Development of High-Throughput Multiplex Serology to Detect Serum Antibodies against Coxiella burnetii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reference Sera
2.2. The Generation of Recombinant C. burnetii Antigens
2.3. Multiplex Serology
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
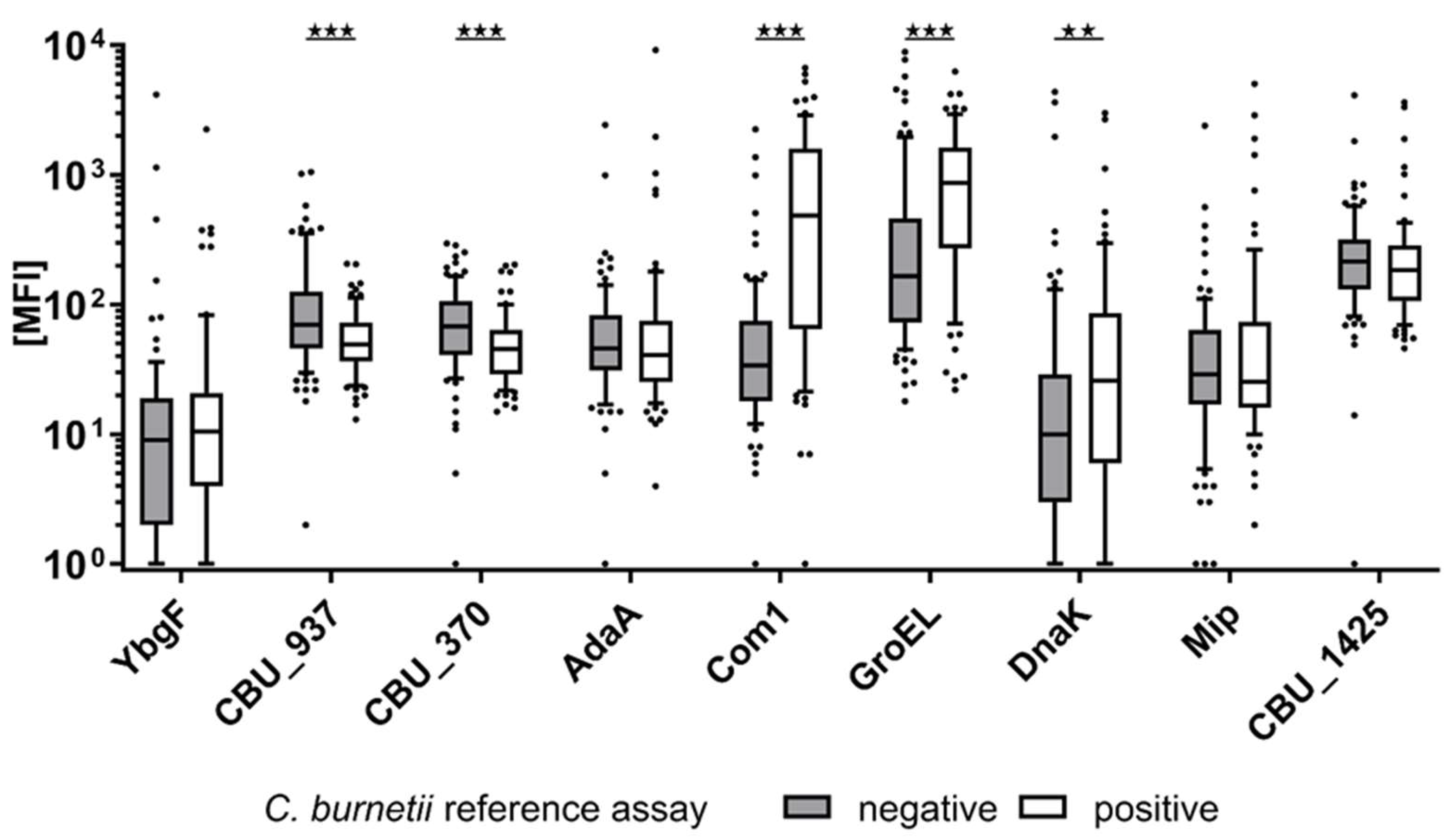
3.1. Seroresponses to C. burnetii Antigens and Concordance with the Reference Assay
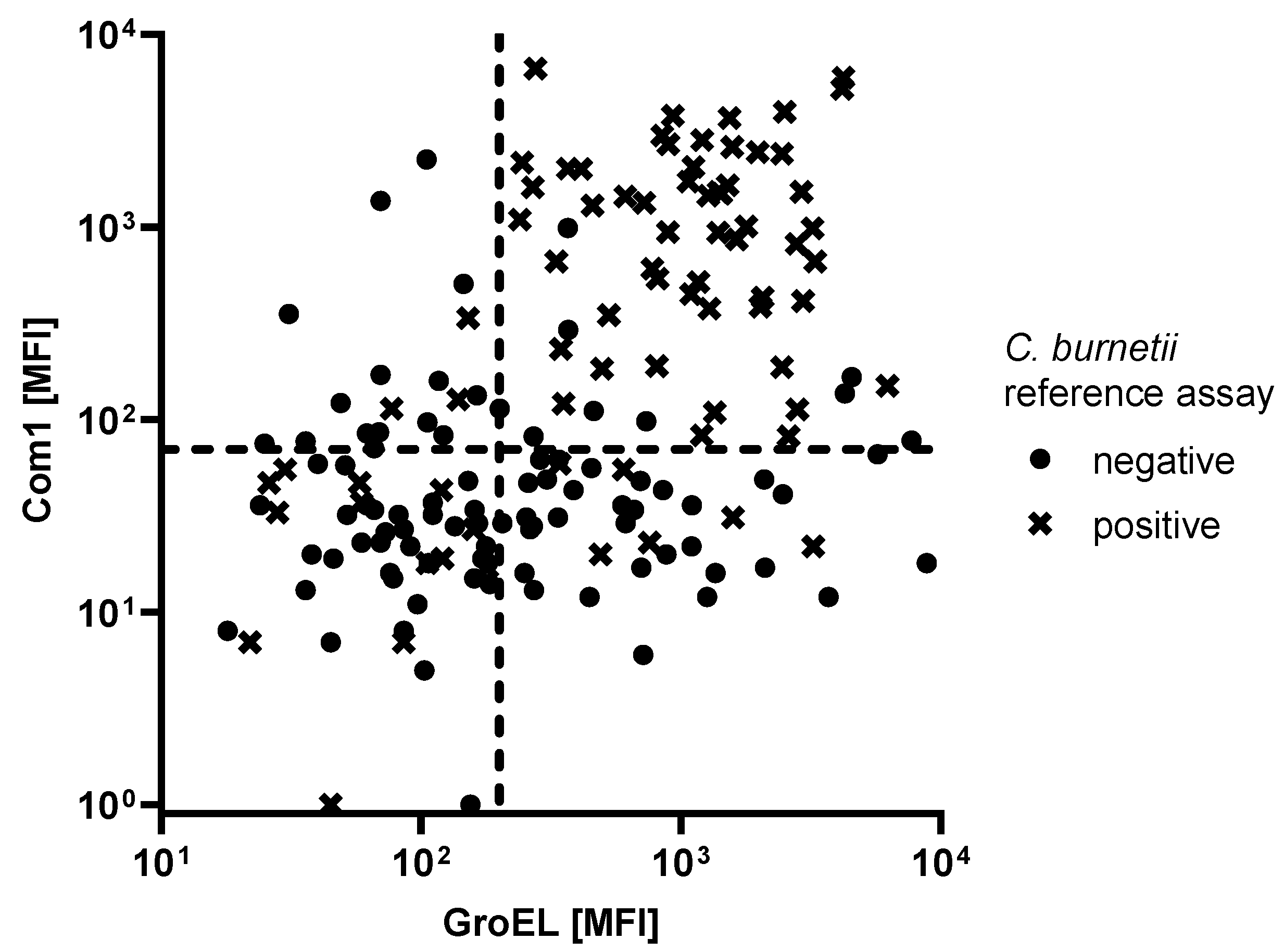
3.2. Assay Performance in Patients with High C. burnetii Phase I Endpoint Titers
3.3. Optimizing Assay Parameters for Seroepidemiological Case-Control Studies
4. Discussion
5. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angelakis, E.; Raoult, D. Q fever. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, M.; Raoult, D. Q fever. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 518–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Technical Report: Risk Assessment on Q Fever; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2010; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmer, B.; Notermans, D.W.; Harms, M.G.; Reimerink, J.H.; Bakker, J.; Schneeberger, P.; Mollema, L.; Teunis, P.; van Pelt, W.; van Duynhoven, Y. Low seroprevalence of Q fever in The Netherlands prior to a series of large outbreaks. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Velasco, F.; Montes, M.; Marimon, J.M.; Cilla, G. High seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii infection in Eastern Cantabria (Spain). Int. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 27, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delsing, C.E.; Kullberg, B.J.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P. Q fever in The Netherlands from 2007 to 2010. Neth. J. Med. 2010, 68, 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Amitai, Z.; Bromberg, M.; Bernstein, M.; Raveh, D.; Keysary, A.; David, D.; Pitlik, S.; Swerdlow, D.; Massung, R.; Rzotkiewicz, S.; et al. A large Q fever outbreak in an urban school in central Israel. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilsdorf, A.; Kroh, C.; Grimm, S.; Jensen, E.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Alpers, K. Large Q fever outbreak due to sheep farming near residential areas, Germany, 2005. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porten, K.; Rissland, J.; Tigges, A.; Broll, S.; Hopp, W.; Lunemann, M.; van Treeck, U.; Kimmig, P.; Brockmann, S.O.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; et al. A super-spreading ewe infects hundreds with Q fever at a farmers′ market in Germany. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenotte, C.; Million, M.; Audoly, G.; Gorse, A.; Dutronc, H.; Roland, G.; Dekel, M.; Moreno, A.; Cammilleri, S.; Carrieri, M.P.; et al. B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma linked to Coxiella burnetii. Blood 2016, 127, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Roeden, S.E.; van Houwelingen, F.; Donkers, C.M.J.; Hogewoning, S.J.; de Lange, M.M.A.; van der Hoek, W.; Kampschreur, L.M.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Hoepelman, A.I.M.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; et al. Exposure to Coxiella burnetii and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A retrospective population-based analysis in The Netherlands. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e211–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenotte, C.; Mezouar, S.; Ben Amara, A.; Benatti, S.; Chiaroni, J.; Devaux, C.; Costello, R.; Kroemer, G.; Mege, J.L.; Raoult, D. A transcriptional signature associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the blood of patients with Q fever. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y. Hairy cell transformation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes by Coxiella burnetii. Yonsei Med. J. 1993, 34, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, P.T.; de Lange, M.M.A.; Wielders, C.C.H.; Dijkstra, F.; van Roeden, S.E.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; Oosterheert, J.J.; Schneeberger, P.M.; van der Hoek, W. Cost-effectiveness of screening program for chronic Q fever, The Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, C.; Melenotte, C.; Mediannikov, O.; Ghigo, E.; Million, M.; Edouard, S.; Mege, J.L.; Maurin, M.; Raoult, D. From Q fever to coxiella burnetii infection: A paradigm change. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 115–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loenhout, J.A.; Wielders, C.C.; Morroy, G.; Cox, M.J.; van der Hoek, W.; Hautvast, J.L.; Paget, W.J.; van der Velden, J. Severely impaired health status of non-notified Q fever patients leads to an underestimation of the true burden of disease. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2580–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoek, W.; Dijkstra, F.; Schimmer, B.; Schneeberger, P.M.; Vellema, P.; Wijkmans, C.; ter Schegget, R.; Hackert, V.; van Duynhoven, Y. Q fever in the Netherlands: An update on the epidemiology and control measures. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 19520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegdam-Blans, M.C.; Kampschreur, L.M.; Delsing, C.E.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; Sprong, T.; van Kasteren, M.E.; Notermans, D.W.; Renders, N.H.; Bijlmer, H.A.; Lestrade, P.J.; et al. Chronic Q fever: Review of the literature and a proposal of new diagnostic criteria. J. Infect. 2012, 64, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegdam-Blans, M.C.; Vainas, T.; van Sambeek, M.R.; Cuypers, P.W.; Tjhie, H.T.; van Straten, A.H.; Teijink, J.A. Vascular complications of Q-fever infections. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 42, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landais, C.; Fenollar, F.; Thuny, F.; Raoult, D. From acute Q fever to endocarditis: Serological follow-up strategy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschreur, L.M.; Wegdam-Blans, M.C.; Wever, P.C.; Renders, N.H.; Delsing, C.E.; Sprong, T.; van Kasteren, M.E.; Bijlmer, H.; Notermans, D.; Oosterheert, J.J.; et al. Chronic Q fever diagnosis-consensus guideline versus expert opinion. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, P.E.; Marrie, T.J.; Raoult, D. Diagnosis of Q fever. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D. Chronic Q fever: Expert opinion versus literature analysis and consensus. J. Infect. 2012, 65, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterboer, T.; Sehr, P.; Michael, K.M.; Franceschi, S.; Nieland, J.D.; Joos, T.O.; Templin, M.F.; Pawlita, M. Multiplex human papillomavirus serology based on in situ-purified glutathione s-transferase fusion proteins. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimer, A.R.; Ferreiro-Iglesias, A.; Nygard, M.; Bender, N.; Schroeder, L.; Hildesheim, A.; Robbins, H.A.; Pawlita, M.; Langseth, H.; Schlecht, N.F.; et al. Timing of HPV16-E6 antibody seroconversion before OPSCC: Findings from the HPVC3 consortium. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, J.; Blot, W.J.; Teras, L.; Visvanathan, K.; Le Marchand, L.; Haiman, C.; Chen, Y.; Sesso, H.D.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Ho, G.; et al. Serological responses to Helicobacter pylori proteins and risk of colorectal cancer in diverse populations across the United States. Helicobacter 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Schroeder, L.; Ingarfield, K.; Diehl, S.; Werner, J.; Brenner, N.; Liu, Z.; Pawlita, M.; Pring, M.; Butt, J.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus and human papillomavirus serum antibodies define the viral status of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a low endemic country. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, J.; Murugan, R.; Hippchen, T.; Olberg, S.; van Straaten, M.; Wardemann, H.; Stebbins, E.; Krausslich, H.G.; Bartenschlager, R.; Brenner, H.; et al. From multiplex serology to serolomics—A novel approach to the antibody response against the SARS-CoV-2 proteome. Viruses 2021, 13, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossai, A.; Waterboer, T.; Nelson, H.H.; Michel, A.; Willhauck-Fleckenstein, M.; Farzan, S.F.; Hoen, A.G.; Christensen, B.C.; Kelsey, K.T.; Marsit, C.J.; et al. Seroepidemiology of human polyomaviruses in a US population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N.; Mentzer, A.J.; Butt, J.; Michel, A.; Prager, K.; Brozy, J.; Weissbrich, B.; Aiello, A.E.; Meier, H.C.S.; Breuer, J.; et al. Validation of multiplex serology detecting human herpesviruses 1–5. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehr, P.; Zumbach, K.; Pawlita, M. A generic capture ELISA for recombinant proteins fused to glutathione S-transferase: Validation for HPV serology. J. Immunol. Methods 2001, 253, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, B.; Graves, S.; Stenos, J. Potential serodiagnostic markers for Q fever identified in Coxiella burnetii by immunoproteomic and protein microarray approaches. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekeyova, Z.; Kowalczewska, M.; Vincentelli, R.; Decloquement, P.; Flores-Ramirez, G.; Skultety, L.; Raoult, D. Characterization of antigens for Q fever serodiagnostics. Acta Virol. 2010, 54, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, S.A.; Fischer, E.R.; Cockrell, D.C.; Voth, D.E.; Howe, D.; Mead, D.J.; Samuel, J.E.; Heinzen, R.A. Proteome and antigen profiling of Coxiella burnetii developmental forms. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Bouman, T.J.; Beare, P.A.; Mertens, K.; Zhang, G.Q.; Russell-Lodrigue, K.E.; Hogaboam, J.P.; Peters, B.; Felgner, P.L.; Brown, W.C.; et al. A systematic approach to evaluate humoral and cellular immune responses to Coxiella burnetii immunoreactive antigens. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15 (Suppl. 2), 156–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stellfeld, M.; Gerlach, C.; Richter, I.G.; Miethe, P.; Fahlbusch, D.; Polley, B.; Sting, R.; Pfeffer, M.; Neubauer, H.; Mertens-Scholz, K. Evaluation of the diagnostic potential of recombinant coxiella burnetii Com1 in an ELISA for the diagnosis of Q fever in sheep, goats and cattle. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Xiong, X.; Qi, Y.; Gong, W.; Duan, C.; Yang, X.; Wen, B. Serological characterization of surface-exposed proteins of Coxiella burnetii. Microbiology 2014, 160, 2718–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, P.A.; Chen, C.; Bouman, T.; Pablo, J.; Unal, B.; Cockrell, D.C.; Brown, W.C.; Barbian, K.D.; Porcella, S.F.; Samuel, J.E.; et al. Candidate antigens for Q fever serodiagnosis revealed by immunoscreening of a Coxiella burnetii protein microarray. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Muller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, L.R.; Mallavia, L.P.; Samuel, J.E. Cloning and sequencing of Coxiella burnetii outer membrane protein gene com1. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, L.R.; Samuel, J.E.; Mallavia, L.P. Identification and cloning of a 27-kDa Coxiella burnetii immunoreactive protein. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 590, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.P.; Malik, S.V.S.; Dhaka, P.; Kumar, M.; Sirsant, B.; Gourkhede, D.; Barbuddhe, S.B.; Rawool, D.B. Comparison of two new in-house Latex Agglutination Tests (LATs), based on the DnaK and Com1 synthetic peptides of Coxiella burnetii, with a commercial indirect-ELISA, for sero-screening of coxiellosis in bovines. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 170, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranakis, I.; Mathioudaki, E.; Kokkini, S.; Psaroulaki, A. Com1 as a promising protein for the differential diagnosis of the two forms of Q fever. Pathogens 2019, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigil, A.; Chen, C.; Jain, A.; Nakajima-Sasaki, R.; Jasinskas, A.; Pablo, J.; Hendrix, L.R.; Samuel, J.E.; Felgner, P.L. Profiling the humoral immune response of acute and chronic Q fever by protein microarray. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschreur, L.M.; Oosterheert, J.J.; Koop, A.M.; Wegdam-Blans, M.C.; Delsing, C.E.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; De Jager-Leclercq, M.G.; Groot, C.A.; Sprong, T.; Nabuurs-Franssen, M.H.; et al. Microbiological challenges in the diagnosis of chronic Q fever. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.K.; Kersh, G.J. Analysis of recombinant proteins for Q fever diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaroulaki, A.; Mathioudaki, E.; Vranakis, I.; Chochlakis, D.; Yachnakis, E.; Kokkini, S.; Xie, H.; Tsiotis, G. In the search of potential serodiagnostic proteins to discriminate between acute and chronic Q fever in humans. Some promising outcomes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 557027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, I.; Rousset, E.; Dufour, P.; Sidi-Boumedine, K.; Cupo, A.; Thiery, R.; Duquesne, V. Evaluation of the recombinant Heat shock protein B (HspB) of Coxiella burnetii as a potential antigen for immunodiagnostic of Q fever in goats. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A.; Waterboer, T.; Kist, M.; Pawlita, M. Helicobacter pylori multiplex serology. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Leung, P.K.; Wong, S.S.; Ho, P.L.; Yuen, K.Y. groEL encodes a highly antigenic protein in Burkholderia pseudomallei. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zella, D.; Curreli, S.; Benedetti, F.; Krishnan, S.; Cocchi, F.; Latinovic, O.S.; Denaro, F.; Romerio, F.; Djavani, M.; Charurat, M.E.; et al. Mycoplasma promotes malignant transformation in vivo, and its DnaK, a bacterial chaperone protein, has broad oncogenic properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E12005–E12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.A.; Burne, R.A.; Castro, A.C. Molecular cloning, purification and immunological responses of recombinants GroEL and DnaK from Streptococcus pyogenes. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 28, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antigen Locus Tag | Antigen Symbol | RefSeq Accession | Protein Description | Subcellular Location | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBU_0092 | YbgF | NP_819144.2 | Cell division coordinator CpoB | Periplasm | Xiong et al. [32] |
| CBU_0937 | NP_819950.2 | LbtU family protein (siderophore porin) | Secreted | Sekeyova et al. [33] | |
| CBU_0370 | NP_819410.1 | Membrane-associated protein | Membrane | ||
| CBU_0952 | AdaA | NP_819961.1 | Acute disease antigen A | Secreted | Coleman et al. [34] Chen et al. [35] |
| CBU_1910 | Com1 | NP_820887.1 | Outer membrane protein | Membrane | Stellfeld et al. [36] Jiao et al. [37] Xiong et al. [32] Chen et al. [35] Beare et al. [38] |
| CBU_1718 | GroEL | NP_820699.1 | 60 kDa chaperonin | Cytoplasm | Xiong et al. [32] Coleman et al. [34] |
| CBU_1290 | DnaK | NP_820282.1 | Chaperone | Cytoplasm, Endoplasm, Membrane | Xiong et al. [32] |
| CBU_0630 | Mip | NP_819660.1 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | Secreted | Xiong et al. [32] |
| CBU_1425 | NP_820409.1 | 17 kDa common antigen | Membrane |
| Antigen Locus Tag | Antigen Symbol | C. burnetii Pos. (MFI) (SD) | C. burnetii Neg. (MFI) (SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBU_0092 | YbgF | 65 (266) | 77 (451) | 0.58 |
| CBU_0937 | 60 (38) | 128 (173) | <0.001 | |
| CBU_0370 | 55 (40) | 84 (60) | <0.001 | |
| CBU_0952 | AdaA | 228 (1073) | 100 (269) | 0.26 |
| CBU_1910 | Com1 | 1094 (1423) | 105 (291) | <0.001 |
| CBU_1718 | GroEL | 1209 (1205) | 697 (1518) | <0.001 |
| CBU_1290 | DnaK | 151 (470) | 138 (621) | <0.01 |
| CBU_0630 | Mip | 206 (703) | 81 (259) | 0.81 |
| CBU_1425 | 324 (584) | 313 (469) | 0.13 |
| Antigen Locus Tag | Antigen Symbol | Cutoff (MFI) | Specificity (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Cohen’s Kappa κ (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBU_0092 | YbgF | 32 | 89 | 21 | 0.11 (−0.05 to 0.27) |
| CBU_0937 | 67 | 54 | 72 | −0.26 (−0.41 to −0.11) | |
| CBU_0370 | 67 | 53 | 80 | −0.32 (−0.47 to −0.18) | |
| CBU_0952 | AdaA | 33 | 74 | 42 | −0.15 (−0.29 to −0.01) |
| CBU_1910 | Com1 | 178 | 93 | 64 | 0.59 (0.47 to 0.72) |
| CBU_1718 | GroEL | 340 | 69 | 72 | 0.41 (0.27 to 0.55) |
| CBU_1290 | DnaK | 30 1 | 77 | 47 | 0.25 (0.10 to 0.40) |
| CBU_0630 | Mip | 30 1 | 51 | 47 | −0.02 (−0.17 to 0.13) |
| CBU_1425 | 124 | 79 | 38 | −0.15 (−0.30 to −0.01) |
| Antigen Locus Tag | Antigen Symbol | Cutoff (MFI) | Specificity (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Cohen’s Kappa κ (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBU_0092 | YbgF | 30 1 | 86 | 25 | 0.12 (−0.13 to 0.37) |
| CBU_0937 | 82 | 42 | 93 | −0.30 (−0.52 to −0.08) | |
| CBU_0370 | 58 | 60 | 82 | −0.31 (−0.48 to −0.14) | |
| CBU_0952 | AdaA | 43 | 63 | 50 | −0.08 (−0.24 to 0.08) |
| CBU_1910 | Com1 | 179 | 93 | 86 | 0.78 (0.64 to 0.91) |
| CBU_1718 | GroEL | 747 | 84 | 79 | 0.56 (0.39 to 0.73) |
| CBU_1290 | DnaK | 31 | 79 | 68 | 0.40 (0.21 to 0.59) |
| CBU_0630 | Mip | 30 1 | 51 | 43 | −0.05 (−0.23 to 0.14) |
| CBU_1425 | 124 | 79 | 43 | −0.10 (−0.24 to 0.03) |
| Seropositive Reference Population | Antigen | Cutoff (MFI) | Specificity (%) | Sensitivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 C. burnetii seropositive patients | Com1 (CBU_1910) | 140 | 90 | 66 |
| GroEL (CBU_1718) | 1360 | 90 | 34 | |
| Com 1 + GroEL (double positives) | 70/200 | 90 | 71 | |
| 28 C. burnetii seropositive patients with a Phase I titer of ≥1:1024 | Com1 (CBU_1910) | 140 | 90 | 86 |
| GroEL (CBU_1718) | 1360 | 90 | 50 | |
| Com 1 + GroEL (double positives) | 100/110 | 90 | 86 | |
| 180/400 | 100 | 79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeske, R.; Dangel, L.; Sauerbrey, L.; Frangoulidis, D.; Teras, L.R.; Fischer, S.F.; Waterboer, T. Development of High-Throughput Multiplex Serology to Detect Serum Antibodies against Coxiella burnetii. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112373
Jeske R, Dangel L, Sauerbrey L, Frangoulidis D, Teras LR, Fischer SF, Waterboer T. Development of High-Throughput Multiplex Serology to Detect Serum Antibodies against Coxiella burnetii. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(11):2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112373
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeske, Rima, Larissa Dangel, Leander Sauerbrey, Dimitrios Frangoulidis, Lauren R. Teras, Silke F. Fischer, and Tim Waterboer. 2021. "Development of High-Throughput Multiplex Serology to Detect Serum Antibodies against Coxiella burnetii" Microorganisms 9, no. 11: 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112373
APA StyleJeske, R., Dangel, L., Sauerbrey, L., Frangoulidis, D., Teras, L. R., Fischer, S. F., & Waterboer, T. (2021). Development of High-Throughput Multiplex Serology to Detect Serum Antibodies against Coxiella burnetii. Microorganisms, 9(11), 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112373







