Comparative Analysis of the Ecological Succession of Microbial Communities on Two Artificial Reef Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Preparation and Deployment of AR Blocks
2.2. Sampling Procedure and Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
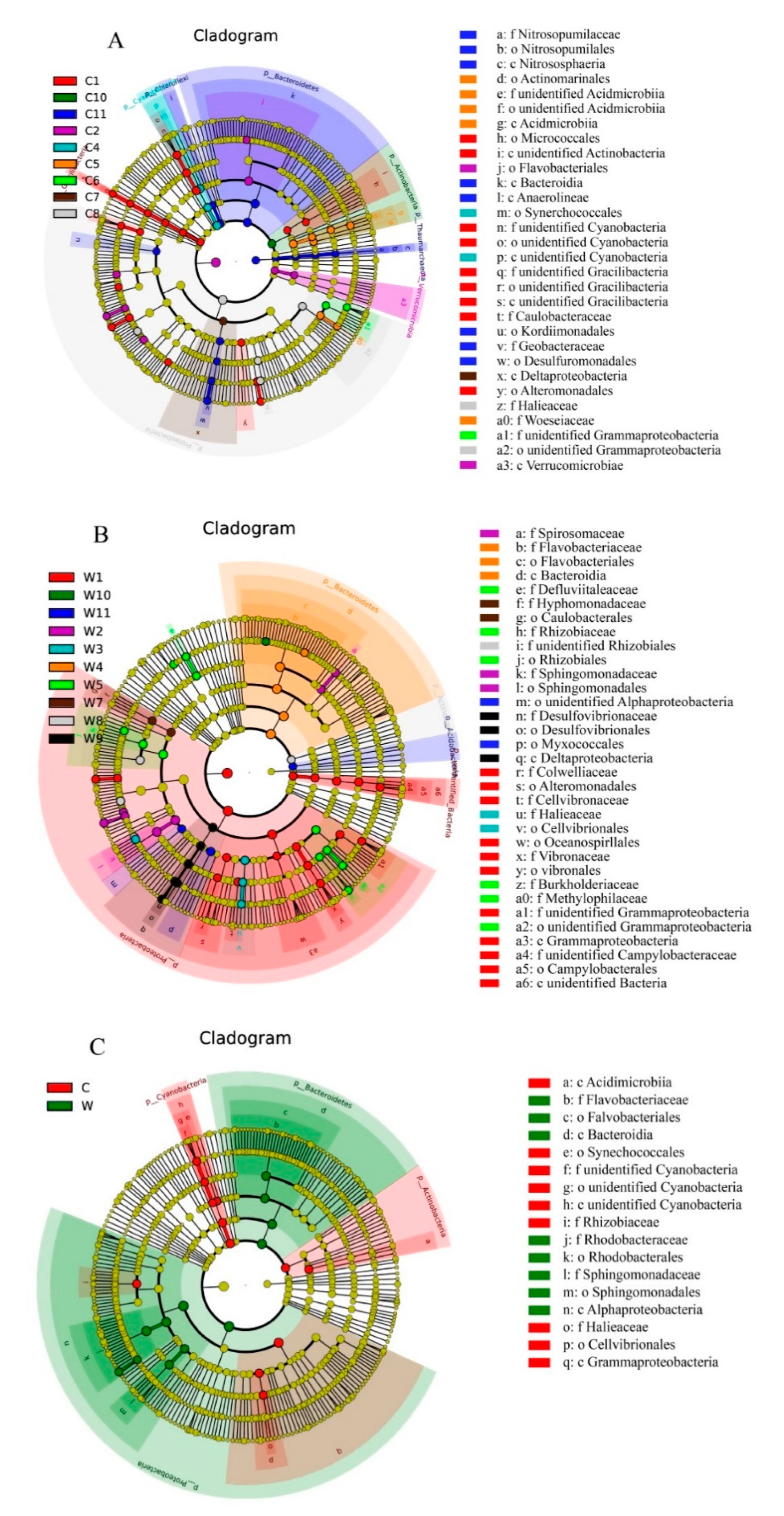
2.4. Statistics and Bioinformatics Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Alpha and Beta Diversity of Microbial Communities of Concrete and Wooden Artificial Reefs
3.2. Temporal Succession of Microbial Communities
3.3. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
3.4. Succession of Macrobiotic Biofouling Community and Correlation with Microbial Community
3.5. Environmental Variables and Relationship with the Microbial Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y. Numerical simulation of effect of guide plate on flow field of artificial reef. Ocean Eng. 2016, 116, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.O.; Otake, S.; Kim, J.K. Transition of artificial reefs (ARs) research and its prospects. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 154, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svane, I.; Petersen, J.K. On the problems of epibioses, fouling and artificial reefs, a review. Mar. Ecol. 2001, 22, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, M.I.; Torres, P.; Díaz, C.; Zamora, V.; López, J.; Olivares, G. Ecological succession of benthic organisms on niche-type artificial reefs. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokwu, N.D.; Vaz, P.G.; Bradshaw, T.; Blake, A.; Henessey, C.; Merten, E. Effects of substrate on the benthic macroinvertebrate community: An experimental approach. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, P.; Tang, D.; Qin, C. Ecological effects of artificial reefs in Daya Bay of China observed from satellite and in situ measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.R.; Ehrenberg, A.; Feldrappe, V.; Kröncke, I.; Bischof, K. The role of artificial material for benthic communities-Establishing different concrete materials as hard bottom environments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J. Epifaunal colonization of the Loch Linnhe artificial reef: Influence of substratum on epifaunal assemblage structure. Biofouling 2005, 21, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.X.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, X. Relationship between environmental factors and benthic macroalgae communities of artificial reefs in Laoshan Bay. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnolo, A.; Cuicchi, C.; Punzo, E.; Santelli, A.; Scarcella, G.; Fabi, G. Patterns of colonization and succession of benthic assemblages in two artificial substrates. J. Sea Res. 2014, 88, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushiama, S.; Smith, J.A.; Suthers, I.M.; Lowry, M.; Johnston, E.L. The effects of substratum material and surface orientation on the developing epibenthic community on a designed artifcial reef. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G. Microbial Colonization in Marine Environments: Overview of Current Knowledge and Emerging Research Topics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorczyk, M.; Pogorzelski, S.J.; Pospiech, A.; Boniewicz-Szmyt, K. Monitoring of marine biofilm formation dynamics at submerged solid surfaces with multi-technique sensors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, A.L.; Robicheau, B.M.; Walker, A.K. Fungal diversity of marine biofilms on artificial reefs in the north-central Gulf of Mexico. Bot. Mar. 2016, 59, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Ammon, U.; Wood, S.A.; Laroche, O.; Zaiko, A.; Tait, L.; Lavery, S.; Inglis, G.; Pochon, X. The impact of artificial surfaces on marine bacterial and eukaryotic biofouling assemblages: A high-throughput sequencing analysis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 133, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, J.F.; Barani, A.; Garnier, C.; Réhel, K.; Urvois, F.; LePoupon, C.; Bouchez, A.; Debroas, D.; Bressy, C. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Marine Biofilm Communities Colonizing Artificial Substrata Including Antifouling Coatings in Contrasted French Coastal Environments. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukrishnan, T.; Khaburi, M.A.; Abed, R.M.M. Fouling Microbial Communities on Plastics Compared with Wood and Steel: Are They Substrate- or Location-Specific? Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.R.; Liang, X.Y.; Zeng, J. Preliminary study on effects of accrete organisms of artificial reef material. South China Fish. Sci. 2006, 2, 34–38, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chlayon, T.; Iwanami, M.; Chijiwa, N. Combined protective action of barnacles and biofilm on concrete surface in intertidal areas. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 179, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UCHIME2: Improved chimera prediction for amplicon sequencing. BioRxiv 2016, 74252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome. Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, R.; Piedrahita-Quintero, P.; Garcia-Sucerquia, J. Image processing and computing for digital holography with ImageJ. Opt. Pura Apl. 2015, 48, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.S.; Yu, Z.; Pan, S.Y.; Huang, J.M.; Meng, F.G. Deciphering the succession dynamics of dominant and rare genera in biofilm development process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Guo, Z.S.; Zhu, L.X.; Liang, Z.L. Structural design principle and research progress of artificial reef. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 1881–1889, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Catão, E.C.P.; Pollet, T.; Misson, B.; Garnier, C.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Barry-Martinet, R.; Maintenay, M.; Bressy, C.; Briand, J.F. Shear Stress as a Major Driver of Marine Biofilm Communities in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejdandzic, M.; Ivankovic, T.; Pfannkuchen, M.; Godrijan, J.; Pfannkuchen, D.M.; Hrenovi, J.; Ljubei, Z. Colonization of diatoms and bacteria on artificial substrates in the northeastern coastal Adriatic Sea. Acta Bot. Croat. 2015, 74, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, T.; Berdjeb, L.; Garnier, C.; Durrieu, G.; Le Poupon, C.; Misson, B.; Jean-Francois, B. Prokaryotic community successions and interactions in marine bioflms: The key role of Flavobacteriia. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fy083. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, R.M.M.; Fahdi, D.I.; Muthukrishnan, T. Shortterm succession of marine microbial fouling communities and the identification of primary and secondary colonizers. Biofouling 2019, 35, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmström, C.; Rittschof, D.; Kjelleberg, S. Inhibition of settlement by larvae of Balanus amphitrite and Ciona intestinalis by a surface-colonizing marine bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2111–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Guo, F.; Geng, X.Y.; Wei, J.L.; Li, X.; Li, J.J. Seasonal changes and diversity of bacteria in Bohai Bay by RFLP analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rDNA gene fragments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Paruch, L.; Paruch, A.M.; Eiken, H.G.; Skogen, M.; Sorheim, R. Seasonal dynamics of lotic bacterial communities assessed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon deep sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, O.R. Marine and estuarine natural microbial biofilms: Ecological and biogeochemical dimensions. AIMS Microbiol. 2016, 2, 304–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsov, S.; Abed, R.M.M.; Voolstra, C.R. The effect of surface colour on the formation of marine micro and macrofouling communities. Biofouling 2013, 29, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.T.; Sousa, A.G.G.; Azevedo, J.; Rego, A.; Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V. Distinct Temporal Succession of Bacterial Communities in Early Marine Biofilms in a Portuguese Atlantic Port. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salta, M.; Wharton, J.A.; Blache, Y.; Stokes, K.R.; Briand, J.F. Marine biofilms on artificial surfaces: Structure and dynamics. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2879–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.M.Y.; Thiyagarajan, V.; Tsoi, M.M.Y.; Qian, P.Y. Qualitative and quantitative changes in marine biofilms as a function of temperature and salinity in summer and winter. Biofilms 2005, 2, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.J.; Webb, H.K.; Truong, V.K.; Hasan, J.; Ivanova, E.P. Surface topographical factors influencing bacterial attachment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 179, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Osborn, A.M.; Duhaime, M.B. Microbes on a bottle: Substrate, season and geography influence community composition of microbes colonizing marine plastic debris. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Wichels, A.; Krohne, G.; Gerdts, G. Mature bioflm communities on synthetic polymers in seawater-Specifc or general? Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 142, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.Y.; Li, T.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xia, J.; Jin, W.L. Influence of marine organisms adhesion on durability of concrete structures. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2020, 5, 116–123, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Magoulick, D.D. Effect of wood hardness, condition, texture and substrate type on community structure of stream invertebrates. Am. Midl. Nat. 1998, 139, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.K.Y. Algal and sessile invertebrate recruitment onto an experimental PFA-concrete artificial reef in Hong Kong. Asian Mar. Biol. 2000, 17, 55–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, J.M.Y.; Thiyagarajan, V.; Pechenik, J.A.; Hung, O.S.; Qian, P.Y. Influence of bacteria and diatoms in biofilms on metamorphosis of the marine slipper limpet Crepidula Onyx. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1417–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Kavouras, J.H.; Maki, J.S. Effects of biofilms on zebra mussel postveliger attachment to artificial surfaces. Invertebr. Biol. 2003, 122, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, J.S.; Rittschof, D.; Costlow, J.D.; Mitchell, R. Inhibition of attachment of larval barnacles, Balanus amphitrite, by bacterial surface films. Mar. Biol. 1988, 97, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Guo, X.P.; Ding, D.W.; Gao, W.; Huang, D.F.; Chen, Y.R.; Liang, X. Interactions between natural bioflm, substratum surface wettability, and mussel plantigrade settlement. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Shen, P.J.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.F.; Bao, W.Y.; Li, J.L. Larval settlement and metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus coruscus in response to monospecific bacterial biofilms. Biofouling 2013, 29, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnig, S.C.; Lorenz, A.W. Substrate-specific macroinvertebrate diversity patterns following stream restoration. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 70, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.S.; Zalmon, I.R.; Love, M. Overview and trends of ecological and socioeconomic research on artificial reefs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 145, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, P.G.; Dias, S.; Pinto, P.; Merten, E.C.; Robinson, C.T.; Warren, D.R.; Rego, F.C. Effects of burn status and preconditioning on wood colonization by stream macroinvertebrates. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 33, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, X.F.; Liu, C.G. Corrosion life of artificial reef under natural seawater conditions. Mar. Sci. B 2019, 21, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.T.; Nie, Z.Y.; Guo, Z.S.; Zhu, L.X.; Cong, W.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Z.L. The Application of Seabed Silt in the Preparation of Artificial Algal Reefs. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Scheme 1 | 1st Week | 2nd Week | 3rd Week | 4th Week | 5th Week | 6th Week | 7th Week | 8th Week | 3 Month | 4 Month | 5 Month | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | W1 | C2 | W2 | C3 | W3 | C4 | W4 | C5 | W5 | C6 | W6 | C7 | W7 | C8 | W8 | C9 | W9 | C10 | W10 | C11 | W11 | |
| Hydroides ezoensis | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| Ciona intestinalis | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||
| Watersipora subovoidea | ○ | ○ | ● | ● | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||
| Crassostrea gigas | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||||||
| Anomia chinensis | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||
| Mitrella bella | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||
| Chlamys farreri | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Balanus amphitrite | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||
| Leptochiton assimilis | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gammarus sp. | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Lumbrineridae sp. | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ophiactis affinis | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Mytilus edulis | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ceramiales sp. | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sample | DO (mg/L) | T (°C) | PH | S (‰) | DIN (μg/L) | PO4-P (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1/W1 | 5.59 | 20.7 | 7.89 | 31.8 | 59.44 | 10.25 |
| C2/W2 | 5.91 | 25.3 | 7.86 | 31.7 | 54.64 | 7.75 |
| C3/W3 | 6.23 | 26.3 | 7.94 | 31.9 | 73.00 | 8.17 |
| C4/W4 | 5.26 | 25.5 | 8.05 | 31.8 | 65.38 | 9.42 |
| C5/W5 | 4.91 | 24.0 | 7.92 | 31.9 | 74.94 | 10.67 |
| C6/W6 | 5.55 | 24.9 | 7.95 | 31.7 | 70.37 | 10.25 |
| C7/W7 | 5.88 | 26.4 | 7.99 | 31.4 | 75.24 | 6.53 |
| C8/W8 | 5.51 | 26.2 | 8.07 | 31.4 | 100.00 | 11.50 |
| C9/W9 | 6.46 | 21.7 | 8.13 | 30.8 | 71.48 | 13.75 |
| C10/W10 | 6.45 | 17.4 | 8.17 | 31.0 | 72.73 | 5.02 |
| C11/W11 | 8.22 | 7.80 | 8.52 | 31.7 | 74.99 | 8.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Cong, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, Z. Comparative Analysis of the Ecological Succession of Microbial Communities on Two Artificial Reef Materials. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010120
Guo Z, Wang L, Cong W, Jiang Z, Liang Z. Comparative Analysis of the Ecological Succession of Microbial Communities on Two Artificial Reef Materials. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010120
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhansheng, Lu Wang, Wei Cong, Zhaoyang Jiang, and Zhenlin Liang. 2021. "Comparative Analysis of the Ecological Succession of Microbial Communities on Two Artificial Reef Materials" Microorganisms 9, no. 1: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010120
APA StyleGuo, Z., Wang, L., Cong, W., Jiang, Z., & Liang, Z. (2021). Comparative Analysis of the Ecological Succession of Microbial Communities on Two Artificial Reef Materials. Microorganisms, 9(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010120




