Impact of Helicobacter pylori-Related Metabolic Syndrome Parameters on Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
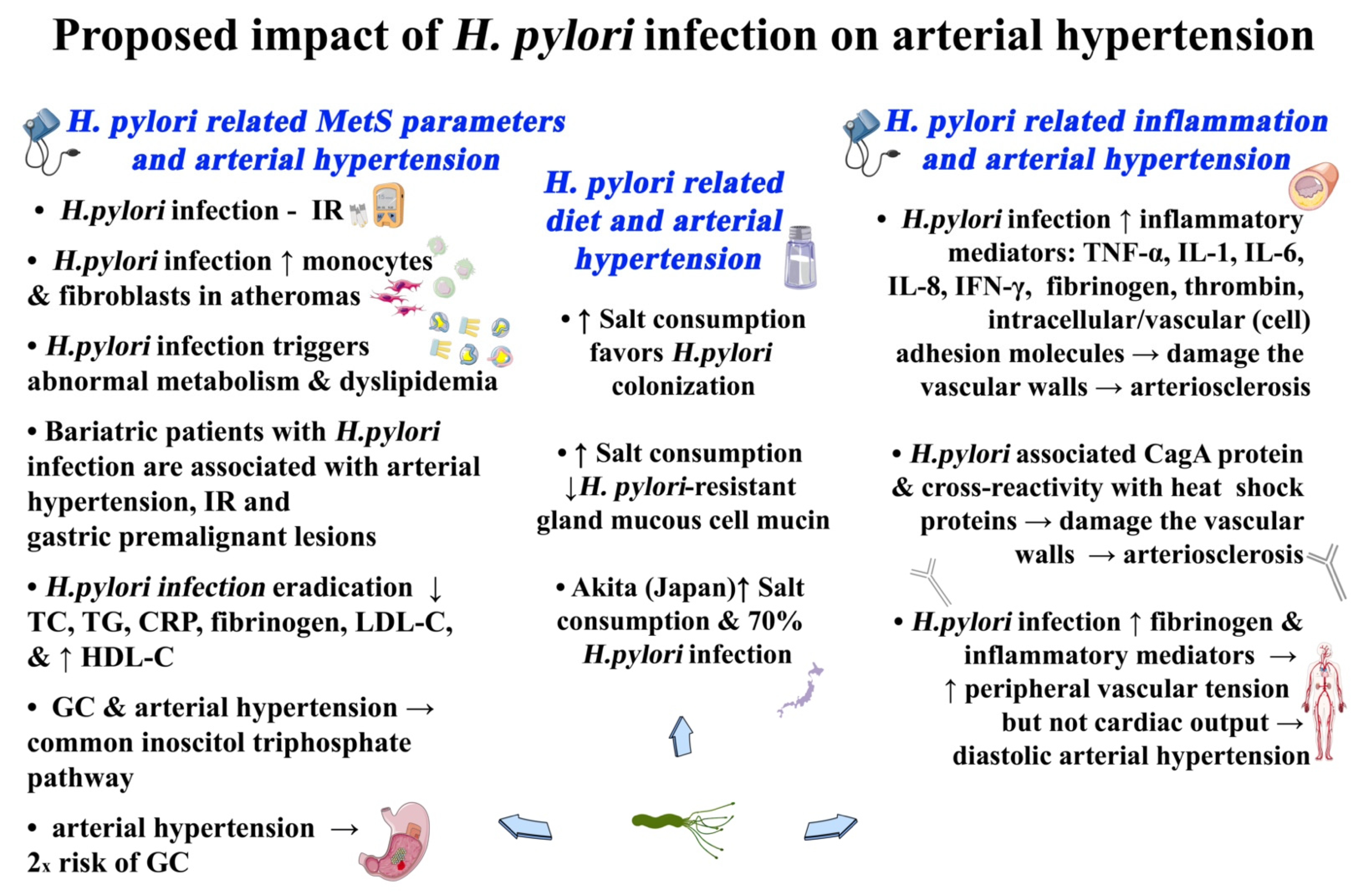
2. H. pylori-Related Arterial Hypertension
2.1. H. pylori and Mets-Related Diet and Arterial Hypertension
2.2. H. pylori-Related MetS-Induced Inflammation and Arterial Hypertension
| Mechanism | Comment | References |
|---|---|---|
| Upregulation of inflammatory mediators | MetS-related inflammatory mediators damage directly or indirectly the vascular walls and trigger atherosclerosis | [93,94,95,96,97] |
| Cag A | H. pylori virulence factor connected with: (1) greater inflammatory response, (2) atherosclerosis, and (3) coronary artery disease. | [100,101,102] |
| VacA | H. pylori virulence factor connected with: (1) gastric inflammation and carcinogenesis, (2) chemotactic activation of bone marrow-derived mast cells and stimulation and damage to the blood–brain barrier, (3) promotion of intracellular H. pylori survival, and (4) brain access of activated monocytes (the Trojan horse theory) | [45,49] |
| Cross reactivity of H. pylori | Autoimmune response triggering by H. pylori cross-reactivity → vascular endothelial damage → MetS-related ischemic disorders | [108,109,110] |
| Atrophic gastritis | Vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency induced by H. pylori and/or MetS → hyperhomocysteinemia resulting in: (1) vascular endothelial cells damage and (2) MetS-related atherosclerosis—arterial hypertension | [111,112,113,114,115,116] |
| Diastolic blood pressure | Higher concentrations of H. pylori/MetS-related fibrinogen → inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase → vasoconstriction and augmented peripheral vascular tension but not cardiac output → isolated diastolic blood pressure | [117,118] |
2.3. H. pylori-Related MetS Parameters and Arterial Hypertension
2.4. H. pylori and MetS-Related NAFLD and Arterial Hypertension
3. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.; Alcantara, R.; Popli, T.; Tariq, U.; Sood, A.; Mahajan, S.; Ayele, H.; Rajeswaran, Y.; Vyas, A.V. Firibastat: A Novel Brain Aminopeptidase Inhibitor—A New Era of Antihypertensive therapy. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 100859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis-Blake, J.M.; Evans, C.V.; Webber, E.M.; Coppola, E.L.; Perdue, L.A.; Weyrich, M.S. Screening for Hypertension in Adults. JAMA 2021, 325, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguedas, J.A.; Leiva, V.; Wright, J.M. Blood pressure targets in adults with hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD004349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Bentham, J.; Di Cesare, M.; Bixby, H.; Danaei, G.; Cowan, M.J.; Paciorek, C.J.; Singh, G.; Hajifathalian, K.; Bennett, J.E.; et al. Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: A pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19·1 million participants. Lancet 2016, 389, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Afshin, A.; Gakidou, E.; Lim, S.S.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases Collaboration. Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes mortality burden of cardiometabolic risk factors from 1980 to 2010: A comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparil, S.; Acelajado, M.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cifkova, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Grassi, G.; Jordan, J.; Poulter, N.R.; Rodgers, A.; et al. Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Xue, J.; Ye, C.; Chen, A. Role of the central renin-angiotensin system in hypertension (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiola, A.; Fuentes, C.A.; Solar, I.; Lagos, C.F.; Opazo, M.C.; Muñoz-Durango, N.; Riedel, C.; Owen, G.I.; Kalergis, A.M.; Fardella, C.E. Eplerenone Implantation Improved Adipose Dysfunction Averting RAAS Activation and Cell Division. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-S.; Schulman, I.; Zeng, Q. Link between the renin–angiotensin system and insulin resistance: Implications for cardiovascular disease. Vasc. Med. 2012, 17, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Yuan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, C.; Yang, Y.; Dong, Y.; He, Q. ATP2B1 gene polymorphisms rs2681472 and rs17249754 are associated with susceptibility to hypertension and blood pressure levels. Medicine 2021, 100, e25530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Li, J.; MacGregor, G.A. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2013, 346, f1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto, N.J.; Hanson, S.; Gutierrez, H.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P. Effect of increased potassium intake on cardiovascular risk factors and disease: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 346, f1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Noce, A.; Di Lauro, M.; Marrone, G.; Cantelmo, M.; Cardillo, C.; Federici, M.; Di Daniele, N.; Tesauro, M. Gut Dysbiosis and Western Diet in the Pathogenesis of Essential Arterial Hypertension: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Campos, H. Dietary Therapy in Hypertension. N. Eng. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2102–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsberg, L. Insulin-mediated sympathetic stimulation: Role in the pathogenesis of obesity-related hypertension (or, how insulin affects blood pressure, and why). J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Giannarelli, C.; Fritsch Neves, M.; Taddei, S.; Ghiadoni, L. Cigarette Smoking and Hypertension. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, C.; Femminò, S.; Alloatti, G.; Brizzi, M.; Angelone, T.; Pagliaro, P. Extracellular Vesicles in Comorbidities Associated with Ischaemic Heart Disease: Focus on Sex, an Overlooked Factor. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoni, D.; Porteri, E.; Castellano, M.; Bettoni, G.; Muiesan, M.L.; Tiberio, G.; Giulini, S.M.; Rossi, G.; Bernini, G.; Agabiti-Rosei, E. Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypertension Is Independent From the Etiology and From Vascular Structure. Hypertension 1998, 31, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Filippis, A.; Ullah, H.; Baldi, A.; DaCrema, M.; Esposito, C.; Garzarella, E.U.; Santarcangelo, C.; Tantipongpiradet, A.; Daglia, M. Gastrointestinal Disorders and Metabolic Syndrome: Dysbiosis as a Key Link and Common Bioactive Dietary Components Useful for their Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, B. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Human Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boziki, M.; Grigoriadis, N.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Doulberis, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Gavalas, E.; Deretzi, G.; Karafoulidou, E.; Kesidou, E.; Taloumtzis, C.; et al. The trimebutine effect on Helicobacter pylori-related gastrointestinal tract and brain disorders: A hypothesis. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 144, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMaster, W.G.; Kirabo, A.; Madhur, M.S.; Harrison, D.G. Inflammation, Immunity, and Hypertensive End-Organ Damage. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.; Leibowitz, A. Role of the immune system in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Harefuah 2021, 160, 256–259. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, U.O.; Ehmke, H.; Bode, M. Immune mechanisms in arterial hypertension. Recent Adv. 2021, 385, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellicha, A.; van Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Busetto, L.; Carraca, E.V.; Dicker, D.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; et al. Effect of exercise training before and after bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungvari, Z.; Toth, P.; Tarantini, S.; Prodan, C.I.; Sorond, F.; Merkely, B.; Csiszar, A. Hypertension-induced cognitive impairment: From pathophysiology to public health. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.R.; Muldoon, M.F.; Ryan, C.; Price, J.C.; Greer, P.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; van der Veen, F.M.; Meltzer, C.C. Reduced cerebral blood flow response and compensation among patients with untreated hypertension. Neurology 2005, 64, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; van der Graaf, Y.; Visseren, F.L.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Geerlings, M.I. Hypertension and longitudinal changes in cerebral blood flow: The SMART-MR study. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immink, R.V.; van den Born, B.-J.H.; van Montfrans, G.A.; Koopmans, R.P.; Karemaker, J.M.; van Lieshout, J.J. Impaired Cerebral Autoregulation in Patients with Malignant Hypertension. Circulation 2004, 110, 2241–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, T.; Singh, M.; Tiu, J.G.; Kim, A.S. Etiology and management of hypertension in patients with cancer. Cardio-Oncology 2021, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocks, T.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Manjer, J.; Bjørge, T.; Ulmer, H.; Hallmans, G.; Lindkvist, B.; Selmer, R.; Nagel, G.; Tretli, S.; et al. Blood Pressure and Risk of Cancer Incidence and Mortality in the Metabolic Syndrome and Cancer Project. Hypertension 2012, 59, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooi, J.K.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.; Wu, J.C.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, K.; Timerga, A. Evaluation of Hematological Parameters of Helicobacter pylori-Infected Adult Patients at Southern Ethiopia: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study. J. Blood Med. 2021, 12, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Are the four meta-analyses favoring an intriguing association pointing to the right direction? Metabolism 2019, 96, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulberis, M.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Polyzos, S.A.; Bargiotas, P.; Liatsos, C.; Srivastava, D.S.; Zavos, C.; Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J. Association between Active Helicobacter pylori Infection and Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J. Extragastric Diseases and Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Polyzos, S.A.; Katsinelos, P.; Zeglinas, C.; Artemaki, F.; Tzivras, D.; Vardaka, E.; Gavalas, E.; Romiopoulos, I.; Simeonidou, C.; et al. Cardio-cerebrovascular disease and Helicobacter pylori—Related metabolic syndrome: We consider eradication therapy as a potential cardio-cerebrovascular prevention strategy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 229, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Doulberis, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Katsinelos, T.; Vardaka, E.; Kountouras, C.; Arapoglou, S.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Deretzi, G.; Tsolaki, M.; et al. Impact of Helicobacter pylori and/or Helicobacter pylor—Related metabolic syndrome on incidence of all-cause and Alzheimer‧s dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, R.; Ianiro, G.; Fagoonee, S.; Settanni, C.R.; Gasbarrini, A. Review: Extragastric diseases and Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doheim, M.F.; Altaweel, A.A.; Elgendy, M.G.; Elshanbary, A.; Dibas, M.; Ali, A.A.H.A.; Dahy, T.M.; Sharaf, A.K.; Hassan, A.E. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and stroke: A meta-analysis of 273,135 patients. J. Neurol. 2020, 268, 3238–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulberis, M.; Kotronis, G.; Gialamprinou, D.; Polyzos, S.A.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J. Alzheimer’s disease and gastrointestinal microbiota; impact of Helicobacter pylori infection involvement. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 131, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Kapetanakis, N.; Zavos, C.; Polyzos, S.A.; Vardaka, E.; Katsinelos, P.; Romiopulos, I.; Anastasiadou, K.; Giorgakis, N.; Nikolaidou, C.; et al. Helicobacter pylori and Colorectal Cancer Risk—Letter. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kountouras, J.; Boziki, M.; Polyzos, S.; Katsinelos, P.; Gavalas, E.; Zeglinas, C.; Tzivras, D.; Romiopoulos, I.; Giorgakis, N.; Anastasiadou, K.; et al. The Emerging Role of Helicobacter pylori—Induced Metabolic Gastrointestinal Dysmotility and Neurodegeneration. Curr. Mol. Med. 2018, 17, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Polyzos, S.A.; Doulberis, M.; Zeglinas, C.; Artemaki, F.; Vardaka, E.; Deretzi, G.; Giartza-Taxidou, E.; Tzivras, D.; Vlachaki, E.; et al. Potential impact of Helicobacter pylori—Related metabolic syndrome on upper and lower gastrointestinal tract oncogenesis. Metabolism 2018, 87, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulberis, M.; Kotronis, G.; Thomann, R.; Polyzos, S.S.A.; Boziki, M.; Gialambrinou, D.; Deretzi, G.; Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J. Impact of Helicobacter pylori on Alzheimer’s disease: What do we know so far? Helicobacter 2017, 23, e12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Zeglinas, C.; Artemaki, F.; Doulberis, M.; Kazakos, E.; Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J. Helicobacter pylori infection and esophageal adenocarcinoma: A review and a personal view. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsinelos, T.; Doulberis, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J. Molecular Links Between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gastrointestinal Microbiota: Emphasis on Helicobacter pylori Infection Involvement. Curr. Mol. Med. 2019, 20, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J. Helicobacter pylori Infection: One More Contributor to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Pathophysiology. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, F.; Annalisa, T.; Teresa, D.R.; Giovanna, D.A.; Laniro, G.; Franco, S.; Viviana, G.; Valentina, T.; Riccard, L.L.; Gasbarinni, A. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection on nutrition and metabolism. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12809–12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kountouras, J.; Doulberis, M.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Polyzos, S.A. Impact of Helicobacter pylori—Linked metabolic syndrome on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its connected atrial fibrillation risk. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2036–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulberis, M.; Srivastava, S.; Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Klukowska-Rötzler, J.; Blank, A.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Srivastava, D.S. Active Helicobacter pylori Infection is Independently Associated with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boziki, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Doulberis, M.; Bakirtzis, C.; Sintila, S.-.A.; Touloumtzi, M.; Grigoriadis, N.; Kountouras, J. Potential impact of Helicobacter pylori—Related metabolic syndrome and Galectin-3 on liver, chronic kidney and brain disorders. Metabolism 2021, 118, 154736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kountouras, J.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Doulberis, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Zavos, C.; Kazakos, E.; Tzika, S.K.; Vardaka, E.; Liatsos, C.; Katsinelos, P. Impact of Helicobacter pylori—Related Metabolic Syndrome and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease on the Risk of Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, J.-N. Pandemic Legion History More Complex than Previously Thought. mBio 2020, 11, e02377-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealey, K.N.; Phillips, J.; Sung, H.-K. COVID-19 and obesity: Fighting two pandemics with intermittent fasting. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Geladari, E.; Kounatidis, D. Microbiome and hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhur, M.S.; Elijovich, F.; Alexander, M.R.; Pitzer, A.; Ishimwe, J.; Van Beusecum, J.P.; Patrick, D.M.; Smart, C.D.; Kleyman, T.R.; Kingery, J.; et al. Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 908–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.W.; Wang, X.M.; Wu, J. Progress in research on the relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and cardiovascular diseases and its risk factors. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 54, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Jukic, A.; Bozic, D.; Kardum, D.; Becic, T.; Luksic, B.; Vrsalovic, M.; Ljubkovic, M.; Fabijanic, D. Helicobacter pylori infection and severity of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with chronic coronary artery disease. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Hu, L.; Hu, M.; Lei, X.; Huang, Y.; Lv, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and prevalence of high blood pressure among Chinese adults. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2017, 32, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrat, S.A.M.; Nasrat, A.M. An Alternative Approach for the Rising Challenge of Hypertensive Illness via Helicobacter pylori Eradication. Cardiol. Res. 2015, 6, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneco, A.; Ojetti, V.; Specchia, L.; Franceschi, F.; Candelli, M.; Mettimano, M.; Montebelli, R.; Savi, L.; Gasbarrini, G. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection improves blood pressure values in patients affected by hypertension. Helicobacter 2003, 8, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newberry, S.J.; Chung, M.; Anderson, C.A.; Chen, C.; Fu, Z.; Tang, A.; Zhao, N.; Booth, M.; Marks, J.; Hollands, S.; et al. Effects of Dietary Sodium and Potassium Intake on Chronic Disease Outcomes and Related Risk Factors. Syst. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. Intersalt: An international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24 hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion. BMJ 1988, 297, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EUROGAST Study Group. An international association between Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer. Lancet 1993, 341, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Dangler, C.A.; Taylor, N.S.; King, A.; Koh, T.J.; Wang, T.C. High-salt diet induces gastric epithelial hyperplasia and parietal cell loss, and enhances Helicobacter pylori colonization in C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4823–4828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Tsukamoto, T.; Mizoshita, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kumagai, T.; Ota, H.; Katsuyama, T.; Asaka, M.; Tatematsu, M. High salt diets dose-dependently promote gastric chemical carcinogenesis in Helicobacter pylori—Infected Mongolian gerbils associated with a shift in mucin production from glandular to surface mucous cells. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, L.K. Possible role of salt intake in the development of essential hypertension*. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 34, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Ismail, A.W.; Mustaffa, N.; Musa, K.I.; Majid, N.A.; Choo, K.E.; Raj, S.M.; Derakhshan, M.H.; Malaty, H.M.; Graham, D.Y. Sociocultural and Dietary Practices Among Malay Subjects in the North-Eastern Region of Peninsular Malaysia: A Region of Low Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2012, 17, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaka, M.; Kimura, T.; Kudo, M.; Takeda, H.; Mitani, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Miki, K.; Graham, D.Y. Relationship of Helicobacter pylori to serum pepsinogens in an asymptomatic Japanese population. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, F.C.; Weinberger, M.H. Heterogeneous responses to changes in dietary salt intake: The salt-sensitivity paradigm. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 612S–617S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Henry, W.L.; Bartter, F.C.; Lake, C.; Delea, C.S. Factors influencing blood pressure in salt-sensitive patients with hypertension. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Delea, C.S.; Bartter, F.C.; Smith, H. The effect of high-sodium and low-sodium intakes on blood pressure and other related variables in human subjects with idiopathic hypertension. Am. J. Med. 1978, 64, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Dell’Italia, L.J.; Sanders, P.W. Novel Paradigms of Salt and Hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, A.C. Kidneys and fluids in pressure regulation. Small volume but large pressure changes. Hypertension 1992, 19, I2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragulat, E.; de la Sierra, A. Salt Intake, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2002, 4, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarazaki, W.; Mizuno, R.; Nishimoto, M.; Ayuzawa, N.; Hirohama, D.; Ueda, K.; Kawakami-Mori, F.; Oba, S.; Marumo, T.; Fujita, T. Salt causes aging-associated hypertension via vascular Wnt5a under Klotho deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4152–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawarazaki, W.; Nagase, M.; Yoshida, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Ishizawa, K.; Ayuzawa, N.; Ueda, K.; Fujita, T. Angiotensin II- and Salt-Induced Kidney Injury through Rac1-Mediated Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.; McDonough, A.A. Impact of angiotensin II-mediated stimulation of sodium transporters in the nephron assessed by computational modeling. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2019, 317, F1656–F1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winternitz, S.R.; Katholi, R.E.; Oparil, S. Role of the Renal Sympathetic Nerves in the Development and Maintenance of Hypertension in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 66, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity-Induced Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polichnowski, A.J.; Griffin, K.A.; Long, J.; Williamson, G.A.; Bidani, A.K. Blood pressure-renal blood flow relationships in conscious angiotensin II- and phenylephrine-infused rats. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2013, 305, F1074–F1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, S.; Nagase, M.; Yoshida, S.; Kawachi, H.; Fujita, T. Podocyte as the Target for Aldosterone. Hypertension 2007, 49, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, M.; Yoshida, S.; Shibata, S.; Nagase, T.; Gotoda, T.; Ando, K.; Fujita, T. Enhanced Aldosterone Signaling in the Early Nephropathy of Rats with Metabolic Syndrome: Possible Contribution of Fat-Derived Factors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3438–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhu, G.; Han, S. Prevalence of and lifestyle factors associated with metabolic syndrome determined using multi-level models in Chinese adults from a cross-sectional survey. Medicine 2020, 99, e22883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Jin, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Gao, X. Prospective study of perceived dietary salt intake and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 32, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsdottir, S.E.; Brader, L.; Gunnarsdóttir, I.; Magnusdottir, O.K.; Schwab, U.; Kolehmainen, M.; Risérus, U.; Herzig, K.-H.; Cloetens, L.; Helgegren, H.; et al. Adherence to the Nordic Nutrition Recommendations in a Nordic population with metabolic syndrome: High salt consumption and low dietary fibre intake (The SYSDIET study). Food Nutr. Res. 2013, 57, 21391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.N.; Shah, R.Y.; Ferguson, J.F.; Reilly, M.P. Human Experimental Endotoxemia in Modeling the Pathophysiology, Genomics, and Therapeutics of Innate Immunity in Complex Cardiometabolic Diseases. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladhami, A.K.; Unger, C.A.; Ennis, S.L.; Altomare, D.; Ji, H.; Hope, M.C.; Velázquez, K.T.; Enos, R.T. Macrophage tumor necrosis factor-alpha deletion does not protect against obesity-associated metabolic dysfunction. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, S.; Kasirga, E.; Yilmaz, O.; Bayindir, P.; Akil, I.; Yuskel, H.; Polat, M.; Ssnlidag, T. Is Helicobacter pylori related to endothelial dysfunction during childhood? Pediatr. Int. 2008, 50, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciorkowska, E. Soluble adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, P-selectin in children with Helicobacter pylori infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consolazio, A.; Borgia, M.C.; Ferro, D.; Iacopini, F.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Crispino, P.; Nardi, F.; Rivera, M.; Paoluzi, P. Increased thrombin generation and circulating levels of tumour necrosis factor-α in patients with chronic Helicobacter pylor—Positive gastritis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Jirillo, E.; Clemente, C.; Messa, C.; Chiloiro, M.; Riezzo, G.; Amati, L.; Caradonna, L.; Di Leo, D. Circulating cytokines and gastrin levels in asymptomatic subjects infected by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2001, 23, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Doulberis, M.; Polyzos, S.A. Influence of Helicobacter pylori—Connected metabolic syndrome on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its related colorectal neoplasm high risk. Liver Int. 2019, 40, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boziki, M.; Grigoriadis, N.; Doulberis, M.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J. Potential impact of Helicobacter pylori—Related Galectin-3 on chronic kidney, cardiovascular and brain disorders in decompensated cirrhosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 52, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, T.; Lakkappa, N.; Lazartigues, E. ADAM17-Mediated Shedding of Inflammatory Cytokines in Hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Casales, M.; Hernanz, R.; Alonso, M.J. Vascular and Macrophage Heme Oxygenase-1 in Hypertension: A Mini-Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 643435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Hassanshahi, G.H.; Nemati, M. Serum Levels of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP) in Helicobacter pylori—Infected Peptic Ulcer Patients and Its Association with Bacterial CagA Virulence Factor. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2612–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccoli, G.; Franceschi, F.; Cosentino, N.; Giupponi, B.; De Marco, G.; Merra, G.; Conte, M.; Montone, R.A.; Ferrante, G.; Bacà, M.; et al. Coronary atherosclerotic burden in patients with infection by CagA-positive strains of Helicobacter pylori. Coron. Artery Dis. 2010, 21, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, M. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in coronary artery disease: Influence of H. pylori eradication on coronary artery lumen after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. The detection of H. pylori specific DNA in human coronary atherosclerot. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001, 52, 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi, F.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Gasbarrini, A.; Polla, P.; Silveri, N.G.; Gasbarrini, G.; Graham, D.Y.; Gengta, R.M. Cross-Reactivity of Anti-CagA Antibodies With Vascular Wall Antigens. Circulation 2002, 106, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomedi, M.; Stanzione, P.; Sallustio, F.; Leone, G.; Renna, A.; Missagi, G.; Fontana, C.; Pasqualetti, P.; Pietroiusti, A. Cytotoxin-Associated Gene-A—Positive Helicobacter pylori S trains Infection Increases the Risk of Recurrent Atherosclerotic Stroke. Helicobacter 2008, 13, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Tamura, T.; Mitsuda, Y.; Gotto, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Kondo, T.; Wakai, K.; Hamajima, N. Significant Association between Serum Interleukin-6 and Helicobacter pylori Antibody Levels among H. pylori -Positive Japanese Adults. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 142358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Lent-Schochet, D.; Ramakrishnan, N.; McLaughlin, M.; Jialal, I. Metabolic syndrome is an inflammatory disorder: A conspiracy between adipose tissue and phagocytes. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 496, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramji, D.P.; Davies, T.S. Cytokines in atherosclerosis: Key players in all stages of disease and promising therapeutic targets. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechciński, T.; Kasprzak, J.D.; Chmiela, M.; Krzemińska-Pakuła, M.; Rudnicka, W. Patients with unstable angina pectoris present increased humoral response against Helicobacter pylori in comparison with patients with aggravated dyspepsia. Acta Microbiol. Pol. 2002, 51, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strachan, D.P. Non-gastrointestinal consequences of Helicobacter pylori infection. Br. Med. Bull. 1998, 54, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Katz, R.J.; Quyyumi, A.A.; Canos, D.A.; Rott, D.; Csako, G.; Zalles-Ganley, A.; Ogunmakinwa, J.; Wasserman, A.G.; Epstein, S.E. Association of Serum Antibodies to Heat-Shock Protein 65 With Coronary Calcification Levels. Circulation 2004, 109, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kountouras, J.; Gavalas, E.; Boziki, M.; Zavos, C. Helicobacter pylori may be involved in cognitive impairment and dementia development through induction of atrophic gastritis, vitamin B-12–folate deficiency, and hyperhomocysteinemia sequence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayvergiya, R.; Vadivelu, R. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. World, J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzolla, G.; Candigliota, M.; Fanelli, M.; Castrovilli, A.; Berardi, E.; Antonica, G.; Battaglia, S.; Solfrizzi, V.; Sabbà, C.; Tortorella, C. Hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent risk factor of atherosclerosis in patients with metabolic syndrome. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, J.; Fan, R. Exploration of the risk factors of essential hypertension with hyperhomocysteinemia: A hospital-based study and nomogram analysis. Clinics 2021, 76, e2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Levi, A.; Vecht-Lifshitz, S.E.; Goldberg, E.; Garty, M.; Krause, I. Assessment of a Possible Link Between Hyperhomocysteinemia and Hyperuricemia. J. Investig. Med. 2015, 63, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostom, A.G.; Shemin, D.; Lapane, K.L.; Sutherland, P.; Nadeau, M.R.; Wilson, P.W.; Yoburn, D.; Bausserman, L.; Tofler, G.; Jacques, P.F.; et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia, hyperfibrinogenemia, and lipoprotein (a) excess in maintenance dialysis patients: A matched case-control study. Atherosclerosis 1996, 125, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo-Mbenza, B.; Mokondjimobe, N.; Mokolndjimobe, E.; Gombet, T.; Assori, I.N.; Ibara, J.R.; Ellenga-Mbola, B.; Vangu, D.N.; Fuele, S.M. Helicobacter pylori infection is identified as a cardiovascular risk factor in Central Africans. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2012, 6, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Chen, J.; He, M.; Wu, T.; Yang, H. Helicobacter pylori infection and the prevalence of hypertension in Chinese adults: The Dongfeng-Tongji cohort. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2020, 22, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Howard, S.C.; Power, D.A.; Gutnikov, S.A.; Algra, A.; van Gijn, J.; Clark, T.; Murphy, M.F.; Warlow, C.P. Fibrinogen Concentration and Risk of Ischemic Stroke and Acute Coronary Events in 5113 Patients With Transient Ischemic Attack and Minor Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 2300–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.-Y.; Bai, C.-H.; Chen, W.-H.; Lien, L.-M.; Pan, W.-H. Fibrinogen Independently Predicts the Development of Ischemic Stroke in a Taiwanese Population. Stroke 2009, 40, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, A.F.; Moreira, C.; Nogueira, J.B.; Santos, N.C.; Carvalho, F.A. Fibrinogen–erythrocyte binding and hemorheology measurements in the assessment of essential arterial hypertension patients. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2757–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Buzzigoli, G.; Bonadonna, R.; Giorico, M.A.; Oleggini, M.; Graziadei, L.; Pedrinelli, R.; Brandi, L.; Bevilacqua, S. Insulin Resistance in Essential Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancusi, C.; Izzo, R.; di Gioia, G.; Losi, M.A.; Barbato, E.; Morisco, C. Insulin Resistance the Hinge Between Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2020, 27, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Kitada, M.; Ogura, Y.; Koya, D. Relationship Between Autophagy and Metabolic Syndrome Characteristics in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Torres, A.; Martínez Gaensly, M. Helicobacter pylori: ¿un nuevo factor de riesgo cardiovascular? Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2002, 55, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.J.; Bamford, K.B.; Kee, F.; McMaster, D.; Cambien, F.; Dallongeville, J.; Evans, A. Infection with virulent strains of Helicobacter pylori is not associated with ischaemic heart disease: Evidence from a population-based case-control study of myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis 2000, 149, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogha, M.; Nikvarz, M.; Pourmoghaddas, Z.; Shirneshan, K.; Dadkhah, D.; Pourmoghaddas, M. Helicobacter pylori infection a risk factor for coronary heart disease? ARYA Atheroscler. 2012, 8, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chimienti, G.; Russo, F.; Lamanuzzi, B.; Nardulli, M.; Messa, C.; Di Leo, A.; Correale, M.; Giannuzzi, V.; Pepe, G. Helicobacter pylori is associated with modified lipid profile: Impact on Lipoprotein(a). Clin. Biochem. 2003, 36, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillich, F.F.; Imig, J.D.; Proschak, E. Multi-Target Approaches in Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 554961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papamichael, K.X.; Papaioannou, G.G.; Karga, H.; Roussos, A.; Mantzaris, G.J. Helicobacter pylori infection and endocrine disorders: Is there a link? World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuely, H.; Wattad, M.; Solodky, A.; Yahav, J.; Samra, Z.; Zafrir, N. Association of Helicobacter pylori with coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction assessed by myocardial perfusion imaging. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2014, 16, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Kucukazman, M.; Yavuz, B.; Sacikara, M.; Asilturk, Z.; Ata, N.; Ertugrul, D.T.; Yalcin, A.A.; Yenigun, E.C.; Kizilca, G.; Okten, H.; et al. The Relationship Between Updated Sydney System Score and LDL Cholesterol Levels in Patients Infected with Helicobacter pylori. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 54, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Chen, H.W.L. Diagnosis and Treatment of Dyslipidemia, 2nd ed.; People’s Military Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pellicano, R.; Oliaro, E.; Fagoonee, S.; Astegiano, M.; Berrutti, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Smedile, A.; Repici, A.; Leone, N.; Castelli, A.; et al. Clinical and biochemical parameters related to cardiovascular disease after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Int. Angiol. 2009, 28, 469. [Google Scholar]
- Majka, J.; Róg, T.; Konturek, P.C.; Konturek, S.J.; Bielanski, W.; Kowalsky, M.; Szczudik, A. Influence of chronic Helicobacter pylori infection on ischemic cerebral stroke risk factors. Med. Sci. Monit. 2002, 8, CR675–CR684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jalalzadeh, M.; Ghadiani, M.H.; Mousavinasab, N. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and body mass index, before and after eradication of infection in hemodialysis batients. J. Nephropathol. 2012, 1, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gen, R.; Demir, M.; Ataseven, H. Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Insulin Resistance, Serum Lipids and Low-Grade Inflammation. South. Med. J. 2010, 103, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejawa, M.; Osadnik, K.; Osadnik, T.; Pawlas, N. Association of Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obesity Phenotypes with Oxidative Stress Parameters and Telomere Length in Healthy Young Adult Men. Analysis of the MAGNETIC Study. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazligul, Y.; Aslan, M.; Horoz, M.; Celik, Y.; Dulger, A.C.; Celik, H.; Erel, O. The effect on serum myeloperoxidase activity and oxidative status of eradication treatment in patients Helicobacter pylori infected. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.-H.; Baik, S.J.; Chun, J.; Youn, Y.H.; Park, H. Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity as Novel Risk Factors for Gastric Carcinogenesis: A Health Checkup Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, Z.; Shen, K.; Chen, X. Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Cancer: Prevalence, Treatment Response, and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, R. Metabolic syndrome and esophageal cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassen, L.J.; Lenihan, D.J.; Baliga, R.R. Hypertension in the Cardio-Oncology Clinic. Heart Fail. Clin. 2019, 15, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulberis, M.; Pierre, N.; Manzini, G.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Kountouras, J.; Klukowska-Rötzler, J.; Polyzos, S.; Srivastava, S.; Exadaktylos, A.; Knuchel, J.; et al. Helicobacter pylori—Related Metabolic Parameters and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Histological Lesions in Swiss Bariatric Patients. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, T.; Shimizu, M.; Ohno, T.; Baba, A.; Sumi, T.; Kubota, M.; Shirakami, Y.; Tsurumi, H.; Tanaka, T.; Moriwaki, H. Enhanced Development of Azoxymethane-Induced Colonic Preneoplastic Lesions in Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14700–14711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C.; Chatzopoulos, D.; Katsinelos, P. New Aspects of Helicobacter pylori Infection Involvement in Gastric Oncogenesis. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 146, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, T.D.; Mitchell, J.A. Cyclooxygenases: New forms, new inhibitors, and lessons from the clinic. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Slomiany, A. Involvement of p38 MAPK-dependent activator protein (AP-1) activation in modulation of gastric mucosal inflammatory responses to Helicobacter pylori by ghrelin. Inflammopharmacology 2013, 21, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Slomiany, A. Induction in gastric mucosal prostaglandin and nitric oxide by Helicobacter pylori is dependent on MAPK/ERK-mediated activation of IKK-β and cPLA2: Modulatory effect of ghrelin. Inflammopharmacology 2013, 21, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebowska, A.; Rechciński, T.; Bak-Romaniszyn, L.; Czkwianianc, E.; Moran, A.; Druszczyńska, M.; Kowalewicz-Kulbat, M.; Owczarek, A.; Dziuba, M.; Krzemińska-Pakuła, M.; et al. Potential role of LPS in the outcome of Helicobacter pylori related diseases. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, J.; Badimon, L. Mechanisms Underlying the Cardiovascular Effects of COX-Inhibition: Benefits and Risks. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollone, F.; Cicolini, G.; Bucci, M. Cyclooxygenase and prostaglandin synthases in atherosclerosis: Recent insights and future perspectives. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 118, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollone, F.; Fazia, M.L. COX-2 and Atherosclerosis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47, S26–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Song, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, S. Combined effects of carotid plaques and hypertension on the risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Taddei, S. Endothelial Dysfunction in Resistance Arteries of Hypertensive Humans. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.T.J.; Tian, X.Y.; Huang, Y. Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes and Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; et al. Roles and Mechanisms of Interleukin-12 Family Members in Cardiovascular Diseases: Opportunities and Challenges. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Circulating IL-37 levels are elevated in patients with hypertension. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.-F.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Liu, T.; Yin, Z.; Wu, C.; Mao, X.-H.; Jia, K.-R.; Wang, F.-J.; et al. Helicobacter pylori—Induced Th17 Responses Modulate Th1 Cell Responses, Benefit Bacterial Growth, and Contribute to Pathology in Mice. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Nemati, M.; Rezayati, M.-T. Circulating interleukin-27 levels in Helicobacter pylori—Infected patients with gastric or duodenal ulcers, independent of the bacterial cytotoxin-associated gene A virulence factor. J. Dig. Dis. 2011, 12, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, E.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Nemati, M.; Bassagh, A.; Abasi, M.H.; Khosravimashizi, A.; Kazemipoor, N.; Ghazizadeh, M.; Mirzaee, M. Circulating concentration of interleukin-37 in Helicobacter pylori—Infected patients with peptic ulcer: Its association with IL-37 related gene polymorphisms and bacterial virulence factor CagA. Cytokine 2019, 126, 154928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Tang, M.; Li, P.; Wu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y. Serum level of interleukin-35 as a potential prognostic factor for gastric cancer. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ding, H.-G. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicine 2021, 100, e26706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aneni, E.C.; Oni, E.T.; Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Agatston, A.S.; Feldman, T.; Veledar, E.; Conçeicao, R.D.; Carvalho, J.A.; Santos, R.D.; et al. Blood pressure is associated with the presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease across the spectrum of cardiometabolic risk. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, J.-H.; Suh, Y.J.; Shin, H.C.; Cho, Y.K.; Choi, J.-M.; Park, S.K. Clinical association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the development of hypertension. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1926–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorbeer, R.; Bayerl, C.; Auweter, S.; Rospleszcz, S.; Lieb, W.; Meisinger, C.; Heier, M.; Peters, A.; Bamberg, F.; Hetterich, H. Association between MRI-derived hepatic fat fraction and blood pressure in participants without history of cardiovascular disease. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.-Y.; Tu, J.-F.; Ding, Y.-H.; Pang, J.; Che, X.-D.; Zou, H.; Huang, D.-S. Association of blood pressure level with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonhypertensive population. Medicine 2016, 95, e4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, F.; Gastaldelli, A.; Bars, F.P.-L.; Natali, A.; Roussel, R.; Petrie, J.; Tichet, J.; Marre, M.; Fromenty, B.; Balkau, B. Gamma-glutamyltransferase, fatty liver index and hepatic insulin resistance are associated with incident hypertension in two longitudinal studies. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Lorbeer, R.; Haring, R.; Schmidt, C.O.; Wallaschofski, H.; Nauck, M.; John, U.; Baumeister, S.E.; Völzke, H. The association between fatty liver disease and blood pressure in a population-based prospective longitudinal study. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasunta, R.-L.; Kesäniemi, Y.A.; Ylitalo, A.S.; Ukkola, O.H. High ambulatory blood pressure values associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver in middle-aged adults. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 2015–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latea, L. Primary non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in hypertensive patients. Australas. Med. J. 2013, 6, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, M.S.; Jaryal, A.K.; Ranjan, P.; Deepak, K.K.; Sharma, S.; Lakshmy, R.; Pandey, R.M.; Vikram, N.K. Diabetic status and grade of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are associated with lower baroreceptor sensitivity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Verhaar, A.P.; Pan, Q.; de Knegt, R.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Serum levels of caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 (CK18-Asp396) predict severity of liver disease in chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bär, H.; Bea, F.; Blessing, E.; Watson, L.; Wende, P.; Kreuzer, J.; Kübler, W.; Jahn, L. Phosphorylation of cytokeratin 8 and 18 in human vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerotic lesions and umbilical cord vessels. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2001, 96, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, D.A.; Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein, inflammation, and coronary risk. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 84, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, V.; Sokic-Milutinovic, A.; Drndarevic, N.; Micev, M.; Mitrovic, O.; Nikolic, I.; Wex, T.; Milosavljevic, T.; Malfertheiner, P. Expression of cytokeratins in Helicobacter pylori—Associated chronic gastritis of adult patients infected with cagA+ strains: An immunohistochemical study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Lawlor, D.A.; Ferreira, D.L.; Hughes, A.D.; Chaturvedi, N.; Callaway, M.; Day, C.; Sattar, N.; Fraser, A. The association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with central and peripheral blood pressure in adolescence. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, V.; Rehermann, B. The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology 2006, 43, S54–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, D.; Zalewski, P.; Hallsworth, K.; Cassidy, S.; Thoma, C.; Avery, L.; Slomko, J.; Hardy, T.; Burt, A.D.; Tiniakos, D.; et al. The degree of hepatic steatosis associates with impaired cardiac and autonomic function. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Damås, J.K.; Konopski, Z.; Løberg, E.M.; Haaland, T.; Goverud, I.; Torjesen, P.A.; Birkeland, K.; Bjøro, K.; Aukrust, P. Systemic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is characterized by elevated levels of CCL2. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potoupni, V.; Georgiadou, M.; Chatzigriva, E.; Polychronidou, G.; Markou, E.; Gakis, C.Z.; Filimidou, I.; Karagianni, M.; Anastasilakis, D.; Evripidou, K.; et al. Circulating tumor necrosis factor-α levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 3002–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, R.; Penrose, H.; Navar, L.G. Inflammation as a Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System and Blood Pressure. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cai, J.; She, Z.; Li, H. Insights into the Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutics of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases. Adv. Sci. 2018, 6, 1801585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Boziki, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Katsinelos, P.; Gavalas, E.; Zeglinas, C.; Tzivras, D.; Romiopoulos, I.; Giorgakis, N.; Anastasiadou, K.; et al. Impact of reactive oxygen species generation on Helicobacter pylori—Related extragastric diseases: A hypothesis. Free. Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Stender, S.; Pietrelli, A.; Mancina, R.M.; Cespiati, A.; Petta, S.; Pelusi, S.; Pingitore, P.; Badiali, S.; Maggioni, M.; et al. Causal relationship of hepatic fat with liver damage and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 283, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J. Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Time for large clinical trials evaluating eradication therapy. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, D.; Montecucco, F.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F. Impact of different ectopic fat depots on cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21630–21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwimmer, J.; Johnson, J.S.; Angeles, J.E.; Behling, C.; Belt, P.H.; Borecki, I.; Bross, C.; Durelle, J.; Goyal, N.P.; Hamilton, G.; et al. Microbiome Signatures Associated With Steatohepatitis and Moderate to Severe Fibrosis in Children With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The gut–liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C.; Polyzos, S.A.; Deretzi, G. Potential impact of Helicobacter pylori—Related human β-defensin-1 on hepatic encephalopathy and neurodegeneration. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2016, 29, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifnia, T.; Antoun, J.; Verriere, T.G.C.; Suarez, G.; Wattacheri, J.; Wilson, K.T.; Peek, R.M.P., Jr.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Hepatic TLR4 signaling in obese NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G270–G278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yola, I.M.; Moser, C.; Duncan, M.S.; Schwedhelm, E.; Atzler, D.; Maas, R.; Hannemann, J.; Böger, R.H.; Vasan, R.S.; Xanthakis, V. Associations of circulating dimethylarginines with the metabolic syndrome in the Framingham Offspring study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogru, T.; Genc, H.; Tapan, S.; Ercin, C.N.; Ors, F.; Aslan, F.; Kara, M.; Sertoglu, E.; Bagci, S.; Kurt, I.; et al. Elevated asymmetric dimethylarginine in plasma: An early marker for endothelial dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 96, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, M.; Masarone, M.; Damato, A.; Ambrosio, M.; Federico, A.; Rosato, V.; Bucci, T.; Carrizo, A.; Vecchione, C. Non alcoholic fatty liver disease and eNOS dysfunction in humans. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhang, G.-W.; Zhang, J.-R.; Jin, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.-T. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with progression of arterial stiffness. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assali, A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Hassani, M.; Kasaian, J.; Tatari, F.; Moohebati, M.; Paydar, R.; Oladi, M.; Esmaeili, H.A.; et al. Association of angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene A1166C polymorphism with the presence of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome in patients with documented coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 22, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Ohno, T.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins on gastric mucosal interleukin 6 and 11 expression in Mongolian gerbils. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, H.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Lei, Q. Identification of key genes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression based on bioinformatics analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7708–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Saba, F.; Cassader, M.; Paschetta, E.; De Michieli, F.; Pinach, S.; Framarin, L.; Berrutti, M.; Leone, N.; Parente, R.; et al. Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor rs5186 Gene Variant Predicts Incident NAFLD and Associated Hypertension: Role of Dietary Fat-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cell Activation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Wu, W.; Ye, J.; Fang, D.; Shi, D.; Li, L. Clinical application of angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24155–24167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | Comment | References |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic factors | ATP2B1 gene polymorphisms rs2681472 and rs17249754 | [12] |
| Diet | High Na+/K+ intake and western-type of diet | [13,14,15] |
| Adiposity | Activation of the SNS and RAAS, and sodium retention | [16] |
| Smoking | Mainly via stimulation of the SNS | [18] |
| Endothelial dysfunction linked with MetS | Excessive release of vasoconstrictive agents and defective secretion of smooth-muscle relaxing mediators | [17] |
| Gut microbiota dysbiosis | Via production, modification, and degradation of microbial-derived bioactive metabolites | [15,21,22,23] |
| Inflammatory mechanisms | Overstimulated immune system induction of pro -inflammatory cytokines and chemokines overexpression, cell infiltration and oxidative stress | [24,25] |
| NAFLD linked with MetS | Mainly but not exclusively with hyperinsulinemia—insulin resistance | [27] |
| MetS-related brain neurodegenerative disorders | Disruption of blood–brain barrier, triggering neuroinflammation and amyloid disorders and decreasing the function of the cerebral blood vessels, including reduced cerebral blood flow, altered brain autoregulation, and compromised neurovascular coupling | [28,29,30,31] |
| MetS–related cancer development | Arterial hypertension displays a two-fold increased risk for GC development | [32,33] |
| Mechanisms |
|---|
| Promotion of arterial hypertension by: |
| • Augmented oxidative stress |
| • Increased insulin resistance |
| • Gastrointestinal dysbiosis • Increased vasoconstriction and decreased vasodilation |
| • Genetic and epigenetic modifications |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kountouras, J.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Polyzos, S.A.; Deretzi, G.; Vardaka, E.; Soteriades, E.S.; Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou, M.; Gkolfakis, P.; Karafyllidou, K.; Doulberis, M. Impact of Helicobacter pylori-Related Metabolic Syndrome Parameters on Arterial Hypertension. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112351
Kountouras J, Papaefthymiou A, Polyzos SA, Deretzi G, Vardaka E, Soteriades ES, Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou M, Gkolfakis P, Karafyllidou K, Doulberis M. Impact of Helicobacter pylori-Related Metabolic Syndrome Parameters on Arterial Hypertension. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(11):2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112351
Chicago/Turabian StyleKountouras, Jannis, Apostolis Papaefthymiou, Stergios A. Polyzos, Georgia Deretzi, Elisabeth Vardaka, Elpidoforos S. Soteriades, Maria Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou, Paraskevas Gkolfakis, Kyriaki Karafyllidou, and Michael Doulberis. 2021. "Impact of Helicobacter pylori-Related Metabolic Syndrome Parameters on Arterial Hypertension" Microorganisms 9, no. 11: 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112351
APA StyleKountouras, J., Papaefthymiou, A., Polyzos, S. A., Deretzi, G., Vardaka, E., Soteriades, E. S., Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou, M., Gkolfakis, P., Karafyllidou, K., & Doulberis, M. (2021). Impact of Helicobacter pylori-Related Metabolic Syndrome Parameters on Arterial Hypertension. Microorganisms, 9(11), 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112351








