Ultrasound-Guided Hook-Wire Localization for Surgical Excision of Non-Palpable Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes in Dogs: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
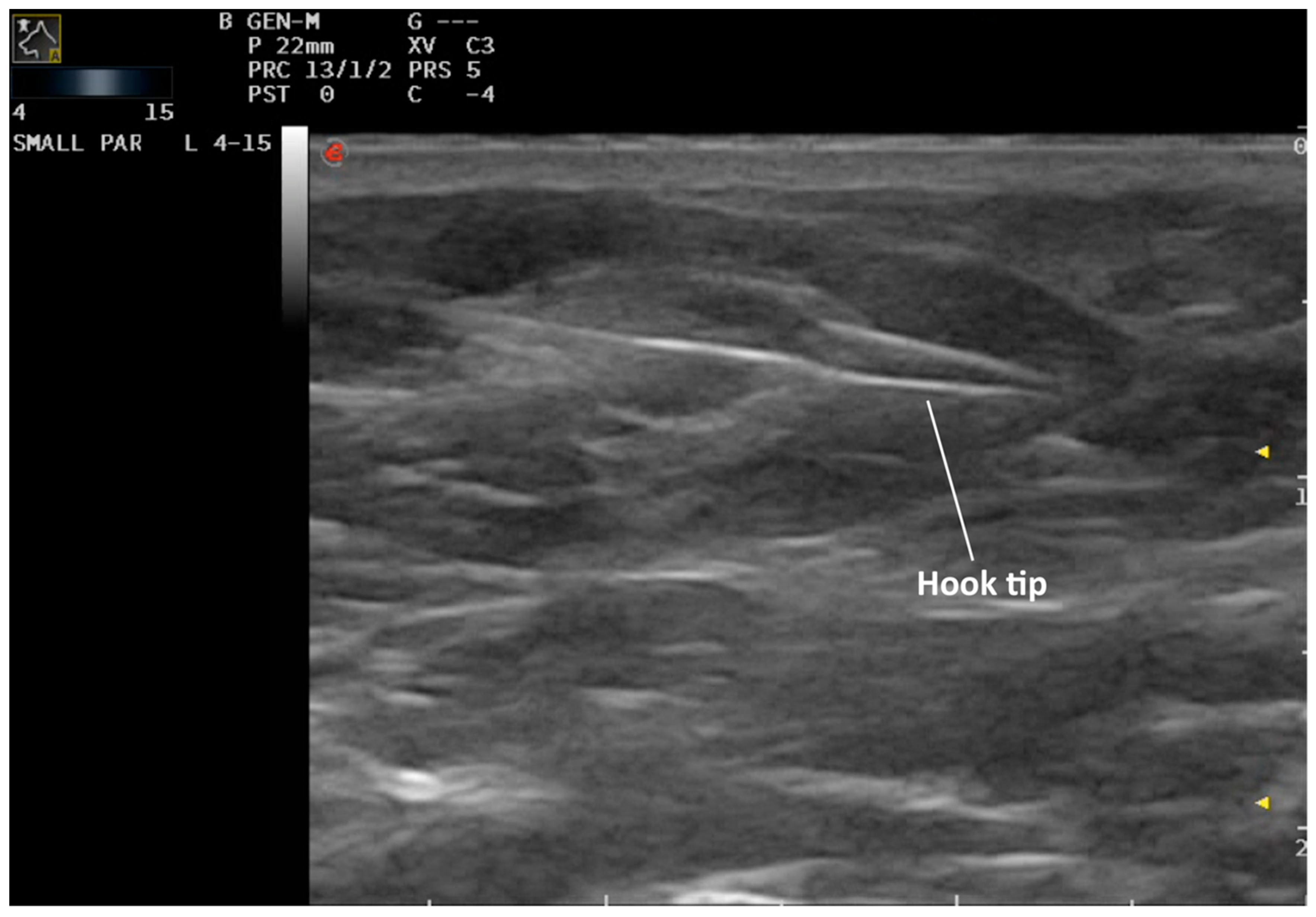
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skinner, O.T.; Boston, S.E.; Souza, C.H.; De Carlos, M. Patterns of Lymph Node Metastasis Identified Following Bilateral Mandibular and Medial Retropharyngeal Lymphadenectomy in 31 Dogs with Malignancies of the Head. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R.; Marconato, L.; Buracco, P.; Boracchi, P.; Giudice, C.; Iussich, S.; Grieco, V.; Chiti, L.E.; Favretto, E.; Stefanello, D. The Impact of Extirpation of Non-Palpable/Normal-Sized Regional Lymph Nodes on Staging of Canine Cutaneous Mast Cell Tumours: A Multicentric Retrospective Study. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2018, 16, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baginski, H.; Davis, G.; Bastian, R.P. The Prognostic Value of Lymph Node Metastasis with Grade 2 MCTs in Dogs: 55 Cases (2001–2010). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2014, 50, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconato, L.; Polton, G.; Stefanello, D.; Morello, E.; Ferrari, R.; Henriques, J.; Tortorella, G.; Benali, S.L.; Bergottini, R.; Vasconi, M.E.; et al. Therapeutic Impact of Regional Lymphadenectomy in Canine Stage II Cutaneous Mast Cell Tumours. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2018, 16, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, S.E.; Drobatz, K.J.; Duda, L.E.; White, P.; Kubicek, L.; Sorenmo, K.U. Treating the Locoregional Lymph Nodes with Radiation and/or Surgery Significantly Improves Outcome in Dogs with High-grade Mast Cell Tumours. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boston, S.E.; Lu, X.; Culp, W.T.N.; Montinaro, V.; Romanelli, G.; Dudley, R.M.; Liptak, J.M.; Mestrinho, L.A.; Buracco, P. Efficacy of Systemic Adjuvant Therapies Administered to Dogs after Excision of Oral Malignant Melanomas: 151 Cases (2001–2012). J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 2014, 245, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, K.; Boston, S.E. Bilateral Removal of the Mandibular and Medial Retropharyngeal Lymph Nodes through a Single Ventral Midline Incision for Staging of Head and Neck Cancers in Dogs: A Description of Surgical Technique. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezuidenhout, A.J. The lymphatic system. In Miller’s Anatomy of the Dog; Evans, H., De Lahunta, A., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013; pp. 535–562. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, M.N.; Lawson, J.A.; Silver, T.I. Sonographic Characteristics of Presumptively Normal Canine Medial Iliac and Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2010, 51, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielssen, A. 55-Lymphadenopathy. In Canine Internal Medicine Secrets; Rubin, S.I., Carr, A.P., Eds.; Mosby: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 2007; pp. 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzee, C.C. Hemolymphatic System. In Veterinary Surgical Oncology; Kudnig, S.T., Séguin, B., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2012; pp. 443–464. [Google Scholar]
- Cheang, E.; Ha, R.; Thornton, C.M.; Mango, V.L. Innovations in Image-Guided Preoperative Breast Lesion Localization. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutten, M.J.C.M.; Schreurs, B.W.; Van Kampen, A.; Schreuder, H.W.B. Excisional Biopsy of Impalpable Soft Tissue Tumors US-Guided Preoperative Localization in 12 Cases. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1997, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masroor, I.; Saeed, S.A.; Shafqat, R. Usefulness of Hook Wire Localization Biopsy under Imaging Guidance for Nonpalpable Breast Lesions Detected Radiologically. Int. J. Women’s Health 2012, 4, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jakimovska Dimitrovska, M.; Mitreska, N.; Lazareska, M.; Stojovska Jovanovska, E.; Dodevski, A.; Stojkoski, A. Hook Wire Localization Procedure and Early Detection of Breast Cancer—Our Experience. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 3, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, L. Reevaluation of the Efficacy of Preoperative Computed Tomography-Guided Hook Wire Localization: A Retrospective Analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 51, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattai, A.; Pierini, A.; Carusi, U.; Carli, A.; Cinti, F.; Pisani, G. Minimally Invasive Excision of Non-Palpable Lymph Nodes after Preoperative Ultrasoundguided Hook-Wire Localization in Dogs. Veterinaria 2020, 36, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Tardioli, S.; Ballesio, L.; Gigli, S.; DI Pastena, F.; D’Orazi, V.; Giraldi, G.; Monti, M.; Amabile, M.I.; Pasta, V. Wire-Guided Localization in Non-Palpable Breast Cancer: Results from Monocentric Experience. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 2423–2427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montrey, J.S.; Levy, J.A.; Brenner, R.J. Wire Fragments after Needle Localization. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 167, 1267–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ernst, M.F.; Avenarius, J.K.A.; Schuur, K.H.; Roukema, J.A. Wire localization of non-palpable breast lesions: Out of date? Breast 2002, 11, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodhouse, C.; Soliman, I.; Cruse, M.; Kastrenakes, J.; Augustine, C.J.; Ludy, A.; Reintgen, E.; Hoadley, A.; Desai, D.; Nguyen, M.; et al. Localization methods for excisional biopsy in women with nonpalpable mammographic abnormalities. Clin. Breast Cancer 2017, 17, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Han, K.; Hur, J.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.W.; Hwang, S.H.; Seo, J.S.; Lee, K.H.; Kwon, W.; Kim, T.H.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Preoperative Lung Localization for Pulmonary Nodules. Chest 2017, 151, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiral, G.; Senol, M.; Bayraktar, B.; Ozturk, H.; Celik, Y.; Boluk, S. Diagnostic Value of Hook Wire Localization Technique for Non-Palpable Breast Lesions. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Case | Breed | Age (mo) | Sex | BW (kg) | BCS (n/9) | Tumor Type and Location | SILN Side | SILN Width (mm) | Concomitant Surgery | UGHW Time (min) | Sx Time of LN Exc. (min) | Hook Location | Complications | LN Metastasis | FU (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JRT | 134 | M | 10.7 | 8 | MCT; L thigh | L | 3 | M | 5 | 8 | I | No | N | 191 |
| L | 4 | 5 | 4 | P | N | ||||||||||
| L | 4 | 6 | 4 | P | N | ||||||||||
| 2 | Pug | 96 | FS | 9.6 | 8 | MCT; R distal hindlimb | R | 2.5 | M | 5 | 10 | P | No | N | 50 |
| 3 | Cross. | 178 | MN | 46.7 | 7 | STS; L distal forelimb | L | 5 * | No | 15 | 15 | P | No | N | 43 |
| 4 | Labrador | 125 | F | 37 | 7 | mMCT; axilla, flank, sternum | R | 4 | M | 20 | 40 | O | Wire dislocation | N | 24 |
| 5 | Cross. | 111 | MN | 31.7 | 7 | MCT; R thigh | R | 5 * | M | 15 | 10 | P | Seroma | Y | 111 |
| 6 | Pug | 91 | FS | 8.6 | 5 | MCT; R thigh | L | 2.8 | M | 5 | 15 | P | No | Y | 42 |
| R | 3.4 | 5 | 15 | P | Y | ||||||||||
| 7 | Cross. | 84 | MN | 20.4 | 7 | STS; L thigh | L | 5 | M | 10 | 10 | P | No | Y | 45 |
| R | 2.5 | 10 | 10 | P | N | ||||||||||
| 8 | Cross. | 98 | M | 6.8 | 4 | MCT; R hindlimb | R | 3 | M | 10 | 25 | P | No | Y | 29 |
| L | 2 | 10 | 15 | P | Y | ||||||||||
| 9 | SBT | 121 | MN | 23.7 | 6 | MCT; scrotal | L | 2.7 | No | 5 | 25 | P | No | N | 135 |
| R | 2.5 | 5 | 15 | P | Y | ||||||||||
| 10 | Boxer | 68 | FS | 31 | 6 | MCT; vulva | L | 3 * | M | 10 | 15 | P | No | Y | 83 |
| 11 | EMD | 37 | M | 56 | 6 | MCT; R thigh | R | 6 | M | 15 | 16 | I | No | Y | 363 |
| 12 | Cross. | 38 | F | 11.6 | 5 | MCT; L thigh | L | 4 | M | 6 | 5 | P | No | N | 372 |
| 13 | Labr. | 89 | F | 31.7 | 6 | MCT; L flank | L | 5 | M + S | 11 | 16 | P | No | Y | 359 |
| 14 | Golden | 126 | FS | 34.2 | 7 | MCT; R tarsus | R | 11 | M + LN | 8 | 7 | I | No | Y | 14 |
| 15 | AST | 118 | M | 37.3 | 6 | mMCT; R Thigh, preputial | R | 3 | M + S | 7 | 6 | P | No | N | 234 |
| 16 | Cocker Sp. | 108 | MN | 17.2 | 6 | MCT; Preputial | L | 2.2 | M + S + O | 10 | 15 | P | No | Y | 57 |
| 17 | Labrador | 71 | FS | 26.8 | 5 | MCT; trunk (L chest) | L | 3 | T | 6 | 20 | O | Wire fragmentation | Y | 108 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pierini, A.; Marchetti, V.; Rossanese, M.; Finotello, R.; Cattai, A.; Pisani, G. Ultrasound-Guided Hook-Wire Localization for Surgical Excision of Non-Palpable Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes in Dogs: A Pilot Study. Animals 2020, 10, 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122314
Pierini A, Marchetti V, Rossanese M, Finotello R, Cattai A, Pisani G. Ultrasound-Guided Hook-Wire Localization for Surgical Excision of Non-Palpable Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes in Dogs: A Pilot Study. Animals. 2020; 10(12):2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122314
Chicago/Turabian StylePierini, Alessio, Veronica Marchetti, Matteo Rossanese, Riccardo Finotello, Andrea Cattai, and Guido Pisani. 2020. "Ultrasound-Guided Hook-Wire Localization for Surgical Excision of Non-Palpable Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes in Dogs: A Pilot Study" Animals 10, no. 12: 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122314
APA StylePierini, A., Marchetti, V., Rossanese, M., Finotello, R., Cattai, A., & Pisani, G. (2020). Ultrasound-Guided Hook-Wire Localization for Surgical Excision of Non-Palpable Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes in Dogs: A Pilot Study. Animals, 10(12), 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122314









