Inactivation of Schistosoma Using Low-Temperature Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Genus Schistosoma
1.2. Non-Thermal Plasma
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Corona Discharges
2.2. Preparation of Plasma-Activated Water
2.3. Preparation of Infectious Larvae
2.4. Infectious Larvae Inactivation by Plasma
2.5. Inactivation of Schistosoma Infectious Larvae in PAW
3. Results
3.1. Direct Action of Discharges on Cercariae
3.2. Effect of PAW on Cercariae
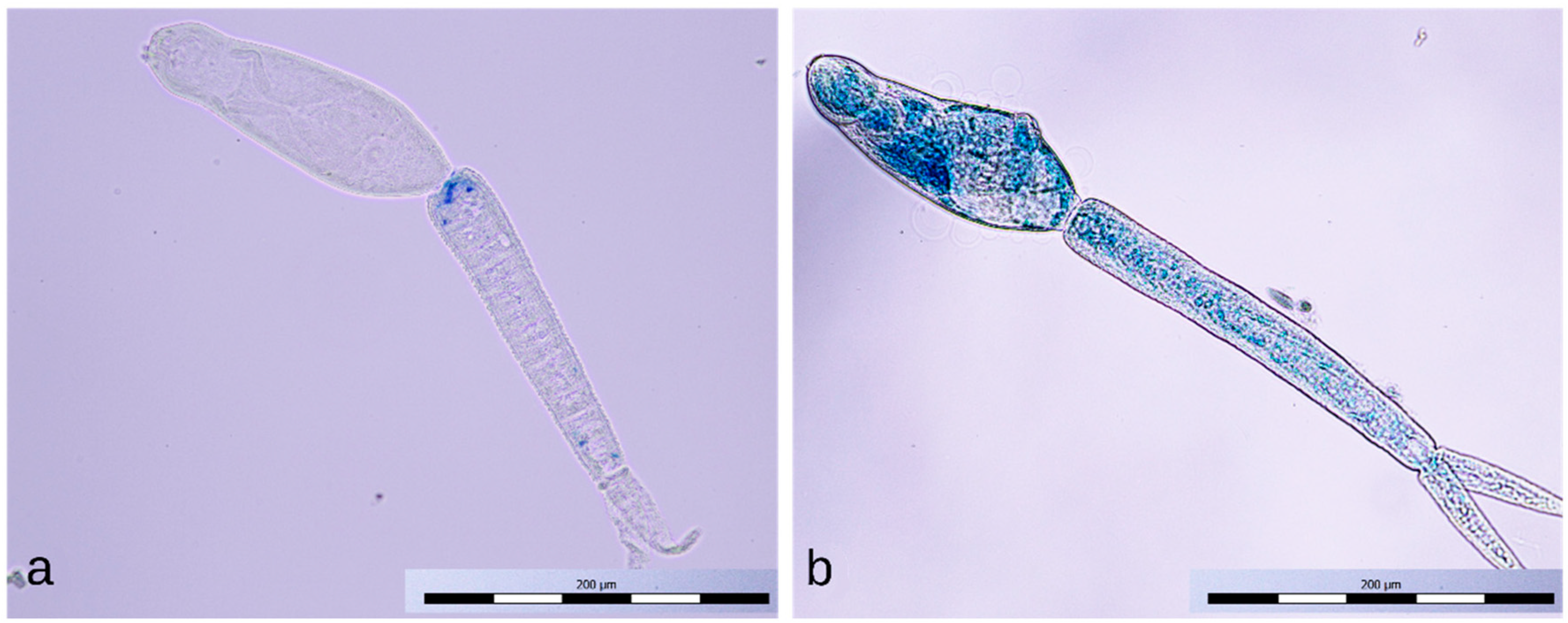
3.3. Microscopic Observation of Exposed Cercariae
3.4. Direct Action of Discharges on Miracidia
3.5. Effect of PAW on Miracidia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Beltrame, A. Schistosomiasis transmission in Europe. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissier, J.; Grech-Angelini, S.; Webster, B.L.; Allienne, J.-F.; Huyse, T.; Mas-Coma, S.; Toulza, E.; Barré-Cardi, H.; Rollinson, D.; Kincaid-Smith, J.; et al. Outbreak of urogenital schistosomiasis in Corsica (France): An epidemiological case study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelwan, M.L. Schistosomiasis: Life Cycle, Diagnosis, and Control. Curr. Ther. Res. 2019, 91, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedail, S.S. Intestinal Schistosomiasis in Africa. In Digestive Diseases in Sub-Saharan Africa; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, F. Schistosomiasis. In Current Protocols in Immunology; Coligan, J.E., Bierer, B.E., Margulies, D.H., Shevach, E.M., Strober, W., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; p. im1901s28. [Google Scholar]
- Dziwornu, G.A.; Attram, H.D.; Gachuhi, S.; Chibale, K. Chemotherapy for human schistosomiasis: How far have we come? What’s new? Where do we go from here? RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 455–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiper, R.T.; Atkinson, E.L. Observations on the Spread of Asiatic Schistosomiasis. BMJ 1915, 1, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, L.; Grimes, J.E.T.; Templeton, M.R. The effectiveness of water treatment processes against schistosome cercariae: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asch, H.L. Effect of selected chemical agents on longevity and infectivity of Schistosoma mansoni cercariae. Exp. Parasitol. 1975, 38, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, K. Slow Sand Filtration for Cercarial Control in North Cameroon Village Water Supply. Water Sci. Technol. 1982, 14, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.; Sylivester, Y.D.; Zerefa, M.D.; Maru, M.; Allan, F.; Zewge, F.; Emery, A.M.; Kinung’Hi, S.; Templeton, M.R. Chlorination of Schistosoma mansoni cercariae. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppel, A.; Shi, Y.E.; Moloney, N.A. Schistosoma mansoni and S. japonicum: Comparison of levels of ultraviolet irradiation for vaccination of mice with cercariae. Parasitology 1990, 101, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlbeck, J.; Schnabel, U.; Polak, M.; Winter, J.; Von Woedtke, T.; Brandenburg, R.; Hagen, T.V.D.; Weltmann, K.-D. Low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma sources for microbial decontamination. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khun, J.; Scholtz, V.; Hozák, P.; Fitl, P.; Julák, J. Various DC-driven point-to-plain discharges as non-thermal plasma sources and their bactericidal effects. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2018, 27, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M. Plasma Medicine: A Brief Introduction. Plasma 2018, 1, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laroussi, M. Low-Temperature Plasmas for Medicine? IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2009, 37, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M.; Lu, X.; Keidar, M. Perspective: The physics, diagnostics, and applications of atmospheric pressure low temperature plasma sources used in plasma medicine. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M.; Akan, T. Arc-Free Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Jets: A Review. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimončicová, J.; Kryštofová, S.; Medvecká, V.; Ďurišová, K.; Kaliňáková, B. Technical applications of plasma treatments: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5117–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousfi, M.; Merbahi, N.; Sarrette, J.P.; Eichwald, O.; Ricard, A.; Gardou, J.; Ducasse, O.; Benhenni, M. Non Thermal Plasma Sources of Production of Active Species for Biomedical Uses: Analyses, Optimization and Prospect. In Biomedical Engineering—Frontiers and Challenges; Fazel, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tendero, C.; Tixier, C.; Tristant, P.; Desmaison, J.; Leprince, P. Atmospheric pressure plasmas: A review. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2006, 61, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, P.; Ziuzina, D.; Han, L.; Cullen, P.; Gilmore, B.F. Microbiological interactions with cold plasma. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Patange, A.; Sunabcd, D.-W.; Tiwari, B.K. Plasma-activated water: Physicochemical properties, microbial inactivation mechanisms, factors influencing antimicrobial effectiveness, and applications in the food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3951–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julák, J.; Scholtz, V.; Vaňková, E. Medically important biofilms and non-thermal plasma. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metelmann, H.-R.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.-D. Plasmamedizin; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gweon, B.; Kim, K.; Choe, W.; Shin, J.H. Therapeutic Uses of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma: Cancer and Wound. In Biomedical Engineering: Frontier Research and Converging Technologies; Jo, H., Jun, H.-W., Shin, J., Lee, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9, pp. 357–385. [Google Scholar]
- Keidar, M.; Yan, D.; Beilis, I.I.; Trink, B.; Sherman, J.H. Plasmas for Treating Cancer: Opportunities for Adaptive and Self-Adaptive Approaches. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julák, J.; Hujacová, A.; Scholtz, V.; Khun, J.; Holada, K. Contribution to the Chemistry of Plasma-Activated Water. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2018, 44, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Xian, Y.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Lu, X.; Cullen, P.J.; Ostrikov, K.; Bazaka, K. Plasma-activated water: Generation, origin of reactive species and biological applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 303001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Al-Sharify, T.A.; Al-Obaidy, B.W.; Al-Azawi, A.M. Investigative Study on the Interaction and Applications of Plasma Activated Water (PAW). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 870, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 263001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.; Turner, M.M. Atomic oxygen patterning from a biomedical needle-plasma source. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 123301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.X.; Liu, Z.C.; Chen, C.; Yang, A.J.; Li, D.; Rong, M.Z.; Chen, H.L.; Kong, M.G. Aqueous reactive species induced by a surface air discharge: Heterogeneous mass transfer and liquid chemistry pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunov, O.; Zablotskii, V.; Churpita, O.; Jäger, A.; Polívka, L.; Syková, E.; Dejneka, A.; Kubinová, Š. The interplay between biological and physical scenarios of bacterial death induced by non-thermal plasma. Biomaterials 2016, 82, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julák, J.; Soušková, H.; Scholtz, V.; Kvasničková, E.; Savická, D.; Kříha, V. Comparison of fungicidal properties of non-thermal plasma produced by corona discharge and dielectric barrier discharge. Folia Microbiol. 2017, 63, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Yadav, B.; Roopesh, M.; Jo, C. Cold Plasma for Effective Fungal and Mycotoxin Control in Foods: Mechanisms, Inactivation Effects, and Applications: Cold plasma for effective fungal…. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 18, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, J.; Kirf, D.; Garvey, M.; Rowan, N.J. Disinfection and toxicological assessments of pulsed UV and pulsed-plasma gas-discharge treated-water containing the waterborne protozoan enteroparasite Cryptosporidium parvum. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 94, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, N. Defining Established and Emerging Microbial Risks in the Aquatic Environment: Current Knowledge, Implications, and Outlooks. Int. J. Microbiol. 2011, 2011, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heaselgrave, W.; Shama, G.; Andrew, P.W.; Kong, M.G. Inactivation of Acanthamoeba spp. and Other Ocular Pathogens by Application of Cold Atmospheric Gas Plasma. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3143–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Wang, F.-P.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Non-equilibrium plasma prevention of Schistosoma japonicum transmission. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hozák, P.; Scholtz, V.; Khun, J.; Mertová, D.; Vaňková, E.; Julák, J. Further contribution to the chemistry of plasma-activated water: Influence on bacteria in planktonic and biofilm forms. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2018, 44, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Exposure Time (min) | pH | NO3− (mg·L−1) | NO2− (mg·L−1) | H2O2 (mg·L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unexposed | 0 | 7 | <15 | 0 | 0 |
| positive discharge | 2 | 6 | 250 | 0 | 25 |
| 30 | 4 | >500 | 40 | >100 | |
| negative discharge | 8 | 6 | 250 | 0 | 10 |
| 30 | 4 | >500 | 40 | 10 | |
| axial discharge | 75 | 6 | 500 | 40 | 25 |
| Damage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Type I normal movement | Fast swimming employing tail movement |
| Type II resting position | Floating in a vertical position without movement |
| Type III sinking to the bottom | No movement; sinking to the bottom |
| Type IV crawling at the bottom | Spasmodic motion at the bottom |
| Type V normal movement with tail detachment | Active crawling of the cercarial body at the bottom |
| Type VI agony | Occasional twitches at the bottom |
| Type VII death | No activity |
| Type VIII death with tail detachment | No activity; the tails detached |
| Damage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Type I normal movement | Swimming in the water |
| Type II slow motion | Floating with active movement rarely seen |
| Type III crawling at the bottom | Active movement at the bottom |
| Type IV agony | Occasional twitches at the bottom |
| Type V death | No activity |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hejzlarová, S.; Chanová, M.; Khun, J.; Julák, J.; Scholtz, V. Inactivation of Schistosoma Using Low-Temperature Plasma. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010032
Hejzlarová S, Chanová M, Khun J, Julák J, Scholtz V. Inactivation of Schistosoma Using Low-Temperature Plasma. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleHejzlarová, Silvie, Marta Chanová, Josef Khun, Jaroslav Julák, and Vladimír Scholtz. 2021. "Inactivation of Schistosoma Using Low-Temperature Plasma" Microorganisms 9, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010032
APA StyleHejzlarová, S., Chanová, M., Khun, J., Julák, J., & Scholtz, V. (2021). Inactivation of Schistosoma Using Low-Temperature Plasma. Microorganisms, 9(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010032





