Environmental DNA Sequencing Reveals a Highly Complex Eukaryote Community in Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, Xisha, South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Environmental Parameters
2.3. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Parameters in Sampling Stations
3.2. Diversity and Composition Analysis of Eukaryote Community
3.3. Comparison of Eukaryote Community Structure
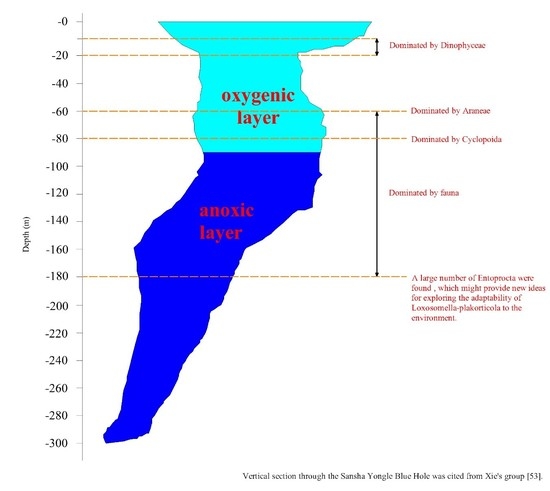
3.3.1. Comparison of Eukaryote Community Structure at Different Depths in the Hole
3.3.2. Comparison of Eukaryote Community Structures in the Hole and the Outer Reef Slope
3.4. Correlations between the Eukaryote Community Structure and Environmental Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iliffe, T.M.; Kornicker, L.S. Worldwide diving discoveries of living fossil animals from the depths of anchialine and marine caves. Smithson. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 2009, 38, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Iliffe, T.M. Anchialine cave ecology. In Ecosystems of the World: Subterranean Ecosystems; Wilkens, H., Culver, D.C., Humphreys, W.F., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Canganella, F.; Bianconi, G.; Kato, C.; Gonzalez, J. Microbial ecology of submerged marine caves and holes characterised by high levels of hydrogen sulphide. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2007, 6, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.R.; Humphreys, W.F.; Mitchell, J.G. Stratification of the microbial community inhabiting an anchialine sinkhole. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 50, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becking, L.E.; Renema, W.; Santodomingo, N.K.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Tuti, Y.; De Voogd, N.J. Recently discoveries landlocked basins in Indonesia reveal high habitat diversity in anchialine systems. Hydrobiologia 2011, 677, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, B.C. Novel Bacterial Diversity in an Anchialine Blue Hole on Abaco Island, Bahamas. Master’s Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pakes, M.J. Anchialine Cave Environments: A Novel Chemosynthetic Ecosystem and Its Ecology. Ph. D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Moreno, J.L.; Iliffe, T.M.; Bracken-Grissom, H.D. Life in the underworld: Anchialine cave biology in the era of speleogenomics. Int. J. Speleol. 2016, 45, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.P.; Wang, B.D.; Pu, X.M.; Xin, M.; He, P.Q.; Li, C.X.; Wei, Q.S.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, T.G. Hydrochemical properties and chemocline of the Sansha Yongle Blue Hole in the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, N.S.; Fu, L.; Chen, H.J.; Liu, R.Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.Q.; Lin, K.X.; Yao, P.; Yang, Z.S. Hydrographic features of the Yongle blue hole in the South China Sea and their influential factors. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 2184–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Fu, L.; Bi, N.S.; Ge, R.P.; Liu, G.X.; Zhuang, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.S.; Fan, D.J.; Yao, P.; Liu, R.Z.; et al. Zooplankton community composition and diel vertical distribution in the Yongle Blue Hole, Xisha Islands, South China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2018, 49, 594–603. [Google Scholar]
- Daenekas, J.; Iliffe, T.M.; Yager, J.; Koenemann, S. Speleonectes kakuki, a new species of Remipedia (Crustacea) from anchialine and sub-seafloor caves on Andros and Cat Island, Bahamas. Zootaxa 2009, 1, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Iliffe, T.M.; Gonzalez, B.; Villalobos, J.L. Triacanthoneus akumalensis, a new species of alpheid shrimp (Crustacea: Caridea: Alpheidae) from an anchialine cave in Quintana Roo, Mexico. Zootaxa 2012, 3154, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medinger, R.; Nolte, V.; Pandey, R.V.; Jost, S.; Ottenwälder, B.; Schlötterer, C.; Boenigk, J. Diversity in a hidden world: Potential and limitation of next-generation sequencing for surveys of molecular diversity of eukaryotic microorganisms. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowrousian, M. Next-generation sequencing techniques for eukaryotic microorganisms: Sequencing-based solutions to biological problems. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahé, F.; Mayor, J.; Bunge, J.; Chi, J.Y.; Siemensmeyer, T.; Stoeck, T.; Wahl, B.; Paprotka, T.; Filker, S.; Dunthorn, M. Comparing high-throughput platforms for sequencing the V4 region of SSU-rDNA in environmental microbial eukaryotic diversity surveys. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2015, 62, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monchy, S.; Grattepanche, J.D.; Breton, E.; Meloni, D.; Sanciu, G.; Chabé, M.; Delhaes, L.; Viscogliosi, E.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Christaki, U. Microplanktonic community structure in a coastal system relative to a Phaeocystis bloom inferred from morphological and tag pyrosequencing methods. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Sogge, H.; Lagesen, K.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Jakobsen, K.S.; Rohrlack, T. Use of high throughput sequencing and light microscopy show contrasting results in a study of phytoplankton occurrence in a freshwater environment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Chen, L.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.S.; Bi, N.S.; Wang, L.S.; Deng, C.M.; Zhu, C.J. Controls on vertical nutrient distributions in the Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; He, H.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Bi, N.S.; Yang, Z.S. Archaeal diversity and community structure in the Yongle Blue Hole, Xisha, South China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2018, 49, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; McCliment, E.A.; Ducklow, H.W.; Huse, S.M. A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talahashi, M.; Fujii, K.; Parsons, T.R. Simulation study of phytoplankton photosynthesis and growth in the Fraser River Estuary. Mar. Biol. 1973, 19, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.T.; Yin, J.P.; Dong, J.D.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Sun, F.L. Scenarios of nutrient alterations and responses of phytoplankton in a changing Daya Bay, South China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 165, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.M.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhou, W.H.; Xu, J.R.; Sun, C.C.; Zhang, F.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Xu, H.Z. Distribution of Macro-nutrients, Dissolved Oxygen, pH and Chl a and Their Relationships in Northern South China Sea. Marin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 25, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Ning, X.R.; Sun, J.; Le, F.F. Responses of phytoplankton growth on nutrient enrichments in the northern South China Sea. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 3959–3968. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.N.; Chen, F.J.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, J.F. Concentration distribution and structural features of nutrients in the northwest of the South China Sea in winter 2012. J. Oceanogr. 2015, 34, 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, R.X.; Zhu, M.Y.; Chen, B.Z.; Hao, Y.J. Study on population growth processes and interspecific competition of Prorocentrum donghaiense and Skeletonema costatum in semi-continuous dilution experiments. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2006, 24, 495–503. [Google Scholar]
- Lejzerowicz, F.; Esling, P.; Pillet, L.; Wilding, T.A.; Black, K.D.; Pawlowski, J. High-throughput sequencing and morphology perform equally well for benthic monitoring of marine ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, W.; Edgcomb, V.; Jeon, S.; Leslin, C.; Bunge, J.; Taylor, G.T.; Varela, R.; Epstein, S. Protistan microbial observatory in the Cariaco Basin, Caribbean.II. Habitat specialization. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1357–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseto, T.; Sugiyama, N.; Hirose, E. A new sponge-inhabiting Loxosomella (Entoprocta: Loxosomatidae) from Okinawa Island, Japan, with special focus on foot structure. Zool. Sci. 2008, 25, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, J.; Iseto, T.; Hirose, M.; Sundberg, P.; Obst, M. The first internal molecular phylogeny of the animal phylum Entoprocta (Kamptozoa). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 56, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseto, T.; Yokuta, Y.; Hirose, E. Seasonal change of species composition, abundance, and reproduction of solitary entoprocts in Okinawa Island, the Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C. Entoprocts: Keys and notes for the identification of the species. Synop. Br. Fauna 1989, 41, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wasson, K. Systematic revision of colonial Kamptozoans (entoprocts) of the Pacific coast of North America. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1997, 121, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, M.Y.; Shao, P.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Qu, L.H. Genetic diversity of small eukaryotes from the coastal waters of Nansha Islands in China. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 240, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Lin, D.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, S.H.; Huang, Q.J.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Chen, Y.Q. Diversity and distribution of planktonic protists in the northern South China Sea. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.X.; Huang, B.Q.; Liao, Y.; Sun, P. Picoeukaryotic diversity and distribution in the subtropical-tropical South China Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Gutiérrez, F.; Solís-Marín, F.A.; Gómez, P.; Sanchez, C.; Hernandez-Alcantara, P.; Alvarez-Noguera, F.; Yáñez-Mendoza, G. Mexican anchialine fauna-With emphasis in the high biodiversity cave El Aerolito. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 9, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.X.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.S.; Bi, N.S.; Fan, D.J.; Yao, P.; Liu, G.X.; Chen, H.J.; Tian, Y.; Liu, R.Z. Components and origin of suspended matter in the Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, South China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2018, 49, 779–792. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Xu, J.; Huang, X.P.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.J.; Ye, F.; Liang, X.M. Relationship between nutrients and plankton biomass in the turbidity maximum zone of the Pearl River Estuary. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Carrasco, N.; Vosloo, A.; Perissinotto, R. Impacts of turbidity on an epibiotic ciliate in the St Lucia Estuary, South Africa. Hydrobiologia 2018, 815, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horppila, J.; Eloranta, P.; Liljendahl-Nurminen, A.; Niemisto, J.; Pekcan-Hekim, Z. Refuge availability and sequence of predators determine the seasonal succession of crustacean zooplankton in a clay-turbid lake. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, P.C. Evidence that fish structure the zooplankton communities of turbid lakes and reservoirs. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, J.D.; Wickham, S.A.; Toalson, S.; Gilbert, J.J. The effect of clays on a fresh-water plankton community: An enclosure experiment. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1993, 127, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Bagatini, I.L.; Spínola, A.L.G.; Peres, B.D.; Mansano, A.D.; Rodrigues, M.A.A.; Batalha, M.A.P.L.; de Lucca, J.V.; Godinho, M.J.L.; Tundisi, T.M.; Seleghim, M.H.R. Protozooplankton and its relationship with environmental conditions in 13 water bodies of the Mogi-Guaçu basin-SP, Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 2013, 13, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qiu, L.L.; Wei, Z.M.; Li, F.H. Spatial heterogeneity in a deep artificial lake plankton community revealed by PCR-DGGE fingerprinting. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.P.; Li, R.; Hu, C.; Sun, P.; Jiao, N.Z.; Warren, A. Microbial eukaryote diversity and activity in the water column of the South China Sea based on DNA and RNA high throughput sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeque, P.K.; Parry, H.E.; Harmer, R.A.; Somerfield, P.J.; Atkinson, A. Next generation sequencing reveals the hidden diversity of zooplankton assemblages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Location | Sample Name | Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Sansha Yongle Blue Hole | LD0 | 0 |
| LD10 | 10 | |
| LD20 | 20 | |
| LD60 | 60 | |
| LD80 | 80 | |
| LD90 | 90 | |
| LD100 | 100 | |
| LD150 | 150 | |
| LD180 | 180 | |
| outer reef slope | WJ0 | 0 |
| WJ50 | 50 |
| Samples | Raw Sequences | Effective Sequences | OTUs | Chao1 | Shannon | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD0 | 82,584 | 80,265 | 1591 | 1573 | 7.62 | 99.7 |
| LD10 | 96,121 | 93,102 | 1594 | 1567 | 6.07 | 99.5 |
| LD20 | 95,414 | 93,308 | 1378 | 1351 | 3.94 | 99.6 |
| LD60 | 81,004 | 76,761 | 41 | 39 | 1.64 | 100.0 |
| LD80 | 90,493 | 85,745 | 1569 | 1550 | 4.73 | 99.5 |
| LD90 | 94,964 | 77,212 | 1318 | 1311 | 8.14 | 99.8 |
| LD100 | 87,143 | 82,482 | 3302 | 3312 | 9.14 | 99.5 |
| LD150 | 82,515 | 68,851 | 1728 | 2591 | 7.55 | 99.5 |
| LD180 | 91,558 | 85,053 | 1306 | 1242 | 3.21 | 99.6 |
| WJ0 | 95,823 | 92,722 | 823 | 809 | 2.43 | 99.8 |
| WJ50 | 84,171 | 82,270 | 1280 | 1278 | 5.54 | 99.8 |
| OTU ID | Species Information | LD0 | LD10 | LD20 | LD60 | LD80 | LD90 | LD100 | LD150 | LD180 | WJ0 | WJ50 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Class | Order | ||||||||||||
| OTU1 | Annelida | Polychaeta | Phascolosomatiformes | 1.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 77.82 | 0.63 |
| OTU2 | Arthropoda | Arachnida | Araneae | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 75.28 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| OTU3 | Entoprocta | Loxosomatidae * | Loxosomella ** | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 60.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| OTU4 | Alveolata | Dinophyceae | Gymnodiniales | 0.30 | 4.13 | 44.01 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.85 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.08 |
| OTU6 | Ascomycota | Leotiomycetes | Thelebolales | 7.21. | 2.60 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 1.49 | 8.53 | 6.37 | 10.53 | 0.69 | 1.29 | 4.11 |
| OTU5 | Alveolata | Dinophyceae | Gymnodiniales | 0.56 | 15.20 | 20.56 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.18 |
| OTU7 | Arthropoda | Hexanauplia | Cyclopoida | 0.16 | 1.25 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 31.18 | 0.91 | 0.39 | 0.79 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| OTU8 | Apicomplexa | Conoidasida | Gregarinasina | 0.05 | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 33.36 |
| OTU9 | Arthropoda | Unclassified | Unclassified | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 20.70 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| OTU10 | Alveolata | Dinophyceae | Gymnodiniales | 0.39 | 13.94 | 1.11 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 1.41 | 0.52 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.30 |
| Samples | Depth (m) | Chao1 | Shannon | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F3 | 25 | 3009.18 | 6.78 | [49] |
| 75 | 2629.52 | 7.29 | ||
| 200 | 2956.26 | 7.59 | ||
| H7 | 5 | 2625.84 | 6.64 | [49] |
| 25 | 3203.35 | 7.44 | ||
| 75 | 3170.70 | 7.43 | ||
| 200 | 3202.02 | 7.16 | ||
| YLBL | 0 | 1762.85 | 7.41 | this study |
| 10 | 1989.03 | 5.93 | ||
| 20 | 1662.53 | 3.74 | ||
| 60 | 28.00 | 1.29 | ||
| 80 | 1908.10 | 4.62 | ||
| 90 | 1489.51 | 7.96 | ||
| 100 | 3344.06 | 8.99 | ||
| 150 | 1698.22 | 7.29 | ||
| 180 | 1432.64 | 2.77 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; He, H.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhen, Y. Environmental DNA Sequencing Reveals a Highly Complex Eukaryote Community in Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, Xisha, South China Sea. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120624
Liu Y, He H, Fu L, Liu Q, Yang Z, Zhen Y. Environmental DNA Sequencing Reveals a Highly Complex Eukaryote Community in Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, Xisha, South China Sea. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(12):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120624
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yueteng, Hui He, Liang Fu, Qian Liu, Zuosheng Yang, and Yu Zhen. 2019. "Environmental DNA Sequencing Reveals a Highly Complex Eukaryote Community in Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, Xisha, South China Sea" Microorganisms 7, no. 12: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120624
APA StyleLiu, Y., He, H., Fu, L., Liu, Q., Yang, Z., & Zhen, Y. (2019). Environmental DNA Sequencing Reveals a Highly Complex Eukaryote Community in Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, Xisha, South China Sea. Microorganisms, 7(12), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120624