Update on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—What the Clinician Should Know
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Increasing Clinical Impact of CoNS
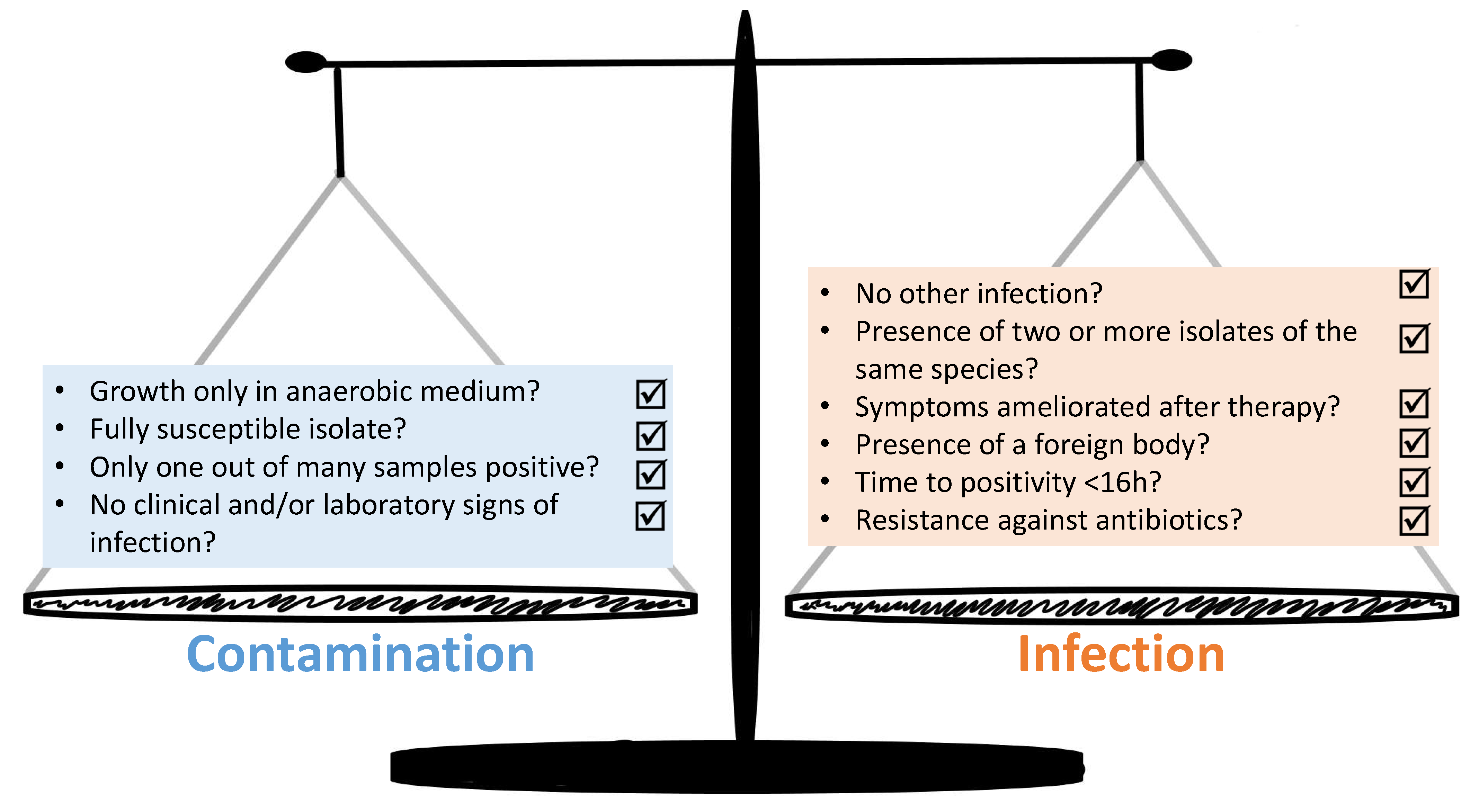
3. The Diagnostic Complexities—How to Distinguish between Infection and Contamination
| Species | Main Source | Case Reports | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. saccharolyticus | Human skin (especially back skin), animal skin (gorilla), contaminated platelet concentrates | 13 Anaerobic endocarditis, prosthetic valve endocarditis, bacteremia, discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis, pneumonia, lung infections in cystic fibrosis patients, infection of the shoulder joint, bone marrow infection, pyomyositis, heart valve disease, spondylodiscitis, empyema. | [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,35,36,37,39,41,42] |
| S. massiliensis | Human skin | 1 Brain abscess. | [43,67,68] |
| S. petrasii | |||
| subsp. petrasii | Human skin and ear canal | 1 Cerebral hemorrhage. | [44] |
| subsp. croceilyticus | Human skin and ear canal | 1 Acute otitis externa. | [44] |
| subsp. jettensis | not documented | / Strains were isolated from human clinical samples which were expected to be sterile (catheters, biopsies, cerebrospinal fluid, blood and deep swabs). Moreover, they were found in mixtures with other CoNS, which made it difficult to assess their clinical significance. | [69,70] |
| subsp. pragensis | not documented | 6 Prostatitis, hand wound infection, appendicitis, pancreatitis, sepsis, phlegmona. | [71] |
4. Therapy and Prevention—Many Old Bugs, Little New Drugs
4.1. General Remarks
4.2. Glycopeptides
4.3. Lipoglycopeptides
4.4. Daptomycin
4.5. Oxazolidinones
4.6. Alternatives and Biofilm-Active Substances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becker, K.; Both, A.; Weißelberg, S.; Heilmann, C.; Rohde, H. Emergence of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pain, M.; Wolden, R.; Jaén-Luchoro, D.; Salvà-Serra, F.; Iglesias, B.P.; Karlsson, R.; Klingenberg, C.; Cavanagh, J.P. Staphylococcus borealis sp. nov., isolated from human skin and blood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Schaumburg, F.; Kearns, A.; Larsen, A.R.; Lindsay, J.A.; Skov, R.L.; Westh, H. Implications of identifying the recently defined members of the Staphylococcus aureus complex S. argenteus and S. schweitzeri: A position paper of members of the ESCMID Study Group for Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Diseases (ESGS). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhussein, F.; Fürstenberg, J.; Gaupp, R.; Eisenbeis, J.; Last, K.; Becker, S.L.; Papan, C. Human infections caused by Staphylococcus argenteus in Germany: Genetic characterisation and clinical implications of novel species designation. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 2461–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurjadi, D.; Last, K.; Klein, S.; Boutin, S.; Schmack, B.; Mueller, F.; Heeg, K.; Ruhparwar, A.; Heininger, A.; Zanger, P. Nasal colonization with Staphylococcus aureus is a risk factor for ventricular assist device infection in the first year after implantation: A prospective, single-centre, cohort study. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldman, M.H.; Rasmussen, M.; Olaison, L.; Påhlman, L.I. Endocarditis due to Staphylococcus lugdunensis—A retrospective national registry-based study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Kohler, C.; Becker, K. Role of SrtA in Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus lugdunensis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, L.; Stegger, M.; Söderquist, B. Staphylococcus lugdunensis: Antimicrobial susceptibility and optimal treatment options. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, S.; Fong, S.S. Computational Modeling of the Human Microbiome. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galvani, A.P.; Parpia, A.S.; Foster, E.M.; Singer, B.H.; Fitzpatrick, M.C. Improving the prognosis of health care in the USA. Lancet 2020, 395, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papan, C.; Förster, K.; Herterich, R.; Schulze, A.; Schubert, S.; Flemmer, A.W. Identification and Containment of a Cluster of Two Bacillus cereus Infections in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 1506583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eichel, V.; Papan, C.; Mutters, N.T. Update Hygiene: Prevention of Vascular Catheter-Associated Infections in Premature and Newborn Infants. Klinische Padiatrie 2019, 231, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papan, C.; Karremann, M.; Weis, M.; Petzold, A.; Zahn, K.; Schroten, H.; Weichert, S.; Tenenbaum, T. A 28-Day-Old Boy with Multifocal Osteomyelitis Mimicking Non-Accidental Injury. Klinische Padiatrie 2021, 233, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, M.J.; Ceriani-Cernadas, J.M.; D’Apremont, I.; Bancalari, A.; Webb, V.; Genes, L.; Villarroel, L.; Munoz, E.; Tapia, J.L. Late Onset Sepsis in Very Low Birth Weight Infants in the South American NEOCOSUR Network. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Bischoff, T.; Tallent, S.M.; Seifert, H.; Wenzel, R.P.; Edmond, M.B. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Chaparro, G.J.; Servolo-Medeiros, E.A.; Souza-Fram, D.; Escudero, D.; Gualtero-Trujillo, S.M.; Morfin-Otero, R.; Gonzalez-Diaz, E.; Rodriguez-Noriega, E.; Altuzar-Figueroa, M.A.; et al. An eight-year multicenter study on short-term peripheral intravenous catheter-related bloodstream infection rates in 100 intensive care units of 9 countries in Latin America: Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Mexico, Panama, and Venezuela. Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, E.; Saathoff, S.; Graf, K.; Schwab, F.; Chaberny, I.F. The prevalence of nosocomial and community acquired infections in a university hospital: An observational study. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Int. 2013, 110, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noshak, M.A.; Rezaee, M.A.; Hasani, A.; Mirzaii, M. The Role of the Coagulase-negative Staphylococci (CoNS) in Infective Endocarditis; A Narrative Review from 2000 to 2020. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjec, C.; Morales Angeles, D.; Torrissen Mårli, M.; Fernández, L.; García, P.; Kjos, M.; Diep, D.B. Staphylococcal Biofilms: Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Gómez, P.; Alonso, C.A.; Camacho, M.C.; Ramiro, Y.; de la Puente, J.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Quevedo, M.Á.; Blanco, J.M.; Báguena, G.; et al. Frequency and Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Wild Birds in Spain. Detection of tst-Carrying, S. sciuri Isolates. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servier Medical Art. Available online: https://smart.servier.com (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Heß, S.; Gallert, C. Staphylococcus argensis sp. nov., a novel staphylococcal species isolated from an aquatic environment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2661–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pantůček, R.; Sedláček, I.; Indráková, A.; Vrbovská, V.; Mašlaňová, I.; Kovařovic, V.; Švec, P.; Králová, S.; Krištofová, L.; Kekláková, J.; et al. Staphylococcus edaphicus sp. nov., Isolated in Antarctica, Harbors the mecC Gene and Genomic Islands with a Suspected Role in Adaptation to Extreme Environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacFadyen, A.C.; Drigo, I.; Harrison, E.M.; Parkhill, J.; Holmes, M.A.; Paterson, G.K. Staphylococcus caeli sp. nov., isolated from air sampling in an industrial rabbit holding. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFadyen, A.C.; Leroy, S.; Harrison, E.M.; Parkhill, J.; Holmes, M.A.; Paterson, G.K. Staphylococcus pseudoxylosus sp. nov., isolated from bovine mastitis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naushad, S.; Kanevets, U.; Nobrega, D.; Carson, D.; Dufour, S.; Roy, J.P.; Lewis, P.J.; Barkema, H.W. Staphylococcus debuckii sp. nov., a coagulase-negative species from bovine milk. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westblom, T.U.; Gorse, G.J.; Milligan, T.W.; Schindzielorz, A.H. Anaerobic endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus saccharolyticus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2818–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, S.; Haglund, L.; Ashfaq, A.; Leist, P.; Roat, T. Prosthetic valve endocarditis due to Staphylococcus saccharolyticus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinbrueckner, B.; Singh, S.; Freney, J.; Kuhnert, P.; Pelz, K.; Aufenanger, J. Facing a mysterious hospital outbreak of bacteraemia due to Staphylococcus saccharolyticus. J. Hosp. Infect. 2001, 49, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godreuil, S.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Morel, J.; Darbas, H.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Bañuls, A.L.; Marchandin, H. Unusual case of spondylodiscitis due to Staphylococcus saccharolyticus. Joint Bone Spine 2005, 72, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhael, M.M.; Bach, H.G.; Huddleston, P.M.; Maus, T.P.; Berbari, E.F. Multilevel diskitis and vertebral osteomyelitis after diskography. Orthopedics 2009, 32, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlitzsch, D.; Rintelen, C.; Böhm, K.; Wollschläger, B.; Merkel, N.; Borneff-Lipp, M.; Döring, G. Antibiotic-resistant obligate anaerobes during exacerbations of cystic fibrosis patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, X. A case of Staphylococcus saccharolyticus pneumonia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, e43–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, H.; Rood, I.G.; de Korte, D.; Ramírez-Arcos, S. Strict anaerobic Staphylococcus saccharolyticus isolates recovered from contaminated platelet concentrates fail to multiply during platelet storage. Transfusion 2012, 52, 916–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, A.G.; Yian, E.; Steens, W. Injection-induced low-grade infection of the shoulder joint: Preliminary results. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2012, 132, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Sun, B.; Guo, J.; He, J.L.; Feng, B.; Wang, H.G.; Cao, K.-K.; Liu, T.; Shen, D.-X. A case of bone marrow infection by Staphylococcus saccharolyticus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 1161–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Young, N.; Bhally, H. Bilateral Neck Pyomyositis Caused by Staphylococcus capitis and Staphylococcus saccharolyticus in a Diabetic Adult. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2017, 3713212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brüggemann, H.; Poehlein, A.; Brzuszkiewicz, E.; Scavenius, C.; Enghild, J.J.; Al-Zeer, M.A.; Brinkmann, V.; Jensen, A.; Söderquist, B. Staphylococcus saccharolyticus Isolated From Blood Cultures and Prosthetic Joint Infections Exhibits Excessive Genome Decay. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbach, A.; Friedrich, M.; Lehmann, S.; Schlichting, N.; Kullnick, Y.; Gräber, S.; Buschmann, T.; Hagl, C.; Bagaev, E.; Gruhle, M.; et al. Bacterial infiltration in structural heart valve disease. J. Thorac Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahle, C.M.; Stødkilde, K.; Afshar, M.; Poehlein, A.; Ogilvie, L.A.; Söderquist, B.; Hüpeden, J.; Brüggemann, H. Staphylococcus saccharolyticus: An Overlooked Human Skin Colonizer. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojani, M.C.; Lamy, B.; Ruimy, R.; Amoretti, N.; Risso, K.; Roux, C. An unusual Staphylococcus saccharolyticus spondylodiscitis post kyphoplasty: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Z. Staphylococcus saccharolyticus infection: Case series with a PRISMA-compliant systemic review. Medicine 2020, 99, e20686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Masalma, M.; Raoult, D.; Roux, V. Staphylococcus massiliensis sp. nov., isolated from a human brain abscess. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantůček, R.; Švec, P.; Dajcs, J.J.; Machová, I.; Černohlávková, J.; Šedo, O.; Gelbíčová, T.; Mašlaňová, I.; Doškař, J.; Zdráhal, Z.; et al. Staphylococcus petrasii sp. nov. including S. petrasii subsp. petrasii subsp. nov. and S. petrasii subsp. croceilyticus subsp. nov., isolated from human clinical specimens and human ear infections. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.P.; Anderson, W.E.; Beam, K.; Taylor, B.; Ellerman, J.; Kowalkowski, M.A. The Association Between Antibiotic Delay Intervals and Hospital Mortality Among Patients Treated in the Emergency Department for Suspected Sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papan, C.; Willersinn, M.; Weiß, C.; Karremann, M.; Schroten, H.; Tenenbaum, T. Antibiotic utilization in hospitalized children under 2 years of age with influenza or respiratory syncytial virus infection—A comparative, retrospective analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Papan, C.; Last, K. A global health perspective on SARS-CoV-2-hazards, disaster and hope. Wien Med. Wochenschr. 2020, 170, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, C.; Pavez, M.; Cerda, A.; Oporto, M.; Villarroel, D.; Hofmann, E.; Rios, E.; Sierralta, A.; Copelli, L.; Barrientos, L. MALDI-TOF MS and 16S RNA Identification of Culturable Gastric Microbiota: Variability Associated with the Presence of Helicobacter pylori. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, I.; Margardt, L.; Ngbede, E.O.; Adah, M.I.; Yusuf, S.T.; Keiser, J.; Rehner, J.; Utzinger, J.; Poppert, S.; Becker, S.L. Identification of Adult Fasciola spp. Using Matrix-Assisted Laser/Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight (MALDI-TOF) Mass Spectrometry. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, K.H.Y.; Lam, R.P.K.; Chan, E.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Emergence of Staphylococcus lugdunensis as a Cause of Urinary Tract Infection: Results of the Routine Use of MALDI-TOF MS. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavecchia, A.; Chiara, M.; De Virgilio, C.; Manzari, C.; Monno, R.; De Carlo, A.; Pazzani, C.; Horner, D.; Pesole, G.; Placido, A. Staphylococcus arlettae Genomics: Novel Insights on Candidate Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Genes in an Emerging Opportunistic Pathogen. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavecchia, A.; Chiara, M.; De Virgilio, C.; Manzari, C.; Pazzani, C.; Horner, D.; Pesole, G.; Placido, A. Comparative genomics suggests a taxonomic revision of the Staphylococcus cohnii species complex. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitzenbichler, F.; Simon, M.; Salzberger, B.; Hanses, F. Clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci other than S. epidermidis blood stream isolates at a tertiary care hospital. Infection 2017, 45, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekmann, S.E.; Diekema, D.J.; Doern, G.V. Determining the clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from blood cultures. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, B.; Hugonnet, S.; Correa, L.; Sax, H.; Rohner, P.; Pittet, D. Nosocomial bacteremia: Clinical significance of a single blood culture positive for coagulase-negative staphylococci. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vázquez, E.; Fernández-Rufete, A.; Hernández-Torres, A.; Canteras, M.; Ruiz, J.; Gómez, J. When is coagulase-negative Staphylococcus bacteraemia clinically significant? Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 45, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méric, G.; Mageiros, L.; Pensar, J.; Laabei, M.; Yahara, K.; Pascoe, B.; Kittiwan, N.; Tadee, P.; Post, V.; Lamble, S.; et al. Disease-associated genotypes of the commensal skin bacterium Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shelburne, S.A.; Dib, R.W.; Endres, B.T.; Reitzel, R.; Li, X.; Kalia, A.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Chaftari, A.-M.; Hachem, R.; Vargas-Cruz, N.S.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of Staphylococcus epidermidis bloodstream isolates from a prospective clinical trial reveals that complicated bacteraemia is caused by a limited number of closely related sequence types. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Benito, N.; Rivera, A.; García, L.; Miró, E.; Mur, I.; González, Y.; Gutiérrez, C.; Horcajada, J.P.; Espinal, P.; et al. Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus epidermidis in prosthetic joint infections: Can identification of virulence genes differentiate between infecting and commensal strains? J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi-Hoffnung, L.; Oved, K.; Navon, R.; Friedman, T.; Boico, O.; Paz, M.; Kronenfeld, G.; Etshtein, L.; Cohen, A.; Gottlieb, T.M.; et al. A host-protein signature is superior to other biomarkers for differentiating between bacterial and viral disease in patients with respiratory infection and fever without source: A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweeney, T.E. Hunting for Genes Linked to Risk of, Not From, Bloodstream Infection. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1696–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, P.; Kuppermann, N.; Mejias, A.; Suarez, N.; Chaussabel, D.; Casper, T.C.; Smith, B.; Alpern, E.R.; Anders, J.; Atabaki, S.M.; et al. Association of RNA Biosignatures With Bacterial Infections in Febrile Infants Aged 60 Days or Younger. JAMA 2016, 316, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, M.B.; Buturovic, L.; Luethy, R.; Midic, U.; Moore, A.R.; Roque, J.A.; Shaller, B.D.; Asuni, T.; Rawling, D.; Remmel, M.; et al. A generalizable 29-mRNA neural-network classifier for acute bacterial and viral infections. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.C.; Chang, J.C.; Mao, X.W.; Hsu, W.T.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; How, C.-K. Combining Procalcitonin and Rapid Multiplex Respiratory Virus Testing for Antibiotic Stewardship in Older Adult Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Infection. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, T.; Bennett, N.; Shemanski, S.; Kennedy, K.; Schlachter, A.; Boyd, S. Use of Procalcitonin and a Respiratory Polymerase Chain Reaction Panel to Reduce Antibiotic Use via an Electronic Medical Record Alert. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, R.; Singh, A.; Jangir, P.K.; Kumari, C.; Muduli, S.; Sharma, R. Genome Sequence of Staphylococcus massiliensis Strain S46, Isolated from the Surface of Healthy Human Skin. Genome Announc. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zong, Z. The newly-recognized species Staphylococcus massiliensis is likely to be part of the human skin microflora. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2012, 101, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bel, A.; Van Hoorde, K.; Wybo, I.; Vandoorslaer, K.; Echahidi, F.; De Brandt, E.; Schumann, P.; Ieven, M.; Soetens, O.; Piérard, D.; et al. Staphylococcus jettensis sp. nov., a coagulase-negative staphylococcal species isolated from human clinical specimens. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 3250–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bel, A.; Švec, P.; Petráš, P.; Sedláček, I.; Pantůček, R.; Echahidi, F.; Piérard, D.; Vandamme, P. Reclassification of Staphylococcus jettensis De Bel et al. 2013 as Staphylococcus petrasii subsp. jettensis subsp. nov. and emended description of Staphylococcus petrasii Pantucek et al. 2013. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 4198–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švec, P.; Bel, A.; Sedláček, I.; Petráš, P.; Gelbíčová, T.; Černohlávková, J.; Mašlanová, I.; Cnockaert, M.; Varbanovová, I.; Echahidi, F.; et al. Staphylococcus petrasii subsp. pragensis subsp. nov., occurring in human clinical material. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moawad, A.A.; Hotzel, H.; Awad, O.; Roesler, U.; Hafez, H.M.; Tomaso, H.; Neubauer, H.; El-Adawy, H. Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Healthy Turkeys in Egypt: First Report of Linezolid Resistance. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, M. Coagulase-negative staphylococci as reservoirs of genes facilitating MRSA infection: Staphylococcal commensal species such as Staphylococcus epidermidis are being recognized as important sources of genes promoting MRSA colonization and virulence. Bioessays 2013, 35, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormick, M.H.; McGuire, J.M.; Pittenger, G.E.; Pittenger, R.C.; Stark, W.M. Vancomycin, a new antibiotic. I. Chemical and biologic properties. Antibiot. Annu. 1955, 3, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, T.M.; Cuba, G.T.; Morgado, P.G.M.; Nicolau, D.P.; Nouér, S.A.; Dos Santos, K.R.N.; Kiffer, C.B.V. Pharmacodynamic comparison of different antimicrobial regimens against Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections with elevated vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rybak, M.J.; Le, J.; Lodise, T.P.; Levine, D.P.; Bradley, J.S.; Liu, C.; Mueller, B.A.; Pai, M.P.; Wong-Beringer, A.; Rotschafer, J.C.; et al. Therapeutic Monitoring of Vancomycin for Serious Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections: A Revised Consensus Guideline and Review by the American Society of Health-system Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, M.J.; Lomaestro, B.M.; Rotschafer, J.C.; Moellering, R.C.; Craig, W.A.; Billeter, M.; Dalovisio, J.R.; Levine, D.P. Vancomycin therapeutic guidelines: A summary of consensus recommendations from the infectious diseases Society of America, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cynamon, M.H.; Granato, P.A. Comparison of the in vitro activities of teichomycin A2 and vancomycin against staphylococci and enterococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1982, 21, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Decousser, J.W.; Desroches, M.; Bourgeois-Nicolaos, N.; Potier, J.; Jehl, F.; Lina, G.; Cattoir, V.; Vandenesh, F.; Doucet-Populaire, F. Susceptibility trends including emergence of linezolid resistance among coagulase-negative staphylococci and meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from invasive infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.D.; Harven, L.T.; Bingley, V. Distinct Effectiveness of Oritavancin against Tolerance-Induced Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravolatz, L.D.; Cleveland, K.O.; Rikabi, K.; Hassoun, A.; Reilly, J.; Johnson, L.B.; Spak, C.; Valenti, S.; Szpunar, S. Real-world use of telavancin in the treatment of osteomyelitis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Mendes, R.E.; Duncan, L.R.; Flamm, R.K.; Sader, H.S. Activity of dalbavancin and comparator agents against Gram-positive cocci from clinical infections in the USA and Europe 2015–16. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2748–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariati, A.; Dadashi, M.; Chegini, Z.; van Belkum, A.; Mirzaii, M.; Khoramrooz, S.S.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. The global prevalence of Daptomycin, Tigecycline, Quinupristin/Dalfopristin, and Linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci strains: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2020, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Berendt, A.R.; Lew, D.; Zimmerli, W.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Rao, N.; Hanssen, A.; Wilson, W.R. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, e1–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satlin, M.J.; Nicolau, D.P.; Humphries, R.M.; Kuti, J.L.; Campeau, S.A.; Lewis, J.S.; Weinstein, M.P.; Jorgensen, J.H. Development of Daptomycin Susceptibility Breakpoints for Enterococcus faecium and Revision of the Breakpoints for Other Enterococcal Species by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.A.; Wenzel, M. More Than a Pore: A Current Perspective on the In Vivo Mode of Action of the Lipopeptide Antibiotic Daptomycin. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matrat, L.; Plaisant, F.; Barreto, C.; Claris, O.; Butin, M. Increasing use of linezolid in a tertiary NICU during a 10-year period: Reasons and concerns for the future. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2020, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, T.S.; Schwab, F.; Behnke, M.; Hansen, S.; Gastmeier, P.; Aghdassi, S.J.S. Linezolid use in German acute care hospitals: Results from two consecutive national point prevalence surveys. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iversen, K.; Ihlemann, N.; Gill, S.U.; Madsen, T.; Elming, H.; Jensen, K.T.; Bruun, N.E.; Høfsten, D.E.; Fursted, K.; Christensen, J.J.; et al. Partial Oral versus Intravenous Antibiotic Treatment of Endocarditis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerschner, H.; Cabal, A.; Hartl, R.; Machherndl-Spandl, S.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W.; Apfalter, P. Hospital outbreak caused by linezolid resistant Enterococcus faecium in Upper Austria. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouiller, K.; Ilic, D.; Wicky, P.H.; Cholley, P.; Chirouze, C.; Bertrand, X. Spread of clonal linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis in an intensive care unit associated with linezolid exposure. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosecka-Strojek, M.; Sadowy, E.; Gawryszewska, I.; Klepacka, J.; Tomasik, T.; Michalik, M.; Hryniewicz, W.; Miedzobrodzki, J. Emergence of linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis in the tertiary children’s hospital in Cracow, Poland. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarouf, L.; Omar, H.; El-Nakeeb, M.; Abouelfetouh, A. Prevalence and mechanisms of linezolid resistance among staphylococcal clinical isolates from Egypt. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Kelesidis, T.; Tsiodras, S.; Hindler, J.; Humphries, R.M. The emerging problem of linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theil, C.; Schmidt-Braekling, T.; Gosheger, G.; Schwarze, J.; Dieckmann, R.; Schneider, K.N.; Möllenbeck, B. Clinical use of linezolid in periprosthetic joint infections—A systematic review. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2020, 6, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortridge, D.; Flamm, R.K. Comparative In Vitro Activities of New Antibiotics for the Treatment of Skin Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68 (Suppl. 3), S200–S205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G.; Lancellotti, P.; Antunes, M.J.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Casalta, J.P.; Del Zotti, F.; Dulgheru, R.; El Khoury, G.; Erba, P.A.; Iung, B.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3075–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Bassi, G.L.; Coenye, T.; Donelli, G.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Holá, V.; Imbert, C.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; et al. ESCMID guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21 (Suppl. 1), S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonello, R.M.; Principe, L.; Maraolo, A.E.; Viaggi, V.; Pol, R.; Fabbiani, M.; Montagnani, F.; Lovecchio, A.; Luzzati, R.; Di Bella, S. Fosfomycin as Partner Drug for Systemic Infection Management. A Systematic Review of Its Synergistic Properties from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michels, R.; Last, K.; Becker, S.L.; Papan, C. Update on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—What the Clinician Should Know. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040830
Michels R, Last K, Becker SL, Papan C. Update on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—What the Clinician Should Know. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(4):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040830
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichels, Ricarda, Katharina Last, Sören L. Becker, and Cihan Papan. 2021. "Update on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—What the Clinician Should Know" Microorganisms 9, no. 4: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040830
APA StyleMichels, R., Last, K., Becker, S. L., & Papan, C. (2021). Update on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—What the Clinician Should Know. Microorganisms, 9(4), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040830







