Effects of Compound Microecological Preparation Supplementation on Production Performance and Nutrient Apparent Digestibility in Hu Sheep from the Rumen Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Ethics
2.2. Blended Feed Additives
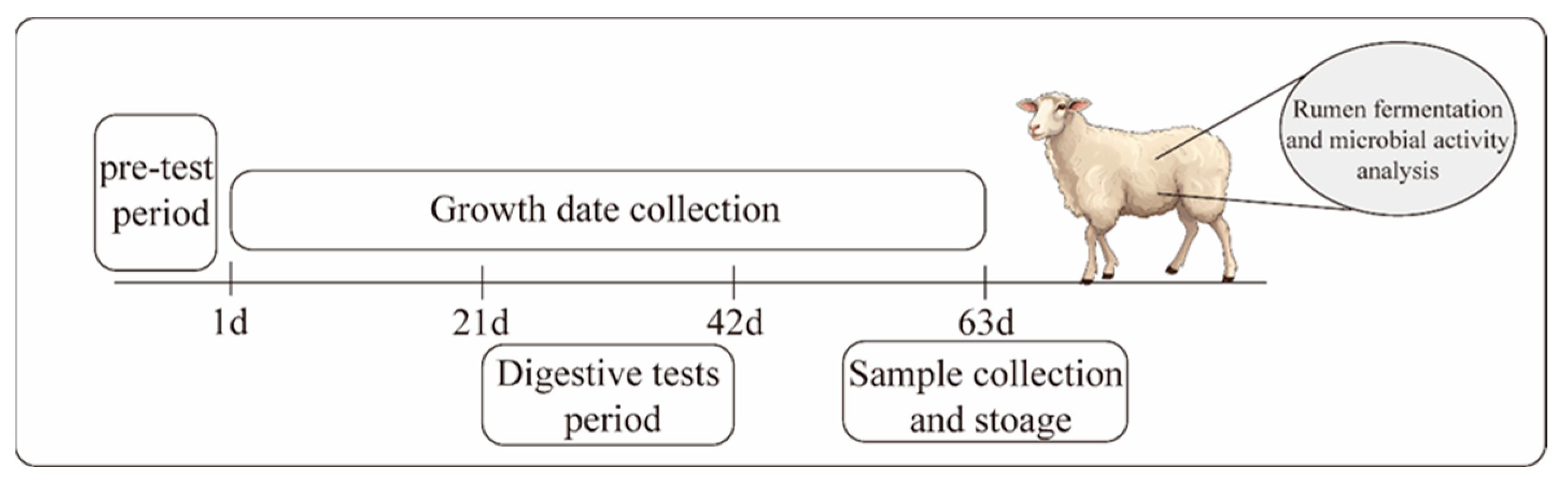
2.3. Experimental Animals and Group Design
2.4. Sample Collection and Procession
2.4.1. Growth Performance and Apparent Digestibility
2.4.2. Determination Method of Nutrient Content
2.4.3. Rumen Fluid Indicators and Rumen Bacteria Sampling
2.4.4. Extraction of DNA and Sequencing of 16S rDNA
2.4.5. Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) Generation Process
2.4.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of ATABG on Hu Sheep’s Growth Performance and Apparent Digestibility
3.2. Effect of ATABG on Hu Sheep’s Ruminal Environment and Histomorphology
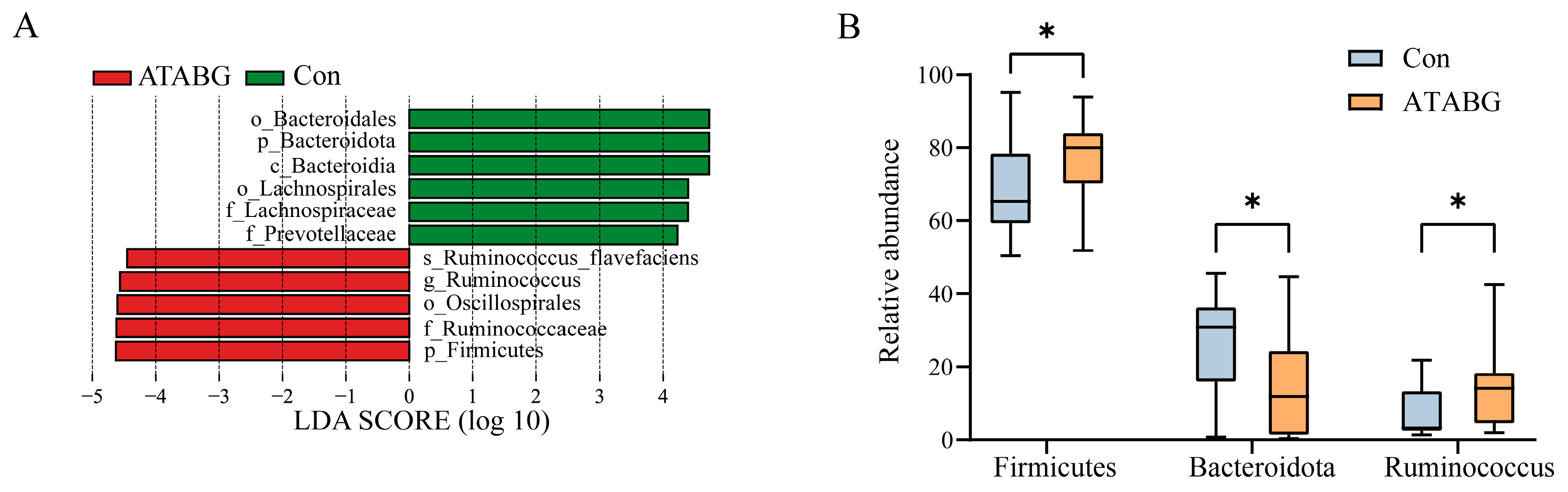
3.3. Effect of ATABG on Hu Sheep’s Ruminal Bacterial Relative Abundance
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Reuben, R.C.; Elghandour, M.M.M.Y.; Alqaisi, O.; Cone, J.W.; Márquez, O.; Salem, A.Z.M. Influence of Microbial Probiotics on Ruminant Health and Nutrition: Sources, Mode of Action and Implications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1319–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, R.; Chang, J.; Chen, L.; Nabi, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, P. Rumen Microbes, Enzymes, Metabolisms, and Application in Lignocellulosic Waste Conversion—A Comprehensive Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 71, 108308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, T.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Ren, C.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Review of Feeding Systems Affecting Production, Carcass Attributes, and Meat Quality of Ovine and Caprine Species. Life 2023, 13, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüfekci, H.; Sejian, V. Stress Factors and Their Effects on Productivity in Sheep. Animals 2023, 13, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Hao, Y.; Mao, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Teng, D.; Wang, J. An Enhanced Variant Designed From DLP4 Cationic Peptide Against Staphylococcus Aureus CVCC 546. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dho, M.; Candian, V.; Tedeschi, R. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides: Advancements, Enhancements and New Challenges. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lei, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, Q.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptides Act on the Rumen Microbiome and Metabolome Affecting the Performance of Castrated Bulls. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, B.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Wang, X.; Hao, Y.; Yang, N. Antimicrobial Peptide ID13, Preparation Method and Use Thereof 2023. Available online: https://www.freepatentsonline.com/y2021/0171585.html (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Kennedy, K.M.; Pintens, D.A.; Kalscheur, K.F.; Shinners, K.J.; Friede, J.C.; Digman, M.F. Effect of Feeding Mechanically Processed Alfalfa Silage on Production Performance of Mid-Lactation Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogstad, K.C.; Herrick, K.J.; Morris, D.L.; Hanford, K.J.; Kononoff, P.J. The Effects of Pelleted Dried Distillers Grains and Solubles Fed with Different Forage Concentrations on Rumen Fermentation, Feeding Behavior, and Milk Production of Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 6633–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Zahoor Khan, M.; Xiao, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Li, C.; Cao, Z. The Impact of Ammoniation Treatment on the Chemical Composition and In Vitro Digestibility of Rice Straw in Chinese Holsteins. Animals 2020, 10, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, G.K.; Hawley, E.; Yusuf, M.; Dorsam, G.; Swanson, K.C. Influence of Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide on Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Nitrogen Balance, and Digestive Enzyme Activity in Lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Sun, H.; Guo, H.; Nie, C.; Nan, S.; Lu, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W. Effect of the Supplementation of Exogenous Complex Non-Starch Polysaccharidases on the Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation and Microflora of Fattening Sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1396993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinos-Rodríguez, J.M.; Robinson, P.H.; Ortega, M.E.; Berry, S.L.; Mendoza, G.; Bárcena, R. Performance and Rumen Fermentation of Dairy Calves Supplemented with Saccharomyces Cerevisiae1077 or Saccharomyces Boulardii1079. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 140, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomenky, B.E.; Chiquette, J.; Bissonnette, N.; Talbot, G.; Chouinard, P.Y.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M. Impact of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Boulardii CNCMI-1079 and Lactobacillus Acidophilus BT1386 on Total Lactobacilli Population in the Gastrointestinal Tract and Colon Histomorphology of Holstein Dairy Calves. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 234, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, T.B.; De Moraes, C.M.; Sturbelle, R.T.; Dummer, L.A.; Fischer, G.; Leite, F.P.L. Probiotics Bacillus Toyonensis and Saccharomyces Boulardii Improve the Vaccine Immune Response to Bovine Herpesvirus Type 5 in Sheep. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 117, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, H.; Wan, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; et al. Yeast Probiotic and Yeast Products in Enhancing Livestock Feeds Utilization and Performance: An Overview. JoF 2022, 8, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 816-2021; Feed Standard of Meat-Producing Sheep and Goats. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Latimer, G.W. (Ed.) Official Methods of Analysis. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL, 22nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2023; ISBN 978-0-19-761013-8. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 39760-2021. Laboratory Animal—Guidelines for Euthanasia; State Administration for Market Supervision and Administration of China. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, H. Effect of coated Brady yeast on growth performance, immunity and nutrient apparent digestibility of calves. Feed Res. 2023, 46, 11–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; Guo, P.; Fang, S.; Ling, X.; Chi, C.; Gan, Q. Effect of Dietary Addition of Brady’s Yeast on Growth Performance, Serum Immunological Indices and Faecal Microbiota of Angus Calves. J. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 34, 3743–3757. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelCurto-Wyffels, H.M.; Dafoe, J.M.; Parsons, C.T.; Boss, D.L.; DelCurto, T.; Wyffels, S.A.; Van Emon, M.L.; Bowman, J.G.P. Diurnal Ruminal pH and Temperature Patterns of Steers Fed Corn or Barley-Based Finishing Diets. Animals 2021, 11, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.R.K.; Hyder, I. Ruminant Digestion. In Textbook of Veterinary Physiology; Das, P.K., Sejian, V., Mukherjee, J., Banerjee, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 353–366. ISBN 978-981-19-9409-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hailemariam, S.; Zhao, S.; He, Y.; Wang, J. Urea Transport and Hydrolysis in the Rumen: A Review. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, D.; Mao, S.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J. Infusion of Sodium Butyrate Promotes Rumen Papillae Growth and Enhances Expression of Genes Related to Rumen Epithelial VFA Uptake and Metabolism in Neonatal Twin Lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieho, K.; Bannink, A.; Geurts, I.A.L.; Schonewille, J.T.; Gort, G.; Dijkstra, J. Morphological Adaptation of Rumen Papillae during the Dry Period and Early Lactation as Affected by Rate of Increase of Concentrate Allowance. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; An, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Kulyar, M.F.-A.; Duan, K.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y.; Wan, X.; Li, J.; et al. Integrated Bacteria-Fungi Diversity Analysis Reveals the Gut Microbial Changes in Buffalo with Mastitis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 918541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Salekdeh, G.H. A Metagenomic Analysis of the Camel Rumen’s Microbiome Identifies the Major Microbes Responsible for Lignocellulose Degradation and Fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.B.; Mao, S. Influence of Yeast on Rumen Fermentation, Growth Performance and Quality of Products in Ruminants: A Review. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Xin, L.; Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Aschalew, N.D.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into Rumen Function Promotion through Yeast Culture (Saccharomyces Cerevisiae) Metabolites Using in Vitro and in Vivo Models. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1407024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, C.; Thapa, D.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Potential for Enriching Next-Generation Health-Promoting Gut Bacteria through Prebiotics and Other Dietary Components. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Xue, M.-Y.; Jia, M.-H.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Q.; Sun, H.-Z. Invited Review—Understanding the Functionality of the Rumen Microbiota: Searching for Better Opportunities for Rumen Microbial Manipulation. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoman, C.J.; Fields, C.J.; Lepercq, P.; Ruiz, P.; Forano, E.; White, B.A.; Mosoni, P. In Vivo Competitions between Fibrobacter Succinogenes, Ruminococcus Flavefaciens, and Ruminoccus Albus in a Gnotobiotic Sheep Model Revealed by Multi-Omic Analyses. mBio 2021, 12, e03533-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, W. Effects of Different Feeding Modes on Rumen Flora and Enzyme Activities of Nanjiang Yellow Sheep (Panax quinquefasciatus). J. Domest. Anim. Ecol. 2024, 46, 50–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Jiayang, L.; Jinxiang, X.; Liu, W.; Tan, H. Effects of Dissolved Organic Carbon and Total Ammonia Nitrogen Concentrations with the Same DOC/TAN on Biofloc Performance. Aquaculture 2023, 574, 739713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Ma, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, T.; Ma, Y. Prickly Ash Seeds Improve Immunity of Hu Sheep by Changing the Diversity and Structure of Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1273714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; et al. Relationship between Rumen Microbial Differences and Traits among Hu Sheep, Tan Sheep, and Dorper Sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zuo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, G.; Lu, C.; Xie, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, W. Effect of Clostridium Butyricum Supplementation on in Vitro Rumen Fermentation and Microbiota with High Grain Substrate Varying with Media pH Levels. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 912042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Cheng, X.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, J.; Degen, A.A.; Jiao, D.; Ji, K.; Liang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, G. Dietary Supplementation of Fruit from Nitraria Tangutorum Improved Immunity and Abundance of Beneficial Ruminal Bacteria in Hu Sheep. Animals 2022, 12, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, Q.; Dong, Y.; Mei, X.; Zhou, S.; Sun, G.; et al. High-Altitude Drives the Convergent Evolution of Alpha Diversity and Indicator Microbiota in the Gut Microbiomes of Ungulates. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 953234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Liu, H.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, S.; Li, K.; Lu, J.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, B.; Ma, Z.; et al. Analysis of Rumen Degradation Characteristics, Attached Microbial Community, and Cellulase Activity Changes of Garlic Skin and Artemisia Argyi Stalk. Animals 2024, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Altermann, E.; Leahy, S.C.; Jauregui, R.; Jonker, A.; Henderson, G.; Kittelmann, S.; Attwood, G.T.; Kamke, J.; Waters, S.M.; et al. Genomic Insights into the Physiology of Quinella, an Iconic Uncultured Rumen Bacterium. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Xue, W.; Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Qi, F.; Ma, T.; Tu, Y.; Diao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Cui, K. Comparison of Rumen Fermentation Parameters and Microbiota of Yaks From Different Altitude Regions in Tibet, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 807512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Ingredients | Content, % | Nutrient Levels 2 | Content 3, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa | 35.00 | ME, MJ/kg | 9.22 |
| Cornstalk | 25.00 | CP | 13.28 |
| Corn | 28.00 | NDF | 44.59 |
| Soybean meal | 5.00 | ADF | 23.60 |
| Wheat bran | 4.00 | EE | 13.95 |
| molasses | 1.00 | NFC | 22.29 |
| NaCl | 1.00 | NFC/NDF | 49.99 |
| Premix 1 | 1.00 | Ca, g/kg | 0.84 |
| Total | 100.00 | TP, g/kg | 0.24 |
| Items | Time | Groups | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | ATABG | Time | Groups | T×G | ||
| BW, kg | 1 d | 21.66 ± 1.37 | 21.64 ± 1.54 | <0.01 | 0.650 | 0.924 |
| 21 d | 25.32 ± 1.66 | 25.54 ± 1.71 | ||||
| 42 d | 29.17 ± 1.79 | 28.70 ± 1.77 | ||||
| 63 d | 33.64 ± 1.96 | 33.07 ± 1.80 | ||||
| ADG, g | 1–21 d | 174.29 ± 10.10 | 185.48 ± 8.70 | 0.024 | 0.384 | 0.490 |
| 21–42 d | 183.43 ± 7.86 | 150.64 ± 6.91 | ||||
| 42–63 d | 212.76 ± 8.32 | 207.93 ± 6.23 | ||||
| 1–63 d | 190.16 ± 7.35 | 181.35 ± 5.84 | ||||
| DMI, g/d | 1–21 d | 1070.83 ± 45.50 | 1035.59 ± 32.03 | <0.01 | 0.140 | 0.968 |
| 21–42 d | 1293.02 ± 44.87 | 1216.76 ± 31.25 | ||||
| 42–63 d | 1645.78 ± 130.57 | 1541.67 ± 104.92 | ||||
| 1–63 d | 1336.54 ± 41.80 | 1264.67 ± 39.84 | ||||
| DMI, % of BW | 1–21 d | 4.57 ± 0.19 | 4.42 ± 0.14 | 0.050 | 0.192 | 0.990 |
| 21–42 d | 4.77 ± 0.17 | 4.54 ± 0.16 | ||||
| 42–63 d | 5.28 ± 0.44 | 4.98 ± 0.32 | ||||
| 1–63 d | 4.84 ± 0.12 | 4.64 ± 0.15 | ||||
| F/G | 1–21 d | 5.80 ± 2.05 | 6.60 ± 1.84 | 0.156 | 0.761 | 0.340 |
| 21–42 d | 7.89 ± 1.72 | 9.50 ± 2.43 | ||||
| 42–63 d | 8.78 ± 2.26 | 7.54 ± 1.55 | ||||
| 1–63 d | 9.26 ± 3.26 | 7.08 ± 0.93 | ||||
| Items | Groups | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | ATABG | |||
| DM | Intake, g | 876.47 ± 16.08 | 886.13 ± 13.54 | 0.649 |
| Digestibility, % | 56.86 ± 1.09 | 58.45 ± 3.28 | 0.650 | |
| OM | Intake, g | 510.74 ± 14.16 | 556.12 ± 13.22 | 0.076 |
| Digestibility, % | 63.05 ± 0.98 | 66.65 ± 1.16 | 0.010 | |
| CP | Intake, g | 65.37 ± 2.07 | 69.90 ± 2.16 | 0.139 |
| Digestibility, % | 56.07 ± 1.21 | 59.33 ± 1.46 | 0.034 | |
| EE | Intake, g | 95.78 ± 2.58 | 98.60 ± 2.10 | 0.401 |
| Digestibility, % | 78.25 ± 1.34 | 79.73 ± 1.07 | 0.252 | |
| NDF | Intake, g | 203.68 ± 7.04 | 226.28 ± 7.49 | 0.034 |
| Digestibility, % | 51.99 ± 1.14 | 57.25 ± 1.68 | 0.011 | |
| ADF | Intake, g | 106.16 ± 4.36 | 122.15 ± 4.39 | 0.014 |
| Digestibility, % | 51.11 ± 1.38 | 58.51 ± 2.20 | <0.01 | |
| Items | Groups | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Con | ATABG | ||
| pH | 6.67 ± 0.03 | 6.73 ± 0.03 | 0.096 |
| TVFA, mmol/L | 71.05 ± 2.59 | 68.91 ± 2.26 | 0.537 |
| acetic acid, mmol/L | 40.47 ± 1.51 | 37.18 ± 1.21 | 0.097 |
| acetic acid, % of TVFA | 57.15 ± 1.17 | 54.16 ± 0.93 | 0.052 |
| propanoic acid, mmol/L | 19.56 ± 1.24 | 20.46 ± 1.28 | 0.615 |
| propanoic acid, % of TVFA | 27.25 ± 1.07 | 29.26 ± 1.08 | 0.193 |
| butyric acid, mmol/L | 11.02 ± 0.57 | 11.26 ± 0.23 | 0.695 |
| butyric acid, % of TVFA | 15.56 ± 0.84 | 16.58 ± 0.50 | 0.322 |
| A/P | 2.18 ± 0.12 | 1.92 ± 0.10 | 0.098 |
| NH3-N, mg/dL | 16.58 ± 0.88 | 15.66 ± 0.57 | 0.384 |
| MCP, mg/dL | 9.34 ± 0.47 | 10.81 ± 0.39 | 0.020 |
| Items | Groups | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Con | ATABG | ||
| lipase, mol/min/mL | 2.24 ± 0.21 | 2.26 ± 0.22 | 0.926 |
| urease, ug/min/mL | 0.51 ± 0.10 | 0.80 ± 0.12 | 0.066 |
| cellulase, ug/min/mL | 4.18 ± 0.57 | 6.56 ± 0.97 | 0.041 |
| pepsin, U/mL | 79.26 ± 14.28 | 68.73 ± 9.50 | 0.543 |
| α-amylase, ug/min/mL | 37.75 ± 4.27 | 27.81 ± 4.12 | 0.102 |
| β-amylase, ug/min/mL | 54.15 ± 5.59 | 64.46 ± 4.76 | 0.168 |
| RPL, mm | 1.65 ± 0.09 | 2.00 ± 0.03 | 0.081 |
| RPW, mm | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 0.625 |
| RMT, mm | 1.36 ± 0.05 | 1.49 ± 0.04 | 0.062 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.-L.; Pan, L.; Zheng, C.; Mao, R.-Y.; Yuan, G.-H.; Shi, C.-Y.; Pu, Z.-H.; Su, H.-X.; Diao, Q.-Y.; Rehemujiang, H.; et al. Effects of Compound Microecological Preparation Supplementation on Production Performance and Nutrient Apparent Digestibility in Hu Sheep from the Rumen Perspective. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050999
Lu M-L, Pan L, Zheng C, Mao R-Y, Yuan G-H, Shi C-Y, Pu Z-H, Su H-X, Diao Q-Y, Rehemujiang H, et al. Effects of Compound Microecological Preparation Supplementation on Production Performance and Nutrient Apparent Digestibility in Hu Sheep from the Rumen Perspective. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050999
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Mu-Long, Long Pan, Chen Zheng, Ruo-Yu Mao, Guo-Hong Yuan, Chen-Yang Shi, Zhe-Huan Pu, Hui-Xin Su, Qi-Yu Diao, Halidai Rehemujiang, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Compound Microecological Preparation Supplementation on Production Performance and Nutrient Apparent Digestibility in Hu Sheep from the Rumen Perspective" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050999
APA StyleLu, M.-L., Pan, L., Zheng, C., Mao, R.-Y., Yuan, G.-H., Shi, C.-Y., Pu, Z.-H., Su, H.-X., Diao, Q.-Y., Rehemujiang, H., & Xu, G.-S. (2025). Effects of Compound Microecological Preparation Supplementation on Production Performance and Nutrient Apparent Digestibility in Hu Sheep from the Rumen Perspective. Microorganisms, 13(5), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050999








