Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Functional Dyspepsia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Methods
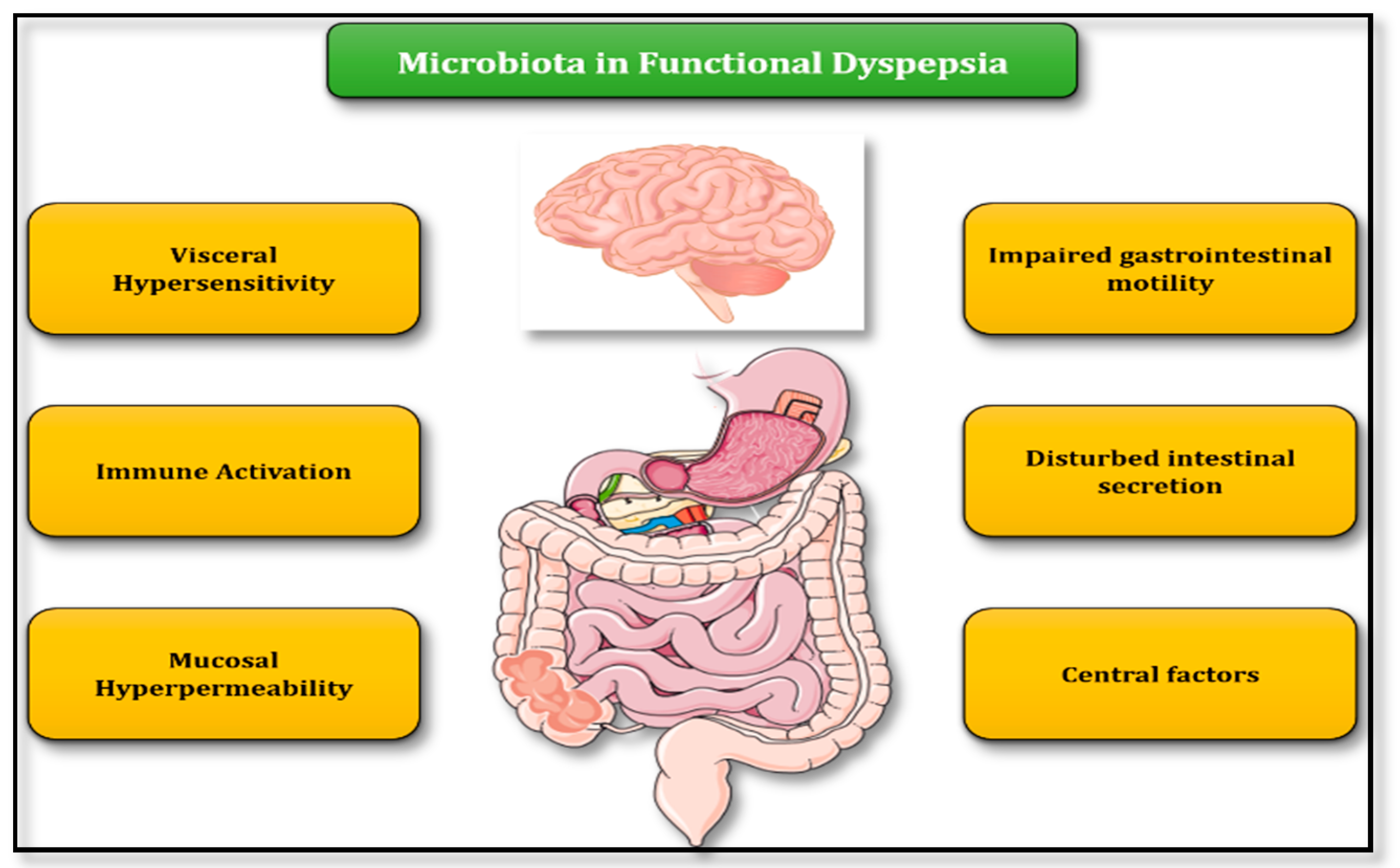
3. Role of Microbiota in FD Pathogenesis—Putative Pathophysiologic Mechanisms
3.1. Abnormal Gastrointestinal Motility
3.2. Intestinal Barrier Integrity
3.3. Immune System Activation and Low-Level Inflammation
3.4. Disturbances in Intestinal Secretion
3.5. Visceral Hypersensitivity
3.6. Central Nervous System Factors
4. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and Gut Microbiota
5. Data from Studies Evaluating Microbiota Dysbiosis in FD
6. Modulating Microbiota as Potential Treatment for FD
6.1. Probiotics
6.2. Antibiotics
6.3. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
7. What Lies in the Future?
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P.; et al. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, R.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Fagoonee, S.; Astegiano, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Megraud, F. A 2016 panorama of Helicobacter pylori infection: Key messages for clinicians. Panminerva Med. 2016, 58, 304–317. [Google Scholar]
- Enck, P.; Azpiroz, F.; Boeckxstaens, G.; Elsenbruch, S.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Holtmann, G.; Lackner, J.M.; Ronkainen, J.; Schemann, M.; Stengel, A.; et al. Functional dyspepsia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J. What Causes Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders? A Proposed Disease Model. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourikou, A.; Karamanolis, G.P.; Dimitriadis, G.D.; Triantafyllou, K. Gene polymorphisms associated with functional dyspepsia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7672–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Quigley, E.M.; Santos, J.; Vanner, S.; Vergnolle, N.; Zoetendal, E.G. The Intestinal Microenvironment and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Dimitriadis, G.; Triantafyllou, K. Gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2015, 14, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Lembo, A. Microbiome and Its Role in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziatzios, G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Pimentel, M.; Dimitriadis, G.D.; Triantafyllou, K. Is small intestinal bacterial overgrowth involved in the pathogenesis of functional dyspepsia? Med. Hypotheses 2017, 106, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Black, C.J.; Howden, C.W.; Ford, A.C. Effectiveness of management strategies for uninvestigated dyspepsia: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2019, 367, 16483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheel, H.; Carbone, F.; Valvekens, L.; Simren, M.; Tornblom, H.; Vanuytsel, T.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Tack, J. Pathophysiological Abnormalities in Functional Dyspepsia Subgroups According to the Rome III Criteria. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigstad, C.S.; Kashyap, P.C. Beyond phylotyping: Understanding the impact of gut microbiota on host biology. NeuroGastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palma, G.; Lynch, M.D.; Lu, J.; Dang, V.T.; Deng, Y.; Jury, J.; Umeh, G.; Miranda, P.M.; Pigrau Pastor, M.; Sidani, S.; et al. Transplantation of fecal microbiota from patients with irritable bowel syndrome alters gut function and behavior in recipient mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebye, E.; Hellstrom, P.M.; Sundler, F.; Chen, J.; Midtvedt, T. Influence of microbial species on small intestinal myoelectric activity and transit in germ-free rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001, 280, G368–G380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, I.; Iwanaga, T.; Watanabe, M.; Guth, P.H.; Engel, E.; Kaunitz, J.D.; Akiba, Y. SCFA transport in rat duodenum. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G188–G197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collares, E.F. Effect of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on gastric emptying of liquids in rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1997, 30, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agrawal, A.; Houghton, L.A.; Morris, J.; Reilly, B.; Guyonnet, D.; Goupil Feuillerat, N.; Schlumberger, A.; Jakob, S.; Whorwell, P.J. Clinical trial: The effects of a fermented milk product containing Bifidobacterium lactis DN-173 010 on abdominal distension and gastrointestinal transit in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanheel, H.; Vicario, M.; Vanuytsel, T.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Martinez, C.; Keita, A.V.; Pardon, N.; Santos, J.; Soderholm, J.D.; Tack, J.; et al. Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia. Gut 2014, 63, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wauters, L.; Talley, N.J.; Walker, M.M.; Tack, J.; Vanuytsel, T. Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gut 2020, 69, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.M.; Myers, L.S.; Kurundkar, A.R.; Maheshwari, A.; Nusrat, A.; Lin, P.W. Probiotic bacteria induce maturation of intestinal claudin 3 expression and barrier function. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukena, S.N.; Singh, A.; Dringenberg, U.; Engelhardt, R.; Seidler, U.; Hansen, W.; Bleich, A.; Bruder, D.; Franzke, A.; Rogler, G.; et al. Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 inhibits leaky gut by enhancing mucosal integrity. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Rosso, C.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Dughera, F.; Fagoonee, S.; Astegiano, M.; Pellicano, R. Physiopathology of intestinal barrier and the role of zonulin. Minerva Biotecnol. 2019, 31, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; Cookson, A.L.; McNabb, W.C.; Park, Z.; McCann, M.J.; Kelly, W.J.; Roy, N.C. Lactobacillus plantarum MB452 enhances the function of the intestinal barrier by increasing the expression levels of genes involved in tight junction formation. BMC MicroBiol. 2010, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsgard, R.A.; Korpela, R.; Stenman, L.K.; Osterlund, P.; Holma, R. Deoxycholic acid induced changes in electrophysiological parameters and macromolecular permeability in murine small intestine with and without functional enteric nervous system plexuses. NeuroGastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, G.; Carroll, G.; Mathe, A.; Horvat, J.; Foster, P.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Keely, S. Evidence for Local and Systemic Immune Activation in Functional Dyspepsia and the Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Srinivasan, S. Gut microbial products regulate murine gastrointestinal motility via Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, N.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J. The mucosal immune system: Master regulator of bidirectional gut-brain communications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.; Morales, W.; Pokkunuri, V.; Brikos, C.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.E.; Triantafyllou, K.; Weitsman, S.; Marsh, Z.; Marsh, E.; et al. Autoimmunity Links Vinculin to the Pathophysiology of Chronic Functional Bowel Changes Following Campylobacter jejuni Infection in a Rat Model. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chira, A.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Serum biomarkers for irritable bowel syndrome. Clujul Med. 2015, 88, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talley, N.J.; Holtmann, G.; Walker, M.M.; Burns, G.; Potter, M.; Shah, A.; Jones, M.; Koloski, N.A.; Keely, S. Circulating Anti-cytolethal Distending Toxin B and Anti-vinculin Antibodies as Biomarkers in Community and Healthcare Populations With Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Peripheral mechanisms in irritable bowel syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Prakash, S. The gut microbiome, probiotics, bile acids axis, and human health. Trends MicroBiol. 2014, 22, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Kong, Y.; Park, S. IBS Subjects with Methane on Lactulose Breath Test Have Lower Postprandial Serotonin Levels Than Subjects with Hydrogen. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simren, M.; Tornblom, H.; Palsson, O.S.; van Tilburg, M.A.L.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Tack, J.; Whitehead, W.E. Visceral hypersensitivity is associated with GI symptom severity in functional GI disorders: Consistent findings from five different patient cohorts. Gut 2018, 67, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, E.; Barba, E.; Huaman, J.W.; Cisternas, D.; Accarino, A.; Soldevilla, A.; Malagelada, J.R.; Azpiroz, F. Mechanisms of postprandial abdominal bloating and distension in functional dyspepsia. Gut 2014, 63, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, D.P.; Gaszner, G.; Quigley, E.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Altered peripheral toll-like receptor responses in the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, H.B. Interstitial cells of Cajal, macrophages and mast cells in the gut musculature: Morphology, distribution, spatial and possible functional interactions. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. NeuroSci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, K.; Papadopoulos, V.; Emanouil, T.; Gkolfakis, P.; Damaskou, V.; Tziatzios, G.; Panayiotides, I.G.; Vafiadis, I.; Ladas, S.D. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection Restores ki67, p53, and Cyclin D1 Immunoreactivity in the Human Gastric Epithelium. Clin. Med. Insights Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütte, K.; Malfertheiner, P.; Schulz, C. What is the Relevance of Gastric Microbiota Beyond H. pylori? Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2019, 17, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, E.M.; Eckburg, P.B.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Purdom, E.A.; Francois, F.; Perez-Perez, G.; Blaser, M.J.; Relman, D.A. Molecular analysis of the bacterial microbiota in the human stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Contreras, A.; Goldfarb, K.C.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Karaoz, U.; Contreras, M.; Blaser, M.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G. Structure of the human gastric bacterial community in relation to Helicobacter pylori status. ISME J. 2011, 5, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantuya, B.; El-Serag, H.B.; Matsumoto, T.; Ajami, N.J.; Oyuntsetseg, K.; Azzaya, D.; Uchida, T.; Yamaoka, Y. Gastric Microbiota in Helicobacter pylori-Negative and -Positive Gastritis Among High Incidence of Gastric Cancer Area. Cancers 2019, 11, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, E.G.; Loke, M.F.; Gunaletchumy, S.P.; Gan, H.M.; Thevakumar, K.; Tay, C.Y.; Young, S.; Aye, T.T.; Maw, W.W.; Aye, M.M.; et al. The Influence of Modernization and Disease on the Gastric Microbiome of Orang Asli, Myanmars and Modern Malaysians. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Sheu, B.S. Metabolic Interaction of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokkas, T.; Rokka, A.; Portincasa, P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the role of Helicobacter pylori eradication in preventing gastric cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Sheu, B.S.; Yang, H.B.; Lu, C.C.; Chuang, C.C. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori increases childhood growth and serum acylated ghrelin levels. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2674–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, B.N.; Ijaz, U.Z.; D’Amore, R.; Burkitt, M.D.; Eccles, R.; Lenzi, L.; Duckworth, C.A.; Moore, A.R.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Varro, A.; et al. Comparison of the human gastric microbiota in hypochlorhydric states arising as a result of Helicobacter pylori-induced atrophic gastritis, autoimmune atrophic gastritis and proton pump inhibitor use. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakae, H.; Tsuda, A.; Matsuoka, T.; Mine, T.; Koga, Y. Gastric microbiota in the functional dyspepsia patients treated with probiotic yogurt. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2016, 3, e000109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Nakae, H.; Matsuoka, T.; Takahashi, S.; Hisada, T.; Tomita, J.; Koga, Y. Alteration in the gastric microbiota and its restoration by probiotics in patients with functional dyspepsia. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Shanahan, E.R.; Raj, A.; Koloski, N.A.; Fletcher, L.; Morrison, M.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Holtmann, G. Dyspepsia and the microbiome: Time to focus on the small intestine. Gut 2017, 66, 1168–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroni Sterbini, F.; Palladini, A.; Masucci, L.; Cannistraci, C.V.; Pastorino, R.; Ianiro, G.; Bugli, F.; Martini, C.; Ricciardi, W.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors on the Gastric Mucosa-Associated Microbiota in Dyspeptic Patients. Appl. Environ. MicroBiol. 2016, 82, 6633–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, E.R.; Shah, A.; Do, A.; Fairlie, T.; Ghasemi, P.; Hansen, T.J.; Koloski, N.A.; Keely, S.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; et al. 146 - Duodenal Mucosa-Associated Microbiota (MAM) and Gastric Emptying: Veillonella in the Duodenal MAM Linked to slow Gastric Emptying. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, A.; Takagi, T.; Naito, Y.; Inoue, R.; Kashiwagi, S.; Mizushima, K.; Inada, Y.; Inoue, K.; Harusato, A.; Dohi, O.; et al. Higher Levels of Streptococcus in Upper Gastrointestinal Mucosa Associated with Symptoms in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. Digestion 2020, 101, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.Y.; Maattanen, P.; Napper, S.; Scruten, E.; Li, B.; Koike, Y.; Johnson-Henry, K.C.; Pierro, A.; Rossi, L.; Botts, S.R.; et al. Non-digestible oligosaccharides directly regulate host kinome to modulate host inflammatory responses without alterations in the gut microbiota. Microbiome 2017, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, T.; Takagi, A.; Uemura, N.; Inoue, K.; Sekino, H.; Kawashima, A.; Uchida, M.; Koga, Y. The Ameliorating Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri OLL2716 on Functional Dyspepsia in Helicobacter pylori-Uninfected Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Study. Digestion 2017, 96, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.M.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, F.; Tang, X. Efficacy of prebiotics and probiotics for functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.; Lembo, A.; Chey, W.D.; Zakko, S.; Ringel, Y.; Yu, J.; Mareya, S.M.; Shaw, A.L.; Bortey, E.; Forbes, W.P.; et al. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, K.; Sioulas, A.D.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. Rifaximin: The Revolutionary Antibiotic Approach for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, V.P.; Liu, K.S.; Lam, F.Y.; Hung, I.F.; Yuen, M.F.; Leung, W.K. Randomised clinical trial: Rifaximin versus placebo for the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, P.H.; Hilpusch, F.; Cavanagh, J.P.; Leikanger, I.S.; Kolstad, C.; Valle, P.C.; Goll, R. Faecal microbiota transplantation versus placebo for moderate-to-severe irritable bowel syndrome: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, single-centre trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ref. | Population | Population Synthesis (FD/Controls, n) | Technique for Microbiota Identification | Principal Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric fluid aspirate | ||||
| Nakae et al. [54] | Adult | 44/44 | 16S rRNA gene sequencing | Higher levels of Prevotella in FD, inverse correlation between Prevotella abundance and severity of PDS-FD |
| Igarashi et al. [55] | Adult | 21/21 | 16S rRNA gene sequencing | Higher Bacteroidetes > Proteobacteria abundance, absence of Acidobacteria in FD; lower Bacteroidetes < Proteobacteria abundance, presence of Acidobacteria in controls |
| Mucosa-associated microbiota (MAM) | ||||
| Zhong et al. [56] | Adult | 9/9 | 16S rRNA gene sequencing | Streptococcus was the predominant genus in both control and FD; inverse relationship between abundance of Streptococcus and Prevotella, Veillonella and Actinomyces; negative correlation between bacterial load and quality of life |
| Sterbini et al. [57] | Adult | 24 | 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing | Higher levels of Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria, and Actinobacteria; higher levels of Firmicutes (Streptococcaceae) and Streptococcus in treatment with proton pump inhibitors |
| Shanahan et al. [58] | Adult | 26/10 | 16S rRNA gene sequencing | Negative correlation between abundance of Veillonella and gastric emptying time |
| Fukui et al. [59] | Adult | 11/7 | 16S rRNA gene sequencing | Higher levels of Firmicutes in FD compared to healthy controls; at genus level, higher levels of Streptococcus in FD; Streptococcus relative abundance positively correlated with symptoms |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tziatzios, G.; Gkolfakis, P.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Mathur, R.; Pimentel, M.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Triantafyllou, K. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Functional Dyspepsia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050691
Tziatzios G, Gkolfakis P, Papanikolaou IS, Mathur R, Pimentel M, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Triantafyllou K. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Functional Dyspepsia. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(5):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050691
Chicago/Turabian StyleTziatzios, Georgios, Paraskevas Gkolfakis, Ioannis S. Papanikolaou, Ruchi Mathur, Mark Pimentel, Evangelos J. Giamarellos-Bourboulis, and Konstantinos Triantafyllou. 2020. "Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Functional Dyspepsia" Microorganisms 8, no. 5: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050691
APA StyleTziatzios, G., Gkolfakis, P., Papanikolaou, I. S., Mathur, R., Pimentel, M., Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E. J., & Triantafyllou, K. (2020). Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Functional Dyspepsia. Microorganisms, 8(5), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050691







