Some Insights into the Inventiveness of Dinoflagellates: Coming Back to the Cell Biology of These Protists
Abstract
1. Preamble
2. Introduction
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. An Autotrophic Free-Living Dinoflagellate: Prorocentrum micans Ehrenberg
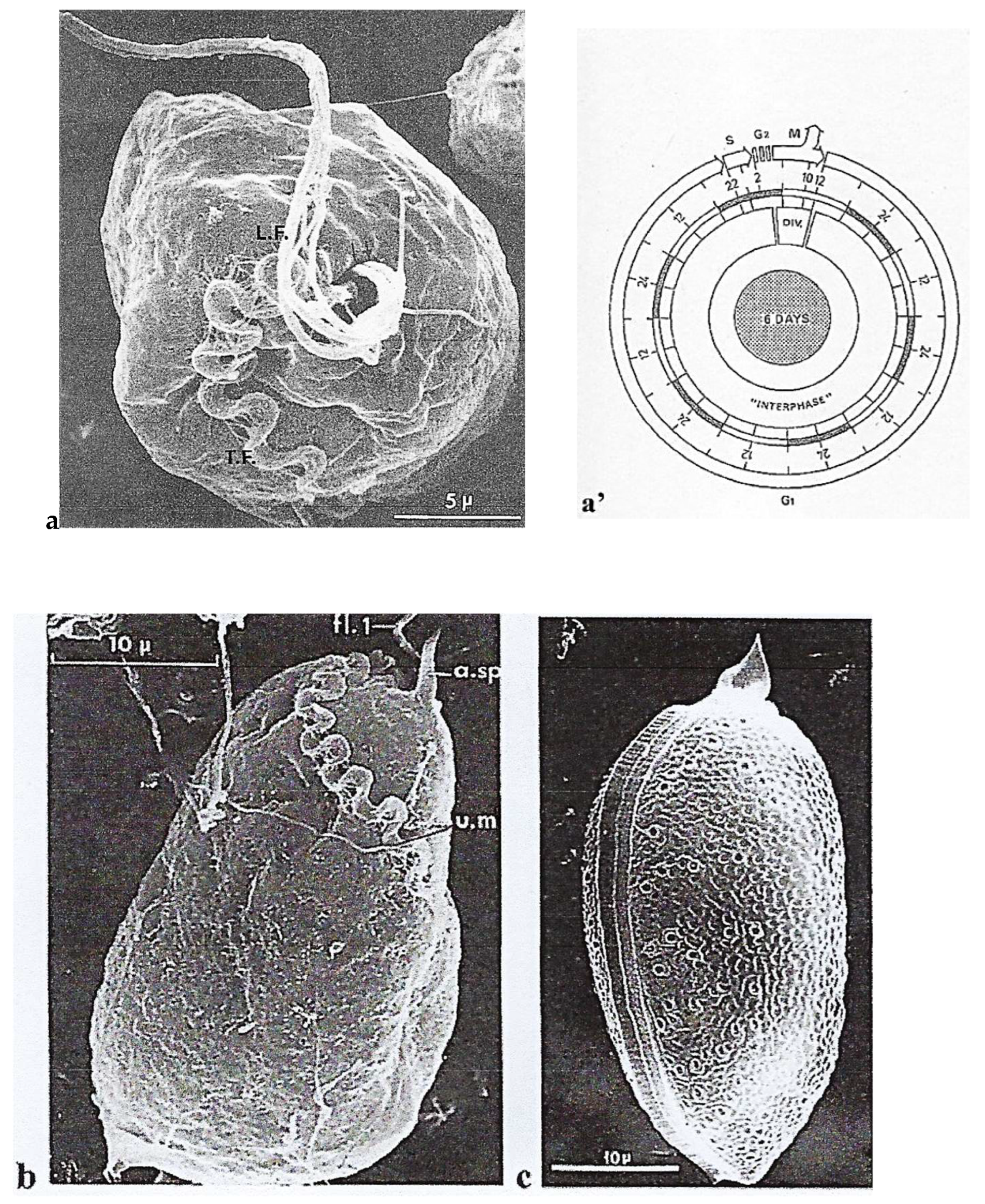
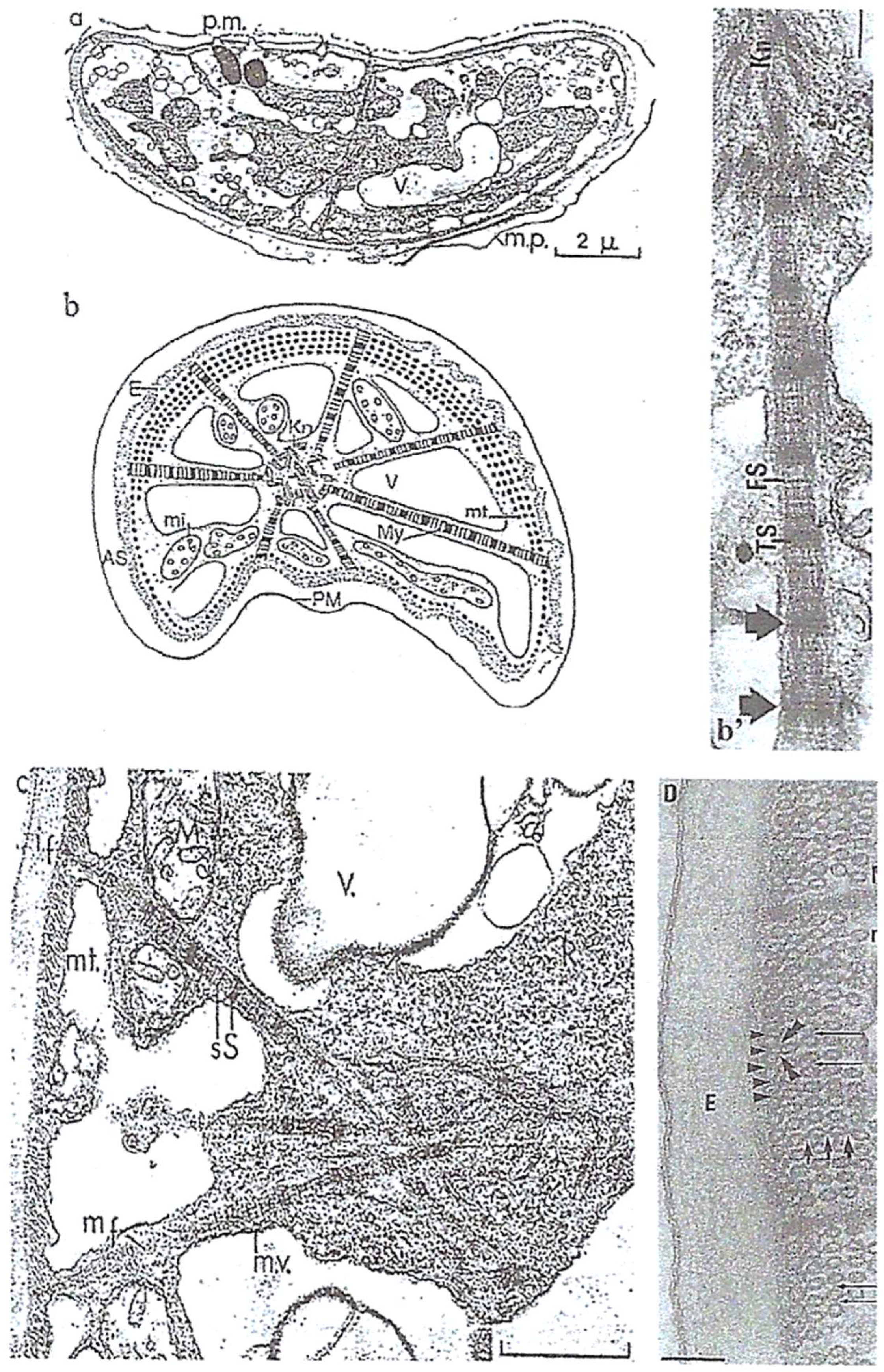
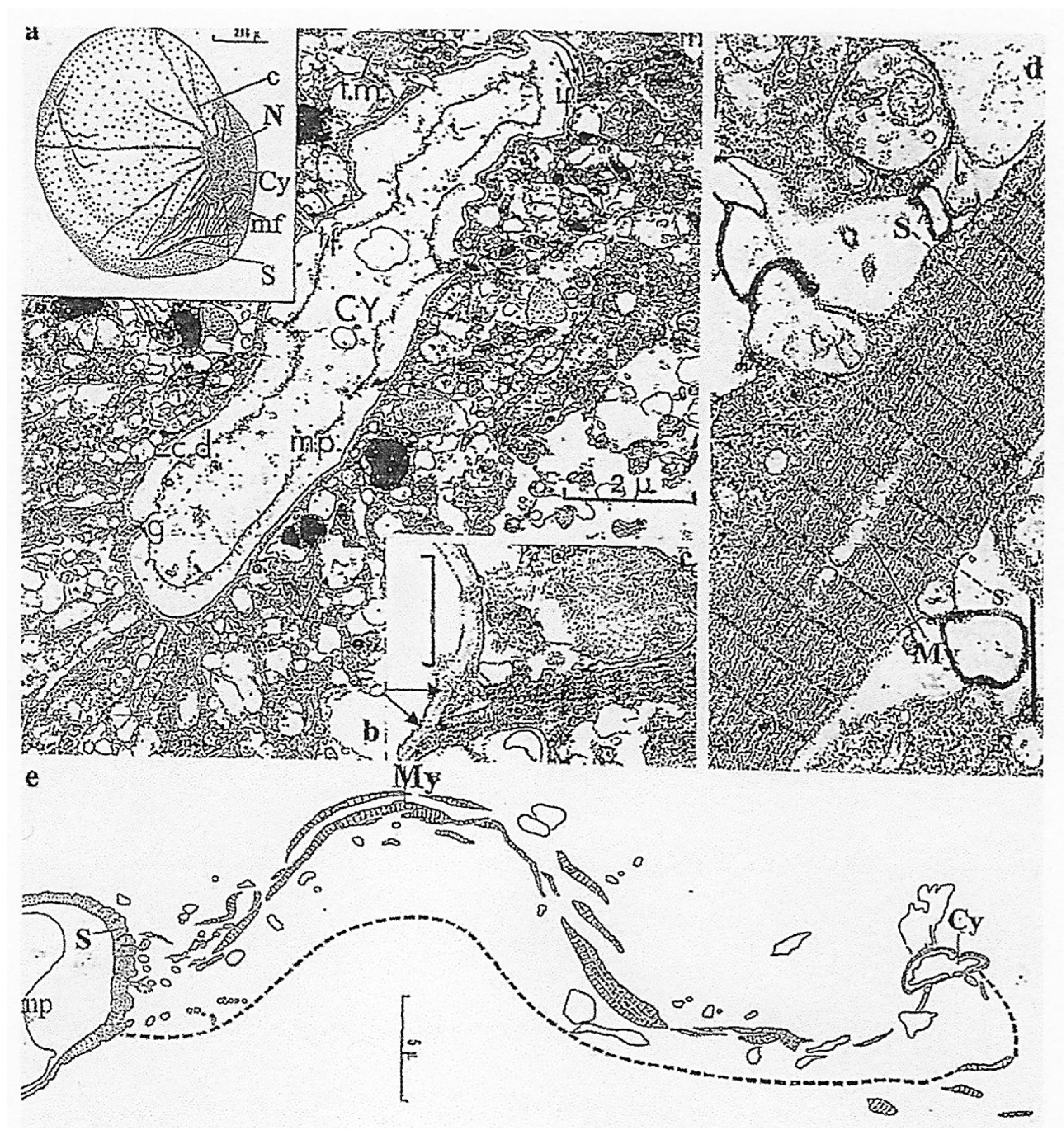
4.1.1. General Features
4.1.2. Original Features
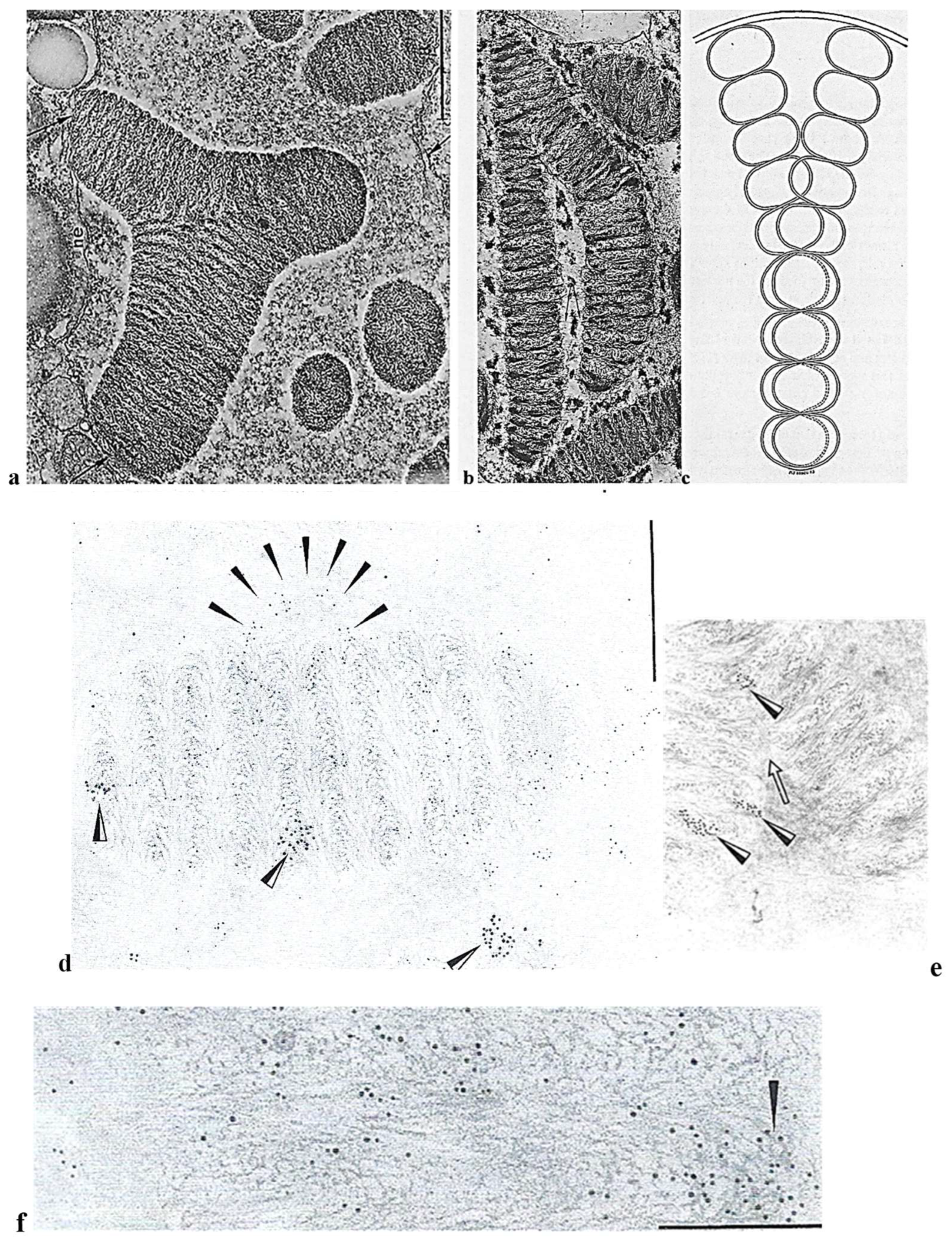
Nucleus
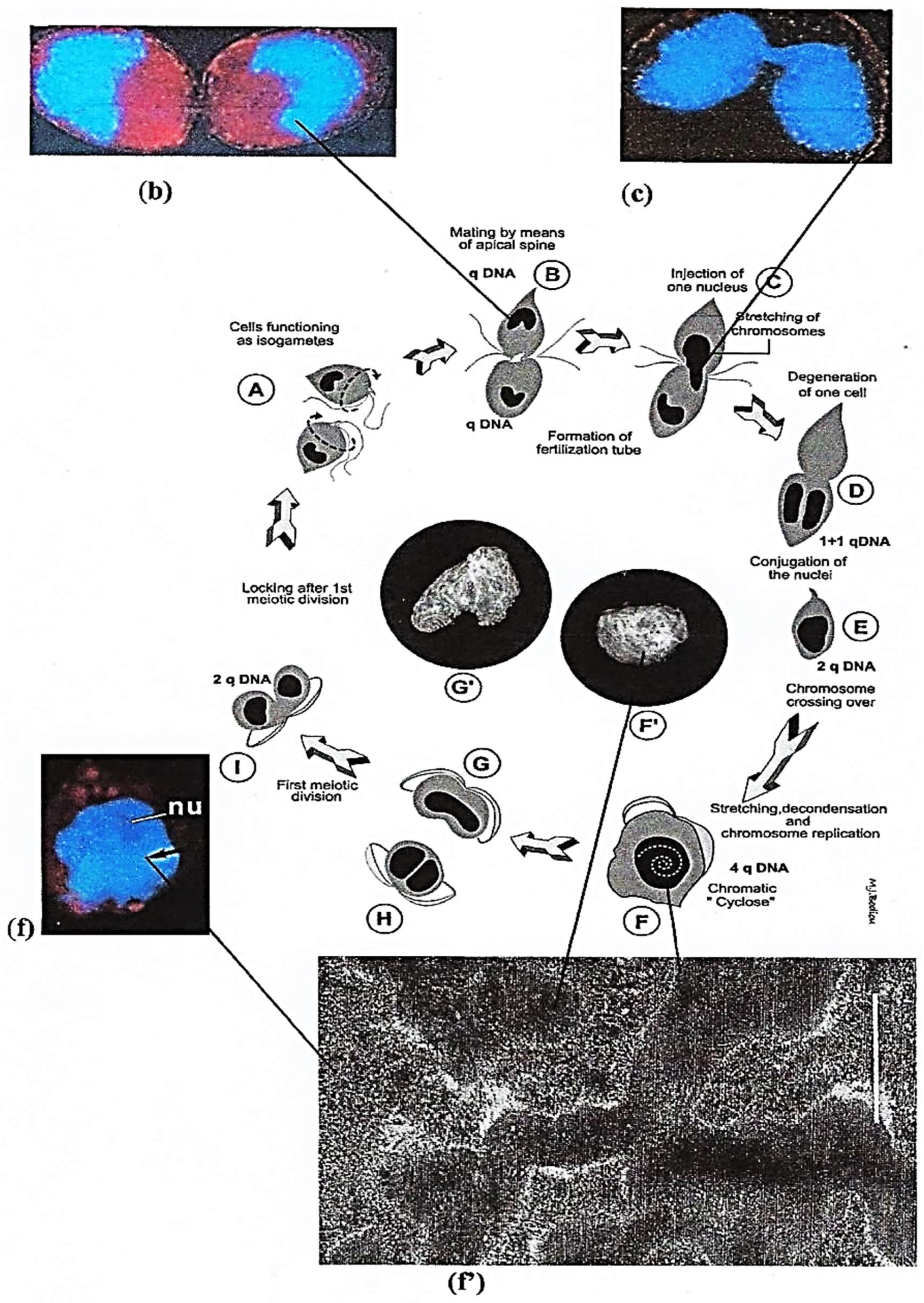
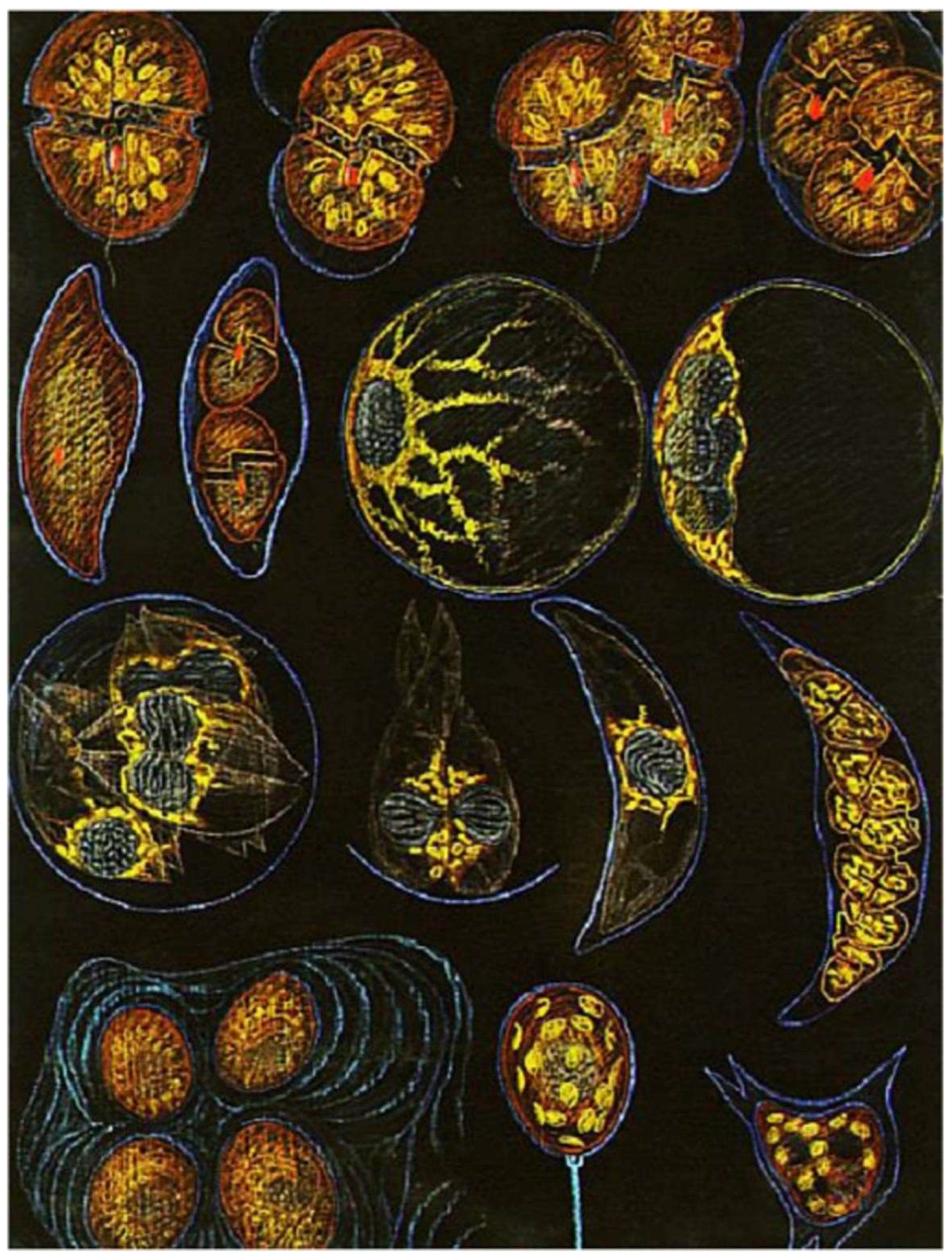
Sexual Reproduction
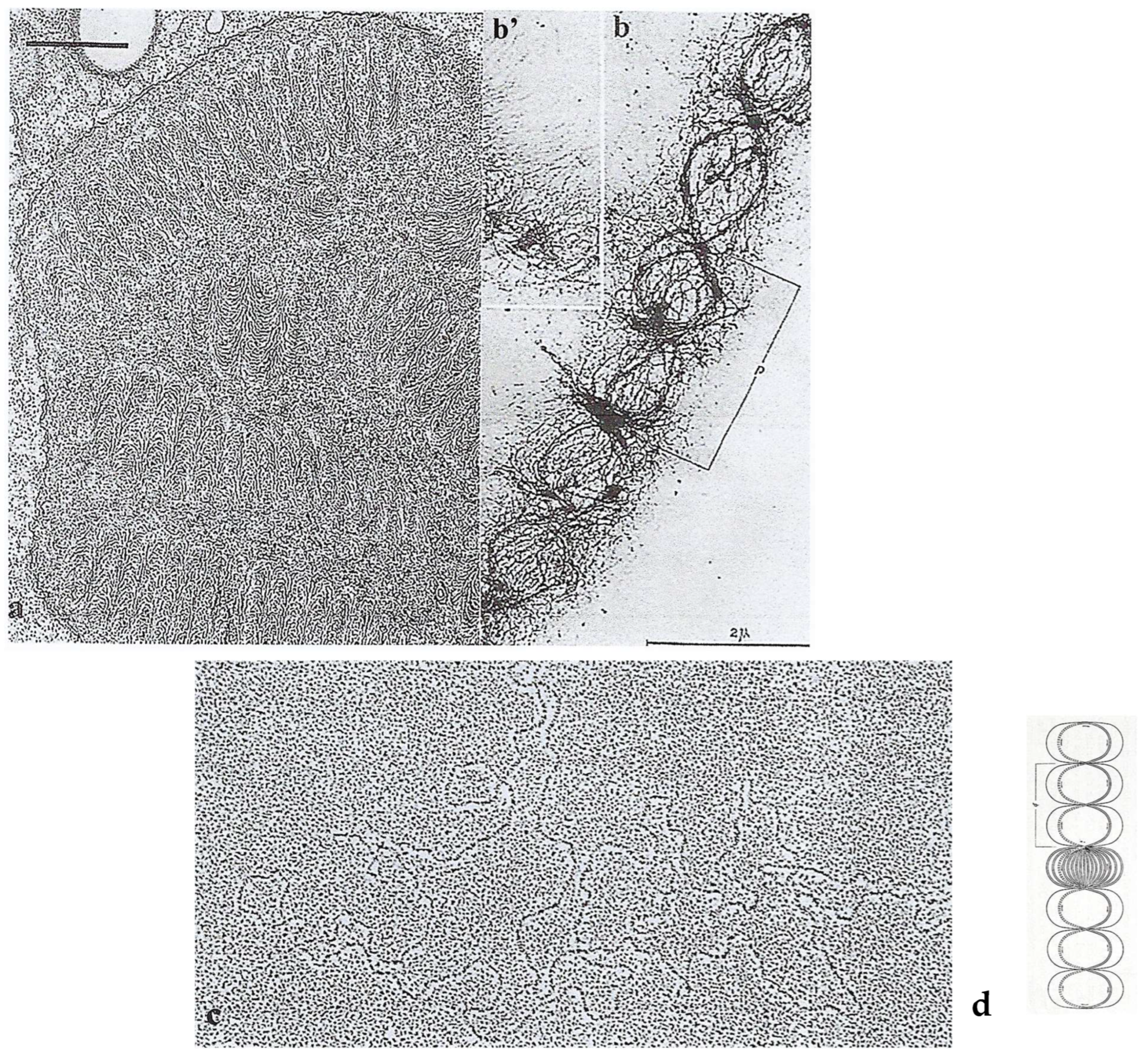
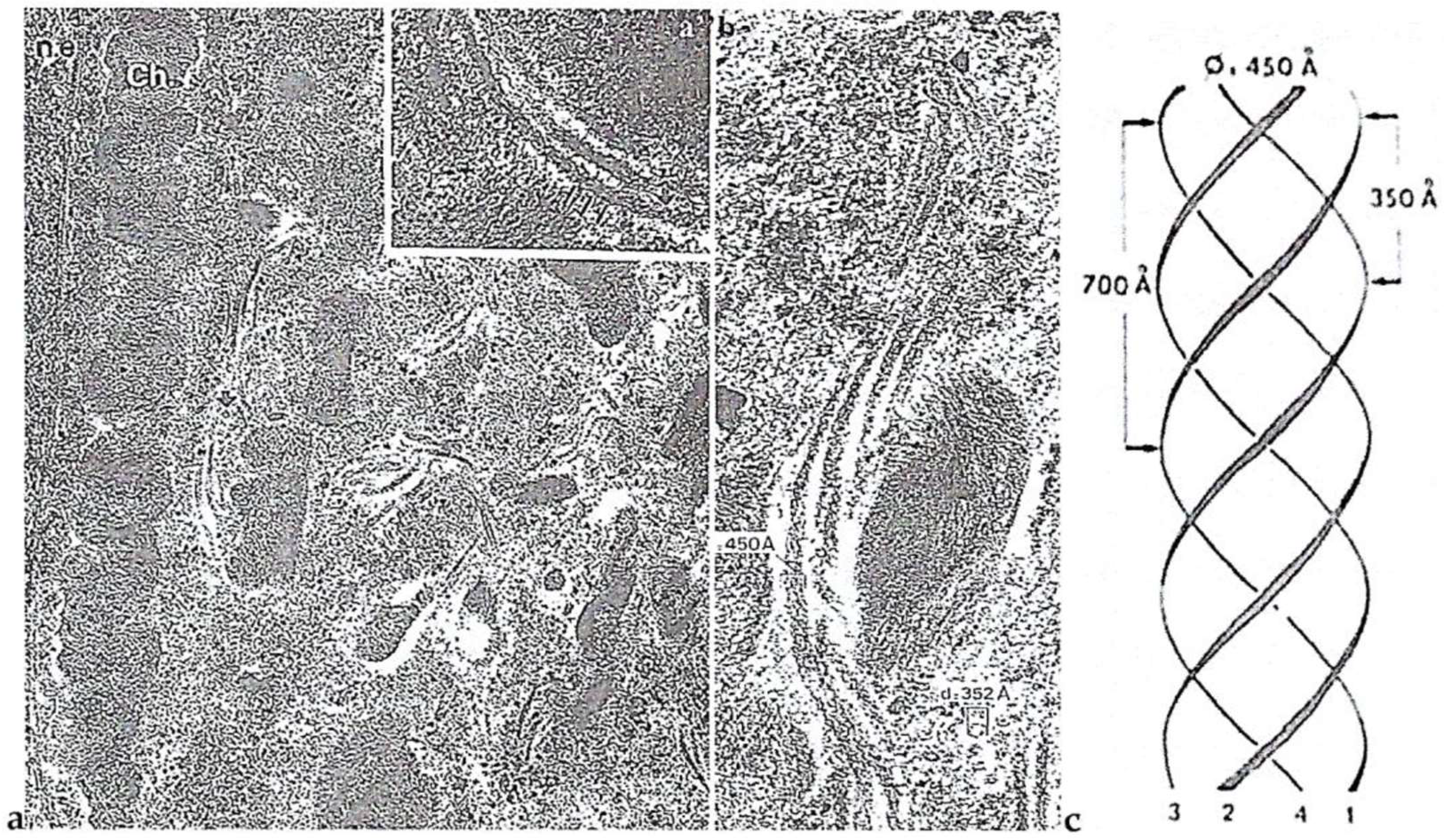
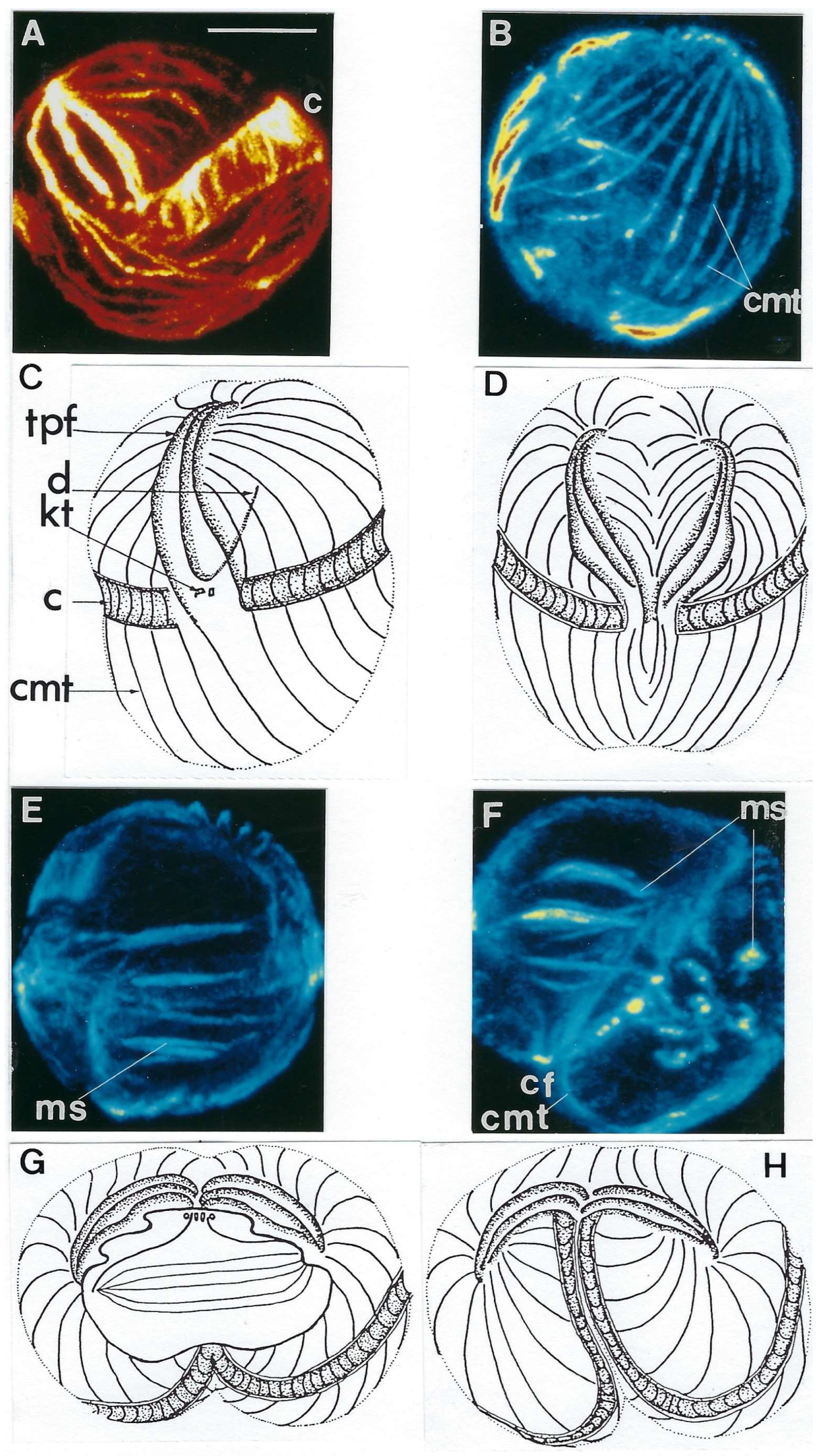
Intriguing Intranuclear Supercoiled Microcables During Meiosis [32]
4.2. Two Heterotrophic Free-Living Dinoflagellates: Noctiluca Scintillans Mc Cartney and Crypthecodinium cohnii Biecheler
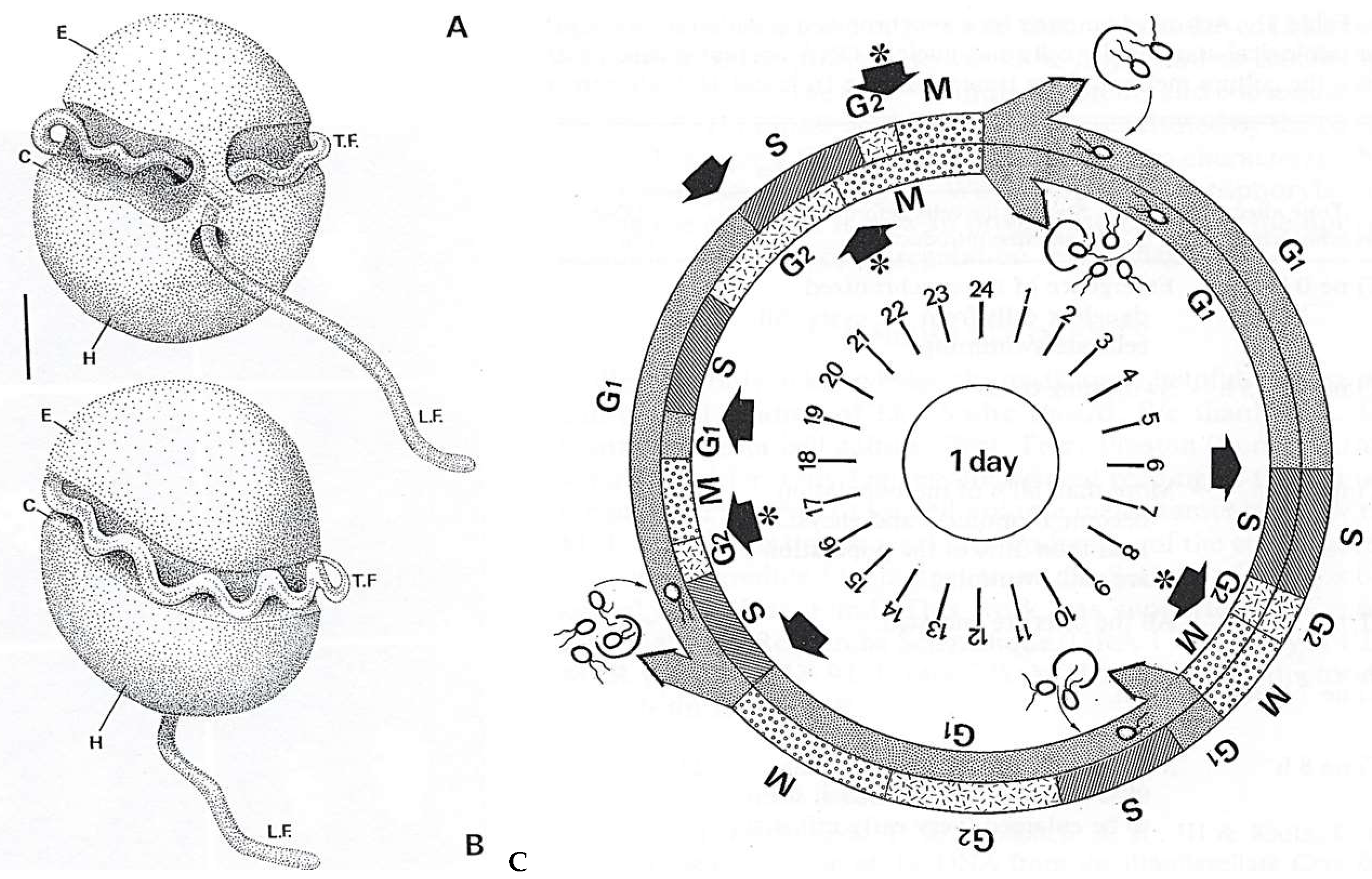
4.2.1. Noctiluca Scintillans McCartney
General Features
Original Features
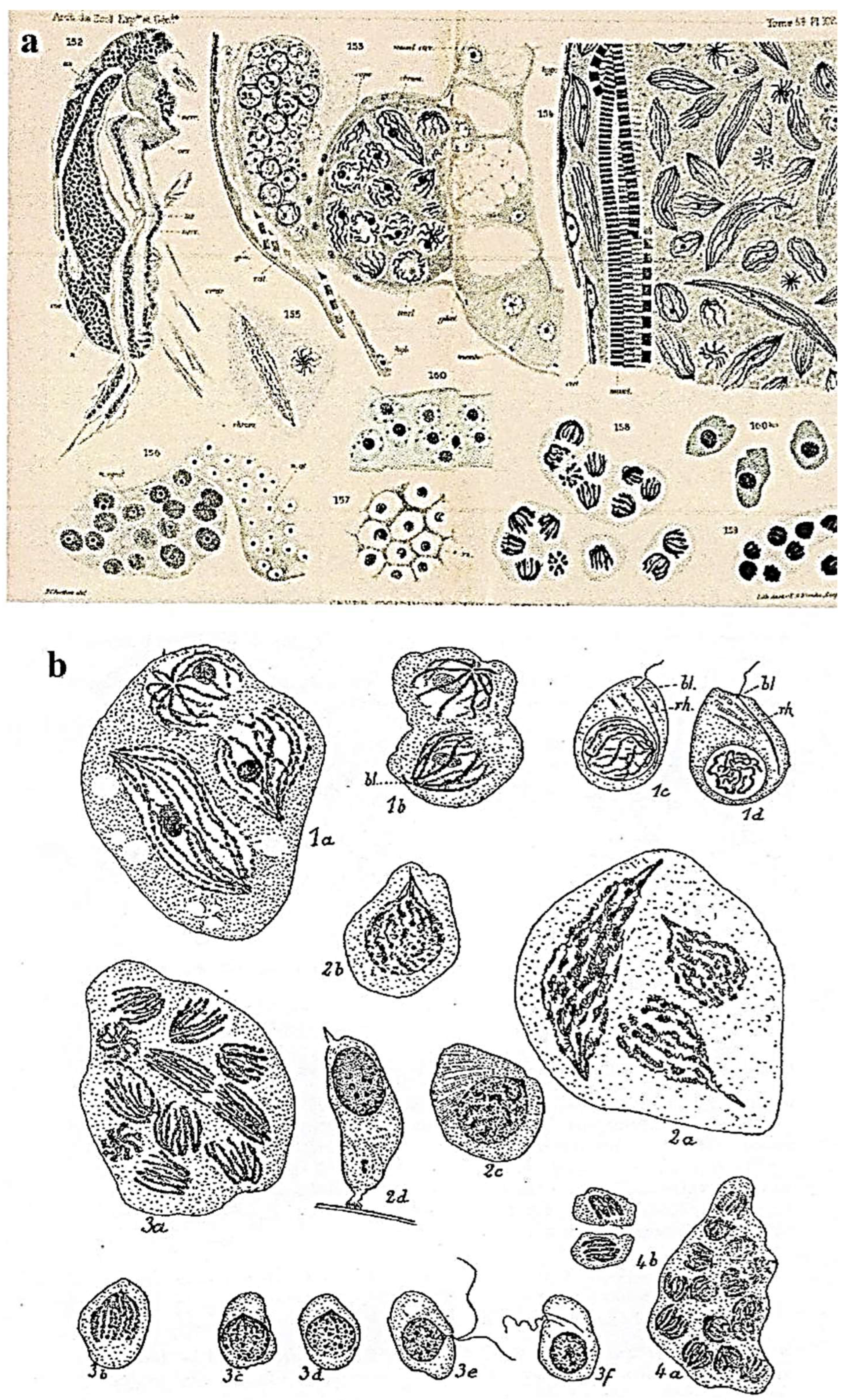
4.2.2. Other Free-Living Bioluminescent Dinoflagellates: An Homage to Edouard Chatton’s Scientific and Artistic Talents [3].
4.2.3. Crypthecodinium cohnii Biecheler
General Features
Innovative Features
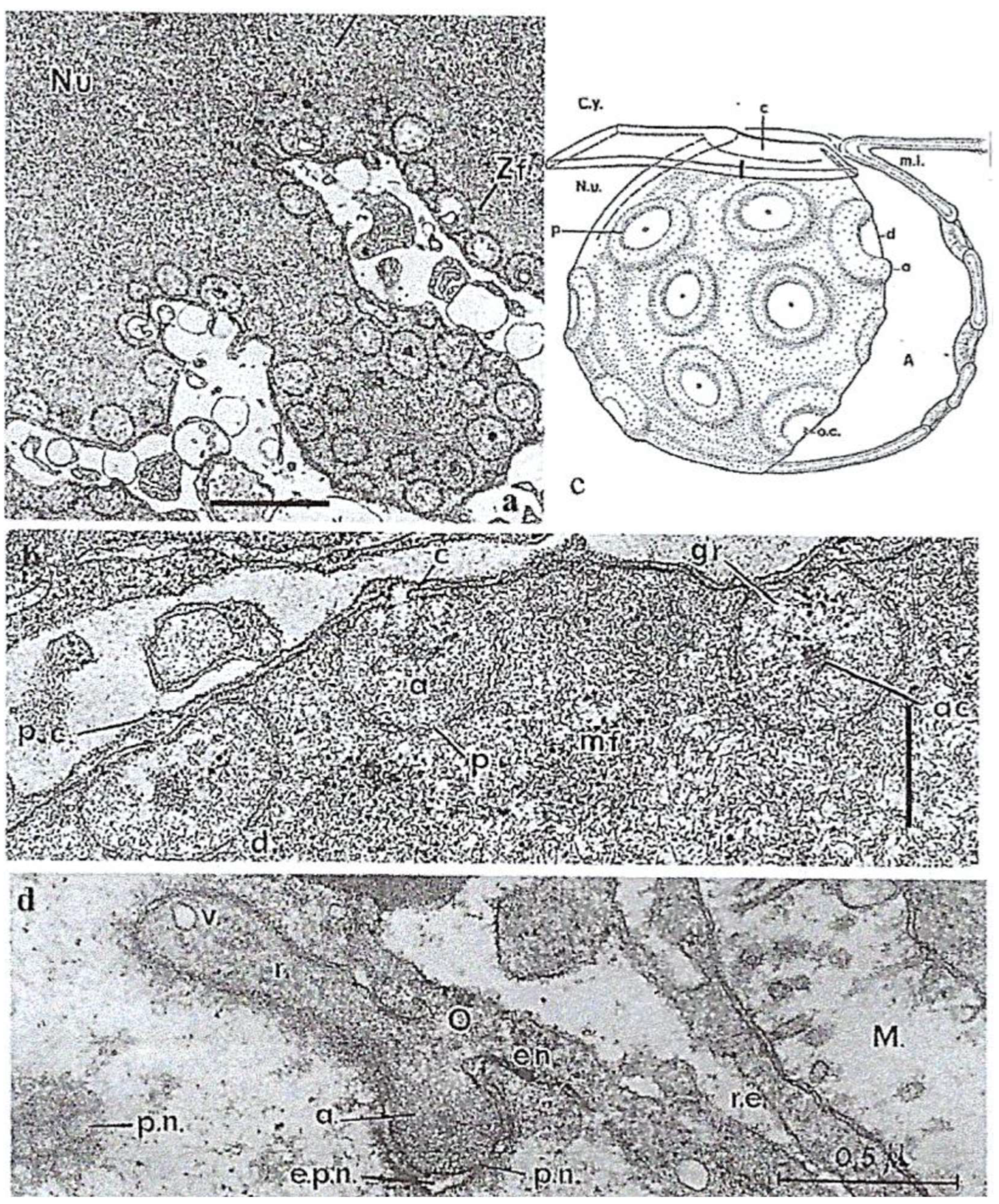
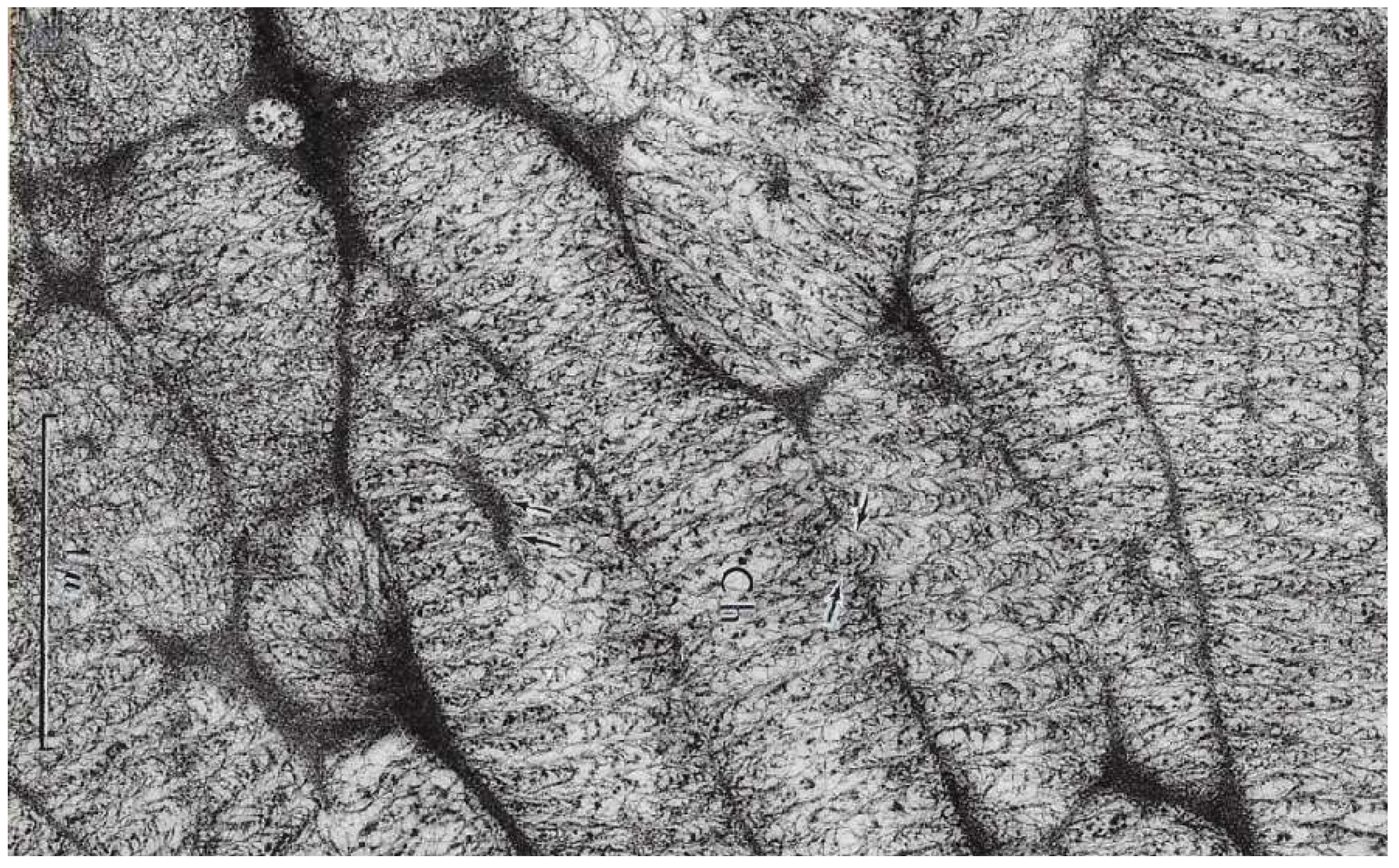
4.3. A Mixotrophic Dinoflagellate: Syndinium spp. Chatton
4.3.1. General Features
4.3.2. Innovative Features
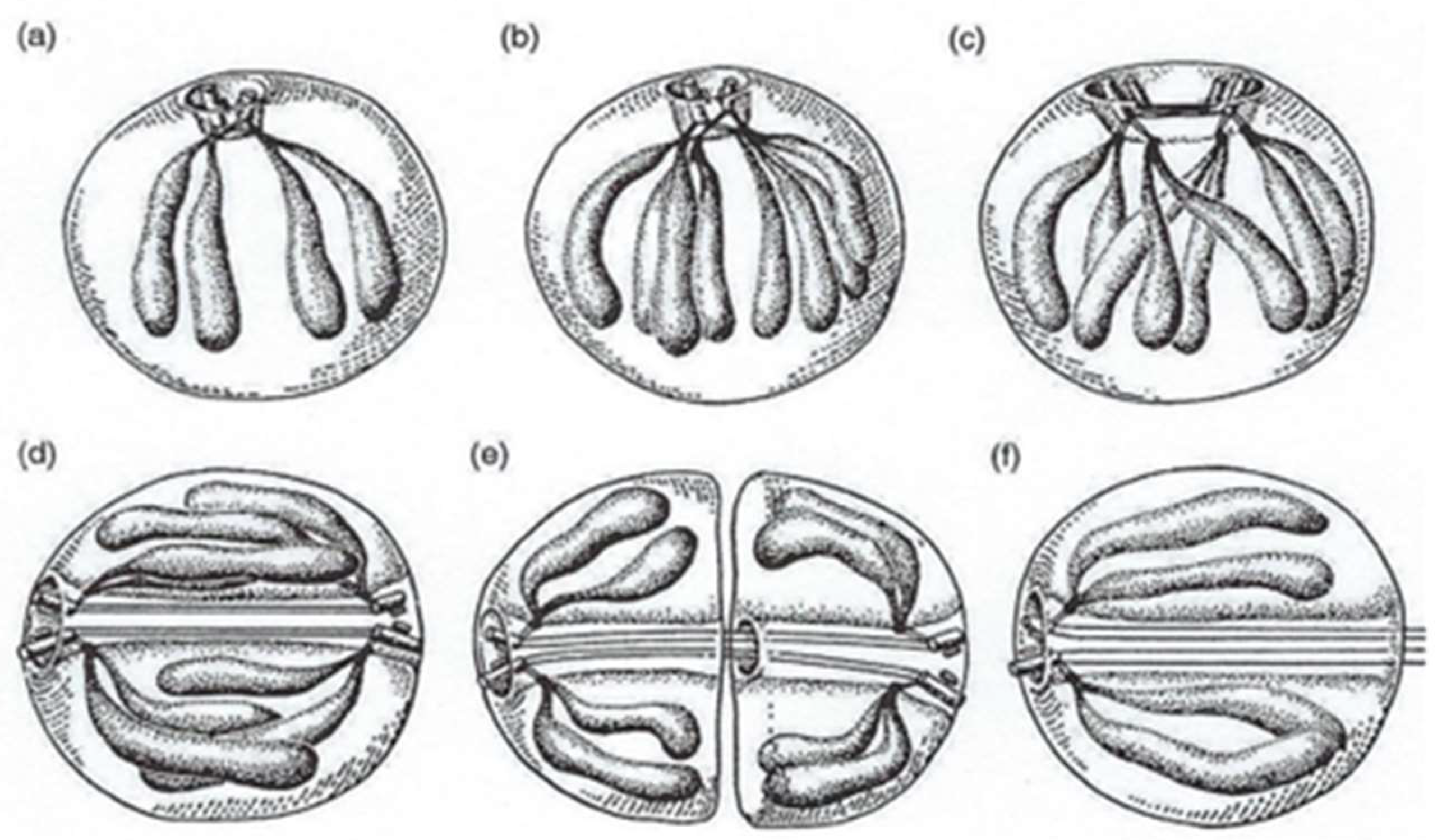
5. Dinoflagellate Mitotic Apparatus as an Evolutionary Marker
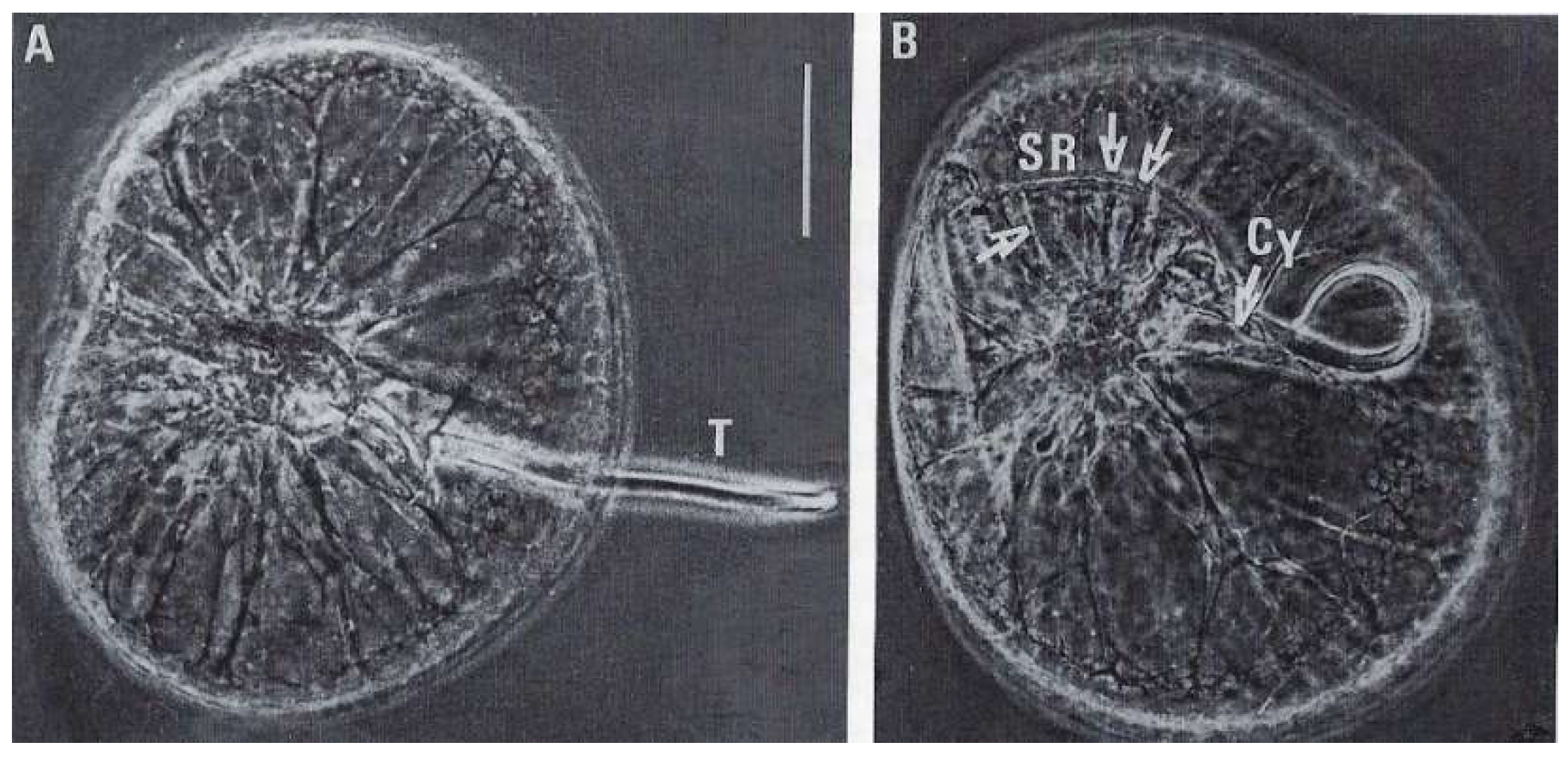
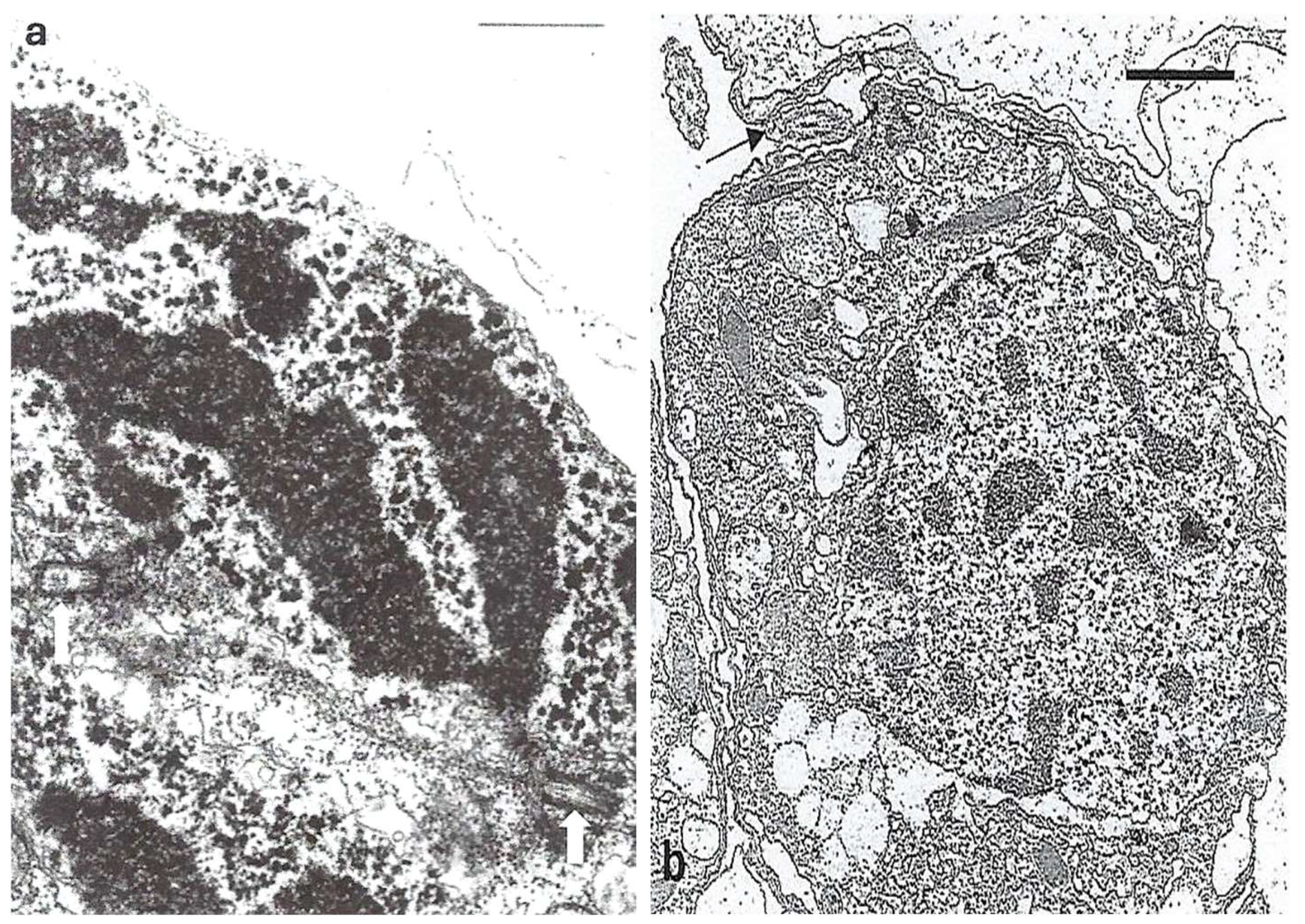
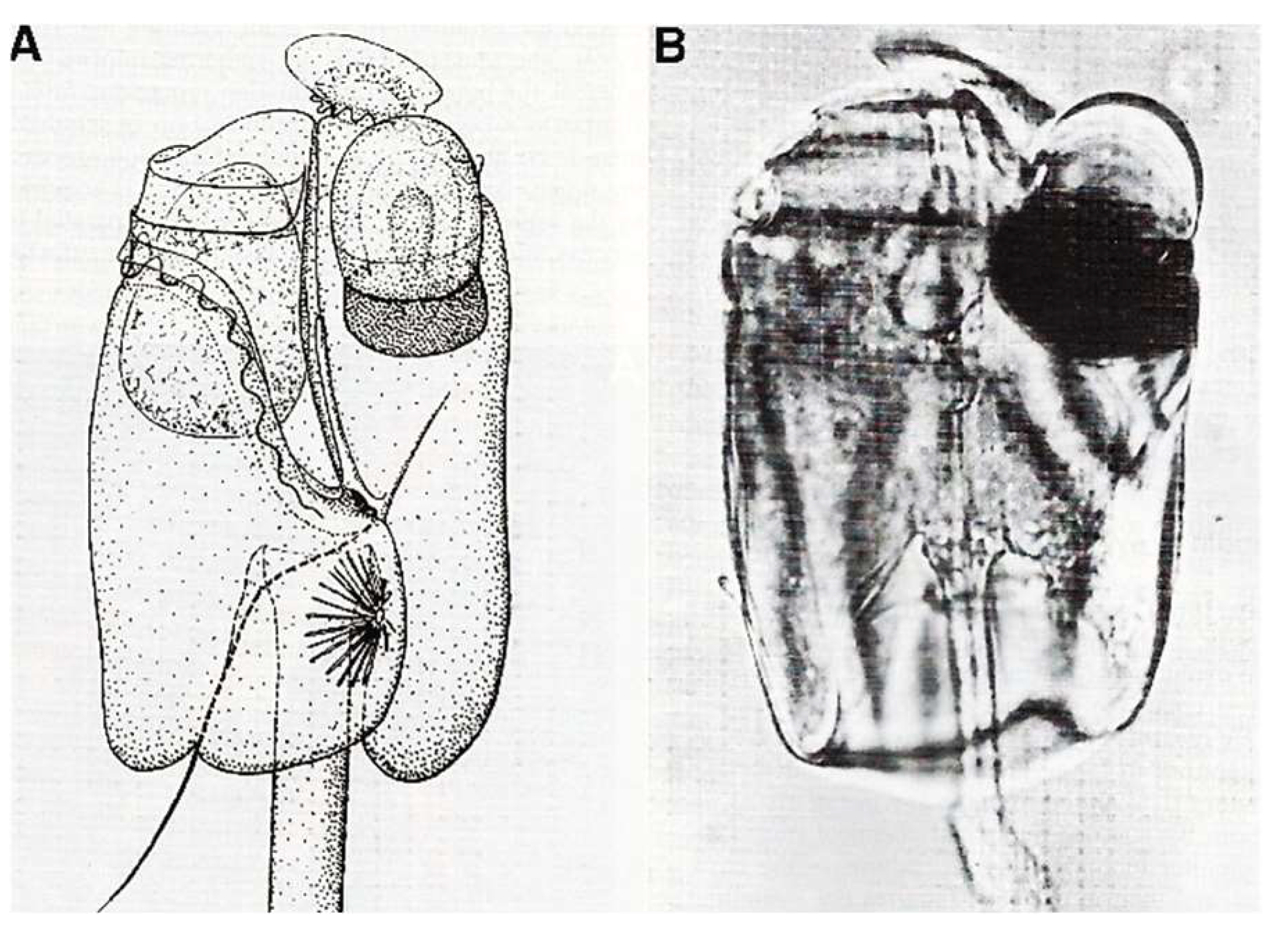
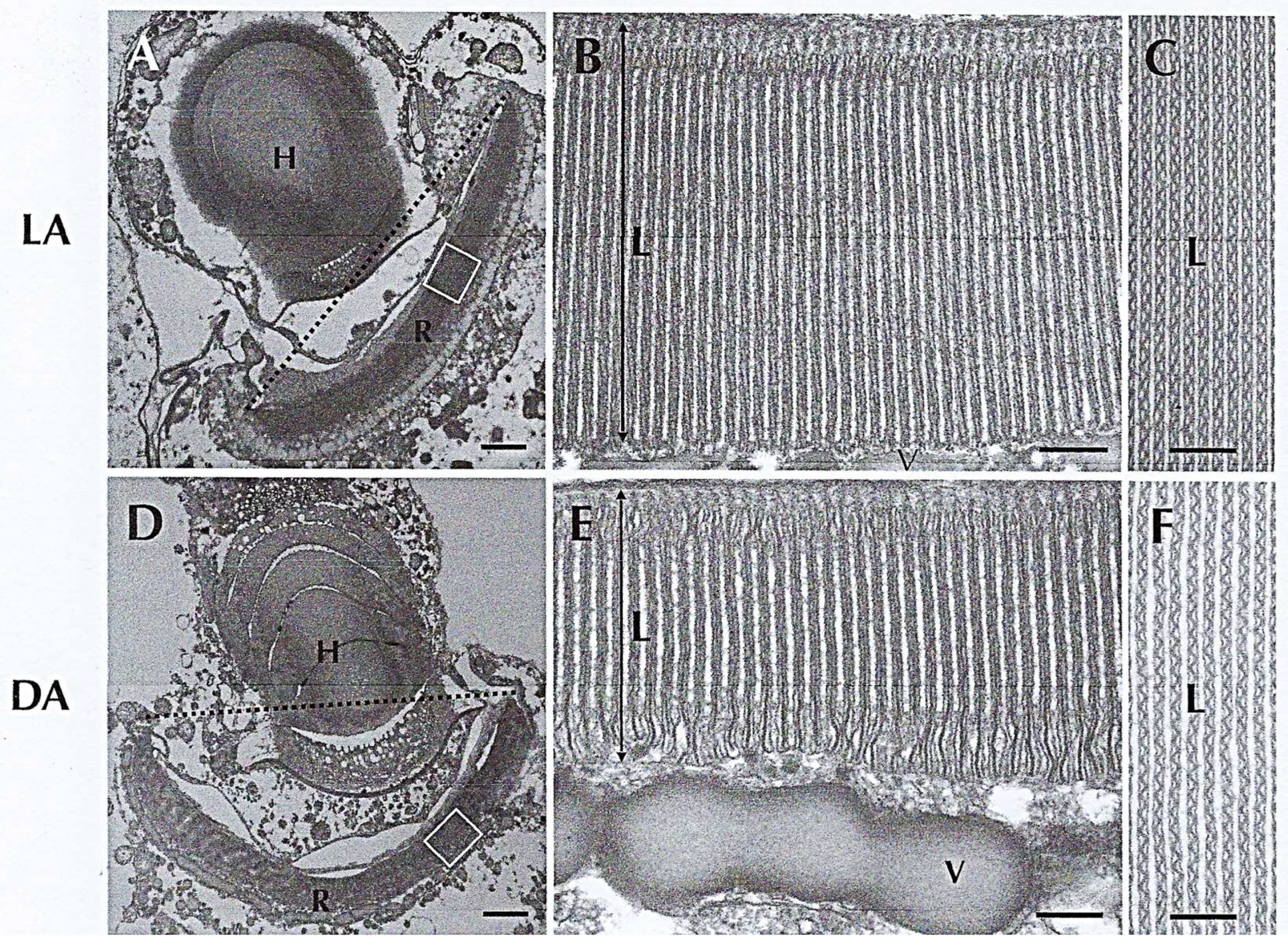
6. A Rather Perfected System: The Eyespot (Ocelloid) of Dinoflagellates
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chatton, E. Les Péridiniens Parasites: Morphologie, Reproduction, Ethologie; Librairie, H. Le Soudier: Paris, France, 1920; pp. 1–475. [Google Scholar]
- Chatton, E. Titres et Travaux Scientifiques (1906–1937); Imp-Editor Sottano: Sète, France, 1938; pp. 1–405. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Schrével, J. The Discoveries and Artistic Talents of Edouard Chatton and André Lwoff, Famous Biologists, 1st ed.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2021; pp. 1–228. [Google Scholar]
- Chatton, E. Pansporella perplexa. Ann. Sci. Nat. Zool. 1925, 8, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, F.J.R. Phylum Dinoflagellata. In Handbook of Protoctista, 1st ed.; Margulis, L., Corliss, J., Melkonian, M., Chapman, D.J., McKhan, H.I., Eds.; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 419–437. [Google Scholar]
- Riding, J.B.; Fensome, R.A.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Medlin, L.K. A Review of the Dinoflagellates and Their Evolution from Fossils to Modern. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldowan, J.M.; Talyzina, N.M. Biogeochemical evidence for dinoflagellate ancestors in the early Cambrian. Science 1998, 281, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, B. Paleontological Evidence for Dinoflagellates and Ciliates as Early Eukaryotes. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachvaroff, T.R.; Gornik, S.G.; Concepcion, G.T.; Waller, R.F.; Mendez, G.S.; Lippmeier, J.C.; Delwiche, C.F. Dinoflagellate phylogeny revisited: Using ribosomal proteins to resolve deep branching dinoflagellate clades. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 70, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwiche, C.F. The Origin and Evolution of Dinoflagellates. In Evolution of Primary Producers in the Sea; Falkovski, P.G., Knoll, A.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, F. A quantitative review of the lifestyle, habitat and trophic diversity of dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata, Alveolata). Syst. Biodivers. 2012, 10, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Dolan, M. Chromosomes of Protists: The crucible of Evolution. Int. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Dinoflagellates. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4th ed.; Volume II. Eukaryotic Microbes; Schmidt, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 28–49. [Google Scholar]
- Medlin, L.; Kooistra, W. Methods to estimate the diversity in marine Protist community with illustrations from case studies: A review. Diversity 2010, 2, 973–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufernez, F.; Derelle, E.; Noël, C.; Wyckmans, J.; Dive, D.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Capron, M.; Pierce, R.J.; Guillebaud, D.; Wintjens, R.; et al. Molecular characterization of Iron-containing Superoxide Dismutases in the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Protist 2008, 159, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. A decade of dinoflagellate genomics illuminating an enigmatic eukaryotic cell. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Methods for studying the nuclei and chromosomes of Dinoflagellates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 463, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Geraud, M.-L.; Coulaud, D.; Barray, M.; Théveny, B.; Révet, B.; Delain, E. Location of B- and Z-DNA in the chromosomes of a primitive Eukaryote dinoflagellate. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 111, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaud, Y.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. DNA synthesis and cell cycle of a primitive Dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum micans E. Protistologica 1986, 2, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Prévot, P.; De Billy, F.; Jalanti, T.; Flach, F.; Gautier, A. Prorocentrum micans E., one of the most primitive dinoflagellates. I. The complex flagellar apparatus as seen in scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Protistologica 1982, 18, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Haapala, O.K.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Structure of Dinoflagellate chromosomes. Nat. New Biol. 1973, 244, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Haapala, O.K. Division and function of Dinoflagellate chromosomes. J. Microsc. Biol. Cell 1974, 19, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Oakley, B.; Dodge, J.D. Evidence for a double-helically coiled toroidal chromonema in the dinoflagellate chromosomes. Chromosoma 1979, 70, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapala, O.K.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Size of circular chromatids and amounts of haploid DNA in the Dinoflagellates Gyrodinium cohnii and Prorocentrum micans. Hereditas 1974, 76, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapala, O.K.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Absence of longitudinal differentiation of Dinoflagellate (Prorocentrum micans) chromosomes. Hereditas 1974, 78, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, M.; De Marcillac, G.D.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. A high level of thymine replacement by 5-hydroxylmethyluracil in nuclear DNA of the primitive Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum micans E. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 27, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, M.S.; Von Boletzky, S.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Ultrastructural and biochemical nuclear aspects of Eukaryote classification: Independent evolution of the Dinoflagellates as a sister group of the actual Eukaryotes? Orig. Life 1984, 13, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaers, G.; Maroteaux, L.; Michot, B.; Herzog, M. Dinoflagellates in evolution: A molecular phylogenetic analysis of large subunit ribosomal-RNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1989, 29, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Bhaud, Y.; Saint-Hilaire, D. New data on mating in an autotrophic dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum micans Ehrenberg. Vie Milieu Life Environ. 2002, 52, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Pouchet, G. Nouvelle contribution à l’ histoire des Péridiniens marins. J. Anat. Physiol. 1885, 21, 28–88. [Google Scholar]
- Biecheler, B. La cyclose chromatique chez les Péridiniens. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1935, 201, 503–505. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Presence of intranuclear microcables in the nucleoplasm of a primitive Dinoflagellate. BioSystems 1981, 14, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Ausseil, J.; Geraud, M.L. Presence of nuclear and cytoplasmic actin in Dinoflagellate protists: Immunocytochemical and biochemical study. Biol. Cell 1996, 87, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdieva, M.; Pozdnyakov, I.; Matantseva, O.; Knyazev, N.; Skarlato, S. Actin as a cytoskeletal basis for cell architecture and a protein essential for ecdysis in Prorocentrum minimum (Dinophyceae, Prorocentrales). Phycol. Res. 2018, 66, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, J.W. Chemistry and control of luminescence in marine organisms. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1983, 33, 818–828. [Google Scholar]
- Valiadi, M.; Iglesias-Rodriguez, D. Understanding Bioluminescence in Dinoflagellates. How Far Have We Come? Microorganisms 2013, 1, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkonian, M.; Höhfeld, I. Amphiesmal ultrastructure in Noctiluca miliaris Suriray (Dinophyceae). Helgol. Meerersunters 1988, 42, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingmark, R. Sexual reproduction in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Suriray. J. Phycol. 1970, 6, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Les ultrastructures liées aux fonctions de relation chez Noctiluca miliaris S. (Dinoflagellata). Z. Zellforsch. Cell Tissue Res. 1970, 104, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. L’enveloppe nucléaire chez Noctiluca miliaris Suriray (Dinoflagellata). I. Quelques données sur son ultrastructure et son evolution au cours de la sporogenèse. J. Microsc. Biol. Cell 1969, 8, 569–580. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. L’enveloppe nucléaire chez Noctiluca miliaris Suriray (Dinoflagellata). II. Rôle des ampoules nucléaires et de certains constituants cytoplasmiques dans la mécanique mitotique. J. Microsc. Biol. Cell 1969, 8, 709–720. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Les ultrastructures nucléaires de la Noctiluque (Dinoflagellé libre) au cours de la sporogenèse. Chromosoma 1972, 39, 419–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métivier, C.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Organization of cytoskeleton during the tentacle contraction and cytostome movement in the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans McCartney. Cell Tissue Res. 1988, 251, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Endoh, H. Phylogenetic analyses of the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans based on beta-tubulin and Hsp90 genes. Eur. J. Protistol. 2008, 44, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, J.S. Nuclear 28S rDNA phylogeny supports the basal placement of Noctiluca scintillans (Dinophyceae; Noctilucales) in dinoflagellates. Eur. J. Protistol. 2010, 46, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubai, D.F.; Ris, H. Division in the dinoflagellate Gyrodinium cohnii (Schiller). A new type of nuclear reproduction. J. Cell Biol. 1969, 40, 508–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaud, Y.; Barbier, M.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. A detailed study of the complex cell cycle of the Dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii Biecheler and evidence for variation in H1 kinase activity. J. Euk. Microbiol. 1994, 41, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Davoust, J.; Albert, M.; Géraud, M.L.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Microtubule organization during the cell cycle of a primitive eukaryote Dinoflagellate. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Besseau, L.; Géraud, M.L.; Guillebault, D.; Albert, M.; Perret, E. Cytoskeleton and mitosis in the dinoflagellate C. cohnii; immunolocalization of P72, an HSP70 related protein. Eur. J. Protistol. 2002, 38, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Albert, M.; Bordes, N.; Bornens, M.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Microtubular spindle and centrosome structures during the cell cycle in the Dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. An immunocytochemical study. BioSystems 1991, 25, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Moudjou, M.; Geraud, M.L.; Derancourt, J.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Bornens, M. Identification of an HSP70-related protein associated with the centrosome from dinoflagellates to human cells. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.C.M.; Law, S.P.C.; Wong, J.T.Y. Oleaginous heterotrophic Dinoflagellates Crypthecodiniaceae. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.; Reis, A.; Vasconcelos, R.; Guerra, P.; Lopes da Silva, T. Crypthecodinium cohnii with emphasis on DHA production: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, E.; Poisson, R. Sur l’existence dans le sang des crabes de Péridiniens parasites: Hematodinium perezi, n.g., n.sp., (Syndinidae). C. R. Soc. Biol. 1931, 105, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Skovgaard, A.; Massana, R.; Balague, V.; Saiz, E. Phylogenetic position of the copepod-infesting parasite Syndinium turbo (Dinoflagellata, Syndinea). Protist 2005, 156, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Viprey, M.; Chambouvet, A.; Welsh, M.; Kikham, A.R.; Massana, R.; Scanlan, D.J.; Worden, A.Z. Widespread occurrence and genetic diversity of marine parasitoids belonging to Syndiniales (Alveolata). Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 3349–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, E. Sur un mécanisme cinétique nouveau: la mitose syndinienne chez les Péridiniens parasites plasmodiaux. Ann. Sci. Nat. 1921, 173, 859. [Google Scholar]
- Ris, H.; Kubai, D.F. An unusual mitotic mechanism in the parasitic protozoan Syndinium sp. J. Cell Biol. 1974, 60, 702–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Etude ultrastructurale de Syndinium sp. Chatton, parasite coelomique de Copépodes pélagiques. Vie Milieu Life Env. 1974, 24, 191–212. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, E.; Nam, S.W.; Shin, W.; Park, M.G.; Coats, D.W. Do all dinoflagellates have an extranuclear spindle? Protist 2015, 166, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greuet, C. Structure fine de l’ocelle d’Erythropsis pavillardi Hertwig, Péridinien Warnowiidae Lindemann. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1965, 261, 1904–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Gehring, W. The genetic control of eye development and its implications for the evolution of the various eye-types. Zoology 2001, 104, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D. On the eyespot of the dinoflagellate, Nematodinium. J. Exp. Biol. 1967, 47, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greuet, C. Organisation ultrastructurale de l’ocelle de deux Peridiniens Warnowiidae, Erythropsis pavillardi Kofoid et Swezy et Warnowia pulchra Schiller. Protistologica 1968, 4, 209–230. [Google Scholar]
- Greuet, C. Évolution structurale et ultrastructurale de l’ocelloide d’Erythropsidinium pavillardi Kofoid et Swezy (Péridinien Warnowiidae Lindemann) au cours des divisions binaires et palintomiques. Protistologica 1977, 13, 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Greuet, C. Ultrastructural organization of the ocelloid of Nematodinium. Phylogenetic aspect of the evolution of Warnowiidae Indemann dinoflagellates photoreceptors. Cytobiologie 1978, 17, 114–136. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppenrath, M.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Handy, S.M.; Delwiche, C.F.; Leander, B.S. Molecular phylogeny of ocelloid-bearing dinoflagellates (Warnowiaceae) as inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA sequences. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooney, E.C.; Holt, C.C.; Jacko-Reynolds, V.K.L.; Leander, B.S.; Keeling, P.J. Photosystems in the eye-like organelles of heterotrophic warnowiid dinoflagellates. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 4252–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreimer, G. Reflective properties of different Eyespot types in Dinoflagellates. Protist 1999, 150, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kite, G.C.; Rothschild, L.J.; Dodge, J.D. Nuclear and plastid DNAs from the binucleate dinoflagellates Glenodinium (Peridinium) foliaceum and Peridinium balticum. Biosystems 1988, 21, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, W.J. New perspectives on eye development and the evolution of eyes and photoreceptors. J. Hered. 2005, 96, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Takaku, Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Horiguchi, T.; Suga, H.; Gehring, W.; Kazuho, I.; Takashi, G. Function and Evolutionary Origin of Unicellular Camera-Type Eye Structure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavelis, G.S.; Hayakawa, S.; White, R.A., III; Gojobori, T.; Suttle, C.; Keeling, P.J.; Leander, B.S. Eye-like ocelloids are built from different endosymbiotically acquired components. Nature 2015, 523, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin, C. The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, 6th ed.; D. Appleton and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1870; 392p. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O. Some Insights into the Inventiveness of Dinoflagellates: Coming Back to the Cell Biology of These Protists. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050969
Soyer-Gobillard M-O. Some Insights into the Inventiveness of Dinoflagellates: Coming Back to the Cell Biology of These Protists. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050969
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoyer-Gobillard, Marie-Odile. 2025. "Some Insights into the Inventiveness of Dinoflagellates: Coming Back to the Cell Biology of These Protists" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050969
APA StyleSoyer-Gobillard, M.-O. (2025). Some Insights into the Inventiveness of Dinoflagellates: Coming Back to the Cell Biology of These Protists. Microorganisms, 13(5), 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050969





