The Functional Network of PrkC and Its Interaction Proteins in Bacillus subtilis Spores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Plasmid
2.2. Induced Expression of PrkC Protein
2.3. Purification of PrkC Protein
2.4. Pull-Down Experiment
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. LC–MS/MS Analysis
2.7. MS Data Analysis and Peptide Identification
2.8. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
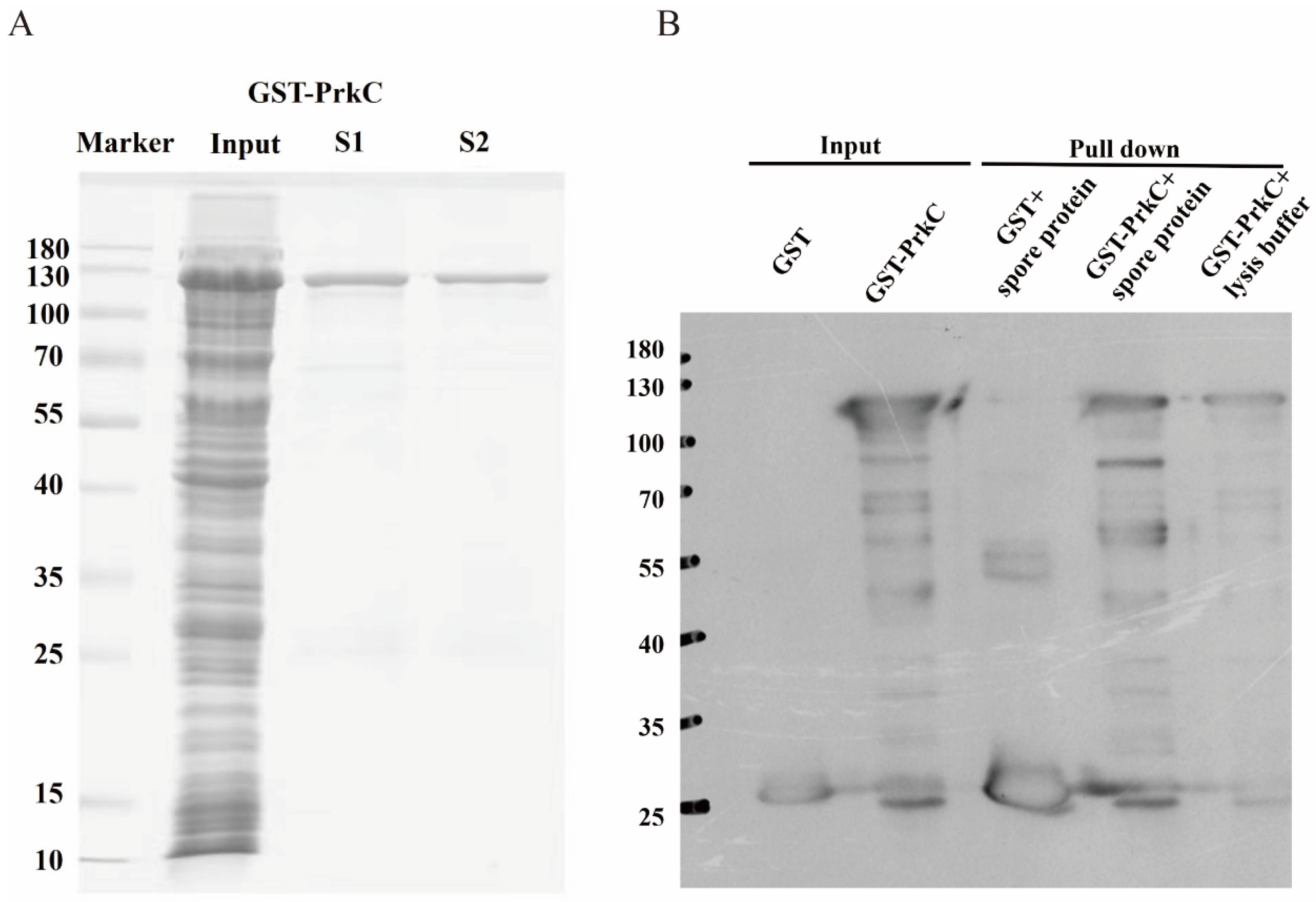
3.1. In Vitro Expression and Purification of PrkC Protein
3.2. Screening of PrkC-Interacting Proteins in B. subtilis Spores
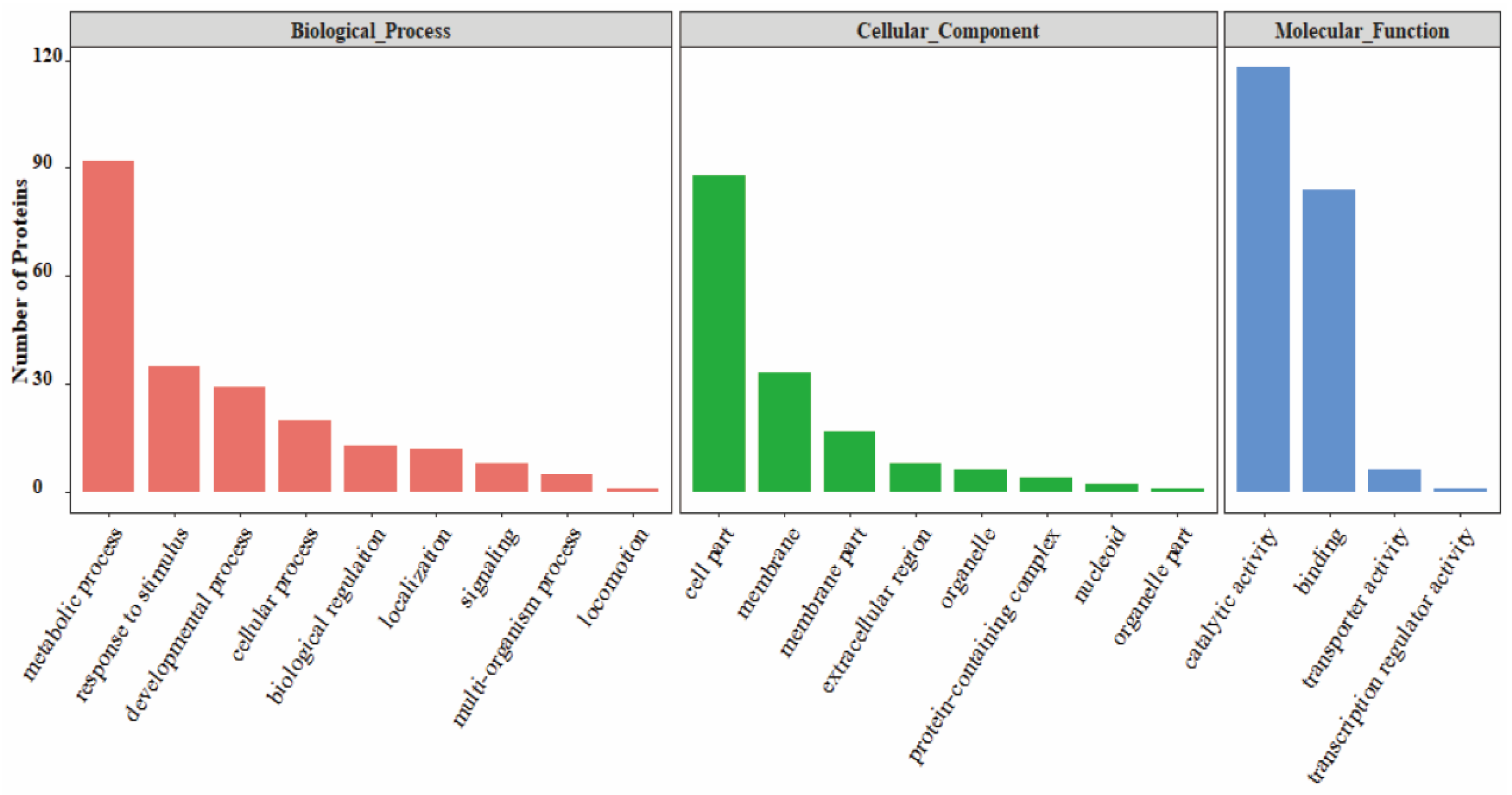
3.3. GO Analysis of PrkC-Interacting Proteins in B. subtilis Spores
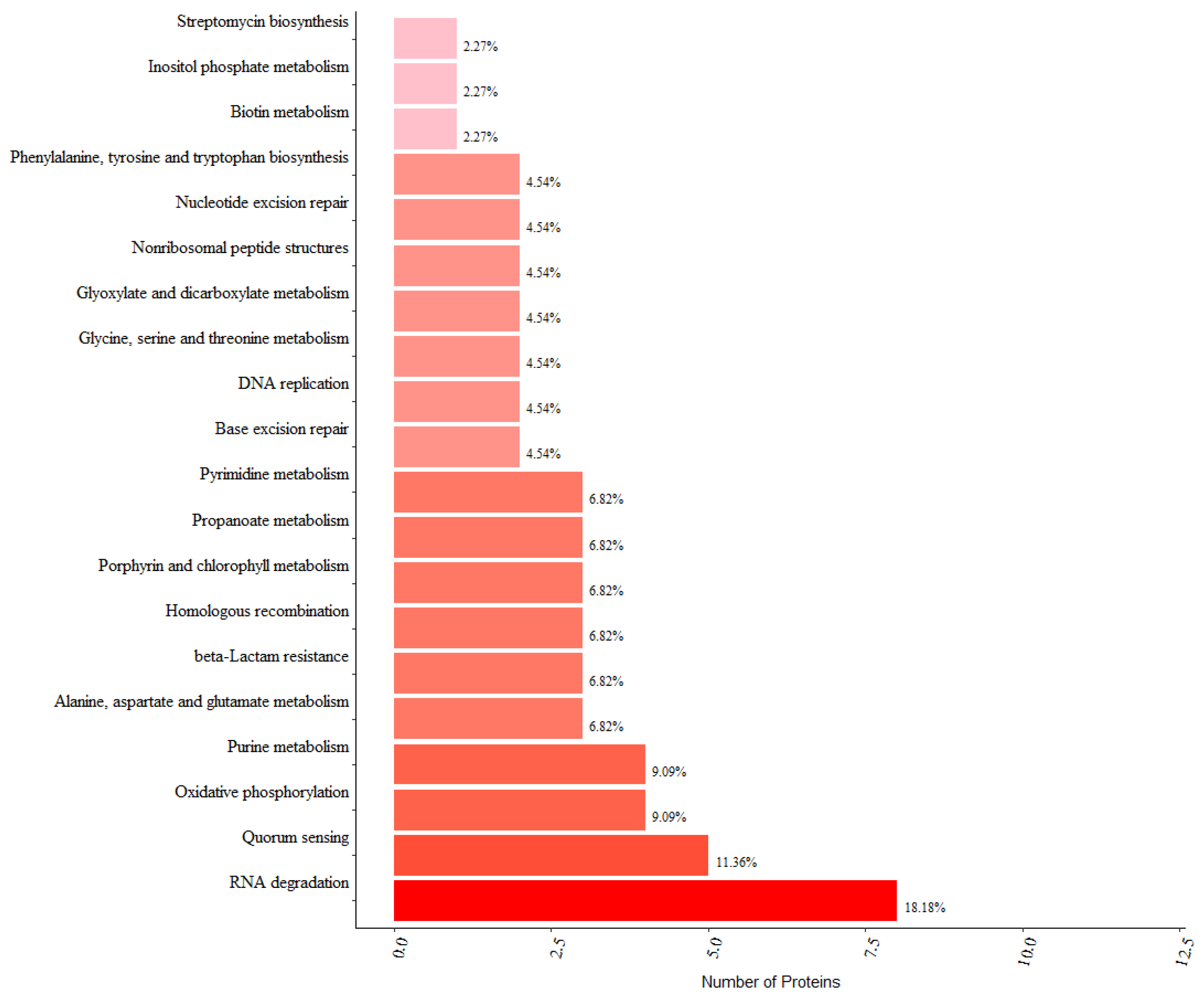
3.4. KEGG Pathway Analysis and Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis of PrkC-Interacting Proteins in B. subtilis Spores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Setlow, P. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: Their Resistance to and Killing by Radiation, Heat and Chemicals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Setlow, P. Germination of Spores of Bacillus Species: What we Know and Do Not Know. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Xin, W.; Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Inactivation of Bacillus subtilis Spores by a Combination of High-Pressure Thermal Treatment and Potassium Sorbate. Food Microbiol. 2023, 115, 104345. [Google Scholar]
- Wells-Bennik, M.; Eijlander, R.T.; Den Besten, H.M.; Berendsen, E.M.; Warda, A.K.; Krawczyk, A.O.; Nierop Groot, M.N.; Xiao, Y.; Zwietering, M.H.; Kuipers, O.P.; et al. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology: Bacterial Spores in Food: Survival, Emergence, and Outgrowth; Doyle, M.P., Klaenhammer, T.R., Eds.; Annual Reviews; PALO ALTO: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 457–482. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Gong, Z.; Zhou, B.; Rao, L.; Liao, X. Recent Progress in Proteins Regulating the Germination of Bacillus subtilis Spores. J. Bacteriol. 2025, 207, e0028524. [Google Scholar]
- Setlow, P.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Germination of Spores of the Orders Bacillales and Clostridiales. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 459–477. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, L.J.; Quirk, A.V.; Welkos, S.L.; Cote, C.K. Incorporating Germination-Induction Into Decontamination Strategies for Bacterial Spores. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, I.M.; Laaberki, M.; Popham, D.L.; Dworkin, J. A Eukaryotic-Like Ser/Thr Kinase Signals Bacteria to Exit Dormancy in Response to Peptidoglycan Fragments. Cell 2008, 135, 486–496. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Shah, I.M.; Ghosh, S.; Dworkin, J.; Hoover, D.G.; Setlow, P. Superdormant Spores of Bacillus Species Germinate Normally with High Pressure, Peptidoglycan Fragments, and Bryostatin. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ray, W.K.; Helm, R.F.; Melville, S.B.; Popham, D.L. Levels of Germination Proteins in Bacillus subtilis Dormant, Superdormant, and Germinating Spores. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e957814. [Google Scholar]
- Humann, J.; Lenz, L.L. Bacterial Peptidoglycan-Degrading Enzymes and their Impact On Host Muropeptide Detection. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T.A.; Delagoutte, B.; Endrizzi, J.A.; Falick, A.M.; Alber, T. Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pknb Supports a Universal Activation Mechanism for Ser/Thr Protein Kinases. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Squeglia, F.; Marchetti, R.; Ruggiero, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Marasco, D.; Dworkin, J.; Petoukhov, M.; Molinaro, A.; Berisio, R.; Silipo, A. Chemical Basis of Peptidoglycan Discrimination by Prkc, a Key Kinase Involved in Bacterial Resuscitation From Dormancy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20676–20679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arora, G.; Sajid, A.; Arulanandh, M.D.; Misra, R.; Singhal, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, L.K.; Mattoo, A.R.; Raj, R.; Maiti, S.; et al. Zinc Regulates the Activity of Kinase-Phosphatase Pair (Basprkc/Basprpc) in Bacillus anthracis. Biometals 2013, 26, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Absalon, C.; Obuchowski, M.; Madec, E.; Delattre, D.; Holland, I.B.; Seror, S.J. Cpga, Ef-Tu and the Stressosome Protein Yezb are Substrates of the Ser/Thr Kinase/Phosphatase Couple, Prkc/Prpc, in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 2009, 155, 932–943. [Google Scholar]
- Virmani, R.; Sajid, A.; Singhal, A.; Gaur, M.; Joshi, J.; Bothra, A.; Garg, R.; Misra, R.; Singh, V.P.; Molle, V.; et al. The Ser/Thr Protein Kinase Prkc Imprints Phenotypic Memory in Bacillus anthracis Spores by Phosphorylating the Glycolytic Enzyme Enolase. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 8930–8941. [Google Scholar]
- Virmani, R.; Pradhan, P.; Joshi, J.; Wang, A.L.; Joshi, H.C.; Sajid, A.; Singh, A.; Sharma, V.; Kundu, B.; Blankenberg, D.; et al. Phosphorylation-Mediated Regulation of the Bacillus anthracis Phosphoglycerate Mutase by the Ser/Thr Protein Kinase Prkc. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 665, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Wu, R.; Cui, T.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; Chen, F.; Hu, X. Proteomic Response of Bacillus subtilis Spores Under High Pressure Combined with Moderate Temperature and Random Peptide Mixture Lk Treatment. Foods 2022, 11, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Liao, X.; Chen, F.; Hu, X. The Effect of High Pressure Combined with Moderate Temperature and Peptidoglycan Fragments On Spore Inactivation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110615. [Google Scholar]
- Lalonde, S.; Ehrhardt, D.W.; Loque, D.; Chen, J.; Rhee, S.Y.; Frommer, W.B. Molecular and Cellular Approaches for the Detection of Protein-Protein Interactions: Latest Techniques and Current Limitations. Plant J. 2008, 53, 610–635. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco-Garcia, R.; Vargas-Martinez, R. The Study of Protein-Protein Interactions in Bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Agirrezabala, X.; Frank, J. Elongation in Translation as a Dynamic Interaction Among the Ribosome, Trna, and Elongation Factors Ef-G and Ef-Tu. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2009, 42, 159–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belland, R.J.; Zhong, G.M.; Crane, D.D.; Hogan, D.; Sturdevant, D.; Sharma, J.; Beatty, W.L.; Caldwell, H.D. Genomic Transcriptional Profiling of the Developmental Cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8478–8483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, J.; Shah, I.M. Exit From Dormancy in Microbial Organisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popham, D.L.; Bernhards, C.B. Spore Peptidoglycan. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunck, R.; Cho, H.; Bernhardt, T.G. Identification of Mltg as a Potential Terminase for Peptidoglycan Polymerization in Bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 700–718. [Google Scholar]
- Libby, E.A.; Goss, L.A.; Dworkin, J. The Eukaryotic-Like Ser/Thr Kinase Prkc Regulates the Essential Walrk Two-Component System in Bacillus subtilis. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e10052756. [Google Scholar]
- Litzinger, S.; Duckworth, A.; Nitzsche, K.; Risinger, C.; Wittmann, V.; Mayer, C. Muropeptide Rescue in Bacillus subtilis Involves Sequential Hydrolysis by β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase and N-Acetylmuramyl-L-Alanine Amidase. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3132–3143. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, K.; Otani, M.; Uehara, R.; Kimura, M.; Umezawa, C. Primary Role of Nadh Formed by Glucose-Dehydrogenase in Atp Provision at the Early Stage of Spore Germination in Bacillus-Megaterium Qm B1551. Microbiol. Immunol. 1988, 32, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.; Otani, M.; Umezawa, C.; Nakatani, Y. Role of Glucose-Dehydrogenase and Glucose Catabolism in Triggering of Spore Germination in Bacillus-subtilis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 931–933. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.O.; Bignon, J.; Rapoport, G.; Debarbouille, M. Regulation of the Acetoin Catabolic Pathway is Controlled by Sigma L in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Pietack, N.; Becher, D.; Schmidl, S.R.; Saier, M.H., Jr.; Hecker, M.; Commichau, F.M.; Stülke, J. In Vitro Phosphorylation of Key Metabolic Enzymes From Bacillus subtilis: Prkc Phosphorylates Enzymes From Different Branches of Basic Metabolism. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 18, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pospisil, J.; Sax, A.; Hubalek, M.; Krasny, L.; Vohradsky, J. Whole Proteome Analysis of Germinating and Outgrowing Bacillus subtilis 168. Proteomics 2024, 24, e2400031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, J.R.; Orozco, A.D.; Rojas, J.A.; López, K.; Setlow, P.; Yasbin, R.E.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Role of the Nfo and Exoa Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonucleases in Repair of Dna Damage During Outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis Spores. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swarge, B.; Abhyankar, W.; Jonker, M.; Hoefsloot, H.; Kramer, G.; Setlow, P.; Brul, S.; de Koning, L.J. Integrative Analysis of Proteome and Transcriptome Dynamics During Bacillus subtilis Spore Revival. Msphere 2020, 5, e00463-204. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, M.B.; Sorg, J.A. Dipicolinic Acid Release by Germinating Clostridium difficile Spores Occurs through a Mechanosensing Mechanism. Msphere 2016, 1, e00306-166. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Barajas-Ornelas, R.D.C.; Amon, J.D.; Ramírez-Guadiana, F.H.; Alon, A.; Brock, K.P.; Marks, D.S.; Kruse, A.C.; Rudner, D.Z. The Spova Membrane Complex is Required for Dipicolinic Acid Import During Sporulation and Export During Germination. Gene Dev. 2022, 36, 634–646. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, G.; Setlow, P.; Germination, B.S. Unknowns and What we Need to Learn. Cell Signal 2020, 74, 109729. [Google Scholar]
- Velasquez, J.; Schuurman-Wolters, G.; Birkner, J.P.; Abee, T.; Poolman, B. Bacillus subtilis Spore Protein Spovac Functions as a Mechanosensitive Channel. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 92, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Amon, J.D.; Brogan, A.P.; Artzi, L.; Ramírez-Guadiana, F.H.; Cofsky, J.C.; Kruse, A.C.; Rudner, D.Z. Spovaf and Figp Assemble Into Oligomeric Ion Channels that Enhance Spore Germination. Gene Dev. 2024, 38, 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Pompeo, F.; Foulquier, E.; Galinier, A. Impact of Serine/Threonine Protein Kinases On the Regulation of Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 568. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Semanjski, M.; Orlovetskie, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Alon, S.; Argaman, L.; Jarrous, N.; Zhang, Y.; Macek, B.; Sinai, L.; et al. Arginine Dephosphorylation Propels Spore Germination in Bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14228–14237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Garrido, J.; Ojkic, N.; Khanna, K.; Wagner, F.R.; Villa, E.; Endres, R.G.; Pogliano, K. Chromosome Translocation Inflates Bacillus Forespores and Impacts Cellular Morphology. Cell 2018, 172, 758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scheeff, E.D.; Axelrod, H.L.; Miller, M.D.; Chiu, H.; Deacon, A.M.; Wilson, I.A.; Manning, G. Genomics, Evolution, and Crystal Structure of a New Family of Bacterial Spore Kinases. Proteins 2010, 78, 1470–1482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinai, L.; Rosenberg, A.; Smith, Y.; Segev, E.; Ben-Yehuda, S. The Molecular Timeline of a Reviving Bacterial Spore. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 695–707. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Ravikumar, V.; Derouiche, A.; Macek, B.; Mijakovic, I. Tyrosine 601 of Bacillus subtilis Dnak Undergoes Phosphorylation and is Crucial for Chaperone Activity and Heat Shock Survival. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 533. [Google Scholar]

| UniprotKBc | Gene Names | Protein Names |
|---|---|---|
| P45867 | acdA | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.-) |
| O34324 | acoL | Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (EC 1.8.1.4) (Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase) (E3 component of acetoin cleaving system) |
| P42064 | appD | Oligopeptide transport ATP-binding protein AppD |
| O31788 | aprX | Serine protease AprX (EC 3.4.21.-) |
| P35146 | aroD | 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase (3-dehydroquinase) (EC 4.2.1.10) (Type I DHQase) (Type I dehydroquinase) (DHQ1) |
| P37808 | atpA | ATP synthase subunit alpha (EC 7.1.2.2) (ATP synthase F1 sector subunit alpha) (F-ATPase subunit alpha) (Vegetative protein 100) (VEG100) |
| P07788 | cotA | Laccase (EC 1.10.3.2) (Bilirubin oxidase) (EC 1.3.3.5) (Spore coat protein A) |
| O34656 | cotI | Spore coat protein I |
| P17820 | dnaK | Chaperone protein DnaK (HSP70) (Heat shock 70 kDa protein) (Heat shock protein 70) |
| P51831 | fabG | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase FabG (EC 1.1.1.100) (3-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein reductase) (Beta-Ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein reductase) (Beta-ketoacyl-ACP reductase) |
| O07639 | ftsW | Probable peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase FtsW (PGT) (EC 2.4.99.28) (Cell division protein FtsW) (Cell wall polymerase) (Peptidoglycan polymerase) (PG polymerase) |
| P54376 | gcvPA | Probable glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) subunit 1 (EC 1.4.4.2) (Glycine cleavage system P-protein subunit 1) (Glycine decarboxylase subunit 1) (Glycine dehydrogenase (aminomethyl-transferring) subunit 1) |
| P12310 | gdh | Glucose 1-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.47) |
| O07621 | hemAT | Heme-based aerotactic transducer HemAT |
| P21248 | hemD | Uroporphyrinogen-III synthase (UROS) (EC 4.2.1.75) (Hydroxymethylbilane hydrolyase [cyclizing]) (Uroporphyrinogen-III cosynthase) |
| P13714 | ldh | L-lactate dehydrogenase (L-LDH) (EC 1.1.1.27) |
| O34338 | mntB | Manganese transport system ATP-binding protein MntB |
| O31667 | mtnX | 2-hydroxy-3-keto-5-methylthiopentenyl-1-phosphate phosphatase (HK-MTPenyl-1-P phosphatase) (EC 3.1.3.87) |
| P40406 | nagZ | Beta-hexosaminidase (EC 3.2.1.52) (Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase) (N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase) (N-acetylglucosaminidase) (ORF1) |
| P38050 | pbpF | Penicillin-binding protein 1F (PBP-1F) (Penicillin-binding protein F) (Peptidoglycan TGase); Penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase (DD-transpeptidase)] |
| O34798 | pdaC | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase PdaC (Peptidoglycan MurNAc deacetylase) (EC 3.5.1.-) (Polysaccharide deacetylase PdaC) |
| O34819 | pelB | Pectin lyase (PNL) (EC 4.2.2.10) |
| O07617 | phoE | Uncharacterized phosphatase PhoE (EC 3.1.3.-) |
| P40806 | pksJ | Polyketide synthase PksJ (PKS) |
| Q05470 | pksL | Polyketide synthase PksL (PKS) |
| P40872 | pksM | Polyketide synthase PksM |
| O34996 | polA | DNA polymerase I (POL I) (EC 2.7.7.7) |
| P39846 | ppsB | Plipastatin synthase subunit B (EC 2.3.1.-) (Peptide synthase 2) [Includes ATP-dependent tyrosine adenylase 1 (TyrA 1) (Tyrosine activase 1); ATP-dependent threonine adenylase (ThrA) (Threonine activase)] |
| O34507 | prkC | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PrkC (Ser/Thr-protein kinase PrkC) (EC 2.7.11.1) |
| O31755 | proS | Proline-tRNA ligase (EC 6.1.1.15) (Prolyl-tRNA synthetase) (ProRS) |
| P54528 | prpB | 2-methylisocitrate lyase (2-MIC) (MICL) (EC 4.1.3.-) |
| P00497 | purF | Amidophosphoribosyltransferase (ATase) (EC 2.4.2.14) (Glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase) (GPATase) |
| P25994 | pyrAB | Carbamoyl phosphate synthase pyrimidine-specific large chain (EC 6.3.4.16) (EC 6.3.5.5) (Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase ammonia chain) |
| P16971 | recA | Protein RecA (Recombinase A) |
| P17894 | recN | DNA repair protein RecN (Recombination protein N) |
| P35161 | resB | Cytochrome c biogenesis protein ResB |
| Q03222 | rho | Transcription termination factor Rho (EC 3.6.4.-) (ATP-dependent helicase Rho) |
| O31466 | rtpA | Tryptophan RNA-binding attenuator protein inhibitory protein (Anti-TRAP protein) (AT) |
| O06714 | sbcC | Nuclease SbcCD subunit C |
| P21458 | spoIIIE | DNA translocase SpoIIIE |
| P17867 | spoIVCA | Putative DNA recombinase (Stage IV sporulation protein CA) |
| P40869 | spoVAD | Stage V sporulation protein AD |
| P39627 | spsG | Spore coat polysaccharide biosynthesis protein SpsG |
| P27206 | srfA1 | Surfactin synthase subunit 1 |
| P40401 | ssuC | Putative aliphatic sulfonates transport permease protein SsuC |
| O32165 | sufD | Iron-sulfur cluster assembly protein SufD |
| P33166 | tuf | Elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) (P-40) |
| P54334 | xkdO | Phage-like element PBSX protein XkdO |
| P37557 | yabO | RQC P-site tRNA stabilizing factor (RqcP) (Hsp15) (Ribosome-associated protein quality control protein P) |
| O34772 | ycdC | Uncharacterized protein YcdC |
| P96605 | ydbJ | Uncharacterized ABC transporter ATP-binding protein YdbJ |
| O31557 | yfjB | Uncharacterized protein YfjB |
| P54601 | yhcQ | Spore coat protein F-like protein YhcQ |
| O07529 | yhdA | FMN-dependent NADPH-azoreductase (EC 1.7.-.-) (Azobenzene reductase) |
| C0SP94 | yhfQ | Putative ABC transporter substrate-binding lipoprotein YhfQ |
| O31607 | yjbI | Group 2 truncated hemoglobin YjbI (Truncated Hb) (trHbO) (Hemoglobin-like protein YjbI) (Truncated BHb) |
| O31649 | yjdH | Uncharacterized protein YjdH |
| O34798 | yjeA | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase PdaC (Peptidoglycan MurNAc deacetylase) (EC 3.5.1.-) (Polysaccharide deacetylase PdaC) |
| O07638 | ylaN | UPF0358 protein YlaN |
| O34549 | ylbO | Uncharacterized protein YlbO |
| O34569 | yoaA | Uncharacterized N-acetyltransferase YoaA (EC 2.3.1.-) |
| O34748 | yocI | ATP-dependent DNA helicase RecQ (DNA 3′-5′ helicase RecQ) |
| O31993 | yolB | SPbeta prophage-derived uncharacterized protein YolB |
| P50830 | yprA | Uncharacterized ATP-dependent helicase YprA (EC 3.6.4.-) |
| P45931 | yqbO | Uncharacterized protein YqbO |
| P45942 | yqcG | Toxin YqcG (DNase YqcG) |
| P54463 | yqeW | Uncharacterized protein YqeW |
| P54516 | yqhR | Uncharacterized protein YqhR |
| O05389 | yrbE | Uncharacterized oxidoreductase YrbE (EC 1.-.-.-) |
| O34758 | yrrL | Endolytic murein transglycosylase (EC 4.2.2.29) (Peptidoglycan lytic transglycosylase) (Peptidoglycan polymerization terminase) |
| O34496 | ytpQ | UPF0354 protein YtpQ |
| C0SPA7 | yukB | ESX secretion system protein YukB |
| O05267 | yumB | NADH dehydrogenase-like protein YumB (EC 1.6.-.-) |
| O34817 | yvoA | HTH-type transcriptional repressor NagR (N-acetylglucosamine utilization regulator) |
| P96726 | ywqN | Putative NAD(P)H-dependent FMN-containing oxidoreductase YwqN (EC 1.-.-.-) |
| P42296 | yxiD | Toxin YxiD (DNase YxiD) |
| P42299 | yxiG | Uncharacterized protein YxiG |
| P55183 | yxjM | Sensor histidine kinase YxjM (EC 2.7.13.3) |
| Q07835 | yxxF | Uncharacterized transporter YxxF |
| C0SP91 | yycJ | Exodeoxyribonuclease YycJ (EC 3.1.11.-) |
| P45867 | acdA | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.-) |
| O34324 | acoL | Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (EC 1.8.1.4) (Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase) (E3 component of acetoin cleaving system) |
| P42064 | appD | Oligopeptide transport ATP-binding protein AppD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, K.; Cui, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Fang, C.; Dong, L.; Hu, X. The Functional Network of PrkC and Its Interaction Proteins in Bacillus subtilis Spores. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040744
Mu K, Cui T, Zhang Z, Shi Y, Fang C, Dong L, Hu X. The Functional Network of PrkC and Its Interaction Proteins in Bacillus subtilis Spores. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040744
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Kangyi, Tianlin Cui, Zequn Zhang, Yicong Shi, Chen Fang, Li Dong, and Xiaosong Hu. 2025. "The Functional Network of PrkC and Its Interaction Proteins in Bacillus subtilis Spores" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040744
APA StyleMu, K., Cui, T., Zhang, Z., Shi, Y., Fang, C., Dong, L., & Hu, X. (2025). The Functional Network of PrkC and Its Interaction Proteins in Bacillus subtilis Spores. Microorganisms, 13(4), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040744







