Baicalein and Baicalin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent-RNA Polymerase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Flavonoids
2.2. Cells and Virus
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Virus Yield Assay
2.5. Antiviral Activity Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
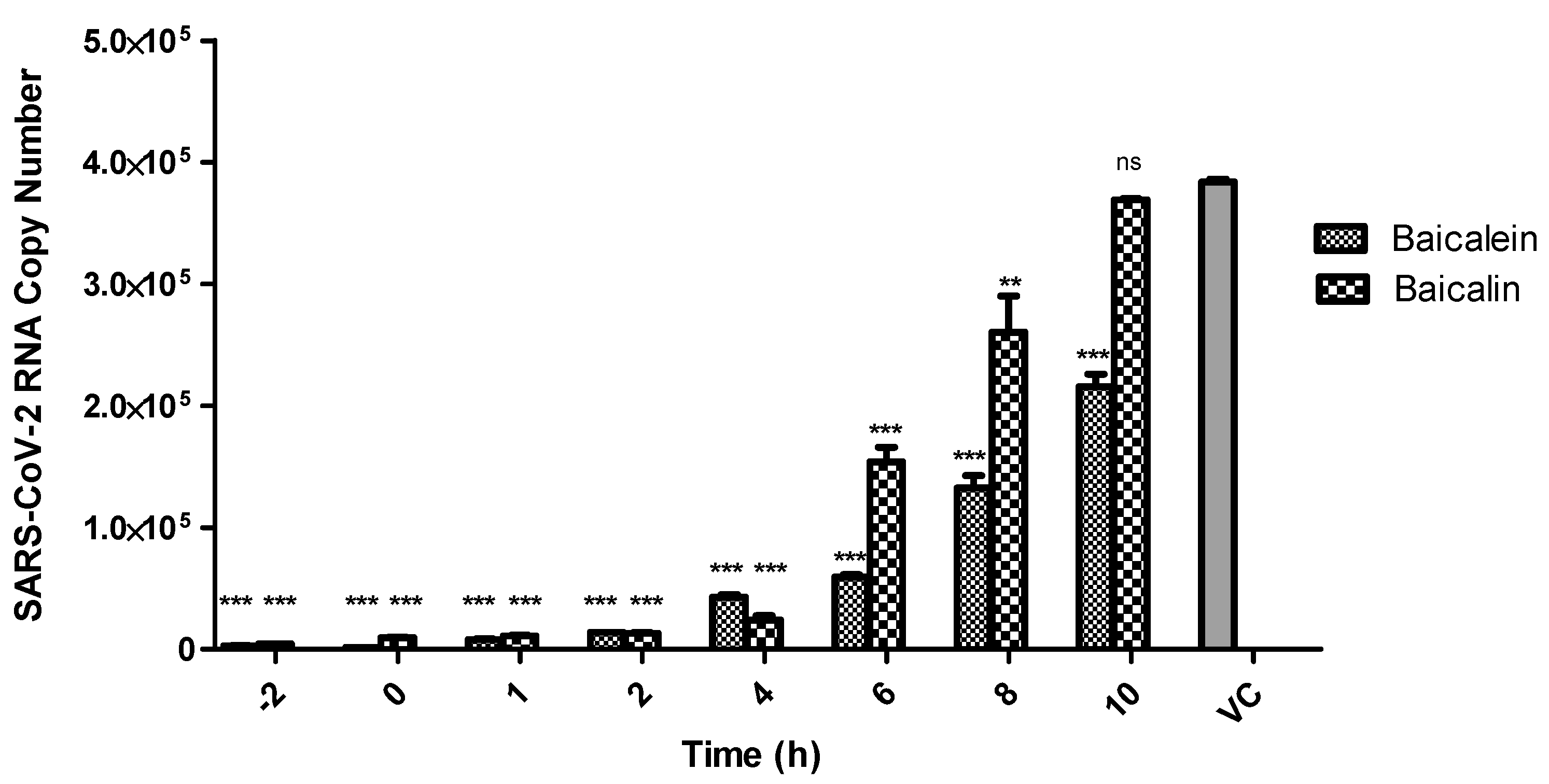
2.7. Time-of-Drug-Addition Assay
2.8. SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Entry Assay
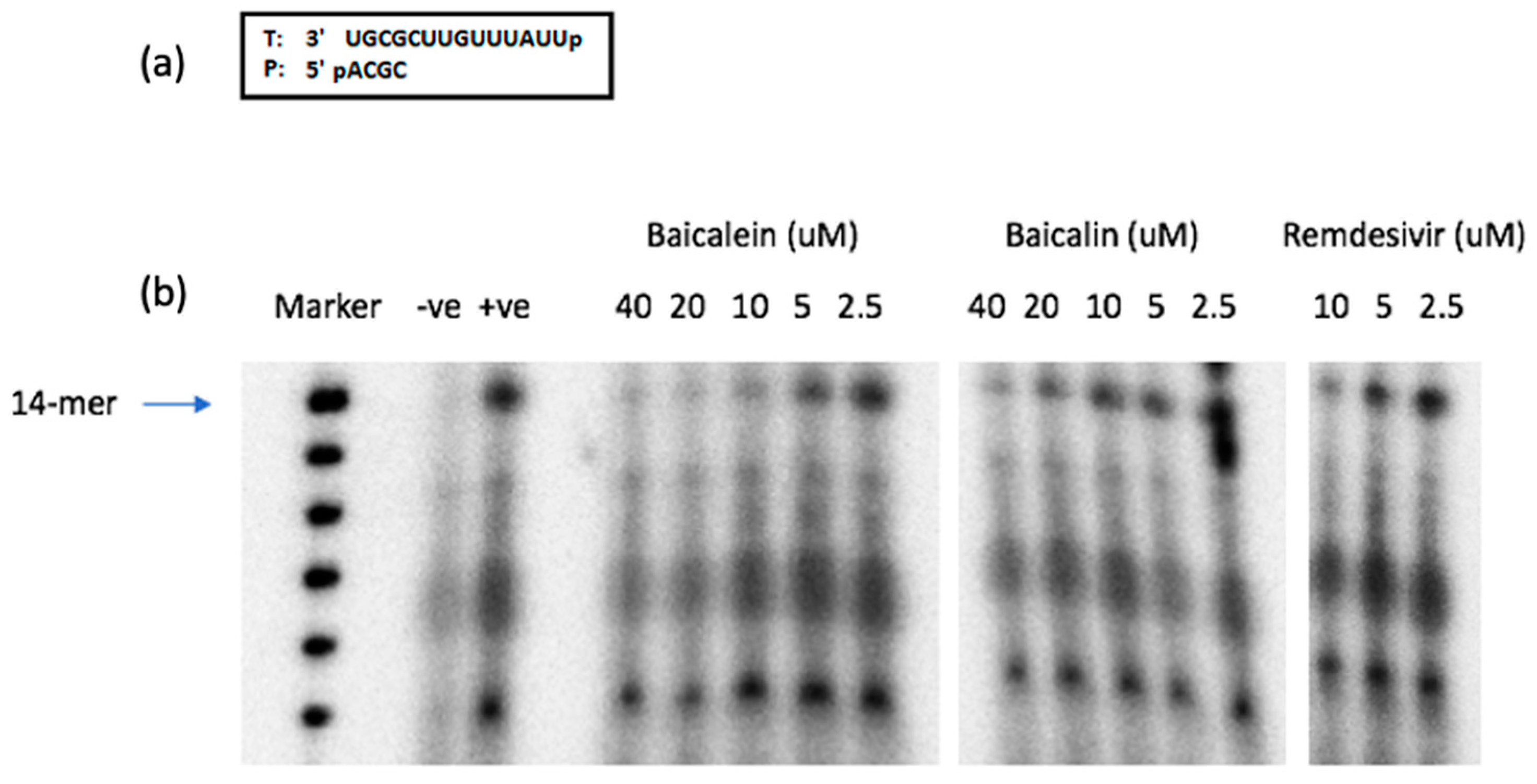
2.9. SARS-CoV-2 RdRp Assay
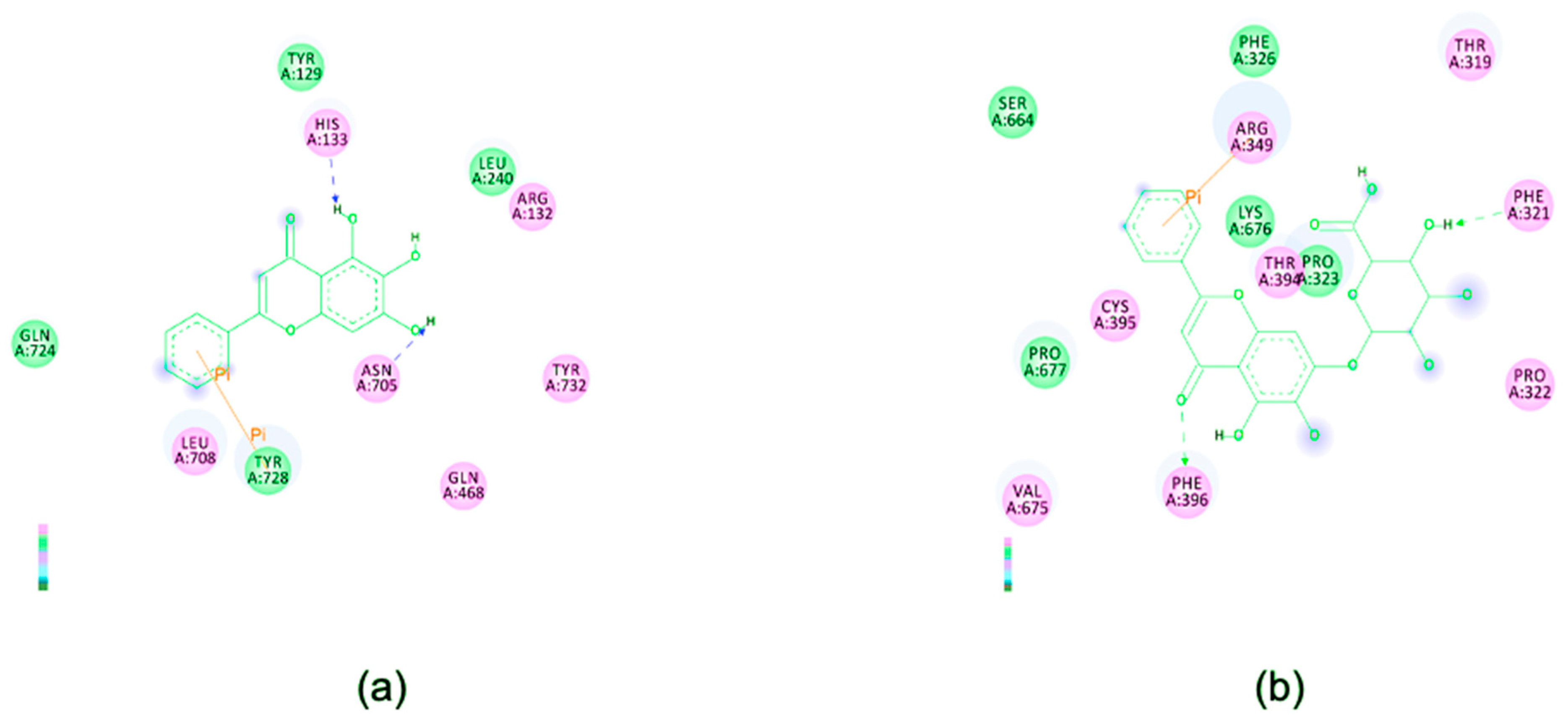
2.10. In Silico Study
2.11. Thermal Shift Assay
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Liu, S.M.; Yu, X.H.; Tang, S.L.; Tang, C.K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Current status and future perspective. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 28, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, N.; Dixit, D. Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: A review. Paediatr. Int. Child. Health 2020, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—Preliminary report. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, E.; Teoh, B.T.; Sam, S.S.; Lani, R.; Hassandarvish, P.; Chik, Z.; Yueh, A.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Baicalin the metabolite of baicalein exhibits in vitro anti-dengue virus activity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zandi, K.; Teoh, B.T.; Sam, S.S.; Wong, P.F.; Mustafa, M.R.; Abubakar, S. Novel antiviral activity of baicalein against Dengue virus type-2 in cell culture. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oo, A.; Teoh, B.T.; Sam, S.S.; Abu Bakar, S.; Zandi, K. Baicalein and baicalin as zika virus inhibitors. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lani, R.; Hassandarvish, P.; Shu, M.H.; Phoon, W.H.; Hann-Chu, J.J.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D.; AbuBakar, S.; Zandi, K. Antiviral activity of selected flavonoids against Chikungunya virus. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oo, A.; Rausalu, K.; Merits, A.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Deciphering the potential of baicalin as an antiviral agent for Chikungunya virus infection. Antivir. Res. 2018, 150, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z.; Xiao-Ya, C.; Martin, C. Scutellaria baicalensis, the golden herb from the garden of Chinese medicinal plants. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Song, K.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, M.; An, N.; Wei, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xing, Y.; Gao, Y. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of baicalin in cerebrovascular and neurological disorders. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 164, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03830684 (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Ramakrishnan, M.A. Determination of 50% endpoint titer using a simple formula. World J. Virol. 2016, 5, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cory, A.H.; Owen, T.C.; Barltrop, J.A.; Cory, J.G. Use of an aqueous soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth assays in culture. Cancer Commun. 1991, 3, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, K.; Amblard, F.; Musall, K.; Downs-Bowen, J.; Kleinbard, R.; Oo, A.; Cao, D.; Liang, B.; Russell, O.O.; McBrayer, T.; et al. Repurposing nucleoside analogs for human coronaviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01652-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, A.O.; Severson, W.; Jonsson, C.; Singh, K.; Weiss, S.R.; Sarafianos, S.G. Novel inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry that act by three distinct mechanisms. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8017–8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.K.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Casey, M.C.; Vernekar, S.K.V.; Do, H.T.; Sahani, R.L.; Kirby, K.A.; Du, H.; Hachiya, A.; Zhang, H.; Tedbury, P.R.; et al. Chemical profiling of HIV-1 capsid targeting antiviral PF74. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 200, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernekar, S.K.V.; Sahani, R.L.; Casey, M.C.; Kankanala, J.; Wang, L.; Kirby, K.A.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Tedbury, P.R.; Xie, J.; et al. Toward structurally novel and metabolically stable HIV-1 capsid-targeting small molecules. Viruses 2020, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grum-Tokars, V.; Ratia, K.; Begaye, A.; Baker, S.C.; Mesecar, A.D. Evaluating the 3C-like protease activity of SARS-Coronavirus: Recommendations for standardized assays for drug discovery. Virus Res. 2008, 133, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minskaia, E.; Hertzig, T.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Campanacci, V.; Cambillau, C.; Canard, B.; Ziebuhr, J. Discovery of an RNA virus 3’->5’ exoribonuclease that is critically involved in coronavirus RNA synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5108–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Tian, S.; Yang, S.; et al. The comprehensive study on the therapeutic effects of baicalein for the treatment of COVID-19 in vivo and in vitro. Biochem. Pharm. 2021, 183, 114302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillen, H.S.; Kokic, G.; Farnung, L.; Dienemann, C.; Tegunov, D.; Cramer, P. Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. bioRxiv 2020, 584, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yan, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, T.; Sun, Q.; Ming, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science 2020, 368, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, W.; Mao, C.; Luan, X.; Shen, D.D.; Shen, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; et al. Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir. Science 2020, 368, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, K.C.; Gulyaeva, A.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C.; Janssen, G.M.; Ruben, M.; Overkleeft, H.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Discovery of an essential nucleotidylating activity associated with a newly delineated conserved domain in the RNA polymerase-containing protein of all nidoviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8416–8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Thai, N.Q.; Truong, D.T.; Li, M.S. Remdesivir Strongly Binds to Both RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase and Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2: Evidence from Molecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 11337–11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Shin, D.H. Flavonoids with inhibitory activity against SARSCoV-2 3CLpro. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X.; Yang, T. Potential treatment of Chinese and Western medicine targeting Nsp14 of SARS-CoV-2. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.X.; Yao, S.; Zhao, W.F.; Li, M.J.; Liu, J.; Shang, W.J.; Xie, H.; Ke, C.Q.; Hu, H.C.; Gao, M.N.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities in vitro of Shuanghuanglian preparations and bioactive ingredients. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalani, S.S.; Anasir, M.I.; Poh, C.L. Antiviral activity of silymarin in comparison with baicalein against EV-A71. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Compound | Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2 | Cytotoxicity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vero | Calu-3 | Vero | Calu3 | |||
| EC50 (µM) | EC90 (µM) | EC50 (µM) | EC90 (µM) | CC50 (µM) | CC50 (µM) | |
| Baicalein | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 7.6 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.03 | 6.2 ± 0.04 | 8 6 ± 0.1 | 91 ± 0.05 |
| Baicalin | 9.0 ± 0.08 | 15.8 ± 0.2 | 8.0 ± 0.11 | 15.1 ± 0.2 | >100 | >100 |
| Remdesivir | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.5 ± 0.03 | > 100 | > 100 |
| Compound | SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Entry Inhibition (%) | Compound | SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Entry Inhibition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baicalin, µM | Baicalein, µM | ||
| 30 | −3.3 | 30 | 14.6 |
| 10 | −6.6 | 10 | 3.9 |
| 3.3 | −11.9 | 3.3 | −1.9 |
| 1.1 | −12.1 | 1.1 | −2 |
| Experiment Components | Tm (°C) | ΔTm (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| nsp5 + DMSO | 43.7 ± 0.1 | - |
| nsp5 + Baicalein | 44.5 ± 0.0 | 0.9 |
| nsp12 + DMSO | 44.4 ± 0.4 | - |
| nsp12 + Baicalein | 48.3 ± 2.6 | 3.9 |
| nsp14 + DMSO | 41.1 ± 0.1 | - |
| nsp14 + Baicalein | 42.6 ± 0.1 | 1.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zandi, K.; Musall, K.; Oo, A.; Cao, D.; Liang, B.; Hassandarvish, P.; Lan, S.; Slack, R.L.; Kirby, K.A.; Bassit, L.; et al. Baicalein and Baicalin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent-RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9050893
Zandi K, Musall K, Oo A, Cao D, Liang B, Hassandarvish P, Lan S, Slack RL, Kirby KA, Bassit L, et al. Baicalein and Baicalin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent-RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(5):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9050893
Chicago/Turabian StyleZandi, Keivan, Katie Musall, Adrian Oo, Dongdong Cao, Bo Liang, Pouya Hassandarvish, Shuiyun Lan, Ryan L. Slack, Karen A. Kirby, Leda Bassit, and et al. 2021. "Baicalein and Baicalin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent-RNA Polymerase" Microorganisms 9, no. 5: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9050893
APA StyleZandi, K., Musall, K., Oo, A., Cao, D., Liang, B., Hassandarvish, P., Lan, S., Slack, R. L., Kirby, K. A., Bassit, L., Amblard, F., Kim, B., AbuBakar, S., Sarafianos, S. G., & Schinazi, R. F. (2021). Baicalein and Baicalin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent-RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms, 9(5), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9050893









