Antibiotic Use in Livestock Farming: A Driver of Multidrug Resistance?
Abstract
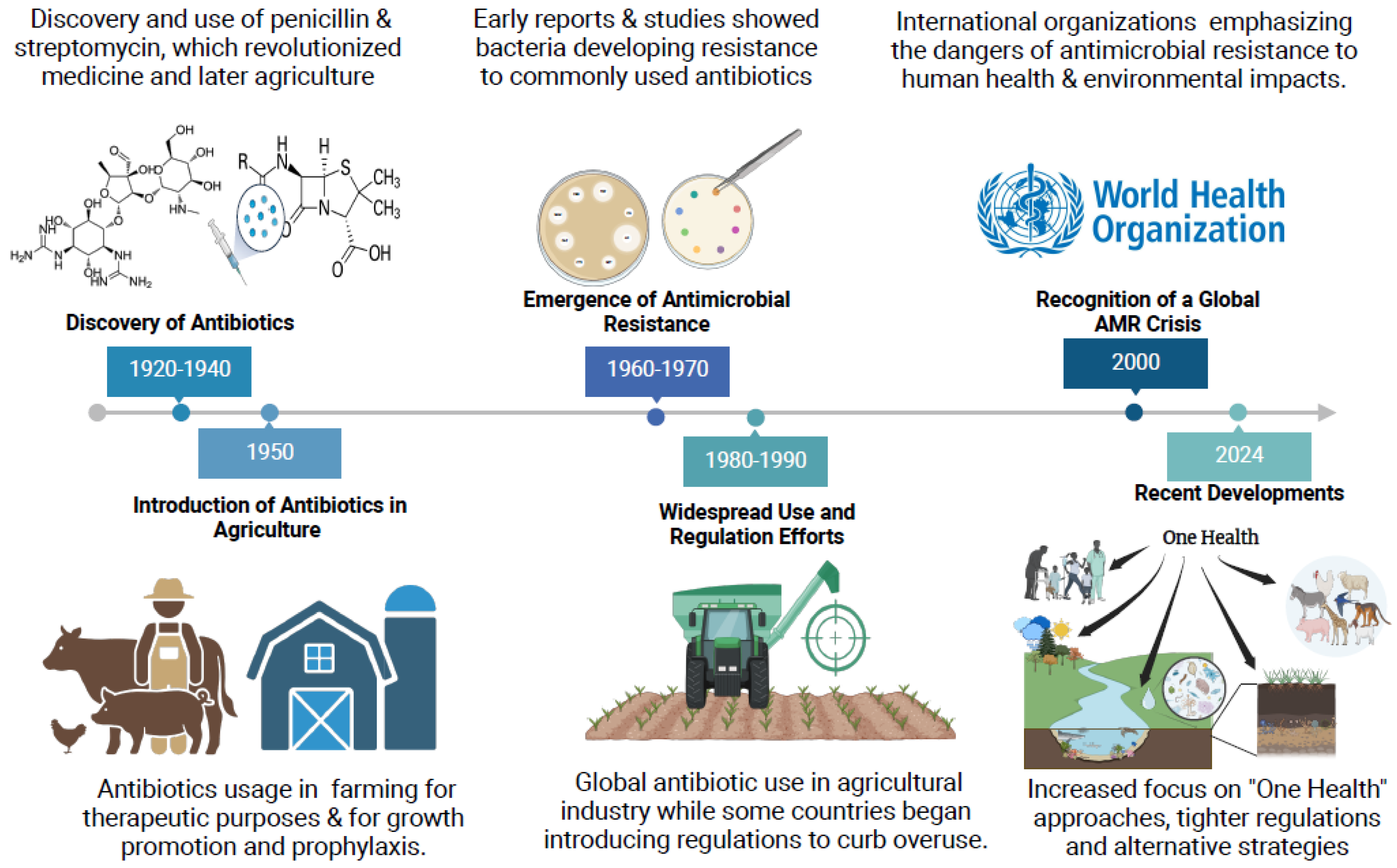
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Emergence of Multidrug Resistance (MDR) in Cattle
1.2. Selective Pressures Driving MDR
1.3. Global Prevalence and Dissemination of MDR Bacteria in Cattle
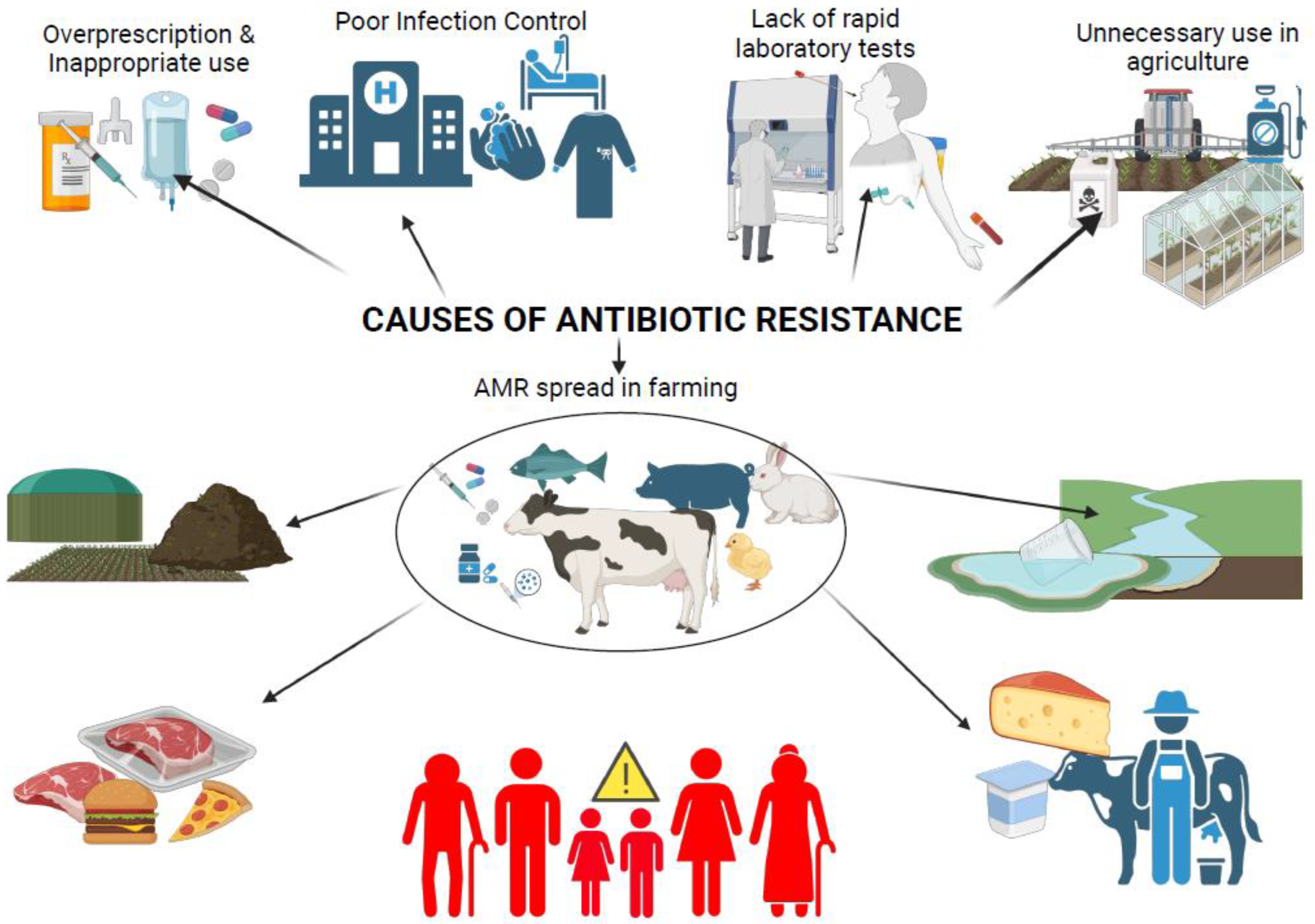
1.4. Factors Driving the Persistence and Spread of MDR Bacteria in Cattle
1.5. Antibiotic Use in Regulated and Unregulated Farming Systems
2. Methodology
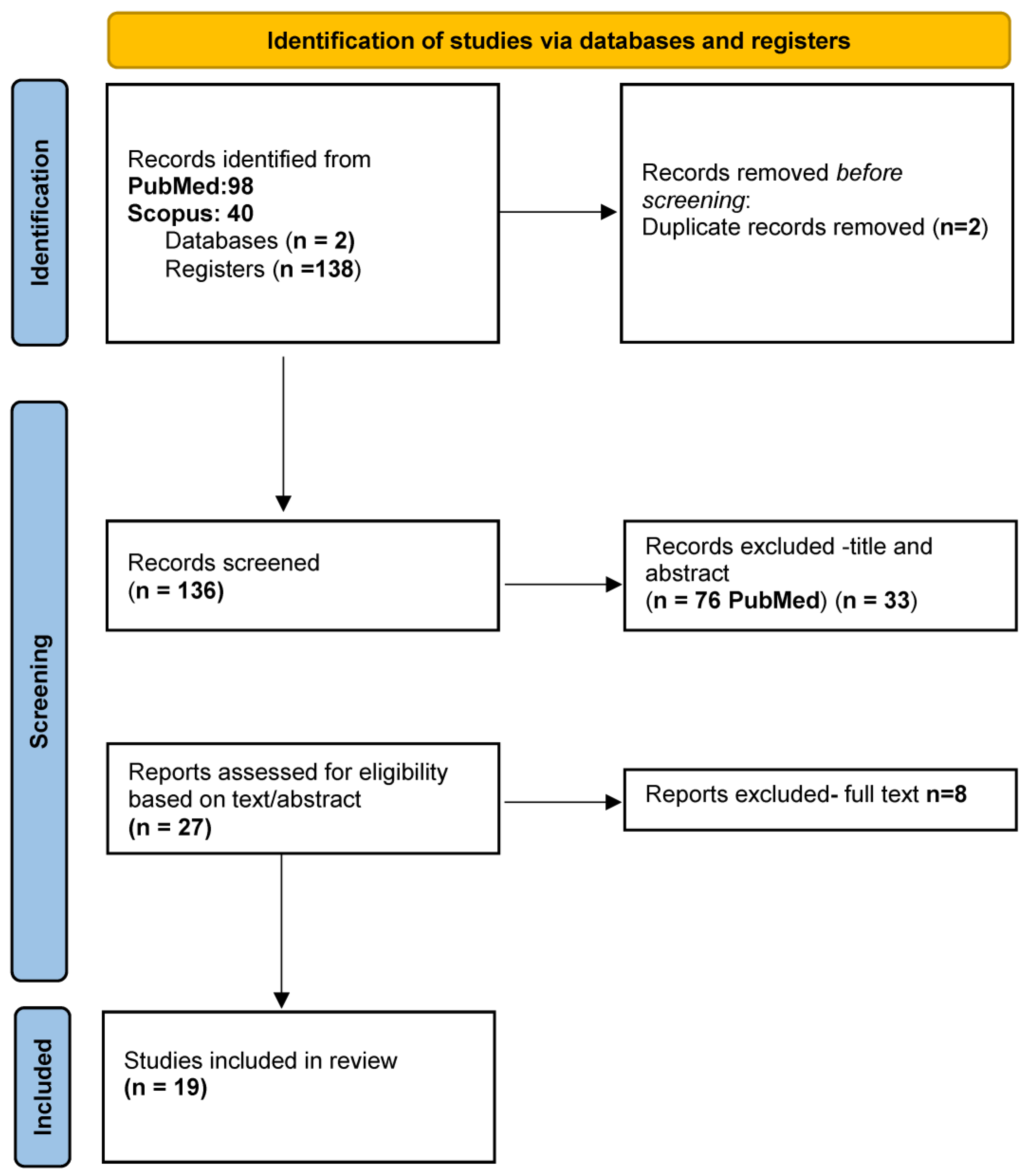
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
- Population: Studies that focus on cows or cattle receiving antibiotic treatments and studies that involve farmers or farm workers who interact with livestock.
- Intervention: Research investigating antibiotic use in cattle, particularly excessive, prolonged, or regular antibiotic administration, and studies comparing different antibiotic usage practices (e.g., organic vs. conventional, high dose vs. limited use, etc.).
- Outcome: Studies reporting the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria in cattle or the environment and studies examining the transmission (direct/indirect) of antibiotic-resistant bacteria from cattle to humans (e.g., farmers, farm workers, or consumers).
- Study Design: Experimental, observational, or cross-sectional studies, as well as systematic reviews, meta-analyses, cohort studies, or case–control studies.
- Studies that focus solely on other livestock (e.g., pigs, poultry) without mentioning cows or cattle, as well as studies that do not involve farmers or farm environments. Additionally, studies that do not specifically focus on antibiotic use in cattle or are not related to the use of antibiotics or even focus only on resistance mechanisms unrelated to cattle or farming environment have also been excluded. Finally, studies that do not address the emergence of multidrug resistance or bacterial transmission to humans or that do not focus on bacterial resistance (e.g., they focus on viral or fungal pathogens) have also been excluded.
2.3. Bacterial Transmission and Resistance Mitigation Framework
2.3.1. Transmission of MDR Bacteria from Cows to Humans
2.3.2. Strategies to Mitigate Antibiotic Resistance in Cattle
3. Discussion
3.1. A Call for Holistic Interventions
3.2. Livestock as Reservoirs for MDR Pathogens
3.3. MDR Transmission and Public Health Implications
3.4. Economic and Clinical Consequences of AMR in Livestock
3.5. A One Health Approach to AMR Mitigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Feed Additives for Animals—Pharmacology—MSD Veterinary Manual. Available online: https://www.msdvetmanual.com/pharmacology/growth-promotants-and-production-enhancers/antimicrobial-feed-additives-for-animals (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, T.; Ju, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhuge, X. Transmission Dynamics and Novel Treatments of High Risk Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: The Lens of One Health. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.Y.; Ponnampalavanar, S.; Chong, C.W.; Dwiyanto, J.; Lee, Y.Q.; Woon, J.J.; Kong, Z.X.; Jasni, A.S.; Lee, M.C.; Obaidellah, U.H.; et al. The Characterisation of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Teaching Hospital in Malaysia. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bava, R.; Castagna, F.; Lupia, C.; Poerio, G.; Liguori, G.; Lombardi, R.; Naturale, M.D.; Mercuri, C.; Bulotta, R.M.; Britti, D.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock: A Serious Threat to Public Health. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiallouris, A. BioRender.com. 2025. Available online: https://BioRender.com (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Argudín, M.A.; Deplano, A.; Meghraoui, A.; Dodémont, M.; Heinrichs, A.; Denis, O.; Nonhoff, C.; Roisin, S. Bacteria from Animals as a Pool of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, U.; Moodley, A.; Osbjer, K. Antimicrobial resistance at the livestock–human interface: Implications for Veterinary Services. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2021, 40, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Pandey, S.; Doo, H.; Keum, G.B.; Kim, E.S.; Kwak, J.; Ryu, S.; Choi, Y.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.R.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in livestock, environment and humans: One Health perspective. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2024, 66, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.C.W.; Karmacharya, D.; Bista, M.; Sharma, A.N.; Goldstein, T.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Johnson, C.K. Antibiotic resistance genes of public health importance in livestock and humans in an informal urban community in Nepal. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.; Rastogi, A.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, S.; Sohal, J.S. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: Their Mechanism of Action and Prophylaxis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5419874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, B.J.; Huang, I.T.; Hanage, W.P. Horizontal gene transfer and adaptive evolution in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 20, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H. Multidrug resistance in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreyes, W.A.; Jackwood, D.; de Oliveira, C.J.B.; Lee, C.-W.; Hoet, A.E.; Thakur, S. Molecular Epidemiology of Infectious Zoonotic and Livestock Diseases. Microbiol. Spectr. 2020, 8, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworh, M.K.; Ekeng, E.; Nilsson, P.; Egyir, B.; Owusu-Nyantakyi, C.; Hendriksen, R.S. Extended-Spectrum ß-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Among Humans, Beef Cattle, and Abattoir Environments in Nigeria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 869314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayu, A.A.; Woldetsadik, D.A.; Woldeamanuel, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Teferi, T. Burden and antimicrobial resistance of S. aureus in dairy farms in Mekelle, Northern Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Shang, W.; Li, Z.; Song, L.; Li, T.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, C.; et al. Molecular Surveillance of MRSA in Raw Milk Provides Insight into MRSA Cross Species Evolution. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0031123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M.; Gollarza, L.; Sockett, D.; Aulik, N.; Patton, E.; Francois Watkins, L.K.; Gambino-Shirley, K.J.; Folster, J.P.; Chen, J.C.; Tagg, K.A.; et al. Outbreak of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg Infections Linked to Dairy Calf Exposure, United States, 2015-2018. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, W.; Thomas, L.F.; Coyne, L.; Rushton, J. Review: Mitigating the risks posed by intensification in livestock production: The examples of antimicrobial resistance and zoonoses. Animal 2021, 15, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanya, S.H.; Bairy, I.; Metok, Y.; Baral, B.P.; Gautam, D.; Nayak, N. Detection and characterization of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae from the gut of subsistence farmers, their livestock, and the surrounding environment in rural Nepal. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Cabassi, C.S.; Fiaccadori, E.; Cavirani, S.; Parisi, A.; Bacci, C.; Lamperti, L.; Rega, M.; Conter, M.; Marra, F.; et al. Detection of carbapenemase- and ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from bovine bulk milk and comparison with clinical human isolates in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 387, 110049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed El-Domany, R.; El-Banna, T.; Sonbol, F.; Hamed Abu-Sayedahmed, S. Co-existence of NDM-1 and OXA-48 genes in Carbapenem Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates in Kafrelsheikh, Egypt. Afr. Health Sci. 2021, 21, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzina, E.S.; Kislichkina, A.A.; Sizova, A.A.; Skryabin, Y.P.; Novikova, T.S.; Ershova, O.N.; Savin, I.A.; Khokhlova, O.E.; Bogun, A.G.; Fursova, N.K. High-Molecular-Weight Plasmids Carrying Carbapenemase Genes blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, and blaOXA-48 Coexisting in Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains of ST39. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschig, J.; Mailänder-Sánchez, D.; Berscheid, A.; Berger, J.; Strömstedt, A.A.; Courth, L.F.; Malek, N.P.; Brötz-Oesterhelt, H.; Wehkamp, J. Ubiquitously expressed Human Beta Defensin 1 (hBD1) forms bacteria-entrapping nets in a redox dependent mode of action. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong’Era, E.; Kagira, J.; Maina, N.; Kiboi, D.; Waititu, K.; Michira, L.; Ngotho, M. Prevalence and Potential Risk Factors for the Acquisition of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus spp. Bacteria among Pastoralist Farmers in Kajiado Central Subcounty, Kenya. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 3573056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, S.; Kering, K.; Wairimu, C.; Onsare, R.; Mbae, C. Antimicrobial Resistance Rates and Surveillance in Sub-Saharan Africa: Where Are We Now? Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 3589–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhamize, B.; Bazira, J. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in the livestock, humans and environmental samples around the globe: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, I.N.; Lozano, C.; Simón, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Within-Host Diversity of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Resistome from Healthy Pigs and Pig Farmers, with the Detection of cfr-Carrying Strains and MDR-S. borealis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.M.A.; Abd-Elhafeez, H.H.; Al-Jabr, O.A.; El-Zamkan, M.A. Characterization of Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Raw Milk. Biology 2022, 11, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angappan, M.; Ghatak, S.; Milton, A.A.P.; Verma, A.K.; Inbaraj, S.; Abhishek; Chaudhuri, P.; Agarwal, R.K.; Thomas, P. Detection of novel sequence types and zoonotic transmission potentiality among strains of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC) from dairy calves, animal handlers and associated environments. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, J.A.; Wilson, W.M.; Nydam, D.V.; Gerlach, S.C.; Kastelic, J.P.; Russell, E.R.; McCubbin, K.D.; Adams, C.L.; Barkema, H.W. Contextualized understandings of dairy farmers’ perspectives on antimicrobial use and regulation in Alberta, Canada. J. Dairy. Sci. 2023, 106, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents and Approaches to Resolve It. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, S.; McKernan, C.; Benson, T.; Elliott, C.; Dean, M. Understanding farmers’ and veterinarians’ behavior in relation to antimicrobial use and resistance in dairy cattle: A systematic review. J. Dairy. Sci. 2021, 104, 4584–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rware, H.; Monica, K.K.; Idah, M.; Fernadis, M.; Davis, I.; Buke, W.; Solveig, D.; Daniel, K.; Duncan, C.; Morten, B.; et al. Examining antibiotic use in Kenya: Farmers’ knowledge and practices in addressing antibiotic resistance. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2024, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudenda, S.; Chabalenge, B.; Daka, V.; Mfune, R.L.; Salachi, K.I.; Mohamed, S.; Mufwambi, W.; Kasanga, M.; Matafwali, S.K. Global Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2023, 14, 271–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, B.A.; Muloi, D.M.; van Bunnik, B.A.D. Quantifying the transmission of antimicrobial resistance at the human and livestock interface with genomics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitt, A.; Lienen, T.; Wichmann-Schauer, H.; Cuny, C.; Tenhagen, B.A. The occurrence and distribution of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 on German dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 11806–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borelli, E.; Ellis, K.; Pamphilis, N.M.; Tomlinson, M.; Hotchkiss, E. Factors influencing Scottish dairy farmers’ antimicrobial usage, knowledge and attitude towards antimicrobial resistance. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 221, 106073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.W.; Hoi, L.T.; Khokhar, F.A.; Hoa, N.T.; Van Giang, T.; Bui, C.; Ninh, T.H.; Co, D.X.; Binh, N.G.; Long, H.B.; et al. A genomic epidemiology study of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii in two intensive care units in Hanoi, Vietnam. medRxiv 2020, 2020, 20246397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjølstrup, N.K.; Vaarst, M.; Jensen, C.S.; Lastein, D.B. Danish cattle veterinarians’ perspectives on antimicrobial use: Contextual and individual influencing factors. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 3377–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendner, A.A.; Lam, T.J.G.M.; Bodmer, M.; Cousin, M.E.; Schüpbach-Regula, G.; van den Borne, B.H.P. Knowledge, attitude and practices of Swiss dairy farmers towards intramammary antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance: A latent class analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 179, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Ahmad, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; et al. Epidemiological, Virulence, and Antibiotic Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae, a Major Source of Threat to Livestock and Poultry in Some Regions of Xinjiang, China. Animals 2024, 14, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellace, M.; Ceniti, C.; Paonessa, M.; Procopio, A.C.; Tilocca, B. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: An underestimated pathogen in veterinary medicine in Italy. Ger. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 4, 112–126. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Ramírez, S. Zoonotic Acinetobacter baumannii: The need for genomic epidemiology in a One Health context. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e895–e896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.S.; Price, L.B. Recent Research Examining Links Among Klebsiella pneumoniae from Food, Food Animals, and Human Extraintestinal Infections. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H. The Animal-foods-environment interface of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany: An observational study on pathogenicity, resistance development and the current situation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelloni, F.; Cagnoli, G.; Bresciani, F.; Scotti, B.; Lazzerini, L.; Marcucci, M.; Colombani, G.; Ebani, V.V. Antimicrobial resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci carried by house flies (Musca domestica) captured in swine and poultry farms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigabie, M.; Assefa, M.; Gashaw, Y.; Amare, A.; Ambachew, A.; Biset, S.; Moges, F. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance patterns of P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii strains isolated from chicken droppings on poultry farms in Gondar city, Northwest Ethiopia. Sci. One Health 2024, 4, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butaye, P.; Stegger, M.; Moodley, A.; Damborg, P.; Williams, A.; Halliday-Simmonds, I.; Guardabassi, L. One Health Genomic Study of Human and Animal Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated at Diagnostic Laboratories on a Small Caribbean Island. Antibiotics 2021, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, H.; Ziegler, D.; Pflüger, V.; Vogel, G.; Zweifel, C.; Stephan, R. Prevalence and characteristics of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from livestock, chicken carcasses, bulk tank milk, minced meat, and contact persons. BMC Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.-J.; Choi, Y.J.; Won, D.; Choi, J.R.; Jeong, S.H. Klebsiella pneumoniae, a human-dog shuttle organism for the genes of CTX-M ESBL. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, R.J.; Van Engelen, E. Pneumonia associated with Acinetobacter baumannii in a group of minks (Neovison vison). Vet. Q. 2015, 35, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Betancourt-Garcia, M.; Kare-Opaneye, Y.O.; Swierczewski, B.E.; Bennett, J.W.; Horne, B.; Fackler, J.; Suazo Hernandez, L.P.; Brownstein, M.J. Critically Ill Patient with Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Respiratory Infection Successfully Treated with Intravenous and Nebulized Bacteriophage Therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0082421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Organism/Source | AMR Genes | Comments | WHO Ranking | OIE Ranking | Animal Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbapenemase Genes in Gram-negative Bacteria | Escherichia coli (cows) | bla_KPC, bla_NDM, bla_OXA-48, bla_VIM, bla_IMP | Found in E. coli isolated from cattle; transferable via plasmids. | CI | VCIA | Cows |
| Carbapenemase Genes in Gram-negative Bacteria | Klebsiella pneumoniae (cows) | bla_NDM, bla_OXA-48 | Often associated with multidrug resistance (MDR). | CI | VCIA | Cows |
| Carbapenemase Genes in Gram-negative Bacteria | Pseudomonas aeruginosa (cows) | bla_VIM, bla_IMP | Notably found in environmental or hospital-related isolates from animal settings. | CI | VCIA | Cows |
| AMR Genes in Staphylococci from Animal and/or Human Origin | Staphylococcus aureus (human) | mecA, mecC, blaZ, erm(A), erm(C), tet(M), dfrG, aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia | Common genes conferring resistance to beta-lactams, macrolides, tetracyclines, and aminoglycosides. | CI | VHIA | Humans |
| AMR Genes in Staphylococci from Animal and/or Human Origin | Staphylococcus aureus (animal) | mecC, erm(C), tet(K), fusB | Resistance to beta-lactams, macrolides, and tetracyclines observed in livestock isolates. | HI | VHIA | Cows, Pigs |
| AMR Genes in Staphylococci from Animal and/or Human Origin | Staphylococcus epidermidis | mecA, mecC, aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia, dfrG | Found in both human and animal isolates; significant role in coagulase-negative staphylococci resistance. | HI | VHIA | Humans, Animals |
| Common AMR Genes in Clostridium, Enterococci, and Staphylococci | Clostridium difficile | tet(M), erm(B) | Resistance to tetracyclines and macrolides; occasionally linked to transposons. | CI | VCIA | Multiple |
| Common AMR Genes in Clostridium, Enterococci, and Staphylococci | Enterococcus faecalis | vanA, vanB, aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia, erm(B), tet(M) | Resistance to glycopeptides, aminoglycosides, macrolides, and tetracyclines. | CI | VCIA | Humans, Livestock |
| Common AMR Genes in Clostridium, Enterococci, and Staphylococci | Enterococcus faecium | vanA, erm(B), tet(M), aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia | Vancomycin-resistant genes prevalent in hospital and animal settings. | CI | VCIA | Humans, Animals |
| Common AMR Genes in Clostridium, Enterococci, and Staphylococci | Staphylococcus aureus | mecA, mecC, blaZ, erm(C), tet(M) | Common resistance genes in both human and animal isolates. | CI | VHIA | Humans, Livestock |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matheou, A.; Abousetta, A.; Pascoe, A.P.; Papakostopoulos, D.; Charalambous, L.; Panagi, S.; Panagiotou, S.; Yiallouris, A.; Filippou, C.; Johnson, E.O. Antibiotic Use in Livestock Farming: A Driver of Multidrug Resistance? Microorganisms 2025, 13, 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040779
Matheou A, Abousetta A, Pascoe AP, Papakostopoulos D, Charalambous L, Panagi S, Panagiotou S, Yiallouris A, Filippou C, Johnson EO. Antibiotic Use in Livestock Farming: A Driver of Multidrug Resistance? Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040779
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatheou, Andreas, Ayah Abousetta, Aphrodite Persephone Pascoe, Demosthenis Papakostopoulos, Loukas Charalambous, Stelios Panagi, Stavros Panagiotou, Andreas Yiallouris, Charalampos Filippou, and Elizabeth O. Johnson. 2025. "Antibiotic Use in Livestock Farming: A Driver of Multidrug Resistance?" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040779
APA StyleMatheou, A., Abousetta, A., Pascoe, A. P., Papakostopoulos, D., Charalambous, L., Panagi, S., Panagiotou, S., Yiallouris, A., Filippou, C., & Johnson, E. O. (2025). Antibiotic Use in Livestock Farming: A Driver of Multidrug Resistance? Microorganisms, 13(4), 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040779





