Engineered Lactococcus lactis Secreting IL-23 Receptor-Targeted REX Protein Blockers for Modulation of IL-23/Th17-Mediated Inflammation
Abstract
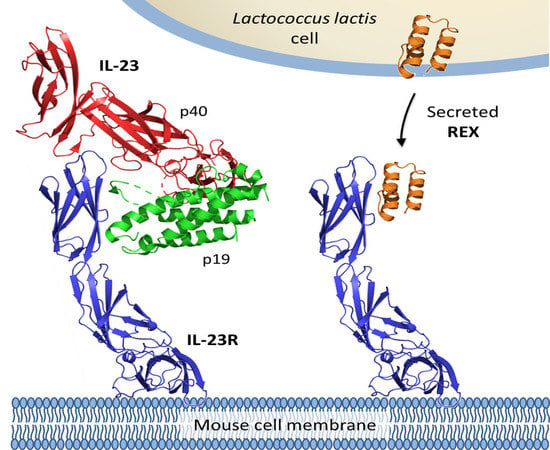
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Media, and Growth Conditions
2.2. DNA Manipulation and Plasmid Construction
2.3. Expression of IL-23R Binding Fusion Proteins in L. lactis
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Production of the Recombinant IL-23 Receptor
2.7. IL-23R Binding Assay
2.8. Modeling of IL-23R/REX Interaction by Docking
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Constructs for the Display and Secretion of REX Binders of IL-23R
3.2. Expression of REX Fusion Protein in L. lactis
3.3. Display of REX Fusion Proteins on the Surface of L. lactis
3.4. Binding of IL-23R-Fc Chimera to the Surface of REX-Displaying L. lactis
3.5. Binding of L. lactis-Secreted REX Variants to Recombinant IL-23R in ELISA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catana, C.S.; Berindan Neagoe, I.; Cozma, V.; Magdas, C.; Tabaran, F.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Contribution of the IL-17/IL-23 axis to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 5823–5830. [Google Scholar]
- Himmel, M.E.; Hardenberg, G.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Steiner, T.S.; Levings, M.K. The role of T-regulatory cells and Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of human inflammatory bowel disease. Immunology 2008, 125, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, C.; Dulai, P.S.; Vermeire, S.; Sandborn, W.J. Lessons Learned From Trials Targeting Cytokine Pathways in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 374–388.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floss, D.M.; Schroder, J.; Franke, M.; Scheller, J. Insights into IL-23 biology: From structure to function. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 569–578. [Google Scholar]
- Duijvestein, M.; Battat, R.; Vande Casteele, N.; D’Haens, G.R.; Sandborn, W.J.; Khanna, R.; Jairath, V.; Feagan, B.G. Novel Therapies and Treatment Strategies for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; Gasink, C.; Jacobstein, D.; Lang, Y.; Friedman, J.R.; Blank, M.A.; Johanns, J.; Gao, L.L.; Miao, Y.; et al. Ustekinumab as Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Crohn’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1946–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiniou, C.; Dominguez-Punaro, M.; Cloutier, F.; Erfani, A.; Ennaciri, J.; Sivanesan, D.; Sanchez, M.; Chognard, G.; Hou, X.; Rivera, J.C.; et al. Specific targeting of the IL-23 receptor, using a novel small peptide noncompetitive antagonist, decreases the inflammatory response. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R1216–R1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretz-Rommel, A.; Wild, M.; Bowdish, K.; Chen, E.; Oltean, D.; Gonzalez, M.; Kapoor, M. Polypeptides that bind IL-23R. Patent WO 2011/043835 A1, 14 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchar, M.; Vankova, L.; Petrokova, H.; Cerny, J.; Osicka, R.; Pelak, O.; Sipova, H.; Schneider, B.; Homola, J.; Sebo, P.; et al. Human interleukin-23 receptor antagonists derived from an albumin-binding domain scaffold inhibit IL-23-dependent ex vivo expansion of IL-17-producing T-cells. Proteins 2014, 82, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrlec, K.; Strukelj, B.; Berlec, A. Non-immunoglobulin scaffolds: A focus on their targets. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavnickova, M.; Kuchar, M.; Osicka, R.; Vankova, L.; Petrokova, H.; Maly, M.; Cerny, J.; Arenberger, P.; Maly, P. ABD-Derived Protein Blockers of Human IL-17 Receptor A as Non-IgG Alternatives for Modulation of IL-17-Dependent Pro-Inflammatory Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, E3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizova, L.; Kuchar, M.; Petrokova, H.; Osicka, R.; Hlavnickova, M.; Pelak, O.; Cerny, J.; Kalina, T.; Maly, P. p19-targeted ABD-derived protein variants inhibit IL-23 binding and exert suppressive control over IL-23-stimulated expansion of primary human IL-17+ T-cells. Autoimmunity 2017, 50, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareckova, L.; Petrokova, H.; Osicka, R.; Kuchar, M.; Maly, P. Novel binders derived from an albumin-binding domain scaffold targeting human prostate secretory protein 94 (PSP94). Protein Cell 2015, 6, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadravec, P.; Mareckova, L.; Petrokova, H.; Hodnik, V.; Perisic Nanut, M.; Anderluh, G.; Strukelj, B.; Maly, P.; Berlec, A. Development of Recombinant Lactococcus lactis Displaying Albumin-Binding Domain Variants against Shiga Toxin 1 B Subunit. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.N.; Li, J.; Biedermannova, L.; Kuchar, M.; Sipova, H.; Semeradtova, A.; Cerny, J.; Petrokova, H.; Mikulecky, P.; Polinek, J.; et al. Novel high-affinity binders of human interferon gamma derived from albumin-binding domain of protein G. Proteins 2012, 80, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, F.; de Vos, W.M. Functional genomics of lactic acid bacteria: From food to health. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E. Probiotics: Definition, sources, selection, and uses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46 (Suppl 2), S58–S61, discussion S144–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavec, T.V.; Berlec, A. Engineering of lactic acid bacteria for delivery of therapeutic proteins and peptides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2053–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravnikar, M.; Strukelj, B.; Obermajer, N.; Lunder, M.; Berlec, A. Engineered lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis capable of binding antibodies and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6928–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlec, A.; Perse, M.; Ravnikar, M.; Lunder, M.; Erman, A.; Cerar, A.; Strukelj, B. Dextran sulphate sodium colitis in C57BL/6J mice is alleviated by Lactococcus lactis and worsened by the neutralization of Tumor necrosis Factor alpha. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 43, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simcic, S.; Berlec, A.; Stopinsek, S.; Strukelj, B.; Orel, R. Engineered and wild-type L. lactis promote anti-inflammatory cytokine signalling in inflammatory bowel disease patient’s mucosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holo, H.; Nes, I.F. Transformation of Lactococcus by electroporation. Methods Mol. Biol. 1995, 47, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Mierau, I.; Kleerebezem, M. 10 years of the nisin-controlled gene expression system (NICE) in Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 68, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrlec, K.; Pucer Janez, A.; Rogelj, B.; Strukelj, B.; Berlec, A. Evasin-displaying lactic acid bacteria bind different chemokines and neutralize CXCL8 production in Caco-2 cells. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrlec, K.; Zadravec, P.; Hlavnickova, M.; Kuchar, M.; Vankova, L.; Petrokova, H.; Krizova, L.; Cerny, J.; Berlec, A.; Maly, P. p19-Targeting ILP Protein Blockers of IL-23/Th-17 Pro-Inflammatory Axis Displayed on Engineered Bacteria of Food Origin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, E1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sali, A.; Blundell, T.L. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol Biol 1993, 234, 779–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinform. 2014, 47, 5.6.1–5.6.30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.U.; Frick, I.M.; Nilsson, H.; Kraulis, P.J.; Hober, S.; Jonasson, P.; Linhult, M.; Nygren, P.A.; Uhlen, M.; Bjorck, L.; et al. Structure, specificity, and mode of interaction for bacterial albumin-binding modules. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8114–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, Y.; Bouchareychas, L.; Merceron, R.; Skladanowska, K.; van den Bossche, L.; Detry, S.; Govindarajan, S.; Elewaut, D.; Haerynck, F.; Dullaers, M.; et al. Structural Activation of Pro-inflammatory Human Cytokine IL-23 by Cognate IL-23 Receptor Enables Recruitment of the Shared Receptor IL-12Rbeta1. Immunity 2018, 48, 45–58.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.Z.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Vajda, S. How good is automated protein docking? Proteins 2013, 81, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Brenke, R.; Comeau, S.R.; Vajda, S. PIPER: An FFT-based protein docking program with pairwise potentials. Proteins 2006, 65, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buist, G.; Kok, J.; Leenhouts, K.J.; Dabrowska, M.; Venema, G.; Haandrikman, A.J. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the major peptidoglycan hydrolase of Lactococcus lactis, a muramidase needed for cell separation. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieye, Y.; Usai, S.; Clier, F.; Gruss, A.; Piard, J.C. Design of a protein-targeting system for lactic acid bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4157–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadravec, P.; Strukelj, B.; Berlec, A. Improvement of LysM-mediated surface display of designed ankyrin repeat proteins (DARPins) in recombinant and nonrecombinant strains of Lactococcus lactis and Lactobacillus Species. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Walker, A.W.; Sanderson, J.D.; Churcher, C.; Parkes, G.C.; Hudspith, B.N.; Rayment, N.; Brostoff, J.; Parkhill, J.; Dougan, G.; Petrovska, L. High-throughput clone library analysis of the mucosa-associated microbiota reveals dysbiosis and differences between inflamed and non-inflamed regions of the intestine in inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamanu, E. Complementary Functional Strategy for Modulation of Human Gut Microbiota. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 4144–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Guarner, F.; Guerrant, R.; Holt, P.R.; Quigley, E.M.; Sartor, R.B.; Sherman, P.M.; Mayer, E.A. An update on the use and investigation of probiotics in health and disease. Gut 2013, 62, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Strain, Plasmid, or Gene | Relevant Features or Sequence (5’–3’) | Ref. or Source |
|---|---|---|
| Strain | ||
| E. coli | ||
| DH5α | endA1 glnV44 thi-1 recA1 relA1 gyrA96 deoR F- Φ80dlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169, hsdR17(rK- mK+), λ– | Invitrogen |
| TOP10 | F– mcrA Δ(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) Φ80lacZΔM15 ΔlacX74 recA1 araD139 Δ(ara leu) 7697 galU galK rpsL (StrR) endA1 nupG | Life technologies |
| BL21 λ(D3) | E. coli B F – dcm ompT hsdS (rB– mB–) gal λ(DE3) | [15] |
| L. lactis | ||
| NZ9000 | MG1363 nisRK ΔpepN | [23] |
| Plasmid | ||
| pNZ8148 | pSH71 derivative, PnisA, CmR, nisin-controlled expression | [23] |
| pSDBA3b | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, B domain, and cA | [24] |
| pET-REX009 | pET28b containing a fusion gene of REX009, tolA protein, and AviTag consensus | [9] |
| pET-REX115 | pET28b containing a fusion gene of REX115, tolA protein, and AviTag consensus | [9] |
| pET-REX125 | pET28b containing a fusion gene of REX125, tolA protein, and AviTag consensus | [9] |
| pSD-REX009 | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, REX009, and cA | This work |
| pSD-REX115 | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, REX115, and cA | This work |
| pSD-REX125 | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, REX125, and cA | This work |
| pSD-REX009-FLAG | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, FLAG tag, REX009, and cA | This work |
| pSD-REX115-FLAG | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, FLAG tag, REX115, and cA | This work |
| pSD-REX125-FLAG | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, FLAG tag, REX125, and cA | This work |
| pSC-REX009 | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide and REX009 | This work |
| pSC-REX115 | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide and REX115 | This work |
| pSC-REX125 | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide and REX125 | This work |
| pSC-REX009-FLAG | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, FLAG tag, and REX009 | This work |
| pSC-REX115-FLAG | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, FLAG tag, and REX115 | This work |
| pSC-REX125-FLAG | pNZ8148 containing gene fusion of Usp45 signal peptide, FLAG tag, and REX125 | This work |
| Primer | ||
| ILP030-F | TGGATCCTTAGCTGAAGCTAAAGTC | This work |
| Rex009-R-Eco | AGAATTCAGGTAACGAAGCTAAAATC | This work |
| Rex009-R-Xba | ATCTAGAAGGTAACGAAGCTAAAATC | This work |
| Rex115-R-Eco | AGAATTCAAGGTAAAACAGCTAAAATCC | This work |
| Rex115-R-Xba | ATCTAGAAGGTAAAACAGCTAAAATCC | This work |
| Rex125-R-Eco | AGAATTCAAGGTAACGCAGCTAAAATAG | This work |
| Rex125-R-Xba | AGAATTCAGGTAACGCAGCTAAAATAG | This work |
| Usp1-NcoI | ATAACCATGGCTAAAAAAAAGATTATCTCAGCTATTTTAATG | [19] |
| FLAG_Bam_R | GGATCCTTTATCATCGTCGTCTTTATAATCAGCGTAAACACCTGACAACG | [25] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plavec, T.V.; Kuchař, M.; Benko, A.; Lišková, V.; Černý, J.; Berlec, A.; Malý, P. Engineered Lactococcus lactis Secreting IL-23 Receptor-Targeted REX Protein Blockers for Modulation of IL-23/Th17-Mediated Inflammation. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050152
Plavec TV, Kuchař M, Benko A, Lišková V, Černý J, Berlec A, Malý P. Engineered Lactococcus lactis Secreting IL-23 Receptor-Targeted REX Protein Blockers for Modulation of IL-23/Th17-Mediated Inflammation. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(5):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050152
Chicago/Turabian StylePlavec, Tina Vida, Milan Kuchař, Anja Benko, Veronika Lišková, Jiří Černý, Aleš Berlec, and Petr Malý. 2019. "Engineered Lactococcus lactis Secreting IL-23 Receptor-Targeted REX Protein Blockers for Modulation of IL-23/Th17-Mediated Inflammation" Microorganisms 7, no. 5: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050152
APA StylePlavec, T. V., Kuchař, M., Benko, A., Lišková, V., Černý, J., Berlec, A., & Malý, P. (2019). Engineered Lactococcus lactis Secreting IL-23 Receptor-Targeted REX Protein Blockers for Modulation of IL-23/Th17-Mediated Inflammation. Microorganisms, 7(5), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050152