Detection of Legionella anisa in Water from Hospital Dental Chair Units and Molecular Characterization by Whole-Genome Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Culture and Species Identification
2.3. Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Short-Read Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.5. Long-Read Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.6.2. Construction of A Core- and Whole-Genome Multi Locus Sequence Typing (cgMLST/wgMLST) Using Publicly Available L. anisa Genomes
2.6.3. Comparative Genomic Analysis
2.6.4. Antibiotic Resistance Genes, Virulence Factors and Dot/Icm Effectors Detection
2.6.5. Plasmid Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Legionella Isolation and Species Identification
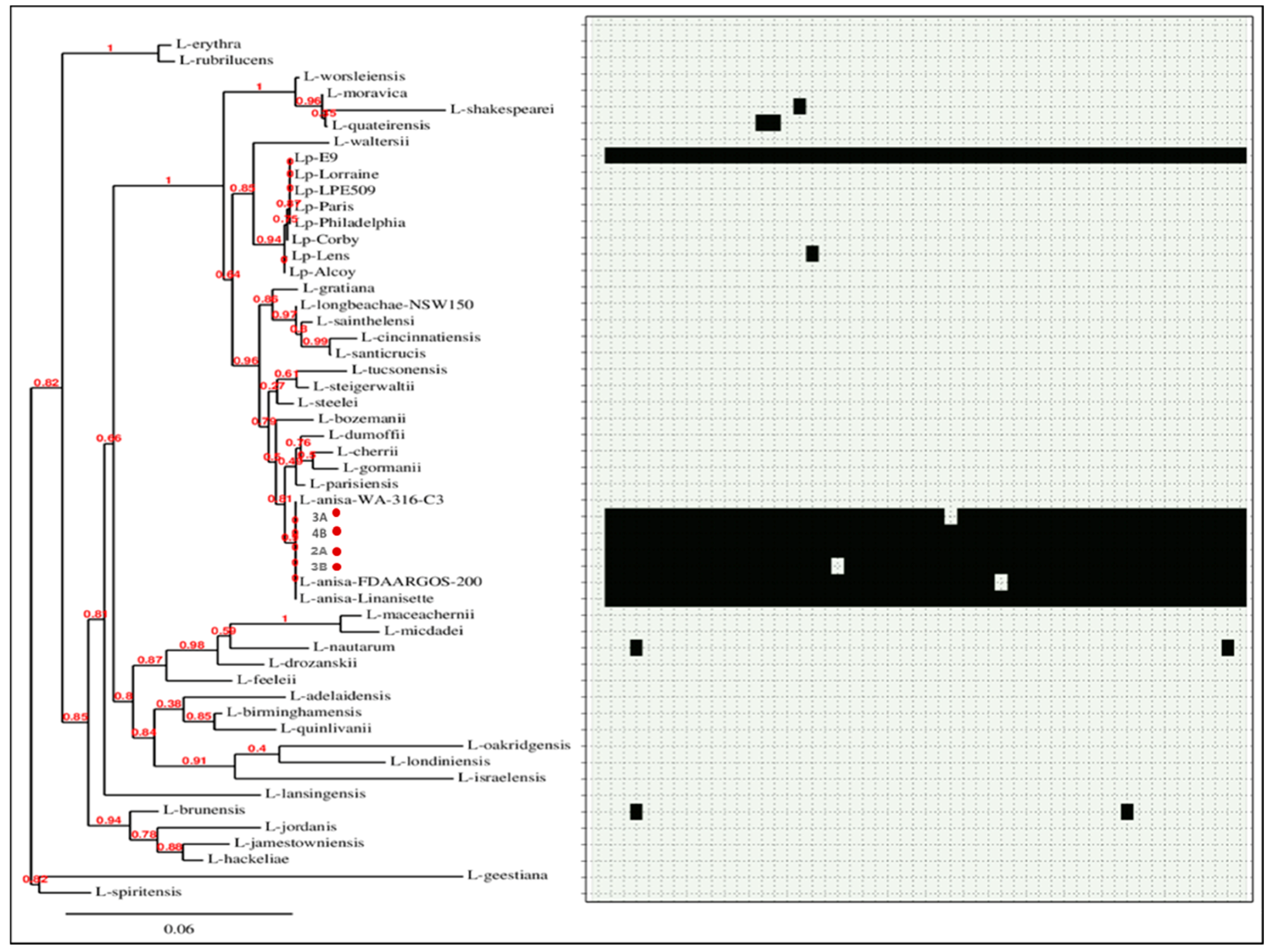
3.2. wgMLST Analysis
3.3. Comparative Genomic Analysis
3.4. ARGs, VFs and Dot/Icm Effectors
3.5. Plasmid Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conza, L.; Casati, S.; Gaia, V. Detection limits of Legionella pneumophila in environmental samples after co-culture with Acanthamoeba polyphaga. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, E.A. Legionella: Virulence factors and host response. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, D.; Amaro, F.; Zusman, T.; Lifshitz, Z.; Cohen, O.; Gilbert, J.; Pupko, T.; Shuman, H.; Segal, G. Genomic analysis of 38 Legionella species identifies large and diverse effector repertoires. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, G.; Feeley, J.; Steigerwalt, A.; Edelstein, P.; Moss, C.; Brenner, D. Legionella anisa: A New Species of Legionella Isolated from Potable Waters and a Cooling Tower. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, L.; Izquierdo, F.; Magnet, A.; Hurtado, C.; Salinas, M.; Gomes, T.; Angulo, S.; Salso, S.; Pelaez, J.; Tejeda, M.; et al. First Case of Legionnaire’s Disease Caused by Legionella anisa in Spain and the Limitations on the Diagnosis of Legionella non-pneumophila Infections. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, N.; Mercatello, A.; Marmet, D.; Surgot, M.; Deveaux, Y.; Fleurette, J. Pleural Infection Caused by Legionella anisa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 2100–2101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Compain, F.; Bruneval, P.; Jarraud, S.; Perrot, S.; Aubert, S.; Napoly, V.; Ramahefasolo, A.; Mainardi, J.; Podglajen, I. Chronic endocarditis due to Legionella anisa: A first case difficult to diagnose. New Microbes New Infections 2015, 8, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Sebti, R.; Hassoun, P.; Mannion, C.; Goy, A.; Feldman, T.; Mato, A.; Hong, T. Osteomyelitis of the Patella Caused by Legionella anisa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2791–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutil, S.; Tessier, S.; Veillette, M.; Laflamme, C.; Meriaux, A.; Leduc, A.; Barbeau, J.; Duchaine, C. Detection of Legionella spp. by fluorescent in situ hybridization in dental unit waterlines. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaeen, M.; Hatamzadeh, M.; Sabzevari, Z.; Zareh, O. Microbial quality of water in dental unit waterlines. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2009, 14, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schönning, C.; Jernberg, C.; Klingenberg, D.; Andersson, S.; Pääjärvi, A.; Alm, E.; Tano, E.; Lytsy, B. Legionellosis acquired through a dental unit: A case study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 96, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Kim, Y.O.; Park, S.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Lovero, G.; Diella, G.; Rutigliano, S.; Caggiano, G.; Montagna, M. Antibiotic susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila strains isolated from hospital water systems in Southern Italy. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loman, N.J.; Quinlan, A.R. Poretools: A toolkit for analyzing nanopore sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3399–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.; Judd, L.; Gorrie, C.; Holt, K. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.; Olsen, G.; Davis, J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.; Cummins, C.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almahmoud, I.; Kay, E.; Schneider, D.; Maurin, M. Mutational paths towards increased fluoroquinolone resistance in Legionella pneumophila. J. Antimicrob. Chemoth. 2009, 64, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descours, G.; Ginevra, C.; Jacotin, N.; Forey, F.; Chastang, J.; Kay, E.; Etienne, J.; Lina, G.; Doublet, P.; Jarraud, S. Ribosomal Mutations Conferring Macrolide Resistance in Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02188-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.; Hindersson, P.; Hoiby, N.; Bangsborg, J. Sequencing of the rpoB Gene in Legionella pneumophila and Characterization of Mutations Associated with Rifampin Resistance in the Legionellaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2679–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, M.; Dashnow, H.; Raven, L.; Schultz, M.; Pope, B.; Tomita, T.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K. SRST2: Rapid genomic surveillance for public health and hospital microbiology labs. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattam, A.R.; Brettin, T.; Davis, J.; Gerdes, S.; Kenyon, R.; Machi, D.; Mao, C.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Pusch, G.; et al. Assembly, Annotation, and Comparative Genomics in PATRIC, the All Bacterial Bioinformatics Resource Center. In Comparative Genomics. Methods in Molecular Biology; Setubal, J., Stoye, J., Stadler, P., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1704. [Google Scholar]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartram, J.; Chartier, Y.; Lee, J.V.; Pond, K.; Lee, S.S. Legionella and the Prevention of Legionellosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; ISBN 978-92-4-156297-3. [Google Scholar]
- David, S.; Afshar, B.; Mentasti, M.; Ginevra, C.; Podglajen, I.; Harris, S.; Chalker, V.; Jarraud, S.; Harrison, T.; Harrison, J. Seeding and Establishment of Legionella pneumophila in Hospitals: Implications for Genomic Investigations of Nosocomial Legionnaires’ Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnier, I.; Croce, O.; Robert, C.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Genome Sequence of Legionella anisa, Isolated from a Respiratory Sample, Using an Amoebal Coculture Procedure. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00031-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Valero, L.; Rusniok, C.; Rolando, M.; Neou, M.; Dervins-Ravault, D.; Demirtas, J.; Rouy, Z.; Moore, R.; Chen, H.; Petty, N.; et al. Comparative analyses of Legionella species identifies genetic features of strains causing Legionnaires’ disease. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschini, N.; Boschi, L.; Pollini, S.; Herman, R.; Perilli, M.; Galleni, M.; Frère, J.; Amicosante, G.; Rossolini, G. Characterization of OXA-29 from Legionella (Fluoribacter) gormanii: Molecular Class D beta -Lactamase with Unusual Properties. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 45, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottman, M.; Benzerara, Y.; Hanau-Berçot, B.; Bizet, C.; Philippon, A.; Arlet, G. Chromosomal ampC genes in Enterobacter species other than Enterobacter cloacae, and ancestral association of the ACT-1 plasmid-encoded cephalosporinase to Enterobacter asburiae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 210, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, A. Breaking the Chain of Infection: Dental Unit Water Quality Control. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Product/Function | Gene | Average Coverage (%) | Average Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macrophage infectivity potentiator | mip | 98.59 | 78.75 |
| Dot/Icm secretion system | ceg5 | 100 | 78.93 |
| dotB | 96.31 | 76.98 | |
| dotC | 88.38 | 76.78 | |
| dotD | 98.78 | 77.5 | |
| icmB/dotO | 99.5 | 76.26 | |
| icmD/dotP | 96.1 | 84.87 | |
| icmD/dotP | 92.2 | 78.46 | |
| icmJ/dotN | 98.6 | 76.92 | |
| icmL/dotI | 99.84 | 79.62 | |
| icmO/dotL | 99.7 | 78 | |
| icmS | 100 | 79.13 | |
| icmT | 98.47 | 75.77 | |
| icmW | 100 | 77.85 | |
| lem8 | 96.35 | 81.57 | |
| lpg0181 | 100 | 80.7 | |
| lpg0260 | 84.46 | 75.29 | |
| lpg2359 | 97.75 | 75.78 | |
| lpg2372 | 100 | 94.65 | |
| lpg2539 | 89.46 | 77.19 | |
| lpg2552 | 98.92 | 86.75 | |
| ravL | 83.33 | 76.24 | |
| Motility | fleR/flrC | 96.48 | 75.38 |
| flgC | 99.76 | 75 | |
| flgI | 94.01 | 76.12 | |
| flhA | 99.71 | 75.62 | |
| fliG | 96.36 | 76.1 | |
| fliP | 89.6 | 78.72 | |
| pilT | 97.29 | 79.05 | |
| Others | ccmC | 99.37 | 75.97 |
| enhA | 89.07 | 75.65 | |
| htpB | 99.88 | 85.07 | |
| iraA | 100 | 75.34 | |
| lspE | 99.66 | 78.49 | |
| lspG | 97.64 | 79.18 | |
| phtA | 98.29 | 76.39 | |
| sodB | 99.66 | 76.74 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fleres, G.; Couto, N.; Lokate, M.; Van der Sluis, L.W.M.; Ginevra, C.; Jarraud, S.; Deurenberg, R.H.; Rossen, J.W.; García-Cobos, S.; Friedrich, A.W. Detection of Legionella anisa in Water from Hospital Dental Chair Units and Molecular Characterization by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030071
Fleres G, Couto N, Lokate M, Van der Sluis LWM, Ginevra C, Jarraud S, Deurenberg RH, Rossen JW, García-Cobos S, Friedrich AW. Detection of Legionella anisa in Water from Hospital Dental Chair Units and Molecular Characterization by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Microorganisms. 2018; 6(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030071
Chicago/Turabian StyleFleres, Giuseppe, Natacha Couto, Mariette Lokate, Luc W. M. Van der Sluis, Christophe Ginevra, Sophie Jarraud, Ruud H. Deurenberg, John W. Rossen, Silvia García-Cobos, and Alex W. Friedrich. 2018. "Detection of Legionella anisa in Water from Hospital Dental Chair Units and Molecular Characterization by Whole-Genome Sequencing" Microorganisms 6, no. 3: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030071
APA StyleFleres, G., Couto, N., Lokate, M., Van der Sluis, L. W. M., Ginevra, C., Jarraud, S., Deurenberg, R. H., Rossen, J. W., García-Cobos, S., & Friedrich, A. W. (2018). Detection of Legionella anisa in Water from Hospital Dental Chair Units and Molecular Characterization by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Microorganisms, 6(3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030071





