Monthly Variation, Environmental Drivers, and Ecological Functions of Marine Bacterial Community in a Eutrophic Coastal Area of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
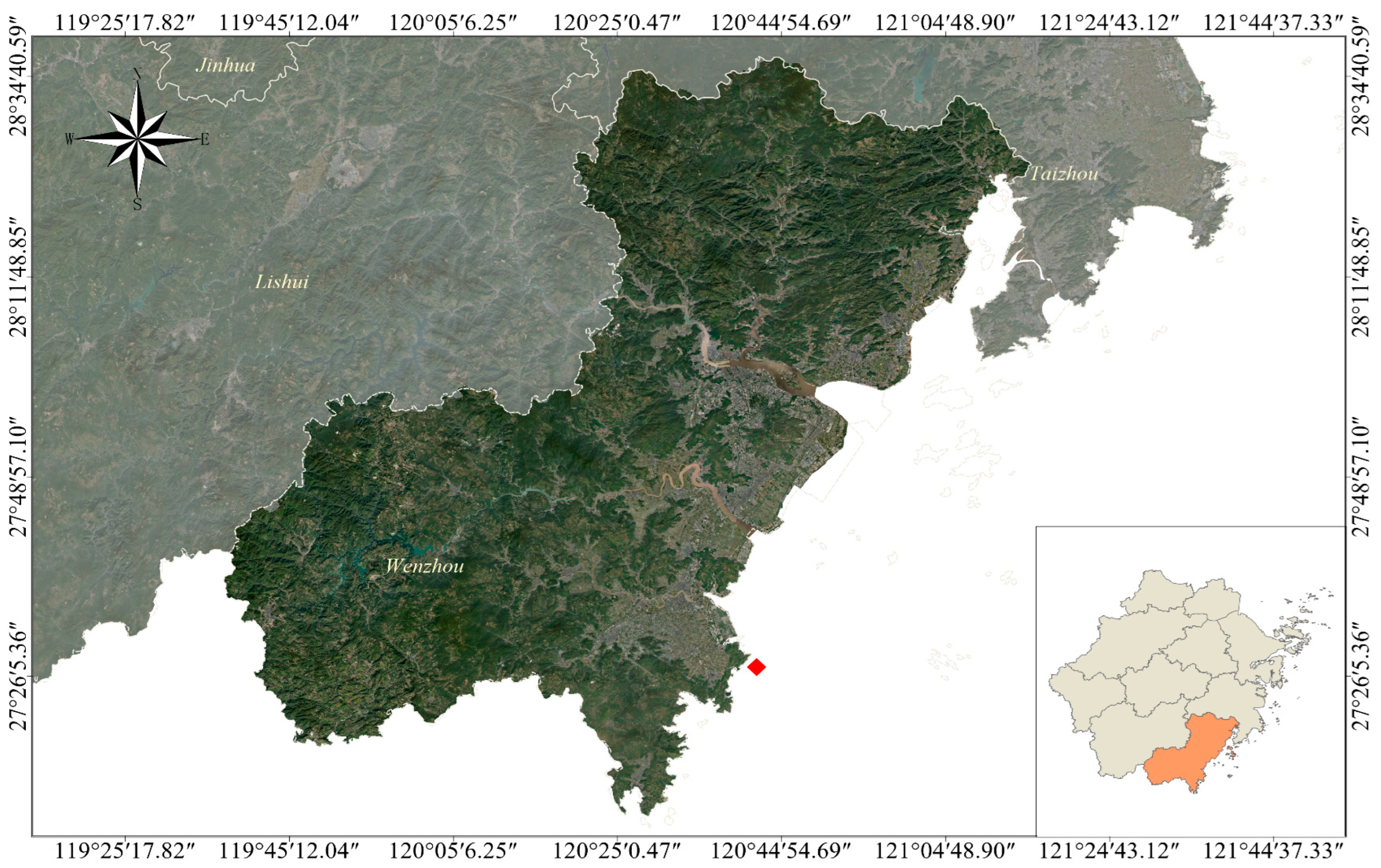
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Data Processing and Information Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Monthly Variation of Environmental Variables
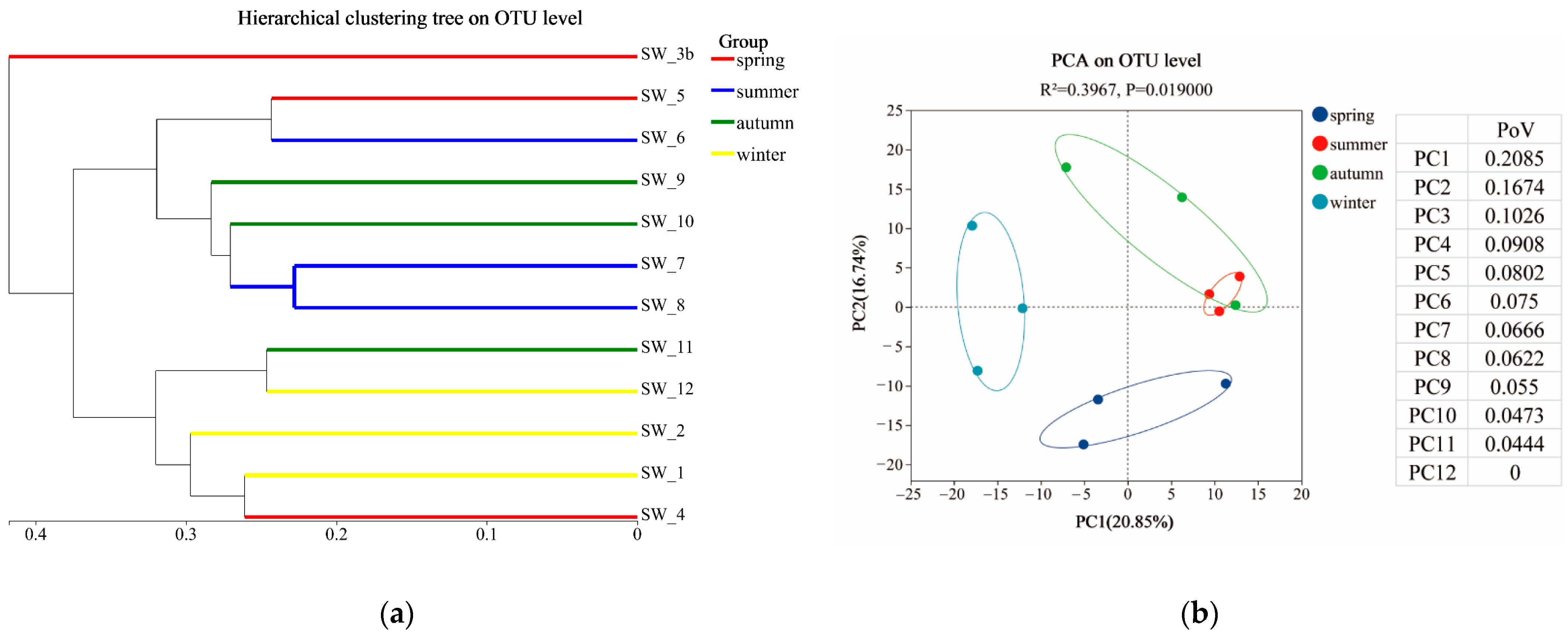
3.2. Bacterial Diversities and Their Temporal Variations
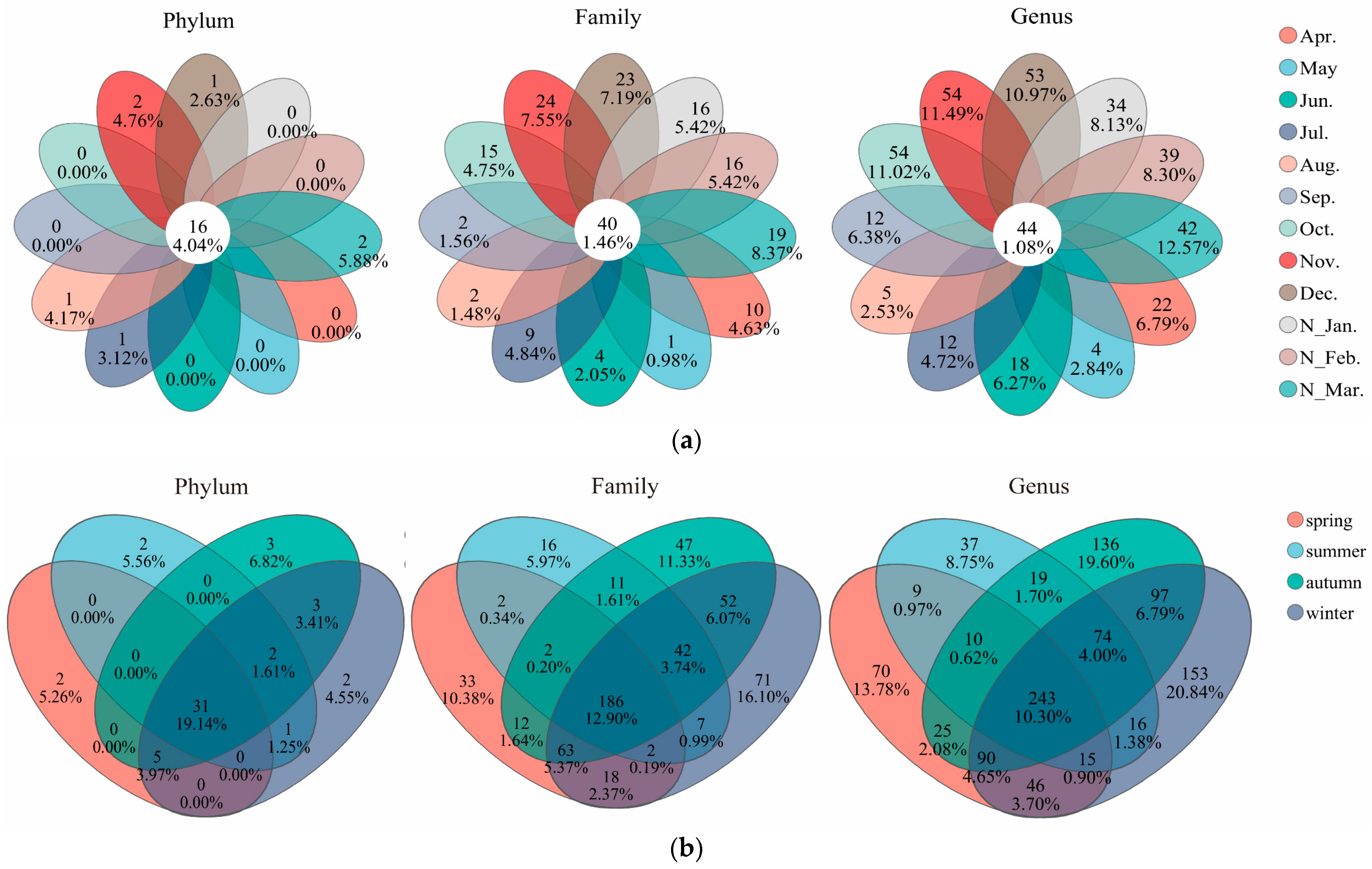
3.3. Microbial Community Structures and Their Monthly Variations
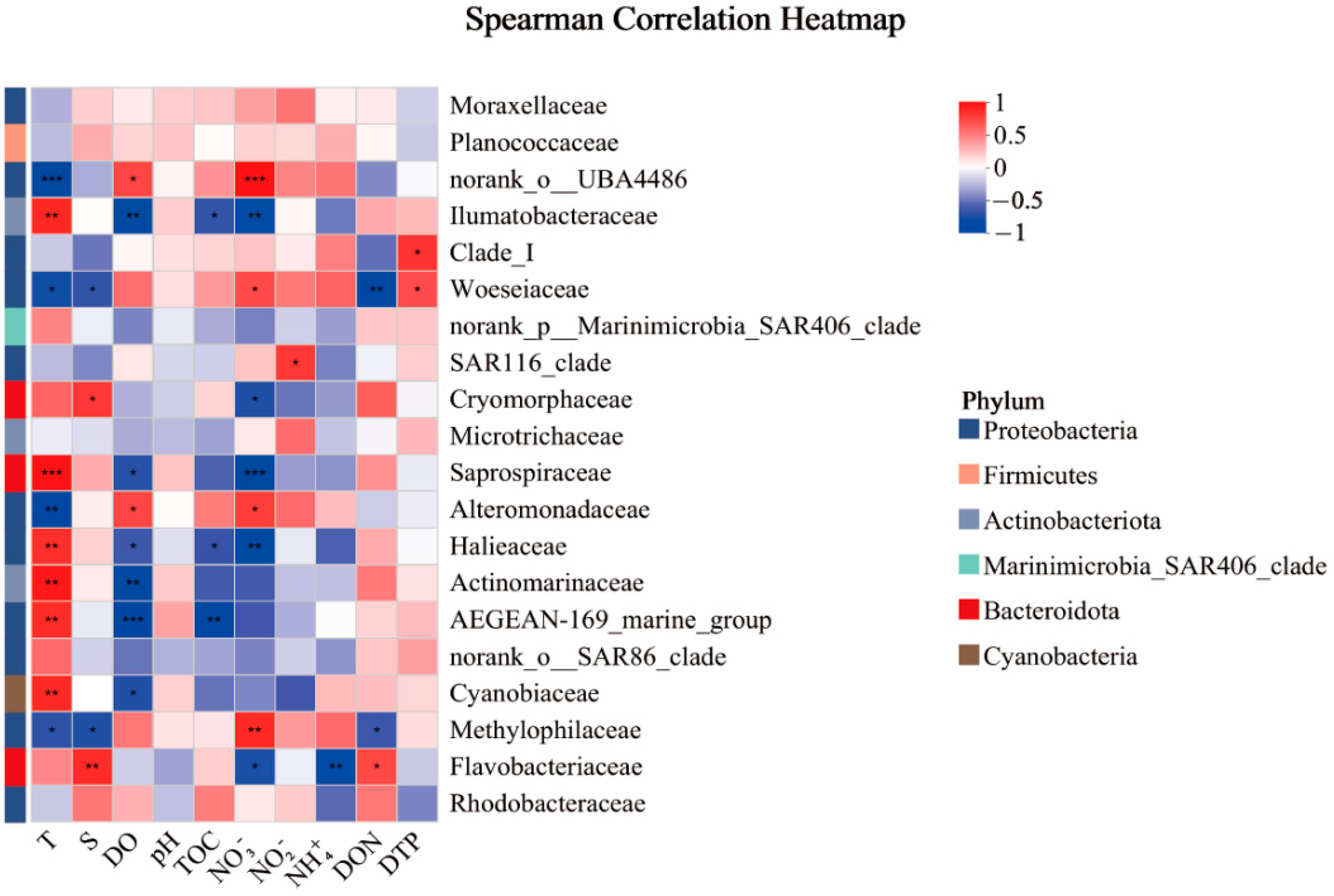
3.4. Influence of Environmental Variables on Microbial Community
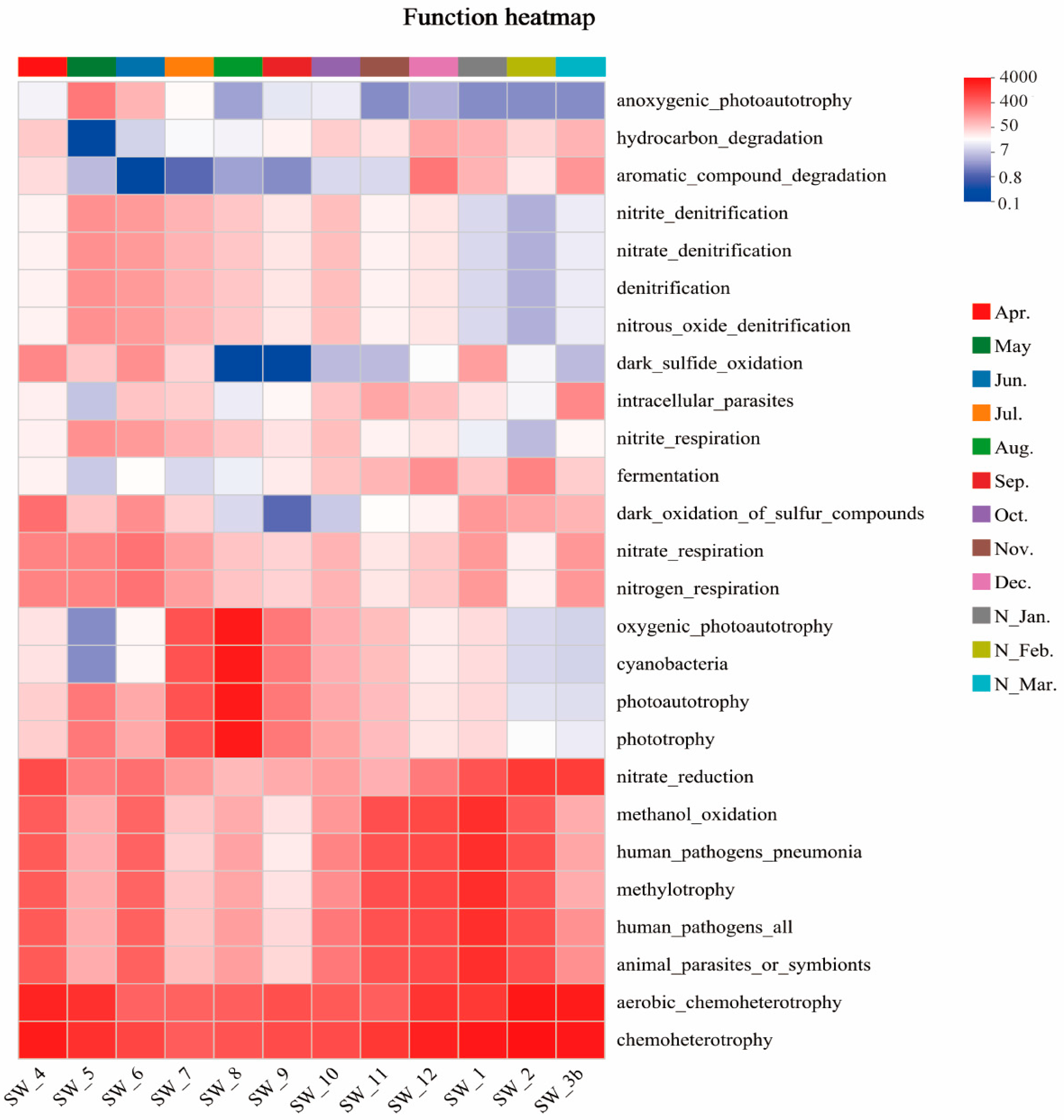
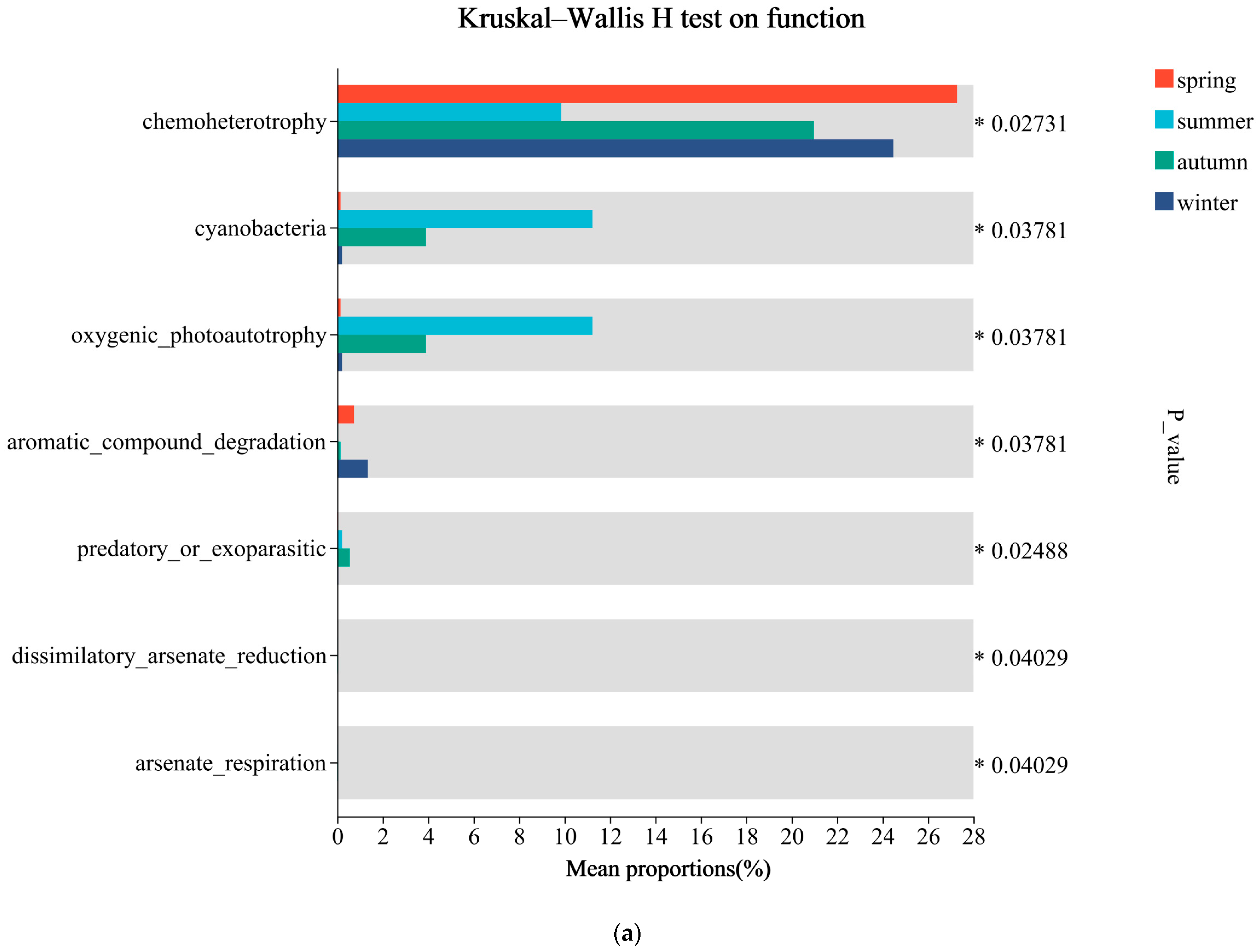
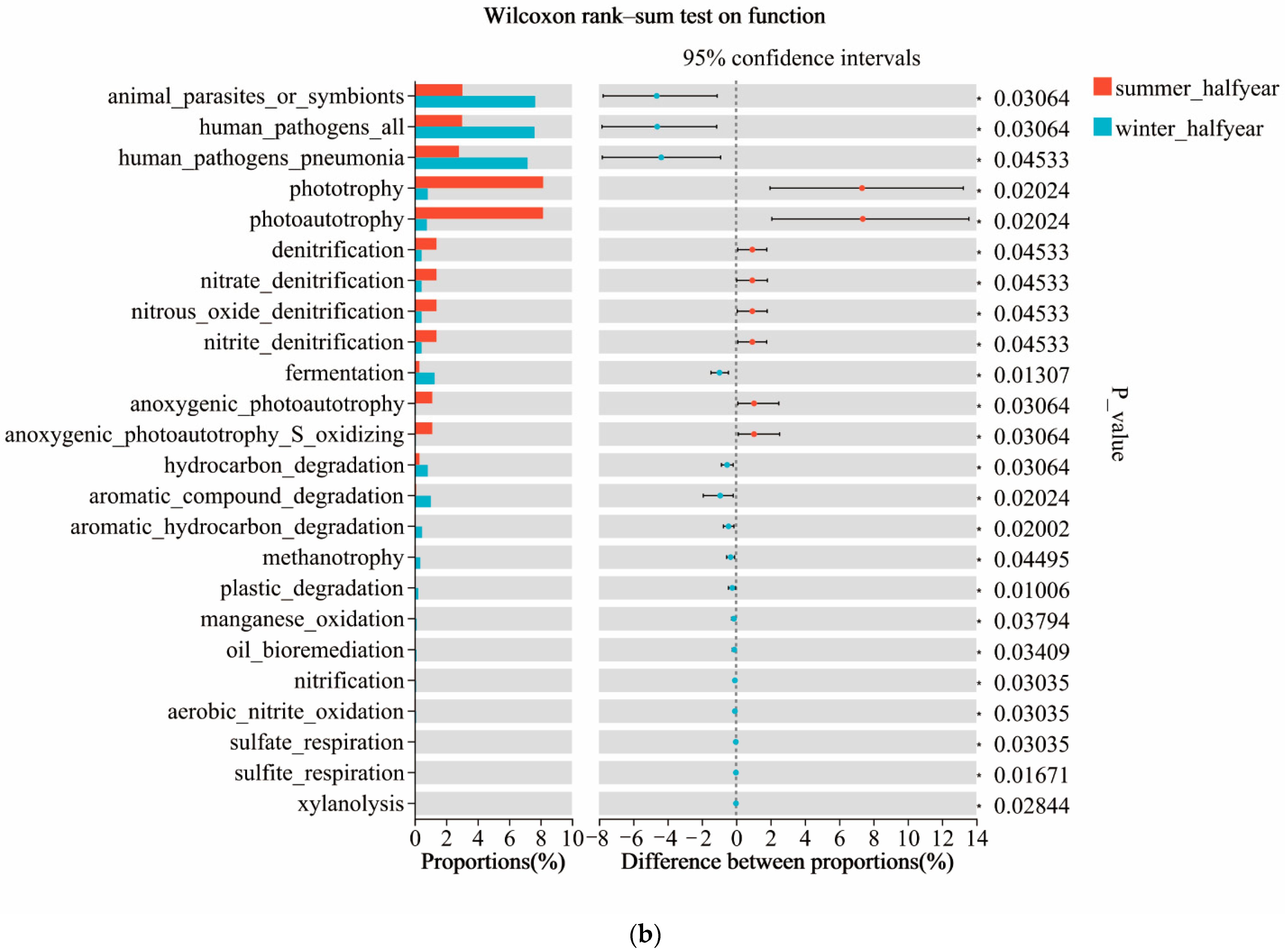
3.5. Predicted Ecological Functions
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Microbial Community Diversity and Influencing Factors
4.2. Composition and Influencing Factors of Microbial Communities
4.3. Ecological Functions of Microbial Communities and Their Monthly Variations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhou, C.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Yang, T.; et al. Global marine microbial diversity and its potential in bioprospecting. Nature 2024, 633, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mangwani, N. Ocean acidification and marine microorganisms: Responses and consequences. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, J.A.; Falkowski, P.G. Oceanic sinks for atmospheric CO2. Plant Cell Environ. 1999, 22, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, D.G.; Zehr, J.P.; Paerl, H.W.; Bergman, B.; Carpenter, E.J. Trichodesmium, a Globally Significant Marine Cyanobacterium. Science 1997, 276, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finster, K.; Liesack, W.; Thamdrup, B. Elemental sulfur and thiosulfate disproportionation by Desulfocapsa sulfoexigens sp. nov., a new anaerobic bacterium isolated from marine surface sediment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makita, H. Iron-oxidizing bacteria in marine environments: Recent progresses and future directions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, E.; Bengtsson-Palme, J. Microbial Community Interactions Are Sensitive to Small Changes in Temperature. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 672910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagri Ozturk, R.; Feyzioglu, A.M.; Capkin, E.; Yildiz, I.; Altinok, I. Effects of environmental parameters on spatial and temporal distribution of marine microbial communities in the southern Black Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 195, 106344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandeparker, L.; Kale, D.; Hede, N.; Anil, A.C. Application of functional metagenomics in the evaluation of microbial community dynamics in the Arabian Sea: Implications of environmental settings. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Cong, W.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z. Response mechanism of microbial community to seasonal hypoxia in marine ranching. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ye, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Spatiotemporal dynamics of bacterioplankton communities in the estuaries of two differently contaminated coastal areas: Composition, driving factors and ecological process. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Q.; Lou, S.; Tu, J.; Yin, W.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.; Radnaeva, L.D.; Nikitina, E.; Makhinov, A.N.; et al. Spatiotemporal distributions of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes and microbial communities in the coastal areas of the Yangtze River Estuary. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 259, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur-Kahlon, G.; Kumar, S.; Rehnstam-Holm, A.S.; Rai, A.; Bhavya, P.S.; Edler, L.; Singh, A.; Andersson, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Ramesh, R.; et al. Response of a coastal tropical pelagic microbial community to changing salinity and temperature. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 77, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, H.M.; Connors, E.; Erazo, N.G.; Sacks, J.S.; Mierzejewski, V.; Rundell, S.M.; Carlson, L.T.; Deming, J.W.; Ingalls, A.E.; Bowman, J.S.; et al. Microbial metabolomic responses to changes in temperature and salinity along the western Antarctic Peninsula. ISME J. 2023, 17, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, E.J.; Tolman, J.; Desai, D.; Ratten, J.-M.; Zorz, J.; Robicheau, B.M.; Haider, D.; LaRoche, J. Seasonal bacterial niche structures and chemolithoautotrophic ecotypes in a North Atlantic fjord. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertagnolli, A.D.; Stewart, F.J. Microbial niches in marine oxygen minimum zones. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, T.; Song, W.; Qi, Q.; Feng, J.; Cui, X.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; et al. Nitrogen addition and warming rapidly alter microbial community compositions in the mangrove sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Z.-L.; Bai, C.-H.; Liu, J.-L.; Nan, J.; Cao, D.; Li, L.-W. Characteristics of groundwater microbial communities’ structure under the impact of elevated nitrate concentrations in north China plain. Environ. Res. 2023, 218, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, D.; Ma, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, Q.; Lee, D.J. Denitrifying sulfide removal process on high-salinity wastewaters in the presence of Halomonas sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Goebel, B.M. Taxonomic note: A place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, S.M.; Mark Welch, D.B.; Voorhis, A.; Shipunova, A.; Morrison, H.G.; Eren, A.M.; Sogin, M.L. VAMPS: A website for visualization and analysis of microbial population structures. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, Y.; Xin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.-H. Seasonal succession and temperature response pattern of a microbial community in the yellow sea cold water mass. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e01169-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Yu, H.; Sheng, H.; Chen, C.; Tang, Y.; Liang, Z. Seasonal variations and co-occurrence networks of bacterial communities in the water and sediment of artificial habitat in Laoshan Bay, China. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12705. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.; Lian, E.; Liu, D.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R. Bacterial and Protistan community variation across the Changjiang estuary to the ocean with multiple environmental gradients. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Kaneko, R.; Kodama, T.; Hashihama, F.; Suwa, S.; Tanita, I.; Furuya, K.; Hamasaki, K. Comparison of community structures between particle-associated and free-living prokaryotes in tropical and subtropical Pacific Ocean surface waters. J. Oceanogr. 2017, 73, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, E.J.; Myles, S.; MacNeil, L.; Wietz, M.; Bienhold, C.; Tait, K.; Somerfield, P.J.; Bissett, A.; van de Kamp, J.; Gasol, J.M.; et al. Seasonal patterns of microbial diversity across the world oceans. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2024, 9, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, M.; Roth Rosenberg, D.; Lalzar, M.; Burgsdorf, I.; Saurav, K.; Lionheart, R.; Lehahn, Y.; Aharonovich, D.; Gómez-Consarnau, L.; Sher, D. Spatiotemporal variation of microbial communities in the ultra-oligotrophic Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 867694. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Qin, C.; Ma, H.; Xi, S.; Zuo, T.; Pan, W.; Li, C. Response of protist community dynamics and co-occurrence patterns to the construction of artificial reefs: A case study in Daya Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šolić, M.; Grbec, B.; Matić, F.; Šantić, D.; Šestanović, S.; Gladan, Ž.N.; Bojanić, N.; Ordulj, M.; Jozić, S.; Vrdoljak, A. Spatio-temporal reproducibility of the microbial food web structure associated with the change in temperature: Long-term observations in the Adriatic Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 161, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hernando-Morales, V.; Ameneiro, J.; Teira, E. Water mass mixing shapes bacterial biogeography in a highly hydrodynamic region of the Southern Ocean. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 19, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Stegen, J.C.; Yu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Nearly a decade-long repeatable seasonal diversity patterns of bacterioplankton communities in the eutrophic Lake Donghu (Wuhan, China). Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3839–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Tang, J.; Jiang, G.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Zou, S.; Dong, K. Spatial distribution and functional profile of the bacterial community in response to eutrophication in the subtropical Beibu Gulf, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.; Zheng, Q.; Jiao, N. Seasonal dynamics of bacterial communities in the surface seawater around subtropical Xiamen Island, China, as determined by 16S rRNA gene profiling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunagawa, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Chaffron, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Labadie, K.; Salazar, G.; Djahanschiri, B.; Zeller, G.; Mende, D.R.; Alberti, A.; et al. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 2015, 348, 1261359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, X. Microbial community structure of Arctic seawater as revealed by pyrosequencing. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, W.-c.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.-l.; Zhao, Z.-h.; Zou, L.-y.; Shen, Y.-c.; Lan, W.-S. Impacts of anthropogenic disturbances on microbial community of coastal waters in Shenzhen, South China. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adyasari, D.; Hassenrück, C.; Oehler, T.; Sabdaningsih, A.; Moosdorf, N. Microbial community structure associated with submarine groundwater discharge in northern Java (Indonesia). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ma, H.; Su, Z.; Lu, W.; Ma, B. Impact of marine aquaculture wastewater discharge on microbial diversity in coastal waters. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 102702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzzi, A.L.; Stat, M.; Gaston, T.F.; Huggett, M.J. Spatial patterns in host-associated and free-living bacterial communities across six temperate estuaries. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Ding, H.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Ji, Z.; Luo, W.; Bi, Y. Characteristics of bacterial communities in aquatic ecosystems near the Collins glacial (Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica). Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-B.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Lin, Y.-Q. Analysis of microbial community li versity in the water from Changli coastal area of Bohai Sea, Hebei. J. Saf. Enviroment 2019, 19, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HUANG, B.; SHAO, J.; MU, Q. Study on Sedimental Bacterial Community and Its Response to Environment Factors in the Western Yellow Sea. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Lin, T.; Xie, W.; Hu, J.; Hou, F.; Han, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, D. Disentangling the Mechanisms Shaping the Prokaryotic Communities in a Eutrophic Bay. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0148122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-X.; Pang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Li, J.-L.; Qin, S. Spatial variation of microbial communities in sediments along the environmental gradients from Xiaoqing River to Laizhou Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zorz, J.; Willis, C.; Comeau, A.M.; Langille, M.G.; Johnson, C.L.; Li, W.K.; LaRoche, J. Drivers of regional bacterial community structure and diversity in the Northwest Atlantic Ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Juarez, D.L.; Pan, J.F.; Blinebry, S.K.; Gronniger, J.; Clark, J.S.; Johnson, Z.I.; Hunt, D.E. Microbial communities across nearshore to offshore coastal transects are primarily shaped by distance and temperature. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3862–3872. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Jia, R.; Sun, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. Insights into the spatio-temporal composition, diversity and function of bacterial communities in seawater from a typical laver farm. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1056199. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.-X.; Pang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Li, J.-L.; Qin, S. Distribution of bacterial communities along the spatial and environmental gradients from Bohai Sea to northern Yellow Sea. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4272. [Google Scholar]
- Roth Rosenberg, D.; Haber, M.; Goldford, J.; Lalzar, M.; Aharonovich, D.; Al-Ashhab, A.; Lehahn, Y.; Segrè, D.; Steindler, L.; Sher, D. Particle-associated and free-living bacterial communities in an oligotrophic sea are affected by different environmental factors. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4295–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Infante, F.; Ngugi, D.K.; Vinu, M.; Alam, I.; Kamau, A.A.; Blom, J.; Bajic, V.B.; Stingl, U. Comprehensive genomic analyses of the OM43 clade, including a novel species from the Red Sea, indicate ecotype differentiation among marine methylotrophs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Rich, V.I.; Pham, V.D.; Eppley, J.M.; Shi, Y.; Delong, E.F. Time-series analyses of Monterey Bay coastal microbial picoplankton using a ’genome proxy’ microarray. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 131, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, C.M.; Guezennec, J.; Bowman, J. Bacterial exopolysaccharides from extreme marine environments with special consideration of the southern ocean, sea ice, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents: A review. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 253–271. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaitzidou, M.P.; Alvanou, M.V.; Papageorgiou, K.V.; Lattos, A.; Sofia, M.; Kritas, S.K.; Petridou, E.; Giantsis, I.A. Pollution Indicators and HAB-Associated Halophilic Bacteria Alongside Harmful Cyanobacteria in the Largest Mussel Cultivation Area in Greece. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 5285. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimipour, G.; Gilavand, F.; Karkhane, M.; Kavyanifard, A.A.; Teymouri, M.; Marzban, A. Bioemulsification activity assessment of an indigenous strain of halotolerant Planococcus and partial characterization of produced biosurfactants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Chang, S. The complete genomic sequence of a novel cold-adapted bacterium, Planococcus maritimus Y42, isolated from crude oil-contaminated soil. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2018, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.D.; Adams, N.G.; Gallego Simon, R.; Kavanaugh, M.T.; Alin, S.R.; Feely, R.A. Nearshore microbial communities of the Pacific Northwest coasts of Canada and the U.S. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1430930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, B.P.; Grote, J.; Whittaker, K.A.; Bender, S.J.; Luo, H.; Grim, S.L.; Brown, J.M.; Casey, J.R.; Dron, A.; Florez-Leiva, L.; et al. Draft genome sequence of marine alphaproteobacterial strain HIMB11, the first cultivated representative of a unique lineage within the Roseobacter clade possessing an unusually small genome. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2014, 9, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.-H. Lentibacter algarum gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from coastal water during a massive green algae bloom. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Hahnke, S.; Brock, N.L.; Zell, C.; Simon, M.; Dickschat, J.S.; Brinkhoff, T. Physiological diversity of Roseobacter clade bacteria co-occurring during a phytoplankton bloom in the North Sea. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolaños, L.M.; Choi, C.J.; Worden, A.Z.; Baetge, N.; Carlson, C.A.; Giovannoni, S. Seasonality of the microbial community composition in the North Atlantic. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 624164. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gu, L.; Bai, S.; Wang, J.; Su, L.; Wei, B.; Zhang, L.; Fang, J. Characterization of particle-associated and free-living bacterial and archaeal communities along the water columns of the South China Sea. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchman, D.L. The ecology of Cytophaga–Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 39, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Benner, R. Molecular indicators of the bioavailability of dissolved organic matter. In Aquatic Ecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 121–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C.; Yu, S.; Yin, Z.; Yang, W.; Bai, L.; Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Seasonal Differences and Driving Factors of Microbial Community Structure in Wetlands Along Shores of Daihai Lake. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, H.; Pernthaler, J.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O.; Gerdts, G.; Amann, R. Isolation of novel pelagic bacteria from the German Bight and their seasonal contributions to surface picoplankton. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5134–5142. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Wu, C.; Guo, C.; Gui, J.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. The composition and primary metabolic potential of microbial communities inhabiting the surface water in the equatorial Eastern Indian Ocean. Biology 2021, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partensky, F. Differential distribution and ecology of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in oceanic waters: A review. In Marine Cyanobacteria; Musee Oceanographique Monaco: Monaco, Monaco, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, H.A.; Ulloa, O.; Scanlan, D.J.; Zwirglmaier, K.; Li, W.K.; Platt, T.; Stuart, V.; Barlow, R.; Leth, O.; Clementson, L. Oceanographic basis of the global surface distribution of Prochlorococcus ecotypes. Science 2006, 312, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Tsui, M.M.; Lam, J.C.; Hu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Lam, P.K. Variation in microbial community structure in surface seawater from Pearl River Delta: Discerning the influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, P.; Yarza, P.; Rapp, J.Z.; Glöckner, F.O. Expanding the world of marine bacterial and archaeal clades. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1524. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lim, J.-H.; Park, J.; Kim, I.-N. Temporal and vertical variation in microbial community composition in response to physicochemical characteristics in a water column of highly eutrophied Jinhae Bay, South Korea. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales, B.; Lanfranconi, M.P.; Piña-Villalonga, J.M.; Bosch, R. Anthropogenic perturbations in marine microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 275–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.S.; Yung, C.-M.; Davis, K.M.; Blinebry, S.K.; Williams, T.C.; Johnson, Z.I.; Hunt, D.E. Annual community patterns are driven by seasonal switching between closely related marine bacteria. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Xu, X.; Kan, J.; Chen, F. Linking seasonal inorganic nitrogen shift to the dynamics of microbial communities in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3219–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettar, I.; Guzman, C.A.; Höfle, M. Human pathogens in the marine environment. In Oceans and Health: Pathogens in the Marine Environment; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billaud, M.; Czerucka, D. Exploring different methods of Exaiptasia diaphana infection to follow Vibrio parahaemolyticus dissemination in the whole animal. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Hinojosa, W.; Pardo-López, L. Analysis of bacterial metagenomes from the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico for pathogens detection. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. A spatiotemporally weighted intelligent method for exploring fine-scale distributions of surface dissolved silicate in coastal seas. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 886, 163981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, T.; Oldenburg, E.; Popa, O.; Dede, B.; Metfies, K.; von Appen, W.-J.; Torres-Valdés, S.; Bienhold, C.; Fuchs, B.M.; Amann, R.; et al. Seasonal recurrence and modular assembly of an Arctic pelagic marine microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baña, Z.; Abad, N.; Uranga, A.; Azúa, I.; Artolozaga, I.; Unanue, M.; Iriberri, J.; Arrieta, J.M.; Ayo, B. Recurrent seasonal changes in bacterial growth efficiency, metabolism and community composition in coastal waters. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Nan, R. A bibliometric analysis of eutrophication literatures: An expanding and shifting focus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17103–17115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnow, N.; Chibani, C.M.; Güllert, S.; Weiland-Bräuer, N. Microbial community changes correlate with impaired host fitness of Aurelia aurita after environmental challenge. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Vásquez, T.; Fagorzi, C.; Mengoni, A.; Oliva, M.; Cavalieri, D.; Pretti, C.; Cangioli, L.; Bacci, G.; Ugolini, A. Metagenomic surveys show a widespread diffusion of antibiotic resistance genes in a transect from urbanized to marine protected area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 213, 117640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Month | T (°C) | S | DO (mg/L) | pH | TOC (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | NO2− (mg/L) | NH4+ (mg/L) | DON (mg/L) | DTP (mg/L) | PO43− (mg/L) | N\P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April | 17.3 | 27.8 | 9.54 | 7.93 | 3.69 | 0.27 | 0.249 | 0.21 | 4.61 | 0.05 | 0.033 | 49 |
| May | 22.8 | 28.6 | 10.57 | 7.94 | 2.89 | 0.04 | 0.010 | 0.22 | 2.87 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 60 |
| June | 23.5 | 27.0 | 7.28 | 7.96 | 2.00 | 0.12 | 0.030 | 0.22 | 3.43 | 0.09 | 0.001 | 826 |
| July | 28.6 | 31.3 | 7.75 | 8.01 | 2.94 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.26 | 3.49 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 60 |
| August | 28.7 | 24.3 | 7.69 | 8.02 | 2.74 | 0.26 | 0.002 | 0.28 | 2.67 | 0.08 | 0.035 | 34 |
| September | 28.9 | 31.7 | 7.63 | 8.21 | 1.79 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.27 | 7.13 | 0.04 | 0.014 | 47 |
| October | 24.6 | 23.5 | 8.00 | 7.85 | 2.39 | 0.05 | 0.065 | 0.25 | 2.07 | 0.12 | 0.005 | 163 |
| November | 20.3 | 24.3 | 8.36 | 8.05 | 2.56 | 0.21 | 0.016 | 0.30 | 1.80 | 0.10 | 0.027 | 43 |
| December | 15.4 | 25.4 | 9.82 | 8.06 | 3.78 | 0.27 | 0.013 | 0.33 | 2.47 | 0.08 | 0.028 | 49 |
| N_January * | 12.0 | 25.3 | 10.87 | 7.93 | 2.28 | 0.30 | 0.007 | 0.34 | 2.38 | 0.07 | 0.025 | 57 |
| N_February * | 9.50 | 23.4 | 11.14 | 8.06 | 5.71 | 0.35 | 0.070 | 0.28 | 2.22 | 0.10 | 0.005 | 310 |
| N_March * | 13.4 | 32.0 | 10.34 | 7.99 | 4.96 | 0.25 | 0.020 | 0.26 | 2.55 | 0.09 | 0.003 | 391 |
| Mean | 20.4 | 27.0 | 9.08 | 8.00 | 3.14 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 3.14 | 0.08 | 0.016 | 174.18 |
| SD | 6.55 | 3.08 | 1.38 | 0.39 | 1.14 | 0.12 | 0.067 | 0.04 | 1.41 | 0.03 | 0.012 | 226.29 |
| RSD (%) | 311.62 | 877.56 | 659.79 | 1999.8 | 275.74 | 153.2 | 60.92 | 676.78 | 223.06 | 309.79 | 136.96 | 76.97 |
| Geographic Location | Dominant Taxa | Influencing Factors | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Distribution | Proteobacteria, SAR11 (Alphaproteobacteria), SAR86 (Gammaproteobacteria); Cyanobacteria, Deferribacteres, Thaumarchaeota; | Light, Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, Nutrients and Carbon sources | [36] |
| Arctic Region | Proteobacteria, Bacteriodetes; class level, Alphaproteobacteria, Flavobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria; | Spatial and Seasonal Variability, Nutrients | [37] |
| Shenzhen Area | Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes; genus level, Acinetobacter, NS5 marine group (Flavobacteriaceae), Candidatus Actinomarina, HIMB11 (Rhodobacteraceae), Candidatus Nitrosopumilus, Candidatus Aquiluna, Aeromonas, Cyanobium PCC-6307, Arcobacter, Synechococcus CC9902 and Ottowia, which accounted for 6.2%, 5.9%, 5.8%, 5.8%, 5.0%, 3.7%, 3.1%, 2.1%, 2.0%, 1.7% and1.5%; | Salinity and TN | [38] |
| Northern Java, Indonesia | Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria and Bacteroidia (38%, 18% and 16%); | Salinity and Temperature | [39] |
| Dongzhai Bay, Hainan (Aquaculture Zone) | Proteobacteria (59.19–75.19%), Cyanobacteria (6.54–22.84%), Bacteroidetes (8.45–14.51%), Actinobacteria (1.36–11.68%), Marinimicrobia SAR406 clade (0–1.72%), Verrucomicrobia (0.23–1.2%), Epsilonbacteraeota (0.14–1.03%), Euryarchaeota (0–0.72%), Chloroflexi (0–0.64%) and Planctomycetes (0.11–0.56%); | Salinity, Temperature, pH, NH4+-N, COD, and TN | [40] |
| Southeastern New South Wales Coast, Australia | Proteobacteria (47.33% ± 2.14), Bacteroidota (21.97% ± 1.35), Cyanobacteria (16.76% ± 2.20), Actinobacteria (11.80% ± 0.84), Verrucomicrobiota (0.56% ± 0.08), Planctomycetota (0.37% ± 0.05), Chloroflexota (0.15% ± 0.04) and SAR324 clade (0.15% ± 0.04); | Seasonal Variability, pH, Salinity, Average depth, Flushing time, and Percentage of the catchment i.e., cleared | [41] |
| Antarctic Region | Bay: Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria and Bacteroidota (42.07%, 24.67% and 33.03%); Lake: Bacteroidota, Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria (34.17%, 24.53% and 21.57%); | pH, Salinity, DO, and PO43−-P | [42] |
| Bohai Sea, China | Proteobacteria (45.93–72.9%), Bacteroidetes (15.03–34.65%), Actinobacteria (2.25–13.68%), Cyanobacteria (0.79–10.20%), Planctomycetes (1.46–2.18%), Firmicutes (0.77–3.75%), Acidobacteria (0.78–2.15%), Chloroflexi (0. 28–3.47%); | Nutrients and Dissolved Oxygen | [43] |
| Yellow Sea | In Sediment: Proteobacteria (47%), Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Planctomycetes and Verrucomicrobia; Bacteroides, Myxococcus, Flavobacterium, Planctomycetes and Verrucomicrobium; | TP, Particle Size, TN, and TOC | [44] |
| Southwestern Coast of India | In the laboratory: Diatoms, Small (<5 µm diameter) flagellated cells and the microzooplankton Protoperidinium spp. | Salinity and Temperature | [13] |
| Wenzhou | Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota, Cyanobacteria, HIMB11, OM43 clade, and SAR86 clade; | Temperature, NO3−, DO, NO2− and TOC | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Z.; Jin, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Ren, C.; Qiao, L. Monthly Variation, Environmental Drivers, and Ecological Functions of Marine Bacterial Community in a Eutrophic Coastal Area of China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040837
Yan Z, Jin Y, Li T, Zhang X, Yang Q, Ren C, Qiao L. Monthly Variation, Environmental Drivers, and Ecological Functions of Marine Bacterial Community in a Eutrophic Coastal Area of China. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040837
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Zezheng, Yanjian Jin, Tiejun Li, Xiaoling Zhang, Qiao Yang, Chengzhe Ren, and Ling Qiao. 2025. "Monthly Variation, Environmental Drivers, and Ecological Functions of Marine Bacterial Community in a Eutrophic Coastal Area of China" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040837
APA StyleYan, Z., Jin, Y., Li, T., Zhang, X., Yang, Q., Ren, C., & Qiao, L. (2025). Monthly Variation, Environmental Drivers, and Ecological Functions of Marine Bacterial Community in a Eutrophic Coastal Area of China. Microorganisms, 13(4), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040837






