Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Hypertension Interaction Research Published from 2001 to 2024
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
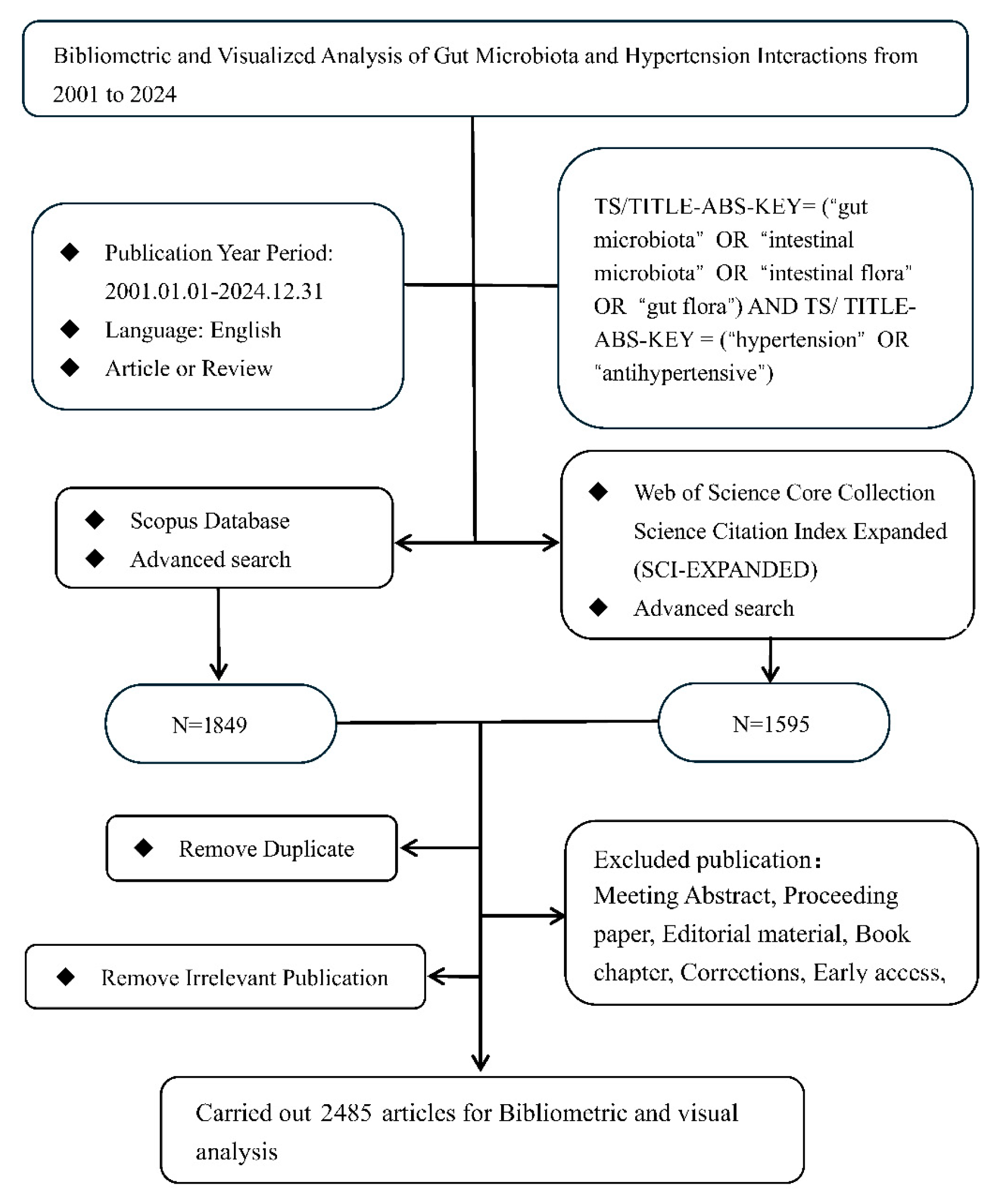
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Search Strategy, Eligibility Criteria, and Data Refinement
- (1)
- Publication Type: “article” or “review article”;
- (2)
- Publication Year Period: 1 January 2001–31 December 2024;
- (3)
- Language: English;
- (4)
- Exported Bibliographic Data: Publication title, Publication year, Author names, Country/Region, Institutional affiliations, Author Keywords, and Citation metrics.
2.3. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
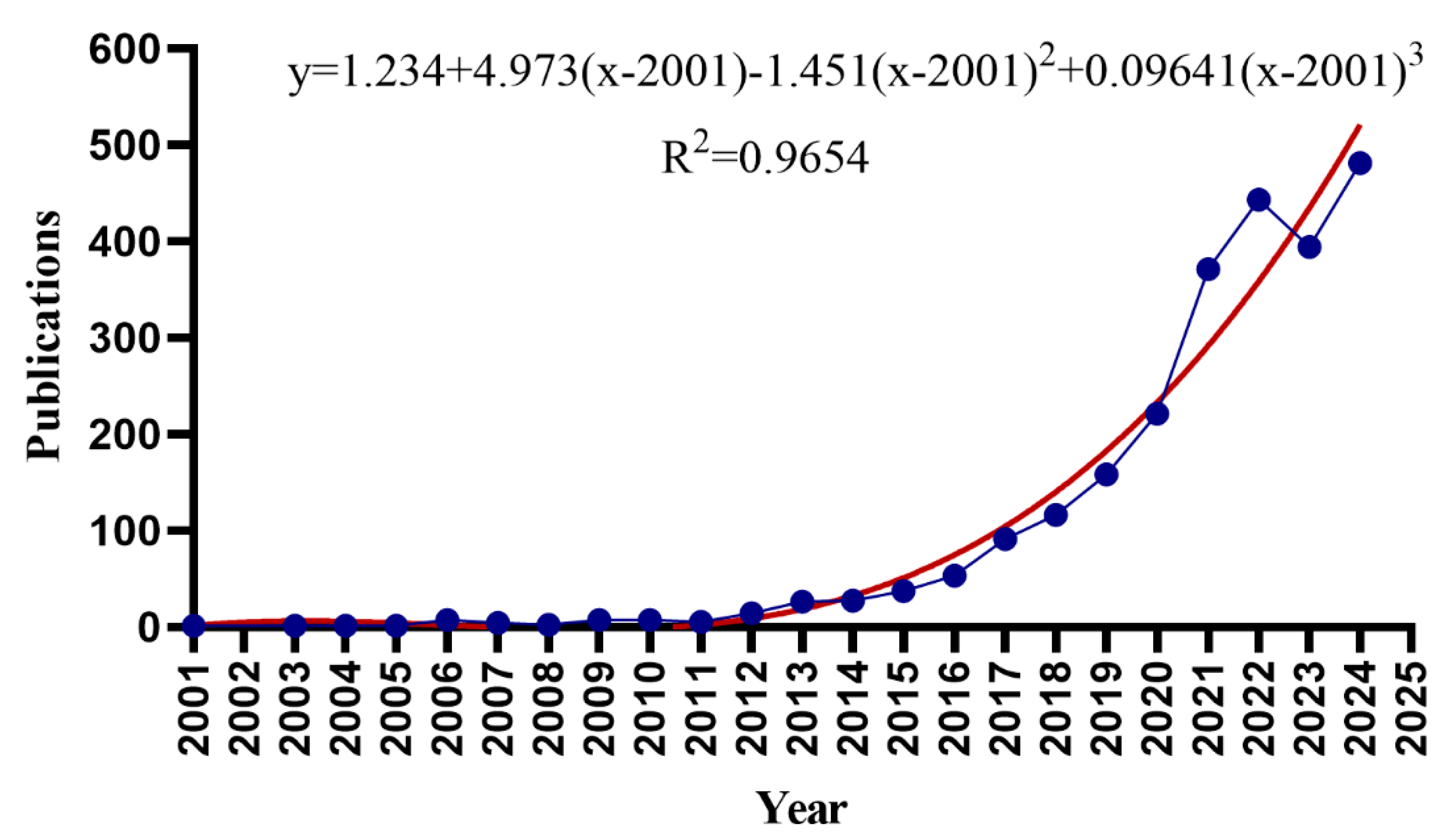
3.1. Basic Information
3.2. Contributions of Countries/Regions to Global Publications
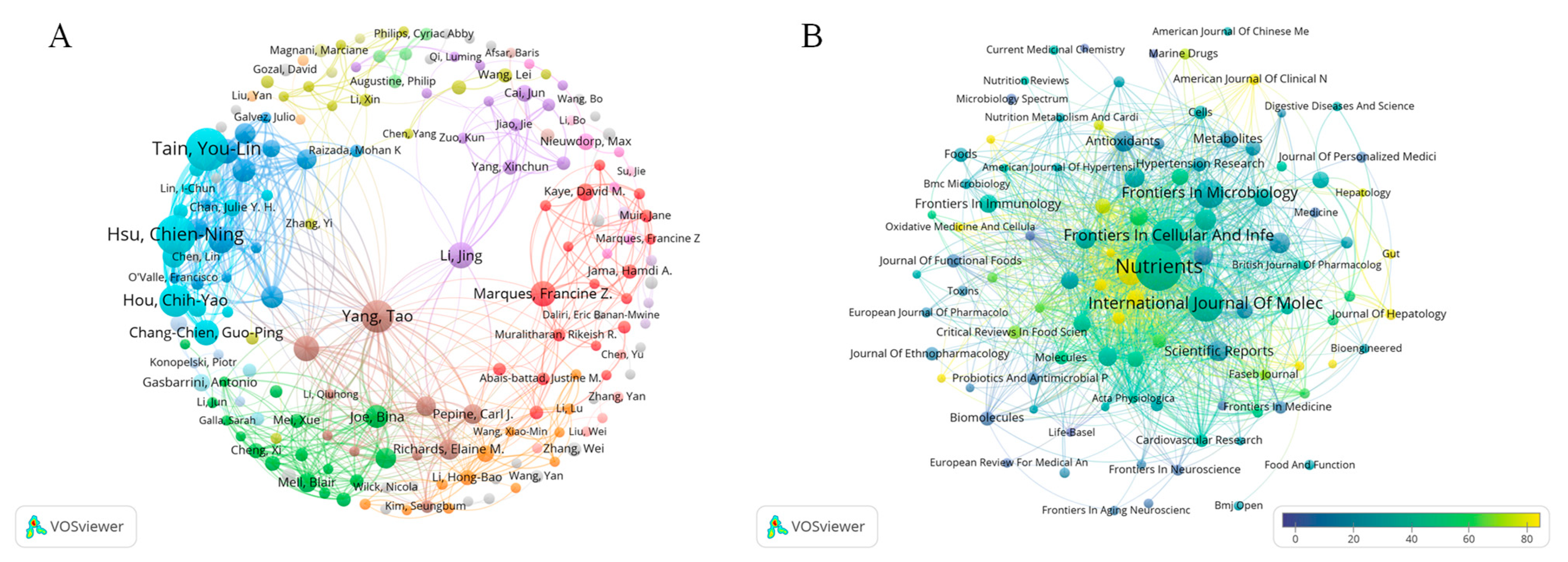
3.3. Author Contribution Analysis
3.4. Institution Contribution Analysis
3.5. Journal Contribution Analysis
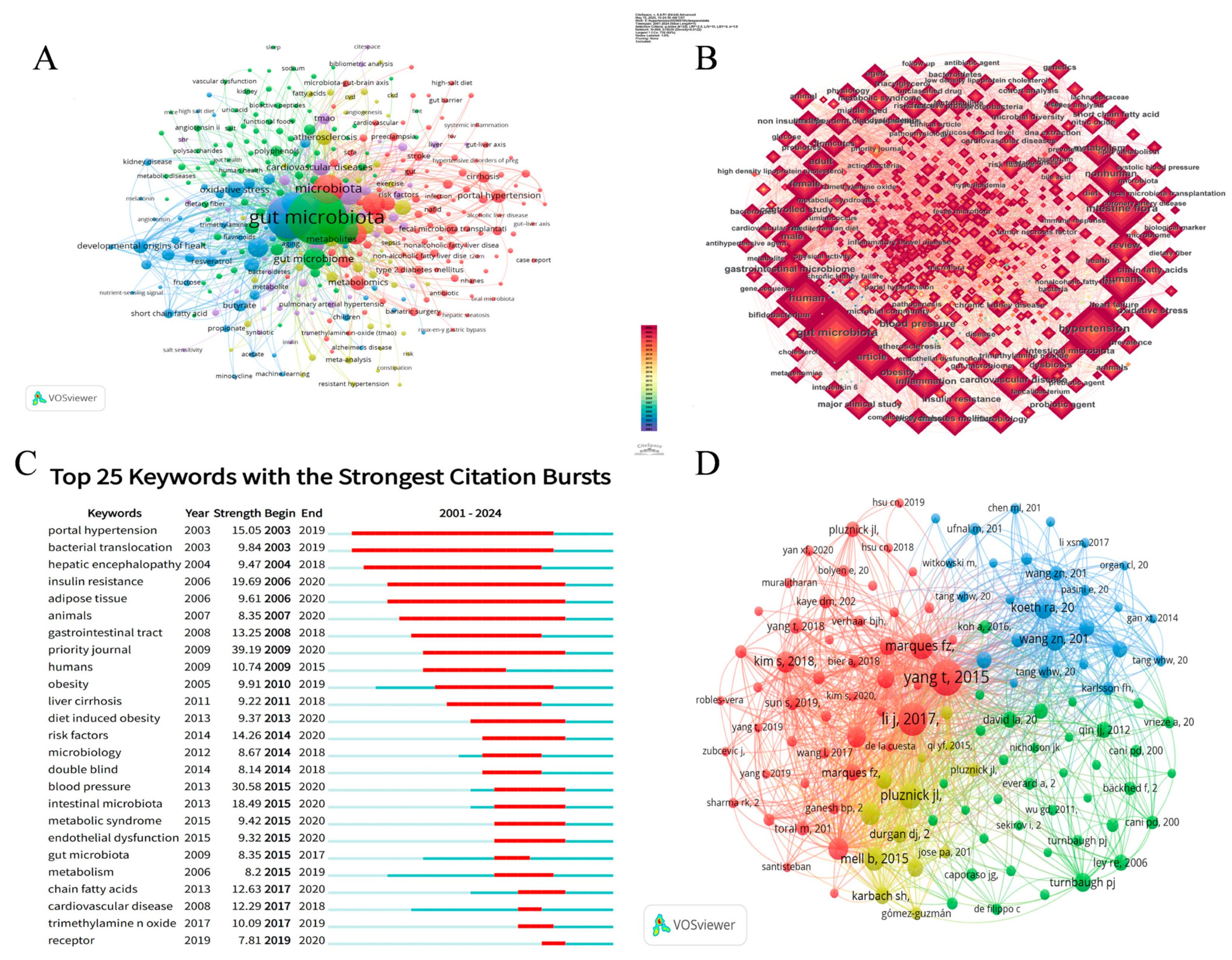
3.6. Analysis of Keywords
3.7. Citation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Caulfield, M. Hypertension. Lancet 2015, 386, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.W.S.; Ng, C.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Kong, G.; Lin, C.; Chin, Y.H.; Lim, W.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Quek, J.; Fu, C.E.; et al. The Global Burden of Metabolic Disease: Data from 2000 to 2019. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krokstad, S. Worldwide Trends in Hypertension Prevalence and Progress in Treatment and Control from 1990 to 2019: A Pooled Analysis of 1201 Population-Representative Studies with 104 Million Participants. Lancet 2022, 399, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Q.C.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Ge, Z.; Li, Z.Z.; Feng, S.L.; Wu, C. Gut Microbiota and Hypertension: Association, Mechanisms and Treatment. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2195135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, R. Gut Microbiota-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites Maintain Gut and Systemic Homeostasis. Cells 2022, 11, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Contributes to the Development of Hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Santisteban, M.M.; Rodriguez, V.; Li, E.; Ahmari, N.; Carvajal, J.M.; Zadeh, M.; Gong, M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis Is Linked to Hypertension. Hypension 2015, 65, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Richards, E.M.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. The Gut Microbiota and the Brain-Gut-Kidney Axis in Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taur, Y.; Coyte, K.; Schluter, J.; Robilotti, E.; Figueroa, C.; Gjonbalaj, M.; Littmann, E.R.; Ling, L.; Miller, L.; Gyaltshen, Y.; et al. Reconstitution of the Gut Microbiota of Antibiotic-Treated Patients by Autologous Fecal Microbiota Transplant. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.-F.; Gao, Z.-X.; Mao, Z.-H.; Pan, S.-K.; Liu, D.-W.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wu, P. Perspectives on the Involvement of the Gut Microbiota in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, S.; Sudano, I.; Kokubo, Y.; Sulaica, E.M. Arterial Hypertension. Lancet 2021, 398, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Han, Z.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Mou, H.; Duan, X. Clostridium Butyricum Prevents Dysbiosis and the Rise in Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikalova, A.E.; Pandey, A.; Xiao, L.; Arslanbaeva, L.; Sidorova, T.; Lopez, M.G.; Billings, F.T.; Verdin, E.; Auwerx, J.; Harrison, D.G.; et al. Mitochondrial Deacetylase Sirt3 Reduces Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension While Sirt3 Depletion in Essential Hypertension Is Linked to Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, F.Z.; Mackay, C.R.; Kaye, D.M. Beyond Gut Feelings: How the Gut Microbiota Regulates Blood Pressure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, F.; Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Al Mamun, A.; Rahaman, M.S.; Islam, M.M.; Meem, A.F.K.; Sutradhar, P.R.; Mitra, S.; Mimi, A.A.; et al. The Gut Microbiota (Microbiome) in Cardiovascular Disease and Its Therapeutic Regulation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 903570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Prodan, A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Muller, M. Gut Microbiota in Hypertension and Atherosclerosis: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninkov, A.; Frank, J.R.; Maggio, L.A. Bibliometrics: Methods for Studying Academic Publishing. Perspect. Med. Educ. 2022, 11, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral-Munoz, J.A.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Santisteban-Espejo, A.; Cobo, M.J. Software Tools for Conducting Bibliometric Analysis in Science: An up-to-Date Review. Prof. Inf. 2020, 29, e290103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, I.D. Bibliometrics Basics. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2015, 103, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Blazun Vosner, H.; Zavrsnik, J. Application of Bibliometrics in Medicine: A Historical Bibliometrics Analysis. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2021, 38, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, G.; Mu, X.; Kong, L. From Low Carbon to Carbon Neutrality: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Status, Evolution and Development Trend. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 322, 116087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q. Gut Microbiota and Hypertension: A Bibliometric Analysis of Recent Research (2014–2023). Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1253803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, A. Exploratory Bibliometrics: Using VOSviewer as a Preliminary Research Tool. Publications 2023, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Tan, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Hou, C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, G. Frontier and Hot Topics in Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Technology Based on CiteSpace Bibliometric Analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 201, 113932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.T.; Liu, Y.G.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.T.; Sang, X.T.; Xu, Y.Y.; Lu, X. Evolutionary Patterns and Research Frontiers in Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy: A Bibliometric Analysis-All Databases. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synnestvedt, M.B.; Chen, C.; Holmes, J.H. CiteSpace II: Visualization and Knowledge Discovery in Bibliographic Databases. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. AMIA Symp. 2005, 2005, 724–728. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zha, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhu, C.; Chen, E. A Bibliometric Analysis Using VOSviewer of Publications on COVID-19. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Kuang, L.; Zhao, J.; Ross, A.E.; Wang, Z.; Ciolino, J.B. Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Ocular Drug Delivery from 2001 to 2020. J. Control. Release 2022, 345, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopyk, D.M.; Grakoui, A. Contribution of the Intestinal Microbiome and Gut Barrier to Hepatic Disorders. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabl, B.; Brenner, D.A. Interactions Between the Intestinal Microbiome and Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The Gut-Liver Axis in Liver Disease: Pathophysiological Basis for Therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Zhou, J.R. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Epigenetic Alterations in Metabolic Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.; Kandalgaonkar, M.R.; Golonka, R.M.; Yeoh, B.S.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Saha, P. Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Host Immunity: Impact on Inflammation and Immunotherapy. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Mueller, N.T.; Alvarez-Quintero, R.; Velasquez-Mejia, E.P.; Sierra, J.A.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Higher Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels Are Associated with Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis, Obesity, Hypertension and Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors. Nutrients 2019, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomaeus, H.; Balogh, A.; Yakoub, M.; Homann, S.; Marko, L.; Hoeges, S.; Tsvetkov, D.; Krannich, A.; Wundersitz, S.; Avery, E.G.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Propionate Protects From Hypertensive Cardiovascular Damage. Circulation 2019, 139, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Preter, V.; Geboes, K.P.; Bulteel, V.; Vandermeulen, G.; Suenaert, P.; Rutgeerts, P.; Verbeke, K. Kinetics of Butyrate Metabolism in the Normal Colon and in Ulcerative Colitis: The Effects of Substrate Concentration and Carnitine on the β-Oxidation Pathway. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, S.; Cai, X.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; He, D.; Fang, A.; Bo, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review and Updated Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-Q.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhang, A.; Ding, Y.-J.; Zhang, X.-N.; Jia, Q.-J.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Li, Y.-Y.; Lv, S.-C.; Zhang, J.-P. TMA/TMAO in Hypertension: Novel Horizons and Potential Therapies. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A.; Cirino, G.; Bucci, M.; Distrutti, E. Decoding the Vasoregulatory Activities of Bile Acid-Activated Receptors in Systemic and Portal Circulation: Role of Gaseous Mediators. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H21–H32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, F.; Kuruba, R.; Gao, X.; Wilson, A.; Li, J.; Billiar, T.R.; Pitt, B.R.; Xie, W.; Li, S. FXR-Mediated Regulation of Angiotensin Type 2 Receptor Expression in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 77, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, E.A.; Richardson, C.J.; Hughes, R.; Cummings, J.H. Contribution of Dietary Protein to Sulfide Production in the Large Intestine: An in Vitro and a Controlled Feeding Study in Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Leroy, F. Cross-Feeding between Bifidobacteria and Butyrate-Producing Colon Bacteria Explains Bifdobacterial Competitiveness, Butyrate Production, and Gas Production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 149, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenguer, A.; Duncan, S.H.; Calder, A.G.; Holtrop, G.; Louis, P.; Lobley, G.E.; Flint, H.J. Two Routes of Metabolic Cross-Feeding between Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Butyrate-Producing Anaerobes from the Human Gut. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.-H.; Zhu, C.-X.; Quan, Y.-S.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, W.-W.; Tan, B.; Wang, X.-Y. Relationship between Intestinal Microbiota and Ulcerative Colitis: Mechanisms and Clinical Application of Probiotics and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak-Kopec, P.; Slizewska, K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids by Human Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface Components and Metabolites of Probiotics for Regulation of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, A.; Xie, A.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Yu, R. Limosilactobacillus reuteri in Immunomodulation: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Applications. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1228754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Ohni, M.; Nakajima, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Takano, T. A Placebo-Controlled Study of the Effect of Sour Milk on Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Riet, L.; van Esch, J.H.M.; Roks, A.J.M.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; Danser, A.H.J. Hypertension Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Alterations. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, H.R. Evolving Role of Alclosterone Blockers Alone and in Combination with Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in Hypertension Management: A Review of Mechanistic and Clinical Data. Am. Heart J. 2004, 147, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Patel, R.A.; Kowey, P.R. The Clinical Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2004, 47, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakai, K.; Okubo, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Takano, T. Purification and Characterization of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitors from Sour Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppo, L.; Jauhiainen, T.; Poussa, T.; Korpela, R. A Fermented Milk High in Bioactive Peptides Has a Blood Pressure-Lowering Effect in Hypertensive Subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kadyan, S.; Hochuli, N.; Pollak, J.; Wang, B.; Salazar, G.; Chakrabarty, P.; Efron, P.; Sheffler, J.; Nagpal, R. A Modified Mediterranean-Style Diet Enhances Brain Function via Specific Gut-Microbiome—Brain Mechanisms. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2323752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendia, J.R.; Li, Y.; Hu, F.B.; Cabral, H.J.; Bradlee, M.L.; Quatromoni, P.A.; Singer, M.R.; Curhan, G.C.; Moore, L.L. Long-Term Yogurt Consumption and Risk of Incident Hypertension in Adults. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive Peptides from Animal Products, Marine Organisms, and Plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorguc, A.; Gencdag, E.; Yilmaz, F.M. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Plant Origin By-Products: Biological Activities and Techno-Functional Utilizations in Food Developments—A Review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Yu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Chu, Q.; Chen, G.; Fen, S.; Yang, M.; Yuan, L.; McClements, D.J.; Sun, Q. Production, Bioactive Properties, and Potential Applications of Fish Protein Hydrolysates: Developments and Challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandelli, A.; Daroit, D.J.; Folmer Correa, A.P. Whey as a Source of Peptides with Remarkable Biological Activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, K.F.; Voo, A.Y.H.; Chen, W.N. Bioactive Peptides from Food Fermentation: A Comprehensive Review of Their Sources, Bioactivities, Applications, and Future Development. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3825–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
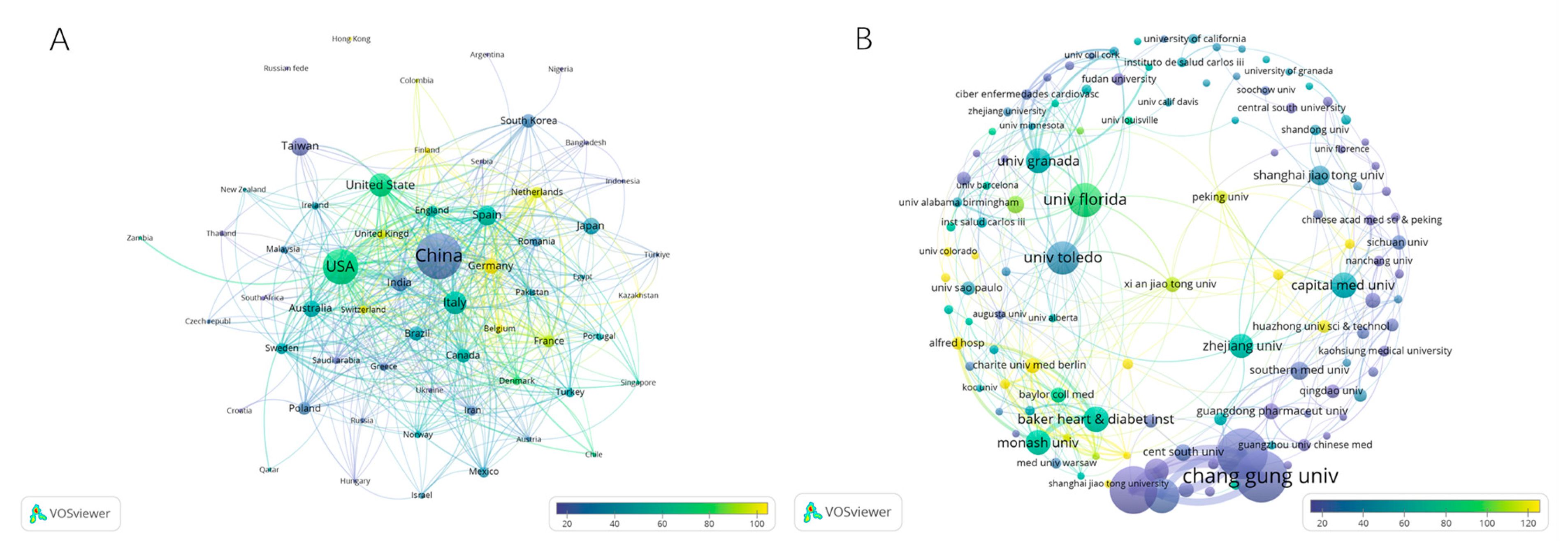
| Rank | Country/Region | Publications (n = 2485) | Citations (n = 104,262) | Total Link Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 888 (35.73%) | 23,999 | 214 |
| 2 | USA | 535 (21.53%) | 38,033 | 386 |
| 3 | Italy | 161 (6.48%) | 8955 | 123 |
| 4 | Spain | 128 (5.15%) | 7467 | 142 |
| 5 | Taiwan Region of China | 111 (4.47%) | 2464 | 15 |
| 6 | Australia | 95 (3.82%) | 4803 | 90 |
| 7 | India | 94 (3.78%) | 2795 | 74 |
| 8 | Japan | 89 (3.58%) | 3584 | 26 |
| 9 | Germany | 80 (3.22%) | 7963 | 125 |
| 10 | Brazil | 72 (2.90%) | 3114 | 50 |
| Rank | Author | Publication Count (%) | Country/Region | Institutions | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | You-Lin Tain | 75 (3.02%) | Taiwan region of China | Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital | 1852 |
| 2 | Chien-Ning Hsu | 66 (2.66%) | Taiwan region of China | Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital | 1483 |
| 3 | Tao Yang | 44 (1.77%) | USA | University of Toledo | 3713 |
| 4 | Chih-Yao Hou | 43 (1.73%) | Taiwan region of China | National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology | 1115 |
| 5 | Jing Li | 29 (1.17%) | China | Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences | 1553 |
| 6 | Guo-Ping Chang-chien, | 28 (1.13%) | Taiwan region of China | Cheng Shiu University | 562 |
| 7 | Francine Marques | 28 (1.13%) | Australia | Monash University | 2117 |
| 8 | Mohan Raizada | 28 (1.13%) | USA | University of Florida | 3346 |
| 9 | Juan Duarte | 27 (1.09%) | Spain | University of Granada | 1627 |
| 10 | Marta Toral | 26 (1.05%) | Spain | University of Granada | 1592 |
| Rank | Institution | Documents | Citations | Total Link Strength | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Florida | 43 | 3858 | 2719 | USA |
| 2 | University of California, San Diego | 11 | 2377 | 120 | USA |
| 3 | Charité–Universitätsmedizin Berlin | 16 | 2337 | 826 | Germany |
| 4 | Monash University | 30 | 2235 | 2041 | Australia |
| 5 | Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute | 31 | 2210 | 2003 | Australia |
| 6 | Washington University | 5 | 2181 | 58 | USA |
| 7 | Yale University | 4 | 2159 | 54 | USA |
| 8 | Cleveland Clinic | 9 | 2094 | 296 | USA |
| 9 | German Centre for Cardiovascular Research | 10 | 1964 | 734 | Germany |
| 10 | Vanderbilt University | 19 | 1947 | 813 | USA |
| Journal | Citations | Publications | Citation Rank | Average Citation Rank | IF2024 | H-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients | 5397 | 135 | 1 | 9 | 5.0 | 75 |
| Hypertension | 3804 | 45 | 2 | 7 | 8.2 | 246 |
| Nature | 3679 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 48.5 | 1096 |
| Science | 3321 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 45.8 | 1058 |
| International Journal of Molecular Sciences | 2979 | 78 | 5 | 8 | 4.9 | 114 |
| Circulation Research | 2610 | 17 | 6 | 6 | 16.2 | 306 |
| Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology | 2447 | 68 | 7 | 10 | 4.8 | 53 |
| Journal of Hepatology | 2180 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 33 | 216 |
| Lancet | 1627 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 88.5 | 700 |
| Circulation | 1612 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 38.6 | 570 |
| Rank | First Author | Journal | Title | Publication Type | Citations | IF2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tao Yang | Hypertension | “Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension” | Article | 443 | 8.2 |
| 2 | Jing Li | Microbiome | “Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension” | Article | 382 | 12.7 |
| 3 | Francine Marques | Circulation | “High-fiber diet and acetate supplementation change the gut microbiota and prevent the development of hypertension and heart failure in hypertensive mice” | Article | 255 | 38.9 |
| 4 | Pluznick Jennifer | The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) | “Olfactory receptor responding to gut microbiota-derived signals plays a role in renin secretion and blood pressure regulation” | Article | 249 | 9.1 |
| 5 | Blair R Mell | Physiological Genomics | “Evidence for a link between gut microbiota and hypertension in the Dahl rat” | Article | 201 | 2.5 |
| 6 | Monica M Santisteban | Circulation Research | “Hypertension-linked pathophysiological alterations in the gut” | Article | 192 | 16.2 |
| 7 | Adnan Sareema H | Physiological Genomics | “Alterations in the gut microbiota can elicit hypertension in rats” | Article | 186 | 2.5 |
| 8 | Zeneng Wang | Nature | “Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease” | Article | 178 | 48.5 |
| 9 | Kim Seungbum | Clinical Science | “Imbalance of gut microbiome and intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in patients with high blood pressure” | Article | 168 | 7.7 |
| 10 | Wilck Nicola | Nature | “Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH17 axis and disease” | Article | 168 | 48.5 |
| 1 | Jorge Henao-Mejia | Nature | “Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of nafld and obesity” | Article | 1868 | 48.5 |
| 2 | Vijay-Kumar Matam | Science | “Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5” | Article | 1730 | 45.8 |
| 3 | Daniel Baumgart | Lancet | “Gastroenterology 2 -inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies” | Review | 1627 | 88.5 |
| 4 | Vijay-Kumar Matam | Science | “Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking toll-like receptor” | Article | 1591 | 45.8 |
| 5 | Clara Depommier | Nature Medicine | “Supplementation with akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: a proof-of-concept exploratory study” | Article | 1428 | 50 |
| 6 | Agustin Albillos | Journal of Hepatology | “The gut-liver axis in liver disease: pathophysiological basis for therapy” | Review | 1228 | 33 |
| 7 | Jing Li | Microbiome | “Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension” | Article | 1158 | 12.7 |
| 8 | W.H. Wilson Tang | Circulation Research | “Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease” | Review | 1095 | 16.2 |
| 9 | Tao Yang | Hypertension | “Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension” | Article | 1083 | 8.2 |
| 10 | Jennifer l Pluznick | The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) | “Olfactory receptor responding to gut microbiota-derived signals plays a role in renin secretion and blood pressure regulation” | Article | 959 | 9.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, J.; Su, W.; Qin, J.; Feng, J.; Yu, R.; Li, S.; Lv, J.; Dong, R.; Cheng, Y.; Han, B. Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Hypertension Interaction Research Published from 2001 to 2024. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071696
Mo J, Su W, Qin J, Feng J, Yu R, Li S, Lv J, Dong R, Cheng Y, Han B. Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Hypertension Interaction Research Published from 2001 to 2024. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071696
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Jianhui, Wanghong Su, Jiale Qin, Jiayu Feng, Rong Yu, Shaoru Li, Jia Lv, Rui Dong, Yue Cheng, and Bei Han. 2025. "Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Hypertension Interaction Research Published from 2001 to 2024" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071696
APA StyleMo, J., Su, W., Qin, J., Feng, J., Yu, R., Li, S., Lv, J., Dong, R., Cheng, Y., & Han, B. (2025). Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Hypertension Interaction Research Published from 2001 to 2024. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071696







