The Species-Level Composition of the Fecal Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Genera in Indonesian Children Differs from That of Their Mothers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment of Volunteers
2.2. Collection of Samples and Sample Processing
2.2.1. HBM Samples
2.2.2. Fecal Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction and High throughput Sequencing
2.4. 16S rRNA Sequence
2.5. GroEL Sequencing of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
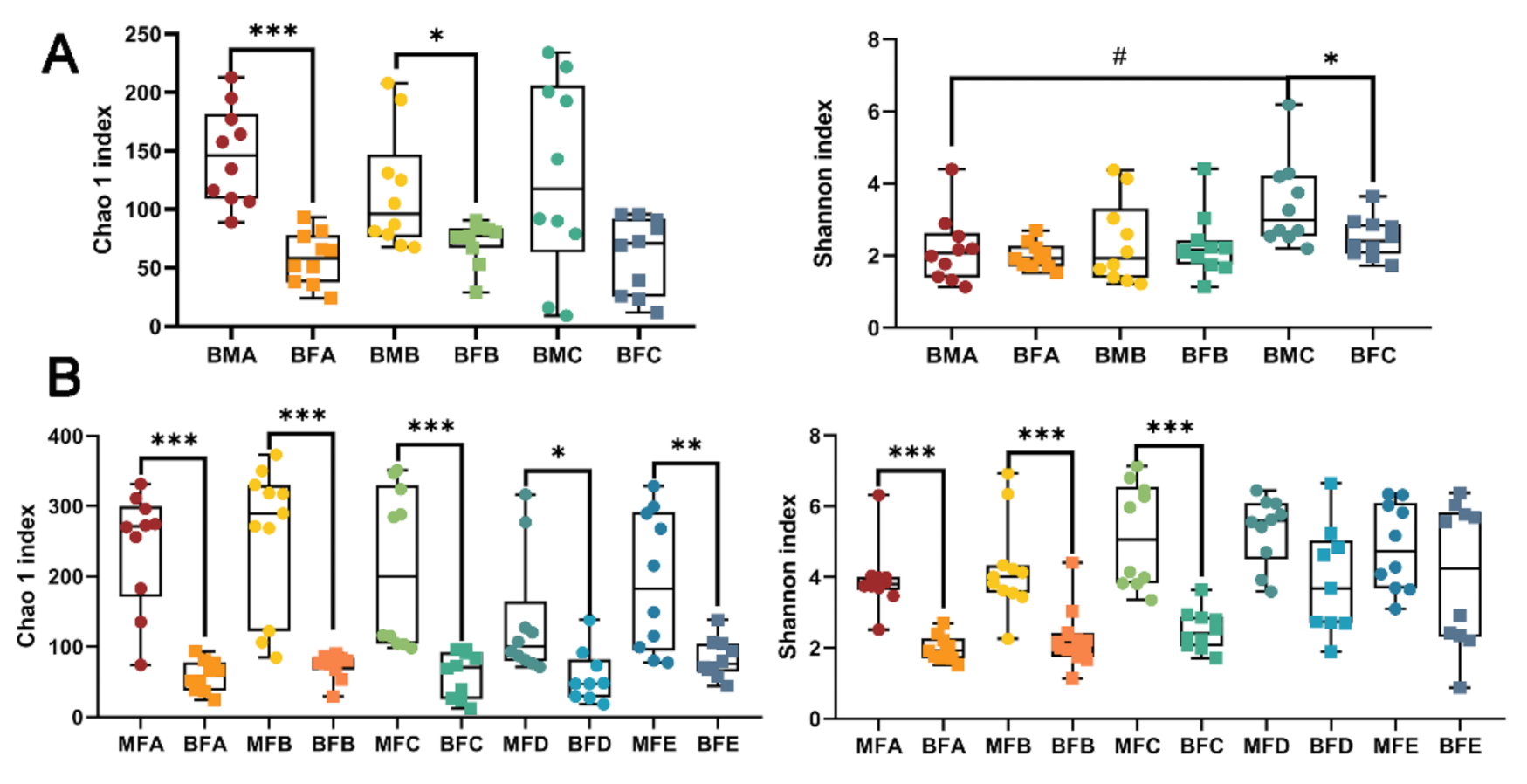
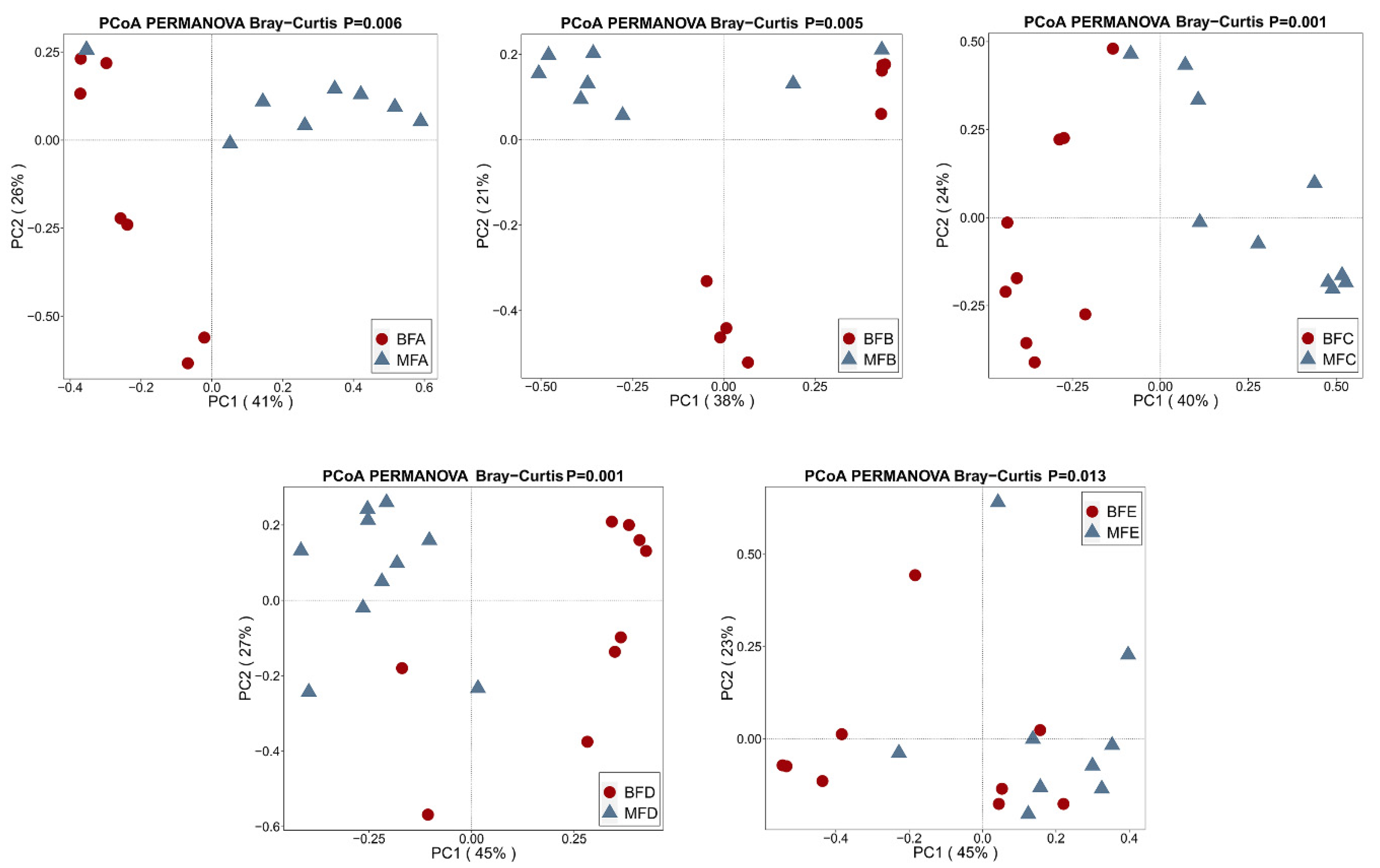
3.1. Bacterial Diversity of HBM, Maternal Feces and Child Feces
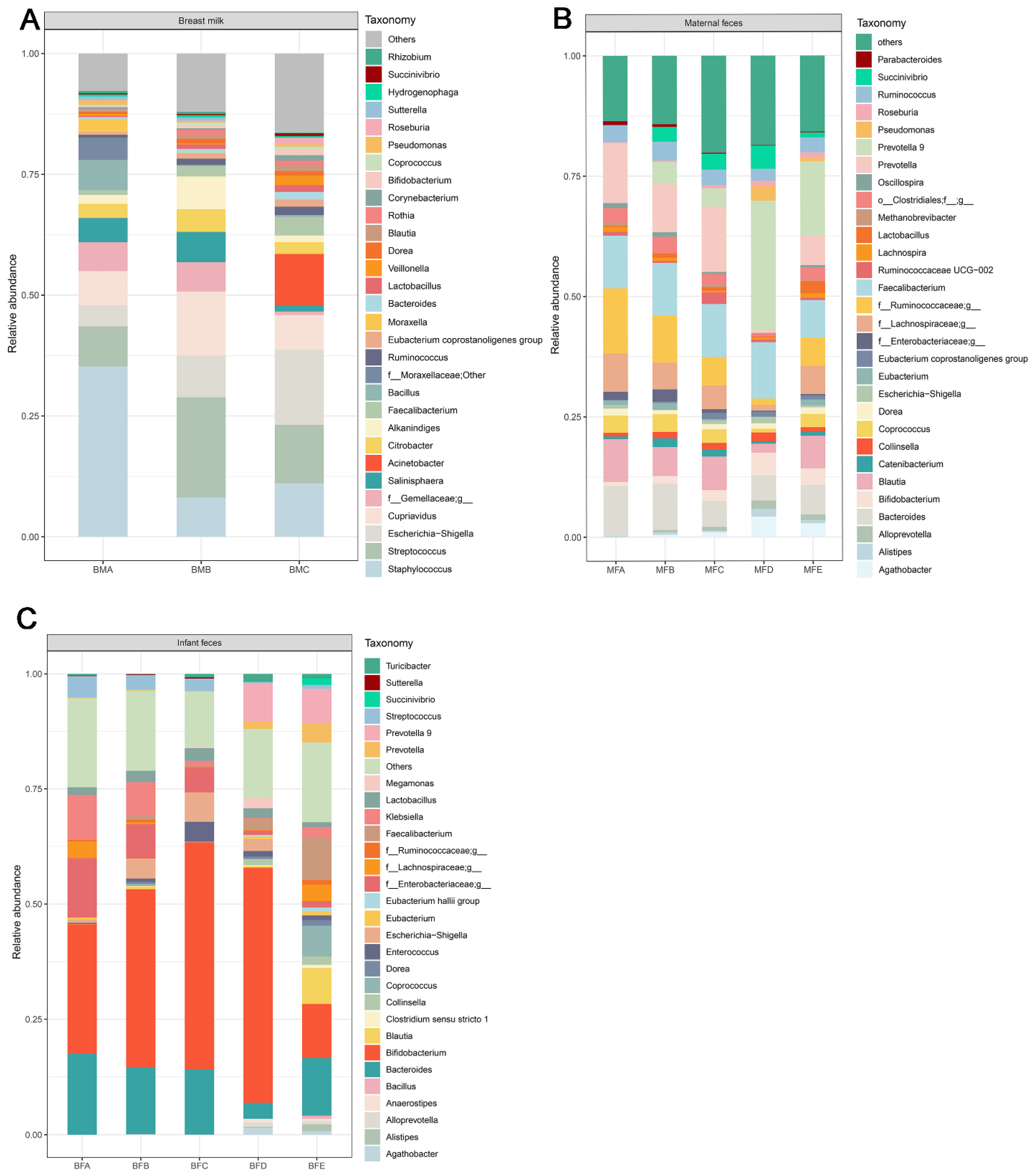
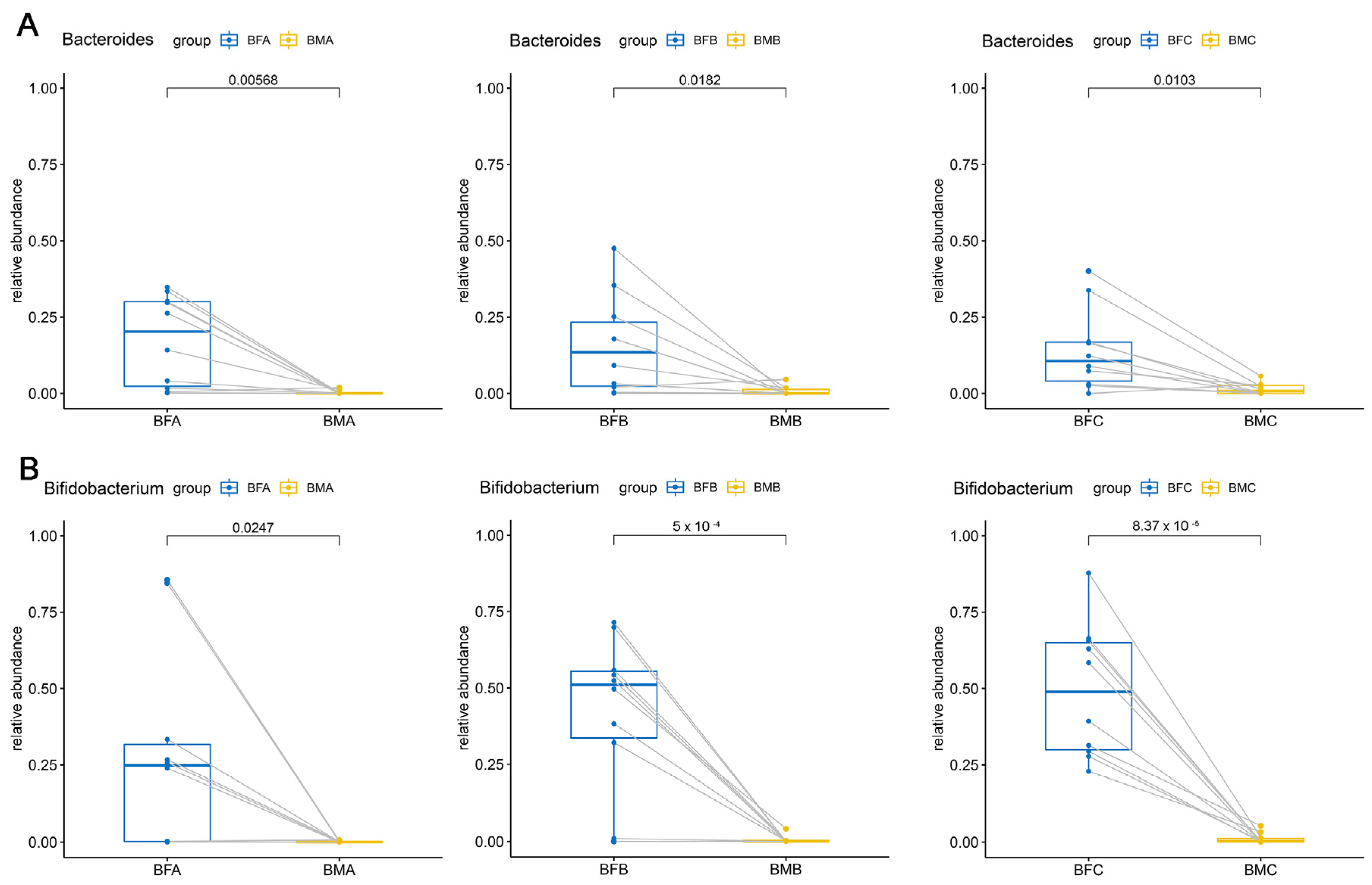
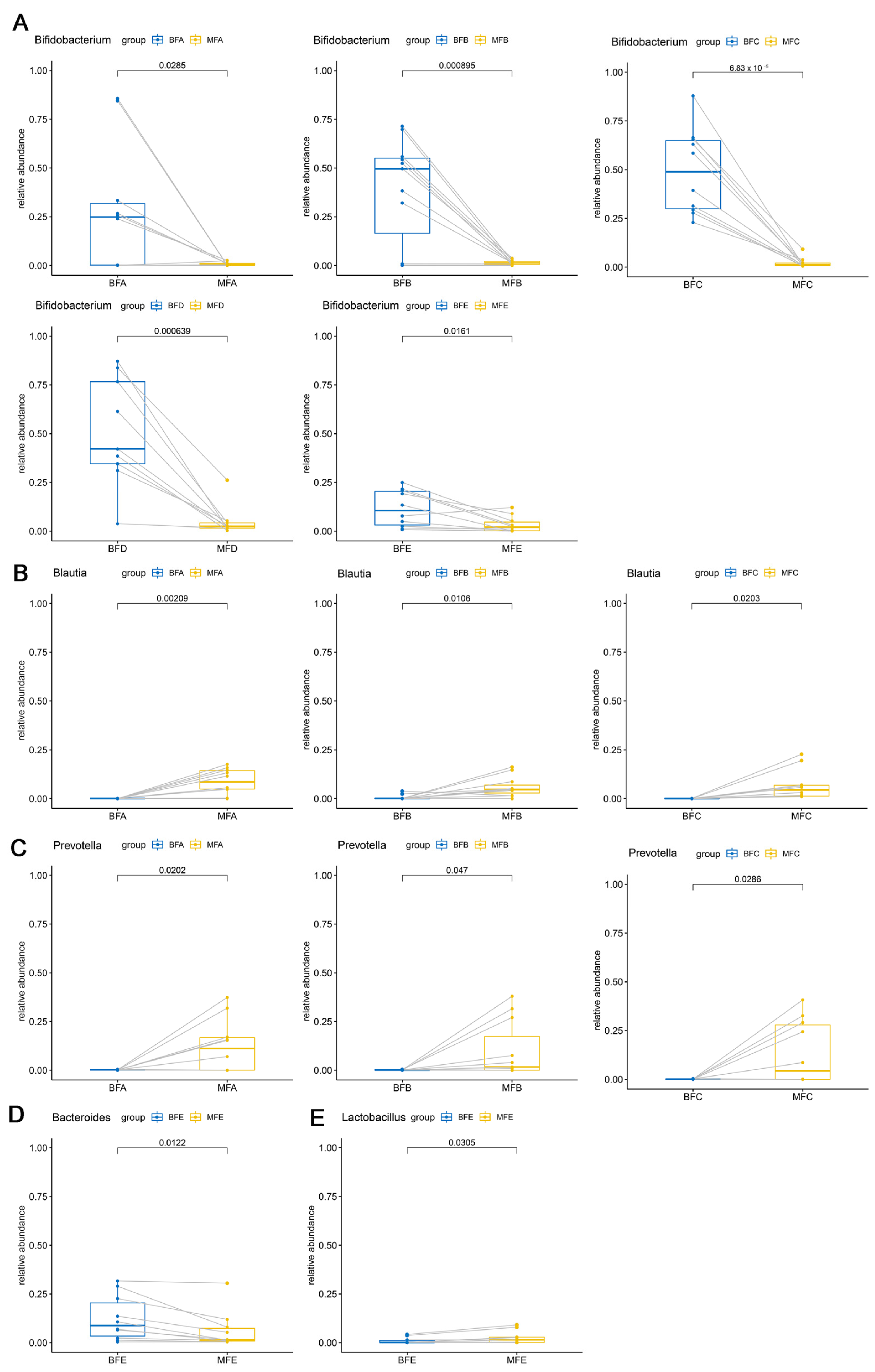
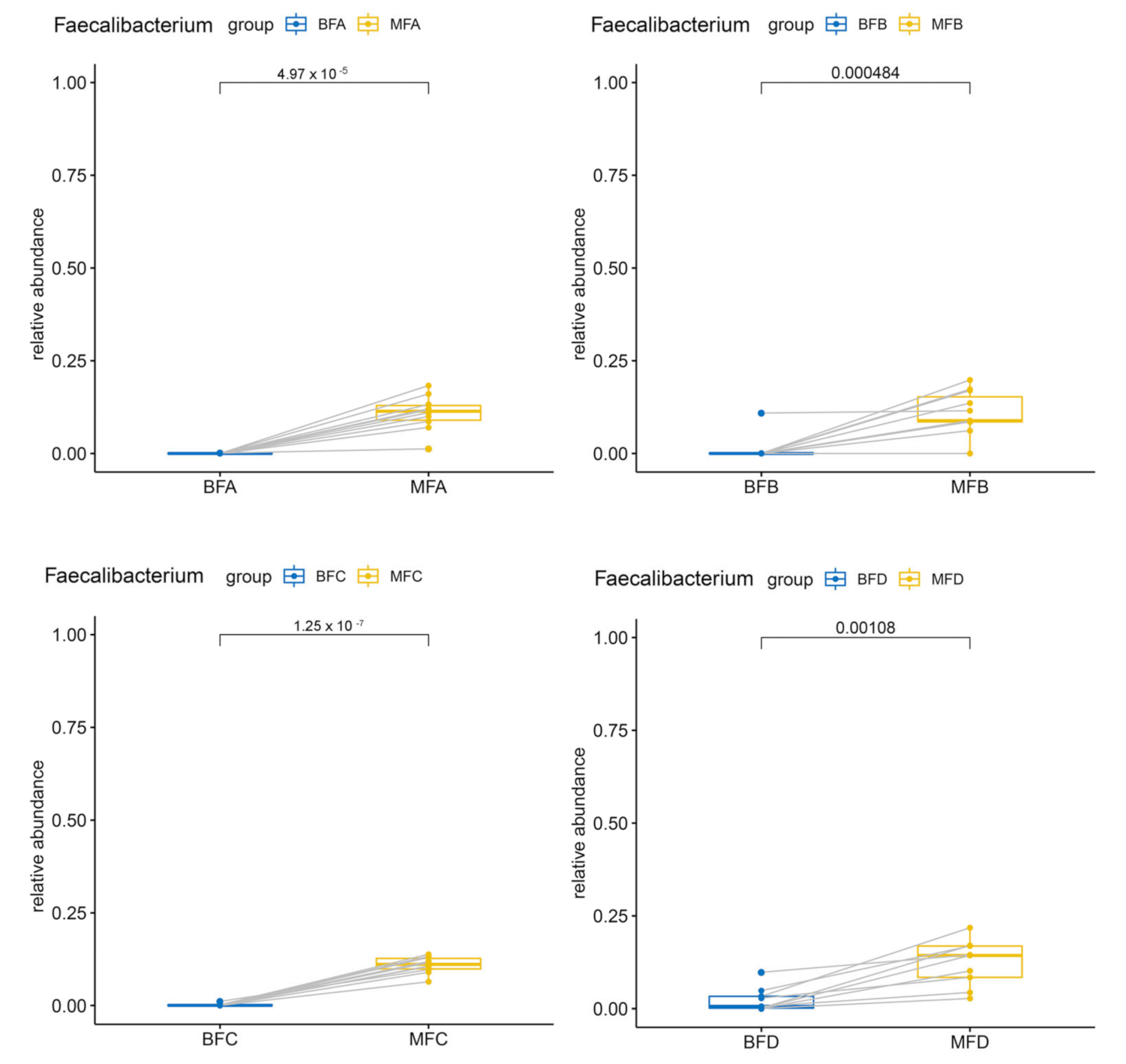
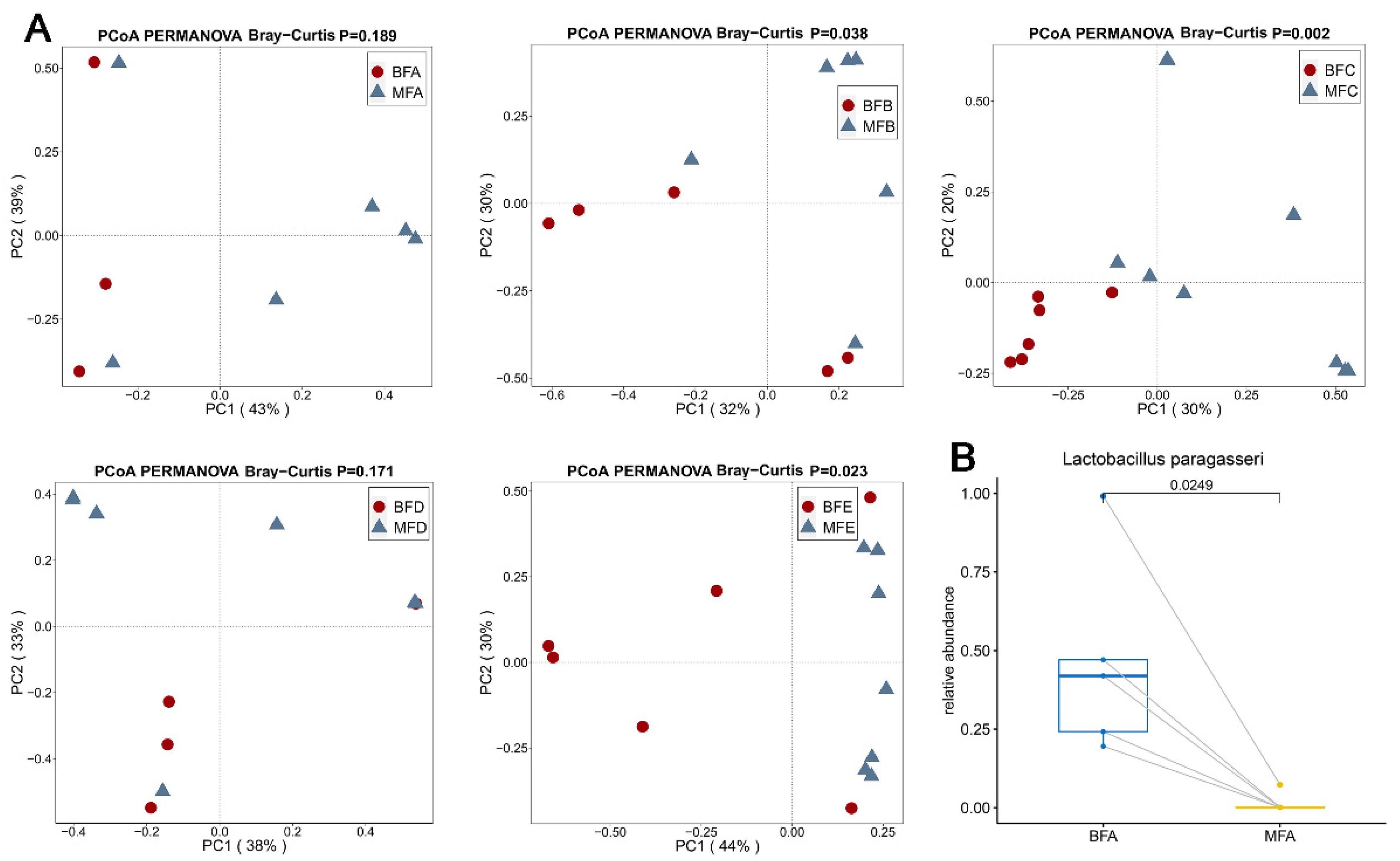
3.2. Bacterial Composition and Difference among HBM, Maternal Feces and Child Feces
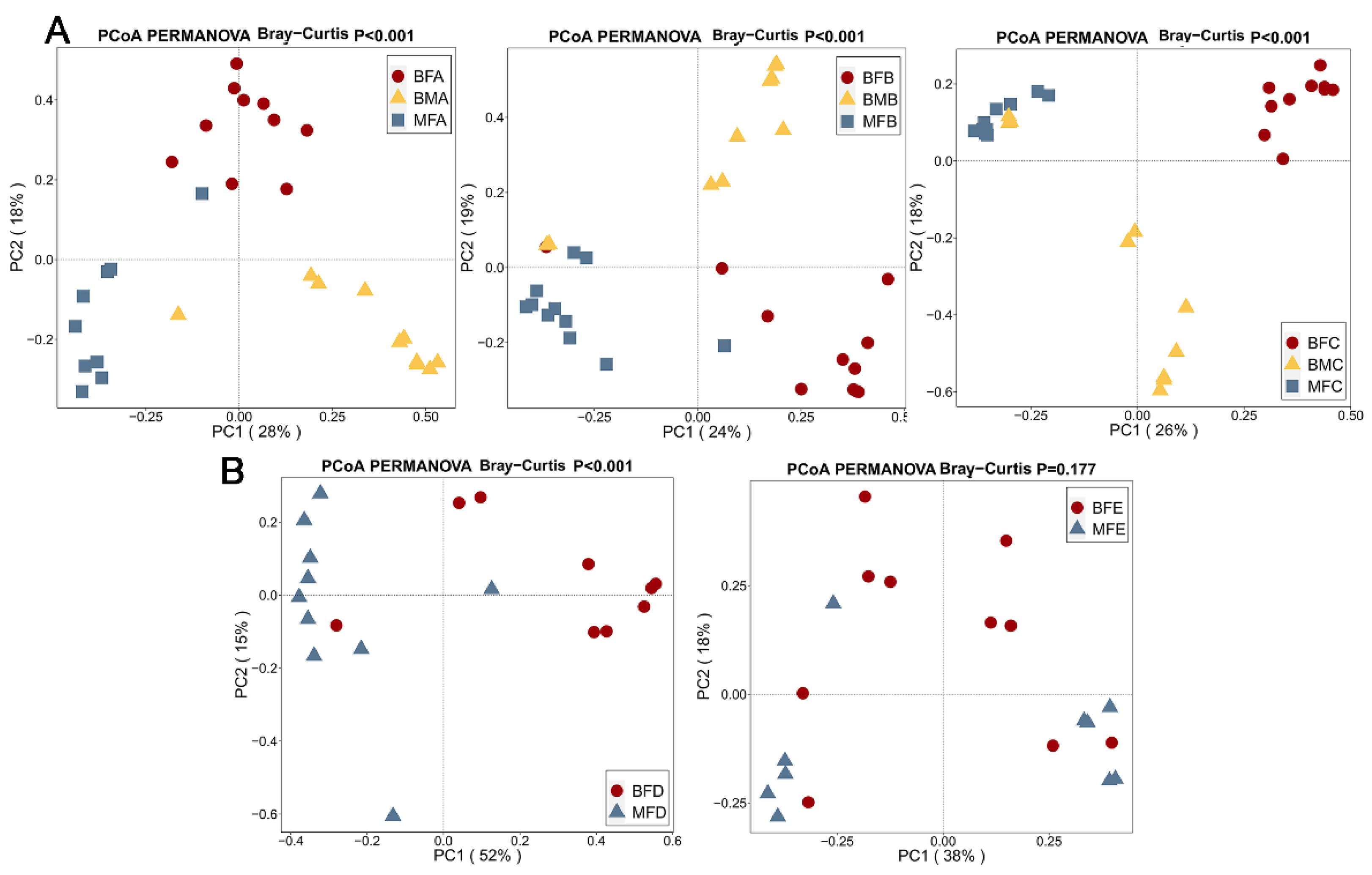
3.3. Bacterial Difference among HBM, Maternal and Child Feces
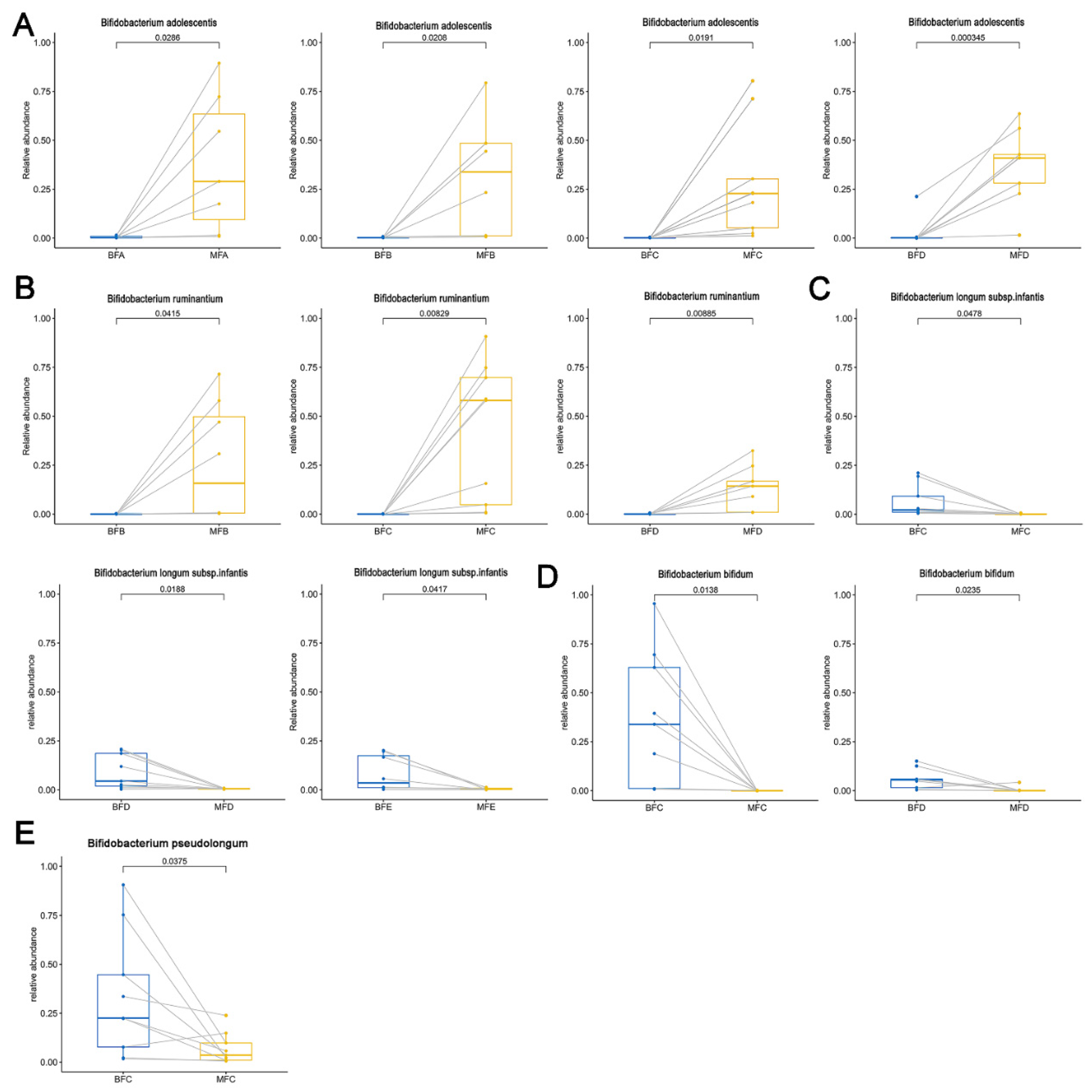
3.4. Diversity and Composition of Bifidobacterium Community in Maternal and Child Feces
3.5. Bifidobacterium Difference between Maternal and Child Feces at Species Level
3.6. Diversity and Composition of Lactobacillus Community in Maternal and Child Feces
3.7. Lactobacillus Difference between Maternal and Child Feces at Species Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, M.; Yang, B.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Crosstalk between sIgA-coated bacteria in infant gut and early-life health. Trends Microbiol 2021, 1, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez de Agüero, M.; Ganal-Vonarburg, S.C.; Fuhrer, T.; Rupp, S.; Uchimura, Y.; Li, H.; Steinert, A.; Heikenwalder, M.; Hapfelmeier, S.; Sauer, U.; et al. The maternal microbiota drives early postnatal innate immune development. Science 2016, 351, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.C.; Manges, A.R.; Finlay, B.B.; Prendergast, A. The Human Microbiome and Child Growth—First 1000 Days and Beyond. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prendergast, A.J.; Humphrey, J.H. The stunting syndrome in developing countries. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2014, 34, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, V.N.R.; Schwab, C.; Krych, L.; Voney, E.; Geirnaert, A.; Braegger, C.; Lacroix, C. Colonization of Cutibacterium avidum during infant gut microbiota establishment. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiy215. [Google Scholar]
- Korpela, K.; Costea, P.I.; Coelho, L.P.; Kandels-Lewis, S.; Willemsen, G.; Boomsma, D.I.; Segata, N.; Bork, P. Selective maternal seeding and environment shape the human gut microbiome. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Ryan, C.A.; Boyaval, P.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.; Stanton, C. Maternal Vertical Transmission Affecting Early-life Microbiota Development. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, P.; Pasolli, E.; Tett, A.; Asnicar, F.; Gorfer, V.; Fedi, S.; Armanini, F.; Truong, D.T.; Manara, S.; Zolfo, M.; et al. Mother-to-Infant Microbial Transmission from Different Body Sites Shapes the Developing Infant Gut Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 133–145.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Bender, J.M.; Yang, S.; Rollie, A.; Adisetiyo, H.; Zabih, S.; Lincez, P.J.; Bittinger, K.; et al. Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.E.; Carrothers, J.M.; A Lackey, K.; Beatty, N.F.; Brooker, S.L.; Peterson, H.K.; Steinkamp, K.M.; A York, M.; Shafii, B.; Price, W.J.; et al. Strong Multivariate Relations Exist Among Milk, Oral, and Fecal Microbiomes in Mother-Infant Dyads During the First Six Months Postpartum. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Differding, M.K.; Mueller, N.T. Human Milk Bacteria: Seeding the Infant Gut? Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, W.W.T.; Rahayu, E.S.; See, T.Y.; Kuah, S.; Salminen, S.; Nakayama, J.; Lee, Y.-K. Indonesian children fecal microbiome from birth until weaning was different from microbiomes of their mothers. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Rochat, F.; Chassard, C. Vertical mother-neonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Ross, R.P.; Jin, Y.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Orally Administered CLA Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice via Intestinal Barrier Improvement, Oxidative Stress Reduction, and Inflammatory Cytokine and Gut Microbiota Modulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13282–13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Ding, M.; Chen, Y.; Han, F.; Yang, C.; Zhao, J.; Malard, P.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Zhang, H.; et al. Development of gut microbiota and Bifidobacterium communities of neonates in the first 6 weeks and their inheritance from mother. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubi, A.; Uchiyama, T.; Hatanaka, K. Capturing consumer value and clustering customer preferences in the Indonesian halal beef market. Meat Sci. 2019, 156, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Arbizu, P. pairwiseAdonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using Adonis. R Package Version 0.3. 2019. Available online: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/CRAN/ (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Gonzalez, E.; Brereton, N.J.B.; Li, C.; Leyva, L.L.; Solomons, N.W.; Agellon, L.B.; Scott, M.E.; Koski, K.G. Distinct Changes Occur in the Human Breast Milk Microbiome Between Early and Established Lactation in Breastfeeding Guatemalan Mothers. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 557180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappan, R.; Classon, C.; Kumar, S.; Singh, O.P.; de Almeida, R.V.; Chakravarty, J.; Kumari, P.; Kansal, S.; Sundar, S.; Blackwell, J.M. Meta-taxonomic analysis of prokaryotic and eukaryotic gut flora in stool samples from visceral leishmaniasis cases and endemic controls in Bihar State India. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, J.M. The origin of human milk bacteria: Is there a bacterial entero-mammary pathway during late pregnancy and lactation? Am. Soc. Nutr. 2014, 5, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.; Chassard, C. Assessment of bacterial diversity in breast milk using culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, K.; Curley, D.; O’Callaghan, T.; O’Shea, C.-A.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’Toole, P.; Ross, R.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. The Composition of Human Milk and Infant Faecal Microbiota Over the First Three Months of Life: A Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Collado, M.C.; Laitinen, K.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Mira, A. The human milk microbiome changes over lactation and is shaped by maternal weight and mode of delivery. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouhy, F.; Clooney, A.G.; Stanton, C.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. 16S rRNA gene sequencing of mock microbial populations- impact of DNA extraction method, primer choice and sequencing platform. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.; Watanabe, K.; Jiang, J.; Matsuda, K.; Chao, S.-H.; Haryono, P.; La-Ongkham, O.; Sarwoko, M.-A.; Sujaya, I.N.; Zhao, L.; et al. Diversity in gut bacterial community of school-age children in Asia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking Long-Term Dietary Patterns with Gut Microbial Enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Princisval, L.; Rebelo, F.; Williams, B.L.; Coimbra, A.C.; Crovesy, L.; Ferreira, A.L.; Kac, G. Association Between the Mode of Delivery and Infant Gut Microbiota Composition Up to six months of Age: A Systematic Literature Review Considering the Role of Breastfeeding. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 00, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackie, R.I.; Sghir, A.; Gaskins, H.R. Developmental microbial ecology of the neonatal gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1035s–1045s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindi, A.S.; Geddes, D.T.; E Wlodek, M.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; Payne, M.S.; Stinson, L.F. Can we modulate the breastfed infant gut microbiota through maternal diet? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, fuab011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Langa, S.; Martin, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jiménez, E.; Martín, R.; Rodríguez, J.M. The human milk microbiota: Origin and potential roles in health and disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Parenti, M.; Grip, T.; Domellöf, M.; Lönnerdal, B.; Hernell, O.; Timby, N.; Slupsky, C.M. Metabolic phenotype of breast-fed infants, and infants fed standard formula or bovine MFGM supplemented formula: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzstevens, J.L.; Smith, K.C.; Hagadorn, J.I.; Caimano, M.J.; Matson, A.P.; Brownell, E.A. Systematic Review of the Human Milk Microbiota. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 32, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treven, P.; Mahnič, A.; Rupnik, M.; Golob, M.; Pirš, T.; Matijašić, B.B.; Lorbeg, P.M. Evaluation of human milk microbiota by 16S rRNA gene next-generation sequencing (NGS) and sultivation/MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry identification. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2612–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wessels, J.M.; Lajoie, J.; Cooper, M.I.H.; Omollo, K.; Felker, A.M.; Vitali, D.; Haley, A.; Dupont, P.V.N. Medroxyprogesterone acetate alters the vaginal microbiota and microenvironment in women and increases susceptibility to HIV-1 in humanized mice. Dis. Model Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Yan, S.; Chen, Y.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Diversity of gut microbiota and Bifidobacterium community of Chinese subjects of different ages and from different regions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Jin, J. Bifidobacterium from breastfed infant faeces prevent high-fat-diet-induced glucose tolerance impairment, mediated by the modulation of glucose intake and the incretin hormone secretion axis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3308–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Perez, A.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Benitez-Paez, A.; Campillo, I.; Sanz, Y. Bifidobacterium CECT 7765 modulates early stress-induced immune, neuroendocrine and behavioral alterations in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.; Yamamoto, A.; Palermo-Conde, L.A.; Higashi, K.; Sonomoto, K.; Tan, J.; Lee, Y.-K. Impact of Westernized Diet on Gut Microbiota in Children on Leyte Island. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.J.; Lynch, D.B.; Murphy, K.; Ulaszewska, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; O’Shea, C.A.; Watkins, C.; Dempsey, E.; Mattivi, F.; Tuohy, K.; et al. Evolution of gut microbiota composition from birth to 24 weeks in the INFANTMET Cohort. Microbiome 2017, 5, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouhy, F.; Watkins, C.; Hill, C.J.; O’Shea, C.A.; Nagle, B.; Dempsey, E.M.; Stanton, C. Perinatal factors affect the gut microbiota up to four years after birth. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dzidic, M.; Boix-Amorós, A.; Selma-Royo, M.; Mira, A.; Collado, M.C. Gut Microbiota and Mucosal Immunity in the Neonate. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Sakamoto, K.; Seo, S.-U.; Pickard, J.M.; Gillilland, M.G.; Pudlo, N.A.; Hoostal, M.; Li, X.; Wang, T.D.; Feehley, T.; et al. Neonatal acquisition of Clostridia species protects against colonization by bacterial pathogens. Science 2017, 356, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Hibberd, M.L.; Pettersson, S.; Lee, Y.K. Enterococcus faecalis from Healthy Infants Modulates Inflammation through MAPK Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Lee, Y.-K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Composition at Species Level and Gut Microbiota Diversity in Infants before 6 Weeks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Feng, J.; Hu, X.-T.; Wang, T.; Gong, W.-X.; Huang, K.; Guo, Y.-X.; Zou, Z.; Lin, X.; et al. Influenza infection elicits an expansion of gut population of endogenous Bifidobacterium animalis which protects mice against infection. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassens, E.S.; Boesten, R.J.; Haarman, M.; Knol, J.; Schuren, F.H.; Vaughan, E.E.; de Vos, W.M. Mixed-Species Genomic Microarray Analysis of Fecal Samples Reveals Differential Transcriptional Responses of Bifidobacteria in Breast- and Formula-Fed Infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Milani, C.; Viappiani, A.; Mangifesta, M.; Gioiosa, L.; Palanza, P.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Genomic Characterization and Transcriptional Studies of the Starch-Utilizing Strain Bifidobacterium adolescentis 22L. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6080–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavini, F.; Delcenserie, V.; Kopeinig, K.; Pollinger, S.; Beerens, H.; Bonaparte, C.; Upmann, M. Bifidobacterium species isolated from animal two and from beef and pork meat. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.; Motherway, M.O.; Bottacini, F.; Van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003 metabolises the human milk oligosaccharides lacto-N-tetraose and lacto-N-neo-tetraose through overlapping, yet distinct pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Ventura, M.; Buttó, L.F.; Duranti, S.; O’Toole, P.; Motherway, M.O.; Van Sinderen, D. Molecular dialogue between the human gut microbiota and the host: A Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mushajiang, S.; Luo, B.; Tian, F.; Ni, Y.; Yan, W. The Composition and Concordance of Lactobacillus Populations of Infant Gut and the Corresponding Breast-Milk and Maternal Gut. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 597911–597929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, M.I.; Lievens, E.; Malik, S.; Imholz, N.; Lebeer, S. Lactobacillus species as biomarkers and agents that can promote various aspects of vaginal health. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortensen, M.S.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Stokholm, J.; Brejnrod, A.D.; Balle, C.; Thorsen, J.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Bisgaard, H.; Sørensen, S.J. Modeling transfer of vaginal microbiota from mother to infant in early life. eLife 2021, 10, e57051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.-H.; Chiu, C.-H.; Kong, M.-S.; Chang, C.-J.; Chen, C.-C. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei: Effective for Managing Childhood Diarrhea by Altering Gut Microbiota and Attenuating Fecal Inflammatory Markers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, C.; Ding, M.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Li, D.; Yu, R.; Sun, J. Sex-dependent modulation of immune development by sIgA coated Lactobacillus reuteri isolated from breast milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 3863–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, M.; Yang, B.; Khine, W.W.T.; Lee, Y.-K.; Rahayu, E.S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. The Species-Level Composition of the Fecal Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Genera in Indonesian Children Differs from That of Their Mothers. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091995
Ding M, Yang B, Khine WWT, Lee Y-K, Rahayu ES, Ross RP, Stanton C, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W. The Species-Level Composition of the Fecal Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Genera in Indonesian Children Differs from That of Their Mothers. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(9):1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091995
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Mengfan, Bo Yang, Wei Wei Thwe Khine, Yuan-Kun Lee, Endang Sutriswati Rahayu, R. Paul Ross, Catherine Stanton, Jianxin Zhao, Hao Zhang, and Wei Chen. 2021. "The Species-Level Composition of the Fecal Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Genera in Indonesian Children Differs from That of Their Mothers" Microorganisms 9, no. 9: 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091995
APA StyleDing, M., Yang, B., Khine, W. W. T., Lee, Y.-K., Rahayu, E. S., Ross, R. P., Stanton, C., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., & Chen, W. (2021). The Species-Level Composition of the Fecal Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Genera in Indonesian Children Differs from That of Their Mothers. Microorganisms, 9(9), 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091995





