Dynamic Succession of Microbiota during Ensiling of Whole Plant Corn Following Inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii Alone or in Combination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ensiling and Experimental Treatments
2.2. Fermentation Profiles and Physical Characterization
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
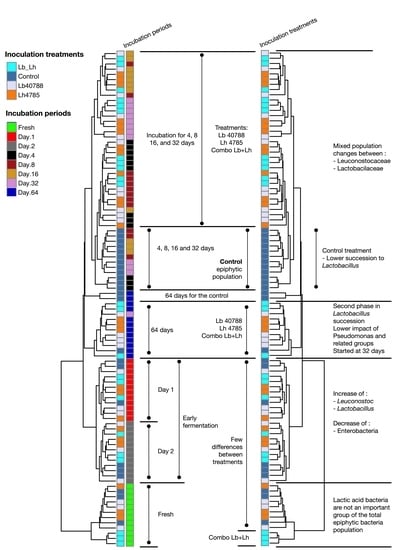
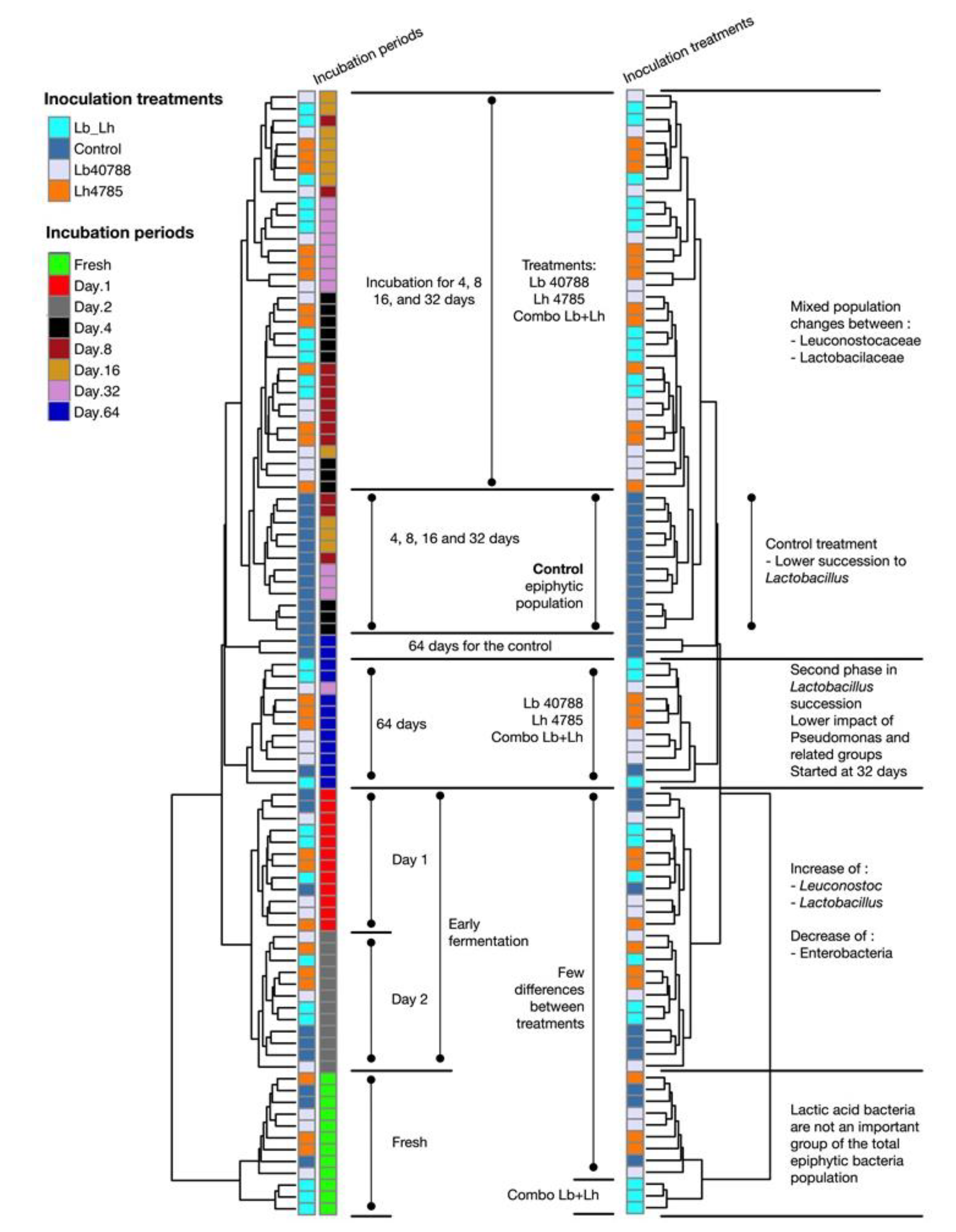
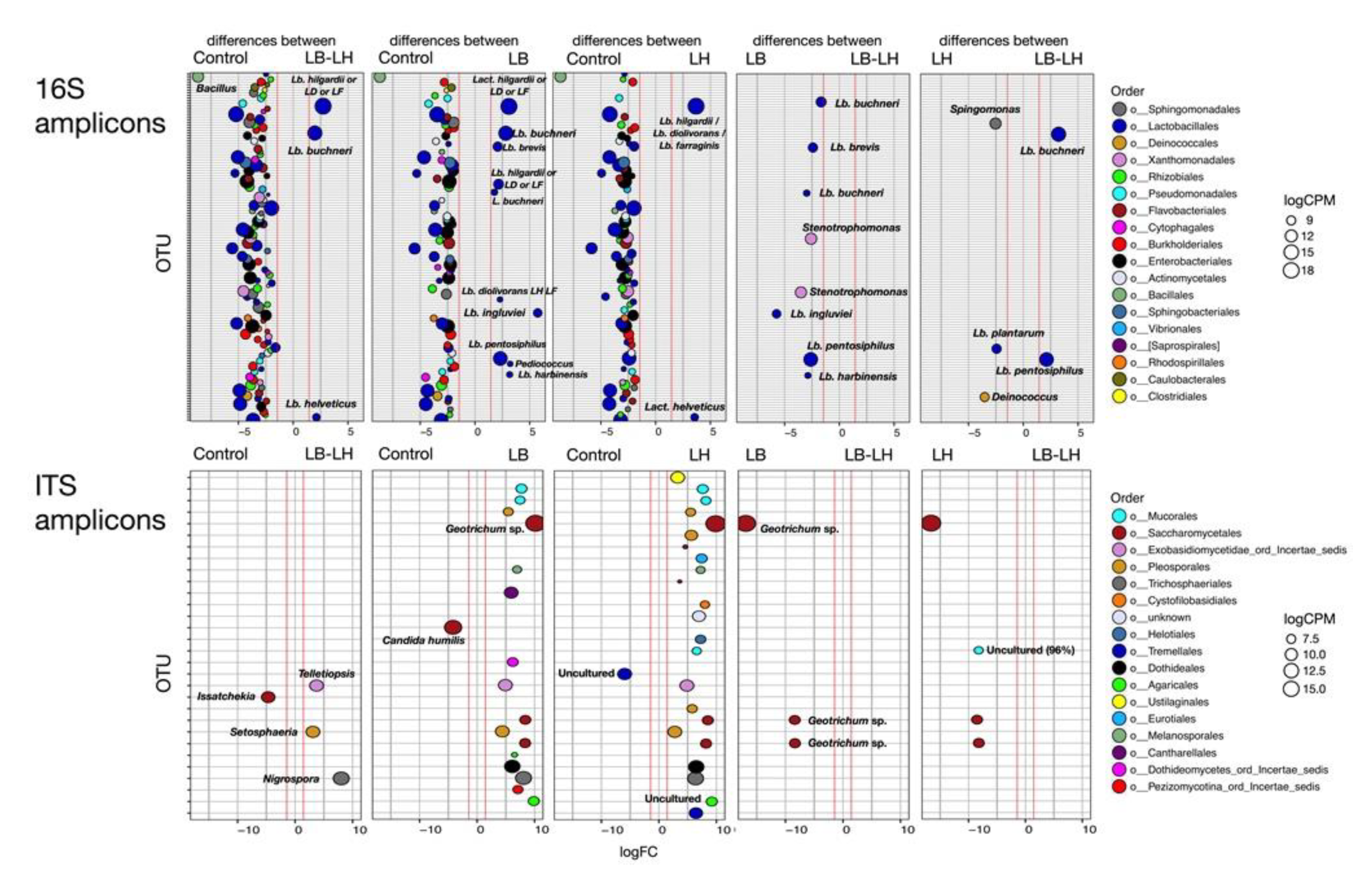
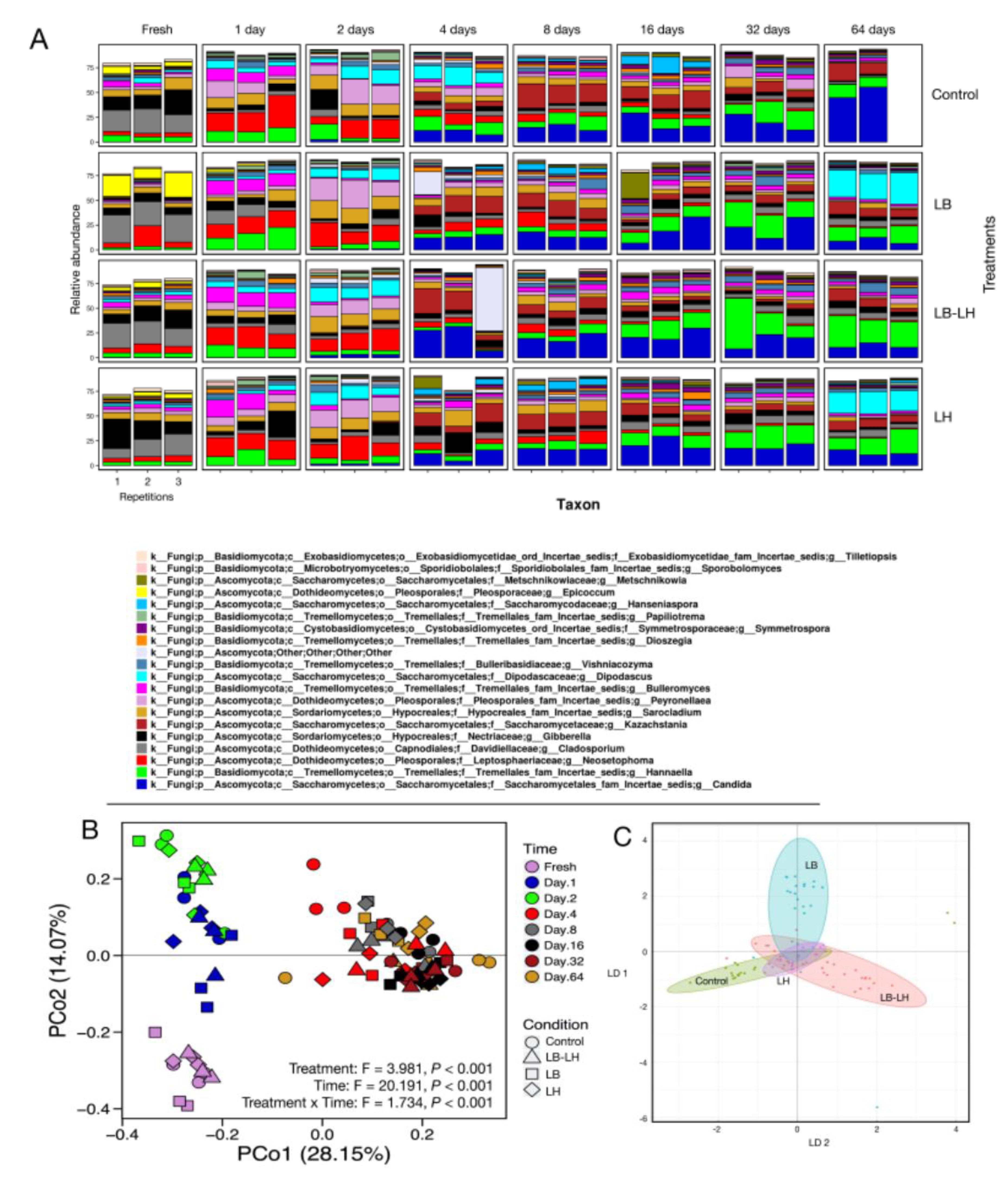
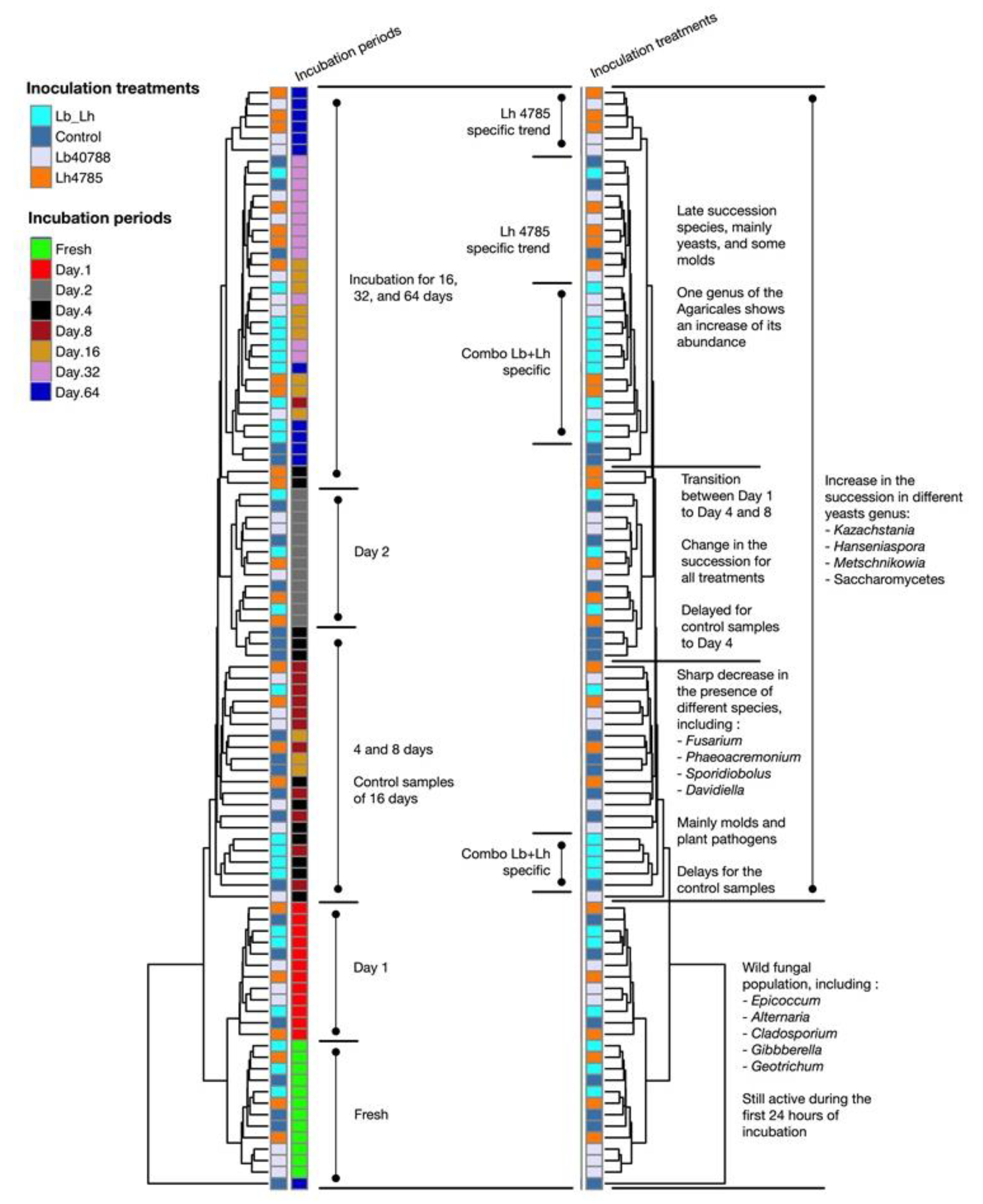
3.1. Eubacterial Succession over the Incubation Period
3.2. Fungal Succession during the Course of the Incubation Period
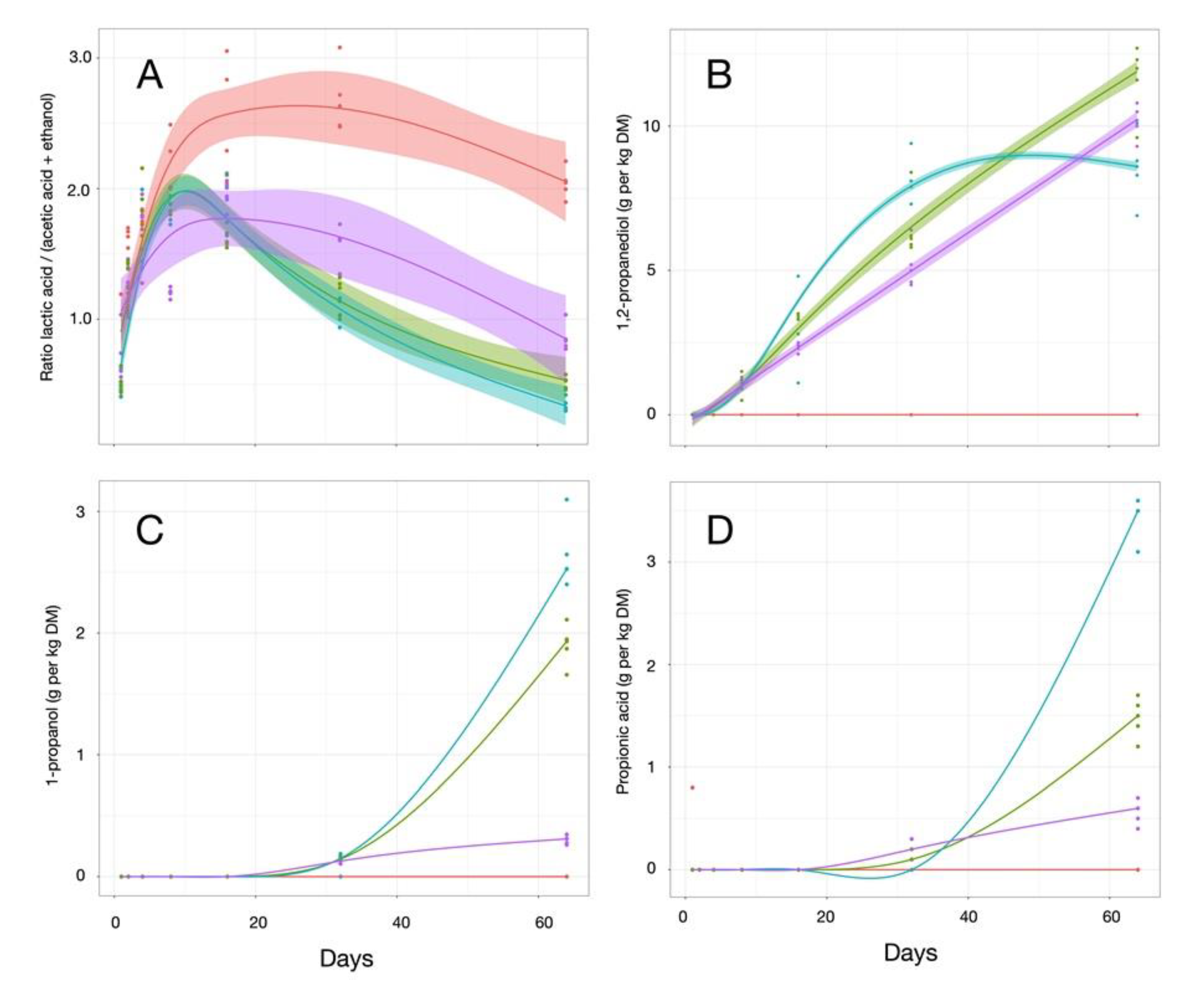
3.3. Fermentation Profiling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Muck, R.E. New trends and opportunities in the development and use of inoculants for silage. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1996, 19, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, F.C.; Adesogan, A.T.; Lara, E.C.; Rabelo, C.H.S.; Berchielli, T.T.; Teixeira, I.A.M.A.; Siqueira, G.R.; Reis, R.A. Effects of feeding corn silage inoculated with microbial additives on the ruminal fermentation, microbial protein yield, and growth performance of lambs. J Anim Sci. 2014, 92, 5640–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.L.; Hindrichsen, I.K.; Klop, G.; Kinley, R.D.; Milora, N.; Bannink, A.; Dijkstra, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria silage inoculation on methane emission and productivity of Holstein Friesian dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7159–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.X.; Amaro, F.X.; Romero, J.J.; Pereira, O.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. The capacity of silage inoculant bacteria to bind aflatoxin B1 in vitro and in artificially contaminated corn silage. J Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7198–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Ogunade, I.M.; Cervantes, A.A.P.; Arriola, K.G.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, D.; Li, X.; Gonçalves, M.C.M.; Vyas, D.; et al. Meta-analysis of effects of inoculation with homofermentative and facultative heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and the performance of dairy cows. J Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4587–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Brent, B.E.; Bolsen, K.K.; Fung, D.Y.C. Epiphytic lactic acid bacteria succession during the pre-ensiling and ensiling periods of alfalfa and corn. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1992, 73, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Oude Elferink, S.J.W.H.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. In Silage science and technology; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Brusetti, L.; Borin, S.; Mora, D.; Rizzi, N.; Sorlini, C.; Daffonchio, D. Usefulness of length heterogeneity-PCR for monitoring lactic acid bacteria succession during maize ensiling. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 56, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L.J. Silage Review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikmeyer, F.; Köfinger, P.; Poschenel, A.; Jünemann, S.; Zakrzewski, M.; Heinl, S.; Mayrhuber, E.; Grabherr, R.; Pühler, A.; Schwab, H.; et al. Metagenome analyses reveal the influence of the inoculant Lactobacillus buchneri CD034 on the microbial community involved in grass ensiling. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.F.; Ávila, C.L.S.; Miguel, M.G.C.P.; Pinto, J.C.; Santos, M.C.; Schwan, R.F. Aerobic stability of sugar-cane silage inoculated with tropical strains of lactic acid bacteria. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 70, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.L.S.; Carvalho, B.F.; Pinto, J.C.; Duarte, W.F.; Schwan, R.F. The use of Lactobacillus species as starter cultures for enhancing the quality of sugar cane silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, W.P.; Ávila, C.L.S.; Pereira, M.N.; Schwan, R.F.; Lopes, N.M.; Pinto, J.C. Effect of the inoculation of sugarcane silage with Lactobacillus hilgardii and Lactobacillus buchneri on feeding behavior and milk yield of dairy cows. J. Anim Sci. 2017, 95, 4613–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.B.; de Oliveira dos Santos, A.; Carvalho, B.F.; Schwan, R.F.; da Silva Ávila, C.L. Wild Lactobacillus hilgardii (CCMA 0170) strain modifies the fermentation profile and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.J.; Zhao, Y.; Balseca-Paredes, M.A.; Tiezzi, F.; Gutierrez-Rodrigues, E.; Castillo, M.S. Laboratory silo type and inoculation effects on nutritional composition, fermentation, and bacterial and fungal communities of oat silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Drouin, P.; Lafrenière, C. Effect of temperature (5-25°C) on epiphytic lactic acid bacteria populations and fermentation of whole-plant corn silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yergeau, E.; Michel, C.; Tremblay, J.; Niemi, A.; King, T.L.; Wyglinski, J.; Lee, K.; Greer, C.W. Metagenomic survey of the taxonomic and functional microbial communities of seawater and sea ice from the Canadian Arctic. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.; Singh, K.; Fern, A.; Kirton, E.S.; He, S.; Woyke, T.; Lee, J.; Chen, F.; Dangl, J.L.; Tringe, S.G. Primer and platform effects on 16S rRNA tag sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsi, M.; Liu, B.; Pop, M. DNACLUST: Accurate and efficient clustering of phylogenetic marker genes. Bioinformatics. 2011, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new Bacteria taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Waste not, want not: Why rarefying microbiome data is inadmissible. PLoS ONE. 2014, 10, e1003531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2-Approximately maximum-likelyhood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE. 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature methods. 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Walters, W.A.; Gonzalez, A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R. Using QIIME to analyze 16S rRNA gene sequences from Microbial Communities. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2011, 36, 10.7.1–10.7.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, M.J. The R book, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A language and environment for statistical computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; Team, R.C. nlme: Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. 2019. R package version 3.1-96. Available online: https://CRAN-R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Chen, Y.; McCarthy, D.; Ritchie, M.; Robinson, M.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: Differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. User’s guide. Available online: https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/vignettes/edgeR/inst/doc/edgeRUsersGuide.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern applied statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 495. [Google Scholar]
- Dunière, L.; Xu, S.; Long, J.; Elekwachi, C.; Wang, Y.; Turkington, K.; Forster, R.; McAllister, T.A. Bacterial and fungal core microbiomes associated with small grain silages during ensiling and aerobic spoilage. BMC Microbiology. 2017, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Biores. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Kharazian, Z.A.; Sarikhan, S.; Jouzani, G.S.; Aghdasi, M.; Salekdeh, G.H. The dynamics of the bacterial communities developed in maize silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Nishino, N. Succession of lactic acid bacteria in wilted rhodesgrass silage assessed by plate culture and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Grassland. Sci. 2010, 56, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolsen, K.K.; Lin, C.; Brent, B.E.; Feyerherm, A.M.; Urban, J.E.; Aimutis, W.R. Effect of silage additives on the microbial succession and fermentation process of alfalfa and corn silages. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 3066–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela, S. Microbiome dynamics during ensiling of corn with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Bacterial and fungal communities of wilted Italian ryegrass silage with and without Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Lactobacillus buchneri. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J.; Du, R.-P.; Gao, M.; Sui, Y.-Q.; Xiu, L.; Wang, X. Naturally occuring lactic acid bacteria isolated from tomato pomace silage. Asian Australas. J. of Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraffa, G.; Chanishvili, N.; Widyastuti, Y. Importance of lactobacilli in food and feed biotechnology. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, H.; Zhang, S.; Kong, J. Effects of inoculants Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus parafarraginis on the fermentation characteristics and microbial communities of corn stover silage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauben, L.; Vauterin, L.; Moore, E.R.B.; Hoste, B.; Swings, J. Genomic diversity of the genus Stenotrophomonas. Int J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Reeleder, R.D. Colonization of bean flowers by Epicoccum purpurascens. Phytopathology. 1991, 81, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gruyter, J.; Woudenberg, J.H.C.; Aveskamp, M.M.; Verkley, G.J.M.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. Systematic reappraisal of species in Phoma section Paraphoma, Pyrenochaeta and Pleurophoma. Mycologia 2010, 102, 1066–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, A.; Gené, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Madrid, H.; de Hoog, G.S.; Cano, J.; Decock, C.; Crous, P.W.; Guarro, J. Phylogeny of Sarocladium (Hypocreales). Persoonia. 2015, 34, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Golt, C.; Joerger, R.D.; Mechor, G.D.; Mourāo, G.B.; Kung, L.J. Identification of the major yeasts isolated from high moisture corn and corn silages in the United States using genetic and biochemical methods. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelhoven, W.J.; van Baalen, A.H.M. Development of the yeast flora of whole-crop maize during ensiling and during subsequent aerobiosis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1988, 42, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, M.A.; Kuldau, G.A. Microbiological and molecular determination of mycobiota in fresh and ensiled maize silage. Mycologia 2007, 99, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, I.; Frenette, M.; Labrie, S. Ribosomal DNA polymorphisms in the yeast Geotrichum candidum. Fungal Biology. 2011, 115, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulo, P.; Laurenčík, M.; Poláková, S.; Minárik, G.; Sláviková, E. Geotrichum bryndzae sp. nov., a novel asexual arthroconidial yeast species related to the genus Galactomyces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2370–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mansfield, M.A. Fungi and mycotoxins in fresh and ensiled maize and the affects of agronomic practices weather conditions and silage characteristics on toxin contamination. Ph.D. Thesis, Pensylvania State University, Pensylvania, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Larpin, S.; Mondoloni, C.; Goerges, S.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Guéguen, M.; Desmasures, N. Geotrichum candidum dominates in yeast population dynamics in Livaro, a french red-smear cheese. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006, 6, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Gente, S.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Guéguen, M. Safety assessment of dairy microorganisms: Geotrichum candidum. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Parker, D.; Allen, D.J.; Tsesmetzis, N. Dynamic bacterial and fungal microbiomes during sweet sorghum ensiling impact bioethanol production. Biores. Technol. 2018, 264, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.; Piano, S.; Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G. Effects of conservation period and Lactobacillus hilgardii inoculum on the fermentation profile and aerobic stability of whole corn and sorghum silages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.J.; Taylor, C.C.; Lynch, M.P.; Neylon, J.M. The effect of treating alfalfa with Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and nutritive value for lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Guchte, M.; Serror, P.; Chervaux, C.; Smokvina, T.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Maguin, E. Stress responses in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2002, 82, 187–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pot, B.; Felis, G.E.; De Bruyne, K.; Tsakalidou, E.; Papadimitriou, K.; Leisner, J.; Vandamme, P. The genus Lactobacillus. In Lactic acid bacteria: Biodiversity and taxonomy; Holzapfel, W.H., Wood, B.J.B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 249–353. [Google Scholar]
- Oude Elferink, S.J.W.H.; Krooneman, J.; Gottschal, J.C.; Spoelstra, S.F.; Faber, F.; Driehuis, F. Anaerobic conversion of lactic acid to acetic acid and 1,2-propanediol by Lactobacillus buchneri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage Review: Interpretation of Chemical, Microbial, and Organoleptic Components of Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Schmidt, R.J.; McDonell, E.E.; Klingerman, C.M.; Kung, L.J. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 or Lactobacillus plantarum MTD-1 on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silages ensiled at two dry matter contents. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandler, O. Carbohydrate metabolism in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 1983, 49, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filya, I.; Sucu, E. The effects of lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation, aerobic stability and nutritive value of maize silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2010, 65, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.J.; Kung, L.J. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri with or without a homolactic bacterium on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silages made at different locations. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.B.; Diez-Gonzalez, F. The effects of fermentation acids on bacterial growth. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1997, 39, 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Krooneman, J.; Faber, F.; Alderkamp, A.C.; Oude Elferink, S.J.W.H.; Driehuis, F.; Cleenwerck, I.; Swings, J.; Gottschal, J.C.; Vancanneyt, M. Lactobacillus diolivorans sp. nov., a 1,2-propanediol-degrading bacterium isolated from aerobically stable maize silage. Int J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.M.; Hashem, A.M.; Ashour, M.S.; Hatti-Kaul, R. 1,2 propanediol utilization by Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 20016, role in bioconversion of glycerol to 1,3 propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde and 3-hydroxypropionic acid. J. Gen. Engin. Biotechnol. 2013, 11, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramulu, D.D.; Liang, M.; Hernandez-Romero, D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Lünsdorf, H.; Parsons, J.B.; Warren, M.J.; Prentice, M.B. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 20016 produces cobalamin-dependent diol dehydratase in metabososomes and metabolizes 1,2-propanediol by disproportionation. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4559–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Sinha, S.; Fan, C.; Liu, Y.; Bobik, T.A. Genetic analysis of the protein shell of the microcompartments involved in coenzyme B12-dependent 1,2-propanediol degradation by Salmonella. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, K.; Fabiszewska, A.; Światek, M.; Szymanowska-Powalowska, D. Evaluation of the ability to metabolize 1,2-propanediol by heterofermentative bacteria of the genus Lactobacillus. Elec. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatments | pH a | Total VFA a | Lactic Acid a | Acetic Acid a | Ratio Lactate/(Acetate + EtOH) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lact. buchneri 40788 | 0.855 | 0.972 | 0.011 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Lact. hilgardii 4785 | 0.736 | 0.206 | 0.410 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Combo LB–LH | 0.552 | 0.396 | 0.109 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F. Dynamic Succession of Microbiota during Ensiling of Whole Plant Corn Following Inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii Alone or in Combination. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120595
Drouin P, Tremblay J, Chaucheyras-Durand F. Dynamic Succession of Microbiota during Ensiling of Whole Plant Corn Following Inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii Alone or in Combination. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(12):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120595
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrouin, Pascal, Julien Tremblay, and Frédérique Chaucheyras-Durand. 2019. "Dynamic Succession of Microbiota during Ensiling of Whole Plant Corn Following Inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii Alone or in Combination" Microorganisms 7, no. 12: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120595
APA StyleDrouin, P., Tremblay, J., & Chaucheyras-Durand, F. (2019). Dynamic Succession of Microbiota during Ensiling of Whole Plant Corn Following Inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii Alone or in Combination. Microorganisms, 7(12), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120595