Laboratory Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis: Current and Future Methods
Abstract
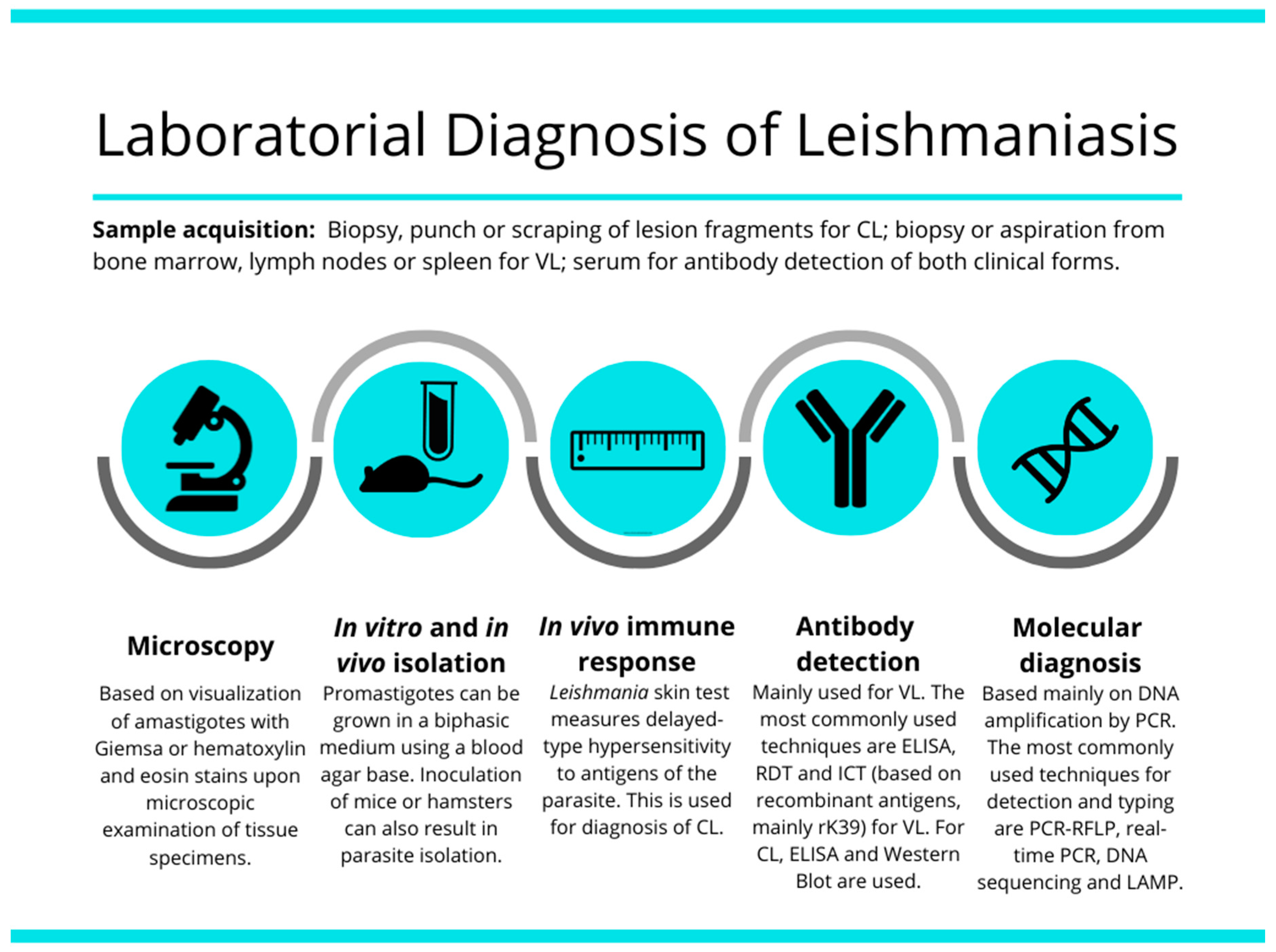
:1. Introduction
2. Parasitological Methods for Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis
2.1. Microscopic Examination
2.2. In Vitro Cultivation of Leishmania
2.3. Inoculation of Leishmania in Experimental Animals
2.4. Xenodiagnosis
3. Molecular Methods for Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis
3.1. Multilocus Enzyme Electrophoresis (MLEE)
3.2. Monoclonal Antibodies
3.3. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
3.4. PCR-Based Methods
3.4.1. PCR-RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism)
3.4.2. DNA Sequencing
3.4.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
3.4.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS)
3.4.5. Real-Time PCR
3.4.6. PCR-High Resolution Melting (HRM)
3.4.7. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
4. Immunological Methods for Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis
4.1. Leishmania Skin Test (LST)
4.2. Methods for Detection of Anti-Leishmania Antibodies
4.2.1. Direct Agglutination Test (DAT)
4.2.2. Indirect Hemagglutination Assay (IHA)
4.2.3. Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Test (IFAT)
4.2.4. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.2.5. Immuno-Chromatographic Test (ICT) (Strip Test)
4.2.6. rK39 Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT)
4.2.7. Western Blot
4.3. Methods for Detection of Antigens of Leishmania
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhoundi, M.; Kuhls, K.; Cannet, A.; Votýpka, J.; Marty, P.; Delaunay, P.; Sereno, D. A Historical Overview of the Classification, Evolution, and Dispersion of Leishmania Parasites and Sandflies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burza, S.; Croft, S.L.; Boelaert, M. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 2018, 392, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvar, J.; Velez, I.D.; Bern, C.; Herrero, M.; Desjeux, P.; Cano, J.; Jannin, J.; den Boer, M. Leishmaniasis worldwide and global estimates of its incidence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimkhani, C.; Wanga, V.; Coffeng, L.E.; Naghavi, P.; Dellavalle, R.P.; Naghavi, M. Global burden of cutaneous leishmaniasis: A cross-sectional analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuis, F.; Sundar, S.; Hailu, A.; Ghalib, H.; Rijal, S.; Peeling, R.W.; Alvar, J.; Boelaert, M. Visceral leishmaniasis: What are the needs for diagnosis, treatment and control? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambulingam, P.; Pradeep Kumar, N.; Nandakumar, S.; Paily, K.P.; Srinivasan, R. Domestic dogs as reservoir hosts for Leishmania donovani in the southernmost Western Ghats in India. Acta Trop. 2017, 171, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, D.; Dalton, J.E.; Kaye, P.M.; Chatterjee, M. Post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis: An unresolved mystery. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zijlstra, E.E. The immunology of post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL). Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhoundi, M.; Downing, T.; Votýpka, J.; Kuhls, K.; Lukeš, J.; Cannet, A.; Ravel, C.; Marty, P.; Delaunay, P.; Kasbari, M.; et al. Leishmania infections: Molecular targets and diagnosis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 57, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Savioli, L.; Fenwick, A. Neglected tropical diseases of the Middle East and North Africa: Review of their prevalence, distribution, and opportunities for control. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silveira, F.T. What makes mucosal and anergic diffuse cutaneous leishmaniases so clinically and immunopathogically different? A review in Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reithinger, R.; Dujardin, J.C.; Louzir, H.; Pirmez, C.; Alexander, B.; Brooker, S. Cutaneous leishmaniasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turetz, M.L.; Machado, P.R.; Ko, A.I.; Alves, F.; Bittencourt, A.; Almeida, R.P.; Mobashery, N.; Johnson, W.D., Jr.; Carvalho, E.M. Disseminated leishmaniasis: A new and emerging form of leishmaniasis observed in northeastern Brazil. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjeux, P. The increase in risk factors for leishmaniasis worldwide. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 95, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjeux, P.; Alvar, J. Leishmania/HIV co-infections: Epidemiology in Europe. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2003, 97 (Suppl. 1), 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Lindoso, J.A. Current diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvar, J.; Canavate, C.; Gutierrez-Solar, B.; Jimenez, M.; Laguna, F.; Lopez-Velez, R.; Molina, R.; Moreno, J. Leishmania and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection: The first 10 years. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindoso, J.A.; Cota, G.F.; da Cruz, A.M.; Goto, H.; Maia-Elkhoury, A.N.; Romero, G.A.; de Sousa-Gomes, M.L.; Santos-Oliveira, J.R.; Rabello, A. Visceral leishmaniasis and HIV coinfection in Latin America. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundar, S.; Rai, M. Laboratory diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarvis, J.N.; Lockwood, D.N. Clinical aspects of visceral leishmaniasis in HIV infection. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, S.R.B.; Trinconi, C.T.; Coelho, A.C. Chemotherapy of leishmaniasis: Present challenges. Parasitology 2018, 145, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, G.A.; Vinitius De Farias Guerra, M.; Gomes Paes, M.; de Oliveira Macêdo, V. Comparison of cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis and L. (V.) guyanensis in Brazil: Clinical findings and diagnostic approach. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aronson, N.; Herwaldt, B.L.; Libman, M.; Pearson, R.; Lopez-Velez, R.; Weina, P.; Carvalho, E.M.; Ephros, M.; Jeronimo, S.; Magill, A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Leishmaniasis: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1539–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.; Dayama, A.; Mehrotra, S.; Sundar, S. Diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 105, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suárez, M.; Valencia, B.M.; Jara, M.; Alba, M.; Boggild, A.K.; Dujardin, J.C.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Arevalo, J.; Adaui, V. Quantification of Leishmania (Viannia) Kinetoplast DNA in Ulcers of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Reveals Inter-site and Inter-sampling Variability in Parasite Load. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, A.Q.; Pompeu, M.M.; Frutuoso, M.S.; Lima, J.W.; Tinel, J.M.; Pearson, R.D. Press imprint smear: A rapid, simple, and cheap method for the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 905–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griensven, J.; Diro, E. Visceral Leishmaniasis: Recent Advances in Diagnostics and Treatment Regimens. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Control of the Leishmaniases. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2010, 949, 1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Saab, M.; El Hage, H.; Charafeddine, K.; Habib, R.H.; Khalifeh, I. Diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis: Why punch when you can scrape? Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandoval Pacheco, C.M.; Araujo Flores, G.V.; Favero Ferreira, A.; Sosa Ochoa, W.; Ribeiro da Matta, V.L.; Zúniga Valeriano, C.; Pereira Corbett, C.E.; Dalastra Laurenti, M. Histopathological features of skin lesions in patients affected by non-ulcerated or atypical cutaneous leishmaniasis in Honduras, Central America. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 99, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.R.; Agudelo, S.; Muskus, C.; Alzate, J.F.; Berberich, C.; Barker, D.; Velez, I.D. Diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Colombia: The sampling site within lesions influences the sensitivity of parasitologic diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3768–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nateghi Rostami, M.; Darzi, F.; Farahmand, M.; Aghaei, M.; Parvizi, P. Performance of a universal PCR assay to identify different Leishmania species causative of Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.R.; Stewart, J.M.; Costa, C.H. Sensitivity of bone marrow aspirates in the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babiker, Z.O.; Davidson, R.; Mazinda, C.; Kipngetich, S.; Ritmeijer, K. Utility of lymph node aspiration in the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in Sudan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, H.J.; Reedijk, S.H.; Schallig, H.D. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: Recent developments in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hockmeyer, W.T.; Kager, P.A.; Rees, P.H.; Hendricks, L.D. The culture of Leishmania donovani in Schneider’s insect medium: Its value in the diagnosis and management of patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, F.L.; Sullivan, J.J. Cultivation of clinically significant hemoflagellates. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagheh, A.; Fakhar, M.; Mesgarian, F.; Gholami, S.; Ahmadpour, E. An improved microculture method for diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis. J. Parasit. Dis. 2014, 38, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, D.; Bern, C.; Ghosh, D.; Rashid, M.; Molina, R.; Chowdhury, R.; Nath, R.; Ghosh, P.; Chapman, L.A.C.; Alim, A.; et al. Quantifying the Infectiousness of Post-Kala-Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis toward Sand Flies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, O.P.; Hasker, E.; Boelaert, M.; Sacks, D.; Sundar, S. Xenodiagnosis to address key questions in visceral leishmaniasis control and elimination. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupolillo, E.; Grimaldi, G., Jr.; Momen, H. A general classification of New World Leishmania using numerical zymotaxonomy. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1994, 50, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, G.; McMahon-Pratt, D. Monoclonal antibodies for the identification of New World Leishmania species. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1996, 91, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaffe, C.L.; Bennett, E.; Grimaldi, G., Jr.; McMahon-Pratt, D. Production and characterization of species-specific monoclonal antibodies against Leishmania donovani for immunodiagnosis. J. Immunol. 1984, 133, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, C.L.; McMahon-Pratt, D. Monoclonal antibodies specific for Leishmania tropica. I. Characterization of antigens associated with stage- and species-specific determinants. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 1987–1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, C.L.; Rachamim, N. Amastigote stage-specific monoclonal antibodies against Leishmania major. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 3770–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassagne, C.; Pratlong, F.; Jeddi, F.; Benikhlef, R.; Aoun, K.; Normand, A.C.; Faraut, F.; Bastien, P.; Piarroux, R. Identification of Leishmania at the species level with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lachaud, L.; Fernández-Arévalo, A.; Normand, A.C.; Lami, P.; Nabet, C.; Donnadieu, J.L.; Piarroux, M.; Djenad, F.; Cassagne, C.; Ravel, C.; et al. Identification of Leishmania by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF) Mass Spectrometry Using a Free Web-Based Application and a Dedicated Mass-Spectral Library. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2924–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mouri, O.; Morizot, G.; Van der Auwera, G.; Ravel, C.; Passet, M.; Chartrel, N.; Joly, I.; Thellier, M.; Jauréguiberry, S.; Caumes, E.; et al. Easy identification of Leishmania species by mass spectrometry. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, Z.J.; Chance, M.L.; el-Safi, S.; Carney, J.; Azazy, A.; El-Hadi, M.; Dourado, C.; Hommel, M. Latex agglutination test for the detection of urinary antigens in visceral leishmaniasis. Acta Trop. 2001, 78, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelaert, M.; El-Safi, S.; Hailu, A.; Mukhtar, M.; Rijal, S.; Sundar, S.; Wasunna, M.; Aseffa, A.; Mbui, J.; Menten, J.; et al. Diagnostic tests for kala-azar: A multi-centre study of the freeze-dried DAT, rK39 strip test and KAtex in East Africa and the Indian subcontinent. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Khan, M.G.; Mondal, D. Urine antigen detection by latex agglutination test for diagnosis and assessment of initial cure of visceral leishmaniasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 105, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Auwera, G.; Dujardin, J.C. Species typing in dermal leishmaniasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 265–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Almeida, M.E.; Koru, O.; Steurer, F.; Herwaldt, B.L.; da Silva, A.J. Detection and Differentiation of Leishmania spp. in Clinical Specimens by Use of a SYBR Green-Based Real-Time PCR Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weirather, J.L.; Jeronimo, S.M.; Gautam, S.; Sundar, S.; Kang, M.; Kurtz, M.A.; Haque, R.; Schriefer, A.; Talhari, S.; Carvalho, E.M.; et al. Serial quantitative PCR assay for detection, species discrimination, and quantification of Leishmania spp. in human samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3892–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talmi-Frank, D.; Nasereddin, A.; Schnur, L.F.; Schönian, G.; Töz, S.O.; Jaffe, C.L.; Baneth, G. Detection and identification of old world Leishmania by high resolution melt analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández, C.; Alvarez, C.; González, C.; Ayala, M.S.; León, C.M.; Ramírez, J.D. Identification of six New World Leishmania species through the implementation of a High-Resolution Melting (HRM) genotyping assay. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, R.A.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Muxel, S.M.; Stocco de Lima, A.C.; Shaw, J.J.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. High Resolution Melting Analysis Targeting hsp70 as a Fast and Efficient Method for the Discrimination of Leishmania Species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasereddin, A.; Jaffe, C.L. Rapid diagnosis of Old World Leishmaniasis by high-resolution melting analysis of the 7SL RNA gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2240–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, K.E.; Zampieri, R.A.; Aoki, J.I.; Muxel, S.M.; Nerland, A.H.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Amino acid permease 3 (aap3) coding sequence as a target for Leishmania identification and diagnosis of leishmaniases using high resolution melting analysis. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boite, M.C.; Mauricio, I.L.; Miles, M.A.; Cupolillo, E. New insights on taxonomy, phylogeny and population genetics of Leishmania (Viannia) parasites based on multilocus sequence analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauricio, I.L.; Yeo, M.; Baghaei, M.; Doto, D.; Pratlong, F.; Zemanova, E.; Dedet, J.P.; Lukes, J.; Miles, M.A. Towards multilocus sequence typing of the Leishmania donovani complex: Resolving genotypes and haplotypes for five polymorphic metabolic enzymes (ASAT, GPI, NH1, NH2, PGD). Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemanová, E.; Jirků, M.; Mauricio, I.L.; Horák, A.; Miles, M.A.; Lukes, J. The Leishmania donovani complex: Genotypes of five metabolic enzymes (ICD, ME, MPI, G6PDH, and FH), new targets for multilocus sequence typing. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukayama, P.; Lucas, C.; Bacon, D.J. Typing of four genetic loci discriminates among closely related species of New World Leishmania. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.G.; Bhaskar, K.R.; Salam, M.A.; Akther, T.; Pluschke, G.; Mondal, D. Diagnostic accuracy of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for detection of Leishmania DNA in buffy coat from visceral leishmaniasis patients. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nzelu, C.O.; Kato, H.; Peters, N.C. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): An advanced molecular point-of-care technique for the detection of Leishmania infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, E.R.; Schoone, G.; Versteeg, I.; Gomez, M.A.; Diro, E.; Mori, Y.; Perlee, D.; Downing, T.; Saravia, N.; Assaye, A.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.; Singh, R.; Sharma, V.; Bumb, R.A.; Negi, N.S.; Ramesh, V.; Salotra, P. Development of a rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for diagnosis and assessment of cure of Leishmania infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badaró, R.; Benson, D.; Eulálio, M.C.; Freire, M.; Cunha, S.; Netto, E.M.; Pedral-Sampaio, D.; Madureira, C.; Burns, J.M.; Houghton, R.L.; et al. rK39: A cloned antigen of Leishmania chagasi that predicts active visceral leishmaniasis. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braz, R.F.; Nascimento, E.T.; Martins, D.R.; Wilson, M.E.; Pearson, R.D.; Reed, S.G.; Jeronimo, S.M. The sensitivity and specificity of Leishmania chagasi recombinant K39 antigen in the diagnosis of American visceral leishmaniasis and in differentiating active from subclinical infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 67, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, Z.; Lírio, M.; Mistro, S.; Mendes, C.M.; Mehta, S.R.; Badaro, R. Comparative study of rK39 Leishmania antigen for serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis: Systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedras, M.J.; de Gouvêa Viana, L.; de Oliveira, E.J.; Rabello, A. Comparative evaluation of direct agglutination test, rK39 and soluble antigen ELISA and IFAT for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.P.; Goyal, R.K.; Singh, R.K.; Sundar, S.; Mohapatra, T.M. In search of an ideal test for diagnosis and prognosis of kala-azar. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2010, 28, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zijlstra, E.E.; Daifalla, N.S.; Kager, P.A.; Khalil, E.A.; El-Hassan, A.M.; Reed, S.G.; Ghalib, H.W. rK39 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of Leishmania donovani infection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1998, 5, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, F.A.; Charest, H.; Tavares, C.A.; Matlashewski, G.; Valente, E.P.; Rabello, A.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Fernandes, A.P. Diagnosis of American visceral leishmaniasis in humans and dogs using the recombinant Leishmania donovani A2 antigen. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 43, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhom-Lemos, L.; Viana, A.G.; Cunha, J.L.R.; Cardoso, M.S.; Mendes, T.A.O.; Pinheiro, G.R.G.; Siqueira, W.F.; Lobo, F.P.; Teles, L.F.; Bueno, L.L.; et al. Leishmania infantum recombinant kinesin degenerated derived repeat (rKDDR): A novel potential antigen for serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghedin, E.; Zhang, W.W.; Charest, H.; Sundar, S.; Kenney, R.T.; Matlashewski, G. Antibody response against a Leishmania donovani amastigote-stage-specific protein in patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1997, 4, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohapatra, T.M.; Singh, D.P.; Sen, M.R.; Bharti, K.; Sundar, S. Compararative evaluation of rK9, rK26 and rK39 antigens in the serodiagnosis of Indian visceral leishmaniasis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2010, 4, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takagi, H.; Islam, M.Z.; Itoh, M.; Islam, A.U.; Saifuddin Ekram, A.R.; Hussain, S.M.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Kimura, E. Short report: Production of recombinant kinesin-related protein of Leishmania donovani and its application in the serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celeste, B.J.; Arroyo Sanchez, M.C.; Ramos-Sanchez, E.M.; Castro, L.G.M.; Lima Costa, F.A.; Goto, H. Recombinant Leishmania infantum heat shock protein 83 for the serodiagnosis of cutaneous, mucosal, and visceral leishmaniases. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quijada, L.; Requena, J.M.; Soto, M.; Alonso, C. Analysis of the antigenic properties of the L. infantum Hsp70: Design of synthetic peptides for specific serodiagnosis of human leishmaniasis. Immunol. Lett. 1998, 63, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, S.; Chakravarty, J.; Sundar, S. A novel 12.6-kDa protein of Leishmania donovani for the diagnosis of Indian visceral leishmaniasis. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, D.; Chakravarty, J.; Rai, M.; Sundar, S. Identification and characterization of a novel Leishmania donovani antigen for serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, D.; Chakravarty, J.; Sundar, S. Identification and Characterization of a Novel, 37-Kilodalton Leishmania donovani antigen for diagnosis of Indian visceral leishmaniasis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, M.C.; Pimenta, D.C.; Menezes-Souza, D.; Magalhães, R.D.; Diniz, J.L.; Costa, L.E.; Chávez-Fumagalli, M.A.; Lage, P.S.; Bartholomeu, D.C.; Alves, M.J.; et al. Proteins Selected in Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis by an Immunoproteomic Approach with Potential Serodiagnosis Applications for Tegumentary Leishmaniasis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, C.M.; Sanchez, M.C.; Celeste, B.J.; Duthie, M.S.; Guderian, J.; Reed, S.G.; de Brito, M.E.; Campos, M.B.; de Souza Encarnação, H.V.; Guerra, J.; et al. Use of Recombinant Antigens for Sensitive Serodiagnosis of American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis Caused by Different Leishmania Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bangert, M.; Flores-Chávez, M.D.; Llanes-Acevedo, I.P.; Arcones, C.; Chicharro, C.; García, E.; Ortega, S.; Nieto, J.; Cruz, I. Validation of rK39 immunochromatographic test and direct agglutination test for the diagnosis of Mediterranean visceral leishmaniasis in Spain. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boelaert, M.; Rijal, S.; Regmi, S.; Singh, R.; Karki, B.; Jacquet, D.; Chappuis, F.; Campino, L.; Desjeux, P.; Le Ray, D.; et al. A comparative study of the effectiveness of diagnostic tests for visceral leishmaniasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 70, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Hira, P.R.; Saroj, G.; Philip, R.; Al-Ali, F.; Madda, P.J.; Sher, A. Imported visceral leishmaniasis: Diagnostic dilemmas and comparative analysis of three assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barroso-Freitas, A.P.; Passos, S.R.; Mouta-Confort, E.; Madeira, M.F.; Schubach, A.O.; Santos, G.P.; Nascimento, L.D.; Marzochi, M.C.; Marzochi, K.B. Accuracy of an ELISA and indirect immunofluorescence for the laboratory diagnosis of American tegumentary leishmaniasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Assis, T.S.; Braga, A.S.; Pedras, M.J.; Oliveira, E.; Barral, A.; de Siqueira, I.C.; Costa, C.H.; Costa, D.L.; Holanda, T.A.; Soares, V.Y.; et al. Multi-centric prospective evaluation of rk39 rapid test and direct agglutination test for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 105, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar, M.; Asadi Kia, A.; Gohardehi, S.; Sharif, M.; Mohebali, M.; Akhoundi, B.; Pagheh, A.; Dadimoghadam, Y.; Cheraghali, F. Emergence of a new focus of visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania infantum in Golestan Province, north-eastern of Iran. J. Parasit. Dis. 2014, 38, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, J.; Hasker, E.; Das, P.; El Safi, S.; Goto, H.; Mondal, D.; Mbuchi, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Rabello, A.; Rijal, S.; et al. A global comparative evaluation of commercial immunochromatographic rapid diagnostic tests for visceral leishmaniasis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejazi, S.A.; Ghosh, S.; Saha, S.; Choudhury, S.T.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Chatterjee, M.; Pandey, K.; Das, V.N.R.; Das, P.; Rahaman, M.; et al. A multicentric evaluation of dipstick test for serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Brazil, Ethiopia and Spain. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Goswami, R.; Pramanik, N.; Guha, S.K.; Saha, B.; Rahman, M.; Mallick, S.; Modak, D.; Silva, F.O.; Mendonca, I.L.; et al. Easy test for visceral Leishmaniasis and post-Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, C.; Lamouroux, D.; Dunan, S.; Quilici, M. Western blot analysis of antibodies to Leishmania infantum antigens: Potential of the 14-kD and 16-kD antigens for diagnosis and epidemiologic purposes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1992, 47, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Gomes, G.; Gomes-Pereira, S.; Campino, L.; Araújo, M.D.; Abranches, P. Performance of immunoblotting in diagnosis of visceral Leishmaniasis in human immunodeficiency virus-Leishmania sp.-coinfected patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeyrek, F.Y.; Korkmaz, M.; Ozbel, Y. Serodiagnosis of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis (ACL) caused by Leishmania tropica in Sanliurfa Province, Turkey, where ACL Is highly endemic. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidari, S.; Gharechahi, J.; Mohebali, M.; Akhoundi, B.; Mirshahvaladi, S.; Azarian, B.; Hajjaran, H. Western Blot Analysis of Leishmania infantum Antigens in Sera of Patients with Visceral Leishmaniasis. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2019, 14, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, M.P.; Burchmore, R.J.; Stich, A.; Lazzari, J.O.; Frasch, A.C.; Cazzulo, J.J.; Krishna, S. The trypanosomiases. Lancet 2003, 362, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlova, J.; Seblova, V.; Votypka, J.; Warburg, A.; Volf, P. Xenodiagnosis of Leishmania donovani in BALB/c mice using Phlebotomus orientalis: A new laboratory model. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawyer, P.; Killick-Kendrick, M.; Rowland, T.; Rowton, E.; Volf, P. Laboratory colonization and mass rearing of phlebotomine sand flies (Diptera, Psychodidae). Parasite 2017, 24, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Joshi, J.; Kaur, S. Leishmaniasis diagnosis: An update on the use of parasitological, immunological and molecular methods. J. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 44, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seng, P.; Rolain, J.M.; Fournier, P.E.; La Scola, B.; Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D. MALDI-TOF-mass spectrometry applications in clinical microbiology. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1733–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veen, S.Q.; Claas, E.C.; Kuijper, E.J. High-throughput identification of bacteria and yeast by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry in conventional medical microbiology laboratories. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nasereddin, A.; Bensoussan-Hermano, E.; Schönian, G.; Baneth, G.; Jaffe, C.L. Molecular diagnosis of Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis and species identification by use of a reverse line blot hybridization assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2848–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galluzzi, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; Diotallevi, A.; Menotta, M.; Magnani, M. Real-time PCR applications for diagnosis of leishmaniasis. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, O.C.; Yadon, Z.E.; Cupolillo, E. The applicability of real-time PCR in the diagnostic of cutaneous leishmaniasis and parasite quantification for clinical management: Current status and perspectives. Acta Trop. 2018, 184, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, C.; Faraut, F.; Drogoul, M.P.; Xeridat, B.; Schleinitz, N.; Cuisenier, B.; Dumon, H. Reference values for Leishmania infantum parasitemia in different clinical presentations: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction for therapeutic monitoring and patient follow-up. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva Nunes Bezerra, G.; Barbosa Júnior, W.L.; Virgínia Batista Vieira, A.; Xavier, A.T.; Sebastião Da Costa Lima Júnior, M.; Maria Xavier, E.; Silva, E.D.D.; Cintra Leal, N.; Medeiros, Z.M. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification methods for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar)—A systematic review. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstraus, M.; Wang, Z.; Chang, S.Y.; DeBonville, D.; Spadoro, J.P. An internal control for routine diagnostic PCR: Design, properties, and effect on clinical performance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.; Lodes, M.J.; Fox, M.; Myler, P.J.; Stuart, K. Characterization of the Leishmania donovani ribosomal RNA promoter. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1999, 103, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonian, G.; Nasereddin, A.; Dinse, N.; Schweynoch, C.; Schallig, H.D.; Presber, W.; Jaffe, C.L. PCR diagnosis and characterization of Leishmania in local and imported clinical samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 47, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupolillo, E.; Grimaldi Junior, G.; Momen, H.; Beverley, S.M. Intergenic region typing (IRT): A rapid molecular approach to the characterization and evolution of Leishmania. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1995, 73, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, S.R.; Nelson, K.; Beverley, S.M.; Camargo, E.P.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Discrimination amongst Leishmania by polymerase chain reaction and hybridization with small subunit ribosomal DNA derived oligonucleotides. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1994, 41, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Kindt, A.; Bermudez, H.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; De Doncker, S.; Arevalo, J.; Wilber Quispe Tintaya, K.; Dujardin, J.C. Culture-independent species typing of neotropical Leishmania for clinical validation of a PCR-based assay targeting heat shock protein 70 genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2294–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga, J.; Montalvo, A.M.; Maes, L.; Dujardin, J.C.; Van der Auwera, G. HindII and SduI digests of heat-shock protein 70 PCR for Leishmania typing. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 77, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, J.; Veland, N.; Montalvo, A.M.; Praet, N.; Boggild, A.K.; Valencia, B.M.; Arevalo, J.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Dujardin, J.C.; Van der Auwera, G. Accurate and rapid species typing from cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis lesions of the New World. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 74, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, A.M.; Fraga, J.; Maes, I.; Dujardin, J.C.; Van der Auwera, G. Three new sensitive and specific heat-shock protein 70 PCRs for global Leishmania species identification. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espada, C.R.; Ortiz, P.A.; Shaw, J.J.; Barral, A.M.P.; Costa, J.M.L.; Uliana, S.R.B.; Coelho, A.C. Identification of Leishmania (Viannia) species and clinical isolates of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis from Brazil using PCR-RFLP of the heat-shock protein 70 gene reveals some unexpected observations. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 91, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, J.; Nasereddin, A.; Niederwieser, I.; Jaffe, C.L.; Beck, H.P.; Felger, I. Identification and differentiation of Leishmania species in clinical samples by PCR amplification of the miniexon sequence and subsequent restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3147–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degrave, W.; Fernandes, O.; Campbell, D.; Bozza, M.; Lopes, U. Use of molecular probes and PCR for detection and typing of Leishmania—A mini-review. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1994, 89, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, M.N.; Margonari, C.; Presot, I.M.; Soares, R.P. Evaluation of 4 polymerase chain reaction protocols for cultured Leishmania spp. typing. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 68, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, J.; Niederwieser, I.; Makia, N.D.; Beck, H.P.; Felger, I. Diagnostic genotyping of Old and New World Leishmania species by PCR-RFLP. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 46, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, J.H.; Nozari, N.; Herremans, T.; Kortbeek, L.M.; Pinelli, E. Evaluation and improvement of two PCR targets in molecular typing of clinical samples of Leishmania patients. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoir, K.; Bañuls, A.L.; Arevalo, J.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Hamers, R.; Noël, S.; De Doncker, S.; Le Ray, D.; Tibayrenc, M.; Dujardin, J.C. The gp63 gene locus, a target for genetic characterization of Leishmania belonging to subgenus Viannia. Parasitology 1998, 117 Pt 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, T.; Van der Auwera, G.; Hide, M.; Mertens, P.; Quispe-Tintaya, W.; Deborggraeve, S.; De Doncker, S.; Leclipteux, T.; Bañuls, A.L.; Büscher, P.; et al. Identification of Old World Leishmania spp. by specific polymerase chain reaction amplification of cysteine proteinase B genes and rapid dipstick detection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 63, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.L.; Kindt, A.; Quispe-Tintaya, K.W.; Bermudez, H.; Llanos, A.; Arevalo, J.; Bañuls, A.L.; De Doncker, S.; Le Ray, D.; Dujardin, J.C. American tegumentary leishmaniasis: Antigen-gene polymorphism, taxonomy and clinical pleomorphism. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2005, 5, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.E.; Englund, P.T. Network news: The replication of kinetoplast DNA. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aransay, A.M.; Scoulica, E.; Tselentis, Y. Detection and identification of Leishmania DNA within naturally infected sand flies by seminested PCR on minicircle kinetoplastic DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahboudi, F.; Abolhassani, M.; Tehrani, S.R.; Azimi, M.; Asmar, M. Differentiation of old and new world Leishmania species at complex and species levels by PCR. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uliana, S.R.; Affonso, M.H.; Camargo, E.P.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Leishmania: Genus identification based on a specific sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA sequence. Exp. Parasitol. 1991, 72, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.E.; Steurer, F.J.; Koru, O.; Herwaldt, B.L.; Pieniazek, N.J.; da Silva, A.J. Identification of Leishmania spp. by molecular amplification and DNA sequencing analysis of a fragment of rRNA internal transcribed spacer 2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Auwera, G.; Ravel, C.; Verweij, J.J.; Bart, A.; Schonian, G.; Felger, I. Evaluation of four single-locus markers for Leishmania species discrimination by sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga, J.; Montalvo, A.M.; De Doncker, S.; Dujardin, J.C.; Van der Auwera, G. Phylogeny of Leishmania species based on the heat-shock protein 70 gene. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.A.; de Sousa Cdos, S.; da Graca, G.C.; Porrozzi, R.; Cupolillo, E. Sequence analysis and PCR-RFLP profiling of the hsp70 gene as a valuable tool for identifying Leishmania species associated with human leishmaniasis in Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, O.; Murthy, V.K.; Kurath, U.; Degrave, W.M.; Campbell, D.A. Mini-exon gene variation in human pathogenic Leishmania species. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1994, 66, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelazny, A.M.; Fedorko, D.P.; Li, L.; Neva, F.A.; Fischer, S.H. Evaluation of 7SL RNA gene sequences for the identification of Leishmania spp. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevenson, L.G.; Fedorko, D.P.; Zelazny, A.M. An enhanced method for the identification of Leishmania spp. using real-time polymerase chain reaction and sequence analysis of the 7SL RNA gene region. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 66, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Curran, M.D.; Middleton, D.; Rastogi, A.K. Characterization of kinetoplast DNA minicircles of an Indian isolate of Leishmania donovani. Acta Trop. 1999, 73, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, C.J.; Goig, G.A.; Kohl, T.A.; Verboven, L.; Dippenaar, A.; Ezewudo, M.; Farhat, M.R.; Guthrie, J.L.; Laukens, K.; Miotto, P.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Current standards and open issues. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantacessi, C.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Nolan, M.J.; Otranto, D. The past, present, and future of Leishmania genomics and transcriptomics. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerner-Smidt, P.; Besser, J.; Concepción-Acevedo, J.; Folster, J.P.; Huffman, J.; Joseph, L.A.; Kucerova, Z.; Nichols, M.C.; Schwensohn, C.A.; Tolar, B. Whole Genome Sequencing: Bridging One-Health Surveillance of Foodborne Diseases. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Isles, N.S.; Seemann, T.; Kilpatrick, T.; Grigg, A.; Leroi, M.; Howden, B.P.; Kwong, J.C. Case Report: Confirmation by Metagenomic Sequencing of Visceral Leishmaniasis in an Immunosuppressed Returned Traveler. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagalska, M.A.; Dujardin, J.C. Next-Generation Molecular Surveillance of TriTryp Diseases. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagalska, M.A.; Imamura, H.; Sanders, M.; Van den Broeck, F.; Bhattarai, N.R.; Vanaerschot, M.; Maes, I.; D’Haenens, E.; Rai, K.; Rijal, S.; et al. Genomes of Leishmania parasites directly sequenced from patients with visceral leishmaniasis in the Indian subcontinent. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, P.; Hasnain, M.G.; Hossain, F.; Khan, M.A.A.; Chowdhury, R.; Faisal, K.; Mural, M.A.; Baker, J.; Nath, R.; Ghosh, D.; et al. Evaluation of Real-time PCR for Diagnosis of Post-Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis in Endemic Foci of Bangladesh. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.M.; Cesetti, M.V.; de Paula, N.A.; Vernal, S.; Gupta, G.; Sampaio, R.N.; Roselino, A.M. Field Validation of SYBR Green- and TaqMan-Based Real-Time PCR Using Biopsy and Swab Samples to Diagnose American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis in an Area Where Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis Is Endemic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valencia, B.M.; Veland, N.; Alba, M.; Adaui, V.; Arevalo, J.; Low, D.E.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Boggild, A.K. Non-invasive cytology brush PCR for the diagnosis and causative species identification of American cutaneous leishmaniasis in Peru. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.R.; Gomez, M.A.; Scheske, L.; Rios, R.; Marquez, R.; Cossio, A.; Albertini, A.; Schallig, H.; Saravia, N.G. Sensitive diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis by lesion swab sampling coupled to qPCR. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina, I.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C.; Falcó, V.; Elizalde, A.; Salvador, F.; Crespo, M.; Curran, A.; López-Chejade, P.; Tebar, S.; et al. Ultrasensitive real-time PCR for the clinical management of visceral leishmaniasis in HIV-Infected patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Disch, J.; Oliveira, M.C.; Orsini, M.; Rabello, A. Rapid clearance of circulating Leishmania kinetoplast DNA after treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Acta Trop. 2004, 92, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, R.; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, B.; Salotra, P.; Rai, M.; Sundar, S. Evaluation of PCR for diagnosis of Indian kala-azar and assessment of cure. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3038–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jara, M.; Adaui, V.; Valencia, B.M.; Martinez, D.; Alba, M.; Castrillon, C.; Cruz, M.; Cruz, I.; Van der Auwera, G.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; et al. Real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of Leishmania (Viannia) organisms in skin and mucosal lesions: Exploratory study of parasite load and clinical parameters. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jara, M.; Valencia, B.M.; Adaui, V.; Alba, M.; Lau, R.; Arevalo, J.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Boggild, A.K. Quantitative Kinetoplast DNA Assessment during Treatment of Mucosal Leishmaniasis as a Potential Biomarker of Outcome: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brito, M.E.; Andrade, M.S.; Mendonca, M.G.; Silva, C.J.; Almeida, E.L.; Lima, B.S.; Felix, S.M.; Abath, F.G.; da Graca, G.C.; Porrozzi, R.; et al. Species diversity of Leishmania (Viannia) parasites circulating in an endemic area for cutaneous leishmaniasis located in the Atlantic rainforest region of northeastern Brazil. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2009, 14, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosales-Chilama, M.; Gongora, R.E.; Valderrama, L.; Jojoa, J.; Alexander, N.; Rubiano, L.C.; Cossio, A.; Adams, E.R.; Saravia, N.G.; Gomez, M.A. Parasitological Confirmation and Analysis of Leishmania Diversity in Asymptomatic and Subclinical Infection following Resolution of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, A.; Ahmadipour, F.; Cannet, A.; Marty, P.; Delaunay, P.; Perrin, P.; Dorkeld, F.; Sereno, D.; Akhoundi, M. Immunodetection and molecular determination of visceral and cutaneous Leishmania infection using patients’ urine. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisa, R.; Riera, C.; López-Chejade, P.; Molina, I.; Gállego, M.; Falcó, V.; Ribera, E.; Portús, M. Leishmania infantum DNA detection in urine from patients with visceral leishmaniasis and after treatment control. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Expansion of its practical application as a tool to achieve universal health coverage. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Avishek, K.; Sharma, V.; Negi, N.S.; Ramesh, V.; Salotra, P. Application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the sensitive and rapid diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis and post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Singh, V.; Naik, S. Immune response to Leishmania: Paradox rather than paradigm. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ejazi, S.A.; Ali, N. Developments in diagnosis and treatment of visceral leishmaniasis during the last decade and future prospects. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, G.F.; de Sousa, M.R.; Demarqui, F.N.; Rabello, A. The diagnostic accuracy of serologic and molecular methods for detecting visceral leishmaniasis in HIV infected patients: Meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Brito, R.C.F.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D.O.; Cardoso, J.M.O.; Coura-Vital, W.; Roatt, B.M.; Reis, A.B. Recent advances and new strategies in Leishmaniasis diagnosis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8105–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, F. Leishmaniasis. In Imported Infectious Diseases: The Impact in Development Countries, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2014; p. 240. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, M.C.; Celeste, B.J.; Franco, E.L. Diagnostic performance indices for immunofluorescent tests and enzyme immunoassays of leishmaniasis sera from northern and north-eastern Brazil. Bull. World Health Organ. 1990, 68, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, M.E.; Mendonça, M.G.; Gomes, Y.M.; Jardim, M.L.; Abath, F.G. Identification of potentially diagnostic Leishmania braziliensis antigens in human cutaneous leishmaniasis by immunoblot analysis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohanteb, J.; Ardehali, S. Cross-reaction of sera from patients with various infectious diseases with Leishmania infantum. Med. Princ. Pract. 2005, 14, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.P.; Soto, M.; Costa, J.M.; Boaventura, V.S.; de Oliveira, C.I.; Cristal, J.R.; Barral-Netto, M.; Barral, A. Towards a more precise serological diagnosis of human tegumentary leishmaniasis using Leishmania recombinant proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abass, E.; Kang, C.; Martinkovic, F.; Semião-Santos, S.J.; Sundar, S.; Walden, P.; Piarroux, R.; El Harith, A.; Lohoff, M.; Steinhoff, U. Heterogeneity of Leishmania donovani parasites complicates diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis: Comparison of different serological tests in three endemic regions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, P.; Bhaskar, K.R.; Hossain, F.; Khan, M.A.; Vallur, A.C.; Duthie, M.S.; Hamano, S.; Salam, M.A.; Huda, M.M.; Khan, M.G.; et al. Evaluation of diagnostic performance of rK28 ELISA using urine for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ejazi, S.A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Bakhteyar, M.A.; Mumtaz, A.A.; Pandey, K.; Das, V.N.; Das, P.; Rahaman, M.; Goswami, R.P.; Ali, N. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis: Development and Evaluation of Two Urine-Based Immunoassays for Detection of Leishmania donovani Infection in India. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostyn, B.; Gidwani, K.; Khanal, B.; Picado, A.; Chappuis, F.; Singh, S.P.; Rijal, S.; Sundar, S.; Boelaert, M. Incidence of symptomatic and asymptomatic Leishmania donovani infections in high-endemic foci in India and Nepal: A prospective study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ter Horst, R.; Tefera, T.; Assefa, G.; Ebrahim, A.Z.; Davidson, R.N.; Ritmeijer, K. Field evaluation of rK39 test and direct agglutination test for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in a population with high prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus in Ethiopia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmahallawy, E.K.; Sampedro Martinez, A.; Rodriguez-Granger, J.; Hoyos-Mallecot, Y.; Agil, A.; Navarro Mari, J.M.; Gutierrez Fernandez, J. Diagnosis of leishmaniasis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoone, G.J.; Hailu, A.; Kroon, C.C.; Nieuwenhuys, J.L.; Schallig, H.D.; Oskam, L. A fast agglutination screening test (FAST) for the detection of anti-Leishmania antibodies. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 95, 400–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.R.; Muliyil, J.P.; Nandy, A.; Addy, A.; Maji, A.K.; Chatterjee, P. Dynamics of the antibodies in cohorts of cured cases of visceral leishmaniasis: Its implication on the validity of serological test, value in prognosis and in post therapeutic assessment. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2012, 8, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hailu, A. The use of direct agglutination test (DAT) in serological diagnosis of Ethiopian cutaneous leishmaniasis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 42, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.S.; Schoone, G.J.; Gontijo, C.M.; Brazil, R.P.; Pacheco, R.S.; Schallig, H.D. Application of direct agglutination test (DAT) and fast agglutination screening test (FAST) for sero-diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in endemic area of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Kinetoplastid Biol. Dis. 2005, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghose, A.C.; Haldar, J.P.; Pal, S.C.; Mishra, B.P.; Mishra, K.K. Serological investigations on Indian kala-azar. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1980, 40, 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, A.-m.; Mohamed Omer, F.; Abdalla, S.; El-Menshawy, N.; Al-Bin-Ali, A. Comparison of an indirect hemagglutination test and bone marrow aspiration for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in Aseer area, Saudi Arabia. Egypt. J. Haematol. 2012, 37, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.; Rojas, A.; Plata, J.; Peis, J.; de la Rosa, M. Comparison of two indirect immunofluorescence techniques for the serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Serodiagn. Immunother. Infect. Dis. 1990, 4, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, M.C.; Celeste, B.J.; Franco, E.L.; Cucé, L.C.; Belda, W., Jr. Evaluation of serological diagnostic indices for mucocutaneous leishmaniasis: Immunofluorescence tests and enzyme-linked immunoassays for IgG, IgM and IgA antibodies. Bull. World Health Organ. 1989, 67, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.M., Jr.; Shreffler, W.G.; Benson, D.R.; Ghalib, H.W.; Badaro, R.; Reed, S.G. Molecular characterization of a kinesin-related antigen of Leishmania chagasi that detects specific antibody in African and American visceral leishmaniasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houghton, R.L.; Petrescu, M.; Benson, D.R.; Skeiky, Y.A.; Scalone, A.; Badaró, R.; Reed, S.G.; Gradoni, L. A cloned antigen (recombinant K39) of Leishmania chagasi diagnostic for visceral leishmaniasis in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 patients and a prognostic indicator for monitoring patients undergoing drug therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, A.; Costa, L.E.; Salles, B.C.S.; Santos, T.T.O.; Ramos, F.F.; Lima, M.P.; Chávez-Fumagalli, M.A.; Silvestre, B.T.; Portela, Á.S.B.; Roatt, B.M.; et al. An ELISA immunoassay employing a conserved Leishmania hypothetical protein for the serodiagnosis of visceral and tegumentary leishmaniasis in dogs and humans. Cell Immunol. 2017, 318, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.A.F.; Dias, D.S.; Lage, D.P.; Costa, L.E.; Salles, B.C.S.; Steiner, B.T.; Ramos, F.F.; Lima, M.P.; Santos, T.T.O.; Chaves, A.T.; et al. A conserved Leishmania hypothetical protein evaluated for the serodiagnosis of canine and human visceral and tegumentary leishmaniasis, as well as a serological marker for the posttreatment patient follow-up. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 92, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindoso, J.A.; Barbosa, R.N.; Posada-Vergara, M.P.; Duarte, M.I.; Oyafuso, L.K.; Amato, V.S.; Goto, H. Unusual manifestations of tegumentary leishmaniasis in AIDS patients from the New World. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, A.G.; Carrington, M.; Miles, M.A.; Barker, D.C.; de Almeida, M.L. Identification of the C-terminal region of 70 kDa heat shock protein from Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis as a target for the humoral immune response. Cell Stress Chaperones 1996, 1, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rey-Ladino, J.A.; Joshi, P.B.; Singh, B.; Gupta, R.; Reiner, N.E. Leishmania major: Molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of the heat shock protein 60 gene reveals unique carboxy terminal peptide sequences. Exp. Parasitol. 1997, 85, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Souza, D.; Mendes, T.A.; Gomes Mde, S.; Reis-Cunha, J.L.; Nagem, R.A.; Carneiro, C.M.; Coelho, E.A.; Galvão, L.M.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Bartholomeu, D.C. Epitope mapping of the HSP83.1 protein of Leishmania braziliensis discloses novel targets for immunodiagnosis of tegumentary and visceral clinical forms of leishmaniasis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, E.A.; Costa, L.E.; Lage, D.P.; Martins, V.T.; Garde, E.; de Jesus Pereira, N.C.; Lopes, E.G.; Borges, L.F.; Duarte, M.C.; Menezes-Souza, D.; et al. Evaluation of two recombinant Leishmania proteins identified by an immunoproteomic approach as tools for the serodiagnosis of canine visceral and human tegumentary leishmaniasis. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 215, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, B.C.S.; Dias, D.S.; Steiner, B.T.; Lage, D.P.; Ramos, F.F.; Ribeiro, P.A.F.; Santos, T.T.O.; Lima, M.P.; Costa, L.E.; Chaves, A.T.; et al. Potential application of small myristoylated protein-3 evaluated as recombinant antigen and a synthetic peptide containing its linear B-cell epitope for the serodiagnosis of canine visceral and human tegumentary leishmaniasis. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, D.P.; Machado, A.S.; Ramos, F.F.; Silveira, P.C.; Dias, D.S.; Ribeiro, P.A.F.; Tavares, G.S.V.; Costa, L.E.; Santos, T.T.O.; Steiner, B.T.; et al. A biomarker for tegumentary and visceral leishmaniasis based on a recombinant Leishmania hypothetical protein. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.L.; Assis, T.S.M.; Avelar, D.M.; Rabello, A.; Cota, G. Evaluation of a new brand of immunochromatographic test for visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil made available from 2018. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2018, 60, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Profiti, M.; Nogarol, C.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Spano, G.; Ferroglio, E.; Mignone, W.; et al. A versatile and sensitive lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4123–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabhi, S.; Whittle, J.; Mohamath, R.; El-Safi, S.; Moulton, G.G.; Guderian, J.A.; Colombara, D.; Abdoon, A.O.; Mukhtar, M.M.; Mondal, D.; et al. Design, development and evaluation of rK28-based point-of-care tests for improving rapid diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaish, M.; Bhatia, A.; Reed, S.G.; Chakravarty, J.; Sundar, S. Evaluation of rK28 antigen for serodiagnosis of visceral Leishmaniasis in India. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimi Kakh, M.; Golchin, M.; Kazemi Arababadi, M.; Daneshvar, H. Application of the Leishmania infantum 21-kDa recombinant protein for the development of an immunochromatographic test. Parasite Immunol. 2020, e12770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejazi, S.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Kamran, M.; Das, S.; Bhowmick, S.; Rahaman, M.; Goswami, R.P.; Ali, N. Investigation of the antigenicity and protective efficacy of Leishmania promastigote membrane antigens in search of potential diagnostic and vaccine candidates against visceral leishmaniasis. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejazi, S.A.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Choudhury, S.T.; Ghosh, S.; Sabur, A.; Pandey, K.; Das, V.N.R.; Das, P.; Rahaman, M.; Goswami, R.P.; et al. Immunoproteomic Identification and Characterization of Leishmania Membrane Proteins as Non-Invasive Diagnostic Candidates for Clinical Visceral Leishmaniasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, S.; Ali, N. Identification of novel Leishmania donovani antigens that help define correlates of vaccine-mediated protection in visceral leishmaniasis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, M.K.; Jamal, F.; Dubey, A.K.; Shivam, P.; Kumari, S.; Pushpanjali; Bordoloi, C.; Narayan, S.; Das, V.N.R.; Pandey, K.; et al. Visceral leishmaniasis: A novel nuclear envelope protein ‘nucleoporins-93 (NUP-93)’ from Leishmania donovani prompts macrophage signaling for T-cell activation towards host protective immune response. Cytokine 2019, 113, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.V.; Costa, L.E.; Katis, I.; Fonseca Ramos, F.; Sanchéz Machado, A.; Sones, C.; Ferraz Coelho, E.A.; Christodoulides, M. A rapid diagnostic test for human Visceral Leishmaniasis using novel Leishmania antigens in a Laser Direct-Write Lateral Flow Device. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boelaert, M.; Verdonck, K.; Menten, J.; Sunyoto, T.; van Griensven, J.; Chappuis, F.; Rijal, S. Rapid tests for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in patients with suspected disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, Cd009135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundar, S.; Singh, O.P. Molecular Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 22, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griensven, J.; van Henten, S.; Mengesha, B.; Kassa, M.; Adem, E.; Endris Seid, M.; Abdellati, S.; Asefa, W.; Simegn, T.; Debasu, D.; et al. Longitudinal evaluation of asymptomatic Leishmania infection in HIV-infected individuals in North-West Ethiopia: A pilot study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Boelaert, M.; Miles, M.A. Comparison of visceral leishmaniasis diagnostic antigens in African and Asian Leishmania donovani reveals extensive diversity and region-specific polymorphisms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, M.C.A.; Celeste, B.J.; Lindoso, J.A.L.; Fujimori, M.; de Almeida, R.P.; Fortaleza, C.; Druzian, A.F.; Lemos, A.P.F.; de Melo, V.C.A.; Miranda Paniago, A.M.; et al. Performance of rK39-based immunochromatographic rapid diagnostic test for serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis using whole blood, serum and oral fluid. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, C.; Fisa, R.; Lopez, P.; Ribera, E.; Carrió, J.; Falcó, V.; Molina, I.; Gállego, M.; Portús, M. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test (KAtex) for detection of Leishmania antigen in urine of patients with HIV-Leishmania coinfection: Value in diagnosis and post-treatment follow-up. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 23, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaplana, C.; Blanco, S.; Domínguez, J.; Giménez, M.; Ausina, V.; Tural, C.; Muñoz, C. Noninvasive method for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis by a latex agglutination test for detection of antigens in urine samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1853–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbosa Júnior, W.L.; Ramos de Araújo, P.S.; Dias de Andrade, L.; Aguiar Dos Santos, A.M.; Lopes da Silva, M.A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Medeiros, Z. Rapid Tests and the Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis and Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Coinfection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, F.; Mengesha, B.; Asmamaw, H.; Mekonnen, T.; Fikre, H.; Takele, Y.; Adem, E.; Mohammed, R.; Ritmeijer, K.; Adriaensen, W.; et al. Antigen Detection in Urine for Noninvasive Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Visceral Leishmaniasis in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfected Patients: An Exploratory Analysis from Ethiopia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abeijon, C.; Kashino, S.S.; Silva, F.O.; Costa, D.L.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Costa, C.H.; Campos-Neto, A. Identification and diagnostic utility of Leishmania infantum proteins found in urine samples from patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abeijon, C.; Campos-Neto, A. Potential non-invasive urine-based antigen (protein) detection assay to diagnose active visceral leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abeijon, C.; Alves, F.; Monnerat, S.; Mbui, J.; Viana, A.G.; Almeida, R.M.; Bueno, L.L.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Campos-Neto, A. Urine-based antigen detection assay for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis using monoclonal antibodies specific for six protein biomarkers of Leishmania infantum/Leishmania donovani. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlais, T.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Pearson, C.; Gardner, B.L.; Marhoon, S.; Airs, S.; Hayes, K.; Falconar, A.K.; Singh, O.P.; Reed, S.G.; et al. Isolation and characterisation of Leishmania donovani protein antigens from urine of visceral leishmaniasis patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diagnostic Method | Clinical Form | Culture Required | Species Discrimination 1 | Reference(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasitological methods | Biopsy, punch, scraping, smear or imprinting followed by microscopic examination | CL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [25,26,29,30] |
| Bone marrow, lymph nodes or spleen aspirates or liver biopsy followed by microscopic examination | VL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [33,34] | |
| In vitro cultivation | VL, CL | Yes | No (only genus Leishmania) | [37] | |
| Inoculation in animals (mice or hamsters) | VL, CL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [22,35] | |
| Xenodiagnosis | VL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [39,40] | |
| Protein-based methods | MLEE | VL, CL | Yes | Yes (almost all currently identified species) | [41] |
| Monoclonal antibodies | VL, CL | Yes | Yes (almost all species endemic in the Americas and also L. (L.) major, L. (L.) donovani and L. (L.) tropica) | [42,43,44,45] | |
| MALDI-TOF MS | VL, CL | Yes | Yes (all species endemic in the Americas, Europe, Asia and Africa) | [46,47,48] | |
| KAtex | VL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [49,50,51] | |
| DNA-based methods | PCR-RFLP | VL, CL | No | Yes (almost all species; depends on the target) | [9,52] |
| DNA sequencing | VL, CL | No | Yes (almost all species; depends on the target) | [9,52] | |
| Real-time PCR | VL, CL | No | Yes (most species) | [53,54] | |
| PCR-HRM | VL, CL | No | Yes (almost all species endemic in the Americas, Europe, Asia and Africa) | [55,56,57,58,59] | |
| MLST | VL, CL | No | Yes (all species) | [60,61,62,63] | |
| LAMP | VL, CL | No | Yes (limited to certain species) | [64,65,66,67] | |
| Immunological-based methods | Leishmania skin test | CL (negative for DCL) | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [16] |
| ELISA (rK39) | VL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [68,69,70,71,72,73] | |
| ELISA (other recombinant antigens) | VL, CL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85] | |
| IFAT | VL, CL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [71,86,87,88,89] | |
| DAT | VL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [50,71,86,87,90,91] | |
| ICT (rK39) | VL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [50,70,86,90,92] | |
| Dipstick test [L. (L.) donovani promastigote antigens] | VL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [93,94] | |
| Western blot | VL, CL | No | No (only genus Leishmania) | [95,96,97,98] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reimão, J.Q.; Coser, E.M.; Lee, M.R.; Coelho, A.C. Laboratory Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis: Current and Future Methods. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111632
Reimão JQ, Coser EM, Lee MR, Coelho AC. Laboratory Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis: Current and Future Methods. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(11):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111632
Chicago/Turabian StyleReimão, Juliana Quero, Elizabeth Magiolo Coser, Monica Ran Lee, and Adriano Cappellazzo Coelho. 2020. "Laboratory Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis: Current and Future Methods" Microorganisms 8, no. 11: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111632
APA StyleReimão, J. Q., Coser, E. M., Lee, M. R., & Coelho, A. C. (2020). Laboratory Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis: Current and Future Methods. Microorganisms, 8(11), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111632







