Extracellular Traps Released by Neutrophils from Cats are Detrimental to Toxoplasma gondii Infectivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Isolation of Neutrophils from Cats
2.4. Parasites Culture
2.5. NET Induction/Inhibition Assay
2.6. Quantification of NET-Derived DNA
2.7. Detection of Myeloperoxidase, Histone H1, and T. gondii
2.8. Ultrastructural Visualization of T. gondii Entrapment in NET
2.9. Production of NET-Enriched Supernatants
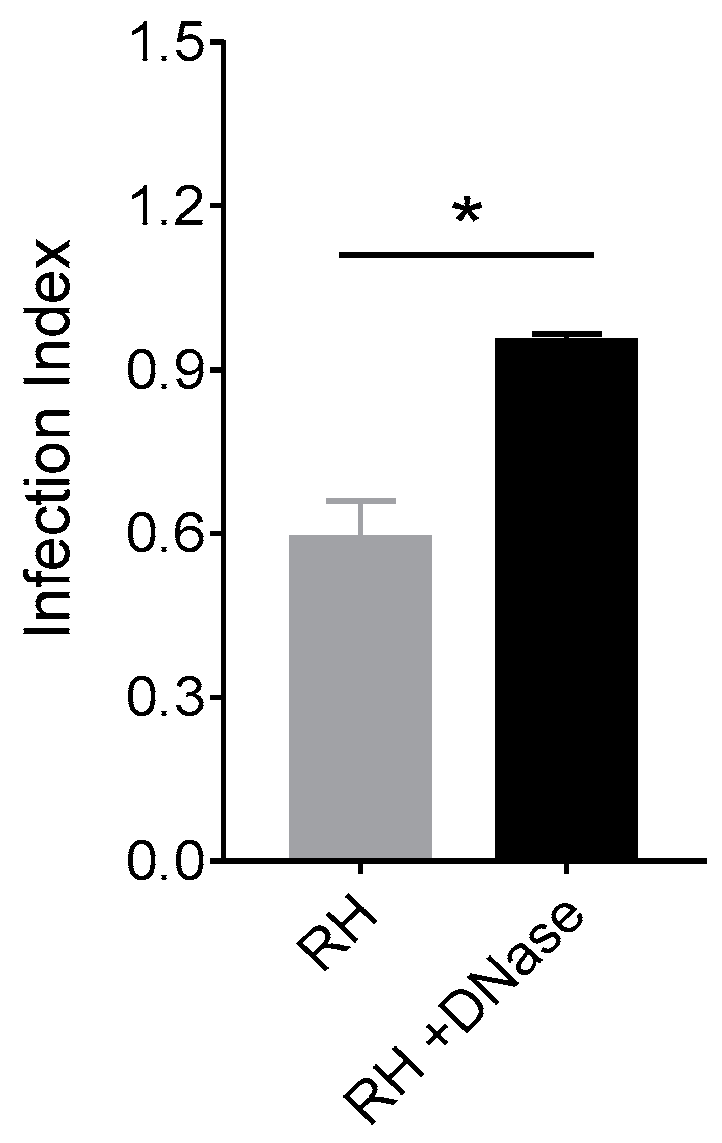
2.10. Parasite Infectivity Assay
2.11. Neutrophil Viability Assay
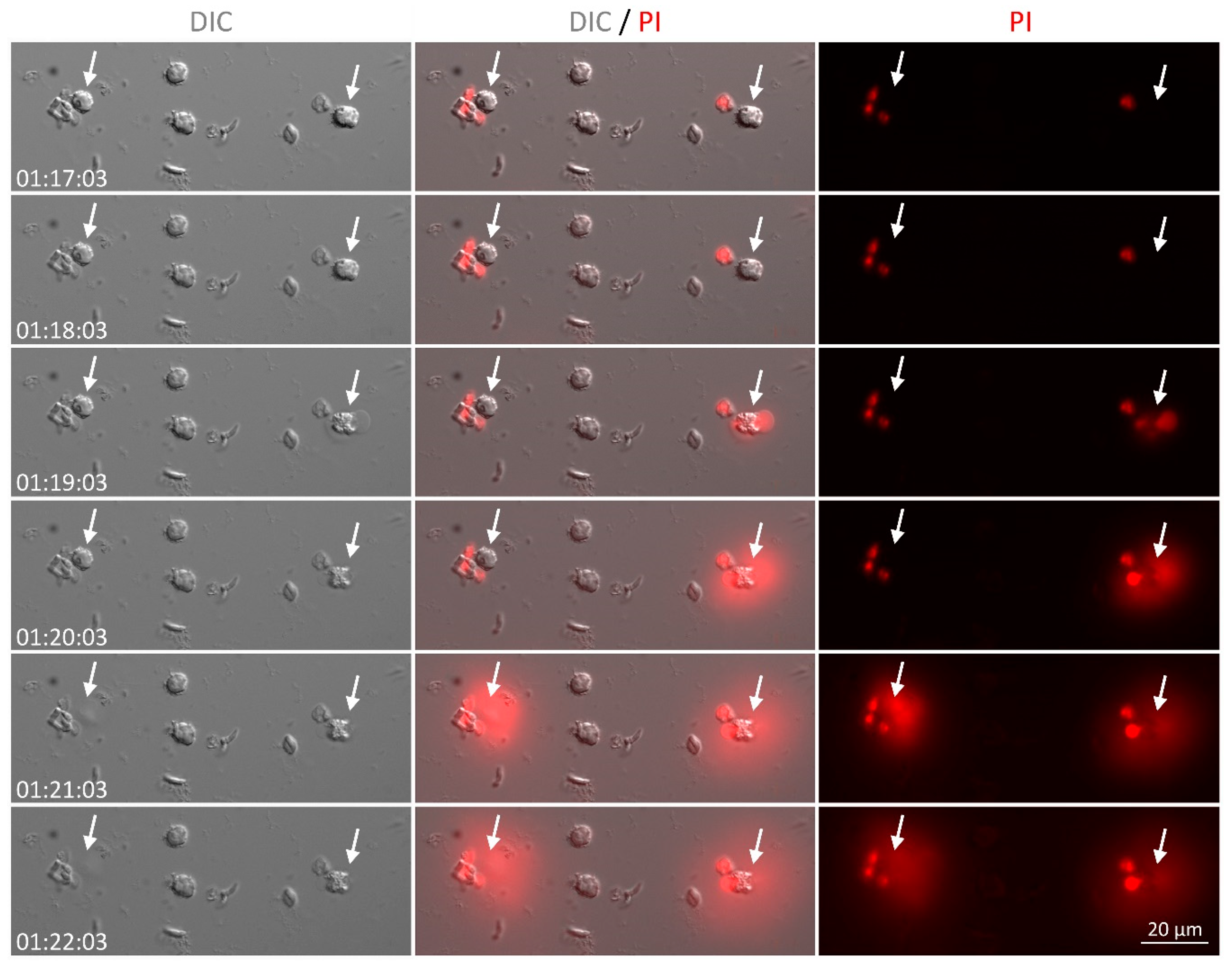
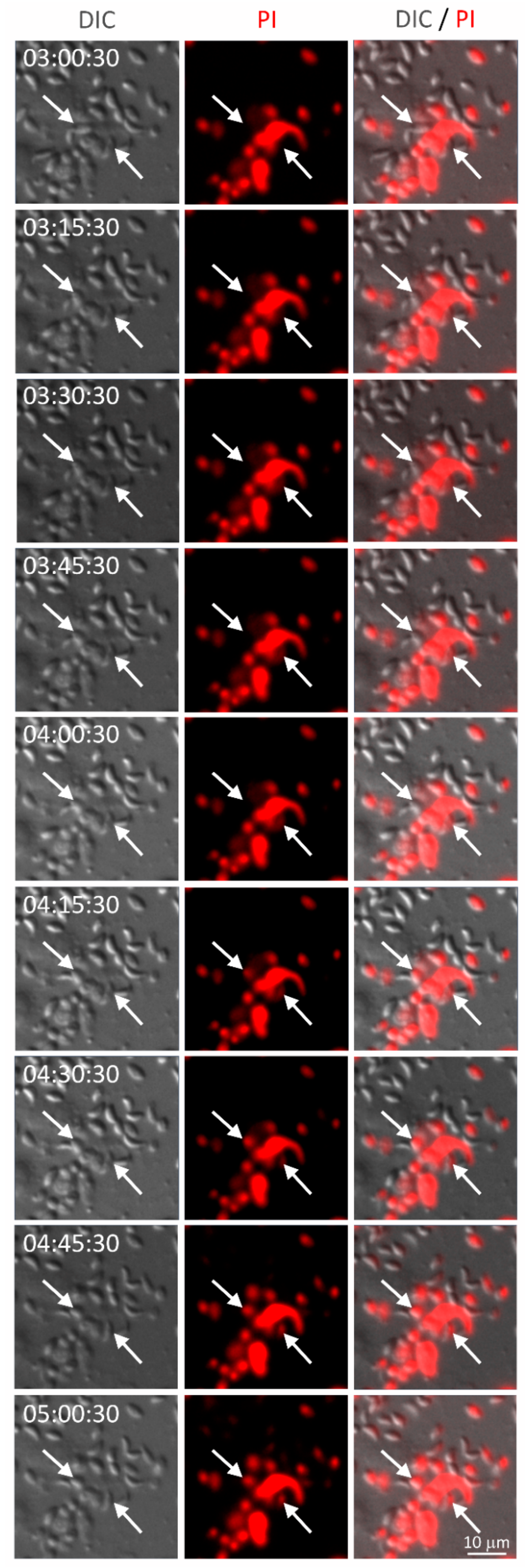
2.12. Live Cell Imaging
2.13. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
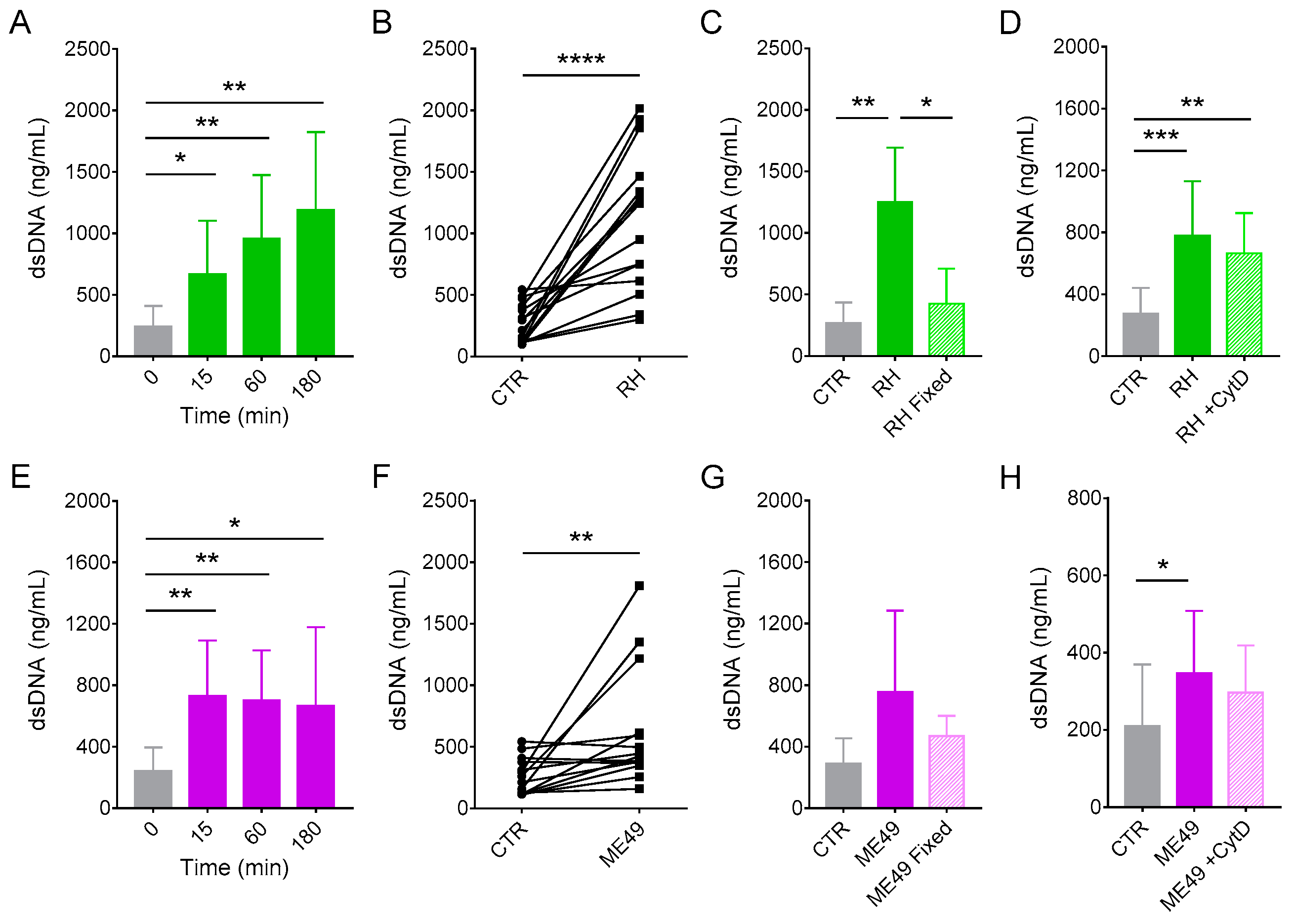
3.1. Neutrophils from Cats Produce Extracellular Traps in Response to Classical Inducers
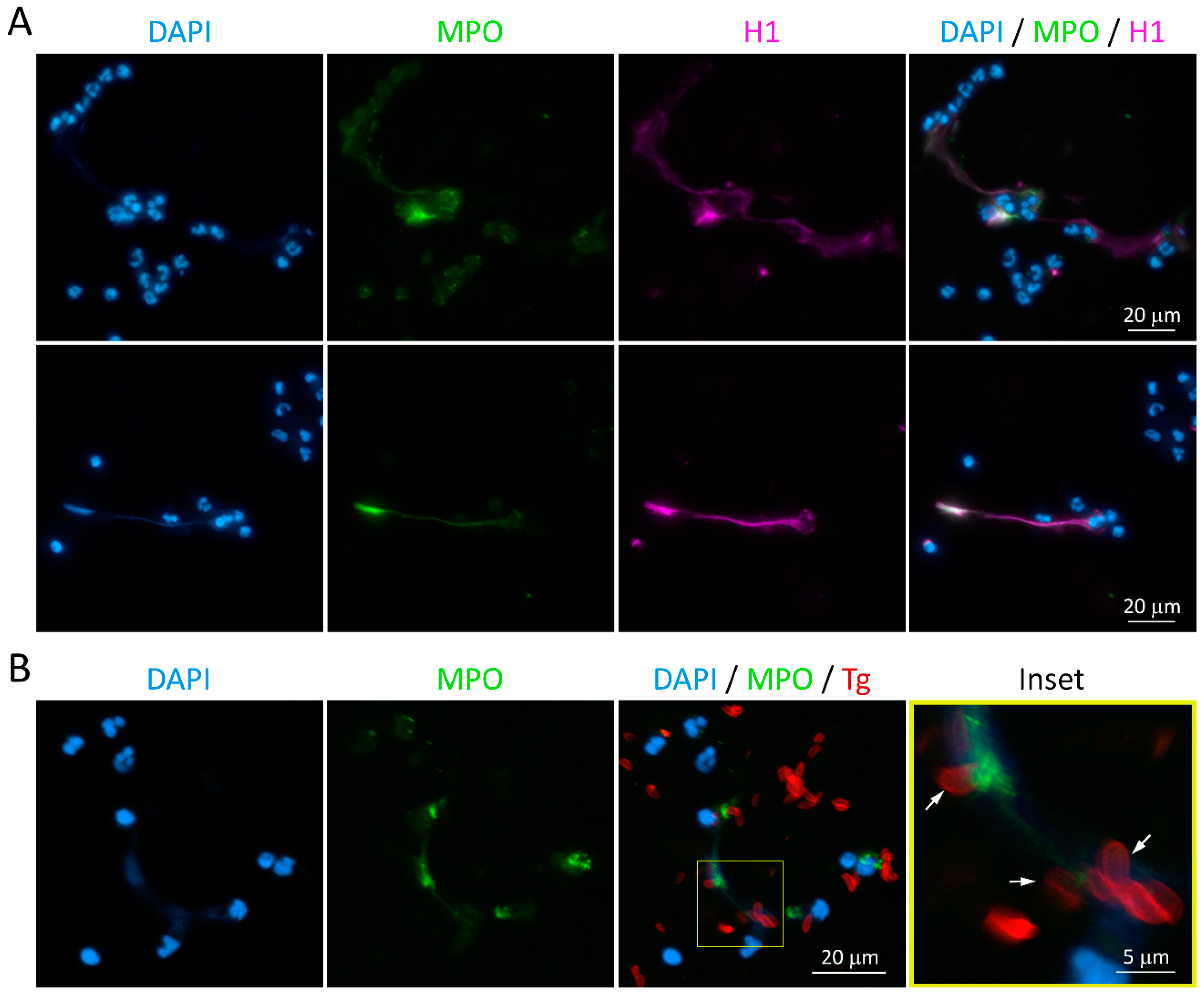
3.2. Cat Neutrophils Produce Extracellular Traps in Response to Toxoplasma gondii
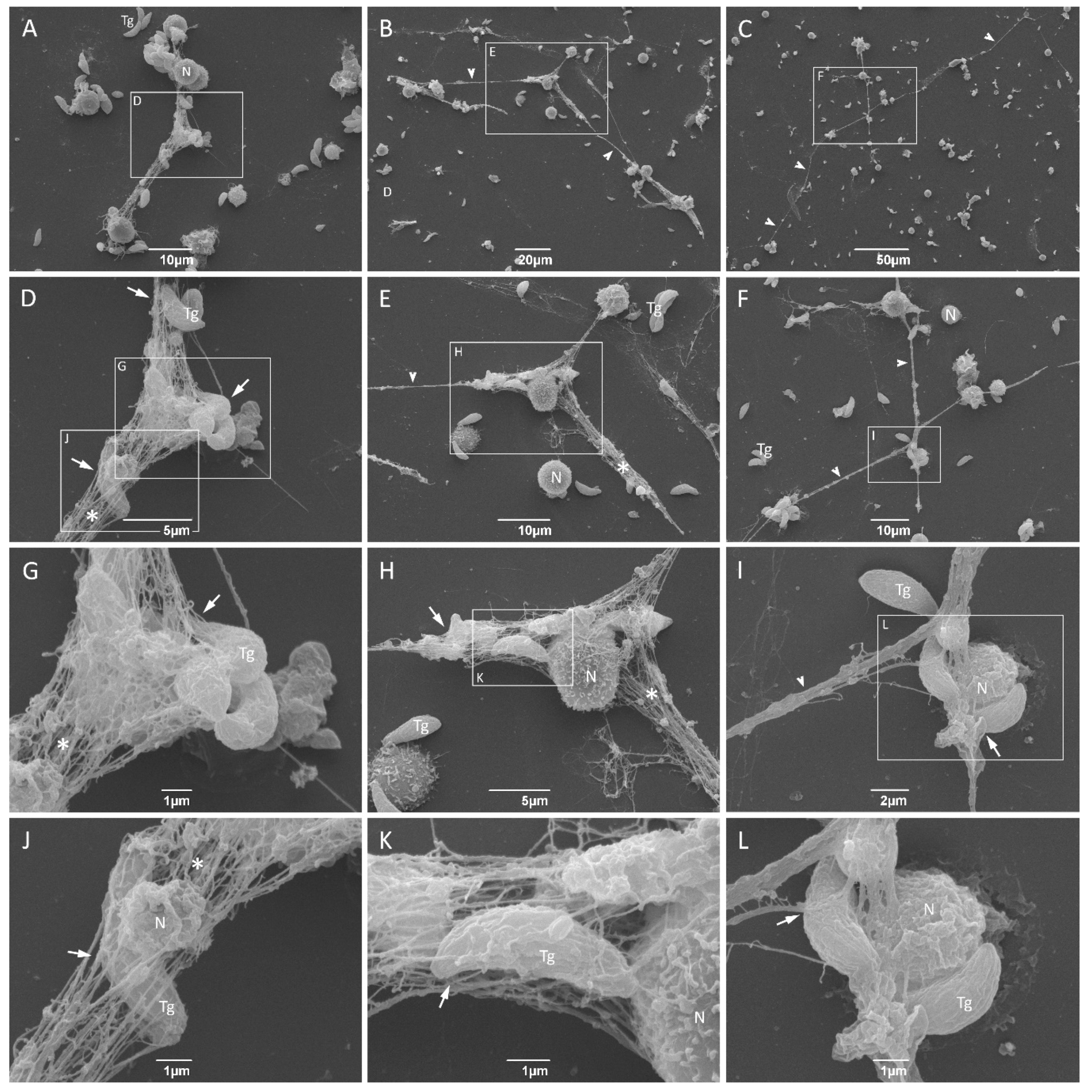
3.3. NET from Cats Entrap Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites
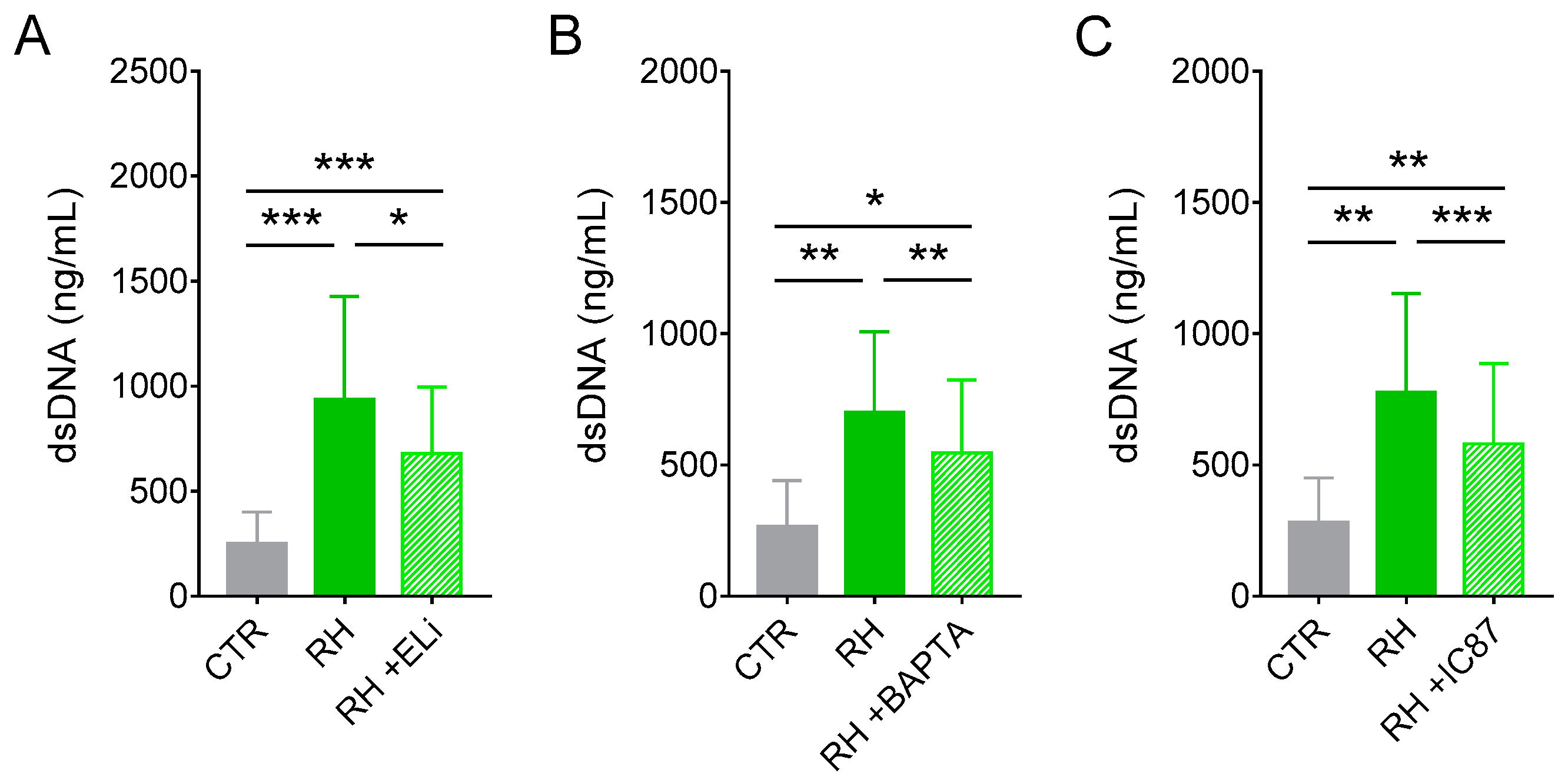
3.4. Release of dsDNA from Cat Neutrophils in Response to T. gondii Depends on Elastase, Calcium, and PI3Kδ
3.5. NET from Cats Kill Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. History of the discovery of the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, G.; Roussos, N.; Falagas, M.E. Toxoplasmosis snapshots: Global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, G.N. Ocular toxoplasmosis: A global reassessment. Part I: Epidemiology and course of disease. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 136, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, C.D.; Christian, D.A.; Hunter, C.A. Immune response and immunopathology during toxoplasmosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 793–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, D.J.P.; Bowker, C.; Jeffery, K.J.M.; Chamberlain, P.; Squier, W. Congenital toxoplasmosis: Continued parasite proliferation in the fetal brain despite maternal immunological control in other tissues. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Swan, G.V.; Frenkel, J.K. A simplified method for isolation of Toxoplasma gondii from the feces of cats. J. Parasitol. 1972, 58, 1005–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis—A waterborne zoonosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbaldiston, G.W. Haematological values in healthy cats. Br. Vet. J. 1978, 134, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gisbergen, K.P.J.M.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.H.; Van Kooyk, Y. Close encounters of neutrophils and DCs. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaillon, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Del Prete, D.; Cassatella, M.A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Neutrophils in innate and adaptive immunity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauseef, W.M.; Borregaard, N. Neutrophils at work. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, P.X.; Kubes, P. The Neutrophil’s Role During Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1223–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, S.K.; Butcher, B.A.; Denkers, E.Y. Rapid recruitment of neutrophils containing prestored IL-12 during microbial infection. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 4515–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norose, K.; Naoi, K.; Fang, H.; Yano, A. In vivo study of toxoplasmic parasitemia using interferon-gamma-deficient mice: Absolute cell number of leukocytes, parasite load and cell susceptibility. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, J.L.; Charsar, B.A.; Han, S.J.; Halkias, J.; Chan, S.W.; Koshy, A.A.; Striepen, B.; Robey, E.A. Motile invaded neutrophils in the small intestine of Toxoplasma gondii-infected mice reveal a potential mechanism for parasite spread. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1913–E1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurschou, M.; Sørensen, O.E.; Johnsen, A.H.; Askaa, J.; Borregaard, N. Defensin-rich granules of human neutrophils: Characterization of secretory properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1591, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurschou, M.; Borregaard, N. Neutrophil granules and secretory vesicles in inflammation. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilsczek, F.H.; Salina, D.; Poon, K.K.H.; Fahey, C.; Yipp, B.G.; Sibley, C.D.; Robbins, S.M.; Green, F.H.Y.; Surette, M.G.; Sugai, M.; et al. A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7413–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yipp, B.G.; Kubes, P. NETosis: How vital is it? Blood 2013, 122, 2784–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochael, N.C.; Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Nascimento, M.T.C.; DeSouza-Vieira, T.S.; Oliveira, M.P.; Garcia e Souza, L.F.; Oliveira, M.F.; Saraiva, E.M. Classical ROS-dependent and early/rapid ROS-independent release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps triggered by Leishmania parasites. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönrich, G.; Raftery, M.J. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Go Viral. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.R.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Burgos, R.A.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Far beyond Phagocytosis: Phagocyte-Derived Extracellular Traps Act Efficiently against Protozoan Parasites In Vitro and In Vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 5898074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppenbrouwers, T.; Autar, A.S.A.; Sultan, A.R.; Abraham, T.E.; Van Cappellen, W.A.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; Van Wamel, W.J.B.; Van Beusekom, H.M.M.; Van Neck, J.W.; De Maat, M.P.M. In vitro induction of NETosis: Comprehensive live imaging comparison and systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Godínez, C.; Carrero, J.C. The state of art of neutrophil extracellular traps in protozoan and helminthic infections. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, C.F.; Nett, J.E. Neutrophil extracellular traps in fungal infection. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 89, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi Abdallah, D.S.A.; Lin, C.; Ball, C.J.; King, M.R.; Duhamel, G.E.; Denkers, E.Y. Toxoplasma gondii triggers release of human and mouse neutrophil extracellular traps. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, M.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Sanchez Contreras, G.; Rubio García, A.; Magdowski, G.; Gärtner, U.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Harbour seal (Phoca vitulina) PMN and monocytes release extracellular traps to capture the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 50, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, K.; Gokpinar, S.; Gazyagci, A.N.; Babur, C.; Sursal, N.; Azkur, A.K. Role of NETs in the difference in host susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii between sheep and cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 189, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imlau, M.; Conejeros, I.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Zhou, E.; Gärtner, U.; Ternes, K.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Dolphin-derived NETosis results in rapid Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite ensnarement and different phenotypes of NETs. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 103, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagra-Blanco, R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Conejeros, I.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Pinniped- and Cetacean-Derived ETosis Contributes to Combating Emerging Apicomplexan Parasites (Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum) Circulating in Marine Environments. Biology (Basel) 2019, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, K.; Gokpinar, S.; Sursal, N.; Babur, C.; Ozen, D.; Azkur, A.K. Extracellular Trap Formation by Donkey Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils Against Toxoplasma gondii. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2019, 73, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Han, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma gondii Triggers Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Release in Dogs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.C.; dos Santos, J.L.; Wardini, A.B.; da Silva, A.N.; Santos, A.G.; Silva Freire, H.P.; dos Anjos, D.O.; Romano, C.C.; Mendes, É.A.; Munhoz, A.D. Toxoplasma gondii induces extracellular traps release in cat neutrophils. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 207, 107770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.F.; Guimares, E.V.; Carvalho, L.; Correa, J.R.; Mendonça-Lima, L.; Barbosa, H.S. Toxoplasma gondii down modulates cadherin expression in skeletal muscle cells inhibiting myogenesis. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, E.V.; de Carvalho, L.; Barbosa, H.S. Interaction and cystogenesis of Toxoplasma gondii within skeletal muscle cells in vitro. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, E.F.; Herzig, A.; Krüger, R.; Muth, A.; Mondal, S.; Thompson, P.R.; Brinkmann, V.; von Bernuth, H.; Zychlinsky, A. Diverse stimuli engage different neutrophil extracellular trap pathways. Elife 2017, 6, e24437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Nascimento, M.T.C.; Froment, G.S.; Soares, R.P.P.; Morgado, F.N.; Conceição-Silva, F.; Saraiva, E.M. Leishmania amazonensis promastigotes induce and are killed by neutrophil extracellular traps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6748–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, F.N.; Nascimento, M.T.; Saraiva, E.M.; de Oliveira-Ribeiro, C.; Madeira, M.; da Costa-Santos, M.; Vasconcellos, E.C.; Pimentel, M.I.; Rosandiski Lyra, M.; Schubach, A.; et al. Are neutrophil extracellular traps playing a role in the parasite control in active American tegumentary leishmaniasis lesions? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Menezes, J.P.; Saraiva, E.M.; Da Rocha-Azevedo, B. The site of the bite: Leishmania interaction with macrophages, neutrophils and the extracellular matrix in the dermis. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardini, A.B.; Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Nascimento, M.T.C.; Nadaes, N.R.; Danelli, M.G.M.; Mazur, C.; Benjamin, C.F.; Saraiva, E.M.; Pinto-da-Silva, L.H. Characterization of neutrophil extracellular traps in cats naturally infected with feline leukemia virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza-Vieira, T.; Guimarães-Costa, A.; Rochael, N.C.; Lira, M.N.; Nascimento, M.T.; Lima-Gomez, P.d.S.; Mariante, R.M.; Persechini, P.M.; Saraiva, E.M. Neutrophil extracellular traps release induced by Leishmania: Role of PI3Kγ, ERK, PI3Kσ, PKC, and [Ca2+]. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, B.; Kersten, G.F.A.; Baart, G.J.E.; De Jong, A.; Meiring, H.; Ten Hove, J.; Van Steenbergen, M.J.; Hennink, W.E.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; Jiskoot, W. Identification of formaldehyde-induced modifications in proteins: Reactions with insulin. Bioconjug. Chem. 2006, 17, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, S.K.; Gavrilescu, L.C.; Alcaraz, A.; Denkers, E.Y. Neutrophil depletion during Toxoplasma gondii infection leads to impaired immunity and lethal systemic pathology. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4898–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, L.; Bennouna, S.; Salinas, J.; Denkers, E.Y. CXCR2 deficiency confers impaired neutrophil recruitment and increased susceptibility during Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 6503–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; French, T.; Düsedau, H.P.; Mueller, N.; Riek-Burchardt, M.; Dudeck, A.; Bank, U.; Schüler, T.; Dunay, I.R. Behavior of neutrophil granulocytes during Toxoplasma gondii infection in the central nervous system. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.; Silva, L.M.R.; Conejeros, I.; Velásquez, Z.D.; Hirz, M.; Gärtner, U.; Jacquiet, P.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Besnoitia besnoiti bradyzoite stages induce suicidal- and rapid vital-NETosis. Parasitology 2020, 147, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, L.C.; Denkers, E.Y. IFN-gamma overproduction and high level apoptosis are associated with high but not low virulence Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisaki, J.H.; Heuser, J.E.; Sibley, L.D. Invasion of Toxoplasma gondii occurs by active penetration of the host cell. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Marple, A.H.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Bzik, D.J.; Yap, G.S. Avirulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii infect macrophages by active invasion from the phagosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6437–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakkim, A.; Fuchs, T.A.; Martinez, N.E.; Hess, S.; Prinz, H.; Zychlinsky, A.; Waldmann, H. Activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, C.; Janko, C.; Munoz, L.E.; Zhao, Y.; Kienhöfer, D.; Frey, B.; Lell, M.; Manger, B.; Rech, J.; Naschberger, E.; et al. Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Rubio, M.C.R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Magdowski, G.; Gärtner, U.; McNeilly, T.N.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Leucocyte-derived extracellular trap formation significantly contributes to Haemonchus contortus larval entrapment. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Q.A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: As Antimicrobial Peptides. Oral Rehabil. Dent. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storisteanu, D.M.L.; Pocock, J.M.; Cowburn, A.S.; Juss, J.K.; Nadesalingam, A.; Nizet, V.; Chilvers, E.R. Evasion of neutrophil extracellular traps by respiratory pathogens. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 56, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; De Souza-Vieira, T.S.; Paletta-Silva, R.; Freitas-Mesquita, A.L.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Saraiva, E.M. 3′-nucleotidase/nuclease activity allows Leishmania parasites to escape killing by neutrophil extracellular traps. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.; MacIntyre, A.; Hawes, M.; Allen, C. Escaping Underground Nets: Extracellular DNases Degrade Plant Extracellular Traps and Contribute to Virulence of the Plant Pathogenic Bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Metzler, K.D.; Hakkim, A.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase regulate the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, M.; Lindberg, M.R.; Kennett, M.J.; Xiong, N.; Wang, Y. PAD4 is essential for antibacterial innate immunity mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, H.D.; Liddle, J.; Coote, J.E.; Atkinson, S.J.; Barker, M.D.; Bax, B.D.; Bicker, K.L.; Bingham, R.P.; Campbell, M.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. Inhibition of PAD4 activity is sufficient to disrupt mouse and human NET formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.A.; Conejeros, I.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Werling, D.; Hermosilla, C. Calcium influx, a new potential therapeutic target in the control of neutrophil-dependent inflammatory diseases in bovines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conejeros, I.; Patterson, R.; Burgos, R.A.; Hermosilla, C.; Werling, D. Induction of reactive oxygen species in bovine neutrophils is CD11b, but not dectin-1-dependent. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 139, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Graupera, M.; Bilanges, B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condliffe, A.M.; Davidson, K.; Anderson, K.E.; Ellson, C.D.; Crabbe, T.; Okkenhaug, K.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Turner, M.; Webb, L.; Wymann, M.P.; et al. Sequential activation of class IB and class IA PI3K is important for the primed respiratory burst of human but not murine neutrophils. Blood 2005, 106, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.; Dragunow, M.; Hampton, M.B.; Kettle, A.J.; Winterbourn, C.C. Requirements for NADPH oxidase and myeloperoxidase in neutrophil extracellular trap formation differ depending on the stimulus. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macedo, I.S.; Lima, M.V.A.; Souza, J.S.; Rochael, N.C.; Caldas, P.N.; Barbosa, H.S.; Lara, F.A.; Saraiva, E.M.; Mariante, R.M. Extracellular Traps Released by Neutrophils from Cats are Detrimental to Toxoplasma gondii Infectivity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111628
Macedo IS, Lima MVA, Souza JS, Rochael NC, Caldas PN, Barbosa HS, Lara FA, Saraiva EM, Mariante RM. Extracellular Traps Released by Neutrophils from Cats are Detrimental to Toxoplasma gondii Infectivity. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(11):1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111628
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacedo, Isabela S., Marcos V. A. Lima, Jéssica S. Souza, Natalia C. Rochael, Pedro N. Caldas, Helene S. Barbosa, Flávio A. Lara, Elvira M. Saraiva, and Rafael M. Mariante. 2020. "Extracellular Traps Released by Neutrophils from Cats are Detrimental to Toxoplasma gondii Infectivity" Microorganisms 8, no. 11: 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111628
APA StyleMacedo, I. S., Lima, M. V. A., Souza, J. S., Rochael, N. C., Caldas, P. N., Barbosa, H. S., Lara, F. A., Saraiva, E. M., & Mariante, R. M. (2020). Extracellular Traps Released by Neutrophils from Cats are Detrimental to Toxoplasma gondii Infectivity. Microorganisms, 8(11), 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111628






