Toll-Like Receptor-4 Is Involved in Mediating Intestinal and Extra-Intestinal Inflammation in Campylobacter coli-Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10−/− Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Generation of Secondary Abiotic Mice
2.3. Bacterial Challenge and Gastrointestinal Colonization and Translocation
2.4. Clinical Conditions
2.5. Sampling Procedures
2.6. Histopathology
2.7. In Situ Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Measurements in Intestinal, Extra-Intestinal, and Systemic Compartments
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
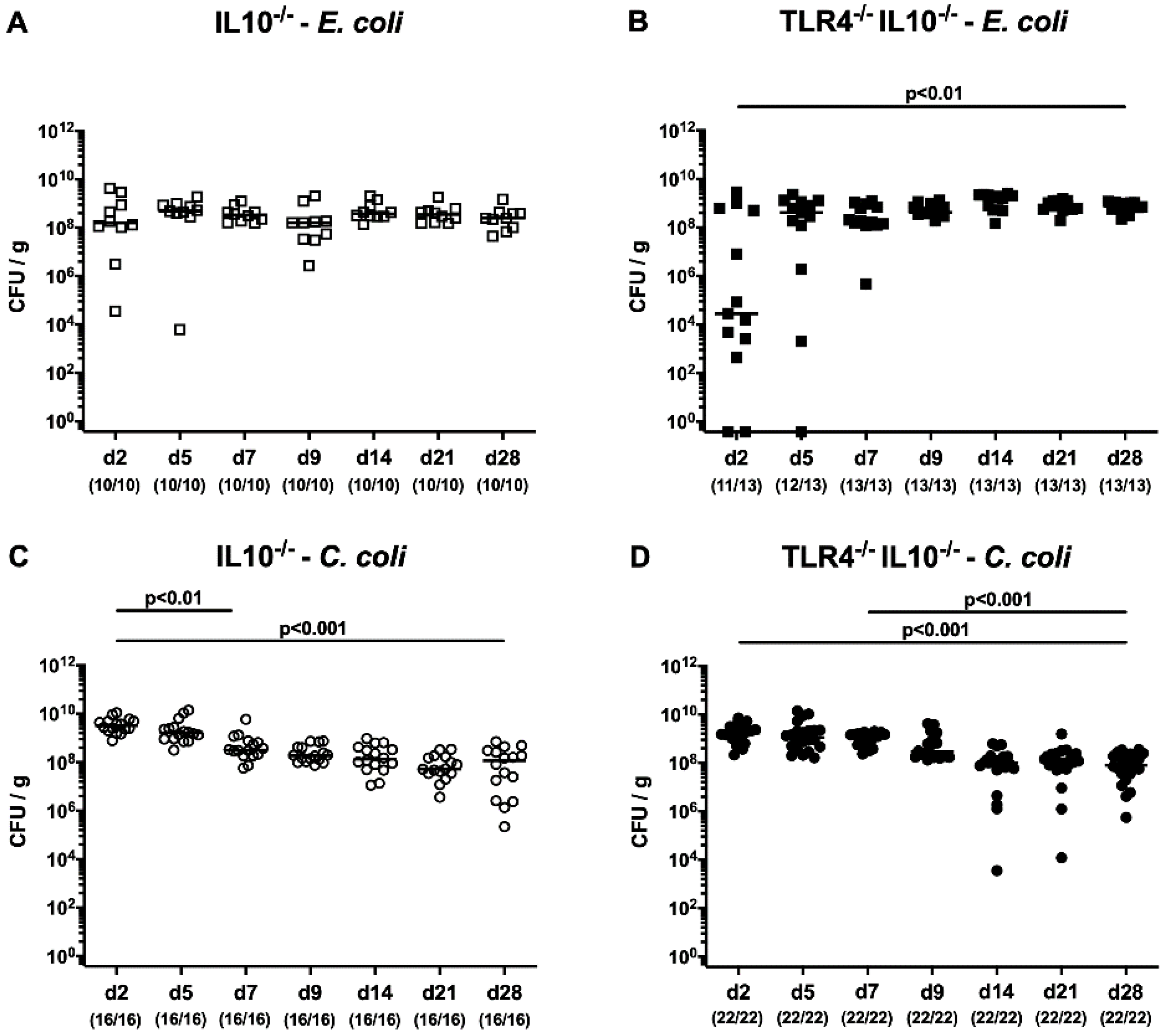
3.1. Role of TLR4 in Intestinal Colonization of C. coli and E. coli in Secondary Abiotic IL-10-/- Mice
3.2. Kinetic Survey of Clinical Signs Following Peroral C. coli or E. coli Application to Secondary Abiotic IL-10-/- Mice Lacking TLR4
3.3. Role of TLR4 in C. coli-Mediated Colonic Histopathology and Apoptosis
3.4. TLR4-Dependent Intestinal Immune Cell Responses Induced by C. coli Infection
3.5. TLR4 is Involved in Mediating Intestinal and Extra-Intestinal Pro-Inflammatory Responses Following C. coli Infection of Secondary Abiotic IL-10−/− Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBA | cytometric bead array |
| CFU | colony forming units |
| HPF | high power fields |
| IFN | interferon |
| IL | interleukin |
| LOS | lipooligosaccharide |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| MLN | mesenteric lymph nodes |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| n.s. | not significant |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| p.i. | post-infection |
| SPF | specific pathogen free |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| Treg | regulatory T cells |
| WT | wildtype |
References
- Wagenaar, J.A.; French, N.P.; Havelaar, A.H. Preventing Campylobacter at the source: Why is it so difficult? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Campylobacter. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Young, K.T.; Davis, L.M.; Dirita, V.J. Campylobacter jejuni: Molecular biology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Cróinín, T.; Boehm, M.; Heimesaat, M. Human Campylobacteriosis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allos, B.M. Association between Campylobacter infection and Guillain-Barre syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176 (Suppl. 2), S125–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kist, M.; Bereswill, S. (Eds.) Campylobacter jejuni. In Emerging Bacterial Pathogens; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2001; Volume 8, pp. 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. as a foodborne pathogen: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05926. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.J.; Gabriel, E.; Leatherbarrow, A.J.H.; Cheesbrough, J.; Gee, S.; Bolton, E.; Fox, A.; Fearnhead, P.; Hart, C.A.; Diggle, P.J. Tracing the source of campylobacteriosis. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alter, T.; Bereswill, S.; Glünder, G.; Haag, L.-M.; Hänel, I.; Heimesaat, M.; Lugert, R.; Rautenschlein, S.; Weber, R.; Zautner, A.; et al. Die Campylobacteriose des Menschen. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2011, 54, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global Epidemiology of Campylobacter Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tam, C.C.; O’Brien, S.J.; Adak, G.K.; Meakins, S.M.; Frost, J.A. Campylobacter coli—An important foodborne pathogen. J. Infect. 2003, 47, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, D.D. Overview of the immune response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S3–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Kagan, J.C. A cross-disciplinary perspective on the innate immune responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, G. Gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial toxins in sepsis: A brief review. Virulence 2014, 5, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; Plickert, R.; Haag, L.M.; Otto, B.; Kuhl, A.A.; Dasti, J.I.; Zautner, A.E.; Munoz, M.; Loddenkemper, C.; et al. Novel murine infection models provide deep insights into the “menage a trois” of Campylobacter jejuni, microbiota and host innate immunity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, L.M.; Fischer, A.; Otto, B.; Plickert, R.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Campylobacter jejuni induces acute enterocolitis in gnotobiotic IL-10-/- mice via Toll-like-receptor-2 and -4 signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stahl, M.; Ries, J.; Vermeulen, J.; Yang, H.; Sham, H.P.; Crowley, S.M.; Badayeva, Y.; Turvey, S.E.; Gaynor, E.C.; Li, X.; et al. A novel mouse model of Campylobacter jejuni gastroenteritis reveals key pro-inflammatory and tissue protective roles for Toll-like receptor signaling during infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rathinam, V.A.; Appledorn, D.M.; Hoag, K.A.; Amalfitano, A.; Mansfield, L.S. Campylobacter jejuni-induced activation of dendritic cells involves cooperative signaling through Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-MyD88 and TLR4-TRIF axes. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Zoete, M.R.; Keestra, A.M.; Roszczenko, P.; van Putten, J.P. Activation of human and chicken toll-like receptors by Campylobacter spp. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortensen, N.P.; Kuijf, M.L.; Ang, C.W.; Schiellerup, P.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Belkum, A.; Endtz, H.P.; Bergman, M.P. Sialylation of Campylobacter jejuni lipo-oligosaccharides is associated with severe gastro-enteritis and reactive arthritis. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, A.; Mandrell, R.E.; Gibson, B.W.; Apicella, M.A. The lipooligosaccharides of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1996, 22, 139–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietschel, E.T.; Kirikae, T.; Schade, F.U.; Mamat, U.; Schmidt, G.; Loppnow, H.; Ulmer, A.J.; Zahringer, U.; Seydel, U.; Di Padova, F.; et al. Bacterial endotoxin: Molecular relationships of structure to activity and function. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culebro, A.; Revez, J.; Pascoe, B.; Friedmann, Y.; Hitchings, M.D.; Stupak, J.; Sheppard, S.K.; Li, J.; Rossi, M. Large sequence diversity within the biosynthesis locus and common biochemical features of Campylobacter coli lipooligosaccharides. J Bacteriol 2016, 198, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, V.P.; Lefebure, T.; Pavinski Bitar, P.D.; Stanhope, M.J. Comparative characterization of the virulence gene clusters (lipooligosaccharide [LOS] and capsular polysaccharide [CPS]) for Campylobacter coli, Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni and related Campylobacter species. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Culebro, A.; Machado, M.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Rossi, M. Origin, evolution, and distribution of the molecular machinery for biosynthesis of sialylated lipooligosaccharide structures in Campylobacter coli. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haag, A.F.; Baloban, M.; Sani, M.; Kerscher, B.; Pierre, O.; Farkas, A.; Longhi, R.; Boncompagni, E.; Herouart, D.; Dall’angelo, S.; et al. Protection of Sinorhizobium against host cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides is critical for symbiosis. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haag, L.M.; Fischer, A.; Otto, B.; Grundmann, U.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Campylobacter jejuni infection of infant mice: Acute enterocolitis is followed by asymptomatic intestinal and extra-intestinal immune responses. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alutis, M.E.; Grundmann, U.; Fischer, A.; Kuhl, A.A.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Selective gelatinase inhibition reduces apoptosis and pro-inflammatory immune cell responses in Campylobacter jejuni-infected gnotobiotic IL-10 deficient mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 4, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bereswill, S.; Ekmekciu, I.; Escher, U.; Fiebiger, U.; Stingl, K.; Heimesaat, M.M. Lactobacillus johnsonii ameliorates intestinal, extra-intestinal and systemic pro-inflammatory immune responses following murine Campylobacter jejuni infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bereswill, S.; Grundmann, U.; Alutis, M.E.; Fischer, A.; Heimesaat, M.M. Campylobacter jejuni infection of conventionally colonized mice lacking nucleotide-oligomerization-domain-2. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekmekciu, I.; Fiebiger, U.; Stingl, K.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Amelioration of intestinal and systemic sequelae of murine Campylobacter jejuni infection by probiotic VSL#3 treatment. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Alutis, M.; Grundmann, U.; Fischer, A.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Bohm, M.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Backert, S.; Bereswill, S. The role of serine protease HtrA in acute ulcerative enterocolitis and extra-intestinal immune responses during Campylobacter jejuni infection of gnotobiotic IL-10 deficient mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Grundmann, U.; Alutis, M.E.; Fischer, A.; Bereswill, S. Small Intestinal Pro-Inflammatory Immune Responses Following Campylobacter Jejuni Infection of Secondary Abiotic IL-10(−/−) Mice Lacking Nucleotide-Oligomerization-Domain-2. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 7, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Grundmann, U.; Alutis, M.E.; Fischer, A.; Bereswill, S. Absence of Nucleotide-Oligomerization-Domain-2 Is Associated with Less Distinct Disease in Campylobacter jejuni Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10 Deficient Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kløve, S.; Genger, C.; Mousavi, S.; Weschka, D.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Toll-Like Receptor-4 Dependent Intestinal and Systemic Sequelae Following Peroral Campylobacter coli Infection of IL10 Deficient Mice Harboring a Human Gut Microbiota. Pathogens 2020, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; Fuchs, D.; Struck, D.; Niebergall, J.; Jahn, H.K.; Dunay, I.R.; Moter, A.; Gescher, D.M.; et al. Gram-negative bacteria aggravate murine small intestinal Th1-type immunopathology following oral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8785–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Fischer, A.; Jahn, H.K.; Niebergall, J.; Freudenberg, M.; Blaut, M.; Liesenfeld, O.; Schumann, R.R.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S. Exacerbation of murine ileitis by Toll-like receptor 4 mediated sensing of lipopolysaccharide from commensal Escherichia coli. Gut 2007, 56, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haag, L.M.; Fischer, A.; Otto, B.; Plickert, R.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Intestinal microbiota shifts towards elevated commensal Escherichia coli loads abrogate colonization resistance against Campylobacter jejuni in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Haag, L.M.; Fischer, A.; Otto, B.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S. Survey of extra-intestinal immune responses in asymptomatic long-term Campylobacter jejuni-infected mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 3, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, U.; Loddenkemper, C.; Doerfel, K.; Spieckermann, S.; Haller, D.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Zeitz, M.; Siegmund, B.; Kühl, A.A. A guide to histomorphological evaluation of intestinal inflammation in mouse models. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4557–4576. [Google Scholar]
- Alutis, M.E.; Grundmann, U.; Fischer, A.; Hagen, U.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. The Role of Gelatinases in Campylobacter Jejuni Infection of Gnotobiotic Mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alutis, M.E.; Grundmann, U.; Hagen, U.; Fischer, A.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Mediates Intestinal Immunopathogenesis in Campylobacter Jejuni-Infected Infant Mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Lugert, R.; Fischer, A.; Alutis, M.; Kuhl, A.A.; Zautner, A.E.; Tareen, A.M.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S. Impact of Campylobacter jejuni cj0268c knockout mutation on intestinal colonization, translocation, and induction of immunopathology in gnotobiotic IL-10 deficient mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Nogai, A.; Bereswill, S.; Plickert, R.; Fischer, A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Steinhoff, U.; Tchaptchet, S.; Thiel, E.; Freudenberg, M.A.; et al. MyD88/TLR9 mediated immunopathology and gut microbiota dynamics in a novel murine model of intestinal graft-versus-host disease. Gut 2010, 59, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.; Lobo de Sa, F.D.; Schulzke, J.D.; Bucker, R.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Vitamin D in Acute Campylobacteriosis-Results From an Intervention Study Applying a Clinical Campylobacter jejuni Induced Enterocolitis Model. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, S.; Schmidt, A.M.; Escher, U.; Kittler, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Thunhorst, E.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Carvacrol ameliorates acute campylobacteriosis in a clinical murine infection model. Gut Pathog. 2020, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, S.; Escher, U.; Thunhorst, E.; Kittler, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Vitamin C alleviates acute enterocolitis in Campylobacter jejuni infected mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo de Sa, F.D.; Butkevych, E.; Nattramilarasu, P.K.; Fromm, A.; Mousavi, S.; Moos, V.; Golz, J.C.; Stingl, K.; Kittler, S.; Seinige, D.; et al. Curcumin Mitigates Immune-Induced Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction by Campylobacter jejuni. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, R.O.; Galan, J.E. Signal transduction in Campylobacter jejuni-induced cytokine production. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mourik, A.; Steeghs, L.; van Laar, J.; Meiring, H.D.; Hamstra, H.J.; van Putten, J.P.; Wosten, M.M. Altered linkage of hydroxyacyl chains in lipid A of Campylobacter jejuni reduces TLR4 activation and antimicrobial resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 15828–15836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Escher, U.; Mousavi, S.; Boehm, M.; Backert, S.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Protease Activity of Campylobacter jejuni HtrA Modulates Distinct Intestinal and Systemic Immune Responses in Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10 Deficient Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Escher, U.; Mousavi, S.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Boehm, M.; Backert, S.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Immunopathological properties of the Campylobacter jejuni flagellins and the adhesin CadF as assessed in a clinical murine infection model. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, R.; Kirschning, C.J.; Sing, A.; Schrottner, P.; Fukase, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Wagner, H.; Heesemann, J.; Ruckdeschel, K. A dominant role of Toll-like receptor 4 in the signaling of apoptosis in bacteria-faced macrophages. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 4294–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Navajas, J.M.; Fine, S.; Law, J.; Datta, S.K.; Nguyen, K.P.; Yu, M.; Corr, M.; Katakura, K.; Eckman, L.; Lee, J.; et al. TLR4 signaling in effector CD4+ T cells regulates TCR activation and experimental colitis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Gao, N. Compartmentalizing intestinal epithelial cell toll-like receptors for immune surveillance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2015, 72, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abreu, M.T. Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: How bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Cava, C.F.; Ishihara, S.; Rumi, M.A.K.; Kawashima, K.; Ishimura, N.; Kazumori, H.; Udagawa, J.; Kadowaki, Y.; Kinoshita, Y. Strategic Compartmentalization of Toll-Like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Gut. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmausser, B.; Andrulis, M.; Endrich, S.; Lee, S.K.; Josenhans, C.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Eck, M. Expression and subcellular distribution of toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on the gastric epithelium in Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 136, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Microbial sensing by Toll-like receptors and intracellular nucleic acid sensors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen-Nissen, E.; Smith, K.D.; Strobe, K.L.; Barrett, S.L.; Cookson, B.T.; Logan, S.M.; Aderem, A. Evasion of Toll-like receptor 5 by flagellated bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9247–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciftci, A.; Savasan, S.; Ica, T.; Diker, K.S. Mouse intestine colonization ability of Campylobacter coli strains. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2009, 116, 255–259. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kløve, S.; Genger, C.; Weschka, D.; Mousavi, S.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Toll-Like Receptor-4 Is Involved in Mediating Intestinal and Extra-Intestinal Inflammation in Campylobacter coli-Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10−/− Mice. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121882
Kløve S, Genger C, Weschka D, Mousavi S, Bereswill S, Heimesaat MM. Toll-Like Receptor-4 Is Involved in Mediating Intestinal and Extra-Intestinal Inflammation in Campylobacter coli-Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10−/− Mice. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(12):1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121882
Chicago/Turabian StyleKløve, Sigri, Claudia Genger, Dennis Weschka, Soraya Mousavi, Stefan Bereswill, and Markus M. Heimesaat. 2020. "Toll-Like Receptor-4 Is Involved in Mediating Intestinal and Extra-Intestinal Inflammation in Campylobacter coli-Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10−/− Mice" Microorganisms 8, no. 12: 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121882
APA StyleKløve, S., Genger, C., Weschka, D., Mousavi, S., Bereswill, S., & Heimesaat, M. M. (2020). Toll-Like Receptor-4 Is Involved in Mediating Intestinal and Extra-Intestinal Inflammation in Campylobacter coli-Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10−/− Mice. Microorganisms, 8(12), 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121882





