patient (Figure 3A). On one hand, it is important to note that Crypto 2 was the only adult patient profiled in this study, and Bifidobacterium is known to possess a less important role in the GMs of adults than in that of children [69,70]. On the other hand, given that this is only one patient, we cannot, at this time, discern whether a reduction of Bifidobacterium is a signature of pediatric cryptosporidiosis, or whether Crypto 2 possessed other characteristics that explain these findings. Future studies are necessary to determine whether or not these differences between Crypto 2 and pediatric patients are due to different GM alterations in response to adult Cryptosporidium infection, or whether it is due to this individual’s own GM variability.
Bifidobacterium, as a whole, is widely recognized as a genus of health-promoting bacteria, which is why it is a very popular genus for the development of probiotic strains, including those designed to combat parasitic infections [71,72,73]. Indeed, one in vitro study found that the supernatants from both Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus strains could inhibit Cryptosporidium oocyst viability [73]. In this context, it is possible that Cryptosporidium either more readily infects patients with low Bifidobacterium abundances, or that it capable of reducing the relative abundances of those bacteria which are more detrimental to its survival. While future longitudinal studies into GM markers for Cryptosporidium predisposition could be very informative, our results seem to suggest that, in children, low levels of Bifidobacterium in the GM are measurable in even in the milder stages of cryptosporidiosis.
The genera Blautia and Gemmiger are far less studied than Bifidobacterium, especially in the context of parasitic infection. Generally speaking, Blautia is positively correlated with metabolic health [74,75], while Gemmiger has been found to be negatively associated with protozoan-induced diarrhea in livestock [76]. Though further studies into the roles of these two genera in parasitic infection would be highly informative, our results still seem to suggest that, as observed with Bifidobacterium, reduced relative abundances in these two genera may be common GM signatures of Cryptosporidium infection in children, even in the mild stages of the disease.
The last variable to consider when interpreting these results is the potential influence of different Cryptosporidium species and genotypes on the GM of immunocompromised patients. So far, over 20 Cryptosporidium species capable of infecting humans have been described, though the two most common species to infect humans are C. parvum and C. hominis. Furthermore, each Cryptosporidium species is further subdivided into genotypes and subgenotypes [77]. However, most clinical protocols for the diagnosis of Cryptosporidium infection do not resolve past the genus level and, therefore, there is incomplete data on the prevalence of these genotypes outside of epidemiological studies, and even less knowledge about the potential infectivity of different Cryptosporidium subtypes. Indeed, in this study, only Crypto 1 was known to be infected with C. parvum, while we do not possess this information for the other 4 patients in this Case Series. We cannot therefore exclude the possibility that different Cryptosporidium species or genotypes modulate the GM in different ways, and/or produce more or less severe manifestations of cryptosporidiosis in infected patients. Though such analyses would be beyond the scope of this study, particularly in light of our small sample size and case-by-case description, we do believe that genotyping Cryptosporidium during studies on larger cohorts may shed light on whether some subtypes, and therefore some parasitic reservoirs, pose a higher risk to vulnerable patients than others.
To our knowledge, this study is only the second description of GM modulations in response to cryptosporidiosis in immunocompromised patients. Given the commonalities found between these otherwise clinically diverse patients, we believe that the field would greatly benefit from further studies on larger patient cohorts, as this sample size is too small to be able to draw firm correlations between disease severity and GM composition. Should common GM signatures of cryptosporidiosis be confirmed and found, the medical community should consider investigating the potential of GM modulations in combatting cryptosporidiosis, particularly in light of what has been reported in preclinical mouse models.
To date, the only FDA-approved anti-Cryptosporidium drugs available rely on the host’s ability to produce CD4+ cells, which is why chronic cryptosporidiosis remains a real threat to immunocompromised patients [3,8]. However, studies in immunodeficient mouse models has shown that GM modulations can bypass the host’s immune system in combatting parasitosis [33,34]. Therefore, if consistent GM responses to mild or severe disease are found in immunodeficient patients with Cryptosporidium infections, these may lead researchers towards which subsequent GM modulations may be most beneficial to patients. Probiotic development, or even FMT, may have potential in aiding to combat this parasitic infection in vulnerable patients.
5. Conclusions
This is the first study to investigate how the immunocompromised GM responds to cryptosporidiosis in more than one patient. Given the differences between these patients in terms of age, underlying pathology, co-morbidities and antibiotics treatment, the fact that their GM profiles are so similar is indeed striking. Though this area of research could benefit greatly from a wider range of patients, these results suggest that severe Cryptosporidium infection has a greater effect on GM composition than does age, immune status, antibiotics use, or other organ involvement, both in terms of species richness and Enterococcus overabundance. This, together with the aforementioned preclinical studies, is further evidence that modulations of the GM may be a promising alternative to those antiparasitic drugs that fail to aid immunocompromised patients. Further studies are needed on larger cohorts of immunocompromised patients affected by cryptosporidiosis, not only to confirm these findings, but also to aid in identifying those microbial signatures which could help to develop the alternative therapies needed to protect these vulnerable populations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.P., P.P. and A.P.; methodology, S.P., F.T. and R.M.; software, M.S.; validation, L.R., S.P., F.D.C. and A.P.; formal analysis, A.P. and M.S.; investigation, A.P., L.R., S.P. and F.D.C.; resources, N.C., P.P. and L.P.; data curation, M.S. and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P. and L.P.; writing—review and editing, F.D.C., A.P., L.P. and P.P.; visualization, A.P. and M.S.; supervision, L.P. and F.D.C.; project administration, L.P. and P.P.; funding acquisition, L.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health with “Current Research funds”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The use of healthy CTRLs was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital, IRCCS (protocol No. 1113_OPBG_2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study or their legal guardians.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed in this study have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the accession number PRJNA1144251 and will be set to private until the acceptance of this manuscript. A reviewer’s link to the data will be provided upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ryan, U.; Zahedi, A.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. An Update on Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes in Humans. Animals 2021, 11, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebbad, M.; Winiecka-Krusnell, J.; Stensvold, C.R.; Beser, J. High Diversity of Cryptosporidium Species and Subtypes Identified in Cryptosporidiosis Acquired in Sweden and Abroad. Pathogens 2021, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitch, G.J.; He, Q. Cryptosporidiosis-an Overview. J. Biomed. Res. 2012, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pane, S.; Putignani, L. Cryptosporidium: Still Open Scenarios. Pathogens 2022, 11, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignani, L. Cryptosporidium; Rezaei, N., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 450–462. ISBN 978-0-323-90303-5. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Rao, P.C.; Blacker, B.F.; Brown, A.; Brewer, T.G.; Colombara, D.V.; De Hostos, E.L.; Engmann, C.; Guerrant, R.L.; et al. Morbidity, Mortality, and Long-Term Consequences Associated with Diarrhoea from Cryptosporidium Infection in Children Younger than 5 Years: A Meta-Analyses Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e758–e768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, S.O.; Muhsen, K.; Nasrin, D.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Wu, Y.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Sur, D.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Faruque, A.S.G.; et al. The Burden of Cryptosporidium Diarrheal Disease among Children <24 Months of Age in Moderate/High Mortality Regions of Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, Utilizing Data from the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.; Aliyu, S.H.; Arumugam, C.; Usman, N.K.; Hunter, P.R. Treatment of Cryptosporidiosis in Immunocompromised Individuals: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 63, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, N.; Gorgani-Firouzjaee, T.; Ghaffari, S.; Bayani, M.; Ghaffari, T.; Chehrazi, M. Association between Cryptosporidium Infection and Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 74, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Karanis, P. Cryptosporidium Sp. Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Pathog. Glob. Health 2024, 118, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Gilja, O.H.; Bråthen Kristoffersen, A.; Hausken, T. Efficacy of Faecal Microbiota Transplantation for Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome in a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Gut 2020, 69, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, S.P.; Hughes, P.A.; Waters, O.; Bryant, R.V.; Vincent, A.D.; Blatchford, P.; Katsikeros, R.; Makanyanga, J.; Campaniello, M.A.; Mavrangelos, C.; et al. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on 8-Week Remission in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, F.; Duan, L. Efficacy of Probiotics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 859967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ma, C.; Zhao, F.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cui, L.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhang, H. Adjunctive Treatment with Probiotics Partially Alleviates Symptoms and Reduces Inflammation in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2553–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, T.; Sequoia, J. Probiotics for Gastrointestinal Conditions: A Summary of the Evidence. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Davar, D.; Dzutsev, A.K.; McCulloch, J.A.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Chauvin, J.-M.; Morrison, R.M.; Deblasio, R.N.; Menna, C.; Ding, Q.; Pagliano, O.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplant Overcomes Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Melanoma Patients. Science 2021, 371, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; Ebadi, M.; Rehman, T.U.; Elhusseini, H.; Kazadi, D.; Halaweish, H.; Khan, M.H.; Hoeschen, A.; Cao, Q.; Luo, X.; et al. Potential of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation to Prevent Acute GVHD: Analysis from a Phase II Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4920–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, N.L.-N.; Lau, H.C.-H.; Yu, J. Cancer Pharmacomicrobiomics: Targeting Microbiota to Optimise Cancer Therapy Outcomes. Gut 2022, 71, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; De La Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a Probiotic on Liver Aminotransferases in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: A Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Carpi, R.Z.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sloan, K.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Gonzaga, H.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Zutin, T.L.M.; Girio, R.J.S.; Repetti, C.S.F.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; et al. The Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics in Non-Alcoholic Fat Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.B.; Jun, D.W.; Kang, B.-K.; Lim, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.-J. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Multispecies Probiotic Mixture in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomhof, M.R.; Parnell, J.A.; Ramay, H.R.; Crotty, P.; Rioux, K.P.; Probert, C.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Raman, M.; Reimer, R.A. Histological Improvement of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis with a Prebiotic: A Pilot Clinical Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.J.; Martinez, E.G.; Gregorio, G.V.; Dans, L.F. Probiotics for Treating Acute Infectious Diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD003048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minkoff, N.Z.; Aslam, S.; Medina, M.; Tanner-Smith, E.E.; Zackular, J.P.; Acra, S.; Nicholson, M.R.; Imdad, A. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for the Treatment of Recurrent Clostridioides Difficile (Clostridium Difficile). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 4, CD013871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fareed, S.; Sarode, N.; Stewart, F.J.; Malik, A.; Laghaie, E.; Khizer, S.; Yan, F.; Pratte, Z.; Lewis, J.; Immergluck, L.C. Applying Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) to Treat Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infections (RCDI) in Children. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bär, A.-K.; Phukan, N.; Pinheiro, J.; Simoes-Barbosa, A. The Interplay of Host Microbiota and Parasitic Protozoans at Mucosal Interfaces: Implications for the Outcomes of Infections and Diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, V.; Mancinelli, L.; Bracaglia, G.; Del Chierico, F.; Vernocchi, P.; Di Girolamo, F.; Garrone, S.; Tchidjou Kuekou, H.; D’Argenio, P.; Dallapiccola, B.; et al. “Omic” Investigations of Protozoa and Worms for a Deeper Understanding of the Human Gut “Parasitome”. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.M.; Graham, A.L.; Knowles, S.C.L. Parasite-Microbiota Interactions with the Vertebrate Gut: Synthesis Through an Ecological Lens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Iorio, A.; Porcari, S.; Masucci, L.; Sanguinetti, M.; Perno, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Putignani, L.; Cammarota, G. How the Gut Parasitome Affects Human Health. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 175628482210915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, S.; Ristori, M.V.; Gardini, S.; Russo, A.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Clinical Parasitology and Parasitome Maps as Old and New Tools to Improve Clinical Microbiomics. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzesi, A.; Putignani, L. Impact of Helminth–Microbiome Interactions on Childhood Health and Development—A Clinical Perspective. Parasite Immunol. 2023, 45, e12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzesi, A.; Pane, S.; Putignani, L. How Modulations of the Gut Microbiota May Help in Preventing or Treating Parasitic Diseases. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2022, 9, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, V.F.; Sparo, M.D.; Sidoti, A.; Santín, M.; Basualdo, J.A.; Córdoba, M.A. Effects of Enterococcus Faecalis CECT 7121 on Cryptosporidium Parvum Infection in Mice. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alak, J.I.; Wolf, B.W.; Mdurvwa, E.G.; Pimentel-Smith, G.E.; Adeyemo, O. Effect of Lactobacillus Reuteri on Intestinal Resistance to Cryptosporidium Parvum Infection in a Murine Model of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funkhouser-Jones, L.J.; Xu, R.; Wilke, G.; Fu, Y.; Schriefer, L.A.; Makimaa, H.; Rodgers, R.; Kennedy, E.A.; VanDussen, K.L.; Stappenbeck, T.S.; et al. Microbiota-Produced Indole Metabolites Disrupt Mitochondrial Function and Inhibit Cryptosporidium Parvum Growth. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignani, L.; Tait, A.; Smith, H.V.; Horner, D.; Tovar, J.; Tetley, L.; Wastling, J.M. Characterization of a Mitochondrion-like Organelle in Cryptosporidium Parvum. Parasitology 2004, 129, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickerd, N.; Tuthill, D. Resolution of Cryptosporidiosis with Probiotic Treatment. Postgrad. Med. J. 2004, 80, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, K.N.C.; Sowmyanarayanan, T.V.; Paul, A.; Babji, S.; Ajjampur, S.S.R.; Priyadarshini, S.; Sarkar, R.; Balasubramanian, K.A.; Wanke, C.A.; Ward, H.D.; et al. Immune Response and Intestinal Permeability in Children with Acute Gastroenteritis Treated with Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzesi, A.; Pane, S.; Russo, A.; Del Chierico, F.; Francalanci, P.; Cotugno, N.; Rossi, P.; Locatelli, F.; Palma, P.; Putignani, L. Case Report: The Impact of Severe Cryptosporidiosis on the Gut Microbiota of a Pediatric Patient with CD40L Immunodeficiency. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1281440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-Related Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition from Newborn to Centenarian: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Abbatini, F.; Russo, A.; Quagliariello, A.; Reddel, S.; Capoccia, D.; Caccamo, R.; Ginanni Corradini, S.; Nobili, V.; De Peppo, F.; et al. Gut Microbiota Markers in Obese Adolescent and Adult Patients: Age-Dependent Differential Patterns. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Onori, M.; Di Bella, S.; Bordi, E.; Petrosillo, N.; Menichella, D.; Cacciò, S.M.; Callea, F.; Putignani, L. Cases of Cryptosporidiosis Co-Infections in AIDS Patients: A Correlation between Clinical Presentation and GP60 Subgenotype Lineages from Aged Formalin-Fixed Stool Samples. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2011, 105, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, J.I.; Surawicz, C. Severe Acute Diarrhea. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 32, 1249–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Chierico, F.; Marzano, V.; Scanu, M.; Reddel, S.; Dentici, M.L.; Capolino, R.; Di Donato, M.; Spasari, I.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Digilio, M.C.; et al. Analysis of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Williams-Beuren Syndrome Reveals Dysbiosis Linked to Clinical Manifestations. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Jiang, Y.; Balaban, M.; Cantrell, K.; Zhu, Q.; Gonzalez, A.; Morton, J.T.; Nicolaou, G.; Parks, D.H.; Karst, S.M.; et al. Greengenes2 Unifies Microbial Data in a Single Reference Tree. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, J.N.; Stine, O.C.; Bravo, H.C.; Pop, M. Differential Abundance Analysis for Microbial Marker-Gene Surveys. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, K.; Pamer, E.G. Enterococci and Their Interactions with the Intestinal Microbiome. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Pei, Z.; Poles, M.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D. Human Microbiome and HIV/AIDS. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2012, 9, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Lu, D.; Huang, J.; Lan, L.; Guo, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites during AIDS: Implications for CD4+ T Cell Reduction and Immune Activation. AIDS 2024, 38, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Poto, R.; Ianiro, G.; Punziano, A.; Marone, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Spadaro, G. Gut Microbiome and Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Few Certainties and Many Outstanding Questions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 712915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosák, J.; Lexa, M.; Fiedorová, K.; Gadara, D.C.; Micenková, L.; Spacil, Z.; Litzman, J.; Freiberger, T.; Šmajs, D. Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) Show Higher Gut Bacterial Diversity and Levels of Low-Abundance Genes than the Healthy Housemates. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 671239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulzhenko, N.; Dong, X.; Vyshenska, D.; Greer, R.L.; Gurung, M.; Vasquez-Perez, S.; Peremyslova, E.; Sosnovtsev, S.; Quezado, M.; Yao, M.; et al. CVID Enteropathy Is Characterized by Exceeding Low Mucosal IgA Levels and Interferon-Driven Inflammation Possibly Related to the Presence of a Pathobiont. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 197, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, S.F.; Trøseid, M.; Kummen, M.; Anmarkrud, J.A.; Michelsen, A.E.; Osnes, L.T.; Holm, K.; Høivik, M.L.; Rashidi, A.; Dahl, C.P.; et al. Altered Gut Microbiota Profile in Common Variable Immunodeficiency Associates with Levels of Lipopolysaccharide and Markers of Systemic Immune Activation. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Zhou, J.; Su, Y.; Mao, K.; Wu, J.; Zhu, C.; He, L.; Cui, Y. Gut Microbiota Composition and Functional Prediction in Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-D.; Liu, B.-N.; Zhao, S.-H.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Bai, L.; Liu, E.-Q. Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity Associated with Post-Cholecystectomy Diarrhea. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jing, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Chang, Q.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z. Disordered Gut Microbiota Correlates with Altered Fecal Bile Acid Metabolism and Post-Cholecystectomy Diarrhea. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 800604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.U.; Al Khatib, H.A.; Al Thani, A.A.; Al Ansari, K.; Yassine, H.M.; Al-Asmakh, M. Microbiome Profiling of Rotavirus Infected Children Suffering from Acute Gastroenteritis. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung The, H.; Le, S.-N.H. Dynamic of the Human Gut Microbiome under Infectious Diarrhea. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2022, 66, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monira, S.; Nakamura, S.; Gotoh, K.; Izutsu, K.; Watanabe, H.; Alam, N.H.; Nakaya, T.; Horii, T.; Ali, S.I.; Iida, T.; et al. Metagenomic Profile of Gut Microbiota in Children during Cholera and Recovery. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, H.C.; Florez de Sessions, P.; Jie, S.; Pham Thanh, D.; Thompson, C.N.; Nguyen Ngoc Minh, C.; Chu, C.W.; Tran, T.A.; Thomson, N.R.; Thwaites, G.E.; et al. Assessing Gut Microbiota Perturbations during the Early Phase of Infectious Diarrhea in Vietnamese Children. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daca, A.; Jarzembowski, T. From the Friend to the Foe—Enterococcus Faecalis Diverse Impact on the Human Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sava, I.G.; Heikens, E.; Huebner, J. Pathogenesis and Immunity in Enterococcal Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazzesi, A.; Putignani, L. Extremely Small and Incredibly Close: Gut Microbes as Modulators of Inflammation and Targets for Therapeutic Intervention. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 958346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaguza, C.; Pöntinen, A.K.; Top, J.; Arredondo-Alonso, S.; Freitas, A.R.; Novais, C.; Torres, C.; Bentley, S.D.; Peixe, L.; Coque, T.M.; et al. The Population-Level Impact of Enterococcus Faecalis Genetics on Intestinal Colonization and Extraintestinal Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00201-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofs, L.; Sparo, M.D.; de Yaniz, M.G.; Lissarrague, S.; Domínguez, M.P.; Álvarez, L.I.; Sánchez Bruni, S.F. Antinematodic Effect of Enterococcus Faecalis CECT7121 Using Trichinella Spiralis as a Model of Nematode Infection in Mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 241, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrová, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Lauková, A.; Dvorožňáková, E. Antiparasitic Activity of Enterocin M and Durancin-like from Beneficial Enterococci in Mice Experimentally Infected with Trichinella Spiralis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleya, S.; Watkins, C.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Gut Bifidobacteria Populations in Human Health and Aging. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuivenberg, G.A.; Burton, J.P.; Bron, P.A.; Reid, G. Why Are Bifidobacteria Important for Infants? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Ho, C.L. Recent Development of Probiotic Bifidobacteria for Treating Human Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 770248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Sequeira, T.C.G.; David, É.B.; Ribeiro, C.; Guimarães, S.; Masseno, A.P.B.; Katagiri, S.; Sequeira, J.L. Effect of Bifidobacterium Animalis on Mice Infected with Strongyloides Venezuelensis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2014, 56, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Foster, J.C.; Glass, M.D.; Courtney, P.D.; Ward, L.A. Effect of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on Cryptosporidium Parvum Oocyst Viability. Food Microbiol. 2003, 20, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudet, J.; Trelis, M.; Cifre, S.; Soriano, J.M.; Rico, H.; Merino-Torres, J.F. Interplay between Intestinal Bacterial Communities and Unicellular Parasites in a Morbidly Obese Population: A Neglected Trinomial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, R.G.; Vasques, A.C.; Fernandes, G.D.; Ribeiro, F.B.; Solar, I.; Barbosa, M.G.; Pititto, B.D.; Geloneze, B.; Ferreira, S.R. Associations of Blautia Genus with Early-Life Events and Later Phenotype in the NutriHS. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 838750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Dhakal, P.; Zhang, L. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals the Relationship Between Intestinal Protozoan Parasites and the Intestinal Microecological Balance in Calves. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujila, I.; Troell, K.; Ögren, J.; Hansen, A.; Killander, G.; Agudelo, L.; Lebbad, M.; Beser, J. Cryptosporidium Species and Subtypes Identified in Human. Domestic Cases through the National Microbiological Surveillance Programme in Sweden from 2018 to 2022. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).