Gut Microbiota and Dietary Intake of Normal-Weight and Overweight Filipino Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Study Sites
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Dietary Data Collection
2.5. Energy, Macronutrient Dietary Fiber Assessment
2.6. Fecal Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.7. Library Preparation and 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.8. Sequencing Data Processing
2.9. Statistical Analysis of the Dietary Data
2.10. Statistical Analysis of the Gut Microbiota Data
2.11. Data Accessibility
3. Results
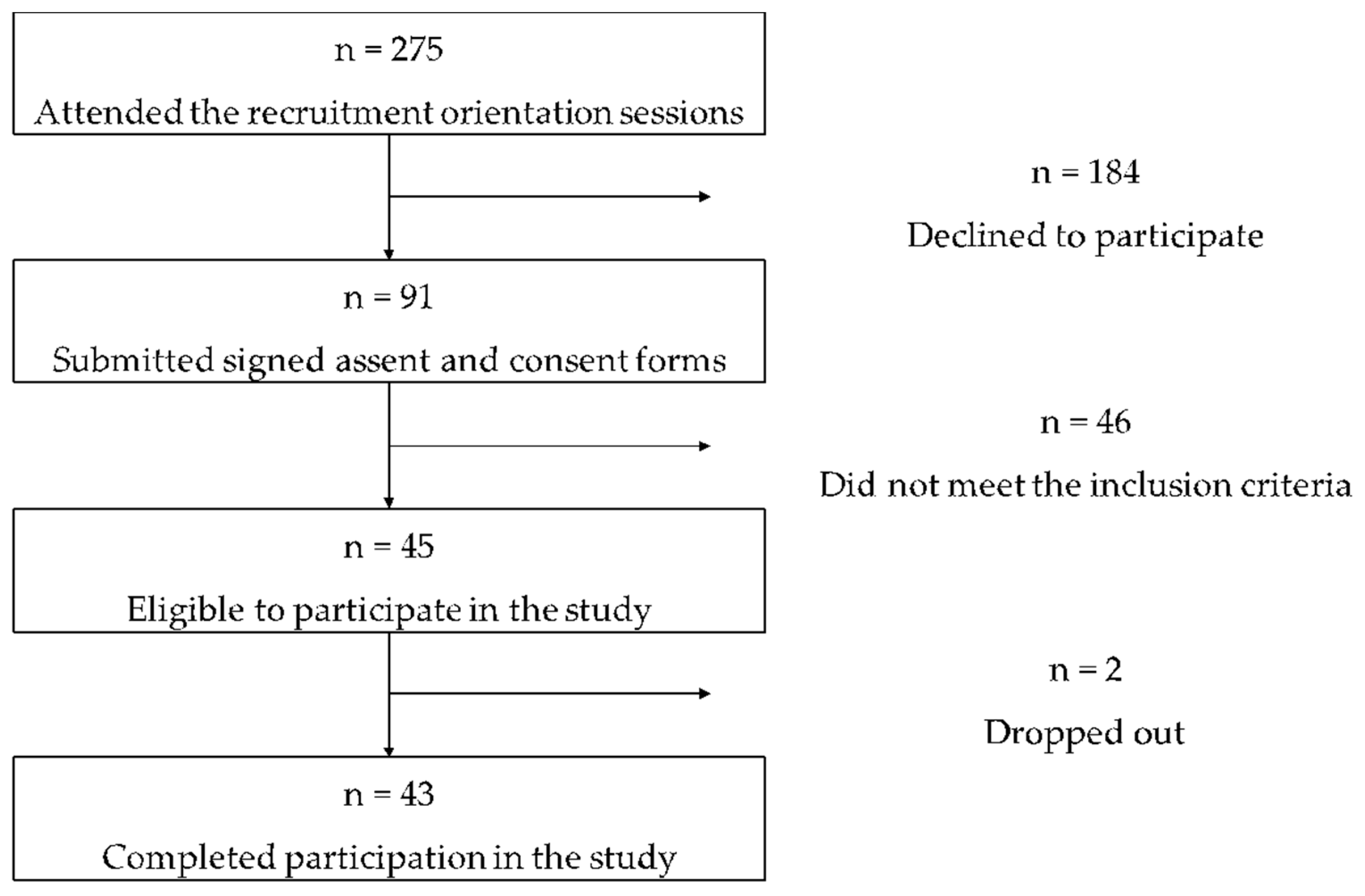
3.1. Study Participants
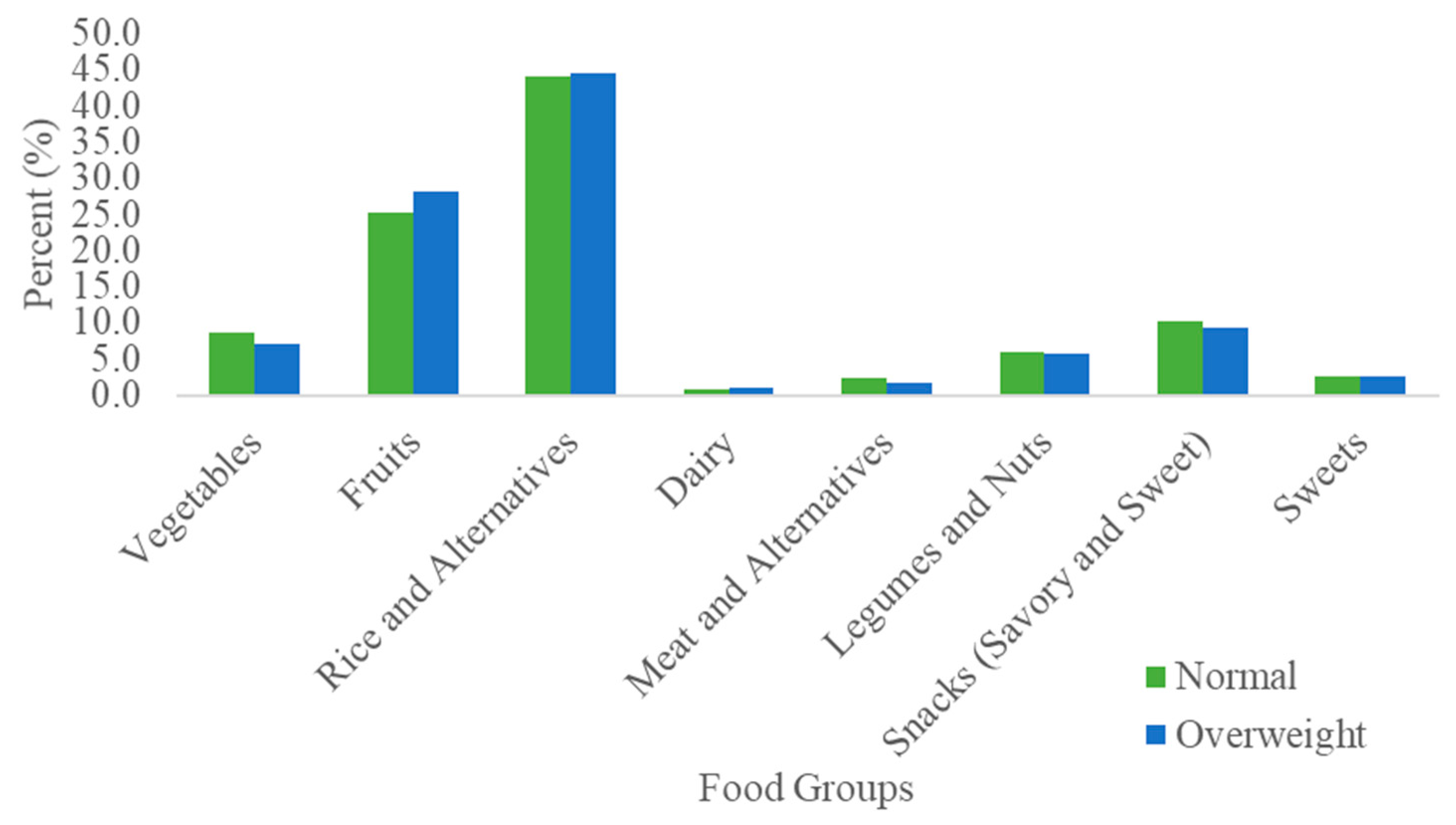
3.2. Dietary Fiber Intake by BMI
3.3. Sequencing Results
3.4. Alpha Diversity
3.5. Bacterial Community Structure
3.6. Differential Abundance Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fishbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deschausaux, M.; Bouter, K.E.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Groen, A.K.; Herrema, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Bakker, G.J.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.J.; van Raalte, D.H.; et al. Depicting the composition of gut microbiota in a population with varied ethnic origins but shared geography. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acd. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakayama, J.; Yamamoto, A.; Palermo-Conde, L.A.; Higashi, K.; Sonomoto, K.; Tan, J.; Lee, Y.K. Impact of westernized diet on gut microbiota in children on Leyte island. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Kamm, M.A.; Colombel, J.F.; Ng, S.C. Urbanization and the gut microbiota in health and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.; Watanabe, K.; Jiang, J.; Matsuda, K.; Chao, S.H.; Haryono, P.; La-ongkham, O.; Sarwoko, M.A.; Sujaya, I.N.; Zhao, L.; et al. Diversity in gut bacterial community of school-age children in Asia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rampelli, S.; Guenther, K.; Turroni, S.; Wolters, M.; Veidebaum, T.; Kourides, Y.; Molnar, D.; Lissner, L.; Benitez-Paez, A.; Sanz, Y.; et al. Pre-obese children’s dysbiotic gut microbiome and unhealthy diets may predict the development of obesity. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, R.; Tamburini, F.B.; Asiimwe, E.; Oduaran, O.; Hazelhurst, S.; Bhatt, A.S. Surveying gut microbiome research in Africans: Toward improved diversity and representation. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N.; et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, M.; Taylor, T.D. The human intestinal microbiome: A new frontier in human biology. DNA Res. 2009, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Nutrition Research Institute. Food Exchange Lists (FEL) for Meal Planning, 3rd ed.; Food and Nutrition Research Institute: Taguig City, Philippines, 1994.
- Department of Science and Technology-Food and Nutrition Research Institute. Philippine Nutrition Facts and Figures 2013: Food Consumption Survey; Department of Science and Technology-Food and Nutrition Research Institute: Taguig City, Philippines, 2015.
- Philippine Food Composition Tables. Available online: https://i.fnri.dost.gov.ph/fct/library (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65 (Suppl. 4), 1220S–1228S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Science and Technology-Food and Nutrition Research Institute. Philippines Dietary Reference Intakes 2015 Summary of Recommendations; Department of Science and Technology-Food and Nutrition Research Institute: Taguig City, Philippines, 2015; p. 14.
- Gao, X.; Jia, R.; Xie, L.; Kuang, L.; Feng, L.; Wan, C. Obesity in school-aged children and its correlation with gut E. coli and Bifidobacteria: A case-control study. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepp, E.; Lõivukene, K.; Julge, K.; Voor, T.; Mikelsaar, M. The association of gut microbiota with body weight and body mass index in preschool children of Estonia. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2013, 24, 19231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliomäki, M.; Collado, M.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Early differences in fecal microbiota composition in children may predict overweight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacio, A.; Fernandes, M.R.; Rodrigues, V.A.; Groppo, F.C.; Cardoso, A.L.; Avila-Campos, M.J.; Nakano, V. Correlation between body mass index and faecal microbiota from children. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 258–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippert, K.; Kedenko, L.; Antonielli, L.; Kedenko, I.; Gemeier, C.; Leitner, M.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Paulweber, B.; Hackl, E. Gut microbiota dysbiosis associated with glucose metabolism disorders and the metabolic syndrome in older adults. Benef. Microbes. 2017, 8, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachon, S.; Zhou, J.; Keenan, M.; Martin, R.; Marco, M.L. The intestinal microbiota in aged mice is modulated by dietary resistant starch and correlated with improvements in host responses. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 83, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byerley, L.O.; Samuelson, D.; Blanchard, E., IV; Luo, M.; Lorenzen, B.N.; Banks, S.; Ponder, M.A.; Welsh, D.A.; Taylor, C.M. Changes in the gut microbial communities following addition of walnuts to the diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 48, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Shen, X.; Wei, P. Alteration of the gut microbiota associated with childhood obesity by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. PeerJ 2020, 8, 8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrone, C.; Vajana, E.; Minuti, A.; Callegari, M.L.; Federico, A.; Loguercio, C.; Dallio, M.; Tolone, S.; Docimo, L.; Morelli, L. Postoperative changes in fecal bacterial communities and fermentation products in obese patients undergoing bilio-intestinal bypass. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, B.A.; Shapiro, J.A.; Church, T.R.; Miller, G.; Trinh-Shevrin, C.; Yuen, E.; Friedlander, C.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J. A taxonomic signature of obesity in a large study of American adults. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bond, S.E.; O’Toole, P.W.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F. Intestinal microbiota, diet and health. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 111, 387–402. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 2016, 65, 1812–1821, (verification in 2015). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušková, D.; Marounek, M. Fermentation of pectin and glucose, and activity of pectin-degrading enzymes in the rumen bacterium Lachnospira multiparus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 33, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, A.; Stewart, L.; Blanchard, J.; Leschine, S. Untangling the genetic basis of fibrolytic specialization by Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae in diverse gut communities. Diversity 2013, 5, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telle-Hansen, V.H.; Holven, K.B.; Ulven, S.M. Impact of a healthy dietary pattern on gut microbiota and systemic inflammation in humans. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, D.R.; Rhoades, N.; Mercado, J.; Argueta, P.; Lopez, U.; Flores, G.E. Dietary Habits of 2-to 9-Year-Old American Children Are Associated with Gut Microbiome Composition. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 120, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayengbam, S.; Lambert, J.E.; Parnell, J.A.; Tunnicliffe, J.M.; Nicolucci, A.C.; Han, J.; Sturzenegger, T.; Shearer, J.; Mickiewicz, B.; Vogel, H.J.; et al. Impact of dietary fiber supplementation on modulating microbiota–host–metabolic axes in obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 64, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisuse, J.; La-Ongkham, O.; Nakphaichit, M.; Therdtatha, P.; Momoda, R.; Tanaka, M.; Fukuda, S.; Popluevhai, S.; Kepechara, K.; Sonomoto, K.; et al. Urban diets linked to gut microbiome and metabolome alterations in children: A comparative cross-sectional study in Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Martínez, I.; Walter, J.; Keshavarzian, A.; Rose, D.J. In vitro characterization of the impact of selected dietary fibers on fecal microbiota composition and short chain fatty acid production. Anaerobe 2013, 23, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayeni, F.A.; Biagi, E.; Rampelli, S.; Fiori, J.; Soverini, M.; Audu, H.J.; Cristino, S.; Caporali, L.; Schnorr, S.L.; Carelli, V.; et al. Infant and adult gut microbiome and metabolome in rural Bassa and urban settlers from Nigeria. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3056–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olukotun, O.; Seal, N. A systematic review of dietary assessment tools for children age 11 years and younger. ICAN Infant Child Adolesc. Nutr. 2015, 7, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Normal-Weight (n = 32) | Overweight (n = 11) | p Value * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years, (SD) | 9.2 (0.9) | 8.6 (0.9) | 0.50 | |
| Sex, n (%) | Male Female | 11 (34) 21 (66) | 5 (45) 6 (55) | |
| Deworming, n (%) | With Without | 17 (53) 15 (47) | 3 (27) 8 (73) | 0.14 |
| Antibiotic use in the past 6 months, n (%) | With Without | 8 (25) 23 (72) | 1 (9) 10 (91) | 0.42 |
| Probiotic intake in the past 6 months, n (%) | With Without | 3 (9) 29 (91) | 0 (0) 10 (91) | 0.14 |
| Normal-Weight (n = 32) | Overweight (n = 11) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy intake (kcal) | 1735.0 (461) | 1950 (546) | 0.20 |
| Carbohydrate intake (g) | 285.5 (74.8) | 322.9 (21.1) | 0.20 |
| Protein intake (g) | 52.9 (16.8) | 60.1 (24.7) | 0.50 |
| Fat intake (g) | 42.4 (13.3) | 46.6 (21.6) | 0.90 |
| Energy-adjusted dietary fiber intake (g) | 14.3 (5.1) | 16.7 (6.0) | 0.20 |
| Meeting the recommended energy intake, n (%) | 16 (50.0) | 4 (36.4) | 0.43 |
| Meeting the recommended fiber intake n (%) | 12 (37.5) | 8 (73.0) | 0.04 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golloso-Gubat, M.J.; Ducarmon, Q.R.; Tan, R.C.A.; Zwittink, R.D.; Kuijper, E.J.; Nacis, J.S.; Santos, N.L.C. Gut Microbiota and Dietary Intake of Normal-Weight and Overweight Filipino Children. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071015
Golloso-Gubat MJ, Ducarmon QR, Tan RCA, Zwittink RD, Kuijper EJ, Nacis JS, Santos NLC. Gut Microbiota and Dietary Intake of Normal-Weight and Overweight Filipino Children. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(7):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolloso-Gubat, Maria Julia, Quinten R. Ducarmon, Robby Carlo A. Tan, Romy D. Zwittink, Ed J. Kuijper, Jacus S. Nacis, and Noelle Lyn C. Santos. 2020. "Gut Microbiota and Dietary Intake of Normal-Weight and Overweight Filipino Children" Microorganisms 8, no. 7: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071015
APA StyleGolloso-Gubat, M. J., Ducarmon, Q. R., Tan, R. C. A., Zwittink, R. D., Kuijper, E. J., Nacis, J. S., & Santos, N. L. C. (2020). Gut Microbiota and Dietary Intake of Normal-Weight and Overweight Filipino Children. Microorganisms, 8(7), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071015





