Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a multi-drug-resistant opportunistic pathogen that adapts to challenging environments by deploying virulence factors, including the type III secretion system (T3SS). Emerging evidence points to a role for NADH dehydrogenase complexes in regulating virulence; however, their precise contributions remain unclear. Here, we identify PA2649, a component of the NADH dehydrogenase complex I (nuo operon), as a key regulator of T3SS-related activities. PA2649 deletion resulted in a twofold increase in exoS expression and enhanced cytotoxicity in both A549 cell and Chinese cabbage models. Full revertant of the nuo operon was necessary to restore exoS expression to wild-type levels, suggesting a critical connection between NADH dehydrogenase activity and T3SS regulation. The PA2649 mutation also disrupted the Rsm-Exs regulatory axis, downregulating gacS, rsmY, rsmZ, and hfq while upregulating exsC. Overexpression of rsmY, rsmZ, gacA, hfq, and exsD partially rescued T3SS function, confirming that PA2649 influences T3SS via the Rsm-Exs pathway. Furthermore, PA2649 deletion altered motility, biofilm formation, pyocyanin production, protease activity, and antibiotic susceptibility. These phenotypes could not be complemented with T3SS regulatory genes alone, indicating that PA2649 modulates these traits through mechanisms independent of the Rsm-Exs axis, potentially involving NADH dehydrogenase-associated pathways. This study underscores the multifaceted role of PA2649 in regulating P. aeruginosa pathogenicity and resistance, providing novel insights into its complex regulatory networks and highlighting new avenues for therapeutic targeting.
1. Introduction
Bacteria can sense a wide range of physical and chemical external cues, adapting their metabolic processes accordingly to survive in diverse environments. Pathogenic bacteria, in particular, detect both physical (e.g., surface properties) and chemical signals (e.g., Ca2+, N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHL), 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone (Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal, PQS), cyclic di-GMP etc.) during infection, enabling them to modulate virulence factors either directly, through mechanisms such as two-component systems, or indirectly, via metabolic adjustments that enhance pathogenicity [1]. While numerous regulatory proteins, including quorum sensing regulators, two-component system regulators, and sigma factors, have been identified as critical in controlling virulence factors at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels [2,3], the mechanisms by which metabolic genes influence virulence factor expression remain incompletely understood.
T3SS, first identified in Yersinia in the 1990s [4], is a virulence-associated protein complex that facilitates the direct injection of bacterial proteins into host cells, thereby enhancing pathogenicity through trans-kingdom communication with eukaryotic hosts [5]. T3SS is commonly found in various in many pathogenic bacteria, including Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, Bordetella, Pseudomonas, and enteropathogenic Escherichia species [6]. The regulation of T3SS continues to be a significant area of research due to its essential role in bacterial virulence and intercellular interactions.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a versatile pathogen, is capable of causing infections in various tissues, including the respiratory tract, urinary system, and bloodstream, particularly in immunocompromised individuals [7]. The T3SS of P. aeruginosa, which consists of several structurally and functionally conserved proteins, can severely compromise host defenses by injecting effector toxins such as ExoU, ExoT, ExoS, and ExoY [8,9]. These toxins disrupt phagocytosis, facilitate immune evasion, and promote colonization. T3SS serves as a model for studying both transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms that regulate T3SS gene expression in bacterial pathogens.
Given its ability to infect a diverse range of hosts (mammals, insects, worms, amoebae, and plants), P. aeruginosa relies on multifaceted regulatory systems for precise spatial and temporal control of its T3SS. The expression of T3SS is finely tuned by various environmental factors such as extracellular calcium, host proteins, abiotic surfaces, nucleoid-associated proteins, and two-component and global regulatory systems [10,11,12]. The core regulatory pathway, which employs a partner-switching mechanism, includes the key genes exsA, exsC, exsD, and exsE, which are involved in the transcription activation of the aforementioned classical effectors (ExoS, ExoT, ExoU, and ExoY) [7]. Upon induction, ExsE is secreted extracellularly, enabling ExsC to bind to ExsD and release ExsA [13]. The liberated ExsA then directly binds to target promoters to activate the T3SS regulon [14]. Additional layers of regulation involve the Rsm system, cAMP, cyclic di-GMP signaling, and other global regulatory systems (Such as quorum sensing (QS) systems and the two-component regulatory systems like GacS-GacA) [12,15]. The Rsm system, including small RNAs (RsmY and RsmZ) and regulatory proteins (RsmA/RsmF), modulates T3SS and other cellular processes, integrating environmental and metabolic signals to optimize the expression of virulence factors [16].
The metabolic state significantly influences the T3SS, as studies have shown that a proficient Proton Motive Force (PMF) is essential for effector secretion [17]. Metabolic defects, such as those observed in the crc mutant, lead to a reduction in T3SS activity [18]. Additionally, NADH metabolism also appears to be linked to virulence in P. aeruginosa, with NADH/NAD⁺ and NADPH/NADP⁺ playing crucial roles in redox reactions that are vital for cellular metabolism and biosynthesis [19]. These studies offer valuable insights into the role of NADH-related genes in the regulation of virulence. Pseudomonas aeruginosa expresses three NADH dehydrogenases (NUO, NQR, and NDH-2), which oxidize cellular NADH and serve as entry points for electrons in the respiratory chain [20,21,22]. This adaptability, combined with the central role of NADH in bacterial physiology, underscores the necessity of investigating the role of NADH dehydrogenases in the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa, as this connection remains largely unexplored.
Here, our findings demonstrate that the deletion of PA2649 in P. aeruginosa significantly upregulates exoS expression and cytotoxicity while disrupting multiple virulence traits, including motility, biofilm formation, and pyocyanin production. The PA2649 gene influences T3SS regulation via the Rsm-Exs pathway, yet its impact on antibiotic resistance and other virulence phenotypes appears to involve separate mechanisms beyond this pathway.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are presented in Table S1. Primers used in this study are showed in Table S2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli were cultured on Luria–Bertani (LB) agar or in LB broth at 37 °C unless otherwise specified. Antibiotics were used at the following concentrations: for E. coli, kanamycin (Kan) at 50 µg/mL, ampicillin (Amp) at 100 µg/mL, tetracycline (Tc) at 15 µg/mL, and gentamicin (Gen) at 15 µg/mL in LB. For P. aeruginosa, Gen at 50 µg/mL in LB or 150 µg/mL in Pseudomonas isolation agar (PIA; Beijing Land Bridge Tech., Ltd., Beijing, China), Tc at 70 µg/mL in LB or 300 µg/mL in PIA, carbenicillin (Cb) at 250 µg/mL in LB, and trimethoprim (Tmp) at 300 µg/mL in LB. Other antibiotics, such as chloramphenicol (Chl), ciprofloxacin (Cip), streptomycin (Strep), and polymyxin B (PMB), were used in LB as indicated. Peptone and Yeast extract were purchased from OXOID (Hampshire, UK). Antibiotics used in this study were all purchased from MP Biomedicals (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Construction and Revertant of Gene Knockout Mutants
Following previously established methods, we employed homologous recombination using the sucrose-lethal sacB gene for knockout mutant construction [23]. To delete the PA2649 gene, we amplified 1575 bp and 976 bp fragments from the regions upstream and downstream of the PA2649 open reading frame, respectively, via PCR. These PCR products were ligated into the pEX18Tc plasmid, which was subsequently transferred into the E. coli conjugation donor strain S17-1 λpir and then introduced into wild-type PAO1 by biparental mating [24]. Single-crossover mutants, with the plasmid integrated into the PAO1 chromosome, were selected using tetracycline. These mutants were cultured in PIA medium (300 µg/mL Tc) overnight and then plated on 15% sucrose plates to select for double-crossover mutants. Mutants were verified by PCR across the target gene region. For constructing revertant and overexpression strains, the promoter and ORF of target genes were cloned into the digested pAK1900 vector, which was then transformed into the corresponding strains.
2.3. Construction of T3SS Gene Expression Reporters
The plasmid pMS402, which carries a promoterless luxCDABE reporter gene cluster, was used to construct promoter-luxCDABE gene fusions as previously described [25]. Promoter regions of target genes were amplified by PCR using high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase and primers designed based on the PAO1 genome sequence. The amplified promoter regions were then cloned into the Bam HI–Xho I sites upstream of the lux genes on pMS402 [26]. The resulting plasmids were introduced into PAO1 by electroporation, and cloned promoter sequences were confirmed by DNA sequencing. In addition to the plasmid-based reporter system, a chromosomal reporter system was constructed using the integration plasmid CTX6.1, derived from the mini-CTX-lux plasmid [26]. CTX6.1 contains all elements required for chromosomal integration, replication origin, and tetracycline resistance. The luxCDABE reporter cassette from pMS402, including the kanamycin resistance marker and multiple cloning sites, was isolated and ligated into CTX6.1. The generated plasmid was first transferred into E. coli SM10-λ pir, and integration into PAO1 was achieved by biparental mating [27]. Gene expression using these lux-based reporters was quantified in liquid culture as counts per second (cps) of light production, measured with a Synergy H1 microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA) [28].
2.4. Gene Expression Detection
Gene expression in liquid cultures was measured using lux-based reporters, quantified as cps of light production with a Synergy H1 microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA) [29]. Overnight bacterial cultures were inoculated at 1% into fresh LB medium containing appropriate antibiotics and incubated for 3 h. For measurement, 95 µL of LB and 5 µL of bacterial culture were added to each well of a black 96-well plate with a clear bottom, mixed thoroughly, and topped with 50 µL of paraffin oil to prevent evaporation. Luminescence (cps) and bacterial growth (OD600) were recorded every 30 min over a 24 h period using a multimode microplate reader, as previously described.
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
Cytotoxicity assays were conducted with slight modifications as previously described [30]. Bacterial cytotoxicity was assessed by measuring the survival of A549 cells following infection with P. aeruginosa. A549 cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum, Amp (100 mg/mL), and Strep (100 mg/mL) at 37 °C with 5% CO2. Approximately 5000 cells were seeded per well in a 96-well plate and cultured overnight until reaching 80–90% confluence. The culture supernatants were removed, and the cell monolayers were washed once with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Overnight bacterial cultures were diluted in fresh LB medium and grown at 37 °C for approximately 12 h to an OD600 of 1.0. The cultures were centrifuged at 12,000× g for 2 min, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 µm membrane. A549 cells were incubated with 25 µL of bacterial supernatant and 75 µL of fresh DMEM per well. After a 3 h infection period, 10 µL of Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) solution (Biosharp, Hefei, China) was added to each well and incubated for an additional hour. OD450 was measured using a Synergy H1 microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA) to calculate cell survival. The cell survival rate (%) was calculated as follows: Cell survival rate (%) = [(OD450 of treated sample − OD450 of blank)/(OD450 of untreated control − OD450 of blank)] × 100.
2.6. Extraction of ExoS Proteins by Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) Precipitation
ExoS proteins were extracted using TCA precipitation as previously described [31]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures were grown under T3SS-inducing conditions (5 mM EGTA, 20 mM MgCl2) for 6 h at 37 °C. After removing bacterial cells by centrifugation at 12,000× g, 110 µL of 100% TCA was added to the supernatant and placed on ice for 10 min. Subsequently, 500 µL of 10% TCA was added, and the mixture was kept on ice for an additional 20 min to precipitate proteins. Following protein precipitation, the supernatant was removed by centrifugation at 20,000× g for 30 min. The protein pellet was washed with acetone and then pelleted again. Proteins were resuspended in buffer, separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized with Coomassie blue staining.
2.7. Chinese Cabbage Infection Assay
The cabbage infection assay was performed as previously reported with minor modifications [32]. Bacterial strains were cultured overnight at 37 °C and harvested by centrifugation. The bacterial pellets were washed with 10 mM MgSO4, the supernatant was removed, and the cells were resuspended. The OD600 of the bacterial suspension was adjusted to 2.0. Cabbage stems, pretreated with 0.1% H2O2, were placed in Petri dishes containing filter paper soaked in 10 mM MgSO4. A 10 µL aliquot of the bacterial suspension was injected into each cabbage stem, and the samples were incubated at 30 °C for 6 days. The extent of cabbage tissue decay was then observed and recorded.
2.8. Biofilm Assay
The biofilm formation assay was conducted as previously described with minor modifications [33]. Overnight cultures of P. aeruginosa were diluted to an OD600 of 0.1 in fresh LB medium. Aliquots of 200 µL of the diluted culture were added to the wells of a 96-well polystyrene microtiter plate. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h to allow biofilm formation. After incubation, the culture medium was carefully aspirated, and the wells were washed three times with sterile PBS to remove nonadherent cells. The biofilm was fixed by adding 200 µL of 100% methanol to each well and incubating at room temperature for 15 min. The methanol was then aspirated, and the wells were air dried. To visualize the biofilm, 200 µL of 1% crystal violet solution was added to each well and incubated for 20 min. After staining, the plates were washed gently with PBS to remove excess dye, and the biofilm was solubilized by adding 200 µL of 95% ethanol to each well. The absorbance of each well was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader.
2.9. Pyocyanin Assay
Pyocyanin production was measured as previously described [34]. Overnight cultures were inoculated at 1% into 5 mL of PB medium and incubated at 37 °C with shaking at 200 g for 16 h. After incubation, cells were removed by centrifugation, and the supernatant was subjected to organic extraction with 3 mL of chloroform. Following centrifugation, the lower chloroform layer was transferred to a new tube, where 1 mL of 0.2 M HCl was added, mixed thoroughly, and allowed to separate into layers. The absorbance of the upper aqueous phase was measured at 520 nm to quantify the pyocyanin concentration.
2.10. Swimming, Swarming, and Twitching Motility Assays
Bacterial motility was assessed as previously described [35]. The swimming medium comprised 0.5% NaCl, 1% tryptone, and 0.3% agar. The swarming medium contained 0.8% nutrient broth, 0.5% glucose, and 0.5% agar. For twitching, the medium consisted of 0.5% yeast extract, 1% tryptone, 1% NaCl, and 1.2% agar. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures were diluted to an OD600 of 0.5, and 2 µL of the diluted culture was placed centrally on the surface of each agar plate. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, after which the diameter of the motility zone was measured. For twitching motility, the bacterial suspension was stabbed into the bottom of the medium and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The diameter of the twitching zone was assessed using crystal violet staining.
2.11. Protease Assay
Protease activity was assessed using a milk medium containing 2.5% skimmed milk powder and 1% agar to detect extracellular protease activity, as previously described [36]. Overnight bacterial cultures were diluted to an OD600 of 0.2, and 2 µL of each bacterial suspension was spotted onto the surface of the milk medium. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 12 h. Protease activity was determined by comparing the diameter of the clear zones surrounding each bacterial spot, indicating proteolytic degradation of the milk proteins.
2.12. Antibiotic Resistance Determination
Antibiotic susceptibility assays were performed as previously described with minor modifications [36]. Overnight bacterial cultures were inoculated into fresh LB medium at 1% and incubated for 3 h. LB media with various antibiotic concentrations were prepared, and 95 µL of each antibiotic-containing medium was combined with 5 µL of bacterial culture in each well of a 96-well plate. To prevent evaporation, 50 µL of liquid paraffin was added to each well. Bacterial growth was monitored every 30 min for 24 h by measuring OD600 with a multimode microplate reader. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was defined as the lowest antibiotic concentration at which no bacterial growth was detected after 24 h. Additionally, antibiotic resistance assays were performed on LB agar plates with various antibiotic concentrations. Overnight cultures were serially diluted, and 5 µL of each dilution was spotted onto the corresponding antibiotic-containing plates. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, and bacterial growth was then observed.
2.13. Extraction and Quantification of Intracellular NADH and NAD+
NADH and NAD+ were extracted using the Beyotime Enhanced NAD+/NADH Assay Kit (WST-8) (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions (Cat No: S0176S). Bacterial strains were cultured overnight in fresh LB medium for approximately 12 h. The OD600 of the bacterial cultures was adjusted to the same level before processing. A 300 µL aliquot of each bacterial culture was centrifuged at 12,000× g for 5 min, and the supernatant was discarded. Subsequently, 200 µL of the NAD+/NADH extraction buffer was added, and the pellet was gently resuspended to facilitate cell lysis. The mixture was then centrifuged at 12,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. The resulting supernatant was collected and used as the sample for analysis.
2.14. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed and visualized using GraphPad Prism, version 9.5. All experiments were conducted in triplicate and independently repeated three times. Statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed unpaired t-tests where applicable, with significance thresholds set as follows: ns (not significant, p > 0.05); * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; and *** p < 0.001.
3. Results
3.1. Upregulation of exoS Expression and Enhancement of Pathogenicity in ∆nuoN
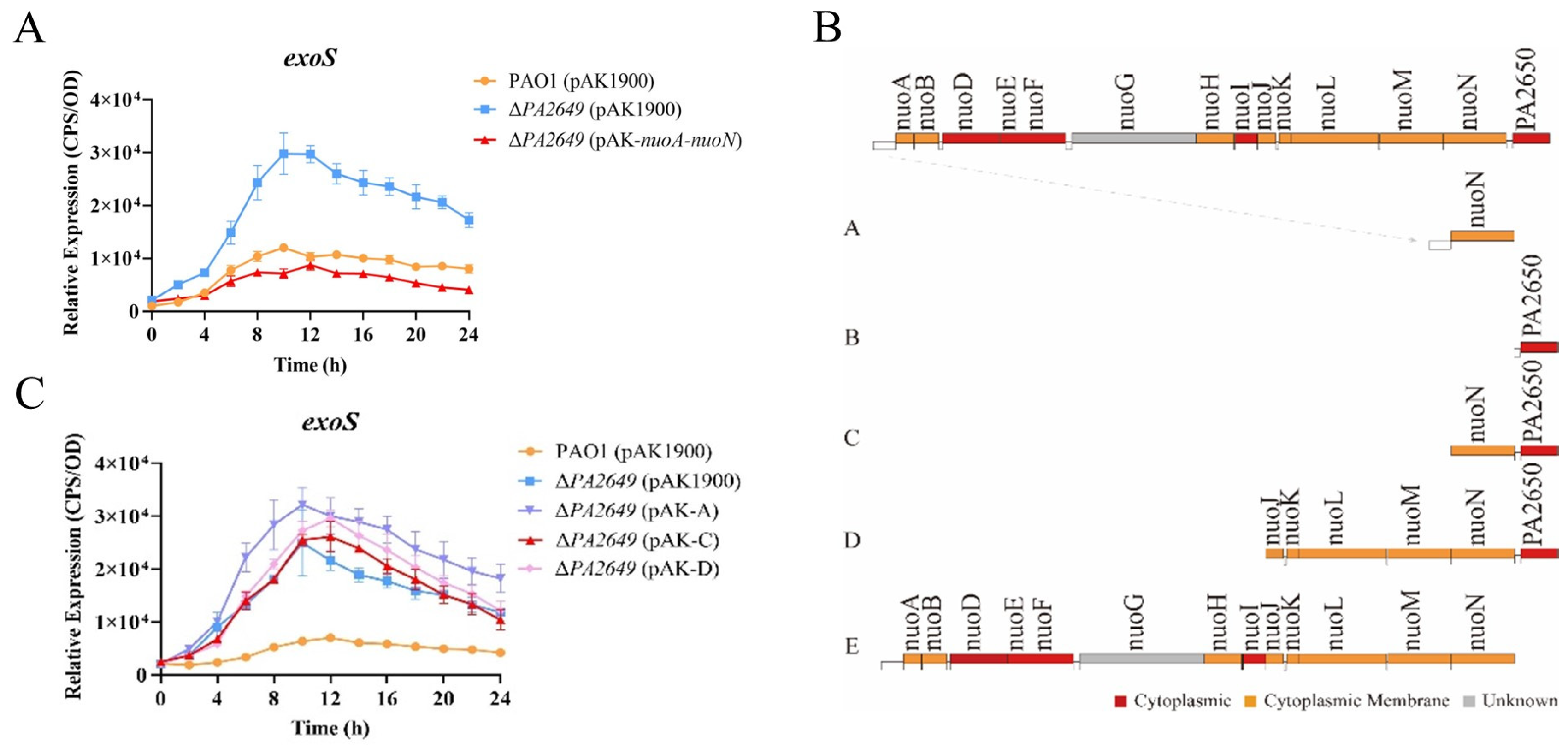
During the preliminary screening for mutants related to the expression of the type III secretion system, several transposon mutants were identified that could potentially affect its expression. We selected one transposon insertion mutant within the PA2649 gene (Figure S1) for further investigation. First, we constructed a PA2649 deletion mutant and integrated an exoS luminescent reporter into the mutant’s genome using a CTX-based system [26]. Expression analysis (Figure 1A) showed that exoS expression in the ∆PA2649 mutant was more than two times higher than in the wild-type strain. Next, to verify that the observed phenotype was indeed caused by the PA2649 mutation, we constructed a PA2649 revertant plasmid with a fragment A (Figure 1B) in pAK1900 and introduced it into the mutant. However, the results showed that exoS expression did not revert to wild-type levels (Figure 1C). According to the literature [37], the NADH oxidase activity lost due to a nuoN gene mutation could be restored by a plasmid containing the previously identified nuoN gene along with the upstream intergenic region between nuoM and nuoN in Escherichia coli. Therefore, we constructed four additional revertant plasmids with different genes (named B–E), as shown (Figure 1B), and introduced them into the mutant to assess exoS expression. The results showed that only the plasmid complementing the entire operon (pAK1900 with E fragment in Figure 1B) was able to restore the exoS expression (Figure 1A). None of the other plasmids could restore the phenotype of the PA2649 mutant (Figure 1C), suggesting that the mutation in PA2649 led to a loss of function in the entire nuo operon, resulting in the upregulation of exoS expression. Additionally, in order to eliminate the polar effect on PA2650, we constructed the pAK-PA2650 plasmid and introduced it separately into both the PA2649 mutant and PAO1 to examine exoS expression. Our results indicated that the overexpression of PA2650 in the PA2649 mutant had no effect on exoS expression (Figure S2A), whereas the overexpression of PA2650 in PAO1 led to approximately a onefold reduction in exoS expression (Figure S2B).
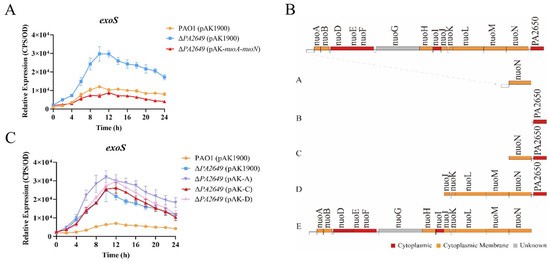
Figure 1.
Effect of the PA2649 mutation on exoS expression. (A) Expression levels of exoS were measured using a chromosomally integrated CTX-exoS reporter fusion under T3SS-inducing conditions in wild-type PAO1, the PA2649 mutant, and the complementary strain. (B) Expression levels with additional revertant plasmids carrying different genes. (C) Expression of exoS in the PA2649 mutant with various revertant plasmids. Fragment A: This construct includes the nuoN coding sequence along with its predicted native promoter of the whole operon. Fragment B: This construct contains the PA2650 coding sequence along with its native promoter. Fragment C: This construct consists of both nuoN and PA2650. Fragment D: This fragment spans a larger region, including nuoJ through PA2650. Fragment E: This construct contains the predicted full operon with a native promoter, covering nuoA to nuoN. Results represent the averages of triplicate experiments, with error bars indicating standard deviations. The assay was independently repeated three times. Cps: counts per second.
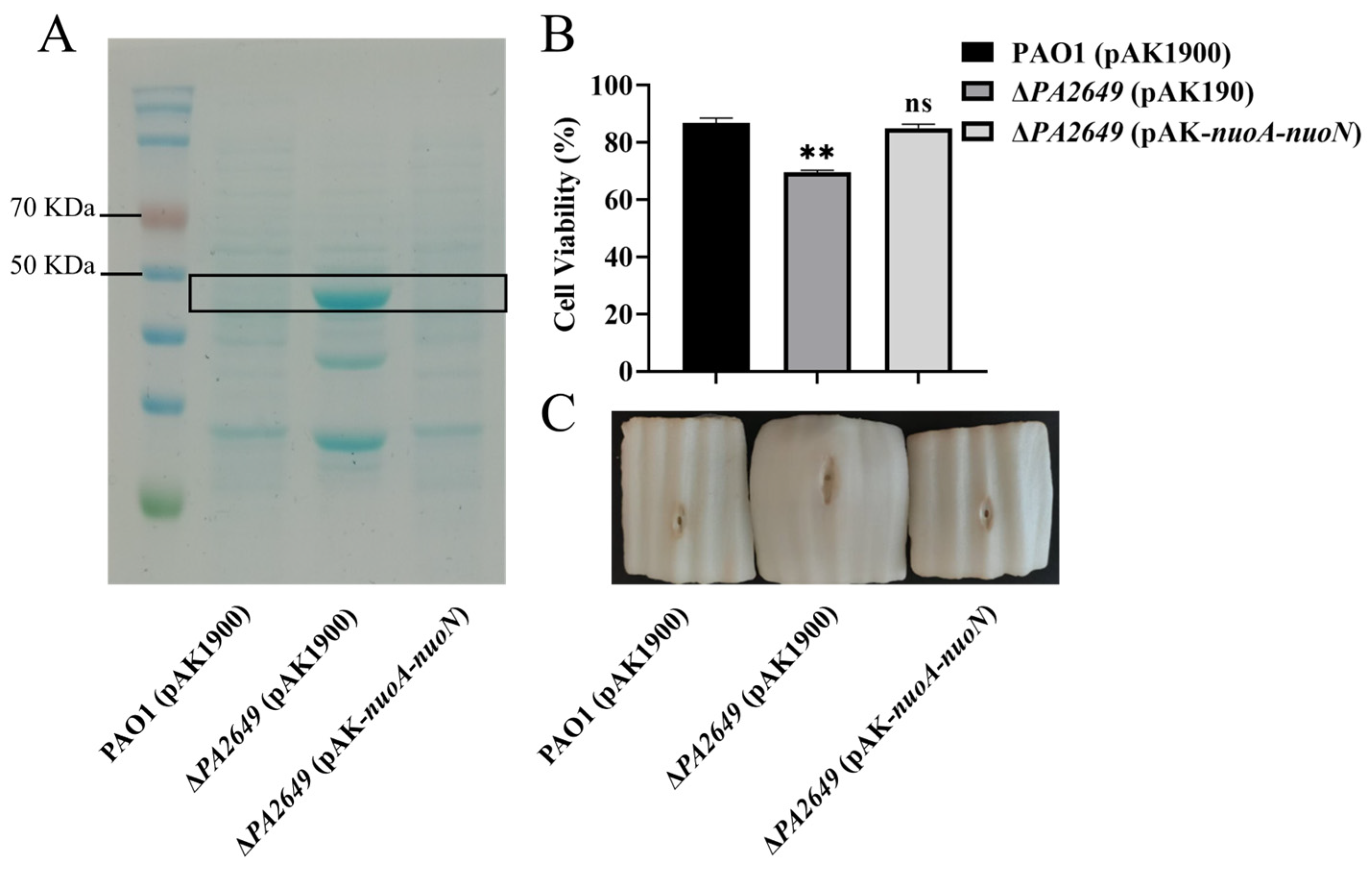
In summary, the results above indicate that the PA2649 mutation leads to elevated exoS expression. To further verify this finding, we extracted proteins from the corresponding culture supernatants and compared the results, which showed that the protein levels in the mutant were higher than those in the wild-type strain (Figure 2A). Due to the increased expression of the exoS caused by the PA2649 mutant, we utilized A549 cells as an in vitro model to assess the cytotoxicity of the mutant. The results of cytotoxicity assays using the supernatant from the PA2649 mutant showed a significant increase in cytotoxicity compared to the wild type and complemented strains (Figure 2B). Furthermore, the mutant exhibited a slightly more pronounced phenotype with enhanced tissue damage in a Chinese cabbage model (Figure 2C).
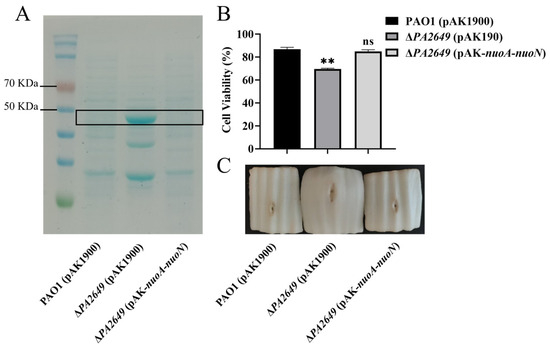
Figure 2.
Characterization of T3SS effectors and cytotoxicity assays. (A) Secreted T3SS effectors in T3SS-inducing medium were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Culture supernatants of various strains after 6 h of growth in T3SS inducing medium were precipitated by TCA and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by staining with Coomassie blue. Bands corresponding to ExoS effector are indicated. The black box marks the area corresponding to the proposed proteins on the gel. (B) Cytotoxicity assays were performed on A549 cells infected with the supernatant and quantified by the CCK-8 assay. Overnight cultures were centrifuged, and bacterial supernatants were filtered. Equal volumes of supernatants were incubated with A549 cells for 3 h, followed by cytotoxicity analysis. (C) Evaluation of necrosis caused by PAO1, PA2649 mutants, and the complementary strain in a Chinese cabbage model. Results represent the averages of triplicate experiments, with error bars indicating standard deviations. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Statistical significance is indicated as ns (not significant), p > 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
3.2. PA2649 Influences the Type III Secretion System Through the Rsm-Exs Regulatory Axis
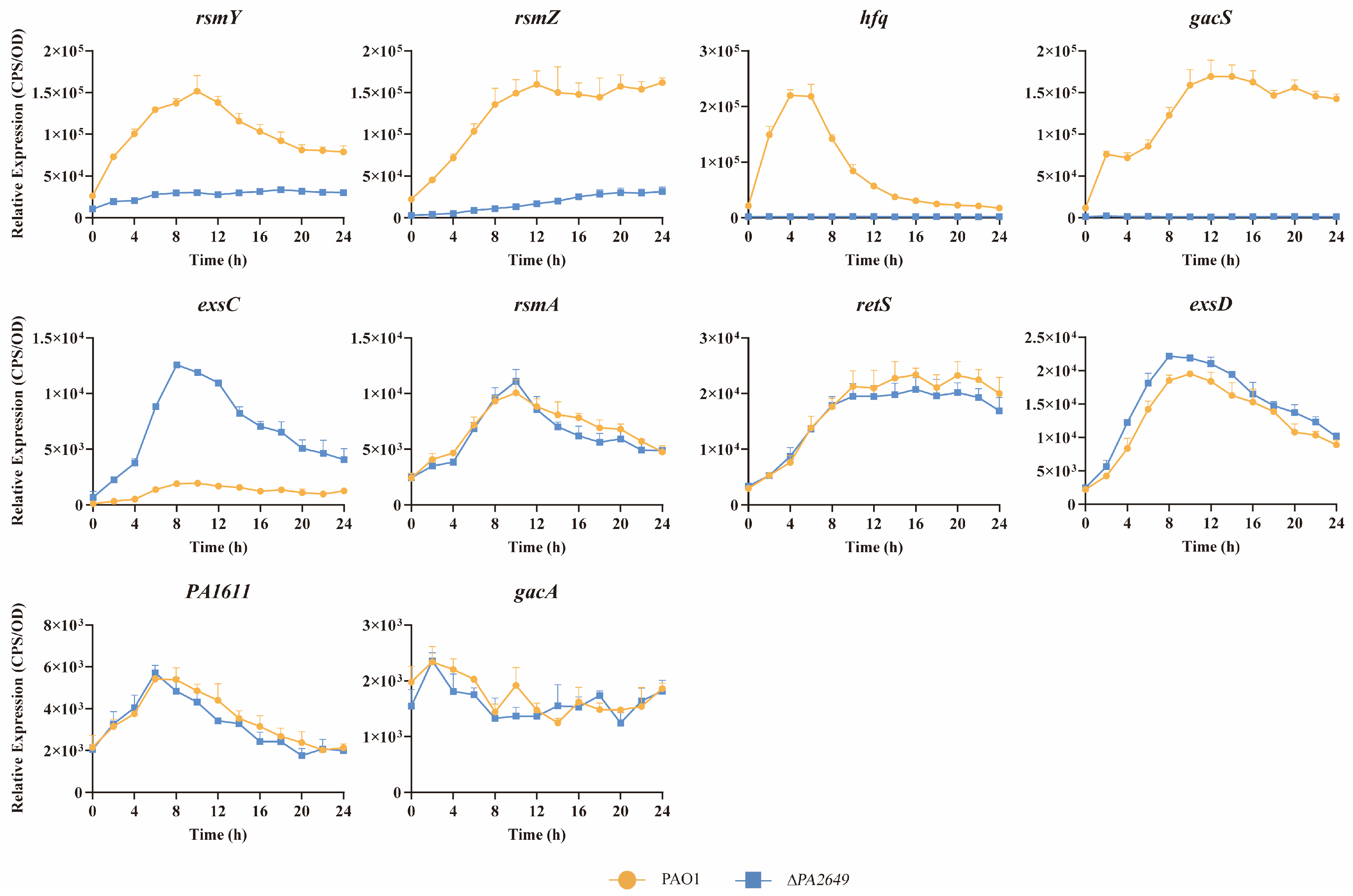
To further explore whether PA2649 exerts its effects through known regulatory pathways, we investigated its potential involvement in the Rsm-Exs regulatory axis, a major pathway controlling T3SS. Literature suggests that this axis plays a crucial role in regulating T3SS expression [12]. Consequently, we analyzed the expression levels of several genes within the Rsm-Exs axis. Our results indicated a reduction in the expression of gacS, rsmY, rsmZ, hfq, and an increased expression of exsC (Figure 3). In contrast, the expression levels of rsmA, retS, exsD, PA1611, and gacA remained unchanged (see Figure 3).
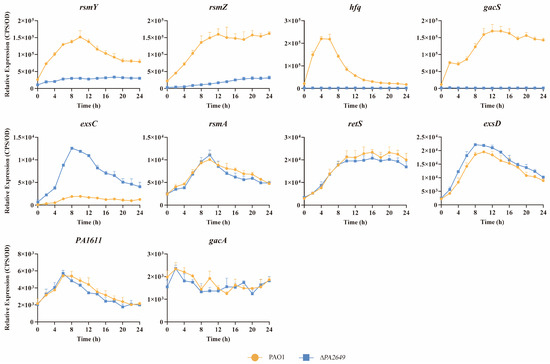
Figure 3.
Impact of PA2649 mutation on expression of T3SS-regulated genes in P. aeruginosa. The expression levels of T3SS-regulated genes (rsmY, rsmZ, hfq, gacS, exsC, rsmA, retS, exsD, PA1611, and gacA) were analyzed in PA2649 mutants. Overnight, different bacterial cultures were inoculated at 1% into fresh LB medium containing appropriate antibiotics and incubated for 3 h. For measurement, 95 µL of LB and 5 µL of bacterial culture were added to each well of a black 96-well plate with a clear bottom, mixed thoroughly, and topped with 50 µL of paraffin oil to prevent evaporation. Luminescence (cps) and bacterial growth (OD600) were recorded every 2 h over a 24 h period using a multimode microplate reader, as previously described. Results are presented as the averages of triplicate experiments, with error bars indicating standard deviations.
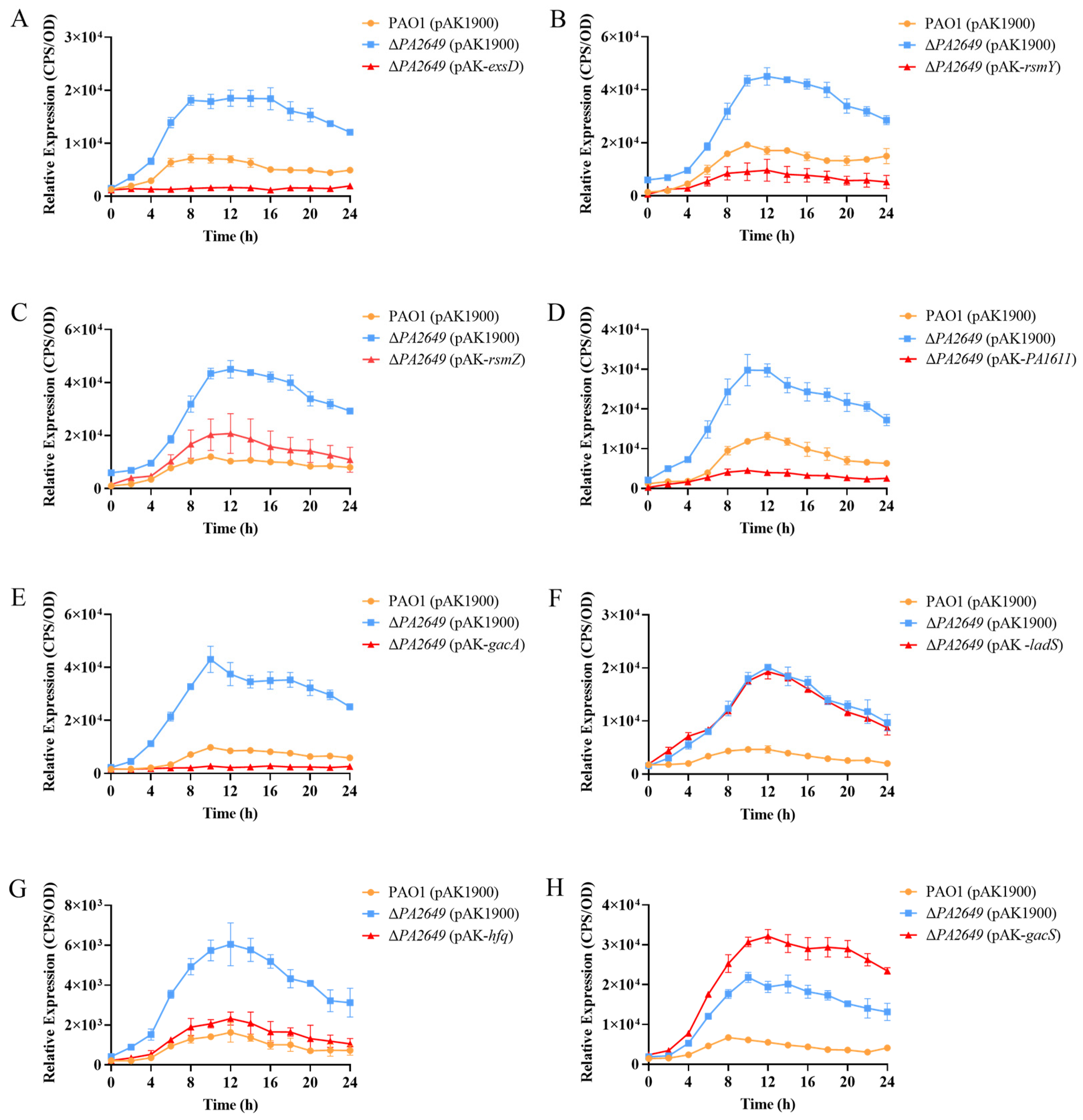
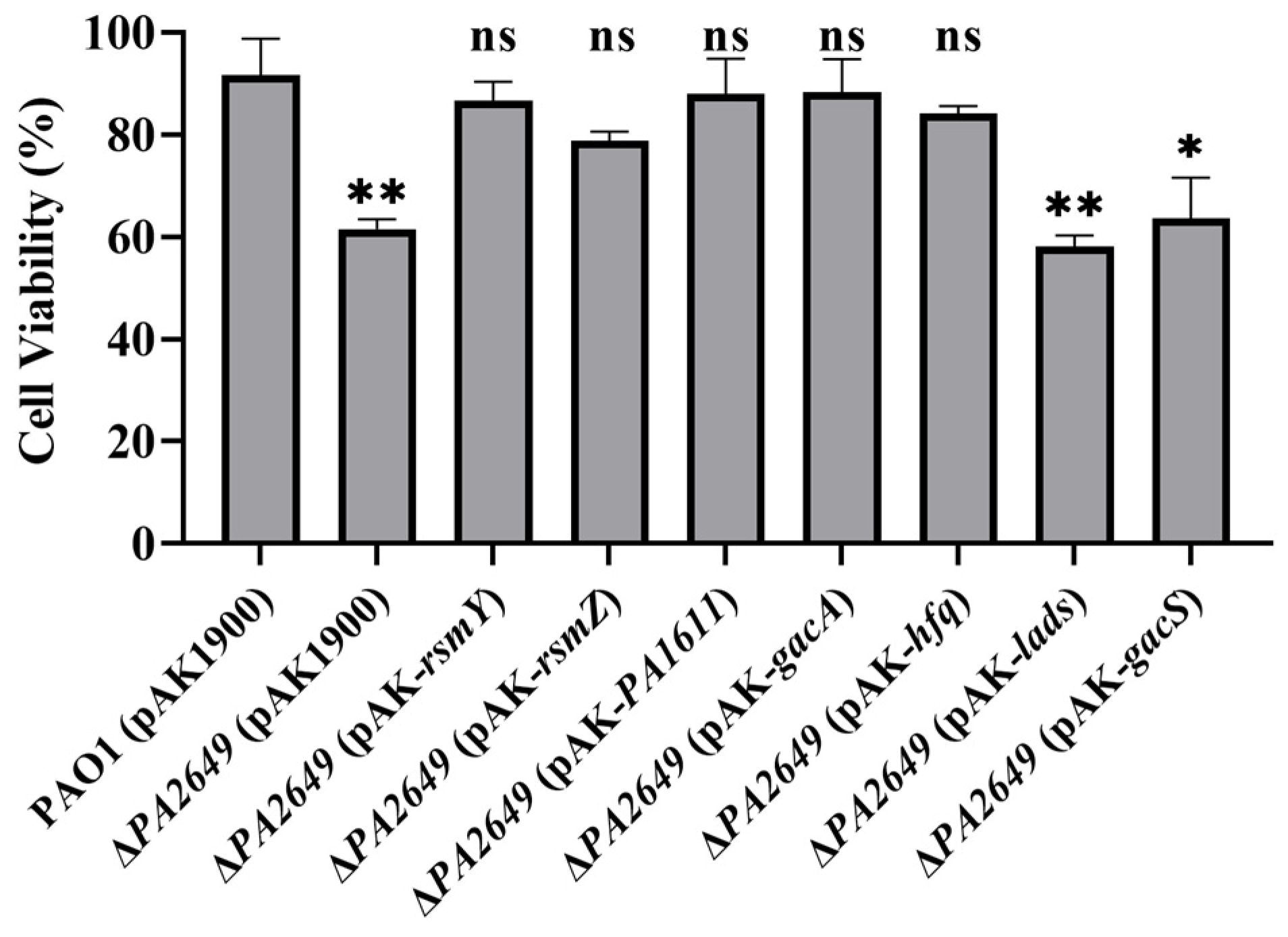
ExsD coding antiactivator which ExsC preferentially binds resulting in the release of ExsA, liberated ExsA then binds to target promoters and recruits RNA polymerase to activate the T3SS regulon [38]. To validate these findings, we first overexpressed the exsD gene in the PA2649 mutant, which successfully restored the mutant phenotype (Figure 4A). Similarly, the overexpression of the upstream regulators rsmY and rsmZ partially restored the mutant phenotype, albeit to varying extents (Figure 4B,C). Given that GacA is known to activate rsmYZ expression, we hypothesized that overexpressing gacA in the PA2649 mutant would restore the T3SS phenotype. As predicted, our results confirmed this hypothesis (Figure 4E). In previous research, we discovered that PA1611 interacts with RetS to regulate T3SS expression via the Rsm-Exs axis [30]. To further confirm this interaction, we overexpressed PA1611 in the PA2649 mutant, which successfully complemented the mutant phenotype (Figure 4D). However, the overexpression of other genes, such as ladS, failed to restore the mutant phenotype (Figure 4F). GacSA is a two-component regulatory system, with GacS acting as a membrane-bound sensor kinase that phosphorylates GacA, thereby activating GacA to regulate the expression of other genes [39]. Unexpectedly, the overexpression of gacS in the PA2649 mutant not only failed to restore the mutant phenotype but also resulted in a slight increase in exoS expression compared to the wild type (Figure 4H).
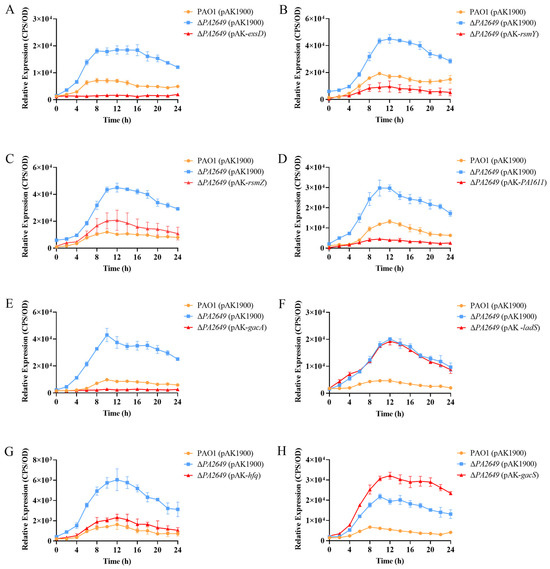
Figure 4.
Impact of overexpression of T3SS-regulatory genes on exoS expression in PA2649 mutants. The expression of exoS was measured using a chromosomally integrated CTX-exoS reporter fusion. Overexpression of T3SS-regulatory genes, which are known to influence the type III secretion system, was analyzed: (A) exsD; (B) rsmY; (C) rsmZ; (D) PA1611; (E) gacA; (F) ladS; (G) hfq; (H) gacS. Overnight, different bacterial cultures were inoculated at 1% into fresh LB medium containing appropriate antibiotics and incubated for 3 h. For measurement, 95 µL of LB and 5 µL of bacterial culture were added to each well of a black 96-well plate with a clear bottom, mixed thoroughly, and topped with 50 µL of paraffin oil to prevent evaporation. Luminescence (cps) and bacterial growth (OD600) were recorded every 2 h over a 24 h period using a multimode microplate reader, as previously described. Results are presented as averages of triplicate experiments, with error bars indicating standard deviations.
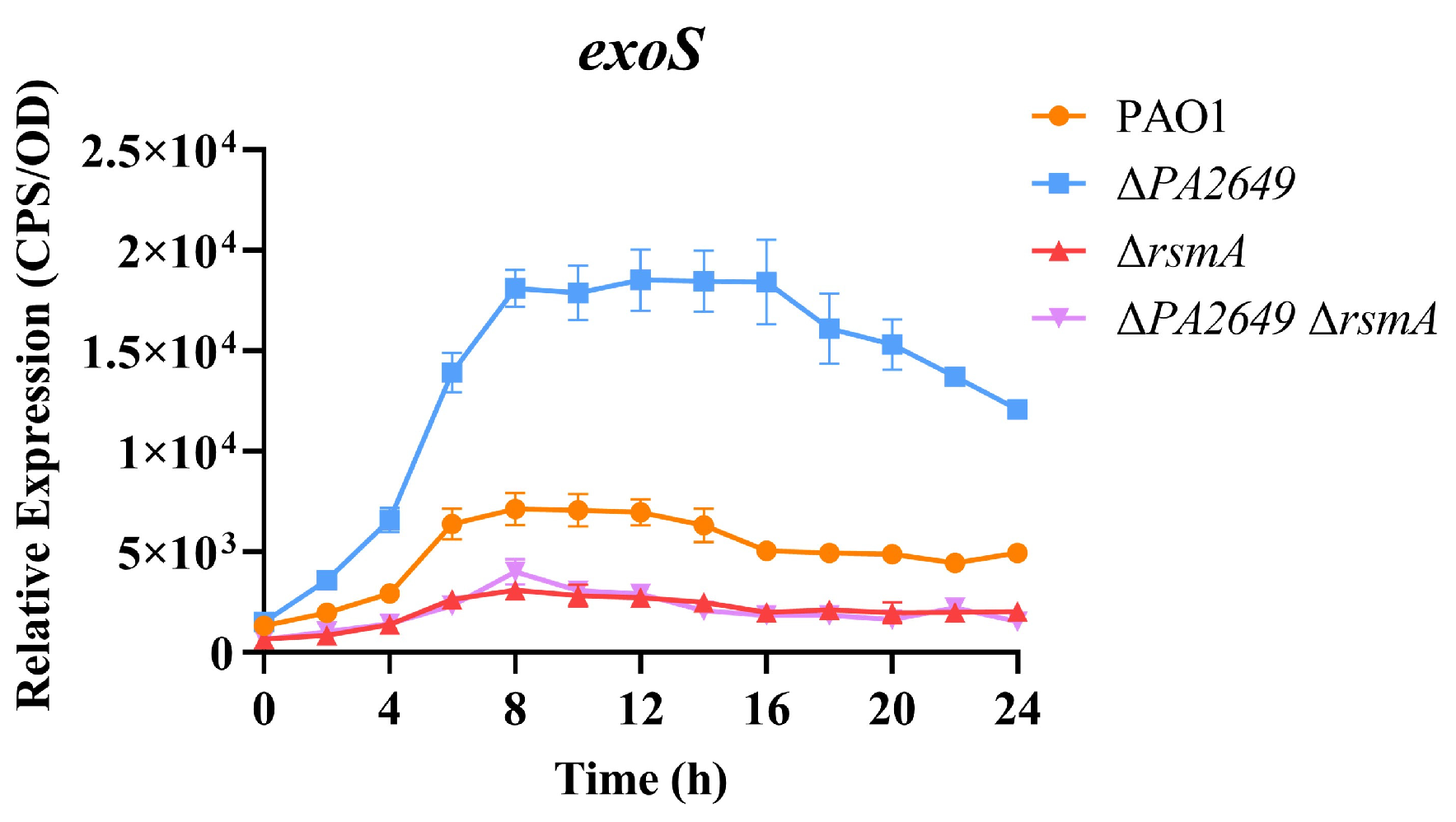
These results presented above suggest that PA2649 modulates T3SS expression via the Rsm-Exs pathway. Accordingly, we hypothesized that the deletion of rsmA in the PA2649 mutant background would substantially suppress T3SS expression. In alignment with this hypothesis, T3SS expression was markedly reduced in the ∆PA2649 ∆rsmA double mutant, exhibiting a phenotype comparable to that of the rsmA single mutant and markedly lower T3SS expression than observed in the wild type (Figure 5).
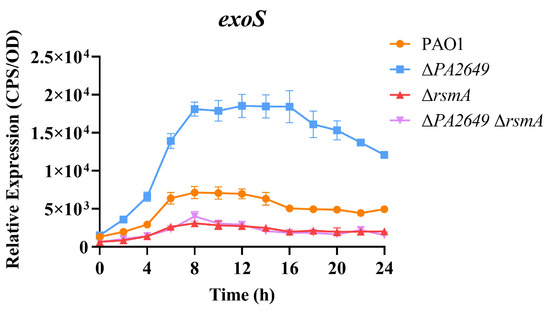
Figure 5.
Impact of rsmA deletion in the PA2649 mutant background on exoS expression. The expression levels of exoS were analyzed in ∆rsmA∆PA2649 double mutants. Overnight, different bacterial cultures were inoculated at 1% into fresh LB medium containing appropriate antibiotics and incubated for 3 h. For measurement, 95 µL of LB and 5 µL of bacterial culture were added to each well of a black 96-well plate with a clear bottom, mixed thoroughly, and topped with 50 µL of paraffin oil to prevent evaporation. Luminescence (cps) and bacterial growth (OD600) were recorded every 2 h over a 24 h period using a multimode microplate reader, as previously described. Results are presented as the averages of triplicate experiments, with error bars indicating standard deviations.
We further validated the above results using cytotoxicity assays. Consistent with the expression data, the cytotoxicity of the supernatants from the overexpression of ladS and gacS in PA2649 mutant, which failed to complement exoS expression, was similar to that of the PA2649 mutant. In contrast, the cytotoxicity of strains that successfully complemented exoS expression was restored to wild-type levels (Figure 6).
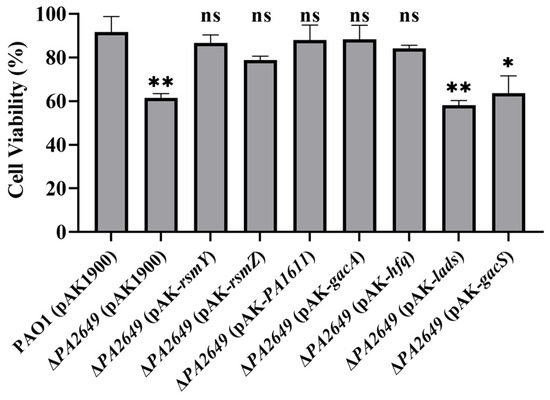
Figure 6.
Cytotoxicity assay of PA2649 mutants overexpressing T3SS-regulatory genes in A549 cells. A549 cells were infected with the supernatants from PA2649 mutants overexpressing PA1611, hfq, gacA, rsmY, rsmZ, ladS, and gacS for 3 h. Bacterial cytotoxicity was assessed using the CCK-8 assay. Overnight, different cultures were centrifuged, and bacterial supernatants were filtered. Equal volumes of supernatants were incubated with A549 cells for 3 h, followed by cytotoxicity analysis. Data represent the results from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Statistical significance is indicated as ns (not significant, p > 0.05), * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.
3.3. Phenotypic Effects of the PA2649 Mutation on Other Virulence Factors
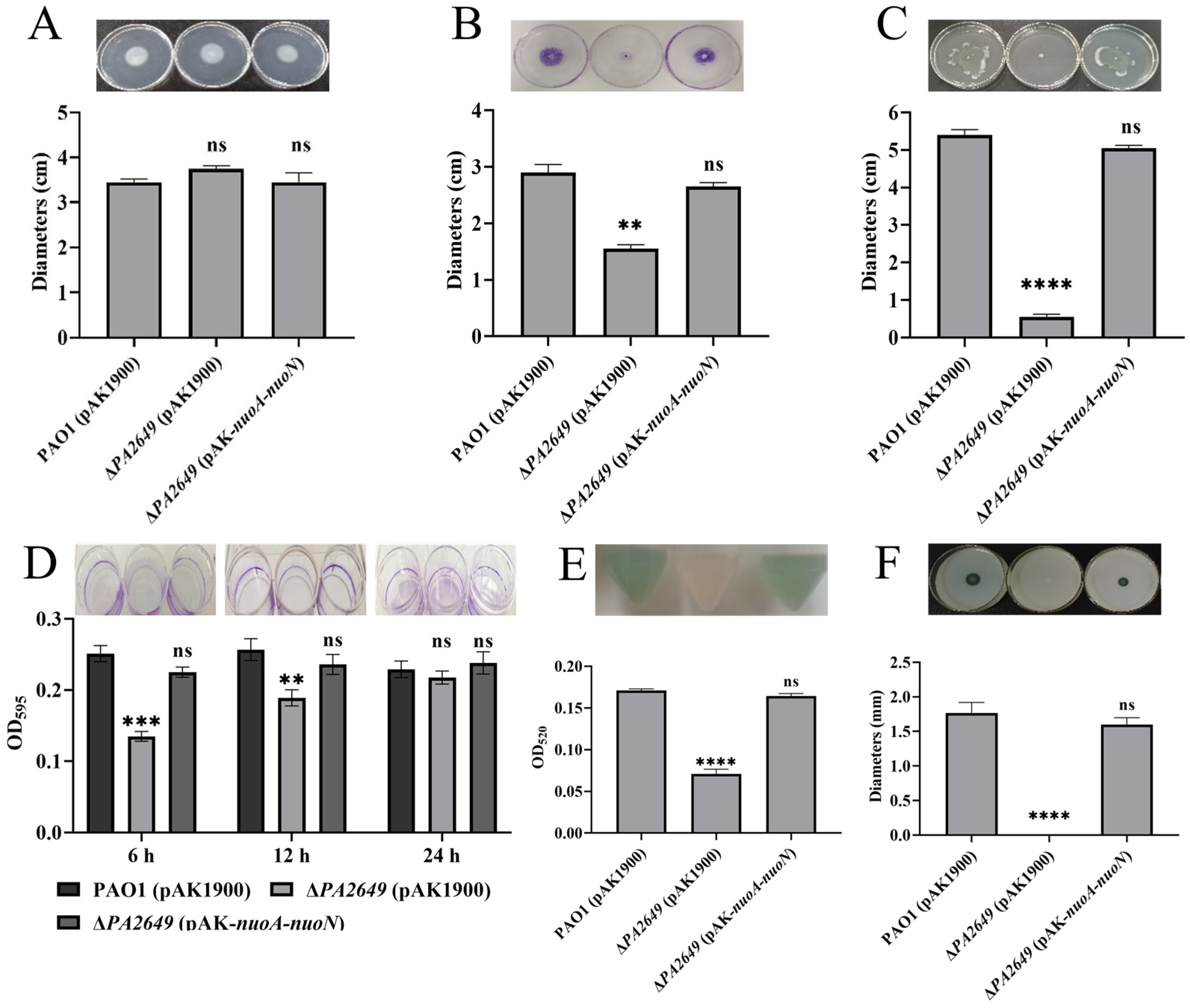
The above results demonstrate that the expression of genes such as gacS and rsmYZ is significantly altered in the PA2649 mutant. These genes are key regulatory components within the Rsm pathway, which ultimately exerts its effects through RsmA. To further investigate the impact of these changes, we assessed additional related phenotypes. While swimming motility showed no significant difference compared to the wild-type strain (Figure 7A), both twitching and swarming motilities were markedly reduced (Figure 7B,C). Biofilm adhesion was significantly decreased at 6 and 12 h (Figure 7D), though no changes were observed at 24 h (Figure 7D). Pyocyanin and proteinase production was also significantly reduced (Figure 7E,F).
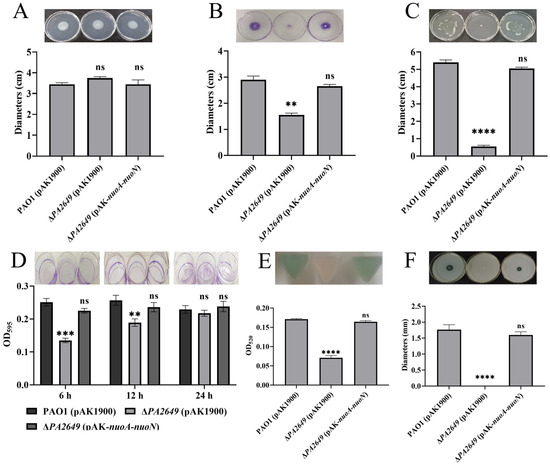
Figure 7.
Effects of PA2649 mutants on the production of virulence factors in P. aeruginosa. The influence of PA2649 mutants on various virulence factors was assessed: (A) swimming motility; (B) twitching motility; (C) swarming motility; (D) biofilm formation; (E) pyocyanin production; (F) protease activity. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Statistical significance is indicated as ns (not significant, p > 0.05), ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001.
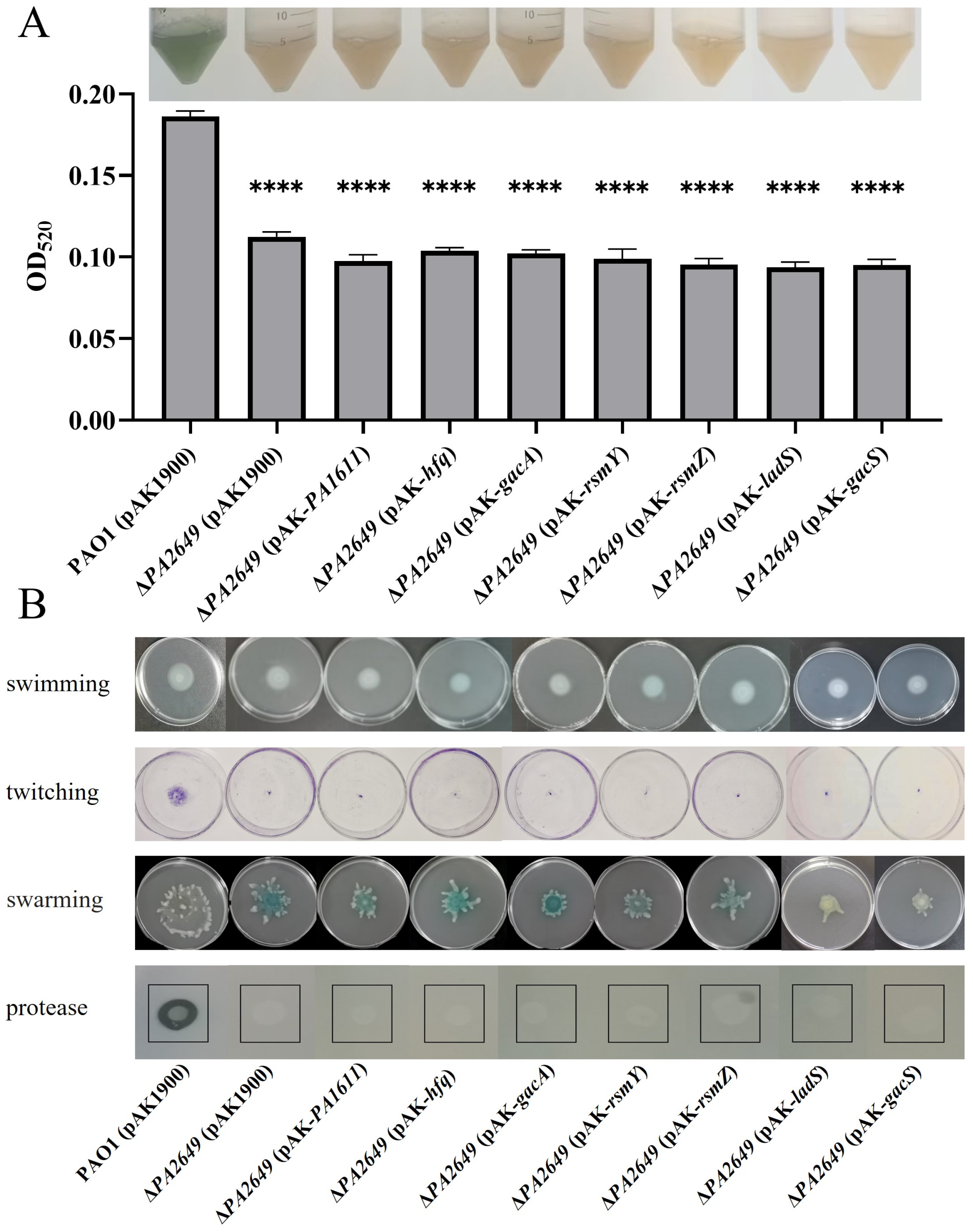
Since the expression of exoS in the PA2649 mutant is regulated by the Rsm-Exs axis, we naturally considered whether the observed phenotypes are also regulated by this axis. The results showed that the overexpression of PA1611, hfq, gacA, rsmY, rsmZ, ladS, and gacS in the PA2649 mutant did not restore the protease, pyocyanin production, or motility-related phenotypes (Figure 8). This suggests that the impact of the PA2649 mutation on protease, pyocyanin, and motility is regulated via a pathway distinct from the one controlling exoS expression.
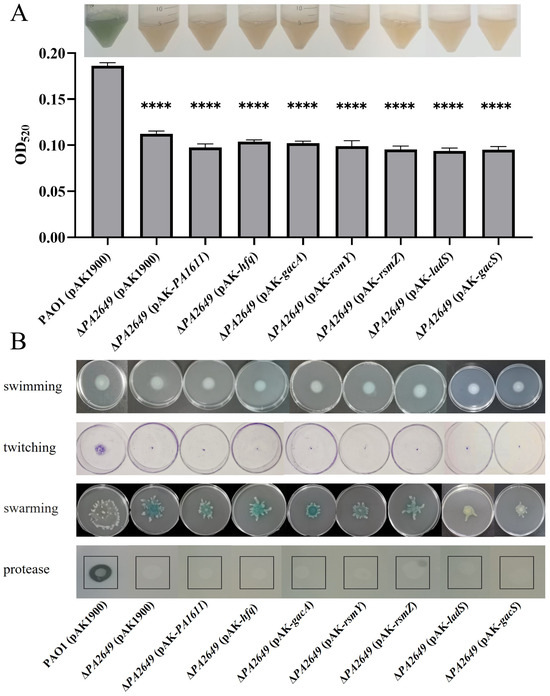
Figure 8.
Impact of overexpression of T3SS-regulatory genes on virulence factor production in PA2649 mutants of P. aeruginosa. The effects of overexpressing PA1611, hfq, gacA, rsmY, rsmZ, ladS, and gacS in PA2649 mutants on the production of virulence factors were assessed: (A) pyocyanin; (B) swimming, twitching, swarming, and protease activity. The black box in the figure highlights the specific area of interest. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Statistical significance is indicated as **** p < 0.0001.
3.4. Role of PA2649 in Perturbation of Central Metabolism and Antibiotic Resistance
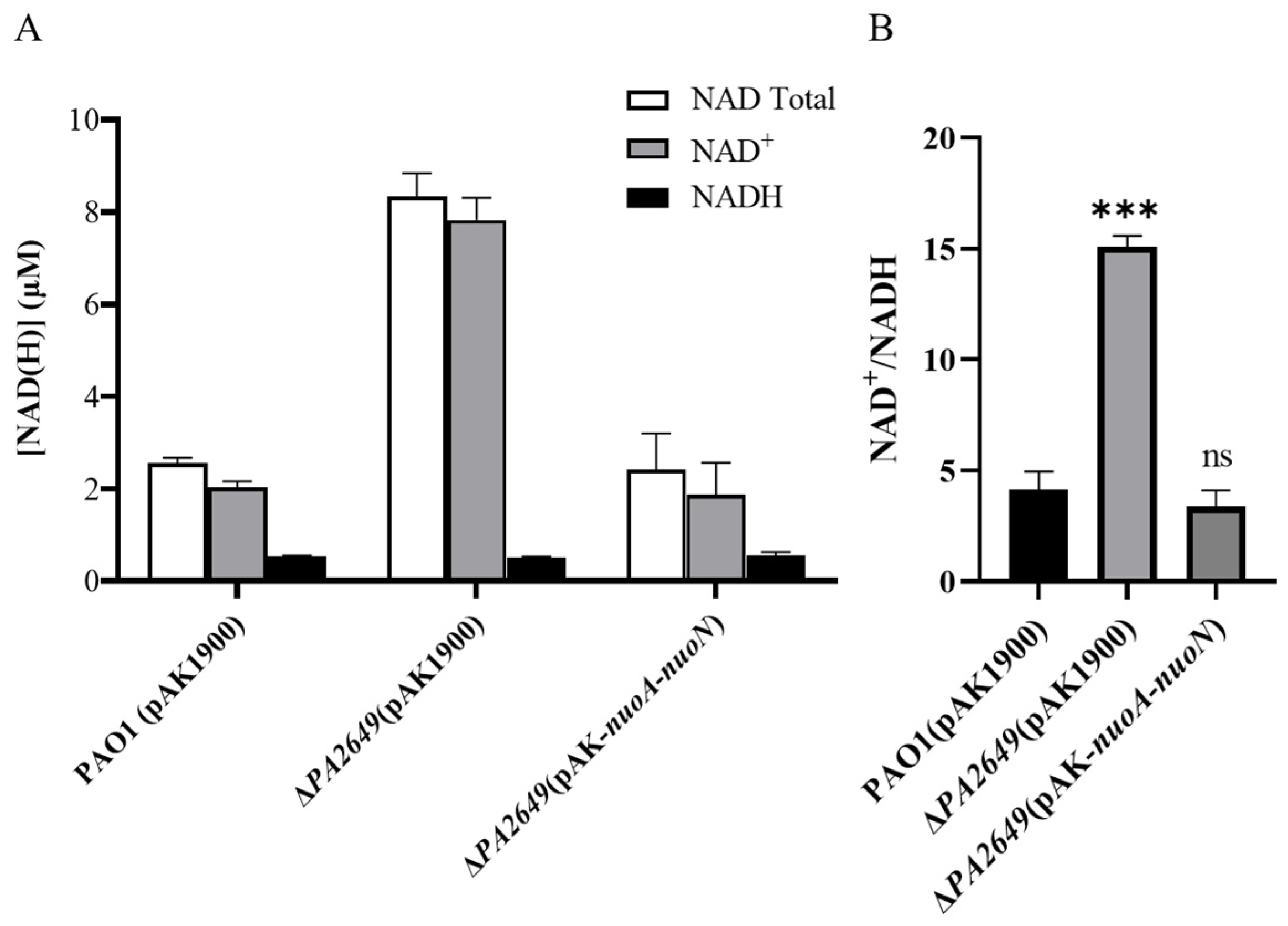
NADH dehydrogenases are commonly found in energy-transducing membranes, where they serve as key sites for initiating electron transport. As an electron acceptor, NAD+ is critical for energy metabolism and cellular processes since it directly impacts an organism’s capacity to generate energy and maintain metabolic homeostasis. The dynamic interconversion between NAD+ and NADH maintains cellular redox balance and influences various physiological processes. Therefore, we tested whether the ratio of NAD+ and NADH was changed in the mutant by using the commercial NAD+/NADH assay kit. A single disruption of the nuoN gene resulted in an increase in the intracellular NAD(H/+) pool (Figure 9A) and the ratio of NAD+ and NADH compared to the control strain (Figure 9B). The changes in the NAD+/NADH ratios and total concentrations of NAD(H/+) were primarily due to changes in NAD+ production, as the NADH concentrations were relatively constant.
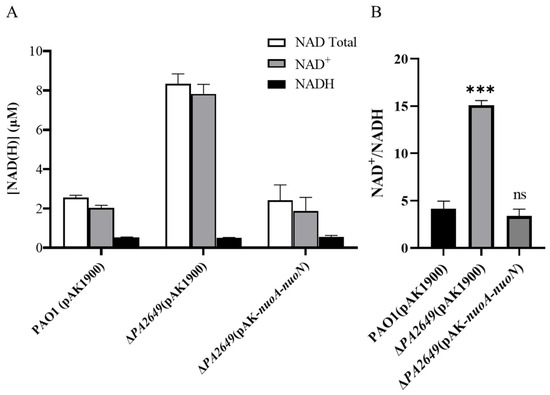
Figure 9.
Levels and ratios of NAD⁺ and NADH in P. aeruginosa. (A) Total concentrations of NADH and NAD⁺ in different strains cultured under the conditions described in the methods section. (B) Corresponding NADH/NAD⁺ ratios for the same strains under identical culture conditions. Bacterial strains were cultured overnight in fresh LB medium for approximately 12 h. The OD600 of the bacterial cultures was adjusted to the same level before processing. NADH and NAD+ were extracted using the Beyotime Enhanced NAD+/NADH Assay Kit (WST-8), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Statistical significance is indicated as ns (not significant, p > 0.05), *** p < 0.001.
In addition, previous research has shown that the MIC of gentamicin for the ∆nuoIJ and ∆nuoG mutants was increased compared to the wild-type strain PA14 [20,21]. Therefore, we investigated whether the ∆nuoN mutation alters sensitivity to various antibiotics. Our results indicated a significant reduction in sensitivity to Chl, with the MIC of PAO1 at 120 μg/mL, and the MIC for the nuoN mutant increased threefold to 480 μg/mL (Table 1). Additionally, we observed a onefold increase in resistance to Gen, with the MIC rising from 1.5 mg/mL in the wild-type to 3 mg/mL in the mutant (Table 1), which is consistent with previously reported trends [20]. Moreover, the nuoN mutant exhibited approximately a onefold increase in resistance to Cip (Table 1), with MICs increasing from 0.3125 μg/mL to 0.625 μg/mL for Cip (Table 1). No changes in resistance were observed for Kan, Strep, and PMB (Table 1). The complemented strain restored sensitivity to wild-type levels (Table 1 and Figure S3). Similarly to protease activity, pyocyanin production, or motility-related phenotypes, revertants of ∆PA2649 with PA1611, hfq, gacA, rsmY, rsmZ, ladS, and gacS failed to restore the mutant’s susceptibility (Figure S3). This suggests that the effect of the PA2649 mutation on antibiotic resistance is also regulated through a pathway distinct from that controlling exoS expression.

Table 1.
Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) of Different Antibiotics for Various Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains.
4. Discussion
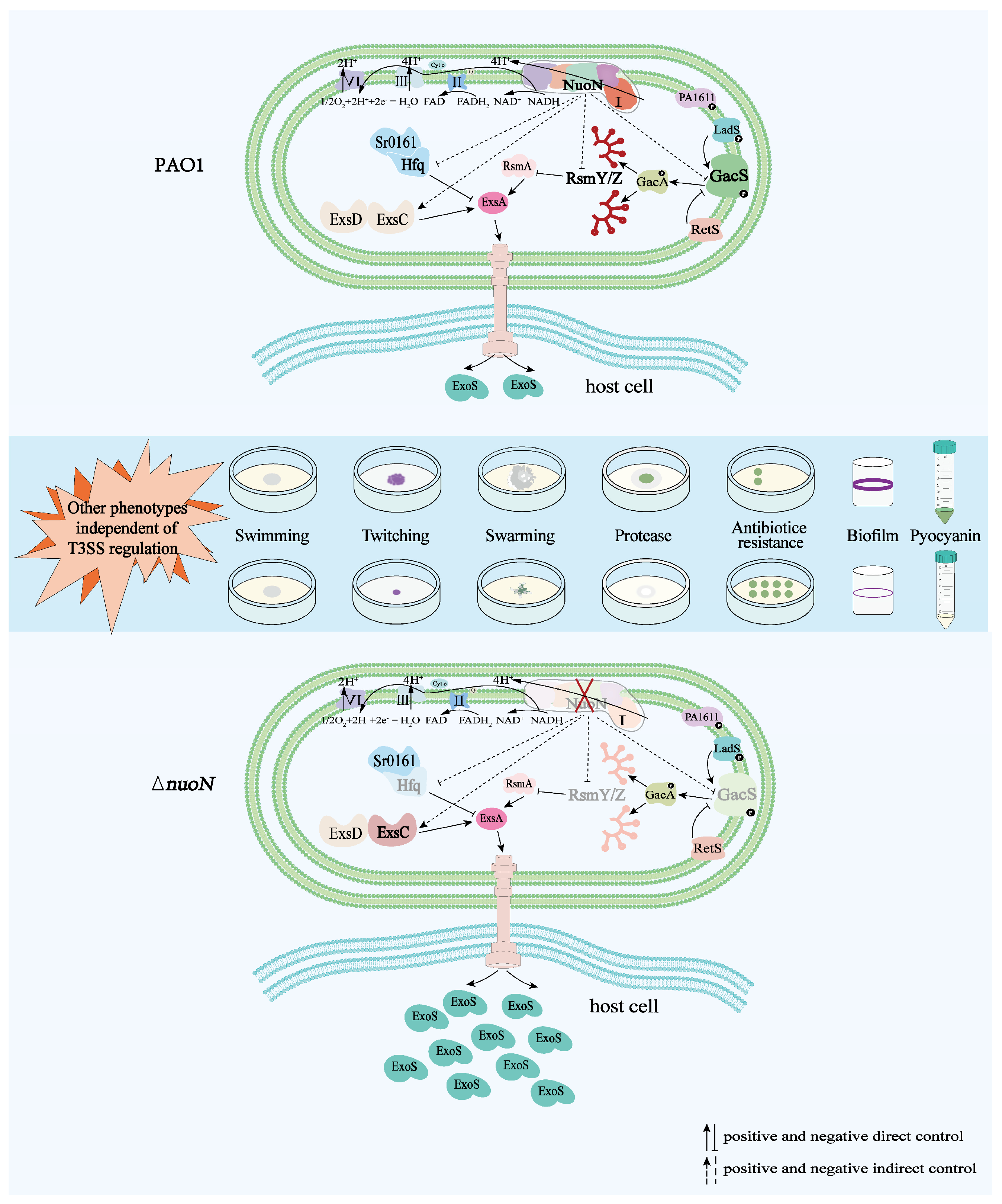
In the present study, we demonstrated that in P. aeruginosa, the PA2649 (nuoN) mutation may affect exoS expression via the Rsm-Exs axis and influence other phenotypic traits through distinct pathways (Figure 10).
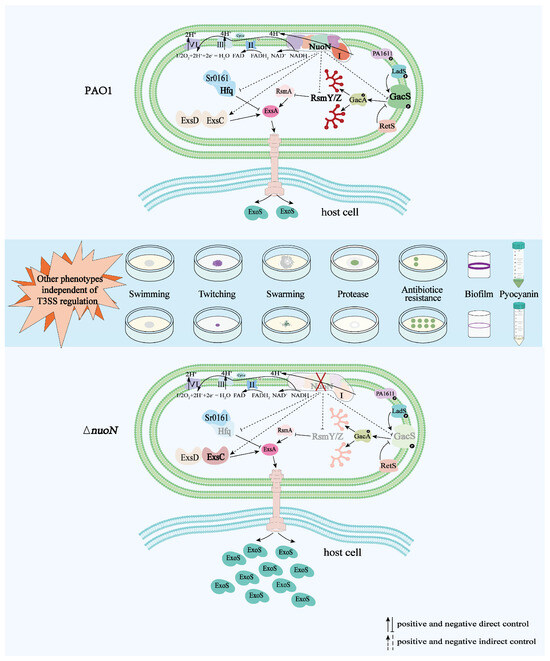
Figure 10.
Proposed model illustrating the regulation of bacterial virulence traits by PA2649 (nuoN) in P. aeruginosa. Compared to PAO1, the expression of gacS, rsmYZ, and hfq is downregulated, while the expression of exsC is upregulated in the ∆nuoN mutant, leading to increased secretion of ExoS. Additionally, phenotypic changes such as altered pyocyanin production, initial biofilm formation, motility, antibiotic resistance, and protease production were observed in the ∆nuoN mutant. The mutant strain exhibits other phenotypes that are regulated by pathways independent of the T3SS regulatory system.
To investigate the effect of the nuoN mutation on T3SS regulation, we constructed a nuoN deletion mutant and observed a significant upregulation of exoS. Restoration of wild-type exoS levels required revertant with the entire nuo operon, whereas partial or gene-specific complementation was ineffective (Figure 1C), indicating that the nuoN mutation likely disrupts the full function of the NUO complex. Previous studies found minimal impacts on NADH dehydrogenase activity in certain NUO mutants [20]; thus, we did not directly measure this activity here. Instead, our results confirm that exoS overexpression specifically results from the PA2649 mutation. Further experiments showed that the overexpression of the full nuo operon in PAO1 did not suppress exoS expression (Figure S4), supporting the hypothesis that exoS upregulation in the mutant is due to the loss of nuoN rather than the overall activity of the nuo operon. Cytotoxicity assays with mutant supernatants revealed increased cell toxicity (Figure 2B), consistent with elevated exoS levels (Figure 1A). Reduced pyocyanin in the mutant supernatant suggests that other virulence factors, likely proteinaceous, contribute to the observed cytotoxicity, as evidenced by decreased toxicity upon protease K treatment (Figure S5). Torres et al. reported that P. aeruginosa NADH dehydrogenase deletion mutants (ΔnuoIJ and Δndh) displayed slightly reduced tissue damage and fewer recoverable CFUs in a lettuce model [20]. Moreover, in an insect model (Galleria mellonella waxworm model), the kinetics of killing was significantly slower in the ∆nuoIJ strain compared to PAO1, though the LD50 was unchanged with the loss of NDH-1 [20]. The strain lacking NUO (ΔnuoG) showed similar macrophage-killing ability as the wild type, while two other NADH dehydrogenase mutants (ΔnqrF and Δndh) demonstrated significantly greater cytotoxicity [21]. These findings seem to contradict our results, but differences in experimental models and mutated genes may account for this discrepancy. This phenomenon is also evident in our observations on antibiotic resistance (see below), suggesting that mutations in different subunits of the NADH dehydrogenase complex can produce distinct phenotypic outcomes.
In P. aeruginosa, T3SS regulation is predominantly controlled by ExsA, an AraC/XylS family transcription factor, whose expression is regulated by the PexsC and PexsA promoters, with PexsC being more active under inducing conditions [14,40,41]. In the nuoN mutant, we observed increased PexsC promoter activity without changes in exsD levels, supporting a model wherein T3SS regulation occurs via the Exs system. Given the upstream complexity of Exs regulation [30,42,43], we examined the expression levels of related regulatory factors, including rsmA, rsmZ, rsmY, gacA, gacS, retS, ladS, and PA1611, all of which influence T3SS expression via the Rsm system [39,44,45]. We detected significant reductions in rsmZ, rsmY, and gacS expression in the mutant, while retS, ladS, PA1611, gacA, and rsmA remained stable (Figure 3). Phenotype restoration through RsmYZ, PA1611, or GacA revertant further underscores the role of the RsmYZA pathway in PA2649-mediated T3SS regulation. Interestingly, revertant with Hfq also restored the mutant phenotype (Figure 4G), suggesting potential regulation via either the Rsm system or direct modulation of ExsA. Hfq, as reported, can stabilize RsmY to indirectly modulate ExsA and Vfr levels [46]. Additionally, Hfq interacts with multiple T3SS-related mRNAs, though its precise regulatory role remains to be fully elucidated [47]. Its involvement here implies a multi-faceted regulatory network that warrants further investigation.
Our data show that GacA successfully complemented the ∆PA2649 phenotype, whereas gacS and ladS overexpression did not, highlighting regulatory distinctions between these components that are also documented in related studies [48,49]. The differential effects of overexpressing GacS and GacA are likely due to their distinct roles and regulatory mechanisms within the two-component system. The overexpression of GacS alone may increase the input signal sensitivity but could saturate the system without sufficient GacA to propagate the signal. On the other hand, the phosphorylation signal from GacS is not appropriately modulated since the regulation of GacS in P. aeruginosa is intricately modulated by multiple interacting proteins, reflecting the complexity of its role in environmental adaptability and virulence. Overexpressing gacS in a plant-beneficial bacterium (Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66-FLUO) restored the biosynthesis of PCN, whereas gacA overexpression did not, suggesting that the regulatory targets of GacA and GacS differ [50]. In the PA2649 mutant strain, GacS expression is significantly reduced (Figure 3). This lower expression level likely results in diminished GacS signaling capacity, potentially disrupting the finely tuned balance between activation and inhibition mediated by LadS and RetS. The observed reduction in GacS expression in the PA2649 mutant suggests that PA2649 plays a previously uncharacterized role in maintaining optimal GacS levels. This reduced expression may exacerbate the effects of regulatory interactions, tipping the balance of activation and inhibition in favor of lower GacS activity. Further investigations into the PA2649-GacS interaction, along with a detailed analysis of how LadS, RetS, and RsmA contribute to GacS signaling under different environmental conditions, will provide deeper insights into this complex regulatory network. Furthermore, our results suggest that GacA functions downstream of PA2649 in the T3SS pathway, as evidenced by GacA revertant restoring T3SS function in a ΔPA2649 background, while PA2649 revertant did not in a ΔgacA background (Figure S6). These findings support a model in which PA2649 primarily regulates T3SS via the Gac-Rsm-Exs axis, although additional pathways, such as Vfr-cAMP, Fis, FleQ, or Crc, may also contribute to this regulatory network.
Antibiotic susceptibility testing of the nuoN mutant revealed increased resistance to Chl, Cip, and Gen, but no significant changes in resistance to PMB, Kan, or Strep. This antibiotic profile suggests alternative resistance mechanisms, likely including MexEF-OprN, which mediates resistance to both chloramphenicol and ciprofloxacin [51]. Full chloramphenicol resistance requires effective uptake and additional mechanisms [32]. Future studies should determine whether chloramphenicol resistance in the nuoN mutant is linked to reduced permeability or another similar efflux pump, such as the ABC extrusion system (PP2669/PP2668/PP2667) or the AgmR regulator (PP2665) in P. putida KT2440 [52]. By contrast, the nuoG mutant, as reported by Rreha et al. [21], displayed increased kanamycin resistance and reduced chloramphenicol sensitivity, underscoring mutation-specific regulatory effects and suggesting that different subunits of NADH dehydrogenase may distinctly influence resistance phenotypes. NUO and NDH-2 function as the primary NADH dehydrogenases during aerobic growth in LB, with polymyxin B known to inhibit NDH-2 activity [53], which may explain the lack of change in polymyxin B resistance in the nuoN mutant. Additionally, the overexpression of genes involved in T3SS regulation, including PA1611, GacA, RsmY, RsmZ, and ExsD, did not restore motility, pyocyanin production, or antibiotic resistance in the ∆nuoN mutant, suggesting that the phenotypic changes in this mutant arise from pathways distinct from those regulated by the T3SS system. The NuoN protein, as part of the NADH dehydrogenase I complex, has been proposed to implicate in the maintenance of PMF [20], which is critical for efflux pump activity in P. aeruginosa. Efflux pumps, such as MexAB-OprM, are known to contribute to resistance against β-lactam antibiotics [54], including penicillin-based therapies. Although our study does not directly investigate this relationship, the potential role of nuoN in modulating efflux pump function and antibiotic resistance deserves further exploration. This perspective underscores the multifaceted impact of nuoN on both virulence and resistance phenotypes, highlighting its importance as a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
Functionally, NADH dehydrogenase, particularly nuoN (a subunit of Complex I), serves as a primary electron entry point in the respiratory chain. Its conservation across bacterial species such as E. coli, S. flexneri (Shigella flexneri), and Y. pestis (Yersinia pestis) implies its critical role in bacterial physiology [55,56]. Although terminal oxidase activity was unaffected by the nuoN mutation (Figure S7), our results clearly showed that NAD+ was increased in the mutant of PA2649 (nuoN). The absolute levels of NAD+ in cells are important since they directly impact an organism’s capacity to generate energy and maintain metabolic homeostasis. Recent work has reported that the expression of virulence factors in P. aeruginosa is regulated by central metabolism [19]. Consistent with this, the ratio of NAD+/NADH in ∆PA2649 (∆nuoN) was increased relative to the wild type and revertant strain (Figure 9A,B). Those results indicated that the mutation evidently influenced bacterial metabolism, which likely accounts for the observed gene expression changes. While a coherent picture is emerging, many fundamental questions about the regulatory link between NADH dehydrogenases and virulence activation remain unresolved.
In summary, our findings demonstrate that the PA2649 (nuoN) mutation induces exoS overexpression and cytotoxicity through the Gac-Rsm-Exs pathway. Additional virulence-related phenotypes in the nuoN mutant, including motility, adhesion, pyocyanin production, and antibiotic resistance, are modulated independently of the Gac-Rsm-Exs axis, suggesting that NADH dehydrogenase influences virulence through complex metabolic adjustments. These findings underscore the critical role of PA2649 in coordinating virulence regulation and antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa, offering insights that may inform the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting this multifunctional pathway. Further research is needed to clarify how central metabolic changes associated with NADH dehydrogenase activity contribute to virulence regulation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13020392/s1. Table S1. Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study; Table S2. Primers used in this study [23,30,57,58]; Figure S1. Schematic illustration of the pBT20 transposon insertion site within the PA2649 gene; Figure S2. Effect of PA2649 mutation and PA2650 overexpression on exoS expression; Figure S3. Antibiotic susceptibility profiles of PAO1, PA2649 mutants, and overexpression strains for PA1611, rsmY, rsmZ, hfq, gacA, gacS, and ladS; Figure S4. Effect of nuo operon overexpression on exoS expression in PAO1; Figure S5. Cytotoxicity assay of P. aeruginosa strains in A549 cells with proteinase K treatment; Figure S6. Expression of exoS in gacA mutants with overexpressed PA2649; Figure S7. Respiratory chain integrity assessment in PA2649 mutant using TTC reduction assay.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C., K.D. and S.F.; methodology, L.C. and Y.S.; software, Y.S. and X.H.; validation, L.C., Y.S. and X.H.; formal analysis, Y.X. and Y.P.; investigation, L.C., Y.S., X.H., Y.X. and Y.P.; resources, K.D.; data curation, L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C. and Y.S.; writing—reviewing and editing, K.D., L.C. and S.F.; visualization, Y.S.; supervision, L.C.; project administration, S.F.; funding acquisition, K.D. and S.F.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The project has been supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Grant number: 2019JM-372) and Shaanxi Fundamental Science Research Project for Chemistry and Biology (grant no. 23JHQ062).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| T3SS | type III secretion system |
| PAO1 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 |
| PMF | Proton Motive Force |
| LB | Luria–Bertani |
| PMB | Polymyxin B |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic acid |
| PIA | Pseudomonas isolation agar |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| cps | Counts per second |
| Strep | Streptomycin |
| Cip | Ciprofloxacin |
| Chl | Chloramphenicol |
| Tmp | Trimethoprim |
| Cb | Carbenicillin |
| Gen | Gentamicin |
| Tc | Tetracycline |
| Amp | Ampicillin |
| Kan | Kanamycin |
References
- Wang, B.X.; Cady, K.C.; Oyarce, G.C.; Ribbeck, K.; Laub, M.T. Two-Component Signaling Systems Regulate Diverse Virulence-Associated Traits in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e03089-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guragain, M.; King, M.M.; Williamson, K.S.; Pérez-Osorio, A.C.; Akiyama, T.; Khanam, S.; Patrauchan, M.A.; Franklin, M.J. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Two-Component Regulator CarSR Regulates Calcium Homeostasis and Calcium-Induced Virulence Factor Production through Its Regulatory Targets CarO and CarP. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Shao, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, X. An integrated genomic regulatory network of virulence-related transcriptional factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.R.; Van Gijsegem, F. Assembly and Function of Type III Secretory Systems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 735–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, S.V.; Kim, E.; Wagner, S. Virulence-associated type III secretion systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology 2023, 169, 001328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, L.J.; Majewski, D.D.; Strynadka, N.C.J. Structural Insights into Type III Secretion Systems of the Bacterial Flagellum and Injectisome. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 77, 669–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, C.; Pu, Q.; Deng, X.; Lan, L.; Liang, H.; Song, X.; Wu, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horna, G.; Ruiz, J. Type 3 secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharajah, A.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P.; Van Bambeke, F. Targeting the Type Three Secretion System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahr, T.L.; Hovey, A.K.; Kulich, S.M.; Frank, D.W. Transcriptional analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S structural gene. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siryaporn, A.; Kuchma, S.L.; O’Toole, G.A.; Gitai, Z. Surface attachment induces Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16860–16865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams McMackin, E.A.; Djapgne, L.; Corley, J.M.; Yahr, T.L. Fitting Pieces into the Puzzle of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System Gene Expression. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00209-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Joshi, S.; Brutinel, E.D.; Yahr, T.L.; Chen, L. Biochemical characterization of a regulatory cascade controlling transcription of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6136–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovey, A.K.; Frank, D.W. Analyses of the DNA-binding and transcriptional activation properties of ExsA, the transcriptional activator of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S regulon. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4427–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klockgether, J.; Tümmler, B. Recent advances in understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a pathogen. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, K.H.; Diaz, M.R.; Golden, M.; Graham, J.W.; Sanders, W.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Yahr, T.L. Functional Analyses of the RsmY and RsmZ Small Noncoding Regulatory RNAs in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00736-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgita, T.; Hayashi, N.; Hama, S.; Tsuchiya, H.; Gotoh, N.; Kogure, K. A novel effector secretion mechanism based on proton-motive force-dependent type III secretion apparatus rotation. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2862–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gil, T.; Cuesta, T.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Reales-Calderón, J.A.; Corona, F.; Linares, J.F.; Martínez, J.L. Virulence and Metabolism Crosstalk: Impaired Activity of the Type Three Secretion System (T3SS) in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Crc-Defective Mutant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perinbam, K.; Chacko, J.V.; Kannan, A.; Digman, M.A.; Siryaporn, A. A Shift in Central Metabolism Accompanies Virulence Activation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2020, 11, e02730-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Kasturiarachi, N.; DuPont, M.; Cooper, V.S.; Bomberger, J.; Zemke, A. NADH Dehydrogenases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Growth and Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreha, T.N.; Foreman, S.; Duran-Pinedo, A.; Morris, A.R.; Diaz-Rodriguez, P.; Jones, J.A.; Ferrara, K.; Bourges, A.; Rodriguez, L.; Koffas, M.A.G.; et al. The three NADH dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Their roles in energy metabolism and links to virulence. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Fang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Raba, D.A.; Ding, J.; Bunn, D.C.; Sanjana, K.; Yang, J.; Rosas-Lemus, M.; et al. The aerobic respiratory chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultured in artificial urine media: Role of NQR and terminal oxidases. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, T.T.; Karkhoff-Schweizer, R.R.; Kutchma, A.J.; Schweizer, H.P. A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: Application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 1998, 212, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Zhao, J.; Kang, H.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, T.; Deng, X.; Liang, H. ChIP-seq reveals the global regulator AlgR mediating cyclic di-GMP synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8268–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Dammel, C.; Stein, J.; Rabin, H.; Surette, M.G. Modulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa gene expression by host microflora through interspecies communication. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, A.; Schweizer, H.P. Integration-proficient Pseudomonas aeruginosa vectors for isolation of single-copy chromosomal lacZ and lux gene fusions. BioTechniques 2000, 29, 948–950, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Li, L.; Dong, Z.; Surette, M.G.; Duan, K. The YebC family protein PA0964 negatively regulates the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal system and pyocyanin production. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6217–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, J.; Tan, B.; Kong, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Liang, H. The P-Type ATPase PA1429 Regulates Quorum-Sensing Systems and Bacterial Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Dong, M.; Yan, R.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Duan, K. A Unique ATPase, ArtR (PA4595), Represses the type III Secretion System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Shen, T.; Surette, M.G.; Shen, L.; Duan, K. Hybrid sensor kinase PA1611 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa regulates transitions between acute and chronic infection through direct interaction with RetS. Mol Microbiol. 2013, 88, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.J.; LaBaer, J. Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) precipitation of proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2011, 2011, 993–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkey, M.; Rahme, L.G. Modeling Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis in plant hosts. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Du, X.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, W.; Lau, G.W.; Chen, G.; Kohli, G.S.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; et al. Glutathione Activates Type III Secretion System Through Vfr in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essar, D.W.; Eberly, L.; Hadero, A.; Crawford, I.P. Identification and characterization of genes for a second anthranilate synthase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Interchangeability of the two anthranilate synthases and evolutionary implications. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.H.; Kornberg, A. Inorganic polyphosphate is needed for swimming, swarming, and twitching motilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4885–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Dong, B.; Wang, K.; Cai, S.; Liu, T.; Cheng, X.; Lei, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Kong, J.; et al. Baicalin inhibits biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence and enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa clearance in a mouse peritoneal implant infection model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarneh, B.; Vik, S.B. Mutagenesis of subunit N of the Escherichia coli complex I. Identification of the initiation codon and the sensitivity of mutants to decylubiquinone. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 4800–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhards, R.C.; Marsden, A.E.; Esher, S.K.; Yahr, T.L.; Schubot, F.D. Self-trimerization of ExsD limits inhibition of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptional activator ExsA in vitro. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.L.; Kulasekara, B.; Rietsch, A.; Boyd, D.; Smith, R.S.; Lory, S. A signaling network reciprocally regulates genes associated with acute infection and chronic persistence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Dev Cell 2004, 7, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, A.E.; Intile, P.J.; Schulmeyer, K.H.; Simmons-Patterson, E.R.; Urbanowski, M.L.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Yahr, T.L. Vfr Directly Activates exsA Transcription To Regulate Expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III Secretion System. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakulskas, C.A.; Brady, K.M.; Yahr, T.L. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExsA. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6654–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambonnier, G.; Roux, L.; Redelberger, D.; Fadel, F.; Filloux, A.; Sivaneson, M.; de Bentzmann, S.; Bordi, C. The Hybrid Histidine Kinase LadS Forms a Multicomponent Signal Transduction System with the GacS/GacA Two-Component System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLOS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, M.; Bernhards, R.C.; Fu, Y.; Ryan, K.; Schubot, F.D. Backbone Interactions Between Transcriptional Activator ExsA and Anti-Activator ExsD Facilitate Regulation of the type III Secretion System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, A.L.; Merighi, M.; Hyodo, M.; Ventre, I.; Filloux, A.; Lory, S. Direct interaction between sensor kinase proteins mediates acute and chronic disease phenotypes in a bacterial pathogen. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brencic, A.; Lory, S. Determination of the regulon and identification of novel mRNA targets of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RsmA. Mol Microbiol. 2009, 72, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, K.H.; Corley, J.M.; Djapgne, L.; Cribbs, J.T.; Voelker, D.; Slusher, Z.; Nordell, R.; Regulski, E.E.; Kazmierczak, B.I.; McMackin, E.W.; et al. Hfq and sRNA 179 Inhibit Expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa cAMP-Vfr and type III Secretion Regulons. mBio 2020, 11, e00363-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillon, J.; Han, K.; Attrée, I.; Lory, S. The core and accessory Hfq interactomes across Pseudomonas aeruginosa lineages. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. GacS/GacA activates pyoluteorin biosynthesis through Gac/Rsm-RsmE cascade and RsmA/RsmE-driven feedback loop in Pseudomonas protegens H78. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 105, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, J.M.; Intile, P.; Yahr, T.L. Direct Inhibition of RetS Synthesis by RsmA Contributes to Homeostasis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gac/Rsm Signaling System. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e0058021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bilal, M.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X. Enhanced Fluorescent Siderophore Biosynthesis and Loss of Phenazine-1-Carboxamide in Phenotypic Variant of Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, A.; Asif, A.; Manzoor, A.; Azeem, M.; Sarwar, G.; Rashid, N.; Qaisar, U. Mutation in pvcABCD operon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa modulates MexEF-OprN efflux system and hence resistance to chloramphenicol and ciprofloxacin. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.; Conde, S.; de la Torre, J.; Molina-Santiago, C.; Ramos, J.L.; Duque, E. Mechanisms of resistance to chloramphenicol in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deris, Z.Z.; Akter, J.; Sivanesan, S.; Roberts, K.D.; Thompson, P.E.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J.; Velkov, T. A secondary mode of action of polymyxins against Gram-negative bacteria involves the inhibition of NADH-quinone oxidoreductase activity. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Ma, D.; Livermore, D.M.; Nikaido, H. Role of efflux pump(s) in intrinsic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Active efflux as a contributing factor to beta-lactam resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 1742–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burschel, S.; Kreuzer Decovic, D.; Nuber, F.; Stiller, M.; Hofmann, M.; Zupok, A.; Siemiatkowska, B.; Gorka, M.; Leimkühler, S.; Friedrich, T. Iron-sulfur cluster carrier proteins involved in the assembly of Escherichia coli NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I). Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neehaul, Y.; Juárez, O.; Barquera, B.; Hellwig, P. Infrared spectroscopic evidence of a redox-dependent conformational change involving ion binding residue NqrB-D397 in the Na(+)-pumping NADH:quinone oxidoreductase from Vibrio cholerae. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K.; Neshat, S.; Krebes, K.; Heinrichs, D.E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the ferripyoverdine receptor gene fpvA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 4597–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashi, M.; Chen, L.; Nasimian, A.; Ghavami, S.; Duan, K. Putative RNA Ligase RtcB Affects the Switch between T6SS and T3SS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).