Co-Infections of Tilapia Lake Virus, Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in Farmed Red Hybrid Tilapia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case History
2.2. Samples Collection
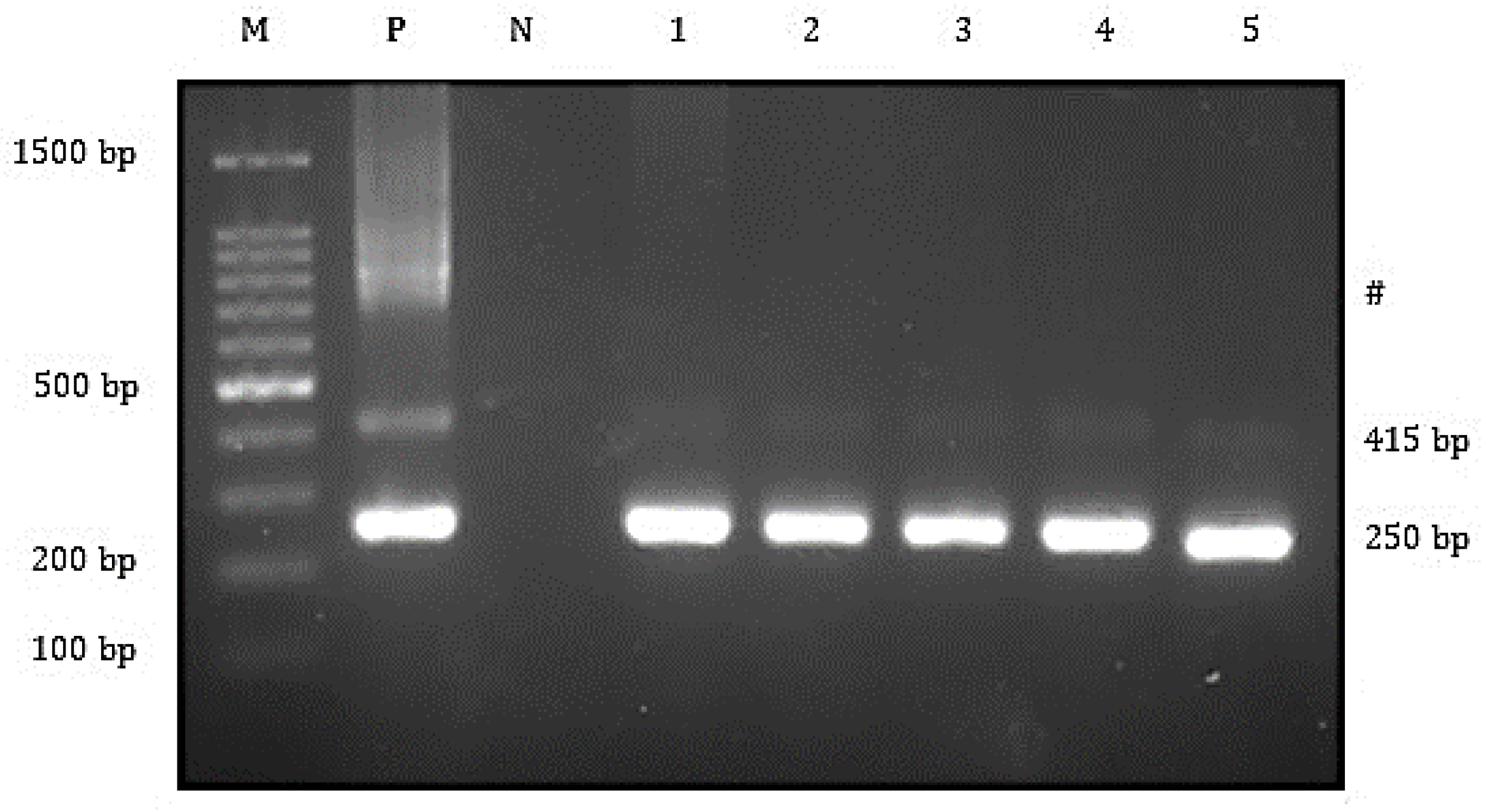
2.3. Virus RNA Extraction and Detection
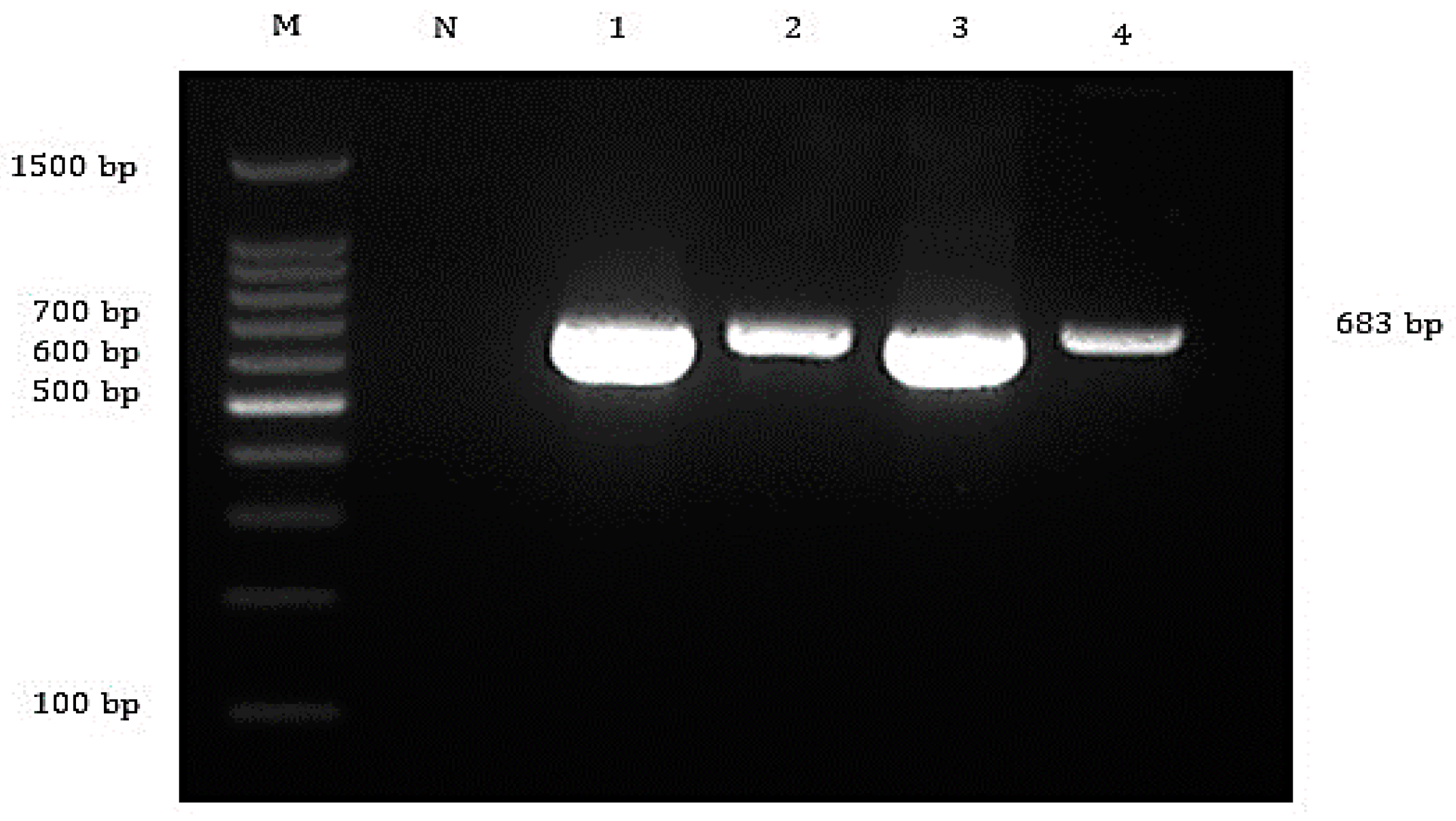
2.4. Bacterial Isolation, DNA Extraction and Identification
2.5. Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
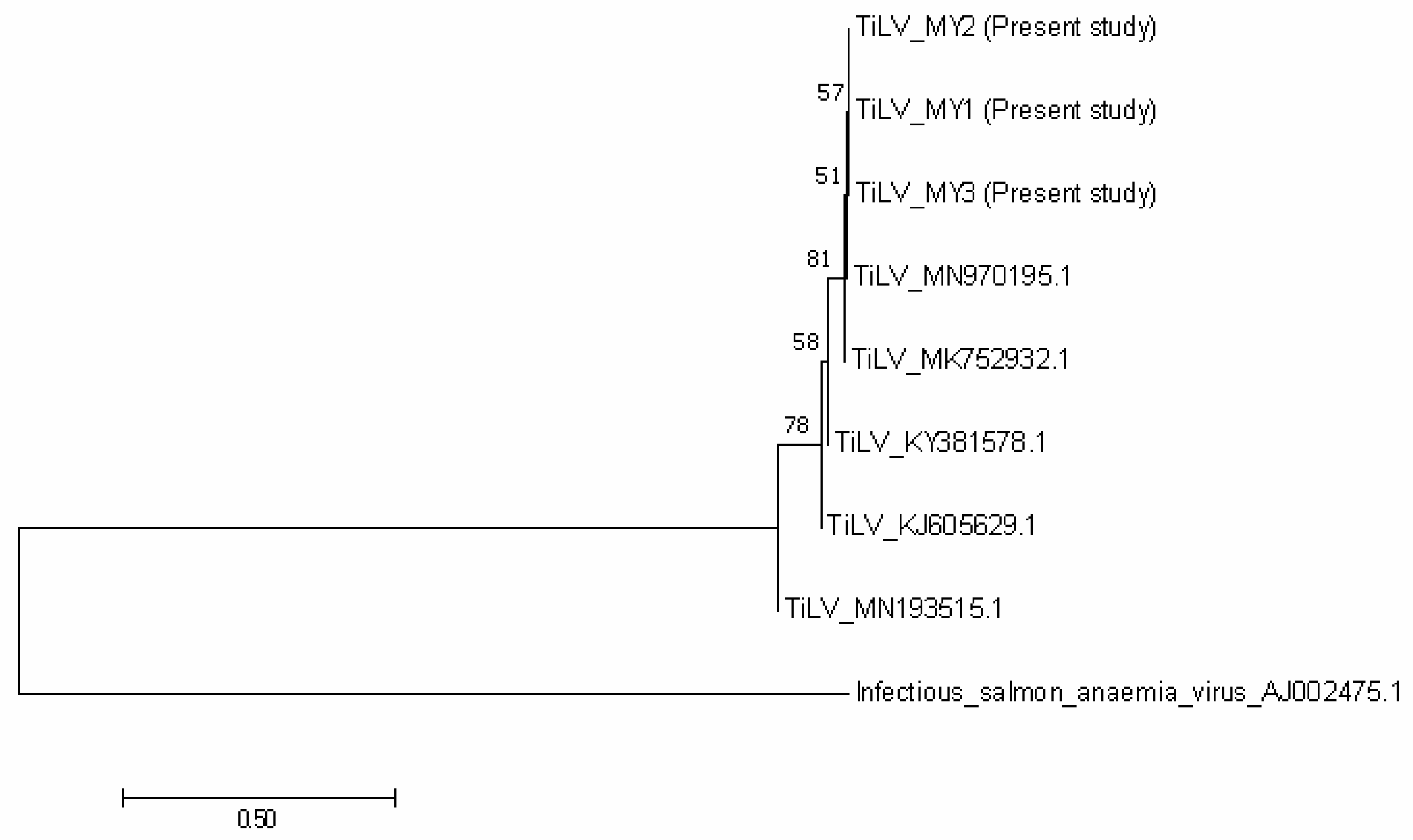
2.6. Virus and Bacteria Sequencing
2.7. Histopathological Assessment
3. Results
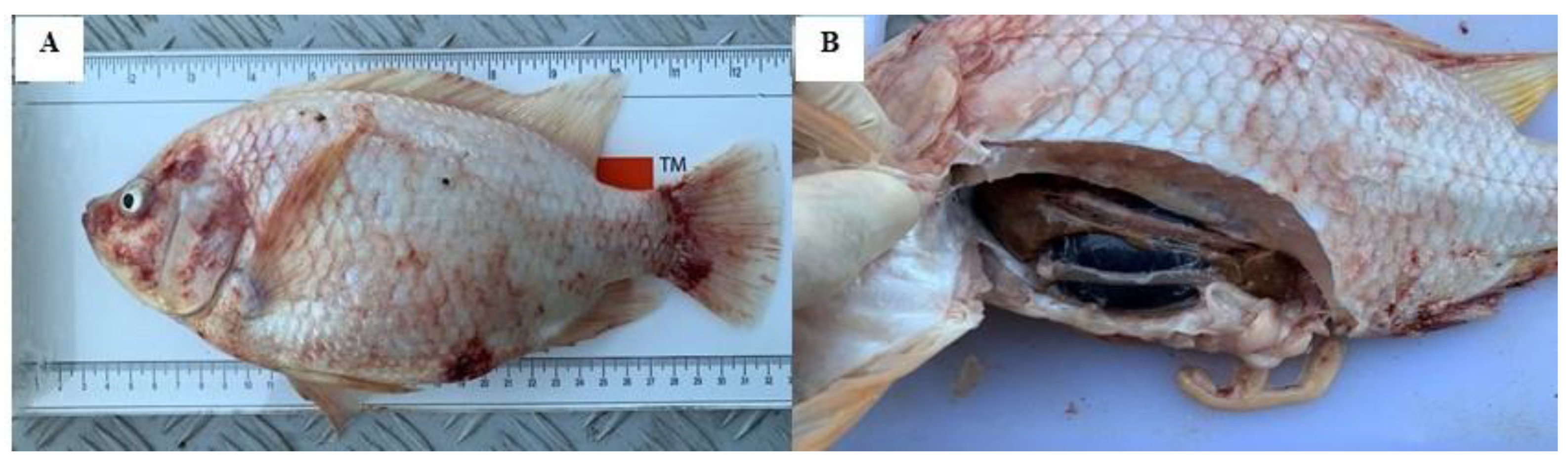
3.1. Disease Characterisation
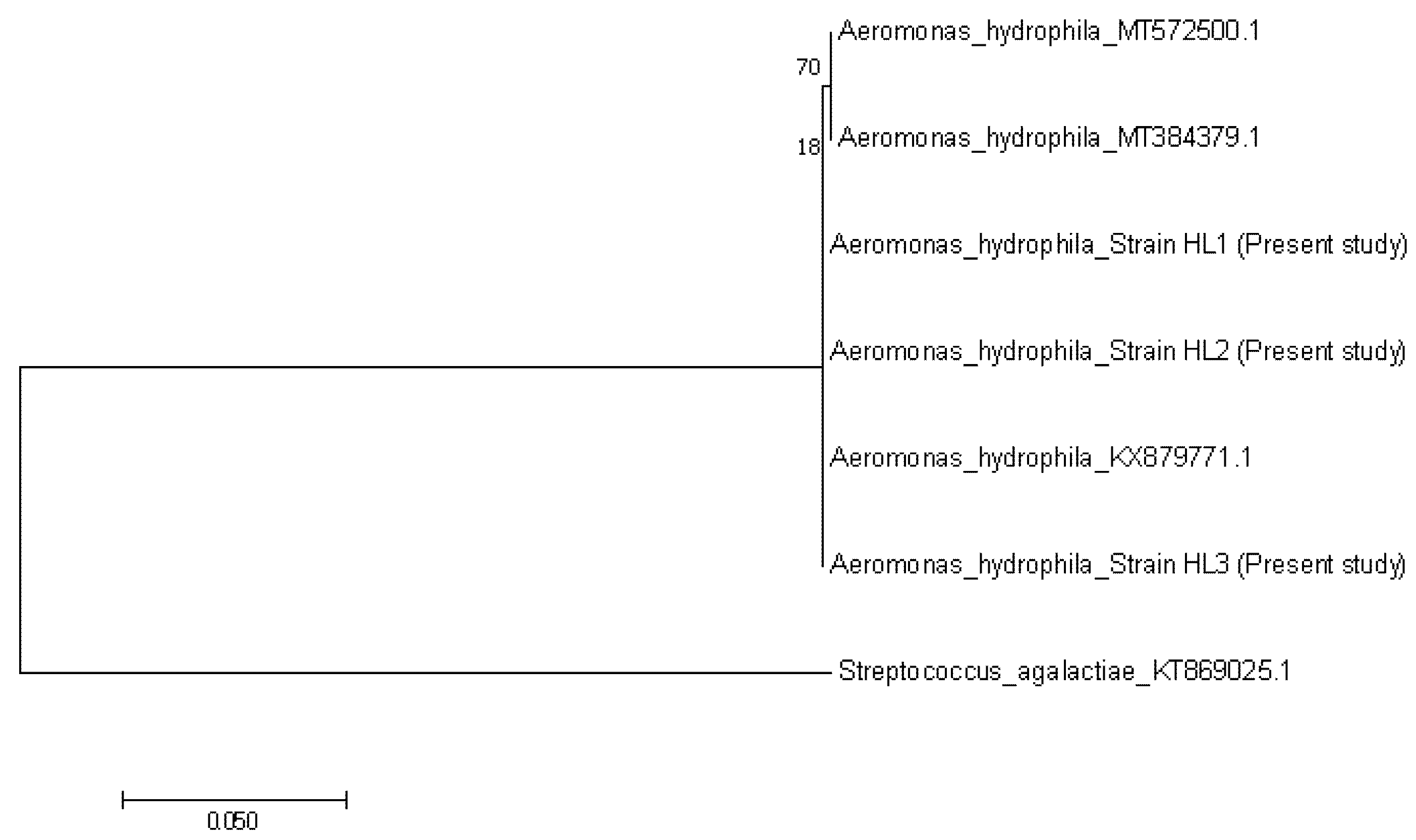
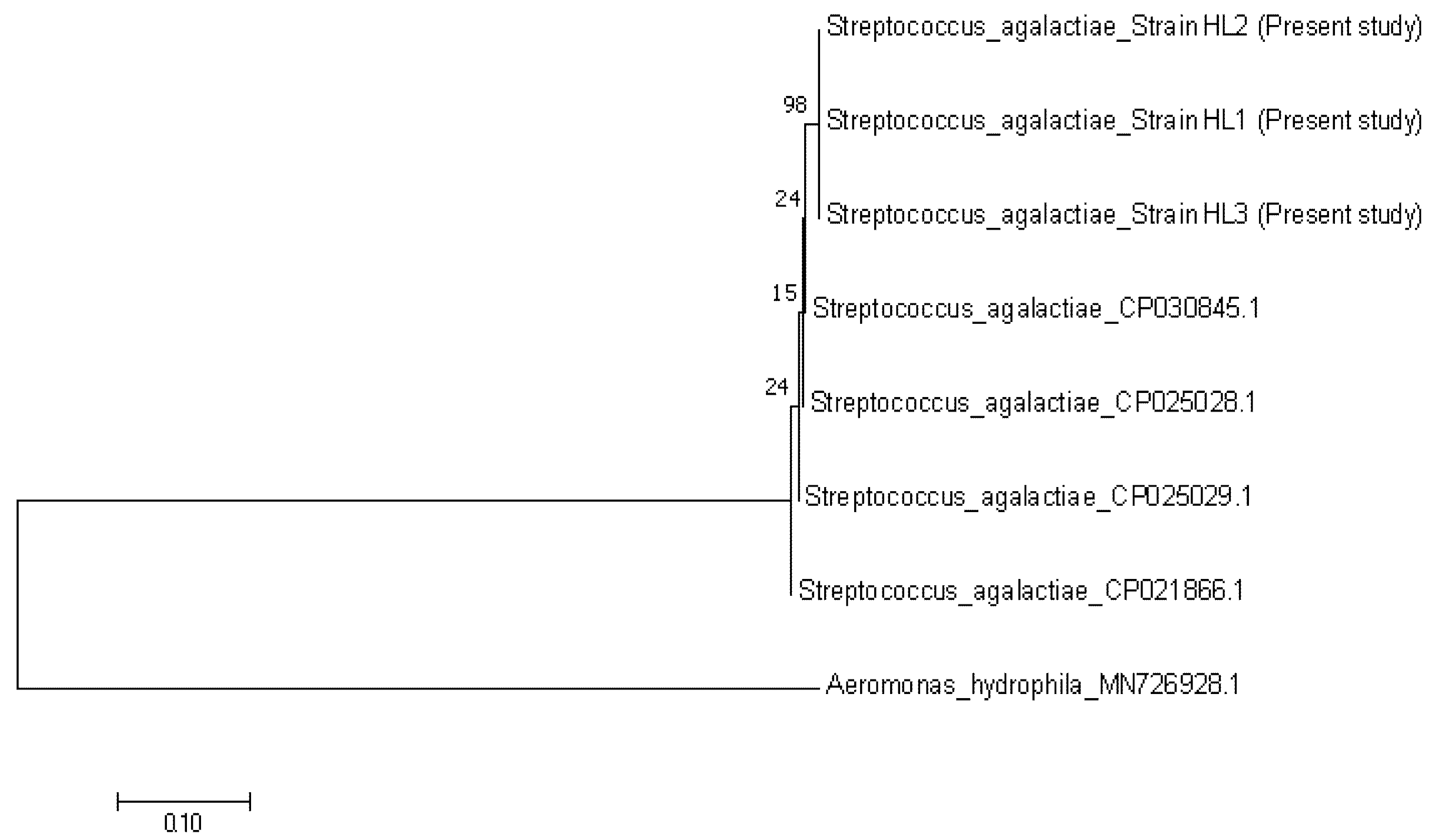
3.2. Bacteria and Virus Identification and Sequencing Analysis
3.3. Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
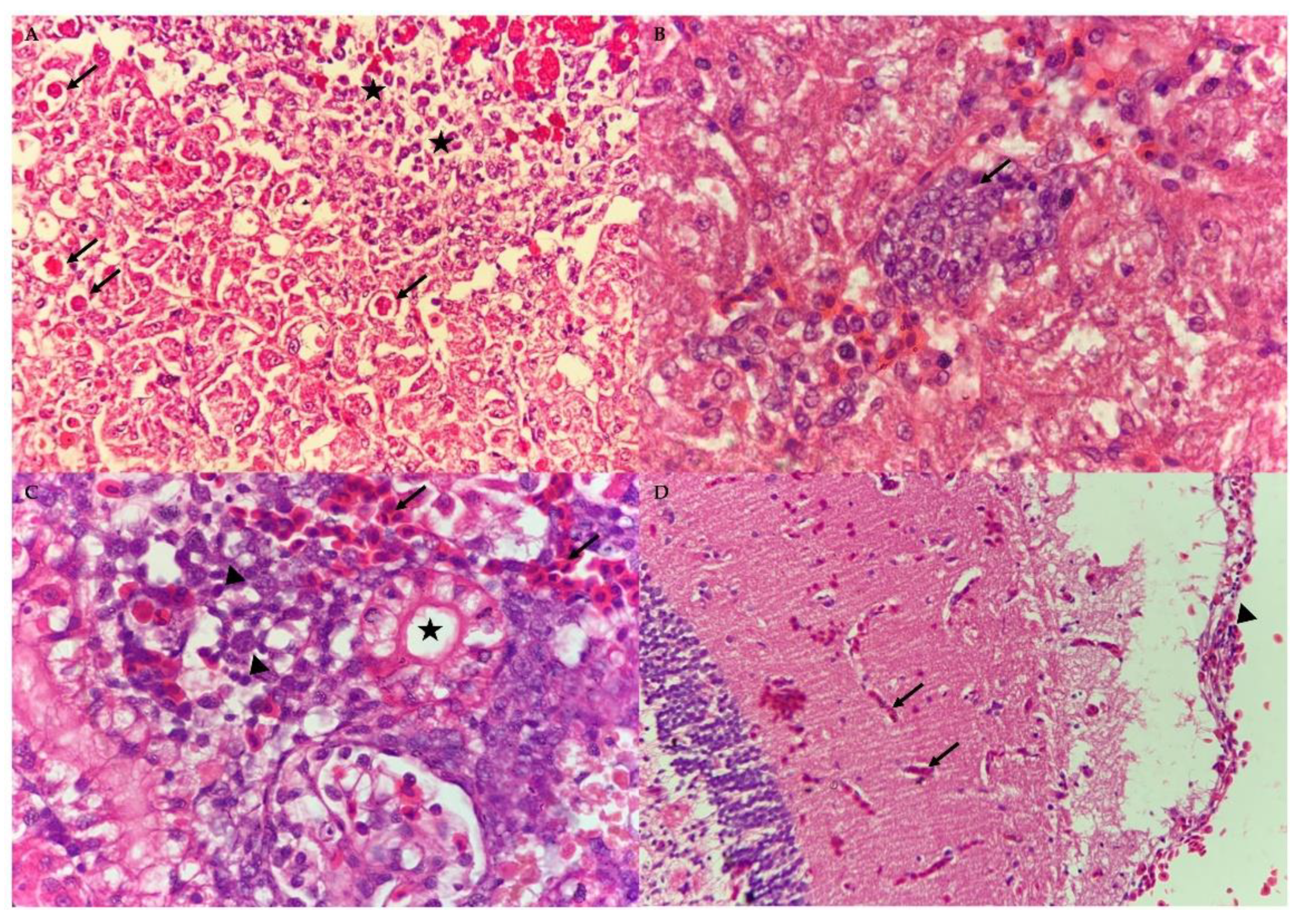
3.4. Histopathological Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Statistics and Information Branch, Fisheries and Aquaculture Department/FAO. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics. Global Production by Production Source 1950–2016 (FishstatJ); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Annual Fisheries Statistic. Annual Fisheries Statistic; Department of Fisheries Malaysia, Ministry of Agriculture & Agro-Based Industry: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Surachetpong, W.; Roy, S.R.K.; Nicholson, P. Tilapia lake virus: The story so far. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyngor, M.; Zamostiano, R.; Tsofack, J.E.K.; Berkowitz, A.; Bercovier, H.; Tinman, S.; Eldar, A. Identification of a novel RNA virus lethal to tilapia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4137–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surachetpong, W.; Janetanakit, T.; Nonthabenjawan, N.; Tattiyapong, P.; Sirikanchana, K.; Amonsin, A. Outbreaks of tilapia lake virus infection, Thailand, 2015–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koesharyani, I.; Lila, G.; Zakiyah, W.; Khumaira, K.; Dita, R. Studi kasus infeksi Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) pada ikan nila (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Ris. Akuakultur 2018, 13, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amal, M.N.A.; Koh, C.B.; Nurliyana, M.; Suhaiba, M.; Nor-Amalina, Z.; Santha, S.; Zamri-Saad, M. A case of natural co-infection of Tilapia Lake Virus and Aeromonas veronii in a Malaysian red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus) farm experiencing high mortality. Aquaculture 2018, 485, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacharach, E.; Mishra, N.; Briese, T.; Zody, M.C.; Tsofack, J.E.K.; Zamostiano, R.; Toussaint, N.C. Characterization of a novel orthomyxo-like virus causing mass die-offs of tilapia. mBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, J.H. Megataxonomy of Negative-Sense RNA Viruses: Phylum Negarnaviricota; Negative strand RNA virus “NSV2018” meeting; Negative Strand RNA Virus Committee: Verona, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, M.; Dickson, C.; Dickson, M.; Leschen, W.; Baily, J.; Muir, F.; Weidmann, M. Identification of Tilapia Lake Virus in Egypt in Nile tilapia affected by ‘summer mortality’ syndrome. Aquaculture 2017, 473, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Syafiq, M.R.M.; Amal, M.N.A.; Firdaus-Nawi, M.; Zamri-Saad, M. Feed-based vaccination regime against streptococcosis in red tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis mossambicus. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, M.S.; Syafiq, M.R.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Fahmi, S.; Shahidan, H.; Hanan, Y.; Amal, M.N.A.; Zamri-Saad, M. The effect of feed-based vaccination on tilapia farm endemic for streptococcosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monir, M.S.; Yusoff, S.M.; Mohamad, A.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y. Vaccination of tilapia against Motile Aeromonas Septicemia: A review. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2020, 32, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauzi, N.A.; Mohamad, N.; Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.D.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Amal, M.N.A. Antibiotic susceptibility and pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis mossambicus) in Malaysia. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laith, A.R.; Najiah, M. Aeromonas hydrophila: Antimicrobial susceptibility and histopathology of isolates from diseased catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell). J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2014, 5, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Amal, M.N.A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Iftikhar, A.R.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Aziel, S.; Fahmi, S. An outbreak of Streptococcus agalactiae infection in cage-cultured golden pompano, Trachinotus blochii (Lacépède), in Malaysia. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2017, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.T.; Nguyen, V.V.; Le, H.D.; Sangsuriya, P.; Jitrakorn, S.; Saksmerprome, V.; Senapin, S.; Rodkhum, C. Naturally concurrent infections of bacterial and viral pathogens in disease outbreaks in cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) farms. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Paredes, J.G.; Paley, R.K.; Hunt, W.; Feist, S.W.; Stone, D.M.; Field, T.R.; Haydon, D.J.; Ziddah, P.A.; Nkansa, M.; Guilder, J.; et al. First detection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) associated with massive mortalities in farmed tilapia in Africa. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, P.; Fathi, M.A.; Fischer, A.; Mohan, C.; Schieck, E.; Mishra, N.; Heinimann, A.; Frey, J.; Wieland, B.; Jores, J. Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus in Egyptian fish farms experiencing high mortalities in 2015. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiani, D.; Sukenda, H.E.; Lusiastuti, A.M. Haematology responses and histopathology of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus to co-infection Streptococcus agalactiae and Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Ris. Akuakultur 2012, 7, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiati, T.; Sukenda, N.S.; Lusiastuti, A.M. Development of ELISA method to detect specific immune response in Nile tilapia O. niloticus vaccinated against A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae. J. Riset Akuakultur 2015, 10, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, A.; Ramli, R.; Ridzuan, M.S.M.; Murni, M.; Hashim, S.; Sudirwan, F.; Abdullah, S.Z.; Mansor, N.N.; Amira, S.; Zamri-Saad, M.; et al. The presence of Vibrionaceae, Betanodavirus and Iridovirus in marine cage-cultured fish: Role of fish size, water physicochemical parameters and relationships among the pathogens. Aquac. Rep. 2017, 7, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Siriroob, S.; Meemetta, W.; Santimanawong, W.; Gangnonngiw, W.; Pirarat, N.; Senapin, S. Emergence of tilapia lake virus in Thailand and an alternative semi-nested RT-PCR for detection. Aquaculture 2017, 476, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoyi, P.; Jinyu, S.; Guijie, H. Development of a duplex PCR for detection of Aeromonas spp. and Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Huazhong Agric. Uni. 2011, 30, 759–763. [Google Scholar]
- Imperi, M.; Pataracchia, M.; Alfarone, G.; Baldassarri, L.; Orefici, G.; Creti, R. A multiplex PCR assay for the direct identification of the capsular type (Ia to IX) of Streptococcus agalactiae. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; CLSI document M100-S23; Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Dawood, M.A.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; El-Matbouli, M. The nature and consequences of co-infections in tilapia: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Ramly, R.; Ridzwan, M.S.M.; Sudirwan, F.; Abas, A.; Ahmad, K.; Kua, B.C. First detection of tilapia lake virus (TiLV) in wild river carp (Barbonymus schwanenfeldii) at Timah Tasoh Lake, Malaysia. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Ataguba, G.A.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Evidence of TiLV infection in tilapia hatcheries from 2012 to 2017 reveals probable global spread of the disease. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Khafaga, A.F. Natural co-infection of cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus with Aeromonas hydrophila and Gyrodactylus cichlidarum experiencing high mortality during summer. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, E.; Wang, R.; Wiles, J.; Baumgartner, W.; Green, C.; Plumb, J.; Hawke, J. Characterization of isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae from diseased farmed and wild marine fish from the US Gulf Coast, Latin America, and Thailand. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2015, 27, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamri-Saad, M.; Amal, M.N.A.; Siti-Zahrah, A. Pathological changes in red tilapias (Oreochromis spp.) naturally infected by Streptococcus agalactiae. J. Comp. Pathol. 2010, 143, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.D.; Dong, H.T.; Mohan, C.V. Tilapia lake virus: A threat to the global tilapia industry? Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, H.W.; Kabuusu, R.; Beltran, S.; Reyes, E.; Lince, J.A.; del Pozo, J. Syncytial hepatitis of farmed tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.): A case report. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattiyapong, P.; Dachavichitlead, W.; Surachetpong, W. Experimental infection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). Vet. Mic. 2017, 207, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE. Immediate Notifications and Follow-ups. Tilapia Lake Virus, Chinese Taipei.. 2017. Available online: https://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Reviewreport/Review?reportid=24033 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- OIE. Tilapia Lake Virus Disease, Malaysia. Immediate Notification. 2017. Available online: https://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Reviewreport/Review?page_refer=MapFullEventReport&reporid=24809 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- OIE. Immediate Notification. Tilapia Lake Virus, Mexico. 2018. Available online: https://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Reviewreport/Review?page_refer=MapFullEventReport&reportid=27650 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Nicholson, P.; Mon-on, N.; Jaemwimol, P.; Tattiyapong, P.; Surachetpong, W. Coinfection of tilapia lake virus and Aeromonas hydrophila synergistically increased mortality and worsened the disease severity in tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisyhah, M.A.S.; Amal, M.N.A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Shaqinah, N.N. Streptococcus agalactiae isolates from cultured fishes in Malaysia manifesting low resistance pattern towards selected antibiotics. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibiotic | Disk Potency (µg) | Aeromonas hydrophila (Zone of Inhibition, mm) | Streptococcus agalactiae (Zone of Inhibition, mm) | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | I | S | ||||
| Ampicillin | 10 | R (6) | S (20) | ≤13 | 14–16 | ≥17 |
| Cefepime | 30 | S (23) | S (25) | ≤14 | 15–17 | ≥18 |
| Cefotaxime | 30 | S (25) | S (23) | ≤14 | 15–22 | ≥23 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 5 | R (13) | I (19) | ≤15 | 16–20 | ≥21 |
| Chloramphenicol | 30 | S (29) | S (18) | ≤12 | 13–17 | ≥18 |
| Gentamicin | 10 | R (11) | R (10) | ≤12 | 13–14 | ≥15 |
| Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim | 1.25/23.75 | R (0) | S (20) | ≤10 | 11–15 | ≥16 |
| Tetracycline | 30 | S (15) | R (9) | ≤11 | 12–14 | ≥15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basri, L.; Nor, R.M.; Salleh, A.; Md. Yasin, I.S.; Saad, M.Z.; Abd. Rahaman, N.Y.; Barkham, T.; Amal, M.N.A. Co-Infections of Tilapia Lake Virus, Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in Farmed Red Hybrid Tilapia. Animals 2020, 10, 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112141
Basri L, Nor RM, Salleh A, Md. Yasin IS, Saad MZ, Abd. Rahaman NY, Barkham T, Amal MNA. Co-Infections of Tilapia Lake Virus, Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in Farmed Red Hybrid Tilapia. Animals. 2020; 10(11):2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112141
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasri, Lukman, Roslindawani Md. Nor, Annas Salleh, Ina Salwany Md. Yasin, Mohd Zamri Saad, Nor Yasmin Abd. Rahaman, Timothy Barkham, and Mohammad Noor Azmai Amal. 2020. "Co-Infections of Tilapia Lake Virus, Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in Farmed Red Hybrid Tilapia" Animals 10, no. 11: 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112141
APA StyleBasri, L., Nor, R. M., Salleh, A., Md. Yasin, I. S., Saad, M. Z., Abd. Rahaman, N. Y., Barkham, T., & Amal, M. N. A. (2020). Co-Infections of Tilapia Lake Virus, Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in Farmed Red Hybrid Tilapia. Animals, 10(11), 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112141







