Abstract
The ciliate parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis poses significant threats to grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) aquaculture. However, the limited understanding of host microbiota shifts and immune responses hinders effective control strategies. This study integrated analyses of host pathological indices, immune response and skin/gill/gut microbiota shifts after I. multifiliis infection. A histopathological examination identified gill and fin tissues embedded with I. multifiliis, accompanied by epithelial necrosis, and inflammatory cell infiltration. Biochemical profiling revealed marked elevations in aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), urea (UREA), and creatinine (CREA) levels, indicating impaired hepatic and renal function. Quantitative RT-PCR analyses demonstrated the up-regulation of mucosal immune gene IgT and pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α while increasing the trend of systemic immune gene IgM. 16S rRNA sequencing revealed significant reductions in skin microbiota diversity. At the genus level, opportunistic pathogens Aeromonas and Vibrio proliferated in the intestine, whereas Flavobacterium and Candidatus Megaira increased in the skin and gills. Correlation analyses identified positive associations between Aeromonas/Vibrio abundance and host phenotype, contrasting with negative correlations observed for Sphingomonas, Acinetobacter, and Leifsonia. These findings demonstrate that I. multifiliis infection induces host microbiome dysbiosis and potentially opportunistic bacterial infections. This investigation advances our understanding of tripartite host–microbiota–parasite interactions and supports microbial community-based parasitosis control in fish culture.
1. Introduction
Parasitic infections pose a significant threat to intensive aquaculture, impacting both fish health and economic productivity. Traditionally, the control of fish parasitic diseases has heavily relied on chemical treatments, which, while effective, raise concerns over food safety and environmental sustainability [1]. This has spurred a growing interest in developing eco-friendly alternatives for parasite control. Based on the discovery of the “host–microbiota–parasite” interaction mechanism [2,3,4], researchers have initiated the study of an alternative strategy utilizing gut microbes to combat parasitic infections in sheep [5].
While the tripartite interactions among the “host, microbiota, and parasite” have been extensively studied in mammals [2,3,6,7,8], research in fish is still catching up. Nonetheless, there has been a notable increase in studies exploring parasite–microbiota interactions in fish, including those involving the skin microbiota and ectoparasites [4], gut microbiota and intestinal parasites [9,10,11,12], and even gut microbiota and kidney parasites [13]. Additionally, there is evidence that ectoparasites on fish gills can influence the gut microbiota at a distance [14]. Despite these advances, the mechanisms underlying “host–microbiota–ectoparasite” interactions in fish remain poorly understood.
Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus), a cornerstone of freshwater aquaculture in China, plays a dual role in food production and water quality management, making it a globally significant species [15,16]. However, its husbandry is frequently challenged by parasitic infections, particularly by the ectoparasite ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, which inflicts substantial economic losses [17,18,19]. Besides grass carp, I. multifiliis infects a wide range of freshwater fish species, including rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus), and goldfish (Carassius auratus) [4,18,19,20,21]. This ectoparasite undergoes a complex life cycle, involving three main stages: invasive theronts in water, feeding trophonts that primarily infest fish gills and skin, and reproductive tomonts that release new infectious larvae. I. multifiliis, characterized by its low host specificity and confinement to the surface epithelial cell layers in fish, serves as an ideal model for studying host mucosal immunity and parasite–microbiota interactions [4,20,21]. In rainbow trout, I. multifiliis infection triggers mucosal immune responses, including IgT binding and TNF-α up-regulation, alongside microbiota alterations [4,22,23]. Similarly, grass carp exhibit immune activation through Toll-like receptor pathways and cytokine interactions [24,25,26], However, the specific mucosal immune responses and associated microbiota alterations during I. multifiliis infection remain poorly understood. Furthermore, the complex mechanisms underlying the tripartite interactions among the host, microbiota, and parasite have yet to be elucidated.
Here, we integrated 16S rRNA sequencing, histopathology, biochemical and qRT-PCR techniques to investigate how the ideal model ectoparasite I. multifiliis infection alters the short-range (skin and gill) and long-range (intestine) microbiota in grass carp while assessing associated tissue damage and immune markers. Our findings attempt to enhance the understanding of “host–microbiota–parasite” interactions, providing a possible foundation for microbial-based disease management in aquaculture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Infection Experiment
All experimental fish protocols were approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethic Committee Pearl River Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS (No.: LAEC-PRFRI-2024-03-44).
2.1.1. Infection of Parasites
Parasite-Free Grass Carp
Juvenile grass carp with a body weight of 30~50 g were obtained from the Pearl River Fisheries Research Institute of CAFS in Guangzhou, China. These fish were cultured in several 1000 L aquaria equipped with aerators, maintaining water temperatures at 24.0 ± 2 °C, dissolved oxygen ≥ 5.0 mg/L, ammonia nitrogen concentrations < 0.35 mg/L, and nitrite nitrogen concentrations < 0.01 mg/L. Prior to their introduction into the tanks, the fish underwent three consecutive formalin baths, each involving immersion in a final concentration of 100 × 10−6 formalin solution for 1 h, with 48 h intervals between treatments, to eliminate all ecto-parasites. Subsequently, grass carp were randomly selected for testing parasitic, bacterial, and viral infections. For parasite detection, 30 fish were randomly chosen and anesthetized by immersion in 100 mg/L Tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA). Following anesthetization, each sample was thoroughly examined for parasites using a stereomicroscope (Zeiss Axio, Germany, 16× continuous zoom) and a microscope (Nikon Eclipse 80i, Japan) at magnifications of ×40, ×100, ×400, and ×1000. It was confirmed that each fish was free of parasitic infection. For bacterial and viral detection, 10 fish were randomly selected and, after MS-222 anesthesia, were handled on a strictly sterile clean bench. Grass carp reovirus (GCRV) was detected from liver, kidney, and spleen tissues using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) methods. For bacterial detection, Flavobacterium species from fish gills were selected isolated by using Shieh selective medium [27]. Additionally, 5% blood agar media and nutrient agar were used to isolate and identify bacteria such as Aeromonas and Vibrio species from liver, spleen, and kidney tissues, according to the methods in the literature [28].
Parasitic Infection in Grass Carp
The methods for parasite isolation and infection were based on procedures previously described the literature [26,29]. The serial passage of I. multifiliis at the Pearl River Fisheries Research Institute of CAFS were overdosed with the anesthetic MS-222 and placed in a water-filled container to facilitate the excretion of trophonts in the water. After 4 h, the fish were removed from the water and the trophonts remained and were kept at 15 °C ± 1.0 °C for approximately 24 h to form tomonts, which subsequently released theronts.
For parasite infection, grass carp were exposed to an optimal parasitic dose after parasite infective dose pre-screening assays. Preliminary studies of dose–response trials showed that the LD50 in grass carp at 14 days of the experiment was approximately 6000 theronts per fish in 600 L water, which was approximately 300 theronts/L water.
Experimental Fish Grouping
After the acclimatization/microbial check phases for 2 weeks, 360 grass carp were divided into two groups, 180 in the control (un-infected) group and 180 in the experimental (infected) group, with each group having 6 replicas. The formal assay used 12 tanks (30 fish/tank), and each tank had an aerator and was filled with 600 L filtered water. During the experiment, 30% of the water was changed every day. The fish were fed with a pellet feed (protein content of 28%) every day, and the daily dosage was approximately 1% of their body weight.
In the formal infection experiment, for the infected group, we added approximately 3000 theronts per fish into each tank (150 theronts/L). The control fish (the uninfected group) were fed and maintained similarly but were not exposed to parasites.
For microbiota, serum biochemical, and immune gene expression analyses, we collected 3 fish tissues and mixed them to form 1 sample. For microbiota analyses, for each group, 6 samples were obtained and sequenced on day 11, while for serum biochemical indicators, 8 samples were tested on day 11. This means we used 24 fish in the uninfected and infected group for the serum biochemical indicator test and 18 fish in each group for microbiota analyses. The fish for the immune gene testing were sampled according to the experimental timeline (at days 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, and 11), with each group tested at 6 time points with 6 samples (18 fish) per time point, which means there were 108 fish in each group for the immune gene expression testing.
2.2. Sample Collection
For the analyses of biochemical indicators, blood was collected from the caudal vein of each fish using sterile, heparin-free syringes and kept at 4 °C for approximately 12 h to allow serum precipitation. Subsequently, the serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000× g for 10 min at 4 °C, and we collected 3 fish sera in one sterile tube, which was stored at −80 °C for further analysis. To analyze microbiota, gill samples, skin mucus samples, and posterior intestinal samples were collected under sterile conditions. Specifically, approximately 0.5 g of gill tissue was collected by using sterile scissors. Skin mucus was collected by scraping the lateral sides of the fish with a sterile scraper. And samples approximately 2.0 cm in length containing intestinal contents were collected by using sterile scissors. Under sterile conditions, each tissue sample from 3 fish was individually placed into sterilized and pre-labeled Eppendorf tubes and stored at −80 °C. For the analyses of immune-related gene expression levels, samples from the gill, skin, and kidney were collected on days 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, and 11 after infection, frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C. Additionally, for histopathological analyses, tissue samples of the gills and skin were collected and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde.
2.3. Biochemical Analysis
To investigate the impact of parasitic infection on the internal organs of grass carp, we measured eight related serum biochemical indicators. These included liver functional parameters—alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBIL), and lactate dehydrogenase 1 (LDH1); heart functional parameters—creatine kinase (CK), creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB), and LDH1; and kidney function parameters—creatinine (CREA) and urea (UREA). All indicators were measured using commercial assay kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
Fish tissue samples were fixed in 4% (w/v) paraformaldehyde for 24 h. Following fixation, the samples underwent dehydration using an ethanol gradient, clearing them with xylene, and were then embedded in paraffin according to standard histological techniques. Sections were cut to a thickness of 5 µm using a rotary microtome (RM2235, Leica Camera Company, Wetzlar, Germany) and mounted onto glass slides. The sections were subsequently stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Histological samples were observed and photographed using a compound microscope (Olympus BX41, Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
2.5. Microbiota Analysis
2.5.1. DNA Extraction
Genomic DNA from posterior intestinal, gill, and skin mucus samples was extracted using the Guide S96 Magnetic Soil/Fecal DNA Extraction Kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). DNA concentration was determined using the Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay Kit and the Qubit 4.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.5.2. PCR Amplification
The V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified from genomic DNA extracted from gill, skin, and posterior intestinal tissues using the universal primers 341F(5′-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′) and 805R(5′-GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3′). To facilitate high-throughput sequencing, sample-specific Illumina index sequences were added to the 5′ ends of both forward and reverse primers. PCR amplification was carried out in a 25 µL reaction mixture containing 50 ng template DNA, 2.5 µL each of forward and reverse primers (10 µM), 12.5 µL Phusion Hot Start Flex 2X Master Mix, and nuclease-free water to reach the final reaction volume. PCR conditions included initial denaturation at 98 °C for 30 s, followed by 35 cycles consisting of denaturation at 98 °C for 30 s, annealing at 54 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 45 s, with a final extension step at 72 °C for 10 min. PCR products were visualized on 2% agarose gels to verify successful amplification. Throughout DNA extraction and amplification processes, ultrapure water was used as a negative control instead of DNA samples to rule out false positive results. PCR products were subsequently purified using AMPure XT beads (Beckman Coulter Genomics, Danvers, MA, USA) and quantified using a Qubit fluorometer (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). The size and concentration of the amplicon libraries were assessed using an Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and Illumina library quantification kits (Kapa Biosystems, Boston, MA, USA), respectively. Finally, The libraries were sequenced on the NovaSeq PE250 platform.
2.5.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
Samples were sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq platform according to the manufacturer’s protocols. Paired-end sequences were sorted based on unique sample barcodes, and the introduced barcode and primer sequences were subsequently trimmed. Overlapping paired-end reads were merged using FLASH software. Raw sequencing reads underwent quality control using fqtrim (version 0.94) under defined filtering parameters to obtain high-quality clean sequences. Chimeric sequences were identified and removed with Vsearch (version 2.3.4). The DADA2 algorithm was employed for sequence denoising, resulting in the generation of a representative feature sequence set and feature abundance tables. Diversity metrics were calculated by normalizing to the same random sequence depth. Taxonomic classifications and relative abundances of microbial features were determined using the SILVA database (release 132). Alpha diversity, representing microbial diversity within samples, was evaluated using the Chao1, Observed Species, Good’s Coverage, Shannon, and Simpson indices through QIIME2 software. Beta diversity was analyzed using QIIME2 and visualized through R packages. Sequence alignment was performed using QIIME2 and lastal+(1.04)BLAST, and each representative sequence was annotated against the SILVA and NT database. Spearman’s rank correlation analyses were conducted to examine associations between microbial taxa and phenotypic traits. Additional figures were produced using R software (version 3.5.2).
2.6. Expression Analysis of Selected Immune-Related Genes
Tissues were homogenized and total RNA was isolated using TRIzol LS reagent (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Total RNA was incubated with RNase-free DNase I (Roche, Indianapolis, IN, USA) to remove contaminating genomic DNA, and then the RNA samples were reverse transcribed into cDNA using random hexamer primers and Moloney murine leukemia virus (MMLV) reverse transcriptase (Takara, Shiga, Japan) and stored at −20 °C until further analysis.
The immune-related genes determined in our study included those encoded for immunoglobulin T (IgT), immunoglobulin M (IgM),and Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-α). The qRT-PCR mixture consisted of 10 μL of 2× SYBR Green PCR master mix (TaKaRa), 7.2 μL of nuclease-free water, 0.4 μL of each gene specific primer (10 mM), and 2 μL of cDNA. The expression levels of immune-related genes were calculated using 2–ΔΔCT to indicate an n-fold difference relative to the calibrator. β-actin was used as the reference gene. The primers are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Primers used to determine relative expression of immune-related genes.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted on the three groups of data. If significant differences were detected (p < 0.05), Duncan’s multiple range test was employed to rank the means. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Pathogen Detection Demonstrated That I. multifiliis Successfully Infected Grass Carp, Followed by Secondary Bacteria Invasion
Detailed parasite detection results indicated that no parasites were found in the gills, skin, fins, muscle, eyes, blood, intestine, liver, spleen, and swim bladder of fish in the control (uninfected) group. In contrast, the infected group exhibited only the parasite I. multifiliis in the gills, skin, fins, and head eye orbit. Additionally, the detection of grass carp reovirus (GCRV) yielded negative results both in the uninfected and infected groups. Interestingly, the bacteria (Flavobacterium and Aeromonas) were determined to be positive in the infected group while negative in the control group. The comprehensive pathogen detection results demonstrated that parasite I. multifiliis infection was identified, followed by opportunistic pathogens being isolated, thereby confirming that the disease in grass carp was primarily caused by I. multifiliis (Table 2).

Table 2.
Pathogen detection results in uninfected and infected grass carp.
3.2. Histopathology Suggested That the Trophonts of I. multifiliis Could Be Embedded in Epithelial Cells of Infected Fish Gills and Skin
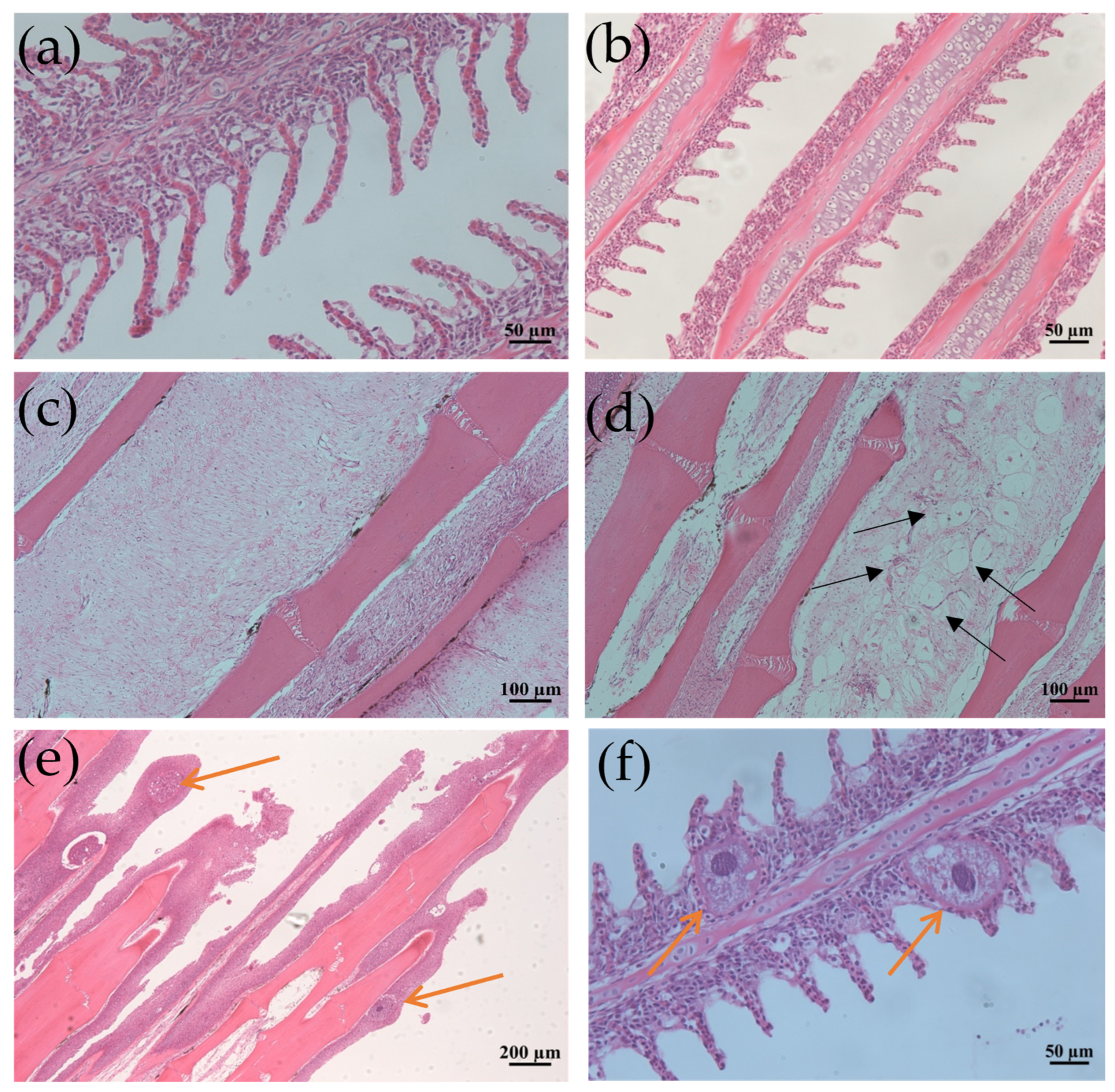
Grass carp infected with I. multifiliis exhibited notable histopathological alterations compared to the control fish. In histological sections of the fins and gills of the infected fish, parasitic trophonts were observed, typically embedded in epithelial cells. The structural features of the parasites, including large horseshoe-shaped nuclei, cytoplasmic food vacuoles, and superficial cilia, were frequently visible. Parasitism by I. multifiliis on the gills led to lamellar deformation, capillary congestion, exudation, or localized ischemia, as well as the swelling and necrosis of respiratory epithelial cells. Additionally, there was the hyperplasia of mucous cells with increased secretion, accompanied by the substantial infiltration of eosinophils and lymphocytes. In cases of severe infection, hyperplasia and inflammatory cell infiltration, along with epithelial cell necro and vacuolar degeneration, were observed (Figure 1).
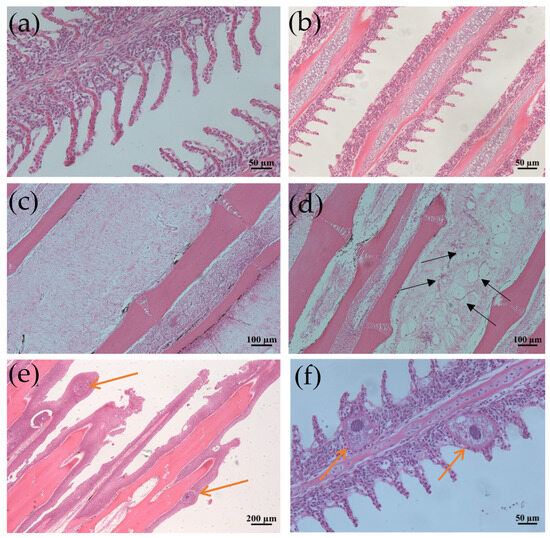
Figure 1.
Histological section changes in gills and fins caused by I. multifiliis infection in grass carp. (a) Normal gill filaments. (b) Gill filaments after infection. (c) Normal fin rays. (d) Fin rays after infection. Black arrows point to the mucous cells. (e) Significant epithelial hyperplasia, partial loss of fins due to severe infection. (f) Enlarged view of gill filaments infected by I. multifiliis. Yellow arrows show trophonts in (e,f).
3.3. Serum Biochemical Changes Indicated That I. multifiliis Infection Significantly Induced Hepatic and Renal Injury in Grass Carp
The results of the biochemical indicator examination for grass carp in the I. multifiliis-infected group and the uninfected group are presented in Table 3. The findings revealed that grass carp in the infected group exhibited significant differences in multiple physiological indicators. Specifically, the activities of AST and ALT were markedly elevated in the infected group, increasing by 3.85-fold and 2.87-fold, respectively, compared to the uninfected group (p < 0.05). This suggests that the infection may have caused liver cell damage. Additionally, the levels of UREA and CREA were significantly higher in the infected group (p < 0.05), indicating a potential impact of the infection on the renal function of grass carp. CK and its isoenzyme CK-MB showed a tendency to increase in the infected group but no significant differences with the control group (p > 0.05), which might reflect certain influences on heart function after I. multifiliis infection. These data indicate that external parasitic infection significantly affects multiple physiological functions in grass carp, particularly with pronounced effects on liver and kidney indicators.

Table 3.
Biochemical indicators of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) infected and uninfected with I. multifiliis.
3.4. Alterations of the Microbiota in Skin, Gills, and Intestine Indicated I. multifiliis Infection Increased the Abundance of Opportunistic Pathogen Bacteria
16S rRNA sequencing showed that after trimming and filtering, a total of 739,796 high-quality clean reads were obtained from gill samples, 738,993 from intestine samples, and 795,376 from skin samples (with six replicates for each sample). Following the removal of sequences classified as “unknown”, “cyanobacteria”, “chloroplast”, and “mitochondria”, similarity clustering resulted in 1931 Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs) in gill samples, 1074 ASVs in intestine samples, and 2369 ASVs in skin samples.
3.4.1. NMDS Analysis
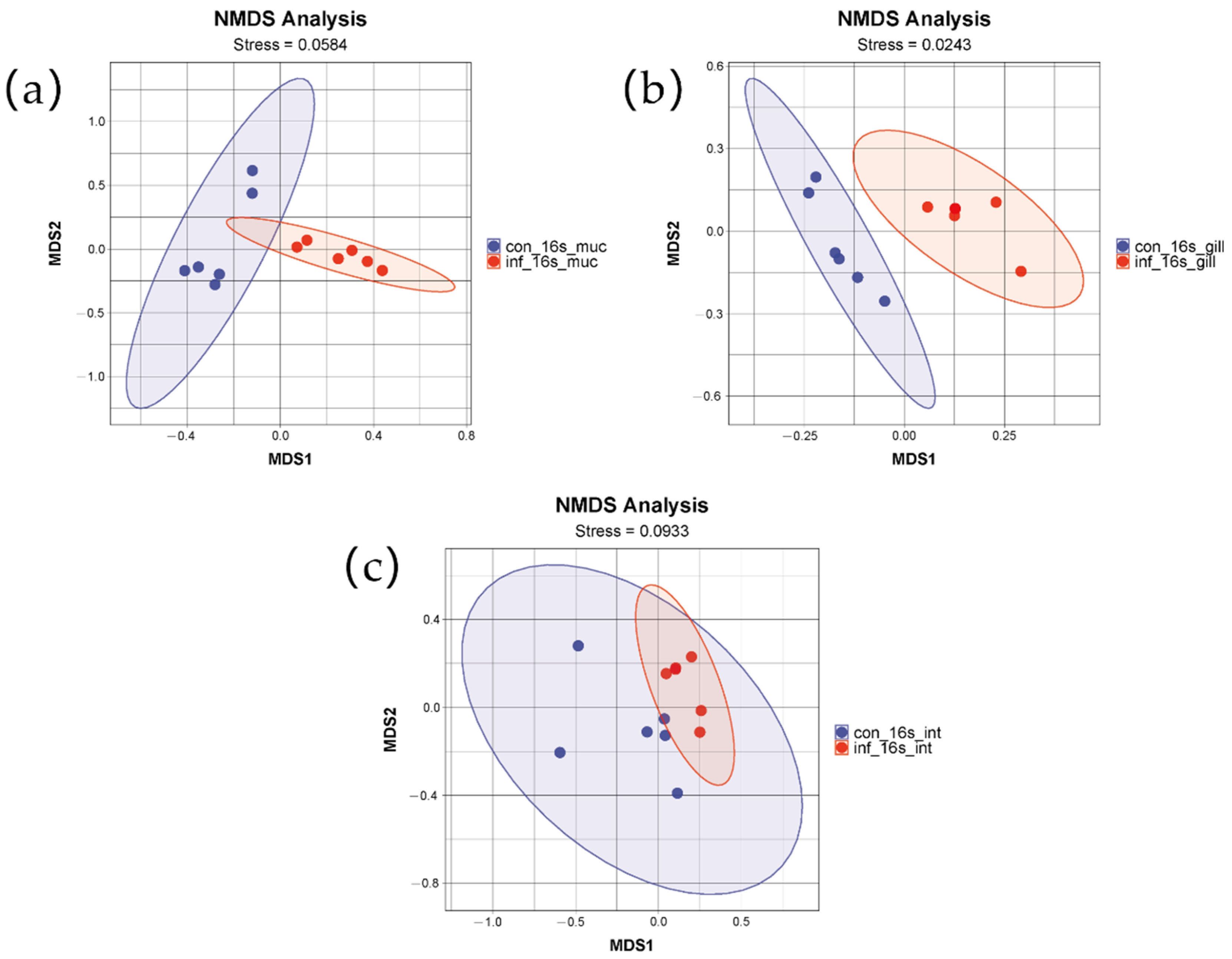
To assess the differences in microbial community structure between the control group and the infected group, non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) based on weighted UniFrac distances was employed. The NMDS results for the gills, intestine, and skin, as depicted in the figures, clearly demonstrate significant differences between the two groups (Figure 2). The distributions of the two groups in the two-dimensional space formed two distinctly separated clusters, indicating that the infection had a significant impact on the microbial community structure. The stress values were 0.02, 0.09, and 0.0584, respectively, indicating that the NMDS analyses for the three tissues exhibited good fitting and were capable of accurately reflecting the multidimensional data characteristics of the community structures.
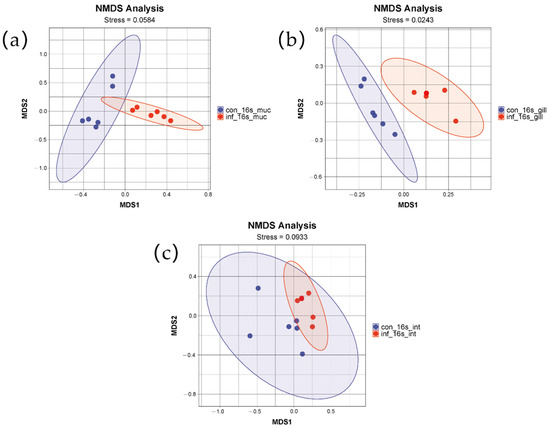
Figure 2.
NMDS analysis of skin, gill, and intestinal microbiomes in grass carp after infection with I. multifiliis. (a) Skin. (b) Gill. (c) Intestine. Red color indicates samples infected with I. multifiliis. Blue color indicates uninfected samples.
3.4.2. Alpha Diversity of Microbiota
Skin
In the skin microbial communities, infection significantly impacted species richness and diversity. The Observed Species decreased from 452.00 ± 10.12 in the control group to 280.17 ± 12.45 in the infected group, the Shannon index from 5.38 ± 0.33 to 3.64 ± 0.45, and the Chao1 index from 455.19 ± 15.45 to 281.92 ± 13.65, all exhibiting significant differences (p < 0.05). These results indicated that infection markedly reduced both the number of species and the diversity in the skin microbiota. However, the Simpson index decreased from 0.86 ± 0.05 to 0.73 ± 0.04, which did not reach statistical significance but suggested a reduction tendency in species evenness (Table 4).

Table 4.
Alpha diversity of skin, gill, and intestine microbiota community in grass carp infected with I. multifiliis and in control group.
Gill
The gill microbial communities experienced less pronounced changes compared to the skin and intestines. The Observed Species decreased from 341.00 ± 10.12 in the control group to 321.50 ± 12.45 in the infection group, the Shannon index from 3.93 ± 0.33 to 3.37 ± 0.45, and the Simpson index from 0.70 ± 0.05 to 0.68 ± 0.04. However, these changes did not achieve statistical significance (p > 0.05), indicating that infection had a minimal impact on the gill microbial communities (Table 4).
Intestine
In the intestinal microbial communities, notably, the Simpson index significantly declined in the infected group (p < 0.05), from 0.65 ± 0.04 to 0.52 ± 0.05, indicating that infection substantially reduced the evenness of the intestinal microbiota. the impact of infection on species richness was minimal, with Observed Species slightly decreasing from 177.33 ± 12.45 in the control group to 172.50 ± 10.12, a change that was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). The Shannon index decreased from 2.88 ± 0.45 to 2.57 ± 0.33, also without significant difference. The Chao1 index exhibited minimal change, suggesting that infection had a limited effect on the potential species richness in the intestine (Table 4).
3.4.3. Skin Microbiota Diversity Reduced from ASV Distribution Venn Diagram Analysis
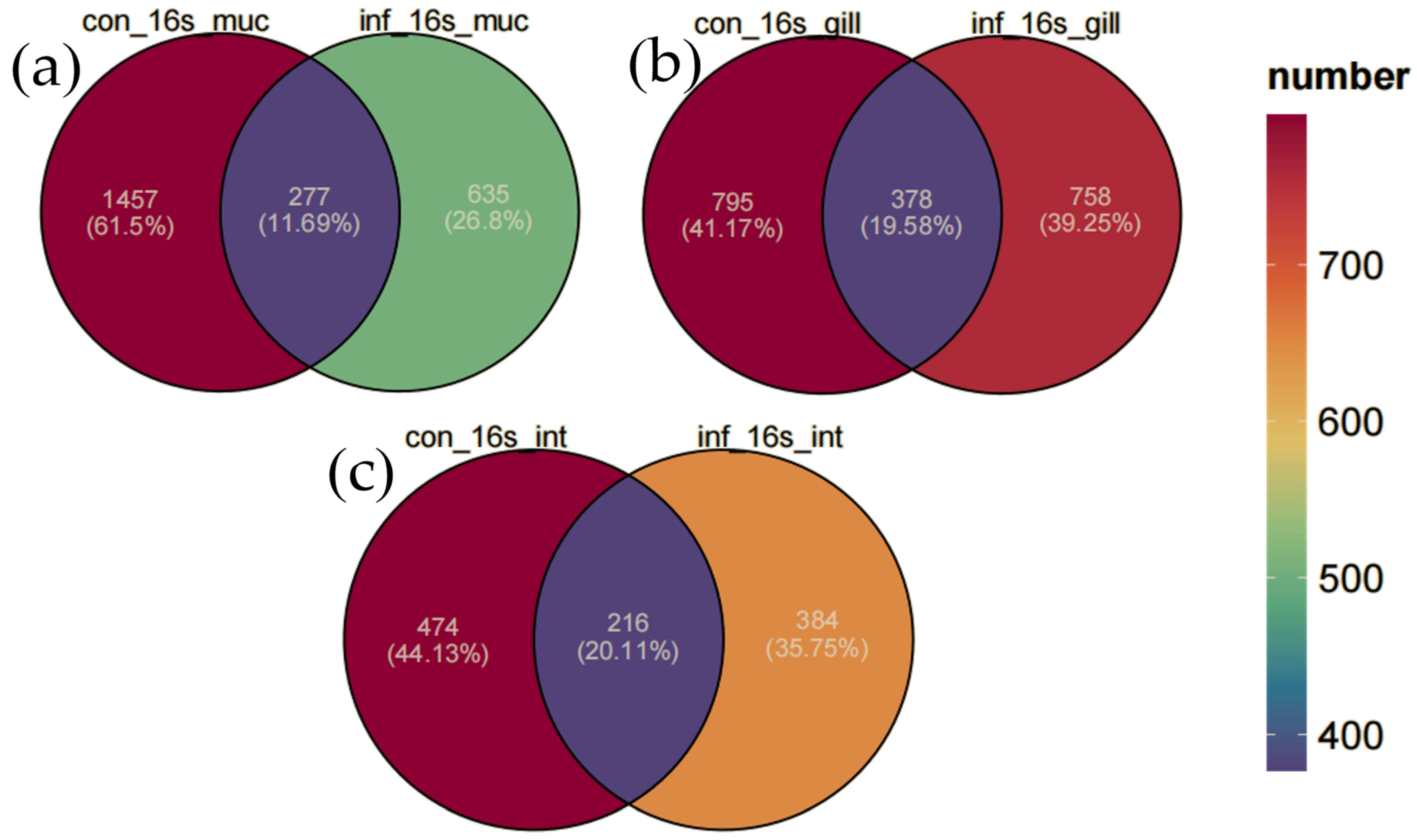
In this study, Venn diagrams were employed to analyze the changes in the microbial communities of the skin, gills, and intestine of grass carp before and after infection (Figure 3). The microbial communities in the skin of the control group possessed 1457 unique ASVs (61.5%), and the infected group had 835 unique ASVs (35.2%). The results revealed that infection significantly reduced the diversity of the skin microbiota, with a substantial decrease in the number of unique ASVs. However, in contrast, the microbial communities in the gills and intestine remained relatively stable. Specifically, in the gills, the control group contained 795 unique ASVs (41.7%), the infected group had 758 unique ASVs (39.8%), and they shared 378 ASVs (19.5%). In the intestine, the control group featured 474 unique ASVs (44.1%), the infected group had 384 unique ASVs (35.7%), and they shared 216 ASVs (20.1%). Overall, the number of ASVs declined in all three tissues in the infected group, with the sharpest decrease in the skin, a moderate reduction in the intestine, and the least in the gill.
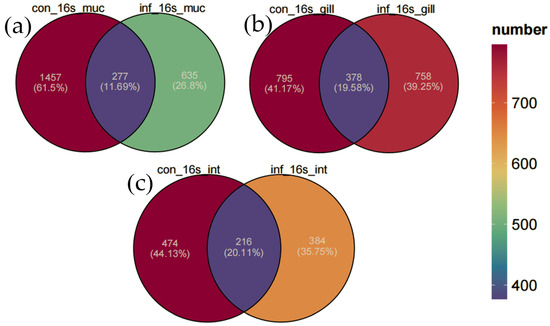
Figure 3.
Venn diagram of ASV distribution. (a) Skin. (b) Gill. (c) Intestine.
These results indicate that the microbial communities of different tissues in grass carp respond differently to I. multifiliis infection. The skin microbiota exhibited the most pronounced changes, while the gill microbiota maintained the highest level of stability despite the infection.
3.4.4. Microbiota Composition Influenced by I. multifiliis Infection
At the Phylum Level
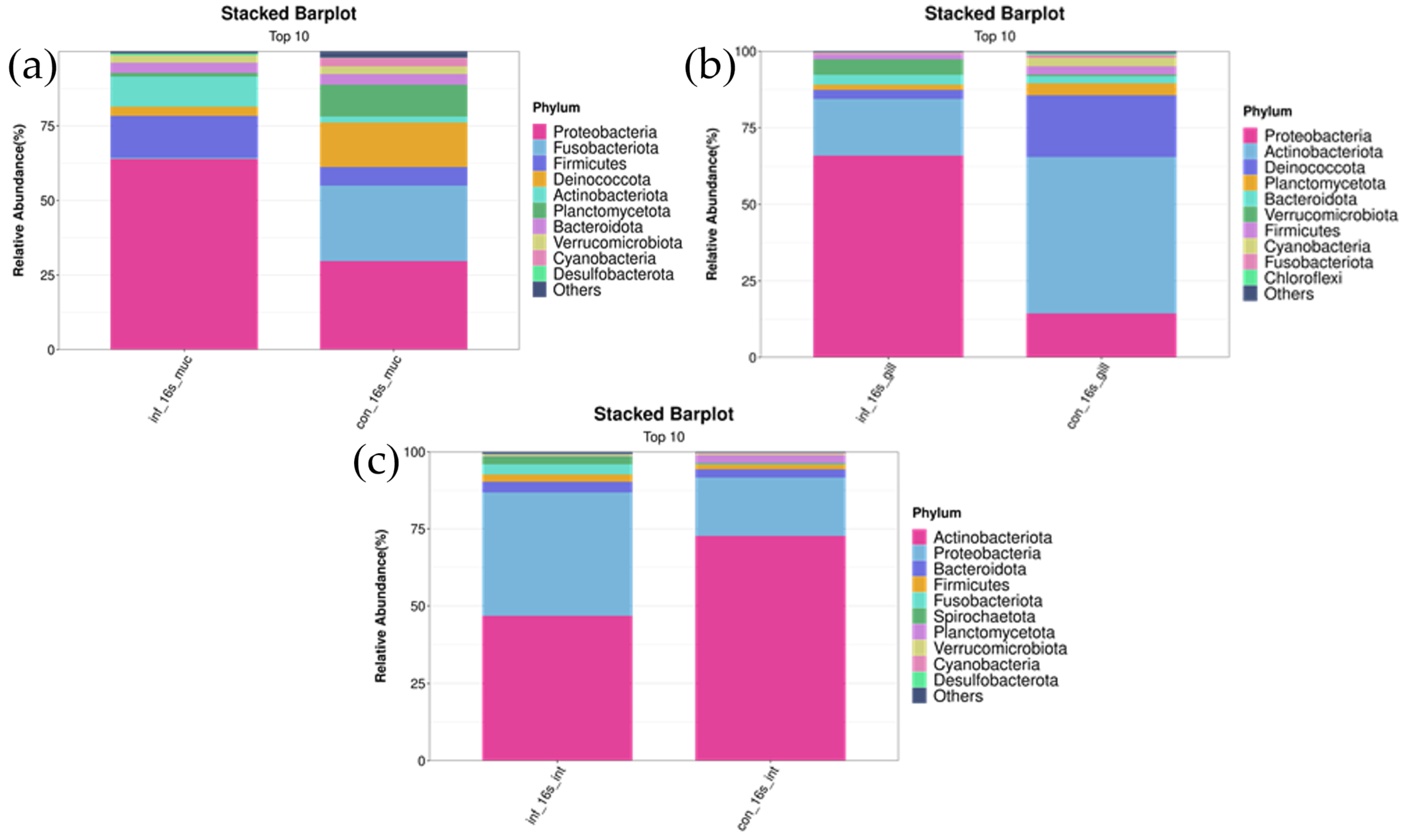
In the skin, Proteobacteria, Deinococcota, and Firmicutes were the most abundant bacterial phyla in both groups. Compared to the control group, the infected group had a lower abundance of Deinococcota (infected group: 3.1 ± 1.9% vs. control group: 14.8 ± 12.0%, p < 0.05), while the abundance of Proteobacteria was higher (infected group: 64.0 ± 18.2% vs. control group: 29.7 ± 19.0%, p < 0.01). As for Firmicutes, although the abundance was higher in the infected group compared to the uninfected group (infected group: 14.0 ± 9.5% vs. control group: 6.2 ± 2.5%), the difference did not reach statistical significance (p > 0.05) (Figure 4a).
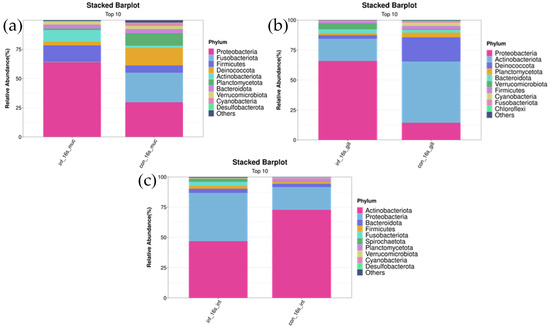
Figure 4.
Stacked bar chart of top 10 bacterial phyla in skin, gill, and intestinal microbiomes of I. multifiliis infection and control grass carp. (a) Skin. (b) Gill. (c) Intestine.
In the gills, Actinobacteriota and Proteobacteria were the two most abundant bacterial phyla in both the control and infected groups. Compared to the uninfected group, the abundance of Actinobacteriota significantly decreased in the infected group (infected group: 18.5 ± 11.3% vs. control group: 51.1 ± 24.1%, p < 0.05), whereas the abundance of Proteobacteria significantly increased (infected group: 66.0 ± 10.7% vs. control group: 14.5 ± 4.5%, p < 0.01) (Figure 4b).
In the intestine, Actinobacteriota, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidota were the most abundant bacterial phyla in both groups. Compared to the uninfected group, the infected group had a lower abundance of Actinobacteriota (infected group: 46.9 ± 31.1% vs. control group: 72.6 ± 9.0%, p < 0.01) and a higher abundance of Proteobacteria (infected group: 40.0 ± 20.4% vs. control group: 18.9 ± 5.4%, p < 0.05). The abundance of Bacteroidota did not differ significantly between the infected and uninfected groups (infected group: 2.6 ± 1.9% vs. control group: 3.5 ± 4.1%, p > 0.05) (Figure 4c).
At the Genus Level
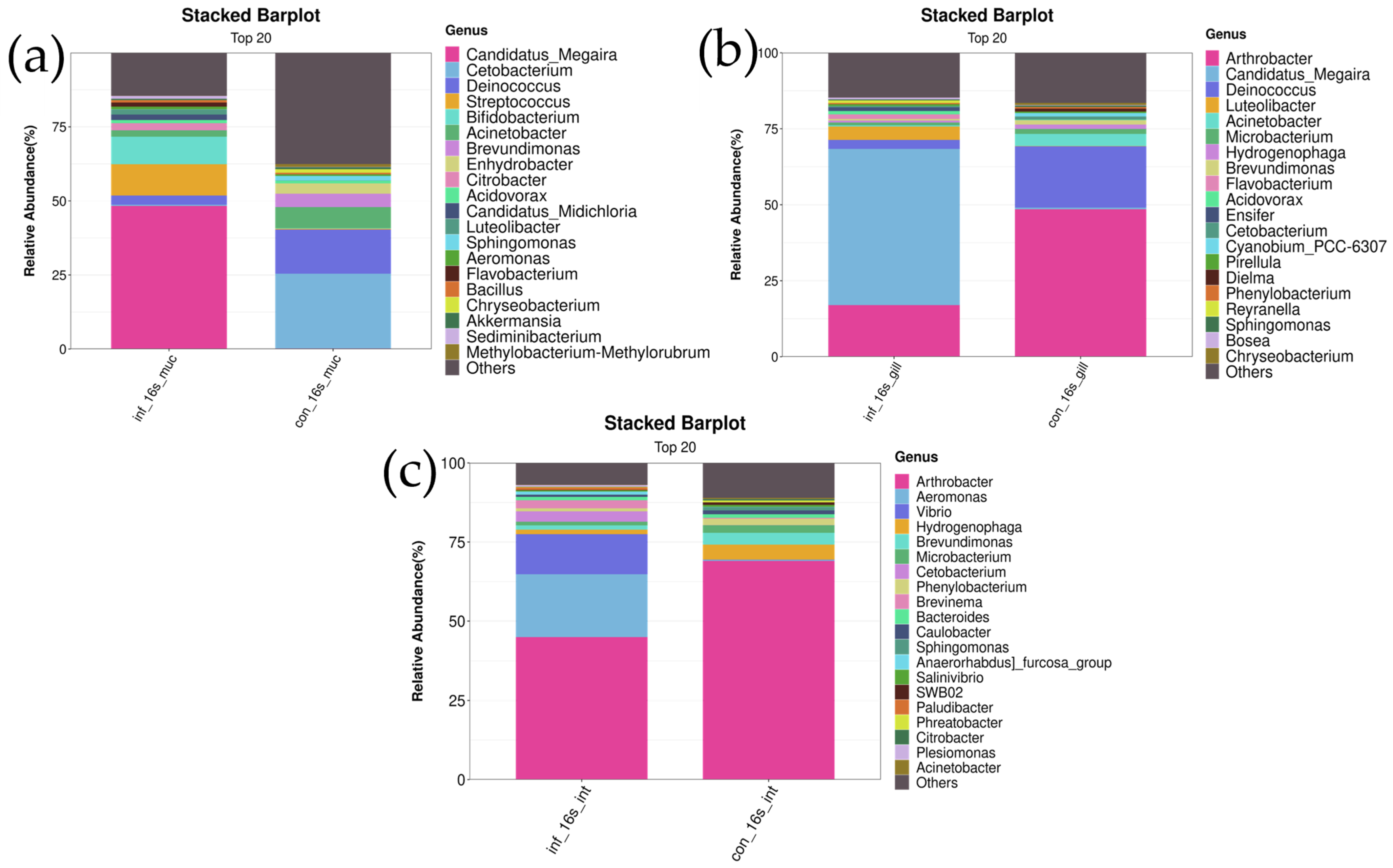
In the skin, the genus Candidatus Megaira was significantly more abundant in the infected group compared to the control group (infected group: 48.1 ± 20.5% vs. control group: 0.3 ± 0.6%, p < 0.01). Additionally, the abundance of the genus Candidatus Midichloria was significantly higher in the infected group compared to the control group (infected group: 1.7 ± 1.2% vs. control group: 0.02 ± 0.05%, p < 0.05). The abundance of the genus Flavobacterium was also significantly higher in the infected group (infected group: 1.7 ± 0.7% vs. control group: 0.01 ± 0.02%, p < 0.01) (Figure 5a).
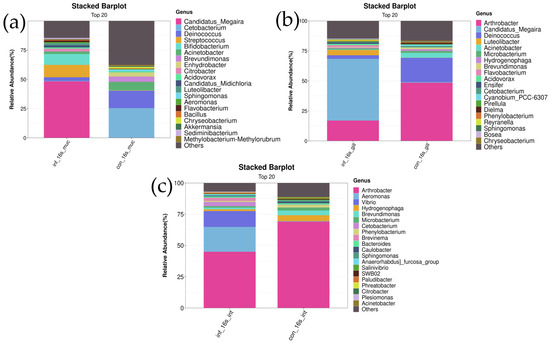
Figure 5.
Stacked bar chart of top 20 bacterial genera in skin, gill, and intestine microbiomes of I. multifiliis infection and control grass carp. (a) Skin. (b) Gill. (c) Intestine.
In the gills, the genus Candidatus Megaira was significantly more abundant in the infected group compared to the control group (infected group: 50.7 ± 23.6% vs. control group: 0.7 ± 0.5%, p < 0.01). The abundance of the genus Luteolibacter was also markedly higher in the infected group (infected group: 4.1 ± 3.9% vs. control group: 0.1 ± 0.1%, p < 0.05). The abundance of the genus Flavobacterium showed a significant difference between the two groups, with the infected group having a higher abundance (infected group: 1.5 ± 2.0% vs. control group: 0.04 ± 0.08%, p < 0.01) (Figure 5b).
In the intestines, differences in the relative abundance of the genera Vibrio and Aeromonas were observed between the control and infected groups. The results showed that the abundance of Vibrio was significantly higher in the infected group compared to the control group (infected group: 18.8 ± 19.7% vs. control group: 0.09 ± 0.1%, p < 0.05). Similarly, the abundance of Aeromonas was also significantly increased in the infected group (infected group: 19.6 ± 24.2% vs. control group: 0.31 ± 0.5%, p < 0.05). These results indicate a significant increase in the abundance of Vibrio and Aeromonas under infection conditions. Additionally, the genus Brevundimonas exhibited a significantly lower relative abundance in the infected group compared to the control group (infected group: 1.4 ± 1.0% vs. control group: 3.7 ± 2.1%, p < 0.05). Similarly, the abundance of Hydrogenophaga was significantly decreased in the infected group (infected group: 1.4 ± 0.9% vs. control group: 4.2 ± 2.3%, p < 0.05). These findings suggest that the abundances of these two genera are significantly reduced under infection conditions (Figure 5c).
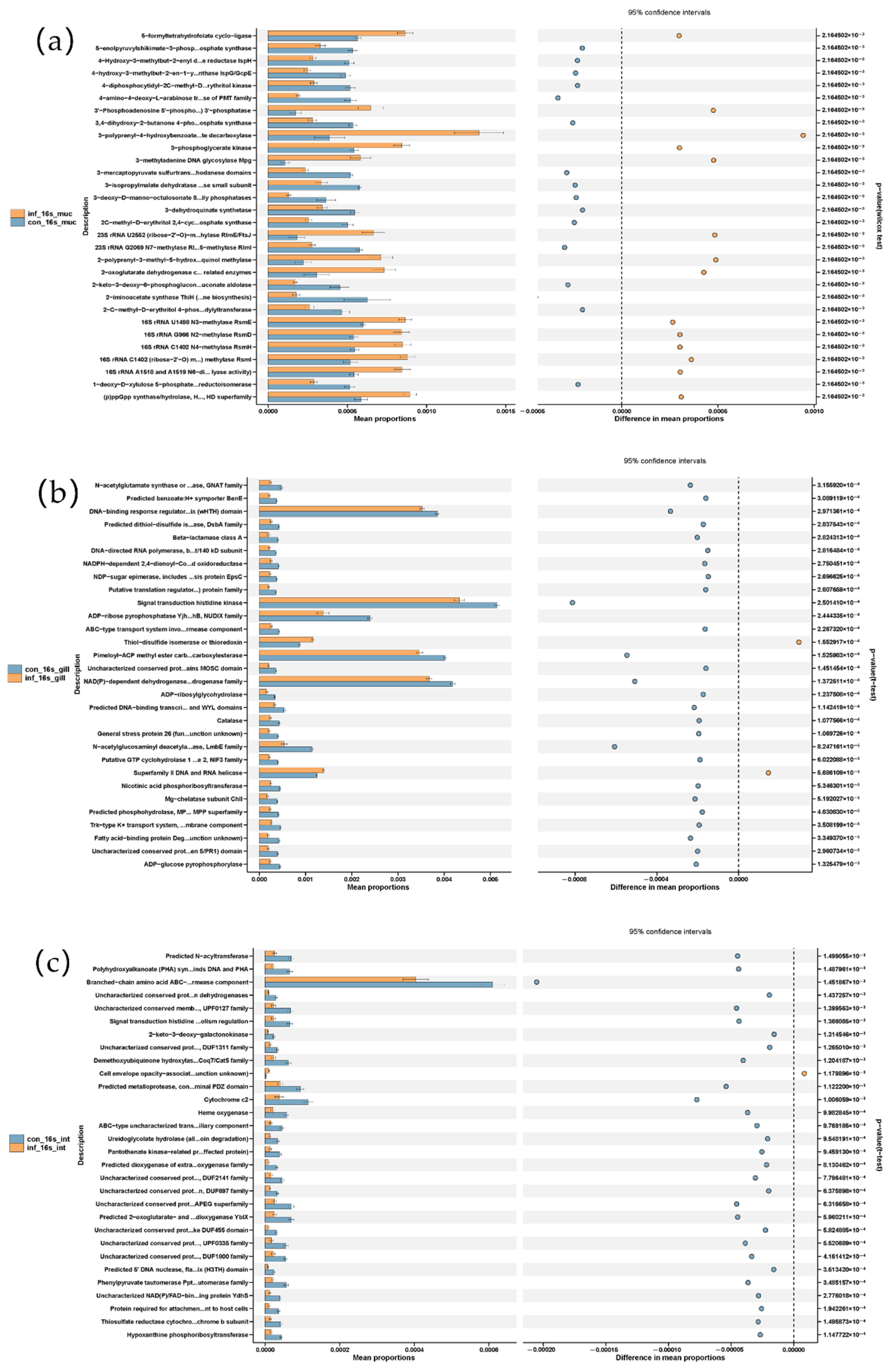
3.5. Functional Prediction of Skin, Gill, and Intestinal Microbiota After I. multifiliis Infection of Grass Carp
PICRUSt-based functional prediction revealed distinct changes in microbial functions across the skin, gill, and intestine of grass carp following I. multifiliis infection. In the skin, the infected group showed increased functions of the “bacterial secretion system” and pathways related to “cell division” and “cell cycle—Caulobacter”, while metabolic pathways such as “fatty acid biosynthesis” and “alanine, aspartate and glutama...amate metabolism” were reduced. In the gill, most metabolic pathways showed reduced functions related to, for example, “signal transduction histidine kinase”, “Pimeloyl-ACP methyl ester carb…carboxylesterase”, and “NAD(P)-dependent dehydrogenase…drogenase family”, while elevated levels of “thiol-disulfide isomerase” and “Superfamily II DNA and RNA helicase” were observed in the infected group. In the intestine, most metabolic pathways showed reduced functions, in which the “branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter, permease component” was most prominent and showed a pronounced decrease in the infected group (Figure 6).
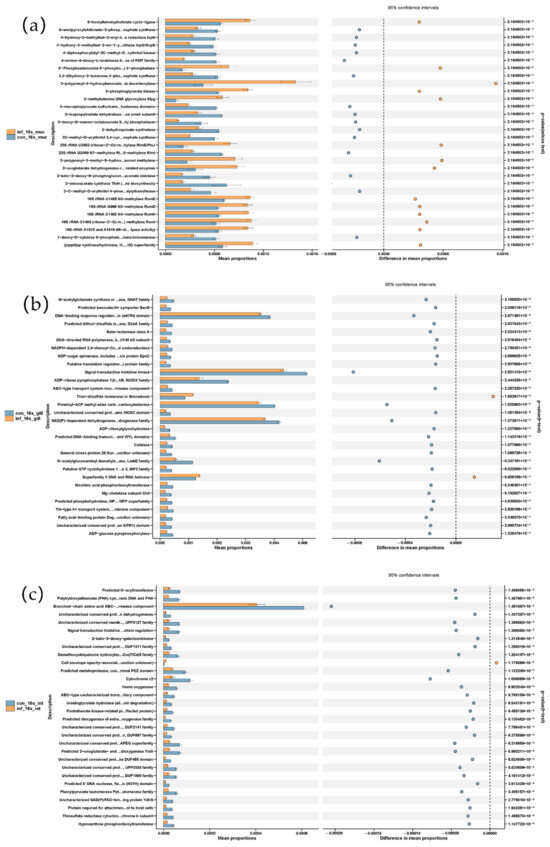
Figure 6.
Microbial metabolic shifts in grass carp after I. multifiliis infection using PICRUSt prediction. (a) Skin. (b) Gill. (c) Intestine.
Altogether, the functional prediction of the microbiota using PICRUSt suggested most metabolic pathways were reduced in the skin, gills and intestine, particularly with a pronounced reduction in the intestine. As in the skin, the pathways “related to the cell division/cycle” and “bacterial secretion system” were significantly increased after I. multifiliis infection.
3.6. qRT-PCR Assays Indicated Expression of Mucosal Immune Marker Genes IgT and TNF-α Up-Regulated While Systemic IgM Fluctuated with Increasing Tendency After Infection
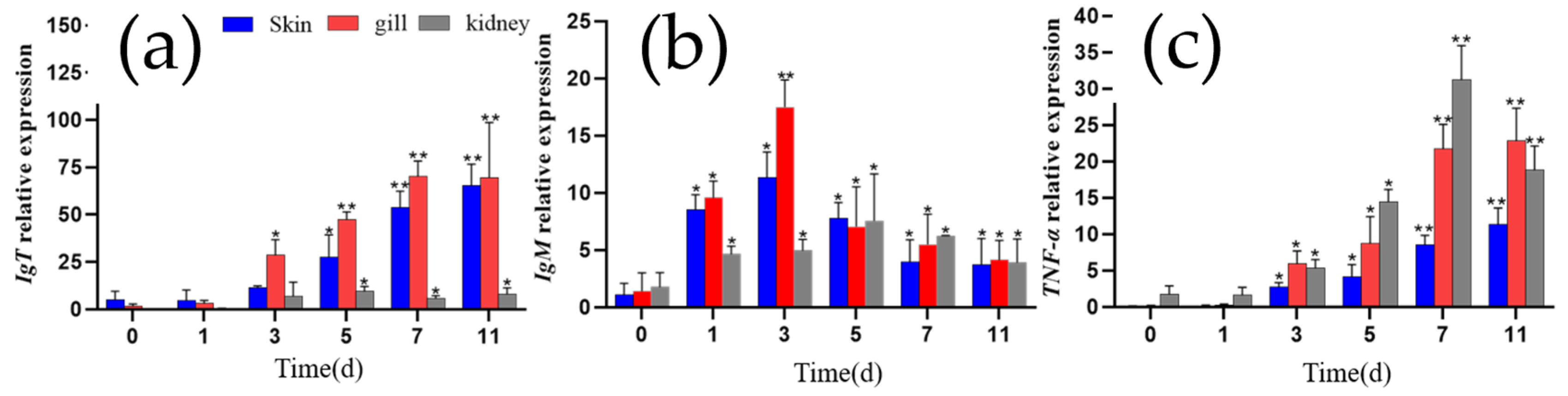
To investigate the changes in mucosal immune marker IgT, pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, and systemic immune marker IgM expression in grass carp infected with I. multifiliis, the relative expression levels of the genes encoding IgT, TNF-α and IgM were analyzed in the gill, skin, and kidney tissues using qRT-PCR. Overall, the expression of the three genes was up-regulated in these three tissues following I. multifiliis infection. Specifically, IgT expression in the gill and skin increased significantly at all tested time points after infection (p < 0.05). IgM expression was significantly up-regulated in all three tissues at the early stages of infection (≤3 days), decreased after 3 days as the infection progressed but also maintained at higher levels than that before infection (p < 0.05). TNF-α expression in all three tissues also showed a significant increase with infection duration (p < 0.05) (Figure 7).
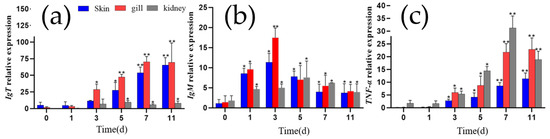
Figure 7.
The relative expression levels of IgT, IgM, and TNF-α in the gills, skin, and kidney of grass carp. (a) IgT. (b) IgM.(c) TNF-α. Each column represents the relative expression levels of genes to β-actin, with the results expressed as the means ± standard error of three qRT-PCR assays (2−ΔΔCT). Differences between different infection days and day 0 were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, with * indicating significant differences (p < 0.05) and ** indicating highly significant differences (p < 0.01).
3.7. Microbiota Were Correlated with Biochemical and Immune Indicators
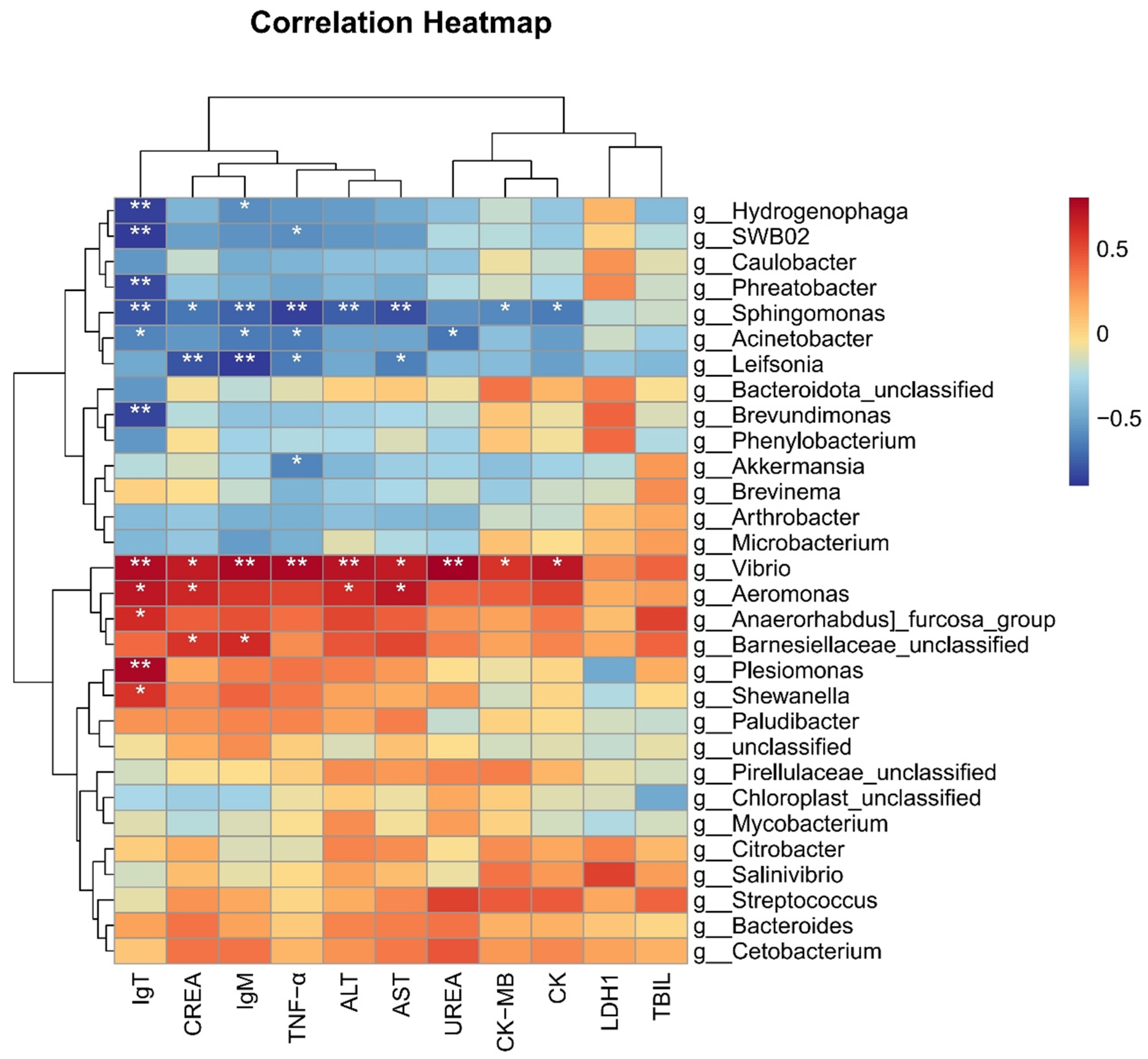
We selected the top 30 microbiota at the genus level based on their relative abundance and performed heatmap analysis with related immune and biochemical indicators. The heatmap analysis in this study revealed that the genus Vibrio exhibited significantly positive correlations with the six biochemical indicators, such as ALT, AST, CK, CK-MB, UREA, and CREA, and the three immune genes IgT, TNF-α, and IgM (Figure 8). Similarly, the genus Aeromonas showed a significant positive correlation with biochemical indicators such as ALT, AST, CREA, and immune gene IgT (Figure 8). These strong positive correlations suggest that an increase in the abundance of Vibrio or Aeromonas may be associated with impaired liver, kidney and cardiac/muscle functions, as well as an enhanced expression of immune genes IgT, TNF-α, and IgM.
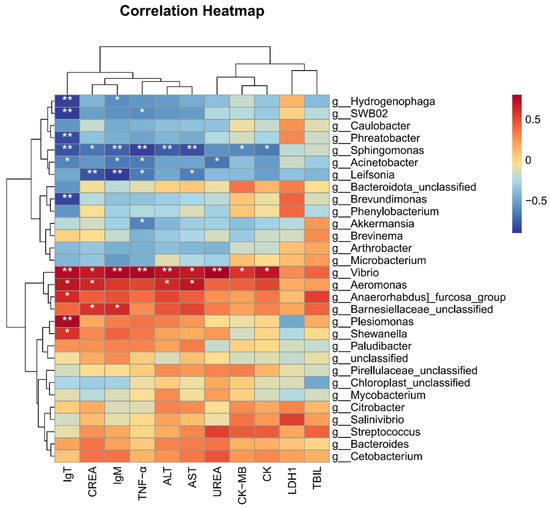
Figure 8.
Correlation heatmap between microbes and phenotypes in grass carp. * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01.
Conversely, the heatmap analysis also indicated that the genus Sphingomonas was significantly negatively correlated with five biochemical indicators, such as ALT, AST, CK, CK-MB and CREA, and three immune genes IgT, TNF-α, and IgM. the genus Acinetobacter exhibited significant negative correlations with the three immune genes and UREA, while Leifsonia was significantly negatively correlated with TNF-α, IgM, CREA, and AST (p < 0.05). Additionally, the genera Hydrogenophaga, SWB02, Phreatobacter, Brevundimonus, and Akkermansia showed significant negative correlations with the expression of immune genes (Figure 8). These findings suggest that a reduction in the abundances of these microbial taxa may be linked to impaired liver, kidney, muscle/heart functions, as well as stimulated immune responses in grass carp.
4. Discussion
In this study, we systematically investigated the multifaceted physiological and microbial community changes in grass carp after infection with I. multifiliis. By analyzing biochemical indicators, histopathology, and skin/gill/gut microbiota, we discovered that infection caused significant liver and kidney damage in grass carp, as well as notable changes in the microbial communities in the skin, gills, and intestine. In addition, immune-related gene (IgM, IgT, and TNF-α) expression levels increased after infection with I. multifiliis. These findings not only further elucidate the complex effects of parasitic infection on host physiological health but also provide new perspectives for understanding the relationship among host–microbiota–parasite interactions. Compared to previous studies, this research is the first to apply 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing technology to systemic investigate skin/gill/intestine microbiota in I. multifiliis infection grass carp. Our findings indicate that I. multifiliis infection not only directly affects the pathology of host tissues but may also exacerbate the proliferation of opportunistic pathogens by disrupting the ecological balance of microbial communities in the skin, gills, and intestine, thereby further affecting the host’s tissue damage and increasing immune response.
4.1. Pathological and Biochemical Changes
Ciliate parasites cause significant tissue damage in fish, particularly affecting skin and gill structures. In turbot (Scophthalmus maximus), infections correlate with high mortality rates characterized by skin swelling, gill necrosis, and inflammatory responses [30]. Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) infected with I. multifiliis exhibit epidermal thickening and increased mucus cell proliferation [4]. Severe I. multifiliis infection might lift the layers of integumental epithelium, accompanied by severe epidermal hyperplasia, cellular necrosis, and histolysis, in the species like goldfish (Carassius auratus), largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) [17,18]. In this study, grass carp infected with I. multifiliis showed similar pathological changes, with parasite attachment and proliferation exacerbating host tissue damage, leading to epithelial cell hyperplasia and necrosis. Parasites may directly impair respiratory and oxygen exchange functions of fish gills and facilitate secondary opportunistic pathogen such as Flavobacterium invasion, which has been proved by this study of pathogen isolation and 16s rRNA sequencing. Additionally, severe infections were marked by the significant infiltration of inflammatory cells, particularly monocytes and lymphocytes, indicating a localized immune response. This was further supported by elevated expression levels of the mucosal immune gene IgT and the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α in this study.
Furthermore, in this study, we observed that I. multifiliis infection led to significant changes in several biochemical indicators of grass carp, which reflect the functions and health status of the liver and kidney. The activities of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), urea (UREA), and creatinine (CREA) were significantly elevated in the infected group. AST and ALT are typically released into the blood when liver cells are damaged, so elevated activities of AST and ALT are considered biomarkers of hepatic destruction [31,32,33]. Elevated levels of UREA and CREA in fish are often associated with damage to the renal tubules or glomeruli, which affect kidney function [34,35]. Studies have shown that infection of cod (Gadus morhua) with the nematode Contracaecum osculatum can cause severe liver damage [36] and fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) infected with trematode Ornithodipl ostomum spp. exhibit significant increases in hepatic lipid peroxidation [37]. In this study, I. multifiliis, an ectoparasite found on gills and skin, caused hepatic and renal impairment despite its distant location from these organs. This internal damage may result from gill tissue disruption, affecting host respiration and energy metabolism. Additionally, microbiota changes, including opportunistic pathogens such as Aeromonas, likely induced secondary infections in internal organs, as confirmed by bacterial isolation and identification assays. Similarly to findings in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) infected with monogenean ectoparasites [38], grass carp infected with ciliate ectoparasite I. multifiliis showed elevated ALT, AST, CREA, and UREA levels in this study.
4.2. Gene Expression Levels of IgT, IgM, and TNF-α
In this study, we systematically evaluated the changes in the expression levels of immune-related genes IgT, IgM, and TNF-α in grass carp after infection with I. multifiliis. Relative quantitative PCR analyses revealed a significant up-regulation in the expression of both IgT and TNF-α, while the expression of IgM showed time-dependent fluctuations.
IgT, a fish-specific immunoglobulin, plays a well-established role in mucosal immunity. For example, in rainbow trout (O. mykiss) infected with Ceratomyxa shasta and I. multifiliis, the number of IgT+ B cells in mucosal tissues was significantly increased, and the concentration of IgT in mucus rose by several orders of magnitude [39]. At the transcriptional level, after I. multifiliis infection, IgT expression was notably higher in the skin and gills of rainbow trout (O.mykiss) and loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) [40,41]. Similarly, the up-regulation of IgT transcription was observed in the skin of rohu (Labeo rohita) infected with Argulus siamensis and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) infected with Gyrodactylus cichlidarum [42].
IgM plays a crucial role in activating systemic and mucosal adaptive immune responses against pathogenic challenges, including parasitic infections [43]. For instance, IgM expression was up-regulated in the spleen and skin of rainbow trout by the eighth day post infection with I. multifiliis [44]. Similarly, in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) vaccinated with live I. multifiliis theronts, IgM levels in the gills and internal immune organs showed time-dependent fluctuations, aligning with our findings [45]. Comparable patterns were observed in Indian major carp (Labeo rohita), where IgM expression in the gills trended upward after infection with the ectoparasite Dactylogyrus scorpius [46].
Moreover, TNF-α, an important pro-inflammatory cytokine, reflects the host’s inflammatory response mechanisms triggered during infection. In helminth infections, TNF-α is involved in protective Th2 immune responses and promotes parasite expulsion. The expression levels of TNF-α were found to be up-regulated in goldfish (Carassius auratus) during Gyrodactylus kobayashii infection [47] and parasite-infected Tilapia nilotica (O. niloticus) [48]. These studies indicated that fish infected with ectoparasites may experience an increase in both innate and adaptive immune responses. PICRUSt-based functional predictions revealed that distinct alterations might be changed in microbial metabolic pathways that are associated with host immunity post infection. Further studies are needed to elucidate how the microbiota modulates host immune responses.
In conclusion, the significant up-regulation of IgT and TNF-α underscores the key roles of mucosal immunity and inflammatory responses in host defense, while the dynamic changes in IgM reflect the complexity of the systemic immune response.
4.3. Impact on Gill, Skin, and Intestinal Microbial Communities
In this study, we employed 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing technology to systematically analyze the microbial communities in the skin, gills, and intestine of grass carp infected with I. multifiliis. The results demonstrated that infection significantly affected the diversity, structure, composition, and function of grass carp microbiota.
4.3.1. Microbial Diversity
Our study revealed a significant decrease in the skin microbial diversity of grass carp following I. multifiliis infection. Similar patterns were observed in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), where parasitic infection reduced skin microbial diversity and destabilized community composition [49]. Likewise, parasitic infection in African elephantnose fish (Gnathonemus petersii) led to declines in biodiversity indices [50]. Gill and intestinal microbial communities showed non-significant decreases in diversity but showed decreasing trends; this may reflect that local microbial communities in gills and intestine were less affected than those in the skin.
4.3.2. Phylum and Genus Abundance
In this study, after infection, the abundance of phylum Proteobacteria significantly increased in the gills, skin, and intestine. This phylum is often closely associated with inflammation. In ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease patients, increased Proteobacteria abundance correlated with heightened inflammation, suggesting the role in pouchitis and disease exacerbation [51,52,53]. Certain members of Proteobacteria are closely associated with inflammation and tissue damage, and their increased abundance may worsen parasitic infection effects. For example, intestine Proteobacteria expansion suggests infection promotes opportunistic pathogens like Aeromonas, intensifying pathological responses [54]. The increase in Proteobacteria in the intestine may indicate impaired intestinal barrier function post infection, making opportunistic pathogenic bacteria more prone to invasion and proliferation. This increase may further exacerbate the host’s pathological stress response and digestive dysfunction. Notably, a contrasting finding was reported by Zhang et al. [4], where they observed a decrease in the relative abundance of Proteobacteria in rainbow trout infected with I. multifiliis, differing from our observations. We hypothesize that these discrepancies could stem from variations in the immune systems, skin barriers between grass carp and rainbow trout, the inherently higher baseline proportion of Proteobacteria in the microbiota of grass carp, and a range of environmental factors such as water temperature, pH, and water quality management.
In this study, Actinobacteriota abundance was significantly decreased in the gills and intestine of the infected grass carp. Actinobacteriota typically includes beneficial microbes that help maintain the host’s immune balance [55]. The reduction in Actinobacteriota may weaken the protective role of the intestinal microbiota for the host. Some beneficial genus microbes belong to Actinobacteriota in the intestine and are closely related to host nutrition absorption and immune regulation, and their reduction may lead to intestinal microbial dysbiosis. Additionally, the decrease in Deinococcota in the infected group’s skin indicates their important protective role in parasitic infection. Some species within Deinococcota are resistant to high temperatures and radiation [56], so their reduction may indicate a weakened skin defense mechanism.
At the genus level, the microbial community changes were also substantial. In the gills, the abundance of the genus Flavobacterium, Luteolibacter and Candidatus Megaira significantly increased in the infected group (p < 0.01, p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). Notably, the genus Flavobacterium is widely studied for its pathogenicity and adaptability in aquatic environments. As an opportunistic pathogen, it causes fish disease symptoms such as gill damage, skin lesions, and necrotizing ulcers when the environment is suitable [57,58]. In this study, grass carp infected with I. multifiliis showed an increased abundance of Flavobacterium spp. in the skin as well as in the gills, indicating that parasitic infection promoted the invasion of this opportunistic pathogen, similarly with trout skin after parasitic infection [4]. Luteolibacter is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria, living in various environments including soil and freshwater [59]. However, there have been no reports to date on whether this bacterial genus is pathogenic or beneficial to fish. Candidatus Megaira, belonging to the order Rickettsiales, is a symbiotic bacterium in the environment, typically forming symbiotic relationships with ciliates, algae, and other prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms. Candidatus Megaira has been found to possess potential for defensive symbiosis, with certain strains playing key roles in host protein interactions. Candidatus Megaira polyxenophila infection enhances host ciliate Paramecium growth performance, suggesting it plays a complex role in ecological adaptation [60]. In this study, the significant increase in Candidatus Megaira suggests that it might play a synergistic role in the ciliate parasitic infection process. Furthermore, whether the symbiotic genus Candidatus Megaira could serve as indicator species for ciliated parasitic infection also deserves a deeper exploration.
In the intestine, the genera Aeromonas and Vibrio were significantly increased in the infected group (p < 0.05), while Brevundimonas and Hydrogenophaga significantly decreased (p < 0.05). Aeromonas, well known as opportunistic pathogens, are frequently associated with diseases such as hemorrhagic septicemia, skin ulcers, and enteritis in aquatic animals, including grass carp, posing a significant threat to fish health [28]. In contrast, Vibrio primarily infects marine or brackish water fish [61]. In this study, Aeromonas were isolated as positive, while Vibrio were negative in grass carp. This observation might be attributed to the higher susceptibility of grass carp to Aeromonas than to Vibrio in freshwater environments, despite the presence of both bacterial taxa in the intestinal microbiota [61]. This study’s results indicate that I. multifiliis infection leads to an increase in opportunistic pathogens, consistent with previous research [4]. Brevundimonas is not a typical probiotic; its presence can enhance the stability of diverse microbial communities to improve the disease resistance of aquatic animals, thereby mitigating the impact of pathogenic bacteria. Additionally, Brevundimonas can promote the absorption and growth of teleosts by decomposing organic matter and releasing minerals and trace elements [62]. Although direct studies on the genus Hydrogenophaga in fish intestine are limited, existing characteristics suggest that they may promote intestinal health in various ways. Firstly, Hydrogenophaga has the ability to degrade organic compounds in the intestine, thereby aiding the host in better nutrient absorption [63]. Additionally, Hydrogenophaga can synergize with other beneficial microbial communities to maintain intestinal microbial balance and inhibit the proliferation of harmful pathogens, thereby reducing infection risks [64].
In the skin of the infected group, besides Flavobacterium, the abundance of the genus Candidatus Midichloria also significantly increased. Candidatus Midichloria is an intriguing group of endosymbiotic bacteria, widely distributed among various hosts, especially in ticks. The representative species Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii is known for inhabiting host mitochondria and is considered the only bacterium capable of infecting mitochondria [65]. Additionally, other species in the Midichloriaceae family exhibit a broad host range, including aquatic invertebrates and protists, indicating the ecological diversity of this genus [66]. Further research is needed to understand why it significantly increased in the infected group.
4.4. Potential Microbial-Based Ciliate Parasitic Disease Management
This study demonstrated that the structure and function of the skin, gill, and intestinal microbiota in grass carp were significantly altered after infection with the ciliate ectoparasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. These changes differed from those induced by another ectoparasite, Dactylogyrus lamellatus, in grass carp [14]. While intestinal microbiota diversity similarly decreased after Dactylogyrus infection, the abundance of the opportunistic genus Aeromonas did not increase, though Aeromonas has been found to be in the top 10 bacterial genera in the intestine [14], which was different to the findings of this study. The observed differences may be attributed not only to the varying degrees of impact exerted by the parasites on the host but also to the host’s health status and immune-driven responses. Research has shown that fish immunity can sense and shape the intestinal microbiota [67]. In the study on Dactylogyrus-infected grass carp, serum pathological changes were less pronounced than those observed in this study with I. multifiliis infection, suggesting that I. multifiliis might pose a higher threat to grass carp health. The PICRUSt-based functional prediction of the microbiota revealed that after I. multifiliis infection, the metabolic function of the intestinal microbiota might be weakened, limiting its ability to provide adequate nutrition to the host. This may indirectly highlight the importance of enhanced nutritional management in aquaculture to improve resistance against parasitic infections.
Following I. multifiliis infection, the abundance of opportunistic pathogens such as Aeromonas and Vibrio in the intestine of grass carp increased significantly. This increase was positively correlated with elevated levels of liver and kidney functional markers (ALT, AST, and CREA), indicating exacerbated tissue damages. The findings suggest that controlling grass carp ichthyophthiriasis could mitigate secondary infections by pathogenic bacteria. Conversely, the reduction in beneficial bacteria such as Brevundimonas and Hydrogenophaga in the intestine may create an environment conducive to the over-proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Further research is warranted on how to increase beneficial microbes in the intestine.
16S rRNA sequencing technology enables the detection of both culturable and unculturable bacteria, providing a more comprehensive profile of microbial communities compared to traditional isolation and cultivation methods. However, further in-depth research is needed to elucidate the functional roles of fish microbiota and their interactions with the host. In this study, Spearman’s rank correlation analysis was used to evaluate the relationships between phenotypic traits (biochemical and immune markers) and microbial communities in I. multifiliis-infected grass carp. This integrative approach enhances our understanding of the complex “host–microbiota–parasite” interactions. Future research should focus on exploring the functional roles of potential beneficial bacteria in preventing parasitic diseases. For instance, supplementing fish feed with these bacteria could be a promising strategy to prevent ichthyophthiriasis.
Interestingly, this study reveals an increase in the abundance of opportunistic pathogens, specifically Aeromonas and Vibrio in the gut and Flavobacterium in the gills and skin. These findings are significant for both researchers and farmers, suggesting that in future research on combating I. multifiliis, the use of oral probiotics to reduce the abundance of Aeromonas and Vibrio in the gut may be beneficial for controlling ichthyophthiriasis. Additionally, could cultured water disinfection and the application of probiotics targeting the abundance decrease in Flavobacterium also help to reduce I. multifiliis infections? These questions warrant further investigation. Moreover, whether the symbiotic genus Candidatus Megaira, which increased in the gills and skin, could serve as indicator species for ciliated parasites (such as I. multifiliis) also deserves a deeper exploration.
5. Conclusions
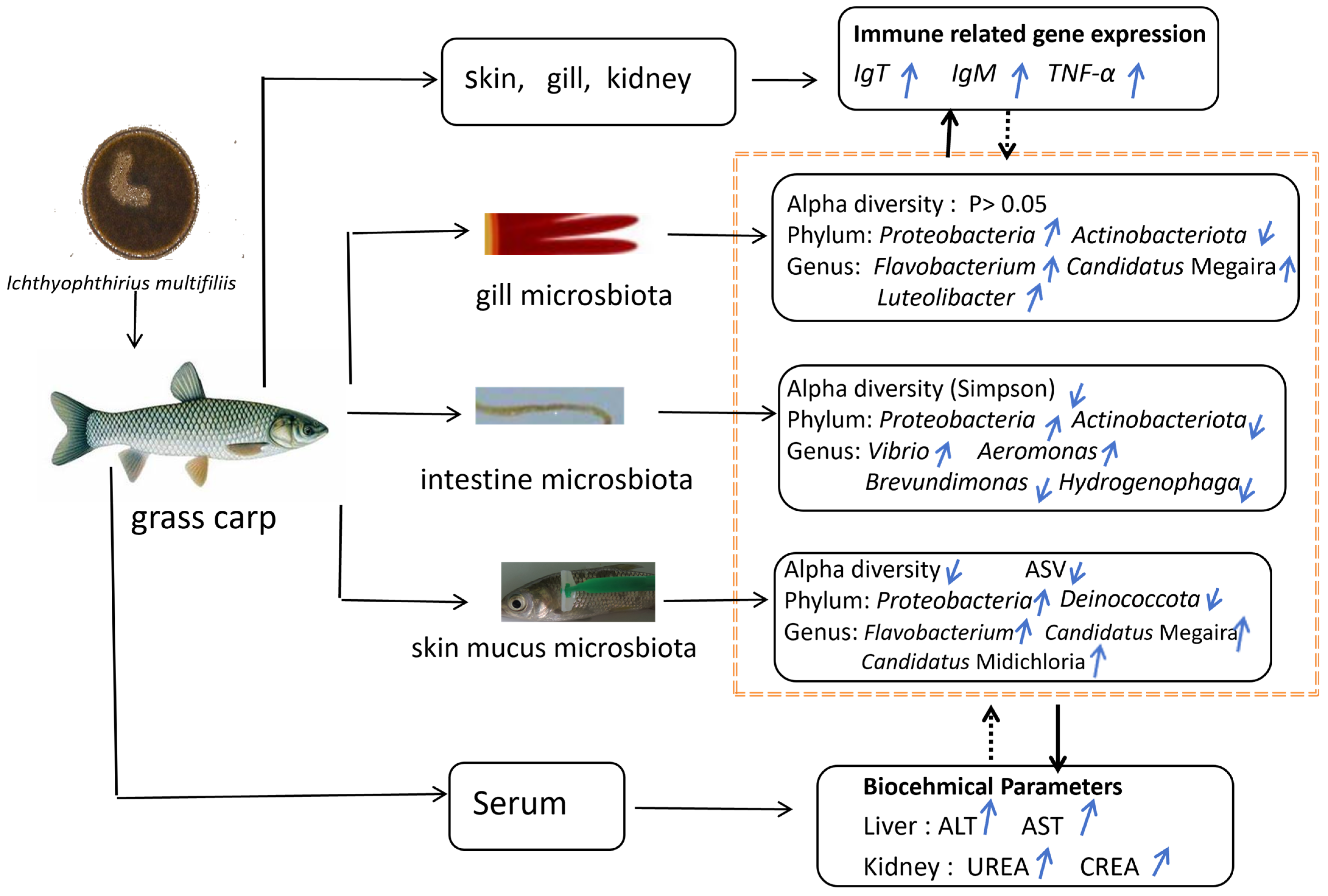
This study investigated the effects of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection on the microbial communities in the gills, skin, and intestine, serum biochemical indices, and immune responses in grass carp. The infection significantly altered the structure and composition of the host microbiota, reducing skin microbial diversity and increasing the abundance of opportunistic pathogens. Specifically, Actinobacteriota decreased in the gills and intestine, while Proteobacteria increased across the skin, gills, and intestine. The symbiotic genus Candidatus Megaira expanded in the gills and skin, while pathogenic genera Flavobacterium (gills/skin), Vibrio (intestine), and Aeromonas (intestine) proliferated markedly. These changes suggest that parasitic infection exacerbates host pathology by promoting opportunistic pathogen colonization and disrupting beneficial microbial symbiosis. Additionally, infected fish exhibited significantly elevated serum biochemical indices, including ALT, AST, UREA, and CREA. The up-regulation of mucosal immune markers (IgT) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α) highlighted their critical role in host defense mechanisms. Meanwhile, IgM expression showed time-dependent fluctuations with an overall increasing trend, reflecting the complexity of the immune response. Microbial alterations were closely correlated with serum biochemical parameters and immune-related gene expression, particularly Vibrio and Aeromonas, which showed strong positive correlations with ALT, AST, and CREA levels. These findings provide insights into “host–microbiota–parasite” interactions and offer potential microbial-based strategies for controlling parasitic diseases in aquaculture (Figure 9).
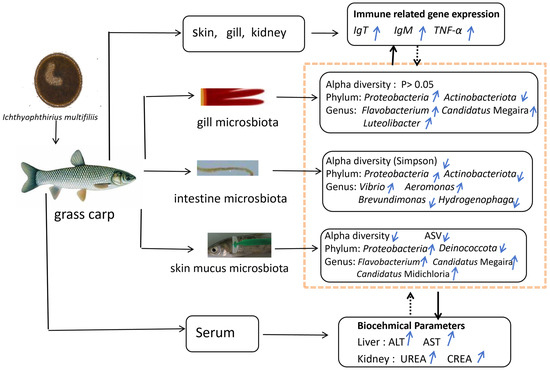
Figure 9.
Graphical abstract of I. multifiliis infection in grass carp: effects on microbiota composition, biochemical parameters, and immune gene expression. Notes: black solid lines represent the mechanisms identified in this study. Black dashed lines represent deduced relationship. Blue upward arrows (↑) indicate increase, while blue downward arrows (↓) indicate decrease.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, investigation, data curation, methodology, F.L.; investigation, methodology, writing—review and editing, D.J.; methodology, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing, Q.W.; methodology, writing—review and editing, O.C.; writing—review and editing, J.Y.; conceptualization, supervision, methodology, writing—review and editing, M.Y.; conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, writing—review and editing, H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (No. 2024B03J1265), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2023YFD2400504), the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-45), and the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (NO. 2023TD49, NO. 2024CG02).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The experimental protocols were approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethic Committee Pearl River Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS (No.: LAEC-PRFRI-2024-03-44, 23 March 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All 16S rRNA genes of microbiota sequences were deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under BioProject PRJNA1224981. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/1224981 (accessed on 18 February 2025).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dejuan Lao and Jiayue Chen for their assistance in the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rohani, M.F. Pesticides Toxicity in Fish: Histopathological and Hemato-Biochemical Aspects—A Review. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peachey, L.E.; Jenkins, T.P.; Cantacessi, C. This Gut Ain’t Big Enough for Both of Us. Or Is It? Helminth–Microbiota Interactions in Veterinary Species. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, A.; Peachey, L.; Scotti, R.; Jenkins, T.P.; Cantacessi, C. Helminth-Microbiota Cross-Talk—A Journey through the Verte brate Digestive System. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2019, 233, 111222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, L.; Yu, Y.; Kong, W.; Yin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z. The Change of Teleost Skin Commensal Microbiota Is Associated With Skin Mucosal Transcriptomic Responses During Parasitic Infection by Ichthyophthirius multifillis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, E.A.; Chua, E.G.; Hassan, S.U.; Greeff, J.C.; Palmer, D.G.; Liu, S.; Lamichhane, B.; Sepúlveda, N.; Liu, J.; Tay, C.Y.; et al. Bacterial Communities in the Gastrointestinal Tract Segments of Helminth-Resistant and Helminth-Susceptible Sheep. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.B.; Sorobetea, D.; Kiilerich, P.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Estellé, J.; Ma, T.; Madsen, L.; Kristiansen, K.; Svensson-Frej, M. Chronic Trichuris muris Infection Decreases Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiota and Concomitantly Increases the Abundance of Lactobacilli. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Singh, S. Site Specific Microbiome of Leishmania Parasite and Its Cross-Talk with Immune Milieu. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 216, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrázek, J.; Mrázková, L.; Mekadim, C.; Jarošíková, T.; Krayem, I.; Sohrabi, Y.; Demant, P.; Lipoldová, M. Effects of Leishmania Major Infection on the Gut Microbiome of Resistant and Susceptible Mice. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.P.; Xiong, F.; Feng, W.W.; Zou, H.; Wu, S.G.; Li, M.; Wang, G.T.; Li, W.X. Effect of Intestinal Tapeworms on the Gut Microbiota of the Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulke, C.A.; Martins, M.L.; Watral, V.G.; Humphreys, I.R.; Spagnoli, S.T.; Kent, M.L.; Sharpton, T.J. A Longitudinal Assess ment of Host-Microbe-Parasite Interactions Resolves the Zebrafish Gut Microbiome’s Link to Pseudocapillaria tomentosa Infection and Pathology. Microbiome 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Steinel, N.; Weber, J.; Ma, L.; Smith, C.; Correa, D.; Zhu, B.; Bolnick, D.; Wang, G. The Gut Microbiota Response to Helminth Infection Depends on Host Sex and Genotype. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.P.; Xiong, F.; Wu, S.G.; Zou, H.; Li, M.; Wang, G.T.; Li, W.X. Effects of Schyzocotyle acheilognathi (Yamaguti, 1934) Infection on the Intestinal Microbiota, Growth and Immune Reactions of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasemägi, A.; Visse, M.; Kisand, V. Effect of Environmental Factors and an Emerging Parasitic Disease on Gut Microbiome of Wild Salmonid Fish. mSphere 2017, 2, e00418-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xie, J.; Chang, O.; Wang, Q.; Shi, C.; Zhao, F.; Gong, H.; Ren, Y.; Musa, N.; et al. Do Ectoparasites on Fish Gills “Talk” with Gut Microbiota Far Away? Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, G.; Angert, E.R.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zou, H. Composition, Diversity, and Origin of the Bacterial Community in Grass Carp Intestine. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Wang, G.-T.; Wu, S.-G. A Review of Intestinal Microbes in Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus (Valenciennes). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3287–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H. Histopathological Study of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) Experimentally Infected with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 3539–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tu, X.; Xiao, J.; Hu, J.; Gu, Z. Investigations on White Spot Disease Reveal High Genetic Diversity of the Fish Parasite, Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Fouquet, 1876) in China. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Q.; Fu, Y.W.; Hou, T.L.; Huang, S.L.; Zhang, Q.Z. Establishment and Application of TaqMan Probe-based Quantitative Real-time PCR for Rapid Detection and Quantification of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in Farming Environments and Fish Tissues. Vet. Parasitol. 2025, 334, 110381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, H.; Clark, T. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis: A Model of Cutaneous Infection and Immunity in Fishes. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Hu, G.; Wang, R.; Zeng, Q.; Li, W.; Zou, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, G.; Li, M. In Vitro Assessment of Berberine against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in Goldfish. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Gersdorff Jørgensen, L.; Heinecke, R.D.; Skjødt, K.; Rasmussen, K.J.; Buchmann, K. Experimental Evidence for Direct in Situ Binding of IgM and IgT to Early Trophonts of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Fouquet) in the Gills of Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.; Taghizadeh, V.; Heidarieh, M.; Hajimoradloo, A. The Key Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Vac cinated Rainbow Trout via Irradiated Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Trophont. Vet. Arh. 2017, 87, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yan, Q.G.; Wang, Z.B.; Lu, Y.J.; Xu, M.J.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.Q. MH II—DAB Gene Expression in Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes) after Infection with the Ciliate Parasite, Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Li, Y.-W.; Pan, H.-J.; Shi, C.-B.; Luo, X.-C.; Li, A.-X.; Wu, S.-Q. TAK1-Binding Proteins (TAB1 and TAB2) in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis after Infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 38, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zheng, R. Transcriptome Analysis of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) and Holland’s Spinibarbel (Spinibarbus hollandi) Infected with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 121, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Gao, R.; Duan, Y.; Han, R.; Guo, W.; Dan, X.; Li, Y. Isolation and Genetic Characterization of Flavobacterium columnare from Grass Carp, Ctenopharyngodon idellus, in China. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samayanpaulraj, V.; Sivaramapillai, M.; Palani, S.N.; Govindaraj, K.; Velu, V.; Ramesh, U. Identification and Characterization of Virulent Aeromonas hydrophila Ah17 from Infected Channa striata in River Cauvery and in Vitro Evaluation of Shrimp Chitosan. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Klesius, P. Two Year Study on the Infectivity of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in Channel Catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 59, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramos, M.; Costa, A.; Barandela, T.; Saraiva, A.; Rodrigues, P. Scuticociliate Infection and Pathology in Cultured Turbot Scophthalmus maximus from the North of Portugal. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2007, 74, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Raya, A.; Coca Zúñiga, R.; Martín Salido, E. Isolated Elevation of Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) in an Asymp tomatic Patient Due to macro-AST. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crudele, L.; De Matteis, C.; Piccinin, E.; Gadaleta, R.M.; Cariello, M.; Di Buduo, E.; Piazzolla, G.; Suppressa, P.; Berardi, E.; Sabbà, C.; et al. Low HDL-Cholesterol Levels Predict Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Individuals with Liver Fibrosis. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R. Serum Alanine Aminotransferase as a Biomarker of Treatment Response in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1731–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou-Savina, S.; Beales, P.L.; Osborn, D.P.S. Evaluation of Zebrafish Kidney Function Using a Fluorescent Clearance Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 96, 52540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R. Chronic Effect Due to Changes in the Contents of Urea & Creatinine in Edible Cat Fish Channa Punctatus (Bloch), Under the Stress of Sub Lethal Concentration of Methyl Parathion - a pesticide. Environ. Conserv. J. 2011, 12, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.W.; Ryberg, M.P.; Chondromatidou, V.; Iburg, T.M. Comparative Histopathology of Livers from Baltic Cod Infected with the Parasitic Nematode Contracaecum osculatum. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumbo, A.D.; Goater, C.P.; Hontela, A. Parasite-Induced Oxidative Stress in Liver Tissue of Fathead Minnows Exposed to Trematode Cercariae. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastiannasab, A.; Afsharmanesh, S.; Rahimi, R.; Sharifian, I. Alternations in the Liver Enzymatic Activity of Common carp, Cyprinus carpio in Response to Parasites, Dactylogyrus spp. and Gyrodactylus spp. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-Y.; Kong, W.; Yin, Y.-X.; Dong, F.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Yin, G.-M.; Dong, S.; Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.-A.; Xu, Z. Mucosal Immuno globulins Protect the Olfactory Organ of Teleost Fish against Parasitic Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Yu, Y.; Dong, S.; Huang, Z.; Ding, L.; Cao, J.; Dong, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Pharyngeal Immunity in Early Vertebrates Provides Functional and Evolutionary Insight into Mucosal Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 3054–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Dong, S.; Luo, Y.; Yu, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Immunoglobulin (Ig) Heavy Chain Gene Locus and Immune Responses upon Parasitic, Bacterial and Fungal Infection in Loach, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, T.; Huang, C.; Sun, R.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Brown, C.L.; Yang, T. Mucosal Immune Response of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus during Gyrodactylus cichlidarum Infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyt, B.A.; Baliga, R.; Sinclair, A.M.; Carroll, S.F.; Peterson, M.S. Structure, Function, and Therapeutic Use of IgM Antibodies. Antibodies 2020, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syahputra, K.; Kania, P.W.; Al-Jubury, A.; Marnis, H.; Setyawan, A.C.; Buchmann, K. Differential Immune Gene Response in Gills, Skin, and Spleen of Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss Infected by Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-H.; Moreira, G.S.A.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Zhang, D.; Beck, B.H. Expression of Immune Genes in Systemic and Mucosal Immune Tissues of Channel Catfish Vaccinated with Live Theronts of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Mohanty, J.; Rajendran, K.V.; Tripathi, G.; Sahoo, P.K. First Report of Dactylogyrus scorpius Infection in Indian Major Carp, Labeo rohita from India: Host Specificity and Kinetics of Immune Gene Expression in Gills. Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Qi, X.; Huang, A.; Ling, F.; Wang, G. Cytokine Gene Expression Profiles in Goldfish (Carassius auratus) during Gyrodactylus kobayashii Infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shater, A.F.; AlGabbani, Q.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; Saleh, F.M.; AbouLaila, M.; Noreldin, A.E.; Raza, S.H.A.; Ullah, H.; Khan, R.; Menshawy, S. Expression of Immune-Related Genes in Parasite-Infected Tilapia Nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) from Egypt and Molecular Characterization of the Parasites. Gene Rep. 2022, 26, 101451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Leadbeater, S.; Garcia, C.; Sylvain, F.-E.; Custodio, M.; Ang, K.P.; Powell, F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Elliot, J.; et al. Parasitism Perturbs the Mucosal Microbiome of Atlantic Salmon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, T.C.; Van Der Ploeg, J.; Bih Awa, S.; Van Der Lingen, C.D.; Reed, C.C. Parasite Community Structure as a Predictor of Host Population Structure: An Example Using Callorhinchus capensis. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.; Pan, C.; Kao, J.Y.; Tsay, F.; Peng, N.; Kao, S.; Wang, H.; Tsai, T.; Wu, D.; Chen, C.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Eradication with Bismuth Quadruple Therapy Leads to Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota with an Increased Relative Abundance of Proteobacteria and Decreased Relative Abundances of Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, A.M.; Mirsepasi-Lauridsen, H.C.; Vester-Andersen, M.K.; Sørensen, N.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Bendtsen, F. High Abundance of Proteobacteria in Ileo-Anal Pouch Anastomosis and Increased Abundance of Fusobacteria Associated with Increased Pouch Inflammation. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vester-Andersen, M.K.; Mirsepasi-Lauridsen, H.C.; Prosberg, M.V.; Mortensen, C.O.; Träger, C.; Skovsen, K.; Thorkilgaard, T.; Nøjgaard, C.; Vind, I.; Krogfelt, K.A.; et al. Increased Abundance of Proteobacteria in Aggressive Crohn’s Disease Seven Years after Diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, D.S.; Othman, A.A. Parasite–Bacteria Interrelationship. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3145–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinas-Vera, M.; Ferreira-Sanabria, G.; Peña, P.; Sandoval-Espinola, W.J. The Paraguayan Gut Microbiome Contains High Abundance of the Phylum Actinobacteriota and Reveals the Influence of Health and Lifestyle Factors. Gut Microbes Rep. 2024, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strompfová, V.; Štempelová, L. Composition and Diversity of 16S rRNA Based Skin Bacterial Microbiome in Healthy Horses. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 2847–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFrentz, B.R.; García, J.C.; Waldbieser, G.C.; Evenhuis, J.P.; Loch, T.P.; Liles, M.R.; Wong, F.S.; Chang, S.F. Identification of Four Distinct Phylogenetic Groups in Flavobacterium columnare With Fish Host Associations. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsdottir, T.; Guttormsdottir, G.; Connaghan, D.; Hjartardottir, S. Longitudinal Survey of Flavobacterium Species in Icelandic Salmonid Fish Farms. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2020, 141, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, H.-J.; Kämpfer, P.; Szostak, M.P.; Spergser, J. Luteolibacter ambystomatis sp. Nov., Isolated from the Skin of an Ander son’s Salamander (Ambystoma andersoni). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualetti, C.; Szokoli, F.; Rindi, L.; Petroni, G.; Schrallhammer, M. The Obligate Symbiont “Candidatus Megaira Polyxenoph ila” Has Variable Effects on the Growth of Different Host Species. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanayake, T.; Salleh, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Zamri-Saad, M. Pathology and Pathogenesis of Vibrio Infection in Fish: A Review. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Meng, X.; Zheng, W.; Peng, H.; Hao, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.-J. The Modulation of Intestinal Commensal Bacteria Possibly Contributes to the Growth and Immunity Promotion in Epinephelus Akaara after Feeding the Antimicrobial Peptide Scy-Hepc. Anim. Microbiome 2024, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Sheng, Q.; Lv, Z.; Lu, H. Novel Pathway and Acetate-Facilitated Complete Atenolol Degradation by Hydrogenophaga sp. YM1 Isolated from Activated Sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Hameed, A.; Wen, C.-Z.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lai, W.-A.; Young, C.-C. Hydrogenophaga aquatica sp. Nov., Isolated from a Hot Spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, G.; Iatta, R.; Lovreglio, P.; Stufano, A.; Laidoudi, Y.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Bezerra-Santos, M.A.; Veneziano, V.; Di Gennaro, F.; Saracino, A.; et al. Detection of Endosymbiont Candidatus Midichloria Mitochondrii and Tickborne Pathogens in Humans Exposed to Tick Bites, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotti, D.; Boscaro, V.; Husnik, F.; Vannini, C.; Keeling, P.J. The “Other” Rickettsiales: An Overview of the Family “Candidatus Midichloriaceae”. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e02432-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Cai, G.; Nie, Q.; Sun, Y. The interactions between the host immunity and intestinal microorganisms in fish. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).