A Microbial Endocrinology-Designed Discovery Platform to Identify Histamine-Degrading Probiotics: Proof of Concept in Poultry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Animals and Histamine Feeding Trials

2.3. Quantitative Measurement of Histamine Levels
2.4. Collection of Biological Samples
2.5. Isolation of Histamine-Degrading Bacteria from Histamine Fed Broilers
2.6. Brevibacterium Culture Stocks
2.7. Incorporation of Histamine-Degrading Brevibacterium Probiotic into Feed
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histamine Feeding Trial and Identification of Histamine-Degrading Bacteria
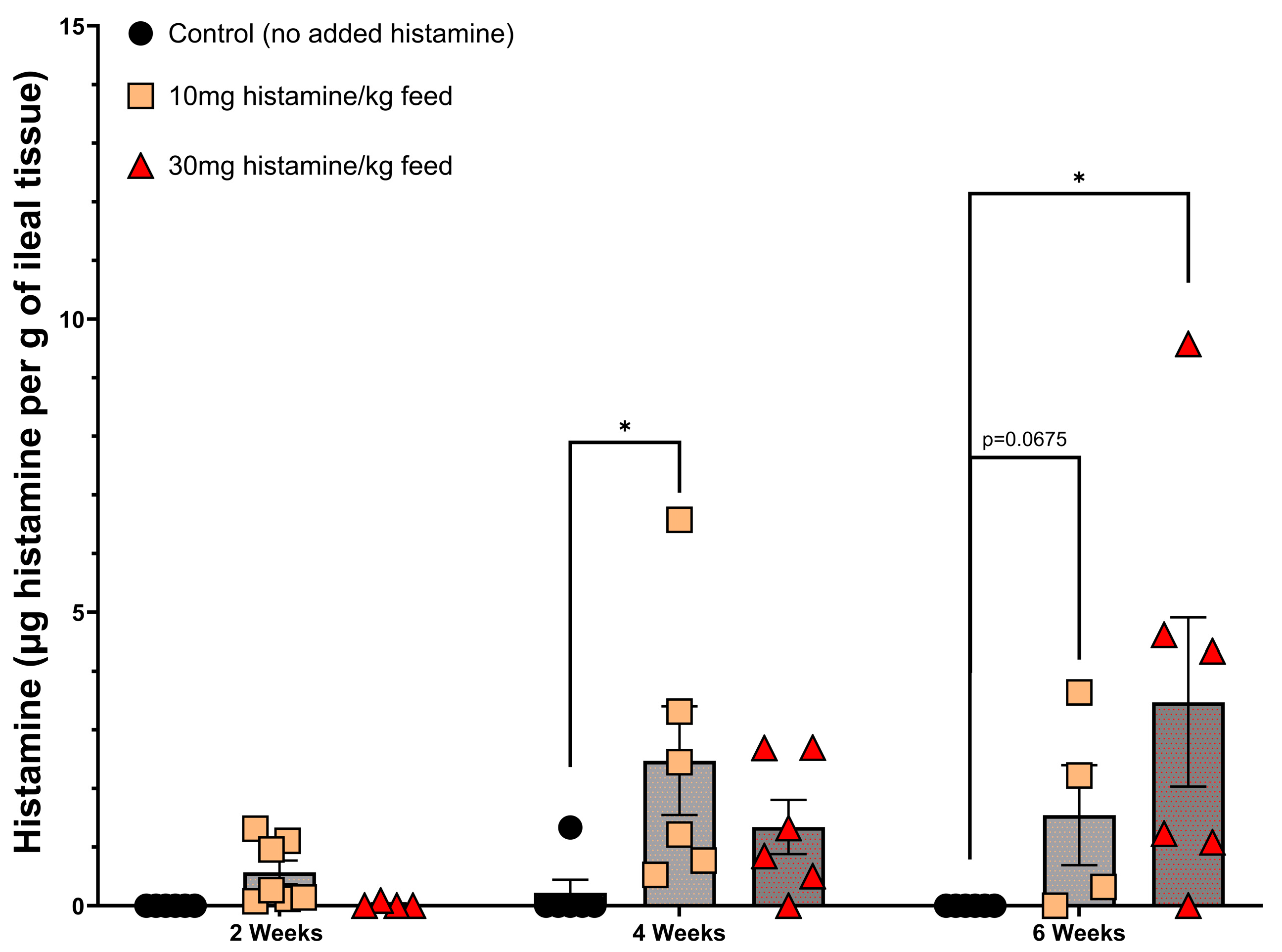
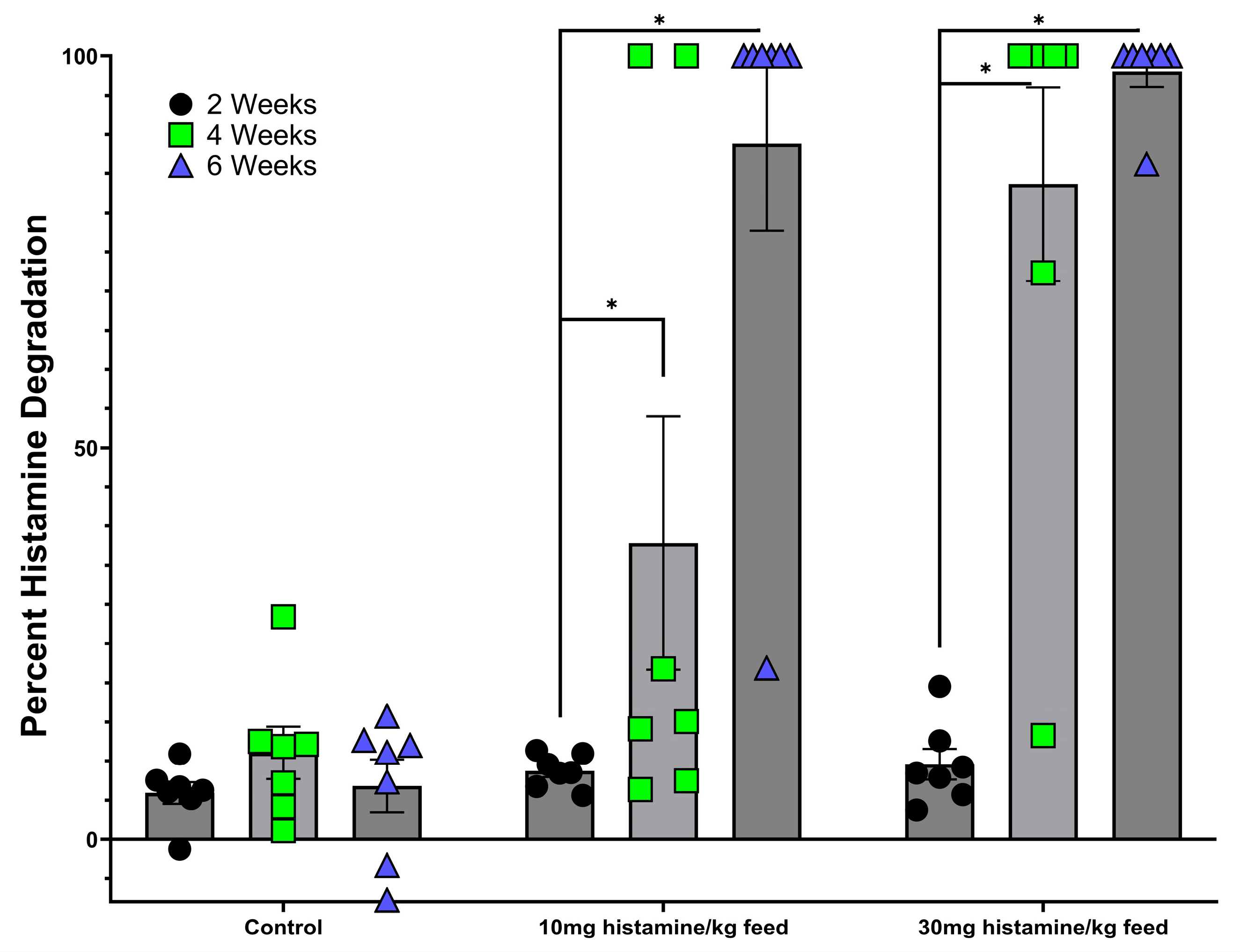
3.2. Evaluation of Brevibacterium spp. Bacteria for Histamine-Degrading Capability

3.3. Evaluation of B. sediminis as a Probiotic Feed Additive to Control Gut Histamine
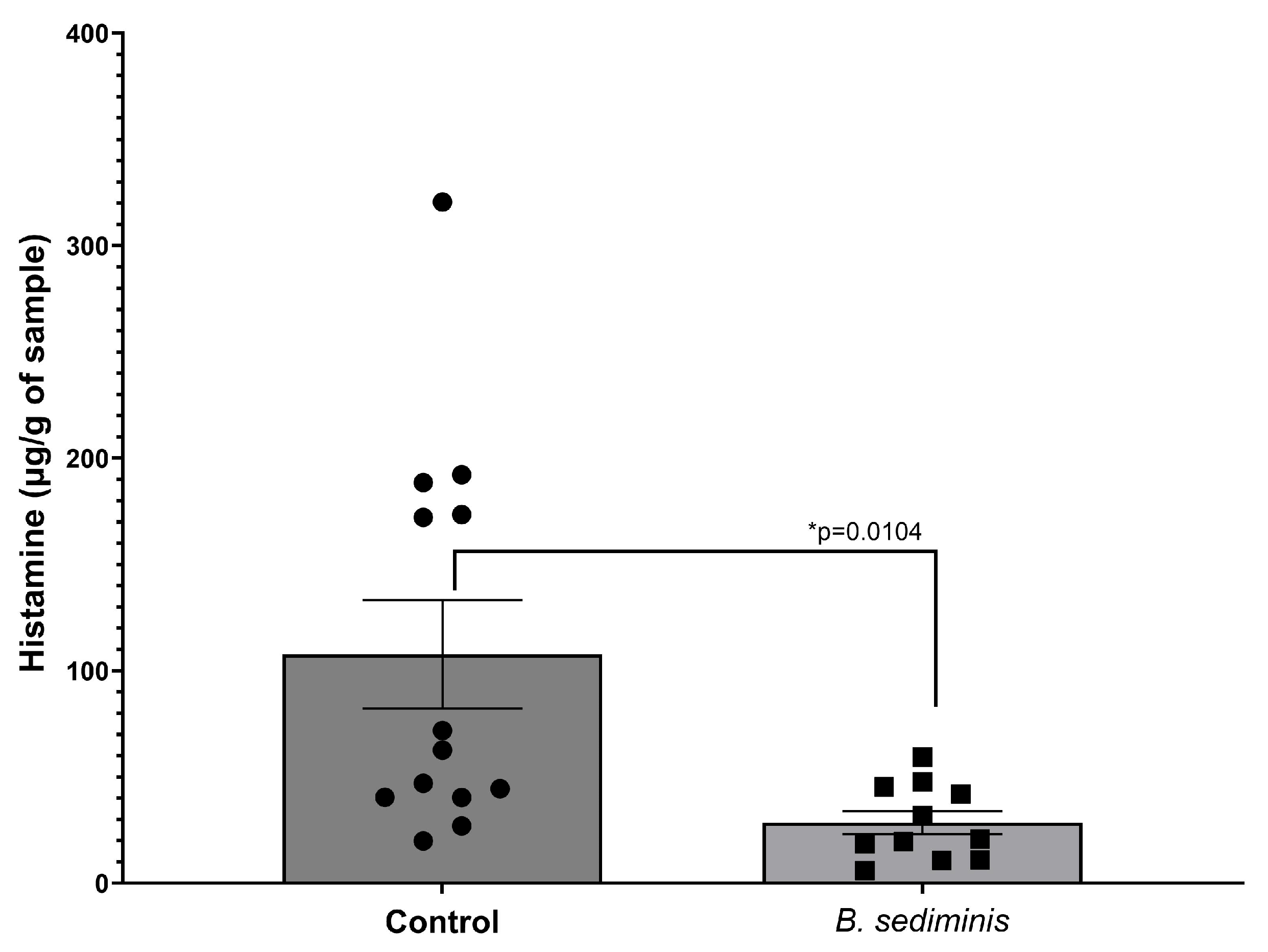

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMM | Histamine minimal medium |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography |
References
- Wojcik, W.; Lukasiewicz-Mierzejewska, M.; Damaziak, K.; Bien, D. Biogenic Amines in Poultry Meat and Poultry Products: Formation, Appearance, and Methods of Reduction. Animals 2022, 12, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulpekova, Y.O.; Nechaev, V.M.; Popova, I.R.; Deeva, T.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Malsagova, K.A.; Kaysheva, A.L.; Ivashkin, V.T. Food Intolerance: The Role of Histamine. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engevik, K.A.; Hazzard, A.; Puckett, B.; Hoch, K.M.; Haidacher, S.J.; Haag, A.M.; Spinler, J.K.; Versalovic, J.; Engevik, M.A.; Horvath, T.D. Phylogenetically diverse bacterial species produce histamine. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 47, 126539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, S.; Winiarska, E.; Globinska, A.; Jutel, M. Histamine: A Mediator of Intestinal Disorders-A Review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, A.; Yoshikawa, F.S.Y.; Pietrobon, A.J.; Sato, M.N. Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9524075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H.L.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Selbach, O. Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1183–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, K.; Shankley, N. One hundred years of histamine research. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 709, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repka-Ramirez, M.S.; Baraniuk, J.N. Histamine in health and disease. Clin. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 17, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Buhner, S.; Schemann, M. Mast cell-nerve axis with a focus on the human gut. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino, L. Histamine in the Crosstalk Between Innate Immune Cells and Neurons: Relevance for Brain Homeostasis and Disease. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 59, 261–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas-Baste, O.; Sanchez-Perez, S.; Veciana-Nogues, M.T.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.D.C. Histamine Intolerance: The Current State of the Art. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maintz, L.; Novak, N. Histamine and histamine intolerance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Perez, S.; Comas-Baste, O.; Duelo, A.; Veciana-Nogues, M.T.; Berlanga, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.C.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.L. The dietary treatment of histamine intolerance reduces the abundance of some histamine-secreting bacteria of the gut microbiota in histamine intolerant women. A pilot study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1018463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, M.M.; Djatougbévi, K.M.; Tchoumi, N.A.; Bruno, M. Plant Histaminase as Bioactive Agent to Lower the Histamine Level: A Mini-Review. J. Gastroenterol. Res. 2017, 1, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kitao, T.; Hattori, K. Purification of pig kidney diamine oxidase (histaminase) and in vivo effects on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis and histamine induced bronchoconstriction of guinea-pigs. Experientia 1982, 38, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, T.G.; Kahl, S.; Long, J.A.; Summers, K.L. Peripheral histamine and neonatal growth performance in swine. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2020, 70, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Fan, J.; Huang, H.; Jiang, W.; Deng, J.; Tan, B. Dietary Histamine Impairs the Digestive Physiology Function and Muscle Quality of Hybrid Grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatusfemale symbol x Epinephelus lanceolatusmale symbol). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Ohya, T.; Homma, S.; Oka, M.; Sato, S.; Nakahara, T. Properties of gizzard erosion-inducing substance in fish meal. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1981, 21, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, J.F.; Harry, E.G.; Laursen-Jones, A.P. The role of histamine and fish meal in the incidence of gizzard erosion and pro-ventricular abnormalities in the fowl. Br. Poult. Sci. 1975, 16, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibi, T.; Kinoshita, H. Biosorption of Histamine by Lactic Acid Bacteria for Detoxification. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2851, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, H.L.; Hu, L.H.; Yang, W.; Ai, C.X.; Sun, Y.Z. Autochthonous Probiotics Alleviate the Adverse Effects of Dietary Histamine in Juvenile Grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 792718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Pont, G.C.; Belote, B.L.; Lee, A.G.; Bortoluzzi, C.; Eyng, C.; Sevastiyanova, M.; Khadem, A.; Santin, E.; Farnell, Y.Z.; Gougoulias, C.; et al. Novel models for chronic intestinal inflammation in chickens: Intestinal inflammation pattern and biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 676628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyte, M. Probiotics function mechanistically as delivery vehicles for neuroactive compounds: Microbial endocrinology in the design and use of probiotics. Bioessays 2011, 33, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyte, J.M.; Martinez, D.A.; Robinson, K.; Donoghue, A.M.; Daniels, K.M.; Lyte, M. A neurochemical biogeography of the broiler chicken intestinal tract. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, M.H.; Wostmann, B.S. Histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the intestinal tract of germ-free animals, animals harbouring one microbial species and conventional animals. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1962, 19, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anast, J.M.; Dzieciol, M.; Schultz, D.L.; Wagner, M.; Mann, E.; Schmitz-Esser, S. Brevibacterium from Austrian hard cheese harbor a putative histamine catabolism pathway and a plasmid for adaptation to the cheese environment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, S.; Jutel, M.; Crameri, R.; O’Mahony, L. Histamine and gut mucosal immune regulation. Allergy 2014, 69, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.M.; Rumbold, G.R. Behavioural effects of histamine and its antagonists: A review. Psychopharmacology 1988, 95, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen Selnø, A.T.; Sumbayev, V.V.; Raap, U.; Gibbs, B.F. Role of Histamine in Inflammatory Diseases. In Immunopharmacology and Inflammation; Riccardi, C., Levi-Schaffer, F., Tiligada, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, S.C.; Wilding, T.; Buka, R.J.; Baretto, R.L.; Huissoon, A.P.; Krishna, M.T. Biomarkers in Human Anaphylaxis: A Critical Appraisal of Current Evidence and Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas-Basté, O.; Luz Latorre-Moratalla, M.; Sánchez-Pérez, S.; Teresa Veciana-Nogués, M.; del Carmen Vidal-Carou, M. Histamine and Other Biogenic Amines in Food. From Scombroid Poisoning to Histamine Intolerance. In Biogenic Amines; Proestos, C., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Healy, D.P.; Sahai, J.V.; Fuller, S.H.; Polk, R.E. Vancomycin-induced histamine release and “red man syndrome”: Comparison of 1- and 2-h infusions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Ghamsari, A.H.; Shaviklo, A.R.; Hosseini, S.A. Effects of a new generation of fish protein hydrolysate on performance, intestinal microbiology, and immunity of broiler chickens. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2023, 65, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Ben-Gigirey, B.; Barros-Velazquez, J.; Price, R.J.; An, H. Histamine and biogenic amine production by Morganella morganii isolated from temperature-abused albacore. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry, E.G.; Tucker, J.F. The effect of orally administered histamine on the weight gain and development of gizzard lesions in chicks. Vet. Rec. 1976, 99, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, E.; Zhang, X.; Dong, B.; Wang, B.; Zhu, Y. Combination of H1 and H2 Histamine Receptor Antagonists: Current Knowledge and Perspectives of a Classic Treatment Strategy. Life 2024, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, F.; Montuori, P.; Schettino, M.; Velotto, S.; Stasi, T.; Romano, R.; Cirillo, T. Level of Biogenic Amines in Red and White Wines, Dietary Exposure, and Histamine-Mediated Symptoms upon Wine Ingestion. Molecules 2019, 24, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callejon, S.; Sendra, R.; Ferrer, S.; Pardo, I. Identification of a novel enzymatic activity from lactic acid bacteria able to degrade biogenic amines in wine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos-Lopes, M.F.P.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Silva, C.C.G. Histamine and cholesterol lowering abilities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from artisanal Pico cheese. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Major, A.; Rendon, D.; Lugo, M.; Jackson, V.; Shi, Z.; Mori-Akiyama, Y.; Versalovic, J. Histamine H2 Receptor-Mediated Suppression of Intestinal Inflammation by Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri. Mbio 2015, 6, e01358-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obianwuna, U.E.; Chang, X.; Oleforuh-Okoleh, V.U.; Onu, P.N.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, K.; Wu, S. Phytobiotics in poultry: Revolutionizing broiler chicken nutrition with plant-derived gut health enhancers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahi, A.; Abd El-Ghany, W.A. Beyond probiotics, uses of their next-generation for poultry and humans: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 108, 1336–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, N.; Sunder, J.; De, A.K.; Bhattacharya, D.; Joardar, S.N. Probiotics in poultry: A comprehensive review. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2024, 85, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villageliu, D.N.; Lyte, M. Microbial endocrinology: Why the intersection of microbiology and neurobiology matters to poultry health. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyte, M. Microbial Endocrinology: Context and Considerations for Probiotic Selection. In The Gut-Brain Axis; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre, M.; Gomez-Botran, J.L.; Olivera, E.R.; Bermejo, F.; Rodriguez-Moran, J.; Luengo, J.M. Histamine catabolism in Pseudomonas putida U: Identification of the genes, catabolic enzymes and regulators. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onraedt, A.; Soetaert, W.; Vandamme, E. Industrial importance of the genus Brevibacterium. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D. The Genus Brevibacterium. In The Prokaryotes: Volume 3: Archaea. Bacteria: Firmicutes, Actinomycetes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1013–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner, R.G.; Hammes, W.P. Degradation of histamine and tyramine by Brevibacterium linens during surface ripening of Munster cheese. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 874–878. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, K. Brevibacterium sp. from poultry. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1981, 47, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidhaas, J.L.; Macbeth, T.W.; Olsen, R.L.; Harwood, V.J. Correlation of quantitative PCR for a poultry-specific brevibacterium marker gene with bacterial and chemical indicators of water pollution in a watershed impacted by land application of poultry litter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krell, T.; Gavira, J.A.; Velando, F.; Fernandez, M.; Roca, A.; Monteagudo-Cascales, E.; Matilla, M.A. Histamine: A Bacterial Signal Molecule. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyte, M. Microbial endocrinology and nutrition: A perspective on new mechanisms by which diet can influence gut-to-brain communication. PharmaNutrition 2013, 1, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Barcik, W.; Pugin, B.; Bresco, M.S.; Westermann, P.; Rinaldi, A.; Groeger, D.; Van Elst, D.; Sokolowska, M.; Krawczyk, K.; Frei, R.; et al. Bacterial secretion of histamine within the gut influences immune responses within the lung. Allergy 2019, 74, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyte, M.; Daniels, K. A Microbial Endocrinology-Designed Discovery Platform to Identify Histamine-Degrading Probiotics: Proof of Concept in Poultry. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040751
Lyte M, Daniels K. A Microbial Endocrinology-Designed Discovery Platform to Identify Histamine-Degrading Probiotics: Proof of Concept in Poultry. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040751
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyte, Mark, and Karrie Daniels. 2025. "A Microbial Endocrinology-Designed Discovery Platform to Identify Histamine-Degrading Probiotics: Proof of Concept in Poultry" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040751
APA StyleLyte, M., & Daniels, K. (2025). A Microbial Endocrinology-Designed Discovery Platform to Identify Histamine-Degrading Probiotics: Proof of Concept in Poultry. Microorganisms, 13(4), 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040751





